Drug Detail:Aristada initio (injection) (Aripiprazole (injection) [ ar-i-pip-ra-zole ])
Drug Class: Atypical antipsychotics
Highlights of Prescribing Information
ARISTADA INITIO® (aripiprazole lauroxil) extended-release injectable suspension, for intramuscular use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2015
WARNING: INCREASED MORTALITY IN ELDERLY PATIENTS WITH DEMENTIA-RELATED PSYCHOSIS
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
- Elderly patients with dementia-related psychosis treated with antipsychotic drugs are at an increased risk of death. (5.1)
- ARISTADA INITIO is not approved for the treatment of patients with dementia-related psychosis. (5.1)
Indications and Usage for Aristada Initio
ARISTADA INITIO, in combination with oral aripiprazole, is indicated for the initiation of ARISTADA® when used for the treatment of schizophrenia in adults (1).
Aristada Initio Dosage and Administration
- Administer one 675 mg injection of ARISTADA INITIO and one 30 mg dose of oral aripiprazole in conjunction with the first ARISTADA injection (2.1).
- ARISTADA INITIO is only to be used as a single dose and is not for repeated dosing (2.1).
- Administer ARISTADA INITIO by intramuscular injection in either the deltoid or gluteal muscle by a healthcare professional (2.1).
- For patients naïve to aripiprazole, establish tolerability with oral aripiprazole prior to initiating treatment with ARISTADA INITIO (2.1).
- See Dosage and Administration for detailed preparation and administration instructions (2.4).
- Avoid use in known CYP2D6 poor metabolizers (2.3, 7.1).
- Avoid use with strong CYP2D6 or CYP 3A4 inhibitors and strong CYP3A4 inducers (2.3, 7.1).
- ARISTADA INITIO is not interchangeable with ARISTADA (2.1, 5.3).
Dosage Forms and Strengths
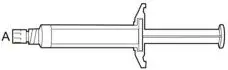
Extended-release injectable suspension: 675 mg single-dose pre-filled syringe (3).
Contraindications
Known hypersensitivity to aripiprazole (4).
Warnings and Precautions
- Cerebrovascular Adverse Reactions in Elderly Patients with Dementia-Related Psychosis: Increased incidence of cerebrovascular adverse reactions (e.g., stroke, transient ischemia attack, including fatalities) (5.2).
- Potential for Dosing and Medication Errors: Substitution and dispensing errors between ARISTADA INITIO and ARISTADA could occur. Do not substitute ARISTADA INITIO for ARISTADA (5.3).
- Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome: Manage with immediate discontinuation and close monitoring (5.4).
- Tardive Dyskinesia: Discontinue if clinically appropriate (5.5).
- Metabolic Changes: Monitor for hyperglycemia, dyslipidemia, and weight gain (5.6).
- Pathological Gambling and Other Compulsive Behaviors: Consider discontinuation (5.7).
- Orthostatic Hypotension: Monitor heart rate and blood pressure and warn patients with known cardiovascular or cerebrovascular disease, and risk of dehydration or syncope (5.8).
- Leukopenia, Neutropenia, and Agranulocytosis: Perform complete blood counts in patients with a history of a clinically significant low white blood cell (WBC) count. Consider discontinuation if clinically significant decline in WBC in the absence of other causative factors (5.10).
- Seizures: Use cautiously in patients with a history of seizures or with conditions that lower the seizure threshold (5.11).
- Potential for Cognitive and Motor Impairment: Use caution when operating machinery (5.12).
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most commonly observed adverse reaction (incidence ≥5% and at least twice that for placebo) was akathisia (6.1).
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Alkermes, Inc. at 1-866-274-7823 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or
WWW.FDA.GOV/MEDWATCH.
Use In Specific Populations
Pregnancy: May cause extrapyramidal and/or withdrawal symptoms in neonates in women exposed during the third trimester of pregnancy (8.1).
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 3/2021
Related/similar drugs
Caplyta, quetiapine, Abilify, Seroquel, aripiprazole, risperidone, olanzapineFull Prescribing Information
WARNING: INCREASED MORTALITY IN ELDERLY PATIENTS WITH DEMENTIA-RELATED PSYCHOSIS
Elderly patients with dementia-related psychosis treated with antipsychotic drugs are at an increased risk of death. ARISTADA INITIO is not approved for the treatment of patients with dementia-related psychosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
1. Indications and Usage for Aristada Initio
ARISTADA INITIO, in combination with oral aripiprazole, is indicated for the initiation of ARISTADA when used for the treatment of schizophrenia in adults.
2. Aristada Initio Dosage and Administration
2.1 Recommended Dosage
ARISTADA INITIO is only to be used as a single dose to initiate ARISTADA treatment or as a single dose to re-initiate ARISTADA treatment following a missed dose of ARISTADA. ARISTADA INITIO is not for repeated dosing.
ARISTADA INITIO is not interchangeable with ARISTADA due to differing pharmacokinetic profiles [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
ARISTADA INITIO is to be administered as an intramuscular injection by a healthcare professional.
For patients who have never taken aripiprazole, establish tolerability with oral aripiprazole prior to initiating treatment with ARISTADA INITIO. Due to the half-life of oral aripiprazole, it may take up to 2 weeks to fully assess tolerability. Refer to the prescribing information of oral aripiprazole for the recommended dosage and administration of the oral formulation.
After establishing tolerability with oral aripiprazole, administer the first ARISTADA intramuscular injection (441 mg, 662 mg, 882 mg, or 1064 mg) in conjunction with both:
- One 675 mg injection of ARISTADA INITIO in the deltoid or gluteal muscle (which corresponds to 459 mg of aripiprazole) [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]; and
- One 30 mg dose of oral aripiprazole.
The first ARISTADA injection may be administered on the same day as ARISTADA INITIO or up to 10 days thereafter. See the ARISTADA prescribing information for additional information regarding dosage and administration of ARISTADA.
Avoid injecting both ARISTADA INITIO and ARISTADA concomitantly into the same deltoid or gluteal muscle.
2.2 Missed Doses of ARISTADA
ARISTADA INITIO may be used to re-initiate treatment with ARISTADA following a missed dose of ARISTADA. When a dose of ARISTADA is missed, administer the next injection of ARISTADA as soon as possible. Depending on the time elapsed since the last ARISTADA injection, supplement the next ARISTADA injection as recommended in Table 1 below.
| Dose of Patient's Last ARISTADA Injection | Length of Time Since Last Injection | ||
| 441 mg | ≤ 6 weeks | > 6 and ≤ 7 weeks | > 7 weeks |
| 662 mg | ≤ 8 weeks | > 8 and ≤ 12 weeks | > 12 weeks |
| 882 mg | ≤ 8 weeks | > 8 and ≤ 12 weeks | > 12 weeks |
| 1064 mg | ≤ 10 weeks | > 10 and ≤ 12 weeks | > 12 weeks |
| Dosage and Administration for Re-initiation of ARISTADA | No Supplementation Required | Supplement with a Single Dose of ARISTADA INITIO | Re-initiate with a Single Dose of ARISTADA INITIO and a Single Dose of Oral Aripiprazole 30 mg |
2.3 Dose Adjustments for CYP450 Considerations
ARISTADA INITIO is only available at a single strength as a single-dose pre-filled syringe, so dosage adjustments are not possible. Therefore, avoid use in patients who are known CYP2D6 poor metabolizers or taking strong CYP3A4 inhibitors, strong CYP2D6 inhibitors, or strong CYP3A4 inducers.
