Drug Detail:Bentyl (Dicyclomine (oral/injection) [ dye-sye-kloe-meen ])
Drug Class: Anticholinergics / antispasmodics
Highlights of Prescribing Information
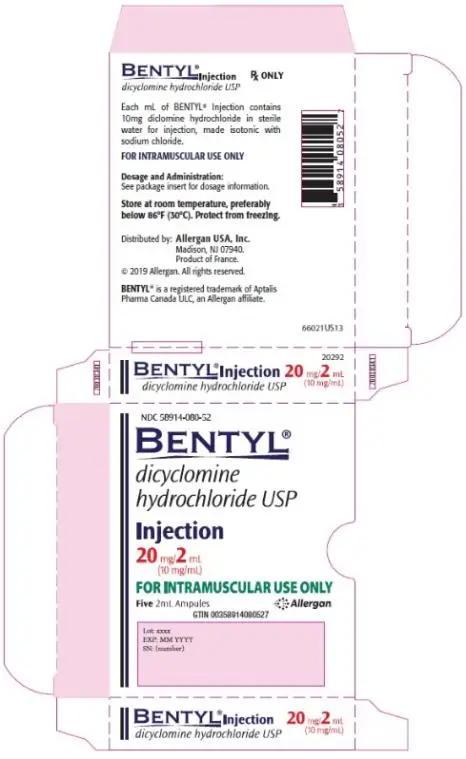
BENTYL (dicyclomine hydrochloride) injection, for intramuscular use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1950
Indications and Usage for Bentyl
BENTYL is an antispasmodic and anticholinergic (antimuscarinic) agent indicated for the treatment of functional bowel/irritable bowel syndrome (1).
Bentyl Dosage and Administration
Dosage for BENTYL must be adjusted to individual patient needs (2).
If a dose is missed, patients should continue the normal dosing schedule (2).
Intramuscular in adults (2.1):
- Intramuscular administration recommended no longer than 1 or 2 days when patients cannot take oral administration
- Recommended dose: 10 mg to 20 mg four times a day
Dosage Forms and Strengths
BENTYL injection 20 mg/2 mL (10 mg/mL) (3).
Contraindications
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Warnings and Precautions
- For Intramuscular injection only; should not be administered by any other route. Intravenous injection may result in thrombosis or thrombophlebitis and injection site reactions (5.1)
-
Cardiovascular conditions: worsening of conditions (5.2)
-
Peripheral and central nervous system: heat prostration can occur with drug use (fever and heat stroke due to decreased sweating); drug should be discontinued and supportive measures instituted (5.3)
-
Psychosis and delirium have been reported in patients sensitive to anticholinergic drugs (such as elderly patients and/or in patients with mental illness): signs and symptoms resolve within 12 to 24 hours after discontinuation of BENTYL (5.3)
-
Myasthenia Gravis: overdose may lead to muscular weakness and paralysis. BENTYL should be given to patients with myasthenia gravis only to reduce adverse muscarinic effects of an anticholinesterase (5.4)
-
Incomplete intestinal obstruction: diarrhea may be an early symptom especially in patients with ileostomy or colostomy. Treatment with BENTYL would be inappropriate and possibly fatal (5.5)
-
Salmonella dysenteric patients: due to risk of toxic megacolon (5.6)
-
Ulcerative colitis: BENTYL should be used with caution in these patients; large doses may suppress intestinal motility or aggravate the serious complications of toxic megacolon (5.7)
-
Prostatic hypertrophy: BENTYL should be used with caution in these patients; may lead to urinary retention (5.8)
-
Hepatic and renal disease: should be used with caution (5.9)
- Geriatric: use with caution in elderly who may be more susceptible to BENTYL’s adverse events (5.10)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The most serious adverse reactions include cardiovascular and central nervous system symptoms. The most common adverse reactions (> 5% of patients) are dizziness, dry mouth, vision blurred, nausea, somnolence, asthenia and nervousness (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Allergan at 1-800-678-1605 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.com
Drug Interactions
-
Antiglaucoma agents: anticholinergics antagonize antiglaucoma agents and may increase intraoccular pressure (7)
-
Anticholinergic agents: may affect the gastrointestinal absorption of various drugs; may also increase certain actions or side effects of other anticholinergic drugs (7)
- Antacids: interfere with the absorption of anticholinergic agents (7)
Use In Specific Populations
- Pregnancy: use only if clearly needed (8.1)
- Pediatric Use: safety and effectiveness not established (8.4)
- Hepatic and renal impairment: caution must be taken with patients with significantly impaired hepatic and renal function (8.6)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 1/2019
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Bentyl
BENTYL® (dicyclomine hydrochloride) is indicated for the treatment of patients with functional bowel/irritable bowel syndrome.
