Drug Detail:Adasuve inhalation (Loxapine (inhalation) [ lox-a-peen ])
Drug Class: Miscellaneous antipsychotic agents
Highlights of Prescribing Information
ADASUVE ® (loxapine) inhalation powder, for oral inhalation use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1975
WARNING: BRONCHOSPASM and INCREASED MORTALITY IN ELDERLY PATIENTS WITH DEMENTIA-RELATED PSYCHOSIS
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
- ADASUVE can cause bronchospasm that has the potential to lead to respiratory distress and respiratory arrest, particularly in patients with lung diseases ( 4, 5.1)
- ADASUVE is available only through a restricted program called the ADASUVE REMS ( 5.2)
- Administer ADASUVE only in a certified healthcare setting that has immediate access on site to supplies and healthcare professionals competent in the management of acute bronchospasm and access to emergency assistance for symptoms that require immediate medical attention. Certified healthcare settings must have a short-acting bronchodilator available for the immediate treatment of bronchospasm ( 5.1, 5.2)
- Elderly patients with dementia-related psychosis treated with antipsychotic drugs are at an increased risk of death. ADASUVE is not approved for the treatment of patients with dementia-related psychosis ( 5.3)
Recent Major Changes
| Boxed Warning | 1/2022 |
| Indications and Usage ( 1) | 1/2022 |
| Dosing and Administration ( 2.2, 2.4) | 1/2022 |
| Warnings and Precautions ( 5.1, 5.2) | 1/2022 |
Indications and Usage for Adasuve
ADASUVE is an atypical antipsychotic indicated for the acute treatment of agitation associated with schizophrenia or bipolar I disorder in adults ( 1).
Limitations of Use:
ADASUVE must be administered only in a certified healthcare setting ( 1).
Adasuve Dosage and Administration
- Must be administered only by a healthcare professional ( 2.1)
- 10 mg by oral inhalation using an inhaler ( 2.1)
- Administer only a single dose within any 24-hour period ( 2.1)
- Prior to administering, screen all patients for a history of pulmonary disease, and assess patients (including chest auscultation) for respiratory abnormalities (e.g. wheezing) ( 2.2)
- Refer to Full Prescribing Information for important instructions on use of the ADASUVE inhaler ( 2.3)
- After administration, monitor patients for signs and symptoms of bronchospasm for at least one hour ( 2.4)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
- Inhalation powder: 10 mg unit in a single-use inhaler ( 3)
Contraindications
- Current diagnosis or history of asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), or other lung disease associated with bronchospasm ( 4)
- Acute respiratory signs/symptoms (e.g., wheezing) ( 4)
- Current use of medications to treat airways disease, such as asthma or COPD ( 4)
- History of bronchospasm following ADASUVE treatment ( 4)
- Known hypersensitivity to loxapine or amoxapine ( 4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome: May develop in patients treated with antipsychotic drugs. Discontinue treatment ( 5.4)
- Hypotension and Syncope: Use with caution in patients with known cardiovascular or cerebrovascular disease ( 5.5)
- Seizure: Use with caution in patients with a history of seizures or with conditions that lower the seizure threshold ( 5.7)
- Potential for Cognitive and Motor Impairment: Use caution when driving or operating machinery ( 5.8)
- Cerebrovascular Adverse Reactions: Increased incidence of stroke and transient ischemic attack in elderly patients with dementia-related psychosis treated with antipsychotic drugs ( 5.9)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥ 2% and greater than placebo) were dysgeusia, sedation, and throat irritation ( 6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS contact Alexza Pharmaceuticals, Inc. at 1-800-284-0062 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch
Use In Specific Populations
- Pregnancy: May cause extrapyramidal and/or withdrawal symptoms in neonates with third trimester exposure ( 8.1).
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 1/2022
Related/similar drugs
Abilify Maintena, Caplyta, quetiapine, Abilify, Seroquel, aripiprazole, risperidoneFull Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Adasuve
ADASUVE is indicated for the acute treatment of agitation associated with schizophrenia or bipolar I disorder in adults [see Clinical Studies (14)] .