2.4 Important Administration Instructions
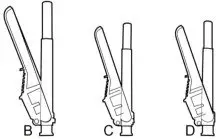
The kit contains a syringe containing ARISTADA INITIO sterile aqueous extended-release injectable suspension and 3 safety needles (a 2-inch 20 gauge needle with yellow needle hub, a 1 ½-inch 20 gauge needle with yellow needle hub, and a 1-inch 21 gauge needle with green needle hub) for intramuscular injection. Store all materials at room temperature.
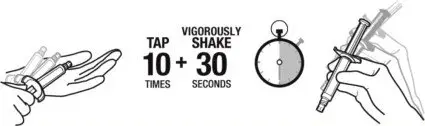
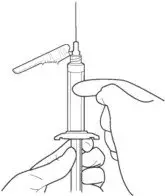
1. TAP and vigorously SHAKE the syringe.
1a. Tap the syringe at least 10 times to dislodge any material which may have settled.
1b. Shake the syringe vigorously for a minimum of 30 seconds to ensure a uniform suspension. If the syringe is not used within 15 minutes, shake again for 30 seconds.
2. SELECT the injection needle.
2a. Select injection site.
2b. Select needle length based on injection site. For patients with a larger amount of subcutaneous tissue overlaying the injection site muscle, use the longer of the needles provided.
| Injection Site | Needle Length |
| 675 mg dose | |
| Deltoid | 21 gauge, 1-inch or 20 gauge, 1½-inch |
| Gluteal | 20 gauge, 1½-inch or 20 gauge, 2-inch |
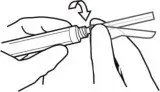
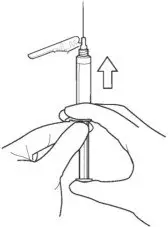
3. ATTACH the injection needle.
Attach the appropriate needle securely with a clockwise twisting motion. Do NOT overtighten. Overtightening could lead to needle hub cracking.
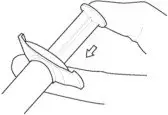
4. PRIME the syringe to remove air.
4a. Bring the syringe into upright position and tap the syringe to bring air to the top.
4b. Depress the plunger rod to remove air until a few drops are released. It is normal to see small air bubbles remaining in the syringe.
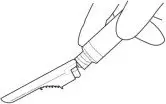
5. Inject in a RAPID and CONTINUOUS manner. Product requires a RAPID injection. Do not hesitate. Administer the entire content intramuscularly. Do not inject by any other route.
6. DISPOSE of the needle. Cover the needle by pressing the safety device. Dispose of used and unused items in a proper waste container.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
ARISTADA INITIO is a white to off-white aqueous extended-release injectable suspension provided in a single-dose pre-filled syringe (see Table 3).
| Dose Strength | Volume | Inject Intramuscularly | Color Label |
|---|---|---|---|
| 675 mg | 2.4 mL | Deltoid or Gluteal Muscle | Gray |
4. Contraindications
ARISTADA INITIO is contraindicated in patients with a known hypersensitivity reaction to aripiprazole. Hypersensitivity reactions have ranged from pruritus/urticaria to anaphylaxis [see Adverse Reactions (6)].
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Increased Mortality in Elderly Patients with Dementia-related Psychosis
Elderly patients with dementia-related psychosis treated with antipsychotic drugs are at an increased risk of death. Analyses of 17 placebo-controlled trials (modal duration of 10 weeks), largely in patients taking atypical antipsychotic drugs, revealed a risk of death in drug-treated patients of between 1.6 to 1.7 times the risk of death in placebo-treated patients. Over the course of a typical 10-week controlled trial, the rate of death in drug-treated patients was about 4.5%, compared to a rate of about 2.6% in the placebo group.
Although the causes of death were varied, most of the deaths appeared to be either cardiovascular (e.g., heart failure, sudden death) or infectious (e.g., pneumonia) in nature. Observational studies suggest that, similar to atypical antipsychotic drugs, treatment with conventional antipsychotic drugs may increase mortality. The extent to which the findings of increased mortality in observational studies may be attributed to the antipsychotic drug as opposed to some characteristic(s) of the patients is not clear. ARISTADA INITIO is not approved for the treatment of patients with dementia-related psychosis [see Boxed Warning, Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
5.2 Cerebrovascular Adverse Reactions, Including Stroke
In placebo-controlled trials with risperidone, aripiprazole, and olanzapine in elderly patients with dementia, there was a higher incidence of cerebrovascular adverse reactions (cerebrovascular accidents and transient ischemic attacks) including fatalities compared to placebo-treated patients. ARISTADA INITIO is not approved for the treatment of patients with dementia-related psychosis [see Boxed Warning, Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
5.3 Potential for Dosing and Medication Errors
Medication errors, including substitution and dispensing errors, between ARISTADA INITIO and ARISTADA could occur. ARISTADA INITIO is intended for single administration only. Do not substitute ARISTADA INITIO for ARISTADA because of differing pharmacokinetic profiles [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
5.4 Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome
A potentially fatal symptom complex sometimes referred to as Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS) may occur in association with antipsychotic drugs, including ARISTADA INITIO. Clinical manifestations of NMS are hyperpyrexia, muscle rigidity, altered mental status, and evidence of autonomic instability (irregular pulse or blood pressure, tachycardia, diaphoresis, and cardiac dysrhythmia). Additional signs may include elevated creatine phosphokinase, myoglobinuria (rhabdomyolysis), and acute renal failure.
The diagnostic evaluation of patients with this syndrome is complicated. In arriving at a diagnosis, it is important to identify cases in which the clinical presentation includes both serious medical illness (e.g., pneumonia, systemic infection, etc.) and untreated or inadequately treated extrapyramidal signs and symptoms (EPS). Other important considerations in the differential diagnosis include central anticholinergic toxicity, heat stroke, drug fever, and primary central nervous system pathology.
The management of NMS should include: (1) immediate discontinuation of antipsychotic drugs and other drugs not essential to concurrent therapy; (2) intensive symptomatic treatment and medical monitoring; and (3) treatment of any concomitant serious medical problems for which specific treatments are available. There is no general agreement about specific pharmacological treatment regimens for uncomplicated NMS.
If a patient appears to require antipsychotic drug treatment after recovery from NMS, reintroduction of drug therapy should be closely monitored, since recurrences of NMS have been reported.
5.5 Tardive Dyskinesia
A syndrome of potentially irreversible, involuntary, dyskinetic movements may develop in patients treated with antipsychotic drugs. Although the prevalence of the syndrome appears to be highest among the elderly, especially elderly women, it is impossible to predict which patients will develop the syndrome. Whether antipsychotic drug products differ in their potential to cause tardive dyskinesia is unknown.
The risk of developing tardive dyskinesia and the likelihood that it will become irreversible appear to increase as the duration of treatment and the total cumulative dose of antipsychotic drugs administered to the patient increase, but the syndrome can develop after relatively brief treatment periods at low doses, although this is uncommon.
Tardive dyskinesia may remit, partially or completely, if antipsychotic treatment is withdrawn. Antipsychotic treatment itself may suppress (or partially suppress) the signs and symptoms of the syndrome and may thus mask the underlying process. The effect of symptomatic suppression on the long-term course of the syndrome is unknown.
