Drug Detail:Zynlonta (Loncastuximab tesirine-lpyl)
Drug Class: Miscellaneous antineoplastics
Highlights of Prescribing Information
ZYNLONTA® (loncastuximab tesirine-lpyl) for injection, for intravenous use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2021
Indications and Usage for Zynlonta Injection
ZYNLONTA is a CD19-directed antibody and alkylating agent conjugate indicated for the treatment of adult patients with relapsed or refractory large B-cell lymphoma after two or more lines of systemic therapy, including diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) not otherwise specified, DLBCL arising from low-grade lymphoma, and high-grade B-cell lymphoma. (1)
This indication is approved under accelerated approval based on overall response rate. Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in a confirmatory trial(s). (1)
Zynlonta Injection Dosage and Administration
- ZYNLONTA is an intravenous infusion over 30 minutes on Day 1 of each cycle (every 3 weeks). The recommended dosage is:
- 0.15 mg/kg every 3 weeks for 2 cycles.
- 0.075 mg/kg every 3 weeks for subsequent cycles. (2.1)
- Premedicate with dexamethasone 4 mg orally or intravenously twice daily for 3 days beginning the day before ZYNLONTA. (2.2)
- See Full Prescribing Information for instructions on preparation and administration. (2.4)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
For injection: 10 mg of loncastuximab tesirine-lpyl as a lyophilized powder in a single-dose vial for reconstitution and further dilution. (3)
Contraindications
None (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Effusion and Edema: Monitor for the development of pleural effusion, pericardial effusion, ascites, peripheral edema, and general edema. Consider diagnostic imaging when symptoms develop or worsen. (5.1)
- Myelosuppression: Monitor blood cell counts. Withhold, reduce, or discontinue ZYNLONTA based on severity. (5.2)
- Infections: Monitor for infection and treat promptly. (5.3)
- Cutaneous Reactions: Monitor patients for new or worsening cutaneous reactions, including photosensitivity reactions. Dermatologic consultation should be considered. (5.4)
- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: Can cause fetal harm. Advise patients of the potential risk to a fetus and to use effective contraception. (5.5, 8.1, 8.3)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common (≥20%) adverse reactions, including laboratory abnormalities, are thrombocytopenia, increased gamma-glutamyltransferase, neutropenia, anemia, hyperglycemia, transaminase elevation, fatigue, hypoalbuminemia, rash, edema, nausea, and musculoskeletal pain. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact ADC Therapeutics at 1-855-690-0340 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Use In Specific Populations
- Lactation: Advise not to breastfeed. (8.2)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 10/2022
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Zynlonta Injection
ZYNLONTA is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with relapsed or refractory large B-cell lymphoma after two or more lines of systemic therapy, including diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) not otherwise specified, DLBCL arising from low-grade lymphoma, and high-grade B-cell lymphoma.
This indication is approved under accelerated approval based on overall response rate [see Clinical Studies (14.1)]. Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in a confirmatory trial(s).
2. Zynlonta Injection Dosage and Administration
2.1 Recommended Dosage
ZYNLONTA as an intravenous infusion administered over 30 minutes on Day 1 of each cycle (every 3 weeks). Administer intravenous infusion as follows:
- 0.15 mg/kg every 3 weeks for 2 cycles.
- 0.075 mg/kg every 3 weeks for subsequent cycles.
2.2 Recommended Premedication
Unless contraindicated, administer dexamethasone 4 mg orally or intravenously twice daily for 3 days beginning the day before administering ZYNLONTA. If dexamethasone administration does not begin the day before ZYNLONTA, dexamethasone should begin at least 2 hours prior to administration of ZYNLONTA.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
For Injection: 10 mg of loncastuximab tesirine-lpyl as a white to off-white lyophilized powder in a single-dose vial for reconstitution and further dilution.
