Drug Detail:Zykadia (Ceritinib [ se-ri-ti-nib ])
Drug Class: Multikinase inhibitors
Highlights of Prescribing Information
ZYKADIA® (ceritinib) capsules, for oral use
ZYKADIA® (ceritinib) tablets, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2014
Recent Major Changes
| Warnings and Precautions, Gastrointestinal Adverse Reactions (5.1) | 8/2021 |
Indications and Usage for Zykadia
ZYKADIA is a kinase inhibitor indicated for the treatment of adults with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) whose tumors are anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK)-positive as detected by an FDA-approved test. (1, 2.1)
Zykadia Dosage and Administration
Recommended Dosage: 450 mg orally once daily with food. (2.2)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
- Capsules: 150 mg (3)
- Tablets: 150 mg (3)
Contraindications
None. (4)
Warnings and Precautions
-
Gastrointestinal Adverse Reactions: ZYKADIA can cause gastrointestinal adverse reactions. If severe or intolerable, withhold if not responsive to antiemetics or antidiarrheals; upon improvement, resume ZYKADIA at a reduced dose. (2.3, 5.1)
-
Hepatotoxicity: ZYKADIA can cause hepatotoxicity. Monitor liver laboratory tests at least monthly. Withhold then dose reduce, or permanently discontinue ZYKADIA. (2.3, 5.2)
-
Interstitial Lung Disease/Pneumonitis: Occurred in 2.4% of patients. Permanently discontinue ZYKADIA in patients diagnosed with treatment-related interstitial lung disease (ILD)/pneumonitis. (2.3, 5.3)
-
QT Interval Prolongation: ZYKADIA can cause QTc interval prolongation. Monitor electrocardiograms and electrolytes in patients with congestive heart failure, bradyarrhythmias, electrolyte abnormalities, or those who are taking medications that are known to prolong the QTc interval. Withhold then dose reduce, or permanently discontinue ZYKADIA. (2.3, 5.4)
-
Hyperglycemia: ZYKADIA can cause hyperglycemia. Monitor fasting glucose prior to treatment and periodically thereafter. Initiate or optimize anti-hyperglycemic medications as indicated. Withhold, then dose reduce, or permanently discontinue ZYKADIA. (2.3, 5.5)
-
Bradycardia: ZYKADIA can cause bradycardia. Monitor heart rate and blood pressure regularly. Withhold, then dose reduce, or permanently discontinue ZYKADIA. (2.3, 5.6)
-
Pancreatitis: Elevations of lipase and/or amylase and pancreatitis can occur. Monitor lipase and amylase prior to treatment and periodically thereafter as clinically indicated. Withhold, then dose reduce ZYKADIA. (2.3, 5.7)
- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: ZYKADIA can cause fetal harm. Advise females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus and to use effective contraception. (5.8, 8.1, 8.3)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The most common adverse reactions (incidence of ≥ 25%) in patients treated with ZYKADIA 450 mg with food are diarrhea, nausea, abdominal pain, vomiting, and fatigue; and with ZYKADIA 750 mg under fasted conditions are diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, fatigue, abdominal pain, decreased appetite, and weight loss. (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation at 1-888-669-6682 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
-
CYP3A Inhibitors and Inducers: Avoid concurrent use of ZYKADIA with strong CYP3A inhibitors or inducers. If concurrent use of a strong CYP3A inhibitor is unavoidable, dose reduce ZYKADIA. (2.4, 7.1)
- CYP3A Substrates: Avoid coadministration of ZYKADIA with sensitive CYP3A substrates. (7.2)
- CYP2C9 Substrates: Avoid coadministration of ZYKADIA with CYP2C9 substrates for which minimal concentration changes may lead to serious toxicities. (7.2)
Use In Specific Populations
- Lactation: Advise not to breastfeed. (8.2)
- Severe Hepatic Impairment: For patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh C), dose reduce ZYKADIA. (8.6)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 10/2021
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Zykadia
ZYKADIA® is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) whose tumors are anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK)-positive as detected by an FDA-approved test [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
2. Zykadia Dosage and Administration
2.1 Patient Selection
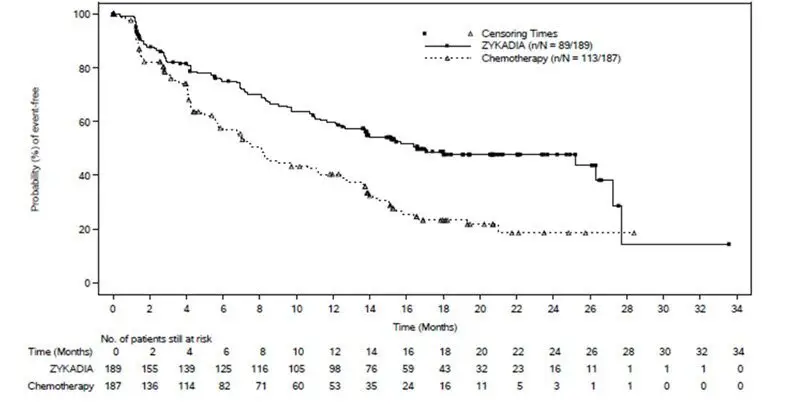
Select patients for treatment of metastatic NSCLC with ZYKADIA based on the presence of ALK positivity in tumor specimens [see Clinical Studies (14.1)].
