Drug Detail:Xacduro (Sulbactam/durlobactam)
Drug Class: Beta-lactamase inhibitors
Highlights of Prescribing Information
XACDURO® (sulbactam for injection; durlobactam for injection), co-packaged for intravenous use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2023
Indications and Usage for Xacduro
XACDURO is a co-packaged product containing sulbactam, a beta-lactam antibacterial and beta lactamase inhibitor, and durlobactam, a beta lactamase inhibitor, indicated in patients 18 years of age and older for the treatment of hospital-acquired bacterial pneumonia and ventilator-associated bacterial pneumonia (HABP/VABP), caused by susceptible isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii-calcoaceticus complex. (1.1)
Limitations of Use:
XACDURO is not indicated for the treatment of HABP/VABP caused by pathogens other than susceptible isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii-calcoaceticus complex. (1.1, 14)
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of XACDURO and other antibacterial drugs, XACDURO should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by bacteria. (1.2)
Xacduro Dosage and Administration
- Administer XACDURO (1 g of sulbactam, 1 g of durlobactam) every 6 hours by intravenous (IV) infusion over 3 hours in patients with creatinine clearance (CLcr) of 45 to 129 mL/min. (2.1)
- Dosing regimen adjustments are recommended for CLcr less than 45 mL/min and CLcr greater than or equal to 130 mL/min. (2.2)
- Administer all doses of XACDURO by IV infusion over 3 hours. (2.3)
- See full prescribing information for instructions on the preparation of the intravenous solution. (2.4)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
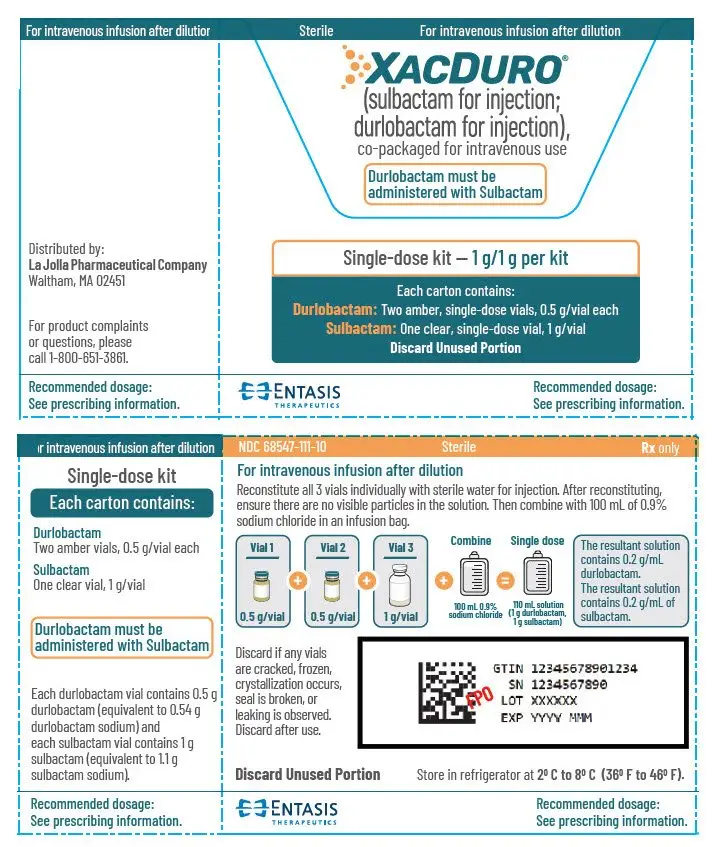
XACDURO is a co-packaged kit containing the following two components as sterile powders for reconstitution (3):
- 1 clear single-dose vial of sulbactam for injection 1 g and
- 2 amber single-dose vials of durlobactam for injection 0.5 g.
