Drug Detail:Ambien (Zolpidem)
Drug Class: Miscellaneous anxiolytics, sedatives and hypnotics
Highlights of Prescribing Information
AMBIEN® (zolpidem tartrate) tablets, for oral use, C-IV
Initial U.S. Approval: 1992
WARNING: COMPLEX SLEEP BEHAVIORS
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
Complex sleep behaviors including sleep-walking, sleep-driving, and engaging in other activities while not fully awake may occur following use of AMBIEN. Some of these events may result in serious injuries, including death. Discontinue AMBIEN immediately if a patient experiences a complex sleep behavior. (4, 5.1)
Recent Major Changes
| Dosage and Administration (2.1) | 2/2022 |
| Warnings and Precautions (5.5) | 2/2022 |
| Warnings and Precautions (5.7) | 2/2022 |
Indications and Usage for Ambien
AMBIEN, a gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) A receptor positive modulator, is indicated for the short-term treatment of insomnia characterized by difficulties with sleep initiation. (1)
Ambien Dosage and Administration
- Use the lowest dose effective for the patient and must not exceed a total of 10 mg daily (2.1)
- Treatment should be as short as possible (2.1)
- Recommended initial dose is a single dose of 5 mg for women and a single dose of 5 or 10 mg for men, immediately before bedtime with at least 7–8 hours remaining before the planned time of awakening (2.1)
- Geriatric patients and patients with mild to moderate hepatic impairment: Recommended dose is 5 mg for men and women (2.2)
- Lower doses of CNS depressants may be necessary when taken concomitantly with AMBIEN (2.3)
- The effect of AMBIEN may be slowed if taken with or immediately after a meal (2.4)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
5 mg and 10 mg tablets. Tablets not scored. (3)
Contraindications
- Patients who have experienced complex sleep behaviors after taking AMBIEN (4)
- Known hypersensitivity to zolpidem (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- CNS-Depressant Effects: Impaired alertness and motor coordination including risk of morning impairment. Risk increases with dose and use with other CNS depressants and alcohol. Caution patients against driving and other activities requiring mental alertness the morning after use. Instruct patients on correct use. (5.2)
- Need to Evaluate for Comorbid Diagnoses: Reevaluate if insomnia persists after 7 to 10 days of use. (5.3)
- Severe Anaphylactic/Anaphylactoid Reactions: Angioedema and anaphylaxis have been reported. Do not rechallenge if such reactions occur. (5.4)
- Abnormal Thinking and Behavioral Changes: Changes including decreased inhibition, bizarre behavior, agitation, and depersonalization have been reported. Immediately evaluate any new onset behavioral changes. (5.5)
- Depression: Worsening of depression or suicidal thinking may occur. Prescribe the least amount of tablets feasible to avoid intentional overdose. (5.6)
- Respiratory Depression: Consider this risk before prescribing in patients with compromised respiratory function. (5.7)
- Hepatic Impairment: Avoid AMBIEN use in patients with severe hepatic impairment. (5.8)
- Withdrawal Effects: Symptoms may occur with rapid dose reduction or discontinuation. (5.9, 9.3)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most commonly observed adverse reactions were:
Short-term (<10 nights): Drowsiness, dizziness, and diarrhea
Long-term (28–35 nights): Dizziness and drugged feelings (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact sanofi-aventis U.S. LLC at 1-800-633-1610 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
- CNS depressants, including alcohol: Possible adverse additive CNS-depressant effects (5.2, 7.1)
- Opioids: Concomitant use may increase risk of respiratory depression (5.7, 7.1)
- Imipramine: Decreased alertness observed (7.1)
- Chlorpromazine: Impaired alertness and psychomotor performance observed (7.1)
- CYP3A4 inducers (rifampin or St. John's wort): Combination use may decrease effect (7.2)
- Ketoconazole: Combination use may increase effect (7.2)
Use In Specific Populations
- Pregnancy: May cause respiratory depression and sedation in neonates with exposure late in the third trimester. (8.1)
- Lactation: A lactating woman may pump and discard breast milk during treatment and for 23 hours after AMBIEN administration. (8.2)
- Pediatric use: Safety and effectiveness not established. Hallucinations (incidence rate 7%) and other psychiatric and/or nervous system adverse reactions were observed frequently in a study of pediatric patients with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. (5.5, 8.4)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 2/2022
Full Prescribing Information
WARNING: COMPLEX SLEEP BEHAVIORS
Complex sleep behaviors including sleep-walking, sleep-driving, and engaging in other activities while not fully awake may occur following use of AMBIEN. Some of these events may result in serious injuries, including death. Discontinue AMBIEN immediately if a patient experiences a complex sleep behavior [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
1. Indications and Usage for Ambien
AMBIEN (zolpidem tartrate) is indicated for the short-term treatment of insomnia characterized by difficulties with sleep initiation. AMBIEN has been shown to decrease sleep latency for up to 35 days in controlled clinical studies [see Clinical Studies (14)].
