Drug Class: Bronchodilator combinations
Highlights of Prescribing Information
BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE Inhalation Aerosol, for oral inhalation use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2006
Indications and Usage for Budesonide and Formoterol Aerosol
BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL is a combination product containing a corticosteroid and a long-acting beta2-adrenergic agonist indicated for:
- •
- Treatment of asthma in patients 6 years of age and older. (1.1)
- •
- Maintenance treatment of airflow obstruction and reducing exacerbations in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) including chronic bronchitis and/or emphysema. (1.2)
Important limitations:
- •
- Not indicated for the relief of acute bronchospasm. (1.1, 1.2)
Budesonide and Formoterol Aerosol Dosage and Administration
For oral inhalation only.
- •
- Treatment of asthma in patients 12 years and older: 2 inhalations of BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL 80/4.5 or 160/4.5 twice daily. Starting dosage is based on asthma severity. (2.2)
- •
- Treatment of asthma in patients aged 6 to less than 12 years: 2 inhalations of BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL 80/4.5 twice daily. (2.2)
- •
- Maintenance treatment in COPD: 2 inhalations of BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL 160/4.5 twice daily. (2.3)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Metered-dose inhaler containing a combination of budesonide (80 or 160 mcg) and formoterol (4.5 mcg) as an inhalation aerosol. (3)
Contraindications
- •
- Primary treatment of status asthmaticus or acute episodes of asthma or COPD requiring intensive measures. (4)
- •
- Hypersensitivity to any of the ingredients in BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL. (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- •
- Serious asthma-related events: Long-acting beta2-adrenergic agonists as monotherapy increase the risk. (5.1)
- •
- Deterioration of disease and acute episodes: Do not initiate in acutely deteriorating asthma or COPD or to treat acute symptoms. (5.2)
- •
- Use with additional long-acting beta2-agonist: Do not use in combination because of risk of overdose. (5.3)
- •
- Localized infections: Candida albicans infection of the mouth and throat may occur. Monitor patients periodically for signs of adverse effects on the oral cavity. Advise the patient to rinse his/her mouth with water without swallowing after inhalation to help reduce the risk. (5.4)
- •
- Pneumonia: Increased risk in patients with COPD. Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of pneumonia and other potential lung infections. (5.5)
- •
- Immunosuppression: Potential worsening of infections (e.g., existing tuberculosis, fungal, bacterial, viral, or parasitic infection; or ocular herpes simplex). Use with caution in patients with these infections. More serious or even fatal course of chickenpox or measles can occur in susceptible patients. (5.6)
- •
- Transferring patients from systemic corticosteroids: Risk of impaired adrenal function when transferring from oral steroids. Taper patients slowly from systemic corticosteroids if transferring to budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate. (5.7)
- •
- Hypercorticism and adrenal suppression: May occur with very high dosages or at the regular dosage in susceptible individuals. If such changes occur, discontinue budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate slowly. (5.8)
- •
- Strong cytochrome P450 3A4 inhibitors (e.g., ritonavir): Risk of increased systemic corticosteroid effects. Exercise caution when used with budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate. (5.9)
- •
- Paradoxical bronchospasm: Discontinue budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate and institute alternative therapy if paradoxical bronchospasm occurs. (5.10)
- •
- Patients with cardiovascular or central nervous system disorders: Use with caution because of beta-adrenergic stimulation. (5.12)
- •
- Decreases in bone mineral density: Assess bone mineral density initially and periodically thereafter. (5.13)
- •
- Effects on growth: Monitor growth of pediatric patients. (5.14)
- •
- Glaucoma and cataracts: Close monitoring is warranted. (5.15)
- •
- Metabolic effects: Be alert to eosinophilic conditions, hypokalemia, and hyperglycemia. (5.16, 5.18)
- •
- Coexisting conditions: Use with caution in patients with convulsive disorders, thyrotoxicosis, diabetes mellitus, and ketoacidosis. (5.17)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions (incidence >3%) are:
- •
- Asthma: nasopharyngitis, headache, upper respiratory tract infection, pharyngolaryngeal pain, sinusitis, influenza, back pain, nasal congestion, stomach discomfort, vomiting, and oral candidiasis. (6.1)
- •
- COPD: nasopharyngitis, oral candidiasis, bronchitis, sinusitis, upper respiratory tract infections. (6.2)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact AstraZeneca at 1-800-236-9933 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
- •
- Strong cytochrome P450 3A4 inhibitors (e.g., ritonavir): Use with caution. May cause increased systemic corticosteroid effects. (7.1)
- •
- Monoamine oxidase inhibitors and tricyclic antidepressants: Use with extreme caution. May potentiate effect of formoterol on vascular system. (7.2)
- •
- Beta-blockers: Use with caution. May block bronchodilatory effects of beta-agonists and produce severe bronchospasm. (7.3)
- •
- Diuretics: Use with caution. Electrocardiographic changes and/or hypokalemia associated with non-potassium-sparing diuretics may worsen with concomitant beta-agonists. (7.4)
Use In Specific Populations
Hepatic impairment: Monitor patients for signs of increased drug exposure. (8.6)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 7/2019
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Budesonide and Formoterol Aerosol
1.1 Treatment of Asthma
BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL is indicated for the treatment of asthma in patients 6 years of age and older.
BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL should be used for patients not adequately controlled on a long-term asthma-control medication such as an inhaled corticosteroid (ICS) or whose disease warrants initiation of treatment with both an inhaled corticosteroid and long-acting beta2-adrenergic agonist (LABA).
