Drug Detail:Barhemsys (Amisulpride [ a-mi-sul-pride ])
Drug Class: Miscellaneous antiemetics
Highlights of Prescribing Information
BARHEMSYS® (amisulpride) injection, for intravenous use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2020
Indications and Usage for Barhemsys
BARHEMSYS is a dopamine-2 (D2) antagonist indicated in adults for:
- Prevention of postoperative nausea and vomiting (PONV), either alone or in combination with an antiemetic of a different class. (1)
- Treatment of PONV in patients who have received antiemetic prophylaxis with an agent of a different class or have not received prophylaxis. (1)
Barhemsys Dosage and Administration
The recommended dosage of BARHEMSYS:
- Prevention of PONV, either alone or in combination with another antiemetic: 5 mg as a single intravenous dose infused over 1 to 2 minutes at the time of induction of anesthesia. (2.1)
- Treatment of PONV: 10 mg as a single intravenous dose infused over 1 to 2 minutes in the event of nausea and/or vomiting after a surgical procedure. (2.1)
- See full prescribing information for preparation and administration instructions. (2.2)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Injection: 5 mg/2 mL (2.5 mg/mL) or 10 mg/4 mL (2.5 mg/mL) in a single-dose vial. (3)
Contraindications
Known hypersensitivity to amisulpride. (4)
Warnings and Precautions
QT Prolongation: Occurs in a dose- and concentration-dependent manner. Avoid use in patients with congenital long QT syndrome and in patients taking droperidol. ECG monitoring is recommended in patients with pre-existing arrhythmias/cardiac conduction disorders; electrolyte abnormalities (e.g., hypokalemia or hypomagnesemia); congestive heart failure; and in patients taking other medicinal products (e.g., ondansetron) or with other medical conditions known to prolong the QT interval. (5.1, 7.2)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions (≥ 2%) are:
- Prevention of PONV: increased blood prolactin concentrations, chills, hypokalemia, procedural hypotension, and abdominal distension. (6.1)
- Treatment of PONV: infusion site pain. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Acacia Pharma at 1-877-357-9237 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Use In Specific Populations
Lactation: A lactating woman may pump and discard breast milk for 48 hours after BARHEMSYS administration. (8.2)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 9/2022
Related/similar drugs
ondansetron, Zofran, metoclopramide, Reglan, amisulpride, Zofran ODTFull Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Barhemsys
BARHEMSYS® is indicated in adults for:
- prevention of postoperative nausea and vomiting (PONV), either alone or in combination with an antiemetic of a different class.
- treatment of PONV in patients who have received antiemetic prophylaxis with an agent of a different class or have not received prophylaxis.
2. Barhemsys Dosage and Administration
2.1 Recommended Dosage
The recommended adult dosage of BARHEMSYS and infusion rate by indication is shown in the table below:
| Indication | Adult Dosage Regimen |
|---|---|
| Prevention of PONV | 5 mg as a single intravenous injection infused over 1 to 2 minutes at the time of induction of anesthesia [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)]. |
| Treatment of PONV | 10 mg as a single intravenous injection infused over 1 to 2 minutes in the event of nausea and/or vomiting after a surgical procedure [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)]. |
2.2 Preparation and Administration
- Dilution of BARHEMSYS is not required before administration. BARHEMSYS is chemically and physically compatible with Water for Injection, 5% Dextrose Injection, 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, and Lactated Ringer's Solution (also known as Ringer's Lactate Solution, Compound Sodium Lactate Solution, and Hartmann's Solution), any of which may be used to flush an intravenous line before or after administration of BARHEMSYS.
- Protect from light. BARHEMSYS is subject to photodegradation. Administer BARHEMSYS within 12 hours of removal of the vial from the protective carton.
- Prior to administration, inspect the BARHEMSYS solution visually for particulate matter and discoloration. Discard if particulate matter or discoloration is observed.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
Injection: 5 mg/2 mL (2.5 mg/mL) or 10 mg/4 mL (2.5 mg/mL) as a clear, colorless sterile solution in a single-dose vial.
4. Contraindications
BARHEMSYS is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to amisulpride [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 QT Prolongation
BARHEMSYS causes dose- and concentration-dependent prolongation of the QT interval [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)]. The recommended dosage is 5 or 10 mg as a single intravenous dose infused over 1 to 2 minutes [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
Avoid use in patients with congenital long QT syndrome and in patients taking droperidol.
Electrocardiogram (ECG) monitoring is recommended in patients with pre-existing arrhythmias/cardiac conduction disorders; electrolyte abnormalities (e.g., hypokalemia or hypomagnesemia); congestive heart failure; and in patients taking other medicinal products (e.g., ondansetron) or with other medical conditions known to prolong the QT interval [see Drug Interactions (7.2)].