The clinical trials performed in support of efficacy were 4–5 weeks in duration with the final formal assessments of sleep latency performed at the end of treatment.
2. Ambien Dosage and Administration
2.1 Dosage in Adults
Use the lowest effective dose for the patient. The recommended initial dose is 5 mg for women and either 5 or 10 mg for men, taken only once per night immediately before bedtime with at least 7–8 hours remaining before the planned time of awakening. If the 5 mg dose is not effective, the dose can be increased to 10 mg. In some patients, the higher morning blood levels following use of the 10 mg dose increase the risk of next-day impairment of driving and other activities that require full alertness [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. The total dose of AMBIEN should not exceed 10 mg once daily immediately before bedtime. AMBIEN should be taken as a single dose and should not be readministered during the same night.
The recommended initial doses for women and men are different because zolpidem clearance is lower in women.
Long-term use of AMBIEN is not recommended. Treatment should be as short as possible. Extended treatment should not take place without re-evaluation of the patient's status because the risk of abuse and dependence increases with the duration of treatment [see Drug Abuse and Dependence (9.3)].
2.2 Special Populations
Elderly or debilitated patients may be especially sensitive to the effects of zolpidem tartrate. The recommended dose of AMBIEN in these patients is 5 mg once daily immediately before bedtime [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2), Use in Specific Populations (8.5)].
Patients with mild to moderate hepatic impairment do not clear the drug as rapidly as normal subjects. The recommended dose of AMBIEN in these patients is 5 mg once daily immediately before bedtime. Avoid AMBIEN use in patients with severe hepatic impairment as it may contribute to encephalopathy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8), Use in Specific Populations (8.7), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
AMBIEN is available in 5 mg and 10 mg strength tablets for oral administration. Tablets are not scored.
AMBIEN 5 mg tablets are capsule-shaped, pink, film coated, with AMB 5 debossed on one side and 5401 on the other.
AMBIEN 10 mg tablets are capsule-shaped, white, film coated, with AMB 10 debossed on one side and 5421 on the other.
4. Contraindications
AMBIEN is contraindicated in patients
- who have experienced complex sleep behaviors after taking AMBIEN [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- with known hypersensitivity to zolpidem. Observed reactions include anaphylaxis and angioedema [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Complex Sleep Behaviors
Complex sleep behaviors, including sleep-walking, sleep-driving, and engaging in other activities while not fully awake, may occur following the first or any subsequent use of AMBIEN. Patients can be seriously injured or injure others during complex sleep behaviors. Such injuries may result in a fatal outcome. Other complex sleep behaviors (e.g., preparing and eating food, making phone calls, or having sex) have also been reported. Patients usually do not remember these events. Postmarketing reports have shown that complex sleep behaviors may occur with AMBIEN alone at recommended doses, with or without the concomitant use of alcohol or other central nervous system (CNS) depressants [see Drug Interactions (7.1)]. Discontinue AMBIEN immediately if a patient experiences a complex sleep behavior [see Contraindications (4)].
5.2 CNS-Depressant Effects and Next-Day Impairment
AMBIEN, like other sedative-hypnotic drugs, has CNS-depressant effects. Coadministration with other CNS depressants (e.g., benzodiazepines, opioids, tricyclic antidepressants, alcohol) increases the risk of CNS depression [see Drug Interactions (7.1)]. Dosage adjustments of AMBIEN and of other concomitant CNS depressants may be necessary when AMBIEN is administered with such agents because of the potentially additive effects. The use of AMBIEN with other sedative-hypnotics (including other zolpidem products) at bedtime or the middle of the night is not recommended [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
The risk of next-day psychomotor impairment, including impaired driving, is increased if AMBIEN is taken with less than a full night of sleep remaining (7 to 8 hours); if a higher than the recommended dose is taken; if coadministered with other CNS depressants or alcohol; or if coadministered with other drugs that increase the blood levels of zolpidem. Patients should be warned against driving and other activities requiring complete mental alertness if AMBIEN is taken in these circumstances [see Dosage and Administration (2), Clinical Studies (14.3)].