Important Limitations of Use:
- •
- BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL is NOT indicated for the relief of acute bronchospasm.
1.2 Maintenance Treatment of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL 160/4.5 is indicated for the maintenance treatment of airflow obstruction in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) including chronic bronchitis and/or emphysema. BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL 160/4.5 is also indicated to reduce exacerbations of COPD. BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL 160/4.5 is the only strength indicated for the treatment of COPD.
Important Limitations of Use:
- •
- BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL is NOT indicated for the relief of acute bronchospasm.
2. Budesonide and Formoterol Aerosol Dosage and Administration
2.1 Administration Information
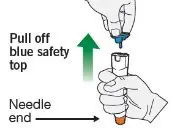
BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL should be administered as 2 inhalations twice daily (morning and evening, approximately 12 hours apart), every day by the orally inhaled route only. After inhalation, the patient should rinse the mouth with water without swallowing.
Prime BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL before using for the first time by releasing two test sprays into the air away from the face, shaking well for 5 seconds before each spray. In cases where the inhaler has not been used for more than 7 days or when it has been dropped, prime the inhaler again by shaking well before each spray and releasing two test sprays into the air away from the face.
More frequent administration or a higher number of inhalations (more than 2 inhalations twice daily) of the prescribed strength of BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL is not recommended as some patients are more likely to experience adverse effects with higher doses of formoterol. Patients using BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL should not use additional LABA for any reason [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3, 5.12)].
2.2 Asthma
If asthma symptoms arise in the period between doses, an inhaled, short-acting beta2-agonist should be taken for immediate relief.
Adult and Adolescent Patients 12 Years of Age and Older
For patients 12 years of age and older, the dosage is 2 inhalations of BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL 80/4.5 or BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL 160/4.5 twice daily.
The recommended starting dosages for BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL for patients 12 years of age and older are based upon patients' asthma severity or level of control of asthma symptoms, and risk of exacerbations on current inhaled corticosteroids.
The maximum recommended dosage in adult and adolescent patients 12 years and older is BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL 160/4.5, two inhalations twice daily.
Improvement in asthma control following inhaled administration of BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL can occur within 15 minutes of beginning treatment, although maximum benefit may not be achieved for 2 weeks or longer after beginning treatment. Individual patients will experience a variable time to onset and degree of symptom relief.
For patients who do not respond adequately to the starting dose after 1-2 weeks of therapy with BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL 80/4.5, replacement with BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL 160/4.5 may provide additional asthma control.
If a previously effective dosage regimen of BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL fails to provide adequate control of asthma, the therapeutic regimen should be re-evaluated and additional therapeutic options, (e.g., replacing the lower strength of BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL with the higher strength, adding additional inhaled corticosteroid, or initiating oral corticosteroids) should be considered.
Pediatric Patients Aged 6 to Less than 12 Years
For patients 6 to less than 12 years of age, the dosage is 2 inhalations of BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL 80/4.5 twice daily.
2.3 Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
For patients with COPD the recommended dose is BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL 160/4.5, two inhalations twice daily.
If shortness of breath occurs in the period between doses, an inhaled, short-acting beta2-agonist should be taken for immediate relief.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL is available as a metered-dose inhaler containing a combination of budesonide (80 or 160 mcg) and formoterol (4.5 mcg) as an inhalation aerosol in the following two strengths: 80/4.5 and 160/4.5. Each dosage strength contains 120 actuations per/canister. Each strength of BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL is supplied with a red plastic actuator with a gray dust cap.
4. Contraindications
The use of budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate is contraindicated in the following conditions:
- •
- Primary treatment of status asthmaticus or other acute episodes of asthma or COPD where intensive measures are required.
- •
- Hypersensitivity to any of the ingredients in BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL.
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Serious Asthma-Related Events – Hospitalizations, Intubations and Death
Use of LABA as monotherapy (without ICS) for asthma is associated with an increased risk of asthma-related death [see Salmeterol Multicenter Asthma Research Trial (SMART)]. Available data from controlled clinical trials also suggest that use of LABA as monotherapy increases the risk of asthma-related hospitalization in pediatric and adolescent patients. These findings are considered a class effect of LABA. When LABA are used in fixed-dose combination with ICS, data from large clinical trials do not show a significant increase in the risk of serious asthma-related events (hospitalizations, intubations, death) compared to ICS alone (see Serious Asthma-Related Events with ICS/LABA).
Serious Asthma-Related Events with ICS/LABA
Four large, 26-week, randomized, blinded, active-controlled clinical safety trials were conducted to evaluate the risk of serious asthma-related events when LABA were used in fixed-dose combination with ICS compared to ICS alone in patients with asthma. Three trials included adult and adolescent patients aged ≥12 years: one trial compared budesonide/formoterol (budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate) to budesonide [see Clinical Studies (14.1)]; one trial compared fluticasone propionate/salmeterol inhalation powder to fluticasone propionate inhalation powder; and one trial compared mometasone furoate/formoterol to mometasone furoate. The fourth trial included pediatric patients 4 to 11 years of age and compared fluticasone propionate/salmeterol inhalation powder to fluticasone propionate inhalation powder. The primary safety endpoint for all four trials was serious asthma-related events (hospitalizations, intubations and death). A blinded adjudication committee determined whether events were asthma-related.