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The data described below reflect exposure to BARHEMSYS in 1,166 patients treated in placebo-controlled trials. 748 of these patients received a dose of 5 mg for prevention of PONV (of whom 572 received another antiemetic concomitantly) and 418 patients received 10 mg for treatment of PONV [see Clinical Studies (14.1, 14.2)]. The mean age of the population was 49 years (range 18 to 91 years), 87% female, 80% White/Caucasian, 9% Black, and 1% Asian.
Prevention of PONV
Common adverse reactions reported in at least 2% of adult patients who received BARHEMSYS 5 mg and at a higher rate than placebo in Studies 1 and 2 for the prevention of PONV are shown in Table 1.
| BARHEMSYS 5 mg | Placebo | |
|---|---|---|
| N=748 | N=741 | |
|
||
| Chills | 4% | 3% |
| Hypokalemia | 4% | 2% |
| Procedural hypotension | 3% | 2% |
| Abdominal distension | 2% | 1% |
Serum prolactin concentrations were measured in Study 1 where 5% (9/176) of BARHEMSYS-treated patients vs 1% (1/166) of placebo-treated patients had increased blood prolactin reported as an adverse reaction. Serum prolactin concentrations increased from a mean of 10 ng/mL at baseline to 32 ng/mL after BARHEMSYS treatment in 112 females (upper limit of normal 29 ng/mL) and from 10 ng/mL to 19 ng/mL in 61 males (upper limit of normal 18 ng/mL). No clinical consequences due to elevated prolactin levels were reported.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval chronic oral use of amisulpride outside of the United States (BARHEMSYS is not approved for oral dosing or chronic use). Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
- Blood and lymphatic system disorders: agranulocytosis
- Cardiac disorders: bradycardia, torsades de pointes, ventricular tachycardia, prolonged QT by electrocardiogram
- General disorders: neuroleptic malignant syndrome
- Immune system disorders: angioedema, hypersensitivity, urticaria
- Hepatic disorders: increased hepatic enzymes
- Nervous system disorders: agitation, anxiety, dystonia, extrapyramidal disorder, seizure
- Psychiatric disorders: confusional state, insomnia, somnolence
- Vascular disorders: hypotension
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 Dopamine Agonists
Reciprocal antagonism of effects occurs between dopamine agonists (e.g., levodopa) and BARHEMSYS. Avoid using levodopa with BARHEMSYS.
7.2 Drugs Prolonging the QT Interval
BARHEMSYS causes dose- and concentration-dependent QT prolongation [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)]. To avoid potential additive effects, avoid use of BARHEMSYS in patients taking droperidol. ECG monitoring is recommended in patients taking other drugs known to prolong the QT interval (e.g., ondansetron) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the total number of patients enrolled in controlled clinical trials who received BARHEMSYS 5 mg for prevention of PONV or 10 mg for treatment of PONV, 235 (17%) were 65 years of age and older, while 59 (4%) were 75 years of age and older. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these patients and younger patients, and other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients, but greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out.
10. Overdosage
Doses of oral amisulpride (BARHEMSYS is not approved for oral dosing) above 1200 mg/day have been associated with adverse reactions related to dopamine-2 (D2) antagonism, in particular:
- cardiovascular adverse reactions (e.g., prolongation of the QT interval, torsades de pointes, bradycardia and hypotension) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- neuropsychiatric adverse reactions (e.g., sedation, coma, seizures, and dystonic and extrapyramidal reactions).
There is no specific antidote for amisulpride overdose. Management includes cardiac monitoring and treatment of severe extrapyramidal symptoms.
Since amisulpride is weakly dialyzed, hemodialysis should not be used to eliminate the drug.
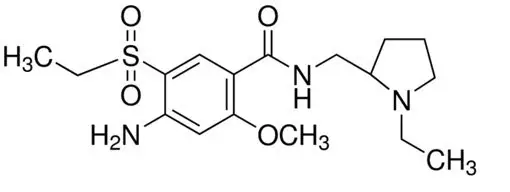
11. Barhemsys Description
The active ingredient of BARHEMSYS is amisulpride, a dopamine-2 (D2) receptor antagonist. Its chemical name is 4-Amino-N-[(1-ethyl-2-pyrrolidinyl)methyl]-5-(ethylsulfonyl)-o-anisamide. It has the following chemical structure:
|
| (racemic) |
The empirical formula is C17H27N3O4S representing a molecular weight of 369.48.