Vehicle drivers and machine operators should be warned that, as with other hypnotics, there may be a possible risk of adverse reactions including drowsiness, prolonged reaction time, dizziness, sleepiness, blurred/double vision, reduced alertness, and impaired driving the morning after therapy. In order to minimize this risk a full night of sleep (7–8 hours) is recommended.
Because AMBIEN can cause drowsiness and a decreased level of consciousness, patients, particularly the elderly, are at higher risk of falls.
5.3 Need to Evaluate for Comorbid Diagnoses
Because sleep disturbances may be the presenting manifestation of a physical and/or psychiatric disorder, symptomatic treatment of insomnia should be initiated only after a careful evaluation of the patient. The failure of insomnia to remit after 7 to 10 days of treatment may indicate the presence of a primary psychiatric and/or medical illness that should be evaluated. Worsening of insomnia or the emergence of new thinking or behavior abnormalities may be the consequence of an unrecognized psychiatric or physical disorder. Such findings have emerged during the course of treatment with sedative/hypnotic drugs, including zolpidem.
5.4 Severe Anaphylactic and Anaphylactoid Reactions
Cases of angioedema involving the tongue, glottis or larynx have been reported in patients after taking the first or subsequent doses of sedative-hypnotics, including zolpidem. Some patients have had additional symptoms such as dyspnea, throat closing or nausea and vomiting that suggest anaphylaxis. Some patients have required medical therapy in the emergency department. If angioedema involves the throat, glottis or larynx, airway obstruction may occur and be fatal. Patients who develop angioedema after treatment with zolpidem should not be rechallenged with the drug.
5.5 Abnormal Thinking and Behavioral Changes
Abnormal thinking and behavior changes have been reported in patients treated with sedative/hypnotics, including AMBIEN. Some of these changes included decreased inhibition (e.g., aggressiveness and extroversion that seemed out of character), bizarre behavior, agitation and depersonalization. Visual and auditory hallucinations have been reported.
In controlled trials of AMBIEN 10 mg taken at bedtime <1% of adults with insomnia reported hallucinations. In a clinical trial, 7% of pediatric patients treated with AMBIEN 0.25 mg/kg taken at bedtime reported hallucinations versus 0% treated with placebo [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)]. There have been postmarketing reports of delirium with zolpidem use [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
It can rarely be determined with certainty whether a particular instance of the abnormal behaviors listed above is drug induced, spontaneous in origin, or a result of an underlying psychiatric or physical disorder. Nonetheless, the emergence of any new behavioral sign or symptom of concern requires careful and immediate evaluation.
5.6 Use in Patients with Depression
In primarily depressed patients treated with sedative-hypnotics, worsening of depression, and suicidal thoughts and actions (including completed suicides), have been reported. Suicidal tendencies may be present in such patients and protective measures may be required. Intentional overdosage is more common in this group of patients; therefore, the lowest number of tablets that is feasible should be prescribed for the patient at any one time.
5.7 Respiratory Depression
Although studies with 10 mg zolpidem tartrate did not reveal respiratory depressant effects at hypnotic doses in healthy subjects or in patients with mild to moderate chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), a reduction in the Total Arousal Index, together with a reduction in lowest oxygen saturation and increase in the times of oxygen desaturation below 80% and 90%, was observed in patients with mild to moderate sleep apnea when treated with zolpidem compared to placebo. Since sedative-hypnotics have the capacity to depress respiratory drive, precautions should be taken if AMBIEN is prescribed to patients with compromised respiratory function or concomitant use with opioids or other CNS depressants. Postmarketing reports of respiratory insufficiency in patients receiving 10 mg of zolpidem tartrate, most of whom had pre-existing respiratory impairment, have been reported. The risk of respiratory depression should be considered prior to prescribing AMBIEN in patients with respiratory impairment including sleep apnea and myasthenia gravis or with concomitant opioid use [see Dosage and Administration (2.3), Drug Interactions (7.1)].