Given these considerations, antipsychotics should be prescribed in a manner that is most likely to minimize the occurrence of tardive dyskinesia. Chronic antipsychotic treatment should generally be reserved for patients who suffer from a chronic illness that is known to respond to antipsychotic drugs. In patients who do require chronic treatment, the smallest dose and the shortest duration of treatment producing a satisfactory clinical response should be sought. The need for continued treatment should be reassessed periodically.
If signs and symptoms of tardive dyskinesia appear in a patient treated with antipsychotics, consider discontinuation of the antipsychotic drug. However, some patients may require antipsychotic treatment despite the presence of the syndrome.
5.6 Metabolic Changes
Atypical antipsychotic drugs have been associated with metabolic changes that include hyperglycemia/diabetes mellitus, dyslipidemia, and weight gain. While all drugs in the class have been shown to produce some metabolic changes, each drug has its own specific risk profile.
Hyperglycemia/ Diabetes Mellitus
Hyperglycemia, in some cases extreme and associated with ketoacidosis or hyperosmolar coma or death, has been reported in patients treated with atypical antipsychotics. There have been reports of hyperglycemia in patients treated with oral aripiprazole. Assessment of the relationship between atypical antipsychotic use and glucose abnormalities is complicated by the possibility of an increased background risk of diabetes mellitus in patients with schizophrenia and the increasing incidence of diabetes mellitus in the general population. Given these confounders, the relationship between atypical antipsychotic use and hyperglycemia-related adverse events is not completely understood. However, epidemiological studies suggest an increased risk of hyperglycemia-related adverse reactions in patients treated with the atypical antipsychotics.
Patients with an established diagnosis of diabetes mellitus who are started on atypical antipsychotics should be monitored regularly for worsening of glucose control. Patients with risk factors for diabetes mellitus (e.g., obesity, family history of diabetes) who are starting treatment with atypical antipsychotics should undergo fasting blood glucose testing at the beginning of treatment and periodically during treatment. Any patient treated with atypical antipsychotics should be monitored for symptoms of hyperglycemia including polydipsia, polyuria, polyphagia, and weakness. Patients who develop symptoms of hyperglycemia during treatment with atypical antipsychotics should undergo fasting blood glucose testing. In some cases, hyperglycemia has resolved when the atypical antipsychotic was discontinued; however, some patients require continuation of anti-diabetic treatment despite discontinuation of the suspect drug.
5.7 Pathological Gambling and Other Compulsive Behaviors
Post-marketing case reports suggest that patients can experience intense urges, particularly for gambling, and the inability to control these urges while taking aripiprazole. Other compulsive urges, reported less frequently include: sexual urges, shopping, eating or binge eating, and other impulsive or compulsive behaviors. Because patients may not recognize these behaviors as abnormal, it is important for prescribers to ask patients or their caregivers specifically about the development of new or intense gambling urges, compulsive sexual urges, compulsive shopping, binge or compulsive eating, or other urges while being treated with aripiprazole. It should be noted that impulse-control symptoms can be associated with the underlying disorder. In some cases, although not all, urges were reported to have stopped when the dose was reduced or the medication was discontinued. Compulsive behaviors may result in harm for the patient and others if not recognized. If compulsive urges develop, consider discontinuing aripiprazole.
5.8 Orthostatic Hypotension
Aripiprazole may cause orthostatic hypotension, perhaps due to its α1-adrenergic receptor antagonism. Associated adverse reactions related to orthostatic hypotension can include dizziness, lightheadedness and tachycardia. Generally, these risks are greatest at the beginning of treatment and during dose escalation. Patients at increased risk of these adverse reactions or at increased risk of developing complications from hypotension include those with dehydration, hypovolemia, treatment with antihypertensive medication, history of cardiovascular disease (e.g., heart failure, myocardial infarction, ischemia, or conduction abnormalities), history of cerebrovascular disease, as well as patients who are antipsychotic-naïve. In such patients, monitor orthostatic vital signs.
5.9 Falls
Antipsychotics including ARISTADA INITIO may cause somnolence, postural hypotension, or motor and sensory instability, which may lead to falls and, consequently, fractures or other injuries. For patients with diseases, conditions, or medications that could exacerbate these effects, complete fall risk assessments when initiating antipsychotic treatment and recurrently for those patients on long-term antipsychotic therapy.
5.10 Leukopenia, Neutropenia, and Agranulocytosis
In clinical trials and/or postmarketing experience, events of leukopenia and neutropenia have been reported temporally related to antipsychotic agents. Agranulocytosis has also been reported.
Possible risk factors for leukopenia/neutropenia include pre-existing low white blood cell count (WBC)/absolute neutrophil count (ANC) and history of drug-induced leukopenia/neutropenia. In patients with a history of a clinically significant low WBC/ANC or drug-induced leukopenia/neutropenia, perform a complete blood count (CBC) frequently during the first few months of therapy. In such patients, consider discontinuation of antipsychotics at the first sign of a clinical significant decline in WBC in the absence of other causative factors.
Monitor patients with clinically significant neutropenia for fever or other symptoms or signs of infection and treat promptly if such symptoms or signs occur. Discontinue antipsychotics in patients with severe neutropenia (absolute neutrophil count <1000/mm3) and follow their WBC until recovery.
5.11 Seizures
As with other antipsychotic drugs, use ARISTADA INITIO cautiously in patients with a history of seizures or with conditions that lower the seizure threshold. Conditions that lower the seizure threshold may be more prevalent in a population of 65 years or older.
5.12 Potential for Cognitive and Motor Impairment
ARISTADA INITIO, like other antipsychotics, has the potential to impair judgment, thinking or motor skills. Patients should be cautioned about operating hazardous machinery, including automobiles, until they are reasonably certain that therapy with ARISTADA INITIO does not affect them adversely.
5.13 Body Temperature Regulation
Disruption of the body's ability to reduce core body temperature has been attributed to antipsychotic agents. Appropriate care is advised when prescribing ARISTADA INITIO for patients who will be experiencing conditions which may contribute to an elevation in core body temperature, (e.g., exercising strenuously, exposure to extreme heat, receiving concomitant medication with anticholinergic activity, or being subject to dehydration).
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following are discussed in more details in other sections of the labeling:
- Increased Mortality in Elderly Patients with Dementia-related Psychosis [see Boxed Warning, Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Cerebrovascular Adverse Reactions, Including Stroke [see Boxed Warning, Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Tardive Dyskinesia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Metabolic Changes [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Pathological Gambling and Other Compulsive Behaviors [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- Orthostatic Hypotension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
- Falls [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]
- Leukopenia, Neutropenia, and Agranulocytosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)]
- Seizures [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)]
- Potential for Cognitive and Motor Impairment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12)]
- Body Temperature Regulation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.13)]
- Dysphagia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.14)]
6.1 Clinical Studies Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The safety of ARISTADA INITIO, in combination with oral aripiprazole, for the initiation of ARISTADA when used for the treatment of schizophrenia in adults has been established and is based on clinical trials of ARISTADA (aripiprazole lauroxil) including 1019 adult patients with schizophrenia.
Patient Exposure
ARISTADA INITIO has been evaluated for safety in 170 adult patients in clinical trials in schizophrenia.
