Drug Detail:Welchol (Colesevelam [ koe-le-sev-e-lam ])
Drug Class: Bile acid sequestrants
Highlights of Prescribing Information
WELCHOL (colesevelam hydrochloride) tablets, for oral use
WELCHOL (colesevelam hydrochloride) for oral suspension
Initial U.S. Approval: 2000
Indications and Usage for Welchol
WELCHOL is a bile acid sequestrant indicated as an adjunct to diet and exercise to:
- reduce elevated low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) in adults with primary hyperlipidemia (1.1).
- reduce LDL-C levels in boys and postmenarchal girls, 10 to 17 years of age, with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (HeFH), unable to reach LDL-C target levels despite an adequate trial of diet and lifestyle modification (1.1).
- improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus (1.2).
Limitations of Use (1.3):
- Do not use for treatment of type 1 diabetes or for diabetic ketoacidosis.
- Not studied in Fredrickson Type I, III, IV, and V dyslipidemias
Welchol Dosage and Administration
- Obtain lipid parameters, including serum triglyceride (TG) levels, before starting WELCHOL (2.1).
- The recommended dosage for adults and for boys and postmenarchal girls aged 10 to 17 years with primary hyperlipidemia is 3.75 grams daily. The recommended dosage for adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus is 3.75 grams daily. WELCHOL should be taken as follows (2.2, 2.4):
Tablets
Take 6 tablets once daily or 3 tablets twice daily with a meal and liquid.
For Oral Suspension
Take one packet once daily with a meal. To prepare, empty the entire contents of one packet into a glass or cup. Add 1 cup of water, fruit juice, or diet soft drinks. Stir well and drink.
Dosage Forms and Strengths
- Tablets: 625 mg (3)
- For Oral Suspension: 3.75 gram packet (3)
Contraindications
- Patients with serum triglyceride levels >500 mg/dL (4)
- Patients with a history of hypertriglyceridemia-induced pancreatitis (4)
- Patients with a history of bowel obstruction (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Hypertriglyceridemia and Pancreatitis: WELCHOL can increase TG. Hypertriglyceridemia can cause acute pancreatitis. Monitor lipids, including TG. Instruct patients to discontinue WELCHOL and seek prompt medical attention if the symptoms of acute pancreatitis occur (5.1).
- Gastrointestinal Obstruction: Cases of bowel obstruction have occurred. WELCHOL is not recommended in patients with gastroparesis, other gastrointestinal motility disorders, and in those who have had major gastrointestinal tract surgery and who may be at risk for bowel obstruction (5.2).
- Vitamin K or Fat-Soluble Vitamin Deficiencies: WELCHOL may decrease absorption of fat-soluble vitamins. Patients with a susceptibility to deficiencies of vitamin K (e.g., patients on warfarin, patients with malabsorption syndromes) or other fat-soluble vitamins may be at increased risk. Patients on oral vitamin supplementation should take their vitamins at least 4 hours prior to WELCHOL (5.3).
- Drug Interactions: Due to the potential for decreased absorption of other drugs that have not been tested for interaction, consider administering at least 4 hours prior to WELCHOL (5.4, 7, 12.3).
- Risks in Patients with Phenylketonuria (PKU): Phenylalanine can be harmful to patients with phenylketonuria. WELCHOL for oral suspension contains 27 mg phenylalanine per 3.75 gram packet (5.5, 11).
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
In clinical trials, the most common (incidence ≥2% and greater than placebo) adverse reactions with WELCHOL included constipation, dyspepsia, and nausea (6.1).
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Daiichi Sankyo, Inc. at 1-877-437-7763 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
Concomitant use with WELCHOL may decrease the exposure of the following drugs: Drugs with a narrow therapeutic index (e.g., cyclosporine), phenytoin, thyroid hormone replacement therapy, warfarin, oral contraceptives containing ethinyl estradiol and norethindrone, olmesartan medoxomil, and sulfonylureas (glimepiride, glipizide, glyburide). Administer these drugs 4 hours prior to WELCHOL. For patients on warfarin, monitor International Normalized Ratio (INR) frequently during initiation then periodically (7.1).