Amisulpride is a white or almost white crystalline powder. It is practically insoluble in water, sparingly soluble in ethanol and freely soluble in methylene chloride, and has a melting point of around 126°C. The compound is racemic and shows no optical rotation and is not hygroscopic. No other polymorphs of amisulpride have been reported.
BARHEMSYS (amisulpride) injection is a clear, colorless, nonpyrogenic, sterile solution formulation of amisulpride 5 mg/2 mL (2.5 mg/mL) or 10 mg/4 mL (2.5 mg/mL) for intravenous infusion presented in a single-dose vial. It has a pH of approximately 5.0 and the osmolality of the product is between 250 and 330 mOsmol/kg.
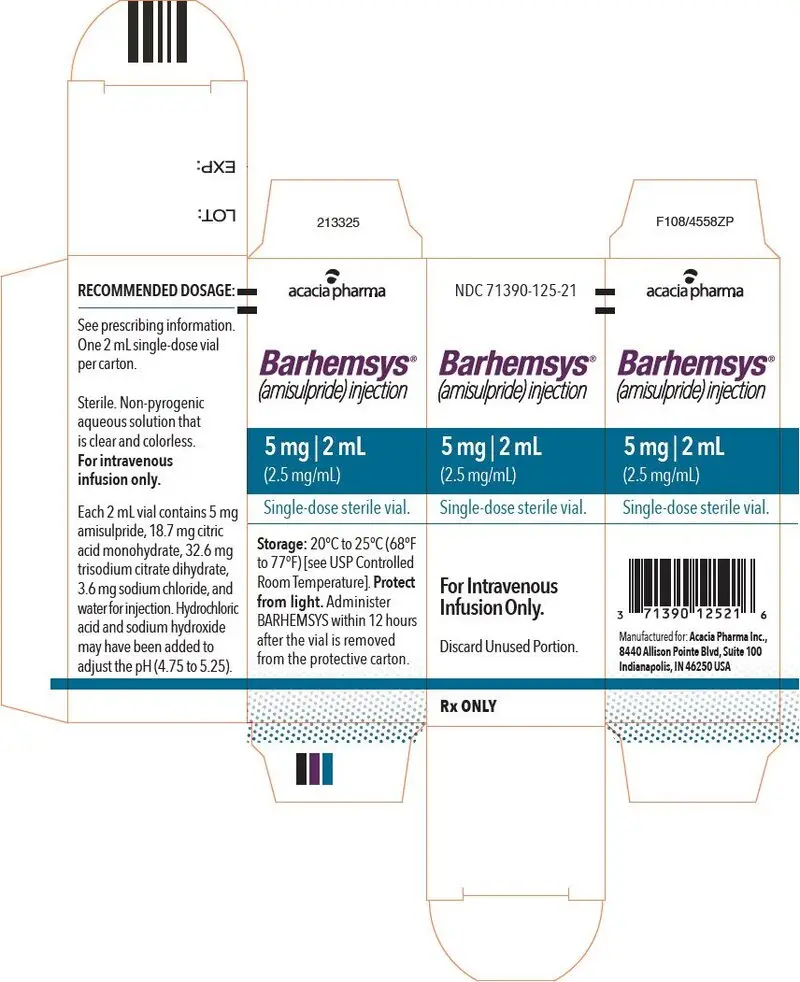
Each 2 mL vial of BARHEMSYS contains 5 mg of amisulpride; 18.7 mg of citric acid monohydrate USP; 3.6 mg of sodium chloride USP; 32.64 mg of trisodium citrate dihydrate; hydrochloric acid NF and sodium hydroxide NF as needed to adjust the pH (4.75 to 5.25); and Water for Injection USP to make up to volume.