2. Adasuve Dosage and Administration
2.1 Dosing Information
ADASUVE must be administered only by a healthcare professional. ADASUVE is administered by oral inhalation only. The recommended dose for acute agitation is 10 mg administered by oral inhalation, using a single-use inhaler. Administer only a single dose within a 24-hour period [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] .
2.2 Required Examination Prior to Dosing
Prior to administering ADASUVE, screen all patients for a history of asthma, COPD, or other pulmonary disease, and assess patients (including chest auscultation) for respiratory signs (e.g. wheezing) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] .
2.3 Important Administration Instructions
Read all of these instructions prior to administering ADASUVE.
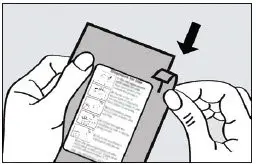
Step 1. Open the Pouch
When ready to use, tear open the foil pouch and remove the inhaler from the package (see Figure 1).
Figure 1. Tearing the pouch
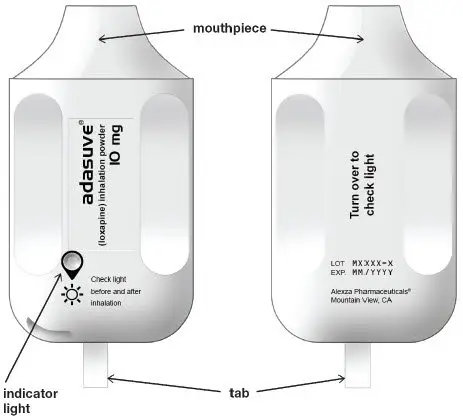
When the ADASUVE inhaler is removed from the pouch, the indicator light is off (see Figure 2).
Figure 2. ADASUVE Inhaler with Indicator Light
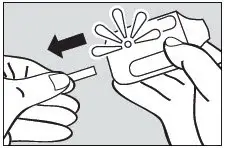
Step 2. Pull Tab
Firmly pull the plastic tab from the rear of the inhaler (see Figure 3). Check that the green light turns on. This indicates that the inhaler is ready for use. Use the inhaler within 15 minutes after removing the tab to prevent automatic deactivation of the inhaler. The green light will turn off, indicating that the inhaler is not usable. Discard the inhaler after one use.
Figure 3.
Step 3. Explain Procedures to the Patient
Explain the administration procedures to the patient prior to use, and advise the patient that it is important to follow the instructions. Inform the patient that the inhaler may produce a flash of light and a clicking sound, and it may become warm during use. These are normal.
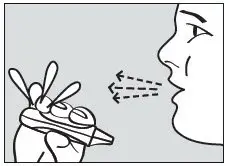
Step 4. Instruct the Patient to Exhale
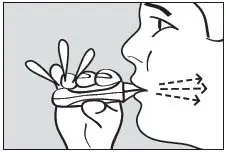
Instruct the patient to hold the inhaler away from the mouth and breathe out fully to empty the lungs (see Figure 4).
Figure 4. Exhale
Step 5. Instruct the Patient to Inhale
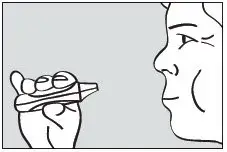
Instruct the patient to put the mouthpiece of the inhaler between the lips, close the lips, and inhale through the mouthpiece with a steady deep breath (see Figure 5). Check that the green light turns off indicating that the dose has been delivered.
Figure 5. Inhale
Step 6. Instruct the Patient to Hold Breath
Instruct the patient to remove the mouthpiece from the mouth and hold the breath for as long as possible, up to 10 seconds (see Figure 6).
Figure 6. Hold Breath
Important: If the green light remains on after the patient inhales, the dose of ADASUVE has NOT been delivered. Instruct the patient to repeat Step 4, Step 5, and Step 6 up to 2 additional times. If the green light still does not turn off, discard the inhaler and use a new one.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
ADASUVE is an inhalation powder supplied in a single-use, disposable inhaler containing 10 mg of loxapine base.