5.8 Precipitation of Hepatic Encephalopathy
Drugs affecting GABA receptors, such as zolpidem tartrate, have been associated with precipitation of hepatic encephalopathy in patients with hepatic insufficiency. In addition, patients with hepatic insufficiency do not clear zolpidem tartrate as rapidly as patients with normal hepatic function. Avoid AMBIEN use in patients with severe hepatic impairment as it may contribute to encephalopathy [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Use in Specific Populations (8.7), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following serious adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the labeling:
- Complex Sleep Behaviors [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- CNS-Depressant Effects and Next-Day Impairment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Severe Anaphylactic and Anaphylactoid Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Abnormal Thinking and Behavior Changes [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Withdrawal Effects [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval use of AMBIEN. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Liver and biliary system: acute hepatocellular, cholestatic or mixed liver injury with or without jaundice (i.e., bilirubin >2 × ULN, alkaline phosphatase ≥2 × ULN, transaminase ≥5 × ULN).
Psychiatric disorders: delirium
7. Drug Interactions
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.2 Lactation
Clinical Considerations
Infants exposed to AMBIEN through breastmilk should be monitored for excess sedation, hypotonia, and respiratory depression. A lactating woman may consider interrupting breastfeeding and pumping and discarding breast milk during treatment and for 23 hours (approximately 5 elimination half-lives) after AMBIEN administration in order to minimize drug exposure to a breast fed infant.
8.4 Pediatric Use
AMBIEN is not recommended for use in children. Safety and effectiveness of zolpidem in pediatric patients below the age of 18 years have not been established.
In an 8-week study in pediatric patients (aged 6–17 years) with insomnia associated with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) an oral solution of zolpidem tartrate dosed at 0.25 mg/kg at bedtime did not decrease sleep latency compared to placebo. Psychiatric and nervous system disorders comprised the most frequent (>5%) treatment emergent adverse reactions observed with zolpidem versus placebo and included dizziness (23.5% vs 1.5%), headache (12.5% vs 9.2%), and hallucinations were reported in 7% of the pediatric patients who received zolpidem; none of the pediatric patients who received placebo reported hallucinations [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]. Ten patients on zolpidem (7.4%) discontinued treatment due to an adverse reaction.
8.5 Geriatric Use
A total of 154 patients in U.S. controlled clinical trials and 897 patients in non-U.S. clinical trials who received zolpidem were ≥60 years of age. For a pool of U.S. patients receiving zolpidem at doses of ≤10 mg or placebo, there were three adverse reactions occurring at an incidence of at least 3% for zolpidem and for which the zolpidem incidence was at least twice the placebo incidence (i.e., they could be considered drug related).
| Adverse Event | Zolpidem | Placebo |
|---|---|---|
| Dizziness | 3% | 0% |
| Drowsiness | 5% | 2% |
| Diarrhea | 3% | 1% |
A total of 30/1,959 (1.5%) non-U.S. patients receiving zolpidem reported falls, including 28/30 (93%) who were ≥70 years of age. Of these 28 patients, 23 (82%) were receiving zolpidem doses >10 mg. A total of 24/1,959 (1.2%) non-U.S. patients receiving zolpidem reported confusion, including 18/24 (75%) who were ≥70 years of age. Of these 18 patients, 14 (78%) were receiving zolpidem doses >10 mg.
The dose of AMBIEN in elderly patients is 5 mg to minimize adverse effects related to impaired motor and/or cognitive performance and unusual sensitivity to sedative/hypnotic drugs [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
8.6 Gender Difference in Pharmacokinetics
Women clear zolpidem tartrate from the body at a lower rate than men. Cmax and AUC parameters of zolpidem were approximately 45% higher at the same dose in female subjects compared with male subjects. Given the higher blood levels of zolpidem tartrate in women compared to men at a given dose, the recommended initial dose of AMBIEN for adult women is 5 mg, and the recommended dose for adult men is 5 or 10 mg.
In geriatric patients, clearance of zolpidem is similar in men and women. The recommended dose of AMBIEN in geriatric patients is 5 mg regardless of gender.
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
The recommended dose of AMBIEN in patients with mild to moderate hepatic impairment is 5 mg once daily immediately before bedtime. Avoid AMBIEN use in patients with severe hepatic impairment as it may contribute to encephalopathy [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Warnings and Precautions (5.8), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
9. Drug Abuse and Dependence
9.1 Controlled Substance
Zolpidem tartrate is classified as a Schedule IV controlled substance by federal regulation.