The three adult and adolescent trials were designed to rule out a risk margin of 2.0, and the pediatric trial was designed to rule out a risk of 2.7. Each individual trial met its pre-specified objective and demonstrated non-inferiority of ICS/LABA to ICS alone. A meta-analysis of the three adult and adolescent trials did not show a significant increase in risk of a serious asthma-related event with ICS/LABA fixed-dose combination compared with ICS alone (Table 1). These trials were not designed to rule out all risk for serious asthma-related events with ICS/LABA compared with ICS.
|
|||
|
ICS/LABA (N = 17,537)* |
ICS (N = 17,552)* |
ICS/LABA vs ICS Hazard ratio (95% CI)† |
|
|
Serious asthma-related event‡ |
116 |
105 |
1.10 (0.85, 1.44) |
|
Asthma-related death |
2 |
0 | |
|
Asthma-related intubation (endotracheal) |
1 |
2 | |
|
Asthma-related hospitalization (≥24-hour stay) |
115 |
105 | |
|
ICS = Inhaled Corticosteroid, LABA = Long-acting Beta2-adrenergic Agonist |
|||
The pediatric safety trial included 6208 pediatric patients 4 to 11 years of age who received ICS/LABA (fluticasone propionate /salmeterol inhalation powder) or ICS (fluticasone propionate inhalation powder). In this trial, 27/3107 (0.9%) patients randomized to ICS/LABA and 21/3101 (0.7%) patients randomized to ICS experienced a serious asthma-related event. There were no asthma-related deaths or intubations. ICS/LABA did not show a significantly increased risk of a serious asthma-related event compared to ICS based on the pre-specified risk margin (2.7), with an estimated hazard ratio of time to first event of 1.29 (95% CI: 0.73, 2.27).
Salmeterol Multicenter Asthma Research Trial (SMART)
A 28-week, placebo-controlled U.S. trial that compared the safety of salmeterol with placebo, each added to usual asthma therapy, showed an increase in asthma-related deaths in patients receiving salmeterol (13/13,176 in patients treated with salmeterol vs. 3/13,179 in patients treated with placebo; relative risk: 4.37 [95% CI 1.25, 15.34]). Use of background ICS was not required in SMART. The increased risk of asthma-related death is considered a class effect of LABA monotherapy.
Formoterol Monotherapy Studies
Clinical studies with formoterol used as monotherapy suggested a higher incidence of serious asthma exacerbation in patients who received formoterol than in those who received placebo. The sizes of these studies were not adequate to precisely quantify the difference in serious asthma exacerbations between treatment groups.
5.2 Deterioration of Disease and Acute Episodes
Budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate should not be initiated in patients during rapidly deteriorating or potentially life-threatening episodes of asthma or COPD. Budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate has not been studied in patients with acutely deteriorating asthma or COPD. The initiation of budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate in this setting is not appropriate.
Increasing use of inhaled, short-acting beta2-agonists is a marker of deteriorating asthma. In this situation, the patient requires immediate re-evaluation with reassessment of the treatment regimen, giving special consideration to the possible need for replacing the current strength of budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate with a higher strength, adding additional inhaled corticosteroid, or initiating systemic corticosteroids. Patients should not use more than 2 inhalations twice daily (morning and evening) of budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate.
Budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate should not be used for the relief of acute symptoms, i.e., as rescue therapy for the treatment of acute episodes of bronchospasm. An inhaled, short-acting beta2-agonist, not budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate, should be used to relieve acute symptoms such as shortness of breath.
When beginning treatment with budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate, patients who have been taking oral or inhaled, short-acting beta2-agonists on a regular basis (e.g., 4 times a day) should be instructed to discontinue the regular use of these drugs.
5.3 Excessive Use of Budesonide and Formoterol Fumarate Dihydrate and Use with Other Long-Acting Beta2-Agonists
As with other inhaled drugs containing beta2-adrenergic agents, budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate should not be used more often than recommended, at higher doses than recommended, or in conjunction with other medications containing LABA, as an overdose may result. Clinically significant cardiovascular effects and fatalities have been reported in association with excessive use of inhaled sympathomimetic drugs. Patients using budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate should not use an additional LABA (e.g., salmeterol, formoterol fumarate, arformoterol tartrate) for any reason, including prevention of exercise-induced bronchospasm (EIB) or the treatment of asthma or COPD.
5.4 Local Effects
In clinical studies, the development of localized infections of the mouth and pharynx with Candida albicans has occurred in patients treated with budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate. When such an infection develops, it should be treated with appropriate local or systemic (i.e., oral antifungal) therapy while treatment with budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate continues, but at times therapy with budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate may need to be interrupted. Advise the patient to rinse his/her mouth with water without swallowing following inhalation to help reduce the risk of oropharyngeal candidiasis.
5.5 Pneumonia and Other Lower Respiratory Tract Infections
Physicians should remain vigilant for the possible development of pneumonia in patients with COPD as the clinical features of pneumonia and exacerbations frequently overlap. Lower respiratory tract infections, including pneumonia, have been reported following the inhaled administration of corticosteroids.
