Drug Detail:Adakveo (Crizanlizumab-tmca)
Drug Class: Miscellaneous uncategorized agents
Highlights of Prescribing Information
ADAKVEO® (crizanlizumab-tmca) injection, for intravenous use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2019
Indications and Usage for Adakveo Injection
ADAKVEO is a selectin blocker indicated to reduce the frequency of vasoocclusive crises in adults and pediatric patients aged 16 years and older with sickle cell disease. (1)
Adakveo Injection Dosage and Administration
Administer 5 mg/kg by intravenous infusion over a period of 30 minutes on Week 0, Week 2, and every 4 weeks thereafter. (2.1)
See Full Prescribing Information for instructions on preparation and administration. (2.2)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Injection: 100 mg/10 mL (10 mg/mL) solution in a single-dose vial. (3)
Contraindications
None. (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Infusion-Related Reactions: Monitor for and advise patients of signs and symptoms. Discontinue ADAKVEO infusion for severe reactions and manage medically. Temporarily interrupt or slow the rate of infusion for mild or moderate infusion-related reactions and initiate symptomatic treatment. Exercise caution with corticosteroids in patients with sickle cell disease unless clinically indicated (e.g., treatment of anaphylaxis). (2.3, 5.1)
- Interference With Automated Platelet Counts (platelet clumping): Run test as soon as possible or use citrate tubes. (5.2)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions (incidence > 10%) are nausea, arthralgia, back pain, abdominal pain, and pyrexia. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation at 1-888-669-6682 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Use In Specific Populations
Pregnancy: May cause fetal harm. (8.1)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 9/2022
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Adakveo Injection
ADAKVEO® is indicated to reduce the frequency of vaso-occlusive crises (VOCs) in adults and pediatric patients aged 16 years and older with sickle cell disease.
2. Adakveo Injection Dosage and Administration
2.1 Recommended Dosage
Administer ADAKVEO 5 mg/kg by intravenous infusion over a period of 30 minutes at Week 0, Week 2, and every 4 weeks thereafter.
If a dose is missed, administer ADAKVEO as soon as possible.
If ADAKVEO is administered within 2 weeks after the missed dose, continue dosing according to the patient's original schedule.
If ADAKVEO is administered more than 2 weeks after the missed dose, continue dosing every 4 weeks thereafter.
ADAKVEO may be given with or without hydroxyurea.
2.2 Preparation and Administration
ADAKVEO should be prepared and administered by a healthcare professional.
Preparation
- Use aseptic technique to prepare the solution for infusion.
- Calculate the dose (mg) and the total volume (mL) of ADAKVEO solution required, and the number of ADAKVEO vials needed based on the patient’s actual body weight.
- Prepare 5 mg of ADAKVEO per kg of actual body weight.
- Calculate the volume of ADAKVEO to be used according to the following equation:
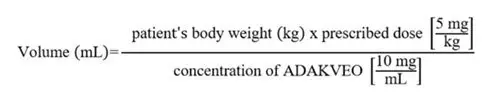
Dilution
Dilute ADAKVEO in 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP or 5% Dextrose Injection, USP to a total volume of 100 mL for intravenous infusion as follows:
- Obtain the number of vials required. One vial is needed for every 10 mL of ADAKVEO.
- Bring vials to room temperature for a maximum of 4 hours prior to the start of preparation (piercing the first vial).
- Visually inspect the vials.
- Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit.
- ADAKVEO is clear to opalescent, colorless or may have a slightly brownish-yellow tint.
- Do not use if particles are present in the solution.
- Obtain a 100 mL 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection or 5% Dextrose Injection infusion bag/container.
- Infusion bags/containers must be made of either polyvinyl chloride (PVC), polyethylene (PE), or polypropylene (PP).
- Remove a volume of 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection or 5% Dextrose Injection from the infusion bag/container that is equal to the required volume of ADAKVEO solution.