4. Contraindications
ADASUVE is contraindicated in patients with the following:
- Current diagnosis or history of asthma, COPD, or other lung disease associated with bronchospasm [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Acute respiratory symptoms or signs (e.g., wheezing) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Current use of medications to treat airways disease, such as asthma or COPD [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- History of bronchospasm following ADASUVE treatment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Known hypersensitivity to loxapine or amoxapine. Serious skin reactions have occurred with oral loxapine and amoxapine.
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Bronchospasm
ADASUVE can cause bronchospasm that has the potential to lead to respiratory distress and respiratory arrest [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] . Administer ADASUVE only in a certified healthcare setting that has immediate access on site to supplies and healthcare professionals competent in the management of acute bronchospasm and access to emergency assistance for symptoms that require immediate medical attention. Certified healthcare settings must have a short-acting bronchodilator (e.g. albuterol) available for the immediate treatment of bronchospasm; this short-acting bronchodilator can be delivered by inhaler (with spacer) or nebulizer [see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] .
Prior to administering ADASUVE, screen patients regarding a current diagnosis or history of asthma, COPD, and other lung disease associated with bronchospasm, acute respiratory symptoms or signs, current use of medications to treat airways disease, such as asthma or COPD; and assess patients (including chest auscultation) for respiratory abnormalities (e.g., wheezing) [See Dosage and Administration (2.2) and Contraindications (4)] . Monitor patients for symptoms and signs of bronchospasm for a minimum of one hour following treatment with ADASUVE [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)] . ADASUVE can cause sedation, which can mask the symptoms of bronchospasm.
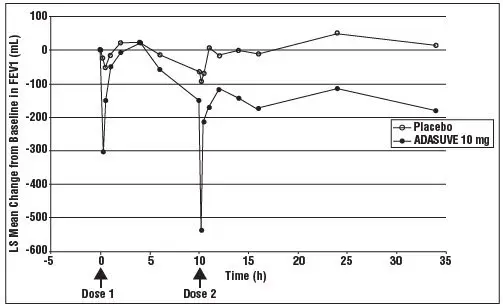
Because clinical trials in patients with asthma or COPD demonstrated that the degree of bronchospasm, as indicated by changes in forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1), was greater following a second dose of ADASUVE, limit ADASUVE use to a single dose within a 24-hour period.
Advise all patients of the risk of bronchospasm. Advise them to inform the healthcare professional if they develop any breathing problems such as wheezing, shortness of breath, chest tightness, or cough following treatment with ADASUVE.
5.2 ADASUVE REMS to Mitigate Bronchospasm
Because of the risk of bronchospasm, ADASUVE is available only through a restricted program under a REMS called the ADASUVE REMS [see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] .
Required components of the ADASUVE REMS are:
- Healthcare settings that dispense and administer ADASUVE must be certified and comply with the REMS requirements. Certified healthcare settings must be able to provide immediate access on site to supplies and healthcare professionals competent in the management of acute bronchospasm and access to emergency assistance for symptoms that require immediate medical attention. Settings must have a short-acting bronchodilator (e.g. albuterol) available for the immediate treatment of bronchospasm; this short-acting bronchodilator can be delivered by inhaler (with spacer) or nebulizer.
- Wholesalers and distributors that distribute ADASUVE must distribute only to certified healthcare settings.
Further information is available at www.adasuverems.com or 1-855-755-0492.
5.3 Increased Mortality in Elderly Patients with Dementia-Related Psychosis
Elderly patients with dementia-related psychosis treated with antipsychotic drugs are at increased risk of death. Analyses of 17 placebo-controlled trials (modal duration of 10 weeks), largely in patients taking atypical antipsychotic drugs, revealed a risk of death in drug-treated patients of 1.6 to 1.7 times the risk of death in placebo-treated patients. Over the course of a typical 10-week controlled trial, the rate of death in drug-treated patients was about 4.5%, compared to a rate of about 2.6% in the placebo group. Although the cases of death were varied, most of the deaths appeared to be either cardiovascular (e.g., heart failure, sudden death) or infectious (e.g., pneumonia) in nature. Observational studies suggest that, similar to atypical antipsychotic drugs, treatment with conventional antipsychotic drugs may increase mortality. The extent to which the findings of increased mortality in observational studies can be attributed to the antipsychotic drug as opposed to some characteristic(s) of the patients is not clear. ADASUVE is not approved for the treatment of elderly patients with dementia-related psychosis [see Boxed Warning] .