9.2 Abuse
Abuse and addiction are separate and distinct from physical dependence and tolerance. Abuse is characterized by misuse of the drug for non-medical purposes, often in combination with other psychoactive substances. Tolerance is a state of adaptation in which exposure to a drug induces changes that result in a diminution of one or more of the drug effects over time. Tolerance may occur to both desired and undesired effects of drugs and may develop at different rates for different effects.
Addiction is a primary, chronic, neurobiological disease with genetic, psychosocial, and environmental factors influencing its development and manifestations. It is characterized by behaviors that include one or more of the following: impaired control over drug use, compulsive use, continued use despite harm, and craving. Drug addiction is a treatable disease, using a multidisciplinary approach, but relapse is common.
Studies of abuse potential in former drug abusers found that the effects of single doses of zolpidem tartrate 40 mg were similar, but not identical, to diazepam 20 mg, while zolpidem tartrate 10 mg was difficult to distinguish from placebo.
Because persons with a history of addiction to, or abuse of, drugs or alcohol are at increased risk for misuse, abuse and addiction of zolpidem, they should be monitored carefully when receiving zolpidem or any other hypnotic.
9.3 Dependence
Use of AMBIEN may lead to the development of physical and/or psychological dependence. The risk of dependence increases with dose and duration of treatment. The risk of abuse and dependence is also greater in patients with a history of alcohol or drug abuse. AMBIEN should be used with extreme caution in patients with current or past alcohol or drug abuse.
Physical dependence is a state of adaptation that is manifested by a specific withdrawal syndrome that can be produced by abrupt cessation, rapid dose reduction, decreasing blood level of the drug, and/or administration of an antagonist.
Sedative/hypnotics have produced withdrawal signs and symptoms following abrupt discontinuation. These reported symptoms range from mild dysphoria and insomnia to a withdrawal syndrome that may include abdominal and muscle cramps, vomiting, sweating, tremors, convulsions, and delirium.
The following adverse events, which are considered to meet the DSM-III-R criteria for uncomplicated sedative/hypnotic withdrawal, were reported during clinical trials with AMBIEN following placebo substitution occurring within 48 hours following last zolpidem treatment: fatigue, nausea, flushing, lightheadedness, uncontrolled crying, emesis, stomach cramps, panic attack, nervousness, and abdominal discomfort. These reported adverse events occurred at an incidence of 1% or less. However, available data cannot provide a reliable estimate of the incidence, if any, of dependence during treatment at recommended doses. There have been postmarketing reports of abuse, dependence and withdrawal with zolpidem.
10. Overdosage
10.1 Signs and Symptoms
In postmarketing experience of overdose with zolpidem tartrate alone, or in combination with CNS-depressant agents, impairment of consciousness ranging from somnolence to coma, cardiovascular and/or respiratory compromise, and fatal outcomes have been reported.
10.2 Recommended Treatment
General symptomatic and supportive measures should be used along with immediate gastric lavage where appropriate. Intravenous fluids should be administered as needed. Zolpidem's sedative hypnotic effect was shown to be reduced by flumazenil and therefore may be useful; however, flumazenil administration may contribute to the appearance of neurological symptoms (convulsions). As in all cases of drug overdose, respiration, pulse, blood pressure, and other appropriate signs should be monitored and general supportive measures employed. Hypotension and CNS depression should be monitored and treated by appropriate medical intervention. Sedating drugs should be withheld following zolpidem overdosage, even if excitation occurs. The value of dialysis in the treatment of overdosage has not been determined, although hemodialysis studies in patients with renal failure receiving therapeutic doses have demonstrated that zolpidem is not dialyzable.
As with the management of all overdosage, the possibility of multiple drug ingestion should be considered. The physician may wish to consider contacting a poison control center for up-to-date information on the management of hypnotic drug product overdosage.
11. Ambien Description
AMBIEN contains zolpidem tartrate, a gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) A receptor positive modulator of the imidazopyridine class. AMBIEN is available in 5 mg and 10 mg strength tablets for oral administration.