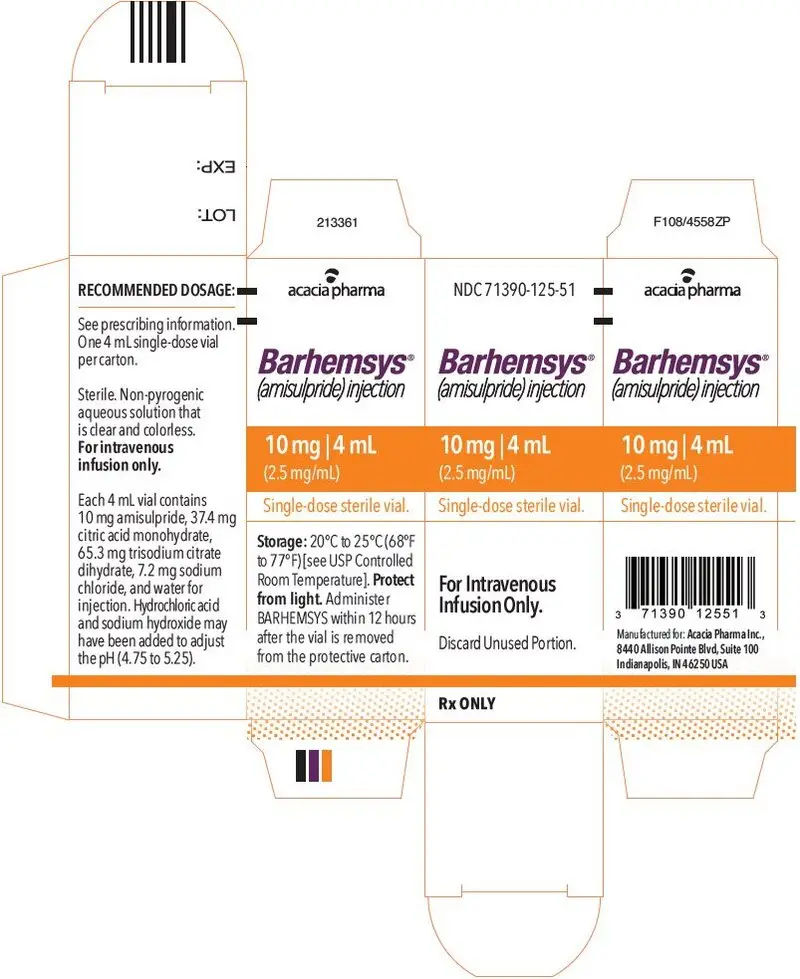
Each 4 mL vial of BARHEMSYS contains 10 mg of amisulpride; 37.4 mg of citric acid monohydrate USP; 7.2 mg of sodium chloride USP; 65.3 mg of trisodium citrate dihydrate; hydrochloric acid NF and sodium hydroxide NF as needed to adjust the pH (4.75 to 5.25); and Water for Injection USP to make up to volume.
12. Barhemsys - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Amisulpride is a selective dopamine-2 (D2) and dopamine-3 (D3) receptor antagonist. D2 receptors are located in the chemoreceptor trigger zone (CTZ) and respond to the dopamine released from the nerve endings. Activation of CTZ relays stimuli to the vomiting center which is involved in emesis. Studies in multiple species indicate that D3 receptors in the area postrema also play a role in emesis. Studies conducted in ferrets have shown that amisulpride inhibits emesis caused by apomorphine, with an estimated ED50 of less than 1 mcg/kg, subcutaneously; and inhibits cisplatin-induced emesis at 2 mg/kg and morphine-induced emesis at 3 to 6 mg/kg, when given intravenously.
Amisulpride has no appreciable affinity for any other receptor types apart from low affinities for 5-HT2B and 5-HT7 receptors.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
After an intravenous infusion, the peak plasma concentration of amisulpride is achieved at the end of the infusion period and the plasma concentration decreases to about 50% of the peak value within approximately 15 minutes. The AUC(0-∞) increases dose-proportionally in the dose range from 5 mg to 40 mg (4-times the maximum recommended dose).
The following mean pharmacokinetic parameters of amisulpride were observed following a single 5 or 10 mg intravenous dose in adult healthy subjects and surgical patients.
| Single Dose | Infusion Duration (minutes) | Number of Subjects | Mean (SD) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peak Plasma Concentration (ng/mL) | AUC(0-∞)
(ng∙h/mL) |
||||
|
|||||
| Healthy Subjects | 5 mg | 2 | 39 | 200 (139) | 154 (30) |
| Healthy Subjects | 10 mg | 1 | 29 | 451 (230) | 136 (28)* |
| Patients | 5 mg | 1 to 2 | 26† | 161 (58) | 260 (65) |
| 27‡ | 127 (64) | 204 (94) | |||
| Patients | 10 mg | 1 to 2 | 31‡ | 285 (446) | 401 (149) |
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Long-term studies to assess the carcinogenic potential of amisulpride have not been conducted. Amisulpride was not genotoxic in the bacterial reverse mutation assay, the in vitro human peripheral blood lymphocytes assay, and the in vivo rat bone marrow micronucleus assay.
The effect of amisulpride on fertility was studied in rats at oral doses up to 160 mg/kg/day (43 times the exposure based on AUC at the highest recommended dose of 10 mg). Most female animals (90% to 95%) at each dose level remained in diestrus and failed to mate. However, this effect on mating reversed following cessation of treatment. No treatment-related effects were observed on uterine/implantation parameters or sperm counts, sperm motility or sperm morphology.