Concomitant use with WELCHOL may increase the exposure of the following drugs: Metformin extended release. Monitor patients' glycemic control (7.2).
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 10/2021
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Welchol
1.1 Primary Hyperlipidemia
WELCHOL is indicated as an adjunct to diet and exercise to reduce elevated low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) in adults with primary hyperlipidemia.
WELCHOL is indicated to reduce LDL-C levels in boys and postmenarchal girls, 10 to 17 years of age, with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (HeFH) who are unable to reach LDL-C target levels despite an adequate trial of dietary therapy and lifestyle modification.
2. Welchol Dosage and Administration
2.1 Testing Prior to Initiation of WELCHOL
Obtain lipid parameters, including triglyceride (TG) levels, before starting WELCHOL. WELCHOL is contraindicated in patients with TG levels >500 mg/dL [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
2.2 Recommended Dosage in Primary Hyperlipidemia and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
The recommended dosage of WELCHOL for adults and for boys and postmenarchal girls aged 10 to 17 years with primary hyperlipidemia is 3.75 grams daily. The recommended dosage of WELCHOL for adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus is 3.75 grams daily. WELCHOL should be taken as follows:
2.3 Important Dosing Information for Primary Hyperlipidemia
WELCHOL can be dosed at the same time as a statin, or WELCHOL and the statin can be dosed apart. Monitor lipid levels within 4 to 6 weeks after initiation of WELCHOL.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
- Tablets: 625 mg tablets are off-white, oval, film-coated and imprinted with "Sankyo" and "C01" on one side.
- For Oral Suspension: 3.75 gram packet containing a white to pale yellow powder with yellow granules.
4. Contraindications
WELCHOL is contraindicated in patients with:
- Serum TG concentrations >500 mg/dL [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- History of hypertriglyceridemia-induced pancreatitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- A history of bowel obstruction [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Hypertriglyceridemia and Pancreatitis
WELCHOL, like other bile acid sequestrants, can increase serum TG concentrations. Hypertriglyceridemia can cause acute pancreatitis.
WELCHOL had effects on serum TG (median increase 5% compared to placebo) in trials of patients with primary hyperlipidemia.
In trials in patients with type 2 diabetes, greater increases in TG levels occurred when WELCHOL was used as monotherapy (median increase 9.7% compared to placebo) and when WELCHOL was used in combination with pioglitazone (median increase 11% compared to placebo in combination with pioglitazone), sulfonylureas (median increase 18% compared to placebo in combination with sulfonylureas), and insulin (median increase 22% compared to placebo in combination with insulin) [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Obtain lipid parameters, including TG levels, before starting WELCHOL and periodically thereafter. WELCHOL is contraindicated in patients with TG levels >500 mg/dL or patients with a history of hypertriglyceridemia-induced pancreatitis [see Contraindications (4)]. Patients with TG levels greater than 300 mg/dL could have greater increases in serum TG levels with WELCHOL and may require additional TG monitoring. Instruct patients to discontinue WELCHOL and seek prompt medical attention if the symptoms of acute pancreatitis occur (e.g., severe abdominal pain with or without nausea and vomiting). Discontinue WELCHOL if TG levels exceed 500 mg/dL [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
5.2 Gastrointestinal Obstruction
Postmarketing cases of bowel obstruction have occurred with WELCHOL [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)]. Because of its constipating effects, WELCHOL is not recommended in patients with gastroparesis, other gastrointestinal motility disorders, and in those who have had major gastrointestinal tract surgery and who may be at risk for bowel obstruction. WELCHOL is contraindicated in patients with a history of bowel obstruction [see Contraindications (4)]. Instruct patients to promptly discontinue WELCHOL and seek medical attention if severe abdominal pain or severe constipation occurs.
