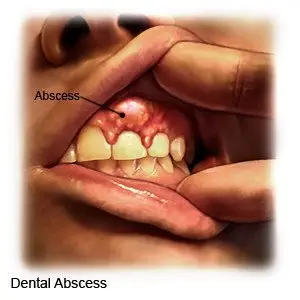
What is a dental abscess?
A dental abscess is a collection of pus in or around a tooth. A dental abscess is caused by bacteria. The bacteria can enter the tooth when the enamel (outer part of the tooth) is damaged by tooth decay. Bacteria can also enter the tooth through a chip in the tooth or a cut in the gum. Food particles that are stuck between the teeth for a long time may also lead to an abscess.
 |
What increases my risk for a dental abscess?
- Poor tooth care
- Medical conditions, such as diabetes, gastric reflux, or diseases that weaken the immune system
- Procedures on the tooth or the gums
- Dry mouth or very little saliva
- Smoking or drinking alcohol
- Radiation therapy of the head and neck
- Certain medicines, such as steroids, allergy, or blood pressure medicines
What are the signs and symptoms of a dental abscess?
- Toothache, a loose tooth, or a tooth that is very sensitive to pressure or temperature
- Bad breath, unpleasant taste, and drooling
- Fever
- Pain, redness, and swelling of the gums, or swelling of your face and neck
- Pain when you open or close your mouth
- Trouble opening your mouth
How is a dental abscess diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider will examine your teeth and gums. He or she will check for pus, redness, swelling, or a mass. You may need an x-ray to check for infection in deeper tissues or broken teeth.
How is a dental abscess treated?
- Medicines may be given to treat a bacterial infection and decrease pain.
- Incision and drainage is a cut in the abscess to allow the pus to drain. A sample of fluid may be collected from your abscess. The fluid is sent to a lab and tested for bacteria. Ask your healthcare provider for more information.
- A root canal is a procedure to remove the bacteria and prevent more infection. It is usually done after an incision and drainage. A filling or crown will be placed over the tooth after you have healed from your root canal.
- Tooth removal may be needed if the infection affects deeper tissues. This is usually done after an incision and drainage.
Treatment options
The following list of medications are in some way related to or used in the treatment of this condition.
- amoxicillin
- Amoxil
- Flagyl
- Erythrocin
- Flagyl 375
View more treatment options
How can I manage my symptoms?
- Rinse your mouth every 2 hours with salt water. This will help keep the area clean.
- Gently brush your teeth twice a day with a soft tooth brush. This will help keep the area clean.
- Eat soft foods as directed. Soft foods may cause less pain. Examples include applesauce, yogurt, and cooked pasta. Ask your healthcare provider how long to follow this instruction.
- Apply a warm compress to your tooth or gum. Use a cotton ball or gauze soaked in warm water. Remove the compress in 10 minutes or when it becomes cool. Repeat 3 times a day.
What can I do to prevent another dental abscess?
- Brush your teeth at least 2 times a day with fluoride toothpaste.
- Use dental floss at least once a day to clean between your teeth.
- Rinse your mouth with water or mouthwash after meals and snacks. Chew sugarless gum.
- Avoid sugary and starchy food that can stick between your teeth. Limit drinks high in sugar, such as soda or fruit juice.
- See your dentist every 6 months for dental cleanings and oral exams.
When should I seek immediate care?
- You have severe pain in your tooth or jaw.
- You have trouble breathing because of pain or swelling.
When should I call my doctor or dentist?
- Your symptoms get worse, even after treatment.
- Your mouth is bleeding.
- You cannot eat or drink because of pain or swelling.
- Your abscess returns.
- You have an injury that causes a crack in your tooth.
- You have questions or concerns about your condition or care.
Care Agreement
You have the right to help plan your care. Learn about your health condition and how it may be treated. Discuss treatment options with your healthcare providers to decide what care you want to receive. You always have the right to refuse treatment. The above information is an educational aid only. It is not intended as medical advice for individual conditions or treatments. Talk to your doctor, nurse or pharmacist before following any medical regimen to see if it is safe and effective for you.© Copyright Merative 2023 Information is for End User's use only and may not be sold, redistributed or otherwise used for commercial purposes.