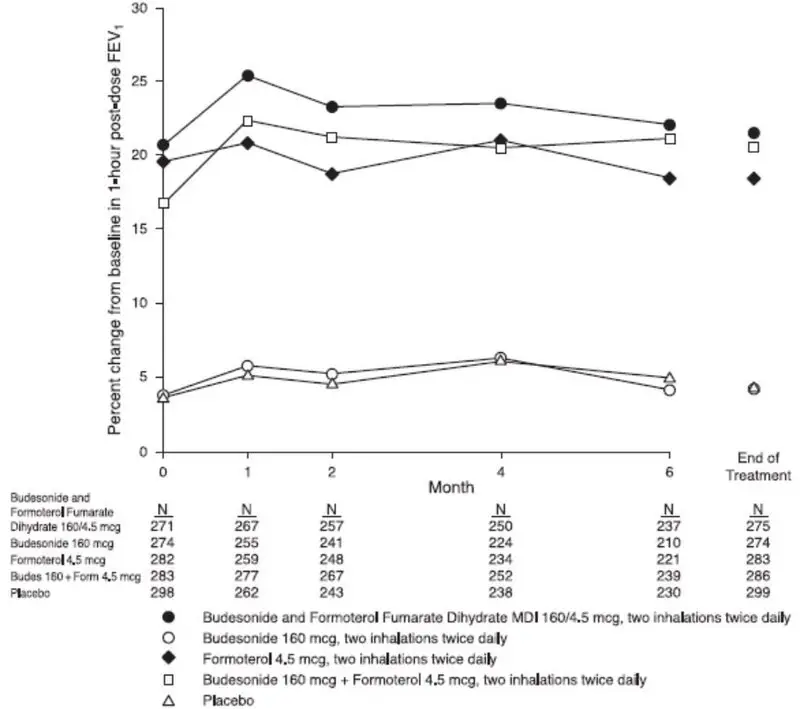
In a 6-month lung function study of 1704 patients with COPD, there was a higher incidence of lung infections other than pneumonia (e.g., bronchitis, viral lower respiratory tract infections, etc.) in patients receiving budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 160/4.5 (7.6%) than in those receiving budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 80/4.5 (3.2%), formotero1 4.5 mcg (4.6%) or placebo (3.3%). Pneumonia did not occur with greater incidence in the budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 160/4.5 group (1.1 %) compared with placebo (1.3%). In a 12-month lung function study of 1964 patients with COPD, there was also a higher incidence of lung infections other than pneumonia in patients receiving budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 160/4.5 (8.1%) than in those receiving budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 80/4.5 (6.9%), formoterol 4.5 mcg (7.1%) or placebo (6.2%). Similar to the 6-month study, pneumonia did not occur with greater incidence in the budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 160/4.5 group (4.0%) compared with placebo (5.0%).
5.6 Immunosuppression
Patients who are on drugs that suppress the immune system are more susceptible to infection than healthy individuals. Chicken pox and measles, for example, can have a more serious or even fatal course in susceptible children or adults using corticosteroids. In such children or adults who have not had these diseases or been properly immunized, particular care should be taken to avoid exposure. How the dose, route, and duration of corticosteroid administration affects the risk of developing a disseminated infection is not known. The contribution of the underlying disease and/or prior corticosteroid treatment to the risk is also not known. If exposed, therapy with varicella zoster immune globulin (VZIG) or pooled intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG), as appropriate, may be indicated. If exposed to measles, prophylaxis with pooled intramuscular immunoglobulin (IG) may be indicated (see the respective package inserts for complete VZIG and IG prescribing information). If chicken pox develops, treatment with antiviral agents may be considered. The immune responsiveness to varicella vaccine was evaluated in pediatric patients with asthma ages 12 months to 8 years with budesonide inhalation suspension.
An open-label, nonrandomized clinical study examined the immune responsiveness to varicella vaccine in 243 asthma patients 12 months to 8 years of age who were treated with budesonide inhalation suspension 0.25 mg to 1 mg daily (n=151) or noncorticosteroid asthma therapy (n=92) (i.e., beta2-agonists, leukotriene receptor antagonists, cromones). The percentage of patients developing a seroprotective antibody titer of >5.0 (gpELISA value) in response to the vaccination was similar in patients treated with budesonide inhalation suspension (85%), compared to patients treated with noncorticosteroid asthma therapy (90%). No patient treated with budesonide inhalation suspension developed chicken pox as a result of vaccination.
Inhaled corticosteroids should be used with caution, if at all, in patients with active or quiescent tuberculosis infections of the respiratory tract; untreated systemic fungal, bacterial, viral, or parasitic infections; or ocular herpes simplex.
5.7 Transferring Patients From Systemic Corticosteroid Therapy
Particular care is needed for patients who have been transferred from systemically active corticosteroids to inhaled corticosteroids because deaths due to adrenal insufficiency have occurred in patients with asthma during and after transfer from systemic corticosteroids to less systemically available inhaled corticosteroids. After withdrawal from systemic corticosteroids, a number of months are required for recovery of hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) function.
Patients who have been previously maintained on 20 mg or more per day of prednisone (or its equivalent) may be most susceptible, particularly when their systemic corticosteroids have been almost completely withdrawn. During this period of HPA suppression, patients may exhibit signs and symptoms of adrenal insufficiency when exposed to trauma, surgery, or infection (particularly gastroenteritis) or other conditions associated with severe electrolyte loss. Although budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate may provide control of asthma symptoms during these episodes, in recommended doses it supplies less than normal physiological amounts of glucocorticoid systemically and does NOT provide the mineralocorticoid activity that is necessary for coping with these emergencies.
During periods of stress, a severe asthma attack or a severe COPD exacerbation, patients who have been withdrawn from systemic corticosteroids should be instructed to resume oral corticosteroids (in large doses) immediately and to contact their physicians for further instruction. These patients should also be instructed to carry a warning card indicating that they may need supplementary systemic corticosteroids during periods of stress, a severe asthma attack, or a severe COPD exacerbation.
