Drug Detail:Solu-medrol (injection) (Methylprednisolone (injection) [ meth-il-pred-nis-oh-lone ])
Generic Name: METHYLPREDNISOLONE SODIUM SUCCINATE 1g in 1mL
Dosage Form: injection, powder, for solution
Drug Class: Glucocorticoids
NOTE: Some of the SOLU-MEDROL formulations contain benzyl alcohol (see DESCRIPTION, WARNINGS and PRECAUTIONS, Pediatric Use)
Because of possible physical incompatibilities, SOLU-MEDROL should not be diluted or mixed with other solutions.
Use only the accompanying diluent or Bacteriostatic Water For Injection with Benzyl Alcohol when reconstituting SOLU-MEDROL (see DESCRIPTION).
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit.
This preparation may be administered by intravenous injection, by intravenous infusion, or by intramuscular injection, the preferred method for initial emergency use being intravenous injection. Following the initial emergency period, consideration should be given to employing a longer acting injectable preparation or an oral preparation.
There are reports of cardiac arrhythmias and/or cardiac arrest following the rapid administration of large intravenous doses of SOLU-MEDROL (greater than 0.5 gram administered over a period of less than 10 minutes). Bradycardia has been reported during or after the administration of large doses of methylprednisolone sodium succinate, and may be unrelated to the speed or duration of infusion. When high dose therapy is desired, the recommended dose of SOLU-MEDROL Sterile Powder is 30 mg/kg administered intravenously over at least 30 minutes. This dose may be repeated every 4 to 6 hours for 48 hours.
In general, high dose corticosteroid therapy should be continued only until the patient's condition has stabilized; usually not beyond 48 to 72 hours.
In other indications, initial dosage will vary from 10 to 40 mg of methylprednisolone depending on the specific disease entity being treated. However, in certain overwhelming, acute, life-threatening situations, administrations in dosages exceeding the usual dosages may be justified and may be in multiples of the oral dosages.
It Should Be Emphasized that Dosage Requirements are Variable and Must Be Individualized on the Basis of the Disease Under Treatment and the Response of the Patient. After a favorable response is noted, the proper maintenance dosage should be determined by decreasing the initial drug dosage in small decrements at appropriate time intervals until the lowest dosage which will maintain an adequate clinical response is reached. Situations which may make dosage adjustments necessary are changes in clinical status secondary to remissions or exacerbations in the disease process, the patient's individual drug responsiveness, and the effect of patient exposure to stressful situations not directly related to the disease entity under treatment. In this latter situation, it may be necessary to increase the dosage of the corticosteroid for a period of time consistent with the patient's condition. If after long-term therapy the drug is to be stopped, it is recommended that it be withdrawn gradually rather than abruptly.
SOLU-MEDROL may be administered by intravenous or intramuscular injection or by intravenous infusion, the preferred method for initial emergency use being intravenous injection. To administer by intravenous (or intramuscular) injection, prepare solution as directed. The desired dose may be administered intravenously over a period of several minutes. If desired, the medication may be administered in diluted solutions by adding Water for Injection or other suitable diluent (see below) to the Act-O-Vial and withdrawing the indicated dose.
To prepare solutions for intravenous infusion, first prepare the solution for injection as directed. This solution may then be added to indicated amounts of 5% dextrose in water, isotonic saline solution, or 5% dextrose in isotonic saline solution. From a microbiological point of view, unless the method of opening/reconstitution/dilution precludes the risk of microbial contamination, the product should be used immediately. If not used immediately, in-use storage times and conditions are the responsibility of the user. Chemical and physical stability of the further diluted product has been demonstrated within 4 hours of preparation if stored below 25°C or within 24 hours of preparation if stored at 2°C to 8°C.
In pediatric patients, the initial dose of methylprednisolone may vary depending on the specific disease entity being treated. The range of initial doses is 0.11 to 1.6 mg/kg/day in three or four divided doses (3.2 to 48 mg/m2bsa/day).
The National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) recommended dosing for systemic prednisone, prednisolone, or methylprednisolone in pediatric patients whose asthma is uncontrolled by inhaled corticosteroids and long-acting bronchodilators is 1–2 mg/kg/day in single or divided doses. It is further recommended that short course, or "burst" therapy, be continued until the patient achieves a peak expiratory flow rate of 80% of his or her personal best or until symptoms resolve. This usually requires 3 to 10 days of treatment, although it can take longer. There is no evidence that tapering the dose after improvement will prevent a relapse.
Dosage may be reduced for infants and children but should be governed more by the severity of the condition and response of the patient than by age or size. It should not be less than 0.5 mg per kg every 24 hours.
Dosage must be decreased or discontinued gradually when the drug has been administered for more than a few days. If a period of spontaneous remission occurs in a chronic condition, treatment should be discontinued. Routine laboratory studies, such as urinalysis, two-hour postprandial blood sugar, determination of blood pressure and body weight, and a chest X-ray should be made at regular intervals during prolonged therapy. Upper GI X-rays are desirable in patients with an ulcer history or significant dyspepsia.
In treatment of acute exacerbations of multiple sclerosis, daily doses of 160 mg of methylprednisolone for a week followed by 64 mg every other day for 1 month have been shown to be effective (see PRECAUTIONS, Neurologic-psychiatric).
For the purpose of comparison, the following is the equivalent milligram dosage of the various glucocorticoids:
| Cortisone, 25 | Triamcinolone, 4 |
| Hydrocortisone, 20 | Paramethasone, 2 |
| Prednisolone, 5 | Betamethasone, 0.75 |
| Prednisone, 5 | Dexamethasone, 0.75 |
| Methylprednisolone, 4 |
These dose relationships apply only to oral or intravenous administration of these compounds. When these substances or their derivatives are injected intramuscularly or into joint spaces, their relative properties may be greatly altered.
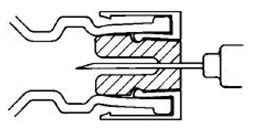
DIRECTIONS FOR USING THE ACT-O-VIAL SYSTEM
- Press down on plastic activator to force diluent into the lower compartment.
- Gently agitate to effect solution.
- Remove plastic tab covering center of stopper.
- Sterilize top of stopper with a suitable germicide.
- Insert needle squarely through center of stopper until tip is just visible. Invert vial and withdraw dose.