Because of the tablet size, WELCHOL tablets can cause dysphagia or esophageal obstruction. For patients with difficulty swallowing tablets, use WELCHOL for oral suspension.
5.3 Vitamin K or Fat-Soluble Vitamin Deficiencies
WELCHOL may decrease the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E, and K. Patients with a susceptibility to deficiencies of vitamin K (e.g., patients on warfarin, patients with malabsorption syndromes) or other fat-soluble vitamins may be at increased risk when taking WELCHOL.
Patients on oral vitamin supplementation should take their vitamins at least 4 hours prior to WELCHOL [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
5.4 Drug Interactions
WELCHOL reduces gastrointestinal absorption of some drugs. Administer drugs with a known interaction at least 4 hours prior to WELCHOL [see Drug Interactions (7)].
Due to the potential for decreased absorption of other drugs that have not been tested for interaction, especially those with a narrow therapeutic index, consider administering at least 4 hours prior to WELCHOL [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
5.5 Risks in Patients with Phenylketonuria (PKU)
Phenylalanine can be harmful to patients with PKU. WELCHOL for oral suspension contains phenylalanine, a component of aspartame. Each 3.75 gram packet contains 27 mg of phenylalanine. Before prescribing WELCHOL for oral suspension to a patient with PKU, consider the combined daily amount of phenylalanine from all sources, including WELCHOL for oral suspension.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following important adverse reactions are described below and elsewhere in the labeling:
- Hypertriglyceridemia and Pancreatitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Gastrointestinal Obstruction [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Vitamin K or Fat-Soluble Vitamin Deficiencies [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
6.1 Clinical Studies Experience
Because clinical studies are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical studies of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in clinical studies of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
6.2 Post-marketing Experience
The following additional adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of WELCHOL. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is generally not possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Adverse Reactions Resulting from Drug Interactions [see Drug Interactions (7)]: Increased seizure activity or decreased phenytoin levels in patients receiving phenytoin, reduced International Normalized Ratio (INR) in patients receiving warfarin therapy, and elevated thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) in patients receiving thyroid hormone replacement therapy
Gastrointestinal: Bowel obstruction (in patients with a history of bowel obstruction or resection), dysphagia or esophageal obstruction (occasionally requiring medical intervention), fecal impaction, pancreatitis, abdominal distension, exacerbation of hemorrhoids, and increased transaminases
Laboratory Abnormalities: Hypertriglyceridemia
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 WELCHOL Drug Interactions that Decrease the Exposure of the Concomitant Medication
Table 4 includes a list of drugs that decrease exposure of the concomitant medication when administered concomitantly with WELCHOL and instructions for preventing or managing them.
| Drugs with a Narrow Therapeutic Index | |
| Clinical Impact: | Concomitant use with WELCHOL may decrease the exposure of the narrow therapeutic index drug. In vivo drug interactions studies showed a decrease in exposure of cyclosporine when coadministered with WELCHOL [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. |
| Intervention: | Administer the narrow therapeutic index drug at least 4 hours prior to WELCHOL. Monitor drug levels when appropriate. |
| Examples: | Cyclosporine |
| Phenytoin | |
| Clinical Impact: | There have been postmarketing reports of increased seizure activity or decreased phenytoin levels in patients receiving phenytoin [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)]. |
| Intervention: | Administer phenytoin 4 hours prior to WELCHOL. |
| Thyroid Hormone Replacement Therapy | |