Chemically, zolpidem is N,N,6-trimethyl-2-p-tolylimidazo[1,2-a] pyridine-3-acetamide L-(+)-tartrate (2:1). It has the following structure:
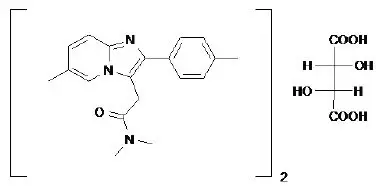
Zolpidem tartrate is a white to off-white crystalline powder that is sparingly soluble in water, alcohol, and propylene glycol. It has a molecular weight of 764.88.
Each AMBIEN tablet includes the following inactive ingredients: hydroxypropyl methylcellulose, lactose, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, polyethylene glycol, sodium starch glycolate, and titanium dioxide. The 5 mg tablet also contains FD&C Red No. 40, iron oxide colorant, and polysorbate 80.
12. Ambien - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Zolpidem is a GABA A receptor positive modulator presumed to exert its therapeutic effects in the short-term treatment of insomnia through binding to the benzodiazepine site of α1 subunit containing GABA A receptors, increasing the frequency of chloride channel opening resulting in the inhibition of neuronal excitation.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Zolpidem binds to GABA A receptors with greater affinity for α1 subunit relative to α2 and α3 subunit containing receptors. Zolpidem has no appreciable binding affinity for α5 subunit containing GABA A receptors. This binding profile may explain the relative absence of myorelaxant effects in animal studies. Zolpidem has no appreciable binding affinity for dopaminergic D2, serotonergic 5HT2, adrenergic, histaminergic or muscarinic receptors.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetic profile of AMBIEN is characterized by rapid absorption from the gastrointestinal tract and a short elimination half-life (T1/2) in healthy subjects.
In a single-dose crossover study in 45 healthy subjects administered 5 and 10 mg zolpidem tartrate tablets, the mean peak concentrations (Cmax) were 59 (range: 29 to 113) and 121 (range: 58 to 272) ng/mL, respectively, occurring at a mean time (Tmax) of 1.6 hours for both. The mean AMBIEN elimination half-life was 2.6 (range: 1.4 to 4.5) and 2.5 (range: 1.4 to 3.8) hours, for the 5 and 10 mg tablets, respectively. AMBIEN is converted to inactive metabolites that are eliminated primarily by renal excretion. AMBIEN demonstrated linear kinetics in the dose range of 5 to 20 mg. Total protein binding was found to be 92.5 ± 0.1% and remained constant, independent of concentration between 40 and 790 ng/mL. Zolpidem did not accumulate in young adults following nightly dosing with 20 mg zolpidem tartrate tablets for 2 weeks.
A food-effect study in 30 healthy male subjects compared the pharmacokinetics of AMBIEN 10 mg when administered while fasting or 20 minutes after a meal. Results demonstrated that with food, mean AUC and Cmax were decreased by 15% and 25%, respectively, while mean Tmax was prolonged by 60% (from 1.4 to 2.2 hr). The half-life remained unchanged. These results suggest that, for faster sleep onset, AMBIEN should not be administered with or immediately after a meal.
14. Clinical Studies
14.1 Transient Insomnia
Normal adults experiencing transient insomnia (n=462) during the first night in a sleep laboratory were evaluated in a double-blind, parallel group, single-night trial comparing two doses of zolpidem (7.5 and 10 mg) and placebo. Both zolpidem doses were superior to placebo on objective (polysomnographic) measures of sleep latency, sleep duration, and number of awakenings.
Normal elderly adults (mean age 68) experiencing transient insomnia (n=35) during the first two nights in a sleep laboratory were evaluated in a double-blind, crossover, 2-night trial comparing four doses of zolpidem (5, 10, 15 and 20 mg) and placebo. All zolpidem doses were superior to placebo on the two primary PSG parameters (sleep latency and efficiency) and all four subjective outcome measures (sleep duration, sleep latency, number of awakenings, and sleep quality).
14.2 Chronic Insomnia
Zolpidem was evaluated in two controlled studies for the treatment of patients with chronic insomnia (most closely resembling primary insomnia, as defined in the APA Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, DSM-IV™). Adult outpatients with chronic insomnia (n=75) were evaluated in a double-blind, parallel group, 5-week trial comparing two doses of zolpidem tartrate and placebo. On objective (polysomnographic) measures of sleep latency and sleep efficiency, zolpidem 10 mg was superior to placebo on sleep latency for the first 4 weeks and on sleep efficiency for weeks 2 and 4. Zolpidem was comparable to placebo on number of awakenings at both doses studied.