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Effusion and Edema
Serious effusion and edema occurred in patients treated with ZYNLONTA. Grade 3 edema occurred in 3% (primarily peripheral edema or ascites) and Grade 3 pleural effusion occurred in 3% and Grade 3 or 4 pericardial effusion occurred in 1% [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Monitor patients for new or worsening edema or effusions. Withhold ZYNLONTA for Grade 2 or greater edema or effusion until the toxicity resolves. Consider diagnostic imaging in patients who develop symptoms of pleural effusion or pericardial effusion, such as new or worsened dyspnea, chest pain, and/or ascites such as swelling in the abdomen and bloating. Institute appropriate medical management for edema or effusions [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
5.2 Myelosuppression
Treatment with ZYNLONTA can cause serious or severe myelosuppression, including neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, and anemia. Grade 3 or 4 neutropenia occurred in 32%, thrombocytopenia in 20%, and anemia in 12% of patients. Grade 4 neutropenia occurred in 21% and thrombocytopenia in 7% of patients. Febrile neutropenia occurred in 3% [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Monitor complete blood counts throughout treatment. Cytopenias may require interruption, dose reduction, or discontinuation of ZYNLONTA. Consider prophylactic granulocyte colony-stimulating factor administration as applicable [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
5.3 Infections
Fatal and serious infections, including opportunistic infections, occurred in patients treated with ZYNLONTA. Grade 3 or higher infections occurred in 10% of patients, with fatal infections occurring in 2%. The most frequent Grade ≥3 infections included sepsis and pneumonia [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Monitor for any new or worsening signs or symptoms consistent with infection. For Grade 3 or 4 infection, withhold ZYNLONTA until infection has resolved [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
5.4 Cutaneous Reactions
Serious cutaneous reactions occurred in patients treated with ZYNLONTA. Grade 3 cutaneous reactions occurred in 4% and included photosensitivity reaction, rash (including exfoliative and maculo-papular), and erythema [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Monitor patients for new or worsening cutaneous reactions, including photosensitivity reactions. Withhold ZYNLONTA for severe (Grade 3) cutaneous reactions until resolution [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)]. Advise patients to minimize or avoid exposure to direct natural or artificial sunlight including exposure through glass windows. Instruct patients to protect skin from exposure to sunlight by wearing sun-protective clothing and/or the use of sunscreen products. If a skin reaction or rash develops, dermatologic consultation should be considered [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13)].
5.5 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on its mechanism of action, ZYNLONTA can cause embryo-fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman because it contains a genotoxic compound (SG3199) and affects actively dividing cells.
Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with ZYNLONTA and for 10 months after the last dose. Advise male patients with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with ZYNLONTA, and for 7 months after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)].
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
Effusion and Edema [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
Myelosuppression [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
Infections [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
Cutaneous Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The pooled safety population described in the WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS reflect exposure to ZYNLONTA as a single agent at an initial dose of 0.15 mg/kg in 215 patients with DLBCL in studies ADCT-402-201 (LOTIS-2) and ADCT-402-101, which includes 145 patients from LOTIS-2 treated with 0.15 mg/kg × 2 cycles followed by 0.075 mg/kg for subsequent cycles. Among 215 patients who received ZYNLONTA, the median number of cycles was 3 (range 1 to 15) with 58% receiving three or more cycles and 30% receiving five or more cycles.
In this pooled safety population of 215 patients, the most common (>20%) adverse reactions, including laboratory abnormalities, were thrombocytopenia, increased gamma-glutamyltransferase, neutropenia, anemia, hyperglycemia, transaminase elevation, fatigue, hypoalbuminemia, rash, edema, nausea, and musculoskeletal pain.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post approval use of ZYNLONTA. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders: telangiectasia, blister, rash vesicular
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
ZYNLONTA can cause fetal harm when administered to pregnant women [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of ZYNLONTA in pediatric patients have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the 145 patients with large B-cell lymphoma who received ZYNLONTA in clinical trials, 55% were 65 years of age and older, while 14% were 75 years of age and older [see Clinical Studies (14.1)]. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these patients and younger patients.
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
No dose adjustment is recommended for patients with mild hepatic impairment (total bilirubin ≤ upper limit of normal [ULN] and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) > ULN or total bilirubin > 1 to 1.5 × ULN and any AST). Monitor patients with mild hepatic impairment for potential increased incidence of adverse reactions and modify the ZYNLONTA dosage in the event of adverse reactions [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
ZYNLONTA has not been studied in patients with moderate or severe hepatic impairment (total bilirubin > 1.5 × ULN and any AST) [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
11. Zynlonta Injection Description
Loncastuximab tesirine-lpyl is a CD19-directed antibody and alkylating agent conjugate, consisting of a humanized IgG1 kappa monoclonal antibody conjugated to SG3199, a pyrrolobenzodiazepine (PBD) dimer cytotoxic alkylating agent, through a protease-cleavable valine-alanine linker. SG3199 attached to the linker is designated as SG3249, also known as tesirine.