5.4 Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome
Antipsychotic drugs can cause a potentially fatal symptom complex termed Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS). Clinical manifestations of NMS include hyperpyrexia, muscle rigidity, altered mental status, and autonomic instability (irregular pulse or blood pressure, tachycardia, diaphoresis, and cardiac dysrhythmia). Associated features can include elevated serum creatine phosphokinase (CPK) concentration, rhabdomyolysis, elevated serum and urine myoglobin concentration, and renal failure. NMS did not occur in the ADASUVE clinical program.
The diagnostic evaluation of patients with this syndrome is complicated. It is important to consider the presence of other serious medical conditions (e.g., pneumonia, systemic infection, heat stroke, primary CNS pathology, central anticholinergic toxicity, extrapyramidal symptoms, or drug fever).
The management of NMS should include: 1) immediate discontinuation of antipsychotic drugs and other drugs that may contribute to the underlying disorder, 2) intensive symptomatic treatment and medical monitoring, and 3) treatment of any concomitant serious medical problems. There is no general agreement about specific pharmacological treatment regimens for NMS.
If a patient requires antipsychotic drug treatment after recovery from NMS, the potential reintroduction of drug therapy should be carefully considered. The patient should be carefully monitored, since recurrences of NMS have been reported.
5.5 Hypotension and Syncope
ADASUVE can cause hypotension, orthostatic hypotension, and syncope. Use ADASUVE with caution in patients with known cardiovascular disease (history of myocardial infarction or ischemic heart disease, heart failure or conduction abnormalities), cerebrovascular disease, or conditions that would predispose patients to hypotension (dehydration, hypovolemia, or treatment with antihypertensive medications or other drugs that affect blood pressure or reduce heart rate).
In the presence of severe hypotension requiring vasopressor therapy, the preferred drugs may be norepinephrine or phenylephrine. Epinephrine should not be used, because beta stimulation may worsen hypotension in the setting of ADASUVE-induced partial alpha blockade.
In short-term (24-hour) placebo-controlled trials of patients with agitation associated with schizophrenia or bipolar I disorder, hypotension occurred in 0.4% and 0.8% in the ADASUVE 10 mg and placebo groups, respectively. There were no cases of orthostatic hypotension, postural symptoms, presyncope or syncope. A systolic blood pressure ≤ 90 mm Hg with a decrease of ≥ 20 mm Hg occurred in 1.5% and 0.8% of the ADASUVE 10 mg and placebo groups, respectively. A diastolic blood pressure ≤ 50 mm Hg with a decrease of ≥15 mm Hg occurred in 0.8% and 0.4% of the ADASUVE 10 mg and placebo groups, respectively.
In 5 Phase 1 studies in normal volunteers, the incidence of hypotension was 3% and 0% in ADASUVE 10 mg and the placebo groups, respectively. The incidence of syncope or presyncope in normal volunteers was 2.3% and 0% in the ADASUVE and placebo groups, respectively. In normal volunteers, a systolic blood pressure ≤ 90 mm Hg with a decrease of ≥ 20 mm Hg occurred in 5.3% and 1.1% in the ADASUVE and placebo groups, respectively. A diastolic blood pressure ≤ 50 mm Hg with a decrease of ≥ 15 mm Hg occurred in 7.5% and 3.3% in the ADASUVE and placebo groups, respectively.
5.6 Falls
ADASUVE may cause somnolence, postural hypotension, motor and sensory instability, which may lead to falls and, consequently, fractures or other injuries. For patients with diseases, conditions, or medications that could exacerbate these effects, complete fall risk assessments when initiating antipsychotic treatment and recurrently for patients on long-term antipsychotic therapy.