Contraindications
Known history of severe hypersensitivity to the components of XACDURO (sulbactam and durlobactam), or other beta-lactam antibacterial drugs. (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Hypersensitivity Reactions: Serious and occasionally fatal hypersensitivity (anaphylactic) reactions have been reported with beta-lactam antibacterial drugs. Hypersensitivity was observed in patients treated with XACDURO. If an allergic reaction occurs, discontinue XACDURO. (5.1)
- Clostridioides difficile-Associated Diarrhea (CDAD): CDAD has been reported with nearly all systemic antibacterial agents, including XACDURO. Evaluate if diarrhea occurs. (5.2)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The most common adverse reactions (incidence > 10%) were liver test abnormalities, diarrhea, anemia, and hypokalemia. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Entasis Therapeutics Inc. at 1-800-651-3861 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
Organic Anion Transporter 1 (OAT1) Inhibitors: Concomitant administration with OAT1 inhibitors may increase plasma concentrations of XACDURO. Concomitant administration is not recommended. (7.1)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 5/2023
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Xacduro
1.1 Hospital-acquired Bacterial Pneumonia and Ventilator-associated Bacterial Pneumonia (HABP/VABP)
XACDURO is indicated in patients 18 years of age and older for the treatment of hospital-acquired bacterial pneumonia and ventilator-associated bacterial pneumonia (HABP/VABP), caused by susceptible isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii-calcoaceticus complex.
1.2 Usage
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of XACDURO and other antibacterial drugs, XACDURO should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible bacteria. When culture and susceptibility information are available, they should be considered in selecting or modifying antibacterial therapy. In the absence of such data, local epidemiology and susceptibility patterns may contribute to the empiric selection of therapy.
2. Xacduro Dosage and Administration
2.1 Recommended Dosage
XACDURO is a co-packaged product containing sulbactam for injection and durlobactam for injection. The recommended dosage of XACDURO is 1 gram (g) of sulbactam and 1 g of durlobactam every 6 hours administered by intravenous (IV) infusion over 3 hours in adults with a creatinine clearance (CLcr) of 45 to 129 mL/min.
Adjustments to the dosing regimen for XACDURO are recommended for patients with CLcr less than 45 mL/min and for patients with CLcr greater than or equal to 130 mL/min [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
The recommended duration of treatment with XACDURO is 7 to 14 days. The duration of therapy should be guided by the patient's clinical status.
2.2 Dosage in Patients (18 Years of Age and Older) Based on Renal Function
See Table 1 for the recommended dosage of XACDURO in patients (18 years of age and older) based on renal function [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Adjustments to the dosing regimen are recommended for patients with creatinine clearance (CLcr) less than 45 mL/min and patients with augmented renal clearance (CLcr greater than or equal to 130 mL/min). For patients undergoing intermittent hemodialysis (HD), start the dosing of XACDURO immediately after the completion of HD.
For patients with fluctuating renal function, monitor CLcr and adjust dosage accordingly [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
| Dose of Sulbactam and Durlobactam (g) | Estimated CLcr (mL/min)* | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
|
||
| sulbactam 1 g and durlobactam 1 g | Greater than or equal to 130 | Every 4 hours |
| 45 to 129 | Every 6 hours | |
| 30 to 44 | Every 8 hours | |
| 15 to 29 | Every 12 hours | |
| less than 15† | For patients initiating XACDURO: Every 12 hours for the first 3 doses (0, 12, and 24 hours), followed by every 24 hours after the third dose†
For patients currently receiving XACDURO whose CLcr declines to less than 15 mL/min: Every 24 hours |
|
2.3 Administration
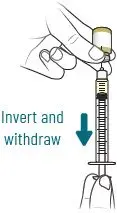
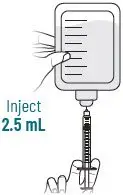
The prepared XACDURO solution [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)] should be brought to ambient room temperature (over 15 to 30 min) prior to infusion to the patient. Administer all doses of XACDURO by intravenous (IV) infusion over 3 hours.
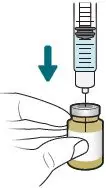
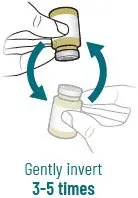
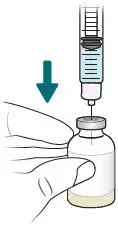
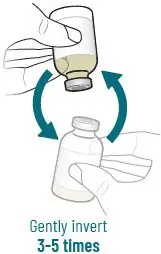
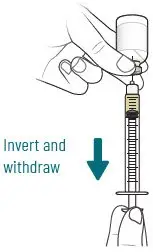
2.4 Preparation of XACDURO for Intravenous Administration
XACDURO is a co-packaged kit containing 1 clear single-dose vial of sulbactam 1g and 2 amber single-dose vials of durlobactam 0.5g as sterile powders that must be reconstituted and further diluted using aseptic technique prior to intravenous infusion.