Information on FDA-approved tests for the detection of ALK rearrangements in NSCLC is available at: http://www.fda.gov/CompanionDiagnostics.
2.2 Recommended Dosage
The recommended dosage of ZYKADIA is 450 mg orally once daily with food until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
If a dose of ZYKADIA is missed, make up that dose unless the next dose is due within 12 hours.
If vomiting occurs during the course of treatment, do not administer an additional dose and continue with the next scheduled dose of ZYKADIA.
2.3 Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions
| Dose Reduction | Recommended Dosage |
| First-dose reduction | 300 mg taken orally once daily with food |
| Second-dose reduction | 150 mg taken orally once daily with food |
Discontinue ZYKADIA for patients unable to tolerate 150 mg taken orally once daily with food.
Dosage modifications for selected adverse reactions of ZYKADIA are provided in Table 2. If dose reduction is required due to an adverse reaction not listed in Table 2, then reduce the daily dose of ZYKADIA by 150 mg.
| Adverse Reaction | ZYKADIA Dose Modification |
| Gastrointestinal Adverse Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] | |
| Severe or intolerable nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea despite optimal antiemetic or anti-diarrheal therapy | Withhold until improved, then resume ZYKADIA at the next lower dosage. |
| Hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] | |
| ALT or AST elevation greater than 5 times ULN with total bilirubin elevation less than or equal to 2 times ULN | Withhold until recovery to baseline or less than or equal to 3 times ULN, then resume ZYKADIA at the next lower dosage. |
| ALT or AST elevation greater than 3 times ULN with total bilirubin elevation greater than 2 times ULN in the absence of cholestasis or hemolysis | Permanently discontinue ZYKADIA. |
| Interstitial Lung Disease/Pneumonitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)] | |
| Any Grade treatment-related ILD/pneumonitis | Permanently discontinue ZYKADIA. |
| QT Interval Prolongation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)] | |
| QTc interval greater than 500 msec on at least 2 separate ECGs | Withhold until QTc interval is less than 481 msec or recovery to baseline if baseline QTc is greater than or equal to 481 msec, then resume ZYKADIA at the next lower dosage. |
| QTc interval prolongation in combination with torsades de pointes or polymorphic ventricular tachycardia or signs/symptoms of serious arrhythmia | Permanently discontinue ZYKADIA. |
| Hyperglycemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)] | |
| Persistent hyperglycemia greater than 250 mg/dL despite optimal anti-hyperglycemic therapy | Withhold until hyperglycemia is adequately controlled, then resume ZYKADIA at the next lower dosage. If adequate hyperglycemic control cannot be achieved with optimal medical management, discontinue ZYKADIA. |
| Bradycardia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)] | |
| Symptomatic bradycardia that is not life-threatening | Withhold until recovery to asymptomatic bradycardia or to a heart rate of 60 bpm or above, evaluate concomitant medications known to cause bradycardia. If bradycardia cannot be attributed to another drug, resume ZYKADIA at the next lower dosage. |
| Clinically significant bradycardia requiring intervention or life-threatening bradycardia in patients taking a concomitant medication also known to cause bradycardia or a medication known to cause hypotension | Withhold until recovery to asymptomatic bradycardia or to a heart rate of 60 bpm or above. If the concomitant medication can be adjusted or discontinued, resume ZYKADIA at the next lower dosage with frequent monitoring. |
| Life-threatening bradycardia in patients who are not taking a concomitant medication also known to cause bradycardia or known to cause hypotension | Permanently discontinue ZYKADIA. |
| Pancreatitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)] | |
| Lipase or amylase elevation greater than 2 times ULN | Withhold until recovery to less than 1.5 times ULN, then resume ZYKADIA at the next lower dosage. |
| Abbreviations: AST, aspartate aminotransferase; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; ULN, upper limit of normal; ILD, interstitial lung disease; ECG, electrocardiogram; bpm, beats per minute. | |
2.4 Dosage Modification for Strong CYP3A Inhibitors
Avoid concurrent use of strong CYP3A inhibitors during treatment with ZYKADIA [see Drug Interactions (7.1), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
If concurrent use of a strong CYP3A inhibitor is unavoidable, reduce the ZYKADIA dose by approximately one-third, rounded to the nearest multiple of the 150 mg dosage strength. After discontinuation of a strong CYP3A inhibitor, resume the ZYKADIA dose that was taken prior to initiating the strong CYP3A inhibitor.
2.5 Dosage Modification for Patients With Severe Hepatic Impairment
For patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh C), reduce the ZYKADIA dose by approximately one-third, rounded to the nearest multiple of the 150 mg dosage strength [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
Capsules: 150 mg hard gelatin capsule with opaque blue cap and opaque white body containing a white to off-white powder. The opaque blue cap is marked in black ink with “LDK 150MG” and the opaque white body is marked in black ink with “NVR”.
Tablets: 150 mg film-coated tablet, light blue, round, biconvex with beveled edges, without score, debossed with “NVR” on one side and “ZY1” on the other side.
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Gastrointestinal Adverse Reactions
Severe gastrointestinal adverse reactions occurred in patients treated with ZYKADIA 750 mg under fasted conditions [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, or abdominal pain occurred in 95% of 925 patients, including severe cases (Grade 3 or 4) in 14% of patients treated with ZYKADIA across clinical studies. Diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, or abdominal pain leading to dose interruptions or reductions occurred in 36% of patients and leading to treatment discontinuation occurred in 1.6% of patients.
The incidence and severity of gastrointestinal adverse reactions were reduced for patients treated with ZYKADIA 450 mg with food in a dose optimization study (ASCEND-8). Diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, or abdominal pain occurred in 79% of 108 patients treated with ZYKADIA at the recommended dose of 450 mg with food. Of these, 53% were Grade 1 events and 24% were Grade 2 events. One patient (0.9%) experienced Grade 3 diarrhea, and one patient (0.9%) experienced Grade 3 vomiting. One patient (0.9%) required dose adjustment due to vomiting. Eleven (10%) patients had diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, or abdominal pain that required at least one dose interruption.
Monitor and manage patients using standard of care, including antidiarrheals, antiemetics, or fluid replacement, as indicated. Withhold ZYKADIA if gastrointestinal adverse reaction is severe or intolerable and is not responsive to antiemetics or antidiarrheals. Upon improvement, resume ZYKADIA at a reduced dose [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
5.2 Hepatotoxicity
Drug-induced hepatotoxicity occurred in patients treated with ZYKADIA [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Elevations in alanine aminotransferase (ALT) > 5 times the upper limit of normal (ULN) occurred in 28% and elevations in aspartate aminotransferase (AST) > 5 times ULN occurred in 16% of 925 patients across clinical studies. Concurrent elevations in ALT > 3 times the ULN and total bilirubin > 2 times the ULN, with alkaline phosphatase < 2 times the ULN occurred in 0.3% of patients across clinical studies. Approximately 1% of patients required permanent discontinuation due to hepatotoxicity.