5.7 Seizures
ADASUVE lowers the seizure threshold. Seizures have occurred in patients treated with oral loxapine. Seizures can occur in epileptic patients even during antiepileptic drug maintenance therapy. In short term (24 hour), placebo-controlled trials of ADASUVE, there were no reports of seizures.
5.8 Potential for Cognitive and Motor Impairment
ADASUVE can impair judgment, thinking, and motor skills. In short-term, placebo-controlled trials, sedation and/or somnolence were reported in 12% and 10% in the ADASUVE and placebo groups, respectively. No patients discontinued treatment because of sedation or somnolence.
The potential for cognitive and motor impairment is increased when ADASUVE is administered concurrently with other CNS depressants [see Drug Interactions (7.1)] . Caution patients about operating hazardous machinery, including automobiles, until they are reasonably certain that therapy with ADASUVE does not affect them adversely.
5.9 Cerebrovascular Reactions, Including Stroke, in Elderly Patients with Dementia-Related Psychosis
In placebo-controlled trials with atypical antipsychotics in elderly patients with dementia-related psychosis, there was a higher incidence of cerebrovascular adverse reactions (stroke and transient ischemic attacks), including fatalities, compared to placebo-treated patients. ADASUVE is not approved for the treatment of patients with dementia-related psychosis [see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5.3)] .
5.10 Anticholinergic Reactions Including Exacerbation of Glaucoma and Urinary Retention
ADASUVE has anticholinergic activity, and it has the potential to cause anticholinergic adverse reactions including exacerbation of glaucoma or urinary retention. The concomitant use of other anticholinergic drugs (e.g., antiparkinson drugs) with ADASUVE could have additive effects.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following adverse reactions are discussed in more detail in other sections of the labeling:
- Hypersensitivity (serious skin reactions) [see Contraindications (4)]
- Bronchospasm [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Increased Mortality in Elderly Patients with Dementia-Related Psychosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Hypotension and syncope [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Falls [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Seizure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- Potential for Cognitive and Motor Impairment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
- Cerebrovascular Reactions, Including Stroke, in Elderly Patients with Dementia-Related Psychosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]
- Anticholinergic Reactions Including Exacerbation of Glaucoma and Urinary Retention [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
The following findings are based on pooled data from three short-term (24-hour), randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trials (Studies 1, 2, and 3) of ADASUVE 10 mg in the treatment of patients with acute agitation associated with schizophrenia or bipolar I disorder. In the 3 trials, 259 patients received ADASUVE 10 mg, and 263 received placebo [see Clinical Studies (14)] .
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 CNS Depressants
ADASUVE is a central nervous system (CNS) depressant. The concurrent use of ADASUVE with other CNS depressants (e.g., alcohol, opioid analgesics, benzodiazepines, tricyclic antidepressants, general anesthetics, phenothiazines, sedative/hypnotics, muscle relaxants, and/or illicit CNS depressants) can increase the risk of respiratory depression, hypotension, profound sedation, and syncope. Therefore, consider reducing the dose of CNS depressants if used concomitantly with ADASUVE.
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of ADASUVE in pediatric patients have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Elderly patients with dementia-related psychosis treated with antipsychotic drugs are at an increased risk of death [see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5.3)] . ADASUVE is not approved for the treatment of dementia-related psychosis. Placebo-controlled studies of ADASUVE in patients with agitation associated with schizophrenia or bipolar disorder did not include patients over 65 years of age.
11. Adasuve Description
ADASUVE, an atypical antipsychotic, is an inhalation powder of loxapine supplied in a single-use, disposable inhaler containing 10 mg of loxapine base. ADASUVE is a drug-device combination product.