Patients requiring oral corticosteroids should be weaned slowly from systemic corticosteroid use after transferring to budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate. Prednisone reduction can be accomplished by reducing the daily prednisone dose by 2.5 mg on a weekly basis during therapy with budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate. Lung function (mean forced expiratory volume in 1 second [FEV1] or morning peak expiratory flow [PEF]), beta-agonist use, and asthma or COPD symptoms should be carefully monitored during withdrawal of oral corticosteroids. In addition, patients should be observed for signs and symptoms of adrenal insufficiency, such as fatigue, lassitude, weakness, nausea and vomiting, and hypotension.
Transfer of patients from systemic corticosteroid therapy to inhaled corticosteroids or budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate may unmask conditions previously suppressed by the systemic corticosteroid therapy (e.g., rhinitis, conjunctivitis, eczema, arthritis, eosinophilic conditions). Some patients may experience symptoms of systemically active corticosteroid withdrawal (e.g., joint and/or muscular pain, lassitude, depression) despite maintenance or even improvement of respiratory function.
5.8 Hypercorticism and Adrenal Suppression
Budesonide, a component of budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate, will often help control asthma and COPD symptoms with less suppression of HPA function than therapeutically equivalent oral doses of prednisone. Since budesonide is absorbed into the circulation and can be systemically active at higher doses, the beneficial effects of budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate in minimizing HPA dysfunction may be expected only when recommended dosages are not exceeded and individual patients are titrated to the lowest effective dose.
Because of the possibility of systemic absorption of inhaled corticosteroids, patients treated with budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate should be observed carefully for any evidence of systemic corticosteroid effects. Particular care should be taken in observing patients postoperatively or during periods of stress for evidence of inadequate adrenal response.
It is possible that systemic corticosteroid effects such as hypercorticism and adrenal suppression (including adrenal crisis) may appear in a small number of patients, particularly when budesonide is administered at higher than recommended doses over prolonged periods of time. If such effects occur, the dosage of budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate should be reduced slowly, consistent with accepted procedures for reducing systemic corticosteroids and for management of asthma symptoms.
5.9 Drug Interactions With Strong Cytochrome P450 3A4 Inhibitors
Caution should be exercised when considering the coadministration of budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate with ketoconazole, and other known strong CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., ritonavir, atazanavir, clarithromycin, indinavir, itraconazole, nefazodone, nelfinavir, saquinavir, telithromycin) because adverse effects related to increased systemic exposure to budesonide may occur [see Drug Interactions (7.1) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
5.10 Paradoxical Bronchospasm and Upper Airway Symptoms
As with other inhaled medications, budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate can produce paradoxical bronchospasm, which may be life threatening. If paradoxical bronchospasm occurs following dosing with budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate, it should be treated immediately with an inhaled, short-acting bronchodilator, BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL should be discontinued immediately, and alternative therapy should be instituted.
5.11 Immediate Hypersensitivity Reactions
Immediate hypersensitivity reactions may occur after administration of budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate, as demonstrated by cases of urticaria, angioedema, rash, and bronchospasm.
5.12 Cardiovascular and Central Nervous System Effects
Excessive beta-adrenergic stimulation has been associated with seizures, angina, hypertension or hypotension, tachycardia with rates up to 200 beats/min, arrhythmias, nervousness, headache, tremor, palpitation, nausea, dizziness, fatigue, malaise, and insomnia [see Overdosage (10)]. Therefore, budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate, like all products containing sympathomimetic amines, should be used with caution in patients with cardiovascular disorders, especially coronary insufficiency, cardiac arrhythmias, and hypertension.
Formoterol, a component of budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate, can produce a clinically significant cardiovascular effect in some patients as measured by pulse rate, blood pressure, and/or symptoms. Although such effects are uncommon after administration of formoterol at recommended doses, if they occur, the drug may need to be discontinued. In addition, beta-agonists have been reported to produce ECG changes, such as flattening of the T wave, prolongation of the QTc interval, and ST segment depression. The clinical significance of these findings is unknown. Fatalities have been reported in association with excessive use of inhaled sympathomimetic drugs.
5.13 Reduction in Bone Mineral Density
Decreases in bone mineral density (BMD) have been observed with long-term administration of products containing inhaled corticosteroids. The clinical significance of small changes in BMD with regard to long-term consequences such as fracture is unknown. Patients with major risk factors for decreased bone mineral content, such as prolonged immobilization, family history of osteoporosis, postmenopausal status, tobacco use, advanced age, poor nutrition, or chronic use of drugs that can reduce bone mass (e.g., anticonvulsants, oral corticosteroids) should be monitored and treated with established standards of care. Since patients with COPD often have multiple risk factors for reduced BMD, assessment of BMD is recommended prior to initiating budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate and periodically thereafter. If significant reductions in BMD are seen and budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate is still considered medically important for that patient's COPD therapy, use of medication to treat or prevent osteoporosis should be strongly considered.