In pharmacokinetic studies, the safety profile of ARISTADA INITIO was generally consistent with that observed for ARISTADA.
Commonly Observed Adverse Reactions with Aripiprazole Lauroxil
The most common adverse reaction (incidence ≥5% and at least twice the rate of placebo in patients treated with aripiprazole lauroxil) was akathisia.
Adverse Reactions Occurring at an Incidence of 2% or More in Aripiprazole Lauroxil-Treated Patients
Adverse reactions associated with the use of aripiprazole lauroxil (incidence of 2% or greater, rounded to the nearest percent and aripiprazole lauroxil incidence greater than placebo) that occurred were: injection site pain, increased weight, increased blood creatinine phosphokinase, akathisia, headache, insomnia, and restlessness.
Injection Site Reactions
ARISTADA INITIO
In pharmacokinetic studies evaluating ARISTADA INITIO, the incidences of injection site reactions with ARISTADA INITIO were similar to the incidence observed with aripiprazole lauroxil.
ARISTADA (Aripiprazole Lauroxil)
Injection site reactions were reported by 4% of patients treated with 441 mg aripiprazole lauroxil and 5% of patients treated with 882 mg aripiprazole lauroxil compared to 2% of patients treated with placebo. Most of these were injection site pain (3%, 4% and 2% in the 441 mg aripiprazole lauroxil, 882 mg aripiprazole lauroxil and placebo groups, respectively). Other injection site reactions (induration, swelling and redness) occurred at less than 1%.
Extrapyramidal Symptoms
In a schizophrenia efficacy study in aripiprazole lauroxil-treated patients, the incidence of other EPS-related events, excluding akathisia and restlessness, was 5% and 7% for patients on 441 mg and 882 mg, respectively, versus 4% for placebo-treated patients.
Dystonia
Symptoms of dystonia, prolonged abnormal contractions of muscle groups, may occur in susceptible individuals during the first few days of treatment. Dystonic symptoms include: spasm of the neck muscles, sometimes progressing to tightness of the throat, swallowing difficulty, difficulty breathing, and/or protrusion of the tongue. While these symptoms can occur at low doses, they occur more frequently and with greater severity with high potency and at higher doses of first generation antipsychotic drugs. An elevated risk of acute dystonia is observed in males and younger age groups.
Other Adverse Reactions Observed in Clinical Studies with Aripiprazole Lauroxil
The following listing does not include reactions: 1) already listed in previous tables or elsewhere in labeling, 2) for which a drug cause was remote, 3) which were so general as to be uninformative, 4) which were not considered to have significant clinical implications, or 5) which occurred at a rate equal to or less than placebo.
Cardiac – angina pectoris, tachycardia, palpitations
Gastrointestinal disorders – constipation, dry mouth
General disorders – asthenia
Musculoskeletal – muscular weakness
Nervous system disorders – dizziness
Psychiatric disorders – anxiety, suicide
Adverse Reactions Reported in Clinical Trials with Oral Aripiprazole
The following is a list of additional adverse reactions that have been reported in clinical trials with oral aripiprazole and not reported above for ARISTADA INITIO or aripiprazole lauroxil.
Blood and Lymphatic System Disorders: thrombocytopenia
Cardiac Disorders: bradycardia, atrial flutter, cardiorespiratory arrest, atrioventricular block, atrial fibrillation, myocardial ischemia, myocardial infarction, cardiopulmonary failure
Eye Disorders: photophobia, diplopia
Gastrointestinal Disorders: gastroesophageal reflux disease
General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions: peripheral edema, chest pain, face edema
Hepatobiliary Disorders: hepatitis, jaundice
Immune System Disorders: hypersensitivity
Injury, Poisoning, and Procedural Complications: fall, heat stroke
Investigations: weight decreased, hepatic enzyme increased, blood glucose increased, blood lactate dehydrogenase increased, gamma glutamyl transferase increased, blood prolactin increased, blood urea increased, blood creatinine increased, blood bilirubin increased, electrocardiogram QT prolonged, glycosylated hemoglobin increased
Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders: anorexia, hypokalemia, hyponatremia, hypoglycemia
Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders: muscle tightness, rhabdomyolysis, mobility decreased
Nervous System Disorders: memory impairment, cogwheel rigidity, hypokinesia, bradykinesia, akinesia, myoclonus, coordination abnormal, speech disorder, choreoathetosis
Psychiatric Disorders: aggression, loss of libido, delirium, libido increased, anorgasmia, tic, homicidal ideation, catatonia, sleep walking
Renal and Urinary Disorders: urinary retention, nocturia
Reproductive System and Breast Disorders: erectile dysfunction, gynaecomastia, menstruation irregular, amenorrhea, breast pain, priapism
Respiratory, Thoracic, and Mediastinal Disorders: nasal congestion, dyspnea
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders: rash, hyperhidrosis, pruritus, photosensitivity reaction, alopecia, urticaria
Vascular Disorders: hypotension, hypertension
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of oral aripiprazole. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or to establish a causal relationship to drug exposure: occurrences of allergic reaction (anaphylactic reaction, angioedema, laryngospasm, pruritus/urticaria, or oropharyngeal spasm), pathological gambling, hiccups, blood glucose fluctuation, oculogyric crisis, and drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS).
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 Drugs Having Clinically Important Interactions with ARISTADA INITIO
| Strong CYP3A4 Inhibitors and CYP2D6 Inhibitors | |
| Clinical Impact: | Concomitant use of oral aripiprazole with strong CYP3A4 or CYP2D6 inhibitors increased the exposure of aripiprazole compared to the use of oral aripiprazole alone [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. |
| Intervention: | Avoid concomitant use of ARISTADA INITIO with strong CYP3A4 or strong CYP2D6 inhibitors because the dosage of ARISTADA INITIO cannot be modified [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)]. |
| Examples: | itraconazole, clarithromycin, quinidine, fluoxetine, paroxetine |
| Strong CYP3A4 Inducers | |
| Clinical Impact: | Concomitant use of oral aripiprazole and carbamazepine decreased the exposure of aripiprazole compared to the use of oral aripiprazole alone [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. |
| Intervention: | Avoid concomitant use of ARISTADA INITIO with strong CYP3A4 inducers because the dosage of ARISTADA INITIO cannot be modified [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)]. |
| Examples: | carbamazepine, rifampin |
| Antihypertensive Drugs | |
| Clinical Impact: | Due to its alpha adrenergic antagonism, aripiprazole has the potential to enhance the effect of certain antihypertensive agents. |
| Intervention: | Avoid concomitant use of ARISTADA INITIO with antihypertensive drugs because the dosage of ARISTADA INITIO cannot be modified [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]. |
| Examples: | carvedilol, lisinopril, prazosin |
| Benzodiazepines | |
| Clinical Impact: | The intensity of sedation was greater with the combination of oral aripiprazole and lorazepam as compared to that observed with aripiprazole alone. The orthostatic hypotension observed was greater with the combination as compared to that observed with lorazepam alone [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]. |
| Intervention: | Avoid concomitant use of ARISTADA INITIO with benzodiazepines because the dosage of ARISTADA INITIO cannot be modified [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]. |
| Example: | lorazepam |
7.2 Drugs Having No Clinically Important Interactions with ARISTADA INITIO
Based on pharmacokinetic studies with oral aripiprazole, no dosage adjustment of ARISTADA INITIO is required when administered concomitantly with famotidine, valproate, or lithium [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
In addition, no dosage adjustment is necessary for substrates of CYP2D6 (e.g., dextromethorphan, fluoxetine, paroxetine, or venlafaxine), CYP2C9 (e.g., warfarin), CYP2C19 (e.g., omeprazole, warfarin, escitalopram), or CYP3A4 (e.g., dextromethorphan) when co-administered with ARISTADA INITIO. Additionally, no dosage adjustment is necessary for valproate, lithium, lamotrigine, or sertraline when co-administered with ARISTADA INITIO [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Exposure Registry
There is a pregnancy exposure registry that monitors pregnancy outcomes in women exposed to ARISTADA INITIO during pregnancy. For more information, contact the National Pregnancy Registry for Atypical Antipsychotics at 1-866-961-2388 or visit
http://womensmentalhealth.org/clinical-and-research-programs/pregnancyregistry/.