2. Bentyl Dosage and Administration
Dosage must be adjusted to individual patient needs.
2.1 Intramuscular Dosage and Administration in Adults
BENTYL Intramuscular Injection must be administered via intramuscular route only. Do not administer by any other route.
The recommended intramuscular dose is 10 mg to 20 mg four times a day [see Clinical Pharmacology (12)].
The intramuscular injection is to be used only for 1 or 2 days when the patient cannot take oral medication.
Intramuscular injection is about twice as bioavailable as oral dosage forms.
4. Contraindications
BENTYL is contraindicated in infants less than 6 months of age [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)], nursing mothers [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)], and in patients with:
- unstable cardiovascular status in acute hemorrhage
- myasthenia gravis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- glaucoma [see Adverse Reactions (6.3) and Drug Interactions (7.1)]
- obstructive uropathy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
- obstructive disease of the gastrointestinal tract [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- severe ulcerative colitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- reflux esophagitis
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Inadvertent Intravenous Administration
BENTYL solution is for intramuscular administration only. Do not administer by any other route. Inadvertent intravenous administration may result in thrombosis, thrombophlebitis, and injection site reactions such as pain, edema, skin color change, and reflex sympathetic dystrophy syndrome [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
5.2 Cardiovascular Conditions
Dicyclomine hydrochloride needs to be used with caution in conditions characterized by tachyarrhythmia such as thyrotoxicosis, congestive heart failure and in cardiac surgery, where they may further accelerate the heart rate. Investigate any tachycardia before administration of dicyclomine hydrochloride. Care is required in patients with coronary heart disease, as ischemia and infarction may be worsened, and in patients with hypertension [see Adverse Reactions (6.3)].
5.3 Peripheral and Central Nervous System
The peripheral effects of dicyclomine hydrochloride are a consequence of their inhibitory effect on muscarinic receptors of the autonomic nervous system. They include dryness of the mouth with difficulty in swallowing and talking, thirst, reduced bronchial secretions, dilatation of the pupils (mydriasis) with loss of accommodation (cycloplegia) and photophobia, flushing and dryness of the skin, transient bradycardia followed by tachycardia, with palpitations and arrhythmias, and difficulty in micturition, as well as reduction in the tone and motility of the gastrointestinal tract leading to constipation [see Adverse Reactions (6)].
In the presence of high environmental temperature heat prostration can occur with drug use (fever and heat stroke due to decreased sweating). It should also be used cautiously in patients with fever. If symptoms occur, the drug should be discontinued and supportive measures instituted. Because of the inhibitory effect on muscarinic receptors within the autonomic nervous system, caution should be taken in patients with autonomic neuropathy.
Central nervous system (CNS) signs and symptoms include confusional state, disorientation, amnesia, hallucinations, dysarthria, ataxia, coma, euphoria, fatigue, insomnia, agitation and mannerisms, and inappropriate affect.
Psychosis and delirium have been reported in sensitive individuals (such as elderly patients and/or in patients with mental illness) given anticholinergic drugs. These CNS signs and symptoms usually resolve within 12 to 24 hours after discontinuation of the drug.
BENTYL may produce drowsiness, dizziness or blurred vision. The patient should be warned not to engage in activities requiring mental alertness, such as operating a motor vehicle or other machinery or performing hazardous work while taking BENTYL.
5.4 Myasthenia Gravis
With overdosage, a curare-like action may occur (i.e., neuromuscular blockade leading to muscular weakness and possible paralysis). It should not be given to patients with myasthenia gravis except to reduce adverse muscarinic effects of an anticholinesterase [see Contraindications (4)].
5.5 Intestinal Obstruction
Diarrhea may be an early symptom of incomplete intestinal obstruction, especially in patients with ileostomy or colostomy. In this instance, treatment with this drug would be inappropriate and possibly harmful [see Contraindications (4)].
Rarely development of Ogilvie’s syndrome (colonic pseudo-obstruction) has been reported. Ogilvie’s syndrome is a clinical disorder with signs, symptoms, and radiographic appearance of an acute large bowel obstruction but with no evidence of distal colonic obstruction.
5.6 Toxic Dilatation of Intestinemegacolon
Toxic dilatation of intestine and intestinal perforation is possible when anticholinergic agents are administered in patients with Salmonella dysentery.
5.7 Ulcerative Colitis
Caution should be taken in patients with ulcerative colitis. Large doses may suppress intestinal motility to the point of producing a paralytic ileus and the use of this drug may precipitate or aggravate the serious complication of toxic megacolon [see Adverse Reactions (6.3)]. BENTYL is contraindicated in patients with severe ulcerative colitis [see Contraindications (4)].
5.8 Prostatic Hypertrophy
BENTYL should be used with caution in patients with known or suspected prostatic enlargement, in whom prostatic enlargement may lead to urinary retention [see Adverse Reactions (6.3)].