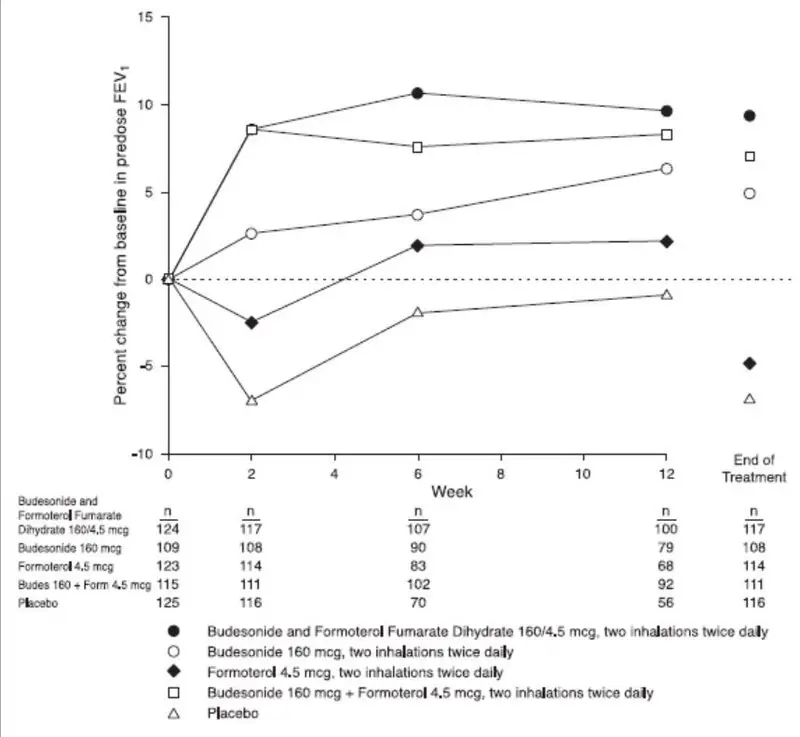
Effects of treatment with budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 160/4.5, budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 80/4.5, formoterol 4.5 mcg, or placebo on BMD was evaluated in a subset of 326 patients (females and males 41 to 88 years of age) with COPD in the 12-month lung function study. BMD evaluations of the hip and lumbar spine regions were conducted at baseline and 52 weeks using dual energy x-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) scans. Mean changes in BMD from baseline to end of treatment were small (mean changes ranged from -0.01 - 0.01 g/cm2). ANCOVA results for total spine and total hip BMD based on the end of treatment time point showed that all geometric LS Mean ratios for the pairwise treatment group comparisons were close to 1, indicating that overall, BMD for total hip and total spine regions for the 12-month time point were stable over the entire treatment period.
5.14 Effect on Growth
Orally inhaled corticosteroids may cause a reduction in growth velocity when administered to pediatric patients. Monitor the growth of pediatric patients receiving budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate routinely (e.g., via stadiometry). To minimize the systemic effects of orally inhaled corticosteroids, including budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate, titrate each patient's dose to the lowest dosage that effectively controls his/her symptoms [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) and Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
5.15 Glaucoma and Cataracts
Glaucoma, increased intraocular pressure, and cataracts have been reported in patients with asthma and COPD following the long-term administration of inhaled corticosteroids, including budesonide, a component of BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL. Therefore, close monitoring is warranted in patients with a change in vision or with history of increased intraocular pressure, glaucoma, and/or cataracts.
Effects of treatment with budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 160/4.5, budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 80/4.5, formoterol 4.5 mcg, or placebo on development of cataracts or glaucoma were evaluated in a subset of 461 patients with COPD in the 12-month lung function study. Ophthalmic examinations were conducted at baseline, 24 weeks, and 52 weeks. There were 26 subjects (6%) with an increase in posterior subcapsular score from baseline to maximum value (>0.7) during the randomized treatment period. Changes in posterior subcapsular scores of >0.7 from baseline to treatment maximum occurred in 11 patients (9.0%) in the budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 160/4.5 group, 4 patients (3.8%) in the budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 80/4.5 group, 5 patients (4.2%) in the formoterol group, and 6 patients (5.2%) in the placebo group.
5.16 Eosinophilic Conditions and Churg-Strauss Syndrome
In rare cases, patients on inhaled corticosteroids may present with systemic eosinophilic conditions. Some of these patients have clinical features of vasculitis consistent with Churg-Strauss syndrome, a condition that is often treated with systemic corticosteroid therapy. These events usually, but not always, have been associated with the reduction and/or withdrawal of oral corticosteroid therapy following the introduction of inhaled corticosteroids. Physicians should be alert to eosinophilia, vasculitic rash, worsening pulmonary symptoms, cardiac complications, and/or neuropathy presenting in their patients. A causal relationship between budesonide and these underlying conditions has not been established.
5.17 Coexisting Conditions
Budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate, like all medications containing sympathomimetic amines, should be used with caution in patients with convulsive disorders or thyrotoxicosis and in those who are unusually responsive to sympathomimetic amines. Doses of the related beta2-adrenoceptor agonist albuterol, when administered intravenously, have been reported to aggravate preexisting diabetes mellitus and ketoacidosis.
5.18 Hypokalemia and Hyperglycemia
Beta-adrenergic agonist medications may produce significant hypokalemia in some patients, possibly through intracellular shunting, which has the potential to produce adverse cardiovascular effects [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)]. The decrease in serum potassium is usually transient, not requiring supplementation. Clinically significant changes in blood glucose and/or serum potassium were seen infrequently during clinical studies with budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate at recommended doses.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
LABA use may result in the following:
- •
- Serious asthma-related events – hospitalizations, intubations, death [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- •
- Cardiovascular and central nervous system effects [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12)].