Risk Summary
Neonates exposed to antipsychotic drugs during the third trimester of pregnancy are at risk for extrapyramidal and/or withdrawal symptoms following delivery. Limited published data on aripiprazole use in pregnant women are not sufficient to inform any drug-associated risks for birth defects or miscarriage. No teratogenicity was observed in animal reproductive studies with intramuscular administration of aripiprazole lauroxil to rats and rabbits during organogenesis at doses up to 8 and 23 times, respectively, the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 675 mg based on body surface area (mg/m2). However, aripiprazole caused developmental toxicity and possible teratogenic effects in rats and rabbits [see Data]. The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population are unknown. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2-4% and 15-20%, respectively. Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus.
Fetal/Neonatal Adverse Reactions
Extrapyramidal and/or withdrawal symptoms, including agitation, hypertonia, hypotonia, tremor, somnolence, respiratory distress and feeding disorder have been reported in neonates who were exposed to antipsychotic drugs during the third trimester of pregnancy. These symptoms have varied in severity. Monitor neonates for extrapyramidal and/or withdrawal symptoms and manage symptoms appropriately. Some neonates recover within hours or days without specific treatment; others required prolonged hospitalization.
Animal Data for ARISTADA (Aripiprazole Lauroxil)
Aripiprazole lauroxil did not cause adverse developmental or maternal effects in rats or rabbits when administered intramuscularly during the period of organogenesis at doses of 18, 49, or 144 mg/animal in pregnant rats which are approximately 1 to 8 times the MRHD of 675 mg based on mg/m2, and at doses of 241, 723, and 2893 mg/animal in pregnant rabbits which are approximately 2 to 23 times the MRHD based on mg/m2. However, aripiprazole caused developmental toxicity and possible teratogenic effects in rats and rabbits [see Data below].
Animal Data for Aripiprazole
Pregnant rats were treated with oral doses of 3, 10, and 30 mg/kg/day which are approximately 1 to 10 times the oral MRHD of 30 mg/day based on mg/m2 of aripiprazole during the period of organogenesis. Treatment at the highest dose caused a slight prolongation of gestation and delay in fetal development, as evidenced by decreased fetal weight, and undescended testes. Delayed skeletal ossification was observed at 3 and 10 times the oral MRHD based on mg/m2.
At 3 and 10 times the oral MRHD based on mg/m2, delivered offspring had decreased body weights. Increased incidences of hepatodiaphragmatic nodules and diaphragmatic hernia were observed in offspring from the highest dose group (the other dose groups were not examined for these findings). A low incidence of diaphragmatic hernia was also seen in the fetuses exposed to the highest dose. Postnatally, delayed vaginal opening was seen at 3 and 10 times the oral MRHD based on mg/m2 and impaired reproductive performance (decreased fertility rate, corpora lutea, implants, live fetuses, and increased post-implantation loss, likely mediated through effects on female offspring) along with some maternal toxicity were seen at the highest dose; however, there was no evidence to suggest that these developmental effects were secondary to maternal toxicity.
In pregnant rabbits treated with oral doses of 10, 30, and 100 mg/kg/day which are 2 to 11 times human exposure at the oral MRHD based on AUC and 6 to 65 times the oral MRHD based on mg/m2 of aripiprazole during the period of organogenesis decreased maternal food consumption and increased abortions were seen at the highest dose as well as increased fetal mortality. Decreased fetal weight and increased incidence of fused sternebrae were observed at 3 and 11 times the oral MRHD based on AUC.
In rats treated with oral doses of 3, 10, and 30 mg/kg/day which are 1 to 10 times the oral MRHD based on mg/m2 of aripiprazole perinatally and postnatally (from day 17 of gestation through day 21 postpartum), slight maternal toxicity and slightly prolonged gestation were seen at the highest dose. An increase in stillbirths and decreases in pup weight (persisting into adulthood) and survival were also seen at this dose.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
Aripiprazole is present in human breast milk; however, there are insufficient data to assess the amount in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. The development and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for ARISTADA INITIO and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from ARISTADA INITIO or from the underlying maternal condition.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of ARISTADA INITIO in pediatric patients have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of ARISTADA INITIO in patients >65 years of age have not been evaluated.
Elderly patients with dementia-related psychosis treated with antipsychotic drugs are at an increased risk of death. ARISTADA INITIO is not approved for the treatment of patients with dementia-related psychosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2)].
8.6 CYP2D6 Poor Metabolizers
Approximately 8% of Caucasians and 3-8% of Black/African Americans cannot metabolize CYP2D6 substrates and are classified as poor metabolizers (PM). Avoid use of ARISTADA INITIO in these patients because dosage adjustments are not possible (it is only available in one strength in a single-dose pre-filled syringe) [see Dosage and Administration (2.3), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.7 Hepatic and Renal Impairment
No dosage adjustment for ARISTADA INITIO is required based on a patient's hepatic function (mild to severe hepatic impairment, Child-Pugh score between 5 and 15), or renal function (mild to severe renal impairment, glomerular filtration rate between 15 and 90 mL/minute) [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
10. Overdosage
10.1 Human Experience
Common adverse reactions (reported in at least 5% of all overdose cases) reported with oral aripiprazole overdosage (alone or in combination with other substances) include vomiting, somnolence, and tremor. Other clinically important signs and symptoms observed in one or more patients with aripiprazole overdoses (alone or with other substances) include acidosis, aggression, aspartate aminotransferase increased, atrial fibrillation, bradycardia, coma, confusional state, convulsion, blood creatine phosphokinase increased, depressed level of consciousness, hypertension, hypokalemia, hypotension, lethargy, loss of consciousness, QRS complex prolonged, QT prolonged, pneumonia aspiration, respiratory arrest, status epilepticus, and tachycardia.
11. Aristada Initio Description
ARISTADA INITIO contains aripiprazole lauroxil, an atypical antipsychotic.