| Clinical Impact: | In vivo drug interactions studies showed a decrease in exposure of levothyroxine when coadministered with WELCHOL [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. There have been postmarketing reports of elevated thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) in patients receiving thyroid hormone replacement therapy [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)]. |
| Intervention: | Administer thyroid hormone replacement therapy 4 hours prior to WELCHOL. |
| Warfarin | |
| Clinical Impact: | There have been postmarketing reports of reduced INR in patients receiving warfarin therapy [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)]. |
| Intervention: | Monitor INR frequently during WELCHOL initiation then periodically thereafter. |
| Oral Contraceptives Containing Ethinyl Estradiol and Norethindrone | |
| Clinical Impact: | In vivo drug interactions studies showed a decrease in exposure of ethinyl estradiol and norethindrone when coadministered with WELCHOL [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. |
| Intervention: | Administer oral contraceptives containing ethinyl estradiol and norethindrone 4 hours prior to WELCHOL. |
| Olmesartan Medoxomil | |
| Clinical Impact: | In vivo drug interactions studies showed a decrease in olmesartan medoxomil when coadministered with WELCHOL [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. |
| Intervention: | Administer olmesartan medoxomil 4 hours prior to WELCHOL. |
| Sulfonylureas | |
| Clinical Impact: | In vivo drug interactions studies showed a decrease in sulfonylureas when coadministered with WELCHOL [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. |
| Intervention: | Administer sulfonylureas 4 hours prior to WELCHOL. |
| Examples: | Glimepiride, glipizide, and glyburide |
| Oral Vitamin Supplements | |
| Clinical Impact: | WELCHOL may decrease the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E, and K [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]. |
| Intervention: | Patients on oral vitamin supplementation should take their vitamins at least 4 hours prior to WELCHOL. |
7.2 WELCHOL Drug Interactions that Increase the Exposure of the Concomitant Medication
| Metformin Extended Release (ER) | |
| Clinical Impact: | In vivo drug interactions studies showed an increase in metformin extended release (ER) when coadministered with WELCHOL [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. |
| Intervention: | Monitor patients' glycemic control. |
8. Use In Specific Populations
10. Overdosage
WELCHOL is not absorbed and the risk of systemic toxicity is low. Excessive doses of WELCHOL may cause more severe local gastrointestinal effects (e.g., constipation).
11. Welchol Description
WELCHOL (colesevelam hydrochloride) is a non-absorbed, polymeric, lipid-lowering and glucose-lowering agent for oral administration. Colesevelam hydrochloride is a high-capacity bile acid-binding molecule.
Colesevelam hydrochloride is poly(allylamine hydrochloride) cross-linked with epichlorohydrin and alkylated with 1-bromodecane and (6-bromohexyl)-trimethylammonium bromide. The chemical name (IUPAC) of colesevelam hydrochloride is allylamine polymer with 1-chloro-2,3-epoxypropane, [6-(allylamino)-hexyl]trimethylammonium chloride and N-allyldecylamine, hydrochloride. The chemical structure of colesevelam hydrochloride is represented by the following formula:
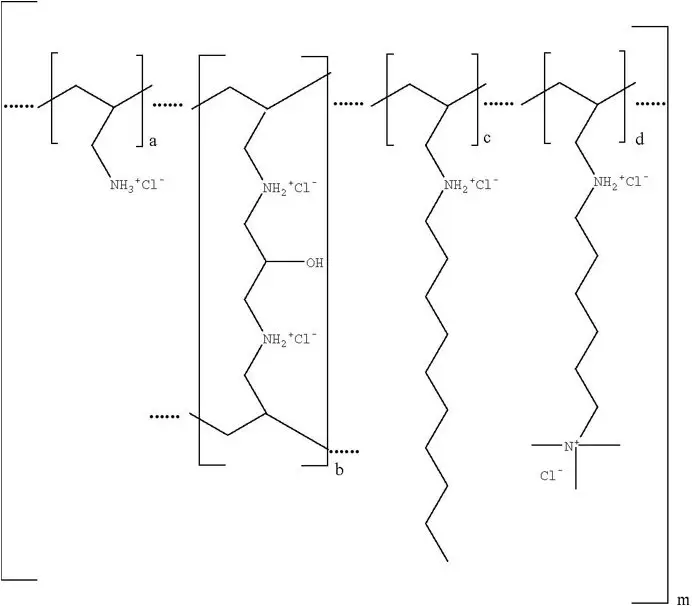
wherein (a) represents allyl amine monomer units that have not been alkylated by either of the 1-bromodecane or (6-bromohexyl)-trimethylammonium bromide alkylating agents or cross-linked by epichlorohydrin; (b) represents allyl amine units that have undergone cross-linking with epichlorohydrin; (c) represents allyl amine units that have been alkylated with a decyl group; (d) represents allyl amine units that have been alkylated with a (6-trimethylammonium) hexyl group, and m represents a number ≥100 to indicate an extended polymer network. A small amount of the amines are dialkylated and are not depicted in the formula above. No regular order of the groups is implied by the structure; cross-linking and alkylation are expected to occur randomly along the polymer chains. A large amount of the amines are protonated. The polymer is depicted in the hydrochloride form; a small amount of the halides are bromide. Colesevelam hydrochloride is hydrophilic and insoluble in water.