12. Adasuve - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
The mechanism of action of loxapine in the treatment of agitation associated with schizophrenia and bipolar I disorder is unclear. However, its efficacy could be mediated through a combination of antagonism of central serotonin and dopamine receptors.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Loxapine acts as a monoaminergic antagonist with binding affinities (K i values) for central serotonin 5-HT 2A, dopamine D 1, D 2, D 3, and D 4, and histamine H 1 receptors of 2, 18, 10, 21, 9, and 15 nM, respectively. Loxapine also acts as an antagonist at muscarinic M1 and adrenergic α 2 receptors with binding affinities of 117 and 250 nM, respectively.
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
In the rat, minimal and reversible squamous metaplasia of the larynx was observed after daily inhalation exposure of loxapine for 14 days at 1.7 to 13 mg/kg/day (approximately 2 to 13 times the MRHD based on a mg/m 2 body surface area, respectively). This finding was considered a nonspecific particle impaction effect. Mammary hyperplasia in males and females and ovarian follicular cysts and mucification of vaginal epithelium in female rats were observed at all doses, with partial or complete recovery at the end of 14 days of treatment. In the dog, no effects on the respiratory tract or reproductive tissues were observed after inhalation exposure to loxapine for 28 days at doses up to 1.8 mg/kg/day (~6 times the MRHD based on a mg/m 2 body surface area).
14. Clinical Studies
The efficacy of ADASUVE 10 mg in the acute treatment of agitation associated with schizophrenia or bipolar I disorder was established in two short-term (24-hour), randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, fixed-dose trials. Study 1 included 344 patients who met DSM-IV criteria for schizophrenia. Study 2 included 314 patients who met DSM-IV criteria for bipolar I disorder, manic or mixed episodes with or without psychotic features.
Patients were judged by the clinical investigators to be clinically agitated, with a level of agitation that met or exceeded a specific severity threshold as measured by the Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale-Excited Component (PEC). The PEC is an investigator-rated instrument consisting of 5 items: poor impulse control, tension, hostility, uncooperativeness, and excitement. Each item is scored on a scale from 1 to 7 (1 = absent, 4 = moderate, 7 = extreme). Thus, the total PEC score can range from 5 to 35. For enrollment in the studies, patients had to have a PEC score of ≥ 14, with at least one individual item score > 4.
Patients whose agitation was related to acute alcohol or drug intoxication were excluded. Patients with clinically significant acute or chronic pulmonary disease (e.g., asthma, COPD, chronic bronchitis, and emphysema) were excluded from the trials [See Contraindications (4)] .
The primary efficacy endpoint in both trials was the mean change from baseline in the PEC score, assessed 2 hours following dosing. The key secondary endpoint was the mean Clinical Global Impression Improvement (CGI-I) Scale score at two hours. The CGI-I is an investigator-rated global assessment of symptom improvement, scored on a scale of 1 to 7: 1 = very much improved; 4 = no change from baseline; 7 = very much worse.
In both studies, mean baseline PEC scores were similar in all treatment groups, averaging 17.3 to 17.7 (Table 4), with individual patient scores ranging from 14 to 31, indicating predominantly moderate levels of agitation. The mean baseline Clinical Global Impression Severity Scale (CGI-S) score in both studies was 4 (moderately ill). In Study 2, 69% of patients had a current manic episode, and 31% had a mixed/manic episode.
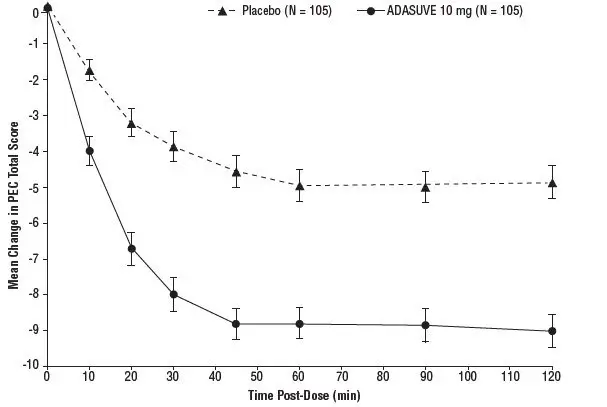
In Studies 1 and 2, treatment with ADASUVE was statistically significantly superior to placebo on the mean change in PEC score at 2 hours (Table 4). In both studies, the effect of ADASUVE was apparent at 10 minutes following dosing (Figures 9 and 10).