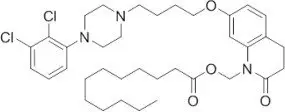
The chemical name of aripiprazole lauroxil is 7-{4-[4-(2,3-dichlorophenyl)-piperazin-1-yl]butoxy}-2-oxo-3,4-dihydro-2H-quinolin-1-yl)methyl dodecanoate. The empirical formula is C36H51Cl2N3O4 and its molecular weight is 660.7 g/mol. The chemical structure is:
ARISTADA INITIO is available as a white to off-white sterile aqueous extended-release injectable suspension for intramuscular injection in the following strength of aripiprazole lauroxil (and deliverable volume from a single-dose pre-filled syringe): 675 mg (2.4 mL). This product's specific extended-release and dosing characteristics are derived from aripiprazole lauroxil's submicron particle size distribution. The inactive ingredients include polysorbate 20 (16.2 mg/mL), sodium chloride (3.3 mg/mL), sodium citrate dihydrate (8.1 mg/mL), sodium phosphate dibasic anhydrous (0.74 mg/mL), sodium phosphate monobasic dihydrate (0.84 mg/mL) and water for injection.
12. Aristada Initio - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Aripiprazole lauroxil is a prodrug of aripiprazole. Following intramuscular injection, aripiprazole lauroxil is likely converted by enzyme-mediated hydrolysis to N-hydroxymethyl aripiprazole, which is then hydrolyzed to aripiprazole. The mechanism of action of aripiprazole in schizophrenia is unclear. However, efficacy could be mediated through a combination of partial agonist activity at dopamine D2 and serotonin 5-HT1A receptors and antagonist activity at 5-HT2A receptors.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Aripiprazole exhibits high affinity for dopamine D2 and D3 (Kis 0.34 and 0.8 nM respectively), serotonin 5-HT1A and 5-HT2A receptors (Kis 1.7 and 3.4 nM respectively), moderate affinity for dopamine D4, serotonin 5-HT2C and 5-HT7, alpha1-adrenergic and histamine H1 receptors (Kis 44 nM, 15 nM, 39 nM, 57 nM, and 61 nM, respectively), and moderate affinity for the serotonin reuptake site (Ki 98 nM). Aripiprazole has no appreciable affinity for cholinergic muscarinic receptors (IC50 > 1000 nM). Actions at receptors other than D2, 5-HT1A, and 5-HT2A could explain some of the adverse reactions of aripiprazole (e.g., the orthostatic hypotension observed with aripiprazole may be explained by its antagonist activity at adrenergic alpha1 receptors).
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
ARISTADA INITIO is a prodrug of aripiprazole and its activity is primarily due to aripiprazole, and to a lesser extent dehydro-aripiprazole (major metabolite of aripiprazole), which has been shown to have affinities for D2 receptors similar to aripiprazole and represents 30-40% of the aripiprazole exposure in plasma.
ARISTADA INITIO and ARISTADA are not interchangeable because of differing pharmacokinetic profiles. ARISTADA INITIO, 30 mg oral aripiprazole, and ARISTADA contribute to systemic aripiprazole exposure at different times throughout treatment initiation.
A pharmacokinetic (PK) bridging study demonstrated that an intramuscular injection of ARISTADA, a 30 mg dose of oral aripiprazole, and a single 675 mg dose of ARISTADA INITIO resulted in aripiprazole concentrations comparable to ARISTADA treatment initiated with 21 days of oral aripiprazole. A single strength of ARISTADA INITIO (i.e., 675 mg) was adequate for all dose levels of oral aripiprazole and ARISTADA.
Absorption
After single intramuscular injection of ARISTADA INITIO, the appearance of aripiprazole in the systemic circulation occurs on the day of injection; the median time to reach peak plasma exposures is approximately 27 days (range: 16 to 35 days).
With the addition of a single intramuscular injection of ARISTADA INITIO and 30 mg oral aripiprazole at the time of the first ARISTADA dose, aripiprazole concentrations reach relevant levels within 4 days.
Aripiprazole exposure was similar for deltoid and gluteal intramuscular injections of ARISTADA INITIO.
Distribution
Based on population pharmacokinetic analysis, the apparent volume of distribution of aripiprazole following intramuscular injection of ARISTADA was 268 L, indicating extensive extravascular distribution following absorption. Aripiprazole and its major metabolite are greater than 99% bound to serum proteins, primarily to albumin. In healthy human volunteers administered 0.5 mg/day to 30 mg/day oral aripiprazole for 14 days, there was dose-dependent D2 receptor occupancy indicating brain penetration of aripiprazole in humans.
Metabolism
The biotransformation of ARISTADA INITIO likely involves enzyme-mediated hydrolysis to form N-hydroxymethyl-aripiprazole, which subsequently undergoes hydrolysis to aripiprazole. Elimination of aripiprazole is mainly through hepatic metabolism involving CYP3A4 and CYP2D6 [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
Excretion
For ARISTADA INITIO, the mean aripiprazole terminal elimination half-life was 15-18 days after injection. The significantly longer aripiprazole apparent half-life compared to oral aripiprazole (mean 75 hours) is attributed to the dissolution and formation rate-limited elimination of aripiprazole following ARISTADA INITIO administration.
Drug Interaction Studies
No specific drug interaction studies have been performed with ARISTADA INITIO. The drug interaction data provided below is obtained from studies with oral aripiprazole.
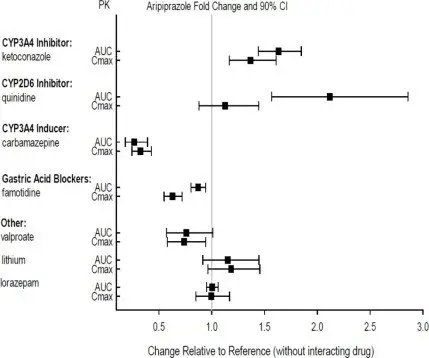
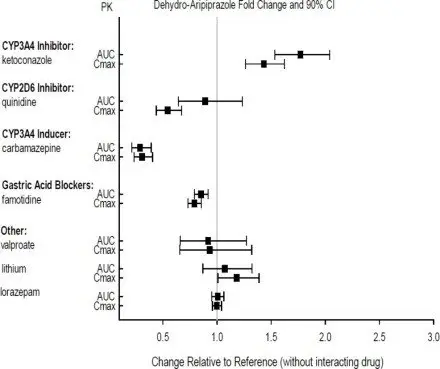
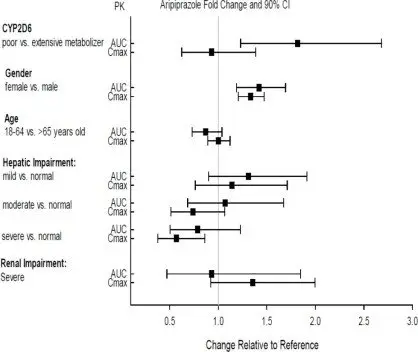
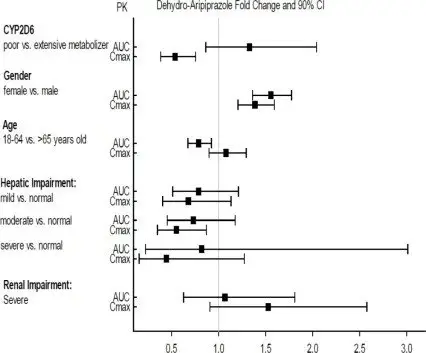
Effects of other drugs on the exposures of aripiprazole and dehydro-aripiprazole are summarized in Figure 1 and Figure 2, respectively. Based on simulation, a 4.5-fold increase in mean Cmax and AUC values at steady-state is expected when extensive metabolizers of CYP2D6 are administered with both strong CYP2D6 and CYP3A4 inhibitors. After oral administration, a 3-fold increase in mean Cmax and AUC values at steady-state is expected in poor metabolizers of CYP2D6 administered with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors.