- Withdraw the necessary amount of ADAKVEO solution and dilute by adding to the infusion bag/container containing 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection or 5% Dextrose Injection.
- The volume of ADAKVEO added to the infusion bag/container should not exceed 96 mL.
- Gently invert the infusion bag to mix the diluted solution. DO NOT SHAKE.
- Single-dose vials. Discard unused portion.
Storage Conditions of the Diluted Solution
Administer ADAKVEO diluted solution as soon as possible. If not administered immediately, store the prepared solution either:
- At room temperature up to 25°C (77°F) for no more than 4.5 hours from the start of the preparation (piercing the first vial) to the completion of infusion.
- Under refrigeration at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) for no more than 24 hours, from the start of the time of the preparation (piercing the first vial) to the completion of infusion. This includes the storage of the diluted solution and the time to warm up to room temperature. Protect the diluted solution from light during storage under refrigeration.
Administration
- Administer ADAKVEO diluted solution by intravenous infusion over a period of 30 minutes through an intravenous line, which must contain a sterile, nonpyrogenic 0.2-micron inline filter.
- No incompatibilities have been observed between ADAKVEO and infusion sets composed of PVC, polyethylene (PE-lined PVC), polyurethane (PU), and in-line filter membranes composed of polyethersulfone (PES, neutral and positively charged), positively charged polyamide (PA), and polysulphone (PSU).
- Do not mix or coadminister with other drugs through the same intravenous line.
- After administration of ADAKVEO, flush the line with at least 25 mL of 0.9% Sodium Chloride or 5% Dextrose Injection.
- Dispose of any unused product or waste material in accordance with local requirements.
2.3 Management of Infusion-Related Reactions
No dose reductions are recommended. Management for infusion-related reactions for ADAKVEO is described in Table 1.
| aExercise caution with the use of corticosteroids in patients with sickle cell disease unless clinically indicated (e.g., treatment of anaphylaxis). | |
| Severity of Adverse Reaction | Recommendation |
| Mild to moderate infusion-related reactions |
|
| Severe infusion-related reactions |
|
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
Injection: 100 mg/10 mL (10 mg/mL) as a clear to opalescent, colorless to slightly brownish-yellow solution in a single-dose vial.
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Infusion-Related Reactions
In the SUSTAIN clinical trial, infusion-related reactions (defined as occurring during/within 24 hours of infusion) were observed in 2 (3%) patients treated with ADAKVEO 5 mg/kg [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
In the postmarketing setting, cases of infusion-related reactions, including severe pain events, have been reported, which required hospitalizations. The majority of these infusion-related reactions occurred during the first and second infusions. The management of pain events has included acetaminophen, NSAIDs, opioids, antihistamines, intravenous fluids, and/or oxygen therapy. Some patients have also experienced subsequent complications, such as acute chest syndrome and fat embolism, particularly those treated with steroids.
Monitor for and advise patients of signs and symptoms of infusion-related reactions, which may include pain in various locations, headache, fever, chills, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, fatigue, dizziness, pruritus, urticaria, sweating, shortness of breath or wheezing.
Discontinue ADAKVEO infusion for severe infusion-related reactions and institute appropriate medical care [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
For management recommendations of a mild or moderate infusion-related reaction [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
Exercise caution with corticosteroids in patients with sickle cell disease unless clinically indicated (e.g., treatment of anaphylaxis).
5.2 Laboratory Test Interference
Interference with automated platelet counts (platelet clumping) has been observed following administration of ADAKVEO, in particular, when blood samples were collected in tubes containing ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA). Mitigation strategies are recommended [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Infusion-related reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Sickle Cell Disease
The safety of ADAKVEO was evaluated in the SUSTAIN trial [see Clinical Studies (14.1)]. Eligible patients were diagnosed with sickle cell disease (any genotype, including HbSS, HbSC, HbS beta0-thalassemia, HbS beta+-thalassemia, and others). Patients received ADAKVEO 5 mg/kg (N = 66) or 2.5 mg/kg (N = 64) or placebo (N = 62) administered by intravenous infusion on Week 0, Week 2, and every 4 weeks thereafter. The safety evaluation below is limited to the patients who received the recommended dose of 5 mg/kg.