| Placebo | ADASUVE | |
|---|---|---|
|
||
| Study 1 (Schizophrenia) | ||
| N | 115 | 112 |
| PEC score | ||
| Mean baseline | 17.4 | 17.6 |
| Change at 2 hours * | -5.8 | -8.7 |
| Difference from placebo (95% CI) † | -- | -2.9 (-4.2, -1.6) |
| p-value | -- | < 0.0001 |
| Study 2 (Bipolar Disorder ) | ||
| N | 105 | 105 |
| PEC score | ||
| Mean baseline | 17.7 | 17.3 |
| Change at 2 hours * | -4.7 | -9.2 |
| Difference from placebo (95% CI) † | -- | -4.5 (-5.8, -3.1) |
| p-value | -- | < 0.0001 |
Examination of population subsets (age, race, and gender) on the primary endpoint did not reveal any differential responsiveness on the basis of these subgroupings.
Figures 9 and 10 show the decreases in PEC score at each time point assessed in the trials. In both trials, the decrease in agitation with ADASUVE was apparent at each time point tested (10, 20, 30, 45, 60, 90, and 120 minutes post-dose).
Figure 9. Mean Change from Baseline in PEC Score through 2 Hours after a Single Dose in Agitated Patients with Schizophrenia (Study 1)
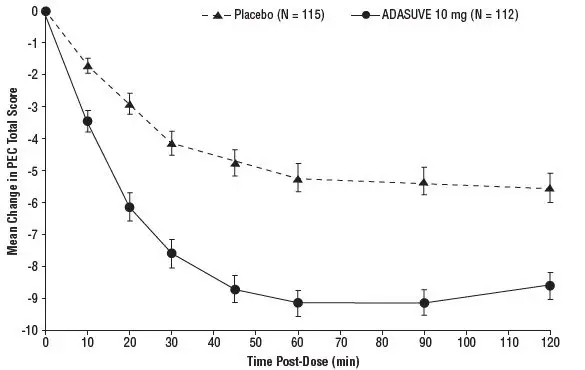
Figure 10. Mean Change from Baseline in PEC Score through 2 Hours after a Single Dose in Agitated Patients with Bipolar Disorder (Study 2)
The results of the secondary endpoint, CGI-I scores, are shown in Table 5.
| Placebo | ADASUVE | |
|---|---|---|
|
||
| Study 1 (Schizophrenia) | ||
| N | 115 | 112 |
| CGI-I score at 2 hours * | 2.8 | 2.1 |
| Difference from placebo (95% CI) * | -- | -0.8, (-1.1, -0.4) |
| p-value | -- | < 0.0001 |
| Study 2 (Bipolar Disorder) | ||
| N | 105 | 105 |
| CGI-I score at 2 hours * | 3.0 | 1.9 |
| Difference from placebo (95% CI) * | -- | -1.1 (-1.4, -0.8) |
| p-value | -- | < 0.0001 |
16. How is Adasuve supplied
16.1 How Supplied
ADASUVE ® (loxapine) inhalation powder is supplied as: ADASUVE 10 mg (NDC 51097-001-01) is a single-use, disposable inhaler containing 10 mg of loxapine, provided in a sealed foil pouch. ADASUVE, 10 mg is supplied in a carton of 5 units per carton (NDC 51097-001-02).
16.2 Restricted Access
ADASUVE is only available through a restricted program called the ADASUVE REMS Program [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] .
16.3 Storage and Handling
Store ADASUVE at room temperature, 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Keep out of reach of children.
Keep ADASUVE in pouch until time of use.
ADASUVE contains a lithium battery. Dispose of ADASUVE in accordance with all federal, state and local laws.
| ADASUVE
loxapine aerosol, powder |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Alexza Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (018849948) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alexza Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | 018849948 | analysis(51097-001) , manufacture(51097-001) , label(51097-001) | |