14. Clinical Studies
14.1 Prevention of Postoperative Nausea and Vomiting
The efficacy of BARHEMSYS for the prevention of PONV was evaluated in two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multi-center trials in patients undergoing general anesthesia and elective surgery (Study 1 and Study 2). In Study 1 (NCT01991860), patients received monotherapy with BARHEMSYS; while in Study 2 (NCT02337062), patients received BARHEMSYS in combination with one other intravenously administered, non-dopaminergic antiemetic (ondansetron, dexamethasone or betamethasone). In both trials, patients were administered BARHEMSYS at the induction of anesthesia.
Study 1 was conducted in the United States in 342 patients. The mean age was 54 years (range 21 to 88 years); 65% female; 87% White/Caucasian, 12% Black, and 1% Asian race. The treatment groups were similarly matched in terms of risk for PONV with 30% of patients having two risk factors, 47% of patients having three risk factors and 23% of patients having four risk factors.
Study 2 was conducted in the United States and Europe in 1,147 patients. The mean age was 49 years (range 18 to 91 years); 97% female; 75% White/Caucasian, 9% Black, 1% Asian, and 14% of unreported race. The treatment groups were similarly matched in terms of risk for PONV with 56% of patients having three risk factors and 43% of patients having four risk factors.
The primary efficacy endpoint in both trials was Complete Response, defined as absence of any episode of emesis or use of rescue medication within the first 24 hours postoperatively. Results for both trials are shown in Table 3.
| Study 1 | Study 2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BARHEMSYS 5 mg (n=176) | Placebo (n=166) | BARHEMSYS 5 mg with Another Antiemetic (n=572) | Placebo with Another Antiemetic (n=575) |
|
|
||||
| Complete Response | 78 (44%) | 54 (33%) | 330 (58%) | 268 (47%) |
| Difference (95% CI)* | 12% (2%, 22%) | 11% (5%, 17%) |
||
14.2 Treatment of Postoperative Nausea and Vomiting
The efficacy of BARHEMSYS 10 mg as a single dose was evaluated in two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multi-center trials in patients experiencing PONV after general anesthesia and elective surgery (Study 3 and Study 4). Study 3 (NCT02449291) enrolled patients who had not received prior PONV prophylaxis, whereas Study 4 (NCT02646566) included patients who had received and failed PONV prophylaxis with an antiemetic of another class. Patients were excluded if they had received a D2 receptor antagonist antiemetic.
Study 3 was conducted in 369 patients (mean age 47 years, range 19 to 82 years; 76% female; 82% White/Caucasian, 8% Black, 2% Asian, and 8% of unreported race). Most of the patients had either two risk factors (36%) or three risk factors (53%) for PONV and these percentages were similar between treatment groups.
Study 4 was conducted in 465 patients (mean age 46 years, range 18 to 85 years; 90% female; 82% White/Caucasian, 9% Black, 3% Asian, and 6% of unreported race). Patients had received prior PONV prophylaxis with one or more non-dopaminergic antiemetics: a 5-HT3-antagonist in 77%, dexamethasone in 65% and another antiemetic class in 10%. Most of the patients had either three risk factors (43%) or four risk factors (51%) for PONV and these percentages were similar between treatment groups.
For both trials, the primary efficacy endpoint was Complete Response defined as absence of any episode of emesis or use of rescue medication within the first 24 hours after treatment (excluding emesis within the first 30 minutes).
BARHEMSYS Complete Response in both studies is shown in Table 4.
| Study 3 (no prophylaxis) | Study 4 (prior prophylaxis)† |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BARHEMSYS 10 mg (n=188) | Placebo (n=181) | BARHEMSYS 10 mg (n=230) | Placebo (n=235) |
|
|
||||
| Complete Response | 59 (31%) | 39 (22%) | 96 (42%) | 67 (29%) |
| Difference (95% CI)‡ | 10% (1%, 19%) | 13% (5%, 22%) | ||
16. How is Barhemsys supplied
BARHEMSYS (amisulpride) injection is supplied as follows:
NDC 71390-125-20: Package of 10 cartons. Each carton (NDC 71390-125-21) contains one single-dose vial of clear, colorless, sterile solution of BARHEMSYS (amisulpride) injection, 5 mg in 2 mL (2.5 mg/mL).
NDC 71390-125-50: Package of 10 cartons. Each carton (NDC 71390-125-51) contains one single-dose vial of clear, colorless, sterile solution of BARHEMSYS (amisulpride) injection, 10 mg in 4 mL (2.5 mg/mL).
| BARHEMSYS
amisulpride injection, solution |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Acacia Pharma Ltd (779660930) |