Adult outpatients (n=141) with chronic insomnia were also evaluated, in a double-blind, parallel group, 4-week trial comparing two doses of zolpidem and placebo. Zolpidem 10 mg was superior to placebo on a subjective measure of sleep latency for all 4 weeks, and on subjective measures of total sleep time, number of awakenings, and sleep quality for the first treatment week.
Increased wakefulness during the last third of the night as measured by polysomnography has not been observed in clinical trials with AMBIEN.
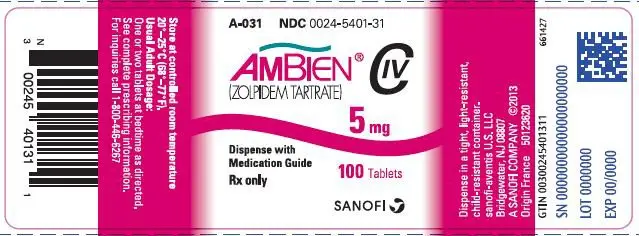
16. How is Ambien supplied
AMBIEN 5 mg tablets are capsule-shaped, pink, film coated, with AMB 5 debossed on one side and 5401 on the other and supplied as:
| NDC Number | Size |
|---|---|
| 0024-5401-31 | bottle of 100 |
AMBIEN 10 mg tablets are capsule-shaped, white, film coated, with AMB 10 debossed on one side and 5421 on the other and supplied as:
| NDC Number | Size |
|---|---|
| 0024-5421-31 | bottle of 100 |
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide).
Inform patients and their families about the benefits and risks of treatment with AMBIEN. Inform patients of the availability of a Medication Guide and instruct them to read the Medication Guide prior to initiating treatment with AMBIEN and with each prescription refill. Review the AMBIEN Medication Guide with every patient prior to initiation of treatment. Instruct patients or caregivers that AMBIEN should be taken only as prescribed.
| This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. | Revised: 2/2022 |
| MEDICATION GUIDE
AMBIEN (ām'bē-ən) (zolpidem tartrate) tablets, for oral use, C-IV |
|
| What is the most important information I should know about AMBIEN?
AMBIEN may cause serious side effects, including:
|
|
| What is AMBIEN?
AMBIEN is a prescription sleep medicine used for the short-term treatment of adults who have trouble falling asleep (insomnia).
|
|
Do not take AMBIEN if you:
|
|
Before taking AMBIEN, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
Especially tell your healthcare provider if you:
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them to show your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medicine. |
|
How should I take AMBIEN?
|
|
| What are the possible side effects of AMBIEN? AMBIEN may cause serious side effects, including:
These are not all the side effects of AMBIEN. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. |
|
How should I store AMBIEN?
|
|
| General Information about the safe and effective use of AMBIEN.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use AMBIEN for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give AMBIEN to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. You can ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for information about AMBIEN that is written for healthcare professionals. |
|
| What are the ingredients in AMBIEN?
Active Ingredient: zolpidem tartrate Inactive Ingredients: hydroxypropyl methylcellulose, lactose, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, polyethylene glycol, sodium starch glycolate, and titanium dioxide. In addition, the 5 mg tablet contains FD&C Red No. 40, iron oxide colorant, and polysorbate 80. Manufactured by: sanofi-aventis U.S. LLC Bridgewater, NJ 08807 A SANOFI COMPANY © 2022 sanofi-aventis U.S. LLC For more information, go to WWW.AMBIEN.com or call 1-800-633-1610. |
|
| AMBIEN
zolpidem tartrate tablet, film coated |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| AMBIEN
zolpidem tartrate tablet, film coated |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - sanofi-aventis U.S. LLC (824676584) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sanofi Winthrop Industrie | 571879985 | ANALYSIS(0024-5401, 0024-5421) , MANUFACTURE(0024-5401, 0024-5421) , PACK(0024-5401, 0024-5421) , LABEL(0024-5401, 0024-5421) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Finorga | 640422218 | ANALYSIS(0024-5401, 0024-5421) , API MANUFACTURE(0024-5401, 0024-5421) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sanofi Chimie | 262600765 | ANALYSIS(0024-5401, 0024-5421) , API MANUFACTURE(0024-5401, 0024-5421) | |