Systemic and inhaled corticosteroid use may result in the following:
- •
- Candida albicans infection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- •
- Pneumonia or lower respiratory tract infections in patients with COPD [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- •
- Immunosuppression [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- •
- Hypercorticism and adrenal suppression [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
- •
- Growth effects in pediatric patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.14)]
- •
- Glaucoma and cataracts [see Warnings and Precautions (5.15)]
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience in Asthma
Adult and Adolescent Patients 12 Years of Age and Older
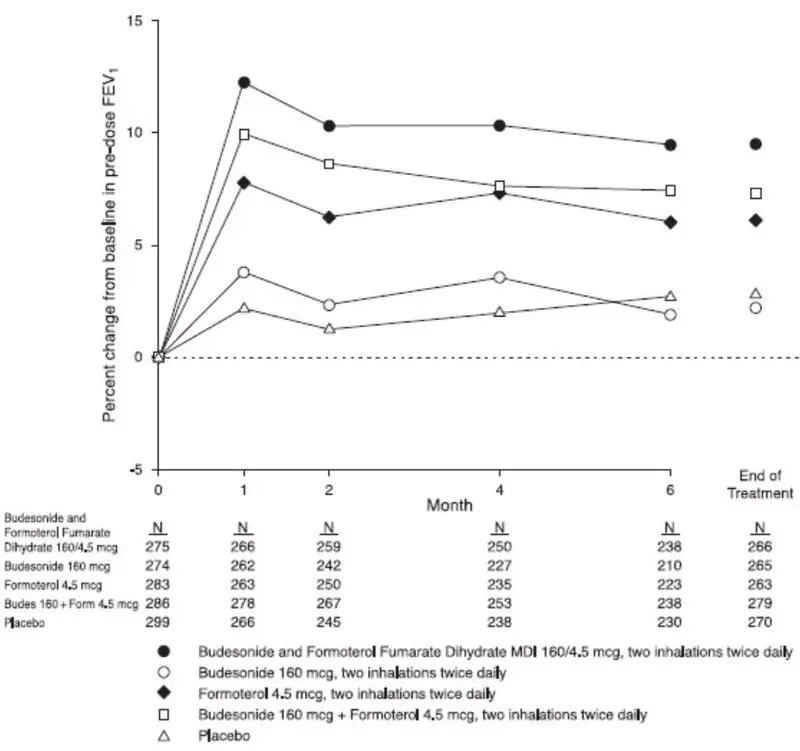
The overall safety data in adults and adolescents are based upon 10 active- and placebo-controlled clinical trials in which 3393 patients ages 12 years and older (2052 females and 1341 males) with asthma of varying severity were treated with budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 80/4.5 or 160/4.5 taken 2 inhalations once or twice daily for 12 to 52 weeks. In these trials, the patients on budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate had a mean age of 38 years and were predominantly Caucasian (82%).
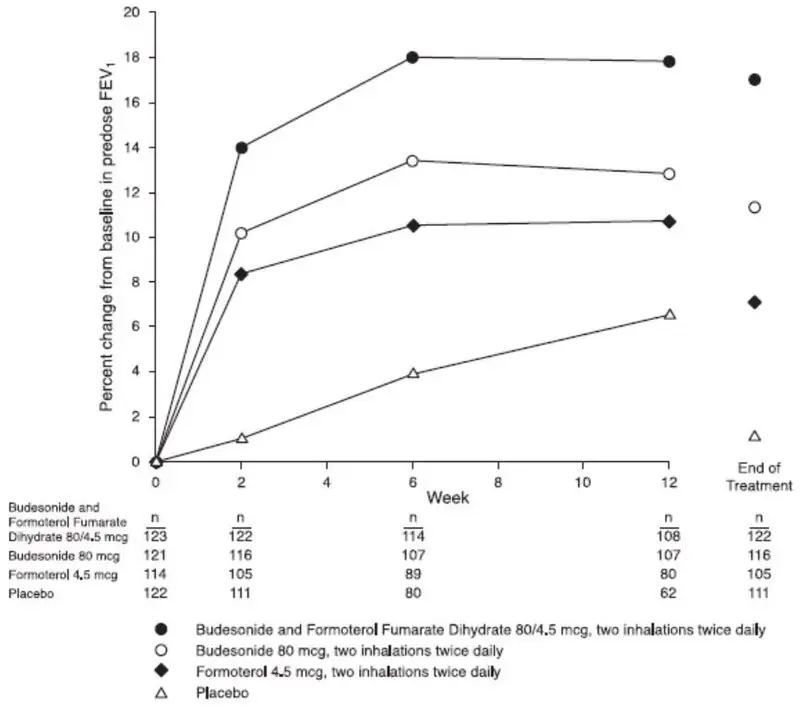
The incidence of common adverse events in Table 2 below is based upon pooled data from three 12-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical studies in which 401 adult and adolescent patients (148 males and 253 females) age 12 years and older were treated with 2 inhalations of budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 80/4.5 or budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 160/4.5 twice daily. The budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate group was composed of mostly Caucasian (84%) patients with a mean age of 38 years, and a mean percent predicted FEV1 at baseline of 76 and 68 for the 80/4.5 mcg and 160/4.5 mcg treatment groups, respectively. Control arms for comparison included 2 inhalations of budesonide HFA metered dose inhaler (MDI) 80 or 160 mcg, formoterol dry powder inhaler (DPI) 4.5 mcg, or placebo (MDI and DPI) twice daily. Table 2 includes all adverse events that occurred at an incidence of >3% in any one budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate group and more commonly than in the placebo group with twice-daily dosing. In considering these data, the increased average duration of patient exposure for budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate patients should be taken into account, as incidences are not adjusted for an imbalance of treatment duration.
