Drug Detail:Lovenox (Enoxaparin [ ee-nox-a-par-rin ])
Generic Name: ENOXAPARIN SODIUM 30mg in 0.3mL
Dosage Form: injection
Drug Class: Heparins
Pretreatment Evaluation
Evaluate all patients for a bleeding disorder before starting Lovenox treatment, unless treatment is urgently needed.
Adult Dosage
Abdominal Surgery
The recommended dose of Lovenox is 40 mg by subcutaneous injection once a day (with the initial dose given 2 hours prior to surgery) in patients undergoing abdominal surgery who are at risk for thromboembolic complications. The usual duration of administration is 7 to 10 days [see Clinical Studies (14.1)].
Hip or Knee Replacement Surgery
The recommended dose of Lovenox is 30 mg every 12 hours administered by subcutaneous injection in patients undergoing hip or knee replacement surgery. Administer the initial dose 12 to 24 hours after surgery, provided that hemostasis has been established. The usual duration of administration is 7 to 10 days [see Clinical Studies (14.2)].
A dose of Lovenox of 40 mg once a day subcutaneously may be considered for hip replacement surgery for up to 3 weeks. Administer the initial dose 12 (±3) hours prior to surgery.
Medical Patients during Acute Illness
The recommended dose of Lovenox is 40 mg once a day administered by subcutaneous injection for medical patients at risk for thromboembolic complications due to severely restricted mobility during acute illness. The usual duration of administration is 6 to 11 days [see Clinical Studies (14.3)].
Treatment of Deep Vein Thrombosis with or without Pulmonary Embolism
The recommended dose of Lovenox is 1 mg/kg every 12 hours administered subcutaneously in patients with acute deep vein thrombosis without pulmonary embolism, who can be treated at home in an outpatient setting.
The recommended dose of Lovenox is 1 mg/kg every 12 hours administered subcutaneously or 1.5 mg/kg once a day administered subcutaneously at the same time every day for inpatient (hospital) treatment of patients with acute deep vein thrombosis with pulmonary embolism or patients with acute deep vein thrombosis without pulmonary embolism (who are not candidates for outpatient treatment).
In both outpatient and inpatient (hospital) treatments, initiate warfarin sodium therapy when appropriate (usually within 72 hours of Lovenox). Continue Lovenox for a minimum of 5 days and until a therapeutic oral anticoagulant effect has been achieved (International Normalization Ratio 2 to 3). The average duration of administration is 7 days [see Clinical Studies (14.4)].
Unstable Angina and Non–Q-Wave Myocardial Infarction
The recommended dose of Lovenox is 1 mg/kg administered subcutaneously every 12 hours in conjunction with oral aspirin therapy (100 to 325 mg once daily) in patients with unstable angina or non–Q-wave myocardial infarction. Treat with Lovenox for a minimum of 2 days and continue until clinical stabilization. The usual duration of treatment is 2 to 8 days [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Clinical Studies (14.5)].
Treatment of Acute ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction
The recommended dose of Lovenox is a single intravenous bolus of 30 mg plus a 1 mg/kg subcutaneous dose followed by 1 mg/kg administered subcutaneously every 12 hours (maximum 100 mg for the first two doses only, followed by 1 mg/kg dosing for the remaining doses) in patients with acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. Reduce the dosage in patients ≥75 years of age [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)]. Unless contraindicated, administer aspirin to all patients as soon as they are identified as having STEMI and continue dosing with 75 to 325 mg once daily.
When administered in conjunction with a thrombolytic (fibrin specific or non–fibrin specific), administer Lovenox between 15 minutes before and 30 minutes after the start of fibrinolytic therapy. The usual duration of Lovenox therapy is 8 days or until hospital discharge.
For patients managed with percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), if the last Lovenox subcutaneous administration was given less than 8 hours before balloon inflation, no additional dosing is needed. If the last Lovenox subcutaneous administration was given more than 8 hours before balloon inflation, administer an intravenous bolus of 0.3 mg/kg of Lovenox [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Dose Reduction for Patients with Severe Renal Impairment
The recommended prophylaxis and treatment dosage regimens for patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance <30 mL/min) are described in Table 1 [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
| Indication | Dosage Regimen |
|---|---|
| Prophylaxis in abdominal surgery | 30 mg administered subcutaneously once daily |
| Prophylaxis in hip or knee replacement surgery | 30 mg administered subcutaneously once daily |
| Prophylaxis in medical patients during acute illness | 30 mg administered subcutaneously once daily |
| Inpatient treatment of acute deep vein thrombosis with or without pulmonary embolism, when administered in conjunction with warfarin sodium | 1 mg/kg administered subcutaneously once daily |
| Outpatient treatment of acute deep vein thrombosis without pulmonary embolism, when administered in conjunction with warfarin sodium | 1 mg/kg administered subcutaneously once daily |
| Prophylaxis of ischemic complications of unstable angina and non–Q-wave myocardial infarction, when concurrently administered with aspirin | 1 mg/kg administered subcutaneously once daily |
| Treatment of acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction in patients <75 years of age, when administered in conjunction with aspirin | 30 mg single intravenous bolus plus a 1 mg/kg subcutaneous dose followed by 1 mg/kg administered subcutaneously once daily |
| Treatment of acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction in geriatric patients ≥75 years of age, when administered in conjunction with aspirin | 1 mg/kg administered subcutaneously once daily (no initial bolus) |
Although no dose adjustment is recommended in patients with creatinine clearance 30 to 50 mL/min and creatinine clearance 50 to 80 mL/min, observe these patients frequently for signs and symptoms of bleeding.