Figure 1: The Effects of Other Drugs on Aripiprazole Pharmacokinetics
Figure 2: The Effects of Other Drugs on Dehydro-aripiprazole Pharmacokinetics
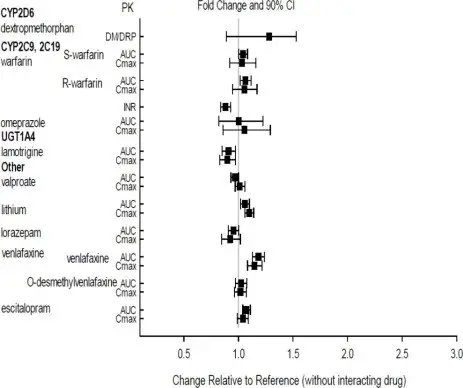
The effects of aripiprazole on the exposures of other drugs are summarized in Figure 3.
Figure 3: The Effects of Oral Aripiprazole on Pharmacokinetics of Other Drugs
Specific Populations
A population pharmacokinetic analysis showed no effect of sex, race or smoking on ARISTADA INITIO pharmacokinetics [see Use in Specific Populations (8.8)].
Exposures of aripiprazole and dehydro-aripiprazole using oral aripiprazole in specific populations are summarized in Figure 4 and Figure 5, respectively.
Figure 4: Effects of Intrinsic Factors on Aripiprazole Pharmacokinetics
Figure 5: Effects of Intrinsic Factors on Dehydro-aripiprazole Pharmacokinetics
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
Lifetime carcinogenicity studies have not been conducted with aripiprazole lauroxil.
Lifetime carcinogenicity studies with oral aripiprazole have been conducted in ICR mice and in Sprague-Dawley (SD) and F344 rats. Aripiprazole was administered for 2 years in the diet at doses of 1, 3, 10, and 30 mg/kg/day to ICR mice and 1, 3, and 10 mg/kg/day to F344 rats (0.2 to 5 times and 0.3 to 3 times the oral MRHD of 30 mg/day based on body surface area (mg/m2), respectively). In addition, SD rats were dosed orally for 2 years at 10, 20, 40, and 60 mg/kg/day (3 to 19 times the oral MRHD based on mg/m2). Aripiprazole did not induce tumors in male mice or rats. In female mice, the incidences of pituitary gland adenomas and mammary gland adenocarcinomas and adenoacanthomas were increased at dietary doses which are 0.1 to 0.9 times human exposure at the oral MRHD based on AUC and 0.5 to 5 times the oral MRHD on mg/m2 basis. In female rats, the incidence of mammary gland fibroadenomas was increased at a dietary dose which is 0.1 times human exposure at the oral MRHD based on AUC and 3 times the oral MRHD on mg/m2 basis; and the incidences of adrenocortical carcinomas and combined adrenocortical adenomas/carcinomas were increased at an oral dose which is 14 times human exposure at oral MRHD based on AUC and 19 times the oral MRHD on mg/m2 basis.
Proliferative changes in the pituitary and mammary gland of rodents have been observed following chronic administration of other antipsychotic agents and are considered prolactin-mediated. The relevance for human risk of the findings of prolactin-mediated endocrine tumors in rodents is unknown.
Mutagenesis
Aripiprazole lauroxil was not mutagenic in the in vitro bacterial reverse mutation assay or clastogenic in the in vitro chromosome aberration assay in human peripheral blood lymphocytes.
Aripiprazole and its metabolite (2,3-DCPP) were clastogenic in the in vitro chromosome aberration assay in Chinese hamster lung (CHL) cells both in the presence and absence of metabolic activation. The metabolite, 2,3-DCPP, produced increases in numerical aberrations in the in vitro assay in CHL cells in the absence of metabolic activation. A positive response was obtained in the oral in vivo micronucleus assay in mice; however, the response was due to a mechanism not considered relevant to humans.
Animal Data for ARISTADA (Aripiprazole Lauroxil)
In a rat fertility study, aripiprazole lauroxil was administered intramuscularly. Males were treated with doses of 18, 49, or 144 mg/animal, which are approximately 0.6 to 5 times the MRHD of 675 mg on mg/m2 basis, on Days 1, 21, and 42 prior to and through mating; females were treated at these doses, which are approximately 0.9 to 8 times the MRHD on mg/m2 basis, once 14 days prior to mating.
In females, persistent diestrus was observed at all doses and the mean number of cycles was significantly decreased at the highest dose together with an increase in the copulatory interval (delay in mating). Additional changes at the high dose included slight increases in corpora lutea and pre-implantation loss, decline in mating, fertility, and fecundity indices in females and lower mating and fertility indices in males.
Animal Data for Aripiprazole
Female rats were treated with oral aripiprazole doses of 2, 6, and 20 mg/kg/day, which are 0.6 to 6 times the oral MRHD of 30 mg/day on mg/m2 basis, from 2 weeks prior to mating through day 7 of gestation. Estrous cycle irregularities and increased corpora lutea were seen at all doses, but no impairment of fertility was observed. Increased pre-implantation loss was found at 2 and 6 times the oral MRHD on mg/m2 basis and decreased fetal weight was noted at the highest dose which is 6 times the oral MRHD on mg/m2 basis.
Male rats were treated with oral aripiprazole doses of 20, 40, and 60 mg/kg/day, which are 6 to 19 times the oral MRHD on mg/m2 basis, from 9 weeks prior to and through mating. Disturbances in spermatogenesis at the highest dose and prostate atrophy at the mid and high doses were noted which are 13 and 19 times the oral MRHD on mg/m2 basis, but no impairment of fertility was observed.
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
Animal Data for ARISTADA INITIO (Aripiprazole Lauroxil)
Intramuscular administration of aripiprazole lauroxil to rats and dogs was associated with injection site tissue reactions at all doses in rats treated up to 4 weeks at doses of 15, 29, and 103 mg/animal (which are approximately 0.6 to 4 times and 0.9 to 6 times the MRHD of 675 mg on mg/m2 basis in males and females, respectively) and in dogs treated up to 4 weeks at doses of 147, 662, and 2058 mg/animal (which are approximately 0.7 to 10 times and 1 to 14 times the MRHD in males and females, respectively on mg/m2 basis). These injection site tissue reactions consisted of localized granulomatous inflammation, granuloma formation, and/or subacute/chronic inflammation. Swelling occurred in both species, and transiently impaired limb function was observed in dogs. The granulomas did not completely resolve 2 months following the last injection in the 4-week studies in rats or dogs.
Orally administered aripiprazole produced retinal degeneration in albino rats in a 26-week chronic toxicity study at a dose of 60 mg/kg, which is 19 times the oral MRHD of 30 mg/day on mg/m2 basis, and in a 2-year carcinogenicity study at doses of 40 mg/kg and 60 mg/kg, which are 13 and 19 times the oral MRHD on mg/m2 basis and 7 to 14 times human exposure at the oral MRHD based on AUC. Evaluation of the retinas of albino mice and of monkeys did not reveal evidence of retinal degeneration. Additional studies to further evaluate the mechanism have not been performed. The relevance of this finding to human risk is unknown.