| Treatment* | Budesonide and Formoterol Fumarate Dihydrate | Budesonide | Formoterol | Placebo | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adverse Event | 80/4.5
N = 277 % | 160/4.5
N = 124 % | 80 mcg
N = 121 % | 160 mcg
N = 109 % | 4.5 mcg
N = 237 % | N = 400
% |
|
||||||
|
Nasopharyngitis |
10.5 |
9.7 |
14.0 |
11.0 |
10.1 |
9.0 |
|
Headache |
6.5 |
11.3 |
11.6 |
12.8 |
8.9 |
6.5 |
|
Upper respiratory tract infection |
7.6 |
10.5 |
8.3 |
9.2 |
7.6 |
7.8 |
|
Pharyngolaryngeal pain |
6.1 |
8.9 |
5.0 |
7.3 |
3.0 |
4.8 |
|
Sinusitis |
5.8 |
4.8 |
5.8 |
2.8 |
6.3 |
4.8 |
|
Influenza |
3.2 |
2.4 |
6.6 |
0.9 |
3.0 |
1.3 |
|
Back pain |
3.2 |
1.6 |
2.5 |
5.5 |
2.1 |
0.8 |
|
Nasal congestion |
2.5 |
3.2 |
2.5 |
3.7 |
1.3 |
1.0 |
|
Stomach discomfort |
1.1 |
6.5 |
2.5 |
4.6 |
1.3 |
1.8 |
|
Vomiting |
1.4 |
3.2 |
0.8 |
2.8 |
1.7 |
1.0 |
|
Oral Candidiasis |
1.4 |
3.2 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0.8 |
|
Average Duration of Exposure (days) |
77.7 |
73.8 |
77.0 |
71.4 |
62.4 |
55.9 |
Long-term safety - asthma clinical trials in patients 12 years and older
Long-term safety studies in adolescent and adult patients 12 years of age and older, treated for up to 1 year at doses up to 1280/36 mcg/day (640/18 mcg twice daily), revealed neither clinically important changes in the incidence nor new types of adverse events emerging after longer periods of treatment. Similarly, no significant or unexpected patterns of abnormalities were observed for up to 1 year in safety measures including chemistry, hematology, ECG, Holter monitor, and HPA-axis assessments.
Pediatric Patients 6 to Less than 12 Years of Age
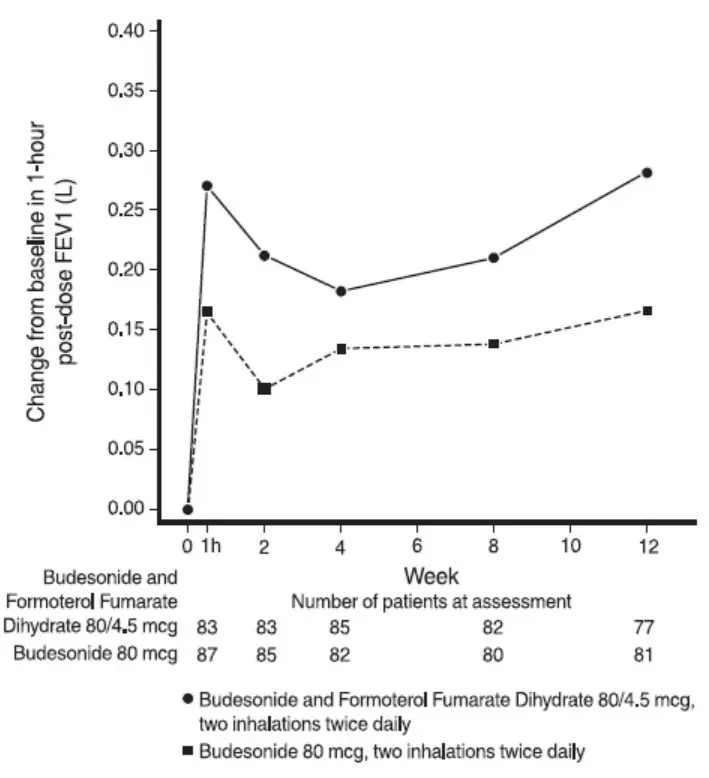
The safety data for pediatric patients aged 6 to less than 12 years is based on 1 trial of 12 weeks treatment duration. Patients (79 female and 105 male) receiving inhaled corticosteroid at trial entry were randomized to budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 80/4.5 (n=92) or budesonide pMDI 80 mcg (n=92), 2 inhalations twice daily. The overall safety profile of these patients was similar to that observed in patients 12 years of age and older who received budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 80/4.5 twice daily in studies of similar design. Common adverse reactions that occurred in patients treated with budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 80/4.5 with a frequency of ≥3% and more frequently than patients treated only with budesonide pMDI 80 mcg included upper respiratory tract infection, pharyngitis, headache, and rhinitis.
6.2 Clinical Trials Experience in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
The safety data described below reflect exposure to budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 160/4.5 in 1783 patients. Budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 160/4.5 was studied in two placebo-controlled lung function studies (6 and 12 months in duration), and two active-controlled exacerbation studies (6 and 12 months in duration) in patients with COPD.
The incidence of common adverse events in Table 3 below is based upon pooled data from two double-blind, placebo-controlled lung function clinical studies (6 and 12 months in duration) in which 771 adult COPD patients (496 males and 275 females) 40 years of age and older were treated with budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 160/4.5, two inhalations twice daily. Of these patients 651 were treated for 6 months and 366 were treated for 12 months. The budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate group was composed of mostly Caucasian (93%) patients with a mean age of 63 years, and a mean percent predicted FEV1 at baseline of 33%. Control arms for comparison included 2 inhalations of budesonide HFA (MDI) 160 mcg, formoterol (DPI) 4.5 mcg or placebo (MDI and DPI) twice daily. Table 3 includes all adverse events that occurred at an incidence of ≥3% in the budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate group and more commonly than in the placebo group. In considering these data, the increased average duration of patient exposure to budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate should be taken into account, as incidences are not adjusted for an imbalance of treatment duration.
|
||||