Among the 66 patients that received the recommended dose (5 mg/kg), 83% were exposed for 6 months or longer and 61% were exposed for approximately one year; forty-two (64%) patients were treated with ADAKVEO in combination with hydroxyurea.
Serious adverse reactions were reported in 2 patients (3%) treated with ADAKVEO 5 mg/kg; both reactions were pyrexia.
Two deaths (3%) occurred in the ADAKVEO 5 mg/kg treatment group. None of the deaths were considered to be related to ADAKVEO.
The most common adverse reactions (≥ 10%) were nausea, arthralgia, back pain, abdominal pain, and pyrexia. These adverse reactions, along with myalgia, musculoskeletal chest pain, and diarrhea may be signs and symptoms of an infusion-related reaction when observed during/within 24 hours of an infusion [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Table 2 summarizes the adverse reactions in the SUSTAIN trial.
| aAbdominal pain: abdominal pain, upper abdominal pain, lower abdominal pain, and abdominal tenderness. | ||||
| ADAKVEO 5 mg/kg N = 66 n (%) | Placebo N = 62 n (%) |
|||
| Adverse Reactions | All Grades (%) | Grade ≥ 3 (%) | All Grades (%) | Grade ≥ 3 (%) |
| Gastrointestinal Disorders | ||||
| Nausea | 12 (18) | 0 | 7 (11) | 1 (2) |
| Abdominal paina | 8 (12) | 0 | 3 (5) | 0 |
| Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders | ||||
| Arthralgia | 12 (18) | 1 (2) | 5 (8) | 1 (2) |
| Back pain | 10 (15) | 0 | 7 (11) | 0 |
| General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions | ||||
| Pyrexia | 7 (11) | 1 (2) | 4 (7) | 0 |
Clinically relevant adverse reactions (all Grades) that were reported in less than 10% of patients treated with ADAKVEO included: oropharyngeal pain, diarrhea, vomiting, pruritus (pruritus and vulvovaginal pruritus), musculoskeletal chest pain, myalgia, infusion-site reaction (infusion-site extravasation, infusion-site pain, and infusion-site swelling), and infusion-related reaction.
6.2 Immunogenicity
As with all therapeutic proteins, there is potential for immunogenicity. The detection of antibody formation is highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assay. Additionally, the observed incidence of antibody (including neutralizing antibody) positivity in an assay may be influenced by several factors, including assay methodology, sample handling, timing of sample collection, concomitant medications, and underlying disease. For these reasons, comparison of the incidence of antibodies in the studies described below with the incidence of antibodies in other studies or to other crizanlizumab products may be misleading.
The immunogenicity of ADAKVEO was evaluated using a validated bridging immunoassay for the detection of binding anti-crizanlizumab-tmca antibodies. In a single arm, open label multiple dose study, 0 of the 45 patients with sickle cell disease treated with ADAKVEO 5 mg/kg tested positive for treatment-induced anti-crizanlizumab-tmca antibodies. In a single-dose study of healthy subjects, 1 of the 61 (1.6%) evaluable subjects tested positive for a treatment-induced anti-crizanlizumab-tmca antibodies.
6.3 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval use of ADAKVEO. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
General Disorders and Administration-site Conditions: Pain (in various locations) occurring during/within 24 hours of the infusion (e.g., potential infusion-related reaction) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 Laboratory Test Interference
Platelet Tests
ADAKVEO interferes with automated platelet counts (platelet clumping) in particular when blood samples are collected in tubes containing EDTA, which may lead to unevaluable or falsely decreased platelet counts. Run blood samples within 4 hours of blood collection or collect blood samples in tubes containing citrate. When needed, estimate platelet count via peripheral blood smear.