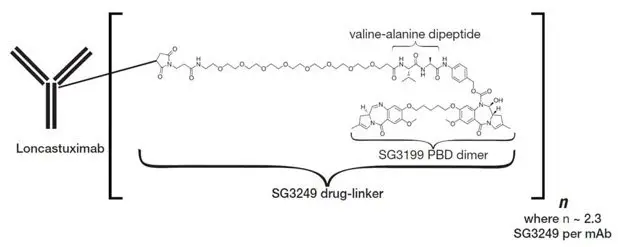
Loncastuximab tesirine-lpyl has an approximate molecular weight of 151 kDa. An average of 2.3 molecules of SG3249 are attached to each antibody molecule. Loncastuximab tesirine-lpyl is produced by chemical conjugation of the antibody and small molecule components. The antibody is produced by mammalian (Chinese hamster ovary) cells, and the small molecule components are produced by chemical synthesis.
ZYNLONTA (loncastuximab tesirine-lpyl) for injection is supplied as a sterile, white to off-white, preservative-free, lyophilized powder, which has a cake-like appearance, for intravenous infusion after reconstitution and dilution. Each single-dose vial delivers 10 mg of loncastuximab tesirine-lpyl, L-histidine (2.8 mg), L-histidine monohydrochloride (4.6 mg), polysorbate 20 (0.4 mg), and sucrose (119.8 mg). After reconstitution with 2.2 mL Sterile Water for Injection, USP, the final concentration is 5 mg/mL with a pH of approximately 6.0.
12. Zynlonta Injection - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Loncastuximab tesirine-lpyl is an antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) targeting CD19. The monoclonal IgG1 kappa antibody component binds to human CD19, a transmembrane protein expressed on the surface of cells of B-lineage origin. The small molecule component is SG3199, a PBD dimer and alkylating agent.
Upon binding to CD19, loncastuximab tesirine-lpyl is internalized followed by release of SG3199 via proteolytic cleavage. The released SG3199 binds to the DNA minor groove and forms highly cytotoxic DNA interstrand crosslinks, subsequently inducing cell death. Loncastuximab tesirine-lpyl had anticancer activity in animal models of lymphoma.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Higher loncastuximab tesirine-lpyl exposure in Cycle 1 was associated with higher incidence of some Grade ≥2 adverse reactions, including skin and nail reactions, liver function test abnormalities and increased gamma-glutamyltransferase. Lower loncastuximab tesirine-lpyl exposure in Cycle 1 was associated with lower efficacy over the dose range of 0.015-0.2 mg/kg (0.1 to 1.33 times the maximum recommended dose).
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The exposure of loncastuximab tesirine-lpyl at the approved recommended dosage in Cycle 2 and at steady state is shown in Table 3. Loncastuximab tesirine-lpyl steady state Cmax was 28.2% lower than the Cmax after the first dose. The time to reach steady state was 105 days.
| Time | Cmax (ng/mL) | AUCtau (ng ∙ day/mL) |
|---|---|---|
| Cmax = Maximum observed serum concentration; AUCtau = Area under curve over the dosing interval | ||
|
||
| Cycle 2 | 2,911 (35.3%) | 21,665 (54.1%) |
| Steady state | 1,776 (32.1%) | 16,882 (38.2%) |
12.6 Immunogenicity
As with all therapeutic proteins, there is potential for immunogenicity. The detection of antibody formation is highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assay. Additionally, the observed incidence of antibody (including neutralizing antibody) positivity in an assay may be influenced by several factors including assay methodology, sample handling, timing of sample collection, concomitant medications, and underlying disease. For these reasons, comparison of the incidence of antibodies in the studies described below with the incidence of antibodies to loncastuximab tesirine-lpyl in other studies or to other products may be misleading.
In LOTIS-2, 0 of 134 patients tested positive for antibodies against loncastuximab tesirine-lpyl after treatment. The potential effect of anti-drug antibodies to ZYNLONTA on pharmacokinetics, efficacy, or safety is unknown.
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenicity studies have not been conducted with loncastuximab tesirine-lpyl or SG3199.
SG3199 was genotoxic in an in vitro micronucleus test and a chromosome aberration assay using human lymphocytes through a clastogenic mechanism. These results are consistent with the pharmacological effect of SG3199 as a covalent DNA crosslinking agent. Results of a bacterial reverse mutation assay (Ames test) were inconclusive due to cytotoxicity.