Recommended Dosage for Geriatric Patients with Acute ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction
For treatment of acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction in geriatric patients ≥75 years of age, do not use an initial intravenous bolus. Initiate dosing with 0.75 mg/kg subcutaneously every 12 hours (maximum 75 mg for the first two doses only, followed by 0.75 mg/kg dosing for the remaining doses) [see Use in Specific Populations (8.5) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
No dose adjustment is necessary for other indications in geriatric patients unless kidney function is impaired [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
Administration
Do not administer Lovenox by intramuscular injection.
Administer Lovenox by intravenous or subcutaneous injection only.
Lovenox is a clear, colorless to pale yellow sterile solution, and as with other parenteral drug products, should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration.
Use a tuberculin syringe or equivalent when using Lovenox multiple-dose vials to assure withdrawal of the appropriate volume of drug.
Patients may self-inject by the subcutaneous route of administration only after their physicians determine that it is appropriate and with medical follow-up, as necessary. Provide proper training in subcutaneous injection technique before allowing self-injection (with or without the assistance of an injection device).
Subcutaneous Injection Technique
- Position patients in a supine position for Lovenox administration by deep subcutaneous injection.
- Do not expel the air bubble from the prefilled syringes before the injection, to avoid the loss of drug.
- Do not inject into skin that has bruises or scars. Do not inject through clothes.
- Alternate injection sites between the left and right anterolateral and left and right posterolateral abdominal wall.
- Introduce the whole length of the needle into a skin fold held between the thumb and forefinger; hold the skin fold throughout the injection. To minimize bruising, do not rub the injection site after completion of the injection.
Lovenox prefilled syringes and graduated prefilled syringes are for single, one-time use only and are available with a system that shields the needle after injection.
Remove the prefilled syringe from the packaging by peeling at the arrow as directed on the lid. Do not remove by pulling on the plunger as this may damage the syringe.
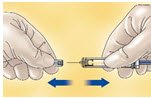
- Remove the needle shield by pulling it straight off the syringe (see Figure A). If less than the full syringe volume is needed to administer the prescribed dose, eject syringe contents until the prescribed dose is left in the syringe.
- Inject using standard technique, pushing the plunger to the bottom of the syringe (see Figure B).
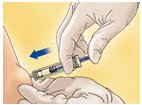
- Remove the syringe from the injection site keeping your finger on the plunger rod (see Figure C).
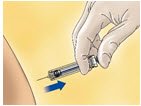
- Orient the needle away from you and others, and activate the safety system by firmly pushing the plunger rod. The protective sleeve will automatically cover the needle and an audible "click" will be heard to confirm shield activation (see Figure D).
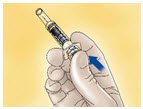
- Immediately dispose of the syringe in the nearest sharps container (see Figure E).

NOTE:
- The safety system can only be activated once the syringe has been emptied.
- Activation of the safety system must be done only after removing the needle from the patient's skin.
- Do not replace the needle shield after injection.
- The safety system should not be sterilized.
Activation of the safety system may cause minimal splatter of fluid. For optimal safety, activate the system while orienting it downwards away from yourself and others.
Intravenous (Bolus) Injection Technique
Use the multiple-dose vial for intravenous injections. Administer Lovenox through an intravenous line. Do not mix or coadminister Lovenox with other medications. Flush the intravenous access device with a sufficient volume of saline or dextrose solution prior to and following the intravenous bolus administration of Lovenox, to prevent mixing of drugs. Lovenox is compatible with normal saline solution (0.9%) or 5% dextrose in water.
Monitoring for Safety
During therapy monitor complete blood counts including platelets and stool occult blood.
Assess for signs and symptoms of bleeding.
In patients with renal impairment anti-Factor Xa levels may be used to monitor the anticoagulant effects of Lovenox.
If during Lovenox therapy abnormal coagulation parameters or bleeding should occur, anti-Factor Xa levels may be used to monitor the anticoagulant effects of Lovenox [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Prothrombin Time (PT) and Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time (aPTT) are not adequate for monitoring the anticoagulant effects of Lovenox.