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The pattern of adverse effects seen with dicylomine is mostly related to its pharmacological actions at muscarinic receptors [see Clinical Pharmacology (12)]. They are a consequence of the inhibitory effect on muscarinic receptors within the autonomic nervous system. These effects are dose-related and are usually reversible when treatment is discontinued.
The most serious adverse reactions reported with dicyclomine hydrochloride include cardiovascular and central nervous system symptoms [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2, 5.3)].
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions, presented by system organ class in alphabetical order, have been identified during post approval use of BENTYL. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
-
Cardiac disorders: palpitations, tachyarrhythmias
-
Eye disorders: cycloplegia, mydriasis, vision blurred
-
Gastrointestinal disorders: abdominal distension, abdominal pain, constipation, dry mouth, dyspepsia, nausea, vomiting
-
General disorders and administration site conditions: fatigue, malaise
-
Immune System Disorders: drug hypersensitivity including face edema, angioedema, anaphylactic shock
-
Nervous system disorders: dizziness, headache, somnolence, syncope
-
Psychiatric disorders: As with the other anti-cholinergic drugs, cases of delirium or symptoms of delirium such as amnesia (or transient global amnesia), agitation, confusional state, delusion, disorientation, hallucination (including visual hallucination) as well as mania, mood altered and pseudodementia, have been reported with the use of Dicyclomine. Nervousness and insomnia have also been reported.
-
Reproductive system and breast disorders: suppressed lactation
-
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders: dyspnoea, nasal congestion
- Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorder: dermatitis allergic, erythema, rash
Cases of thrombosis, thrombophlebitis and injection site reactions such as local pain, edema, skin color change and even reflex sympathetic dystrophy syndrome have been reported following Inadvertent IV injection of BENTYL.
6.3 Adverse Reactions Reported with Similar Drugs with Anticholinergic/Antispasmodic Action
Gastrointestinal: anorexia
Central Nervous System: tingling, numbness, dyskinesia, speech disturbance, insomnia
Peripheral Nervous System: with overdosage, a curare-like action may occur (i.e., neuromuscular blockade leading to muscular weakness and possible paralysis)
Ophthalmologic: diplopia, increased ocular tension
Dermatologic/Allergic: urticaria, itching, and other dermal manifestations
Genitourinary: urinary hesitancy, urinary retention in patients with prostatic hypertrophy
Cardiovascular: hypertension
Respiratory: apnea
Other: decreased sweating, sneezing, throat congestion, impotence. With the injectable form, there may be temporary sensation of light-headedness. Some local irritation and focal coagulation necrosis may occur following the intramuscular injection of BENTYL.
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 Antiglaucoma Agents
Anticholinergics antagonize the effects of antiglaucoma agents. Anticholinergic drugs in the presence of increased intraocular pressure may be hazardous when taken concurrently with agents such as corticosteroids. Use of BENTYL in patients with glaucoma is not recommended [see Contraindications (4)].
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Adequate and well-controlled studies have not been conducted with BENTYL in pregnant women at the recommended doses of 80 to 160 mg/day. However, epidemiologic studies did not show an increased risk of structural malformations among babies born to women who took products containing dicyclomine hydrochloride at doses up to 40 mg/day during the first trimester of pregnancy. Reproduction studies have been performed in rats and rabbits at doses up to 33 times the maximum recommended human dose based on 160 mg/day (3 mg/kg) and have revealed no evidence of harm to the fetus due to dicyclomine. Because animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, this drug should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
BENTYL is contraindicated in women who are breastfeeding. Dicyclomine hydrochloride is excreted in human milk. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in breast-fed infants from BENTYL, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established.
BENTYL is contraindicated in infants less than 6 months of age [see Contraindications (4)]. There are published cases reporting that the administration of dicyclomine hydrochloride to infants has been followed by serious respiratory symptoms (dyspnea, shortness of breath, breathlessness, respiratory collapse, apnea and asphyxia), seizures, syncope, pulse rate fluctuations, muscular hypotonia, and coma, and death, however; no causal relationship has been established.
8.6 Renal Impairment
Effects of renal impairment on PK, safety and efficacy of BENTYL have not been studied. BENTYL drug is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of toxic reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. BENTYL should be administered with caution in patients with renal impairment.
| BENTYL
dicyclomine hydrochloride injection, solution |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Allergan, Inc. (144796497) |




![the following structural formula for BENTYL (dicyclomine hydrochloride) is [bicyclohexyl]-1-carboxylic acid, 2-(diethylamino) ethyl ester, hydrochloride, with a molecular formula of C19H35NO2•HCl.](https://cdn.themeditary.com/images/2023/08/31/bentyl-01.webp)