Fertility studies have not been conducted with loncastuximab tesirine-lpyl. Results from repeat-dose toxicity studies with intravenous administration of loncastuximab tesirine-lpyl in cynomolgus monkeys indicate the potential for impaired male reproductive function and fertility. Administration of loncastuximab tesirine-lpyl to cynomolgus monkeys every 3 weeks at 0.6 mg/kg for a total of 2 doses, or every 3 weeks at 0.3 mg/kg for 13 weeks resulted in adverse findings that included decreased weight and/or size of the testes and epididymis, atrophy of the seminiferous tubules, germ cell degeneration, and/or reduced sperm content. The dose of 0.3 mg/kg in animals results in an exposure (AUC) that is approximately 3 times the exposure at the maximum recommended human dose [MRHD] of 0.15 mg/kg. Findings were not reversible at the end of the 12-week recovery period following 4 or 13 weeks of dosing.
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
Inflammatory-mediated toxicities associated with PBDs have been observed at low incidence in animals. In repeat-dose toxicity studies in cynomolgus monkeys, administration of loncastuximab tesirine-lpyl was associated with potential inflammatory mediated-toxicities, including in the lungs and kidneys. Renal toxicity including increased kidney weights and nephropathy with variable inflammation and fibrosis that was reversible was observed in monkeys. Black skin spots potentially related to phototoxicity were observed and were still present after the 12-week treatment-free period.
14. Clinical Studies
14.1 Relapsed or Refractory Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma
The efficacy of ZYNLONTA was evaluated in LOTIS-2 (NCT03589469), an open-label, single-arm trial in 145 adult patients with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) after at least 2 prior systemic regimens. The trial excluded patients with bulky disease and active central nervous system lymphoma. Patients received ZYNLONTA 0.15 mg/kg every 3 weeks for 2 cycles, then 0.075 mg/kg every 3 weeks for subsequent cycles and received treatment until progressive disease, or unacceptable toxicity.
Of the 145 patients enrolled, the median age was 66 years (range 23 to 94), 59% male, and 94% had an ECOG performance status of 0 to 1. Race was reported in 97% of patients; of these patients, 90% were White, 3% were Black, and 2% were Asian. The diagnosis was DLBCL not otherwise specified (NOS) in 88% (including 20% with DLBCL arising from low-grade lymphoma) and high-grade B-cell lymphoma in 7%. The median number of prior therapies was 3 (range 2 to 7), 63% with refractory disease, 17% with prior stem cell transplant, and 9% with prior chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy.
Efficacy was established on the basis of overall response rate (ORR) as assessed by an Independent Review Committee (IRC) using Lugano 2014 criteria (Table 4). The median follow-up time was 7.3 months (range 0.3 to 20.2).
| Efficacy Parameter | ZYNLONTA N = 145 |
|---|---|
| CI = confidence interval, NE = not estimable | |
|
|
| Overall response rate by IRC*, (95% CI) | 48.3% (39.9, 56.7) |
| Complete response rate (95% CI) | 24.1% (17.4, 31.9) |
| Partial response rate (95% CI) | 24.1% (17.4, 31.9) |
| Duration of overall response† | N = 70 |
| Median (95% CI), months | 10.3 (6.9, NE) |
The median time to response was 1.3 months (range 1.1 to 8.1).
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
- Effusion and Edema: Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider if they experience swelling, weight gain, shortness of breath, or difficult, labored breathing [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- Myelosuppression: Advise patients to immediately contact their healthcare provider for a fever of 100.4°F (38°C) or greater, or signs or symptoms of bruising or bleeding. Advise patients of the need for periodic monitoring of blood counts [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
- Infections: Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider for signs or symptoms of infection, including fever, chills, weakness and/or difficulty breathing [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
- Cutaneous Reactions: Advise patients that skin reaction or rash can occur. Patients should be directed to minimize or avoid exposure to direct natural or artificial sunlight, including sunlight exposure through glass windows. Patients should be instructed to protect skin from exposure to sunlight by wearing sun-protective clothing and/or the use of sunscreen products [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
-
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity:
- -
- Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise female patients of reproductive potential to contact their healthcare provider if they become pregnant, or if pregnancy is suspected, during treatment with ZYNLONTA [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
- -
- Advise women of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with ZYNLONTA and for 10 months after the last dose.
- -
- Advise male patients with female partners of reproductive potential, to use effective contraception during treatment with ZYNLONTA and for 7 months after the last dose [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5) and Use in Specific Populations (8.1), (8.3)].
- Lactation: Advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with ZYNLONTA and for 3 months after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
| ZYNLONTA
loncastuximab tesirine injection, powder, lyophilized, for solution |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - ADC Therapeutics America, Inc. (035224001) |