Monitor with liver laboratory tests, including ALT, AST, and total bilirubin, once a month and as clinically indicated, with more frequent testing in patients who develop transaminase elevations. Based on the severity of the adverse reaction, withhold ZYKADIA with resumption at a reduced dose, or permanently discontinue ZYKADIA [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
5.3 Interstitial Lung Disease/Pneumonitis
Severe, life-threatening, or fatal interstitial lung diseases (ILD)/pneumonitis occurred in patients treated with ZYKADIA [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Across clinical studies, ILD/pneumonitis was reported in 2.4% of 925 patients treated with ZYKADIA. Grade 3 or 4 ILD/pneumonitis was reported in 1.3% of patients, with fatal events reported in 0.2% of patients. Ten patients (1.1%) discontinued ZYKADIA across clinical studies due to ILD/pneumonitis.
Monitor patients for pulmonary symptoms indicative of ILD/pneumonitis. Exclude other potential causes of ILD/pneumonitis and permanently discontinue ZYKADIA in patients diagnosed with treatment-related ILD/pneumonitis [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
5.4 QT Interval Prolongation
QTc interval prolongation, which may lead to an increased risk for ventricular tachyarrhythmia (e.g., torsades de pointes) or sudden death, occurred in patients treated with ZYKADIA [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Across clinical studies, 6% of 919 patients with at least one post-baseline electrocardiogram (ECG) assessment had an increase from baseline of QTc > 60 msec. Approximately 1.3% of patients taking ZYKADIA 750 mg under fasted conditions were found to have a QTc > 500 msec. ZYKADIA causes concentration-dependent increases in the QTc interval [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)]. Across clinical studies, 0.2% of patients discontinued ZYKADIA due to QTc prolongation.
When possible, avoid use of ZYKADIA in patients with congenital long QT syndrome. Conduct periodic monitoring with ECGs and electrolytes in patients with congestive heart failure, bradyarrhythmias, electrolyte abnormalities, or those who are taking medications that are known to prolong the QTc interval. Based on the severity of the adverse reaction, withhold ZYKADIA, with resumption at a reduced dose, or permanently discontinue ZYKADIA [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
5.5 Hyperglycemia
Hyperglycemia occurred in patients treated with ZYKADIA [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Across clinical studies, Grade 3 or 4 hyperglycemia, based on laboratory values, occurred in 13% of 925 patients.
Monitor fasting serum glucose prior to the start of ZYKADIA treatment and periodically thereafter as clinically indicated. Initiate or optimize anti-hyperglycemic medications as indicated. Based on the severity of the adverse reaction, withhold ZYKADIA with resumption at a reduced dose, or permanently discontinue ZYKADIA [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
5.6 Bradycardia
Bradycardia occurred in patients treated with ZYKADIA [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Across clinical studies, sinus bradycardia, defined as a heart rate < 50 beats per minute, was noted as a new finding in 1.1% of 925 patients. Bradycardia was reported as an adverse reaction in 1% of patients. No patient required discontinuation and 0.1% required interruption with subsequent dose reduction for bradycardia.
Avoid using ZYKADIA in combination with other products known to cause bradycardia (e.g., beta-blockers, non-dihydropyridine calcium channel blockers, clonidine, and digoxin) to the extent possible. Monitor heart rate and blood pressure regularly. Based on the severity of the adverse reaction, withhold ZYKADIA with resumption at a reduced dose upon resolution of bradycardia, or permanently discontinue ZYKADIA [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
5.7 Pancreatitis
Pancreatitis occurred in patients treated with ZYKADIA [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Pancreatitis, including one fatality, occurred in less than 1% of patients receiving ZYKADIA in clinical studies. Grade 3 or 4 elevations of amylase occurred in 7% of patients receiving ZYKADIA across clinical studies, while Grade 3 or 4 elevations of lipase occurred in 14% of patients.
Monitor lipase and amylase prior to the start of ZYKADIA treatment and periodically thereafter as clinically indicated. Based on the severity of the laboratory abnormalities, withhold ZYKADIA with resumption at a reduced dose [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
5.8 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on its mechanism of action and findings from animal studies, ZYKADIA can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. In animal studies, administration of ceritinib to rats and rabbits during organogenesis at maternal plasma exposures below the recommended human dose caused increases in skeletal anomalies in rats and rabbits.
Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with ZYKADIA and for 6 months following completion of therapy. Based on the potential for genotoxicity, advise males with female partners of reproductive potential to use condoms during treatment with ZYKADIA and for 3 months following completion of therapy [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3), Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Gastrointestinal Adverse Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Interstitial Lung Disease/Pneumonitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- QT Interval Prolongation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Hyperglycemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Bradycardia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Pancreatitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 Effect of Other Drugs on ZYKADIA
Strong CYP3A Inhibitors
A strong CYP3A4/P-gp inhibitor (ketoconazole) increased the systemic exposure of ceritinib [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)], which may increase the incidence and severity of adverse reactions of ZYKADIA. Avoid concurrent use of strong CYP3A inhibitors during treatment with ZYKADIA. If concurrent use of strong CYP3A inhibitors is unavoidable, reduce the ZYKADIA dose [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
Do not consume grapefruit and grapefruit juice as they may inhibit CYP3A.
Strong CYP3A Inducers
A strong CYP3A4/P-gp inducer (rifampin) decreased the systemic exposure of ceritinib [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)], which may decrease the efficacy of ZYKADIA. Avoid concurrent use of strong CYP3A inducers during treatment with ZYKADIA.
7.2 Effect of ZYKADIA on Other Drugs
CYP3A Substrates
Ceritinib increased the systemic exposure of a sensitive CYP3A substrate (midazolam) [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Avoid coadministration of ZYKADIA with sensitive CYP3A substrates. If concomitant use is unavoidable, consider dose reduction of the sensitive CYP3A substrate(s). If ZYKADIA is coadministered with other CYP3A substrates, refer to the CYP3A substrate labeling for dosage recommendation with strong CYP3A inhibitors.
CYP2C9 Substrates
Ceritinib increased the systemic exposure of a CYP2C9 substrate (warfarin) [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Increase the frequency of INR monitoring if coadministration with warfarin is unavoidable as the anti-coagulant effect of warfarin may be enhanced.
Avoid coadministration of ZYKADIA with CYP2C9 substrates for which minimal concentration changes may lead to serious toxicities. If concomitant use of such CYP2C9 substrates is unavoidable, consider dose reduction for the coadministered CYP2C9 substrates.
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on animal studies and its mechanism of action [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)], ZYKADIA can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. The limited available data on the use of ZYKADIA in pregnant women are insufficient to inform a risk. Administration of ceritinib to rats and rabbits during the period of organogenesis at maternal plasma exposures below the recommended human dose caused increases in skeletal anomalies in rats and rabbits (see Data). Advise a pregnant woman of the potential risk to a fetus.
In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies are 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
In an embryo-fetal development study in which pregnant rats were administered daily doses of ceritinib during organogenesis, dose-related skeletal anomalies were observed at doses as low as 50 mg/kg (less than 0.5-fold the human exposure by AUC at the recommended dose). Findings included delayed ossifications and skeletal variations.
In pregnant rabbits administered ceritinib daily during organogenesis, dose-related skeletal anomalies, including incomplete ossification, were observed at doses equal to or > 2 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.015-fold the human exposure by AUC at the recommended dose). A low incidence of visceral anomalies, including absent or malpositioned gallbladder and retroesophageal subclavian cardiac artery, was observed at doses equal to or > 10 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.13-fold the human exposure by AUC at the recommended dose). Maternal toxicity and abortion occurred in rabbits at doses of 35 mg/kg or greater. In addition, embryolethality was observed in rabbits at a dose of 50 mg/kg.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data regarding the presence of ceritinib or its metabolites in human milk, the effects of ceritinib on the breastfed child or its effects on milk production. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in breastfed children, advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with ZYKADIA and for 2 weeks following completion of therapy.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Pregnancy Testing
Verify pregnancy status in females of reproductive potential prior to initiating ZYKADIA [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Contraception
ZYKADIA can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Females
Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with ZYKADIA and for 6 months following completion of therapy.
Males
Based on the potential for genotoxicity, advise males with female partners of reproductive potential to use condoms during treatment with ZYKADIA and for 3 months following completion of therapy [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
| ZYKADIA
ceritinib tablet, film coated |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation (002147023) |