XACDURO does not contain a bacteriostatic preservative and the prepared solution must be used within 24 hours when stored refrigerated at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F). Discard unused portion.
2.5 Compatibility
XACDURO is compatible with 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP.
The compatibility of XACDURO for administration with solutions containing other drugs or other diluents has not been established. XACDURO should not be mixed with other drugs or physically added to solutions containing other drugs.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
XACDURO is a co-packaged kit containing the following two components as sterile powders for reconstitution:
- 1 clear single-dose vial of sulbactam for injection 1g (as white to off-white powder) and
- 2 amber single-dose vials of durlobactam for injection 0.5g (as solid cake or powder) in each vial.
4. Contraindications
XACDURO is contraindicated in patients with a history of known severe hypersensitivity to the components of XACDURO (sulbactam and durlobactam), or other beta-lactam antibacterial drugs [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Hypersensitivity Reactions
Serious and occasionally fatal hypersensitivity (anaphylactic) reactions and serious skin reactions have been reported in patients receiving beta-lactam antibacterial drugs. These reactions are more likely to occur in individuals with a history of beta-lactam hypersensitivity and/or a history of sensitivity to multiple allergens. Hypersensitivity was observed in patients treated with XACDURO in clinical trials [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Before initiating therapy with XACDURO, careful inquiry should be made concerning previous hypersensitivity reactions to carbapenems, penicillins, cephalosporins, other beta lactams, and other allergens. Discontinue XACDURO if an allergic reaction occurs.
5.2 Clostridioides difficile-Associated Diarrhea (CDAD)
Clostridioides difficile-associated diarrhea (CDAD) has been reported with use of nearly all antibacterial agents, including XACDURO, and may range in severity from mild diarrhea to fatal colitis. Treatment with antibacterial agents alters the normal flora of the colon leading to overgrowth of C. difficile.
C. difficile produces toxins A and B which contribute to the development of CDAD. Hypertoxin producing strains of C. difficile cause increased morbidity and mortality, as these infections can be refractory to antimicrobial therapy and may require colectomy. CDAD must be considered in all patients who present with diarrhea following antibacterial drug use. Careful medical history is necessary since CDAD has been reported to occur over two months after the administration of antibacterial agents.
If CDAD is suspected or confirmed, the risk/benefit of continuing treatment with XACDURO should be assessed. Appropriate fluid and electrolyte management, protein supplementation, antibacterial drug treatment of C. difficile, and surgical evaluation should be instituted as clinically indicated.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following serious adverse reactions are described in greater detail in the Warnings and Precautions section:
- Hypersensitivity Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Clostridioides difficile-Associated Diarrhea (CDAD) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, therefore adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The safety of durlobactam with or without sulbactam was evaluated in 380 adult subjects across six phase 1 trials, one phase 2 trial in patients with complicated urinary tract infections (cUTIs) including acute pyelonephritis, and one phase 3 trial (also referred to as Trial 1) in adult patients with infections caused by Acinetobacter baumannii-calcoaceticus complex including hospital-acquired bacterial pneumonia (HABP), ventilator-associated bacterial pneumonia (VABP), and ventilated pneumonia (VP) [see Clinical Studies (14)].
In the randomized, active-controlled portion of the phase 3 trial, 91 patients received XACDURO (1 g sulbactam and 1 g durlobactam, or renally adjusted dose) intravenously over 3 hours every 6 hours and 86 patients were treated with colistin 2.5 mg/kg (or renally adjusted dose) intravenously over 30 minutes every 12 hours after an initial loading dose of colistin 2.5 to 5 mg/kg. Both treatment arms also received 1 g imipenem/1 g cilastatin (or renally adjusted dose) intravenously every 6 hours as background therapy for potential HABP/VABP pathogens other than Acinetobacter baumannii-calcoaceticus complex. The mean duration of XACDURO therapy was 9 days versus 8 days for colistin.