WELCHOL tablets are off-white, oval, film-coated, solid tablets each containing 625 mg colesevelam hydrochloride. In addition, each tablet contains the following inactive ingredients: magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, silicon dioxide, HPMC (hydroxypropyl methylcellulose), and acetylated monoglyceride. The tablets are imprinted using a water-soluble black ink (<5 calories per 6 tablets).
WELCHOL for oral suspension is a citrus-flavored, white to pale yellow powder containing yellow granules packaged in a packet containing 3.75 gram colesevelam hydrochloride. In addition, each packet contains the following inactive ingredients: lemon flavor, orange flavor, propylene glycol alginate, simethicone, aspartame, citric acid, medium chain triglycerides, and magnesium trisilicate (<5 calories per 3.75 gram single-dose packet). PHENYLKETONURICS: WELCHOL for oral suspension contains 27 mg phenylalanine per 3.75 gram dose.
12. Welchol - Clinical Pharmacology
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
A maximum therapeutic response to the lipid-lowering effects of WELCHOL was achieved within 2 weeks and was maintained during long-term therapy. In the diabetes clinical studies, a therapeutic response to WELCHOL, as reflected by a reduction in HbA1c, was initially noted following 4-6 weeks of treatment and reached maximal or near-maximal effect after 12-18 weeks of treatment.
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
14. Clinical Studies
14.1 Primary Hyperlipidemia
WELCHOL reduces total cholesterol (TC), LDL-C, apolipoprotein B (Apo B), and non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (non-HDL-C) when administered alone or in combination with a statin in patients with primary hyperlipidemia.
Approximately 1600 patients were studied in 9 clinical trials with treatment durations ranging from 4 to 50 weeks. With the exception of one open-label, uncontrolled, long-term extension study, all studies were multicenter, randomized, double-blind, and placebo-controlled. A maximum therapeutic response to WELCHOL was achieved within 2 weeks and was maintained during long-term therapy.
14.2 Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
WELCHOL has been studied as monotherapy and in combination with metformin, pioglitazone, sulfonylureas, and insulin. In these studies, WELCHOL and placebo were administered either as 3 tablets twice daily with lunch and dinner or as 6 tablets with dinner alone.
16. How is Welchol supplied
WELCHOL 625 mg tablets are supplied as off-white, solid tablets imprinted with the word "Sankyo" and "C01" on one side and are available as follows:
- Bottles of 180 – NDC 65597-701-18
WELCHOL 3.75 gram packets for oral suspension contain a white to pale yellow powder containing yellow granules and are available as follows:
- Cartons of 30 packets – NDC 65597-902-30
| WELCHOL
colesevelam hydrochloride tablet, film coated |
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
| WELCHOL
colesevelam hydrochloride for suspension |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| WELCHOL
colesevelam hydrochloride for suspension |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| WELCHOL
colesevelam hydrochloride bar, chewable |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| WELCHOL
colesevelam hydrochloride bar, chewable |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| WELCHOL
colesevelam hydrochloride bar, chewable |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Daiichi Sankyo Inc. (068605067) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Powdersize, LLC | 080120056 | PARTICLE SIZE REDUCTION(65597-701, 65597-902) | |