14. Clinical Studies
The effectiveness of ARISTADA INITIO, in combination with oral aripiprazole, for initiation of ARISTADA when used for the treatment of schizophrenia in adults was established by adequate and well-controlled studies of oral aripiprazole and ARISTADA in adult patients with schizophrenia [see ARISTADA prescribing information] and a single PK bridging study [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
16. How is Aristada Initio supplied
16.1 How Supplied
ARISTADA INITIO extended-release injectable suspension is available in a strength of 675 mg in 2.4 mL. The kit contains a 5-mL pre-filled syringe containing ARISTADA INITIO as a sterile white to off-white aqueous extended-release injectable suspension with safety needles.
- A 675 mg strength kit (NDC 65757-500-03; gray label) contains three safety needles; a 1-inch (25 mm) 21 gauge, a 1½-inch (38 mm) 20 gauge, and a 2-inch (50 mm) 20 gauge needle.
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise patients to read FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide).
Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome
Counsel patients about a potentially fatal adverse reaction referred to as NMS that has been reported in association with administration of antipsychotic drugs. Advise patients to contact a healthcare provider or report to the emergency room if they experience signs or symptoms of NMS [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Tardive Dyskinesia
Advise patients that abnormal involuntary movements have been associated with administration of antipsychotic drugs. Counsel patients to notify their healthcare provider if they notice any movements which they cannot control in their face, tongue, or other body part [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Metabolic Changes (Hyperglycemia and Diabetes Mellitus, Dyslipidemia, and Weight Gain)
Educate patients about the risk of metabolic changes, how to recognize symptoms of hyperglycemia and diabetes mellitus, and the need for specific monitoring, including blood glucose, lipids, and weight [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
Pathological Gambling and Other Compulsive Behaviors
Advise patients and their caregivers of the possibility that they may experience compulsive urges to shop, intense urges to gamble, compulsive sexual urges, binge eating and/or other compulsive urges and the inability to control these urges. In some cases, but not all, the urges were reported to have stopped when the dose was reduced or stopped [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
Orthostatic Hypotension
Educate patients about the risk of orthostatic hypotension (symptoms include feeling dizzy or lightheaded upon standing), particularly at the time of initiating treatment, or re-initiating treatment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
Falls
Advise patients and their caregivers of the possibility that they may experience somnolence, postural hypotension, or motor and sensory instability, which may lead to the risk of falls, particularly in patients with diseases, conditions, or medications that could exacerbate these effects [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)].
Leukopenia, Neutropenia and Agranulocytosis
Advise patients with a pre-existing low WBC count or a history of drug-induced leucopenia/neutropenia that they should have their CBC monitored [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)].
Interference with Cognitive and Motor Performance
Because ARISTADA INITIO may have the potential to impair judgment, thinking or motor skills, instruct patients to be cautious about operating hazardous machinery, including automobiles, until they are reasonably certain that therapy does not affect them adversely [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12)].
Heat Exposure and Dehydration
Advise patients regarding appropriate care in avoiding overheating and dehydration [see Warnings and Precautions (5.13)].
Concomitant Medication
Advise patients to inform their physicians if they are taking, or plan to take, any prescription or over-the-counter drugs, since there is a potential for interactions [see Drug Interactions (7)].
Pregnancy
Advise patients that ARISTADA INITIO may cause extrapyramidal and/or withdrawal symptoms in a neonate and to notify their healthcare provider with a known or suspected pregnancy [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Pregnancy Registry
Advise patients that there is a pregnancy exposure registry that monitors pregnancy outcomes in women exposed to ARISTADA INITIO during pregnancy [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
For additional information, visit www.ARISTADA.com or call 1-866-274-7823
Manufactured and marketed by:
Alkermes, Inc.
852 Winter Street
Waltham, MA 02451-1420
Alkermes
©2020 Alkermes, Inc. All rights reserved.
ALKERMES® is a registered trademark of Alkermes, Inc., ARISTADA INITIO® is a registered trademark used by Alkermes, Inc. under license and ARISTADA® is a registered trademark used by Alkermes, Inc. under license.
Printed in U.S.A.
|
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration |
Revised 03/2021 |
|
| MEDICATION GUIDE
ARISTADA INITIO® (air-is-TAH-dah i-ni'-she-oh) (aripiprazole lauroxil) extended-release injectable suspension, for intramuscular use |
||
|
||
| What is ARISTADA INITIO?
ARISTADA INITIO is a prescription medicine given as a one-time injection and is used in combination with oral aripiprazole to start ARISTADA treatment, or re-start ARISTADA treatment after a missed dose, when ARISTADA is used for the treatment of schizophrenia in adults. It is not known if ARISTADA INITIO is safe and effective in children. |
||
| Do not receive ARISTADA INITIO if you are allergic to aripiprazole or any of the ingredients in ARISTADA INITIO. See the end of this Medication Guide for a complete list of ingredients in ARISTADA INITIO. | ||
Before you receive ARISTADA INITIO, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
|
||
| Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. ARISTADA INITIO and other medicines may affect each other causing possible serious side effects. ARISTADA INITIO may affect the way other medicines work, and other medicines may affect how ARISTADA INITIO works. Your healthcare provider can tell you if it is safe to receive ARISTADA INITIO with your other medicines. Do not start or stop any medicines after you receive ARISTADA INITIO without talking to your healthcare provider first. |
||
How will I receive ARISTADA INITIO?
|
||
|
What should I avoid after I receive ARISTADA INITIO?
|
||
| What are the possible side effects of ARISTADA INITIO?
ARISTADA INITIO may cause serious side effects, including:
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
||
| The most common side effects of ARISTADA INITIO include restlessness or feeling like you need to move (akathisia). These are not all the possible side effects of ARISTADA INITIO. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. |
||
| General information about ARISTADA INITIO
If you would like more information, talk with your healthcare provider. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about ARISTADA INITIO that is written for health professionals. |
||
| What are the ingredients in ARISTADA INITIO?
Active ingredient: aripiprazole lauroxil Inactive ingredients: polysorbate 20, sodium chloride, sodium citrate dihydrate, sodium phosphate dibasic anhydrous, sodium phosphate monobasic dihydrate and water for injection Manufactured and marketed by: Alkermes, Inc., 852 Winter Street, Waltham, MA 02451-1420 For more information, go to www.ARISTADA.com or call 1-866-274-7823. |
||
Principal Display Panel - Aristada Initio Carton Label
NDC: 65757-500-03
675 mg/2.4 mL
Rx only
Aristada Initio®
aripiprazole lauroxil
extended-release injectable suspension
Starter Dose
675 mg
STARTER
DOSE
- For initiation with any Aristada® dose
- Only use to initiate or re-initiate Aristada treatment
- NOT for repeated dosing
For gluteal or deltoid intramuscular injection only
Aristada Initio is
NOT
interchangeable with Aristada due to
differing pharmacokinetic profiles
Single-dose injection - Entire Content of Syringe Must
Be Administered by Healthcare Professional Only
OPEN HERE
| ARISTADA INITIO
aripiprazole lauroxil injection, suspension, extended release |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Alkermes, Inc. (185481132) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alkermes, Inc | 858582083 | MANUFACTURE(65757-500) , ANALYSIS(65757-500) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sharp Corporation | 143696495 | LABEL(65757-500) , PACK(65757-500) | |