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of XACDURO in pediatric patients younger than 18 years of age have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the 91 patients treated with XACDURO in Trial 1, 49 (54%) were 65 years of age and older, including 17 (19%) patients 76 years of age and older. Clinical studies of XACDURO did not include sufficient numbers of patients aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently than younger patients.
XACDURO is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney and elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function. Adjust dosing regimen for elderly patients based on renal function [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Use in Specific Populations (8.6) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
The effects of hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics of sulbactam and durlobactam have not been evaluated. Hepatic impairment is not expected to alter the elimination of XACDURO as neither sulbactam nor durlobactam undergo substantial hepatic metabolism/excretion. Dosage adjustments are not necessary in patients with impaired hepatic function.
10. Overdosage
There is no information on the clinical signs and symptoms associated with an overdose of XACDURO. Neurological adverse reactions, including convulsions, may occur with the attainment of high CSF levels of beta-lactams. Sulbactam and durlobactam are removed by hemodialysis [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. No clinical information is available on the use of hemodialysis to treat overdosage.
11. Xacduro Description
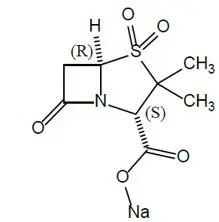
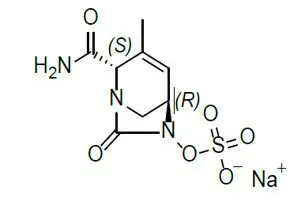
XACDURO (sulbactam for injection and durlobactam for injection) is an antibacterial co-packaged product containing sulbactam sodium, a penicillin derivative beta-lactam antibacterial and beta-lactamase inhibitor, and durlobactam sodium, a diazabicyclooctane beta-lactamase inhibitor, for intravenous administration.
12. Xacduro - Clinical Pharmacology
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
For sulbactam, the percent time of dosing interval that unbound plasma concentrations of sulbactam exceed the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of A. baumannii has been shown to be the best predictor of efficacy in animal and in vitro models of infection. For durlobactam, the ratio of the 24-hour unbound plasma durlobactam AUC to the sulbactam-durlobactam MIC (fAUC0–24/MIC) best predicts the activity in in vivo and in vitro models of infection.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Sulbactam and durlobactam pharmacokinetics are similar following single- and multiple-dose administrations. The Cmax and AUC of sulbactam increase in proportion to dose (0.5 times the recommended single dose to 1 g single dose). Durlobactam demonstrated dose-proportional pharmacokinetics across the dose range studied (0.25 times the recommended single dose to 2 times the recommended single dose infused over 3 hours every 6 hours).
The pharmacokinetic properties of the components of XACDURO and the pharmacokinetic parameters of sulbactam and durlobactam are summarized in Table 3.
| Pharmacokinetic Parameters | Sulbactam | Durlobactam |
|---|---|---|
| AUC0-6 = area under the plasma concentration time curve from time of dosing to 6 hours post dose; AUC0-24 = area under the plasma concentration time curve from time of dosing to 24 hours; CL = clearance; Cmax = maximum concentration; ELF = epithelial lining fluid; SD = standard deviation, T1/2 = terminal half-life; Vss = volume of distribution at steady state | ||
|
||
| Cmax (µg/mL)* | 32.4 ± 24.7 | 29.2 ± 13.2 |
| AUC0-24 (h∙µg/mL)* | 515 ± 458 | 471 ± 240 |
| Distribution | ||
| % Bound to human plasma protein | 38% | 10% |
| AUC0-6 ELF/plasma ratio | 0.5 | 0.37 |
| Vss (L)* | 25.4 ± 11.3 | 30.3 ± 12.9 |
| Metabolism | Minimally metabolized | |
| Elimination | ||
| CL (L/h)* | 11.6 ± 5.64 | 9.96 ± 3.11 |
| T1/2 (h)* | 2.15 ± 1.16 | 2.52 ± 0.77 |
| Excretion | ||
| Major route of elimination | Renal | |
| % excreted unchanged in urine | 75% to 85% | 78% |
| XACDURO
sulbactam and durlobactam kit |
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
| Labeler - LaJolla Pharmaceutical Company (613541192) |
| Registrant - Entasis Therapeutics Inc. (ETI) (079834275) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mitim S.r.l. | 438137085 | MANUFACTURE(68547-211) | |