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on data from animal studies, ADAKVEO has the potential to cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. In an animal reproduction study, intravenous administration of crizanlizumab-tmca to pregnant cynomolgus monkeys from the onset of organogenesis through delivery resulted in a non-dose related increased fetal loss (abortions/stillbirths) at doses approximately 2.8 times the exposure at the recommended clinical dose at 5 mg/kg/dose once every 4 weeks (see Data).
There are insufficient human data on ADAKVEO use in pregnant women to evaluate for a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus. ADAKVEO should only be used during pregnancy if the expected benefit to the patient justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is approximately 14% and up to 43%, respectively. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes.
Clinical Considerations
Disease-Associated Maternal and/or Embryo/Fetal Risk
Women with sickle cell disease have an increased risk of adverse pregnancy outcomes for the mother and the fetus. Pregnant women are at greater risk for VOCs, pre-eclampsia, eclampsia, and maternal mortality. For the fetus, there is an increased risk for intrauterine growth restriction, preterm delivery, low birth weight, and perinatal mortality.
Data
Animal Data
In an enhanced pre- and postnatal development study in cynomolgus monkeys, pregnant animals received intravenous doses of crizanlizumab-tmca at 10 and 50 mg/kg once every 2 weeks during the period of onset of organogenesis through delivery. No maternal toxicity was observed. Maternal exposures at doses of 10 and 50 mg/kg were between 2.8 and 16 times, respectively, the human clinical exposure based on area under the curve (AUC) in patients with sickle cell disease at 5 mg/kg/dose once every 4 weeks. There was an increase in fetal loss (abortions or still births) at both crizanlizumab-tmca doses which was higher in the third trimester.
There were no effects on infant growth and development through 6-months postpartum that were attributable to crizanlizumab-tmca.
Measurable crizanlizumab-tmca serum concentrations were observed in the infant monkeys at postnatal Day 28, confirming that crizanlizumab crosses the placental barrier.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There is no data on the presence of crizanlizumab-tmca in human or animal milk, the effects on the breastfed child, or the effects on milk production. Maternal IgG is known to be present in human milk. The effects of local gastrointestinal exposure and limited systemic exposure in the breastfed child to crizanlizumab-tmca are unknown.
The developmental and health benefits of breast-feeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for ADAKVEO and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from ADAKVEO or from the underlying maternal condition.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of ADAKVEO for sickle cell disease have been established in pediatric patients aged 16 years and older. Use of ADAKVEO for sickle cell disease is supported by evidence from adequate and well-controlled studies in adults and pediatric patients (SUSTAIN Trial). The SUSTAIN trial enrolled one pediatric patient treated with ADAKVEO 5 mg/kg aged 16 years old [see Adverse Reactions (6.1), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3), Clinical Studies (14)].
The safety and efficacy of ADAKVEO in pediatric patients below the age of 16 years have not been established.
11. Adakveo Injection Description
Crizanlizumab-tmca is a P-selectin blocker humanized IgG2 kappa monoclonal antibody that binds to P-selectin. Crizanlizumab-tmca is produced using recombinant DNA technology in Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells. It is composed of 2 heavy chains, each containing 448 amino acids, and 2 light chains each containing 218 amino acids, with a theoretical molecular weight of approximately 146 kDa.
ADAKVEO (crizanlizumab-tmca) injection is supplied as a sterile, preservative-free, clear to opalescent, colorless to slightly brownish-yellow solution for dilution and subsequent administration by intravenous infusion. Each 10 mL vial contains 100 mg crizanlizumab-tmca, citric acid (5.4 mg), polysorbate 80 (2 mg), sodium citrate (50.5 mg), sucrose (753.3 mg) and water for injection with a pH of 6.
| ADAKVEO
crizanlizumab injection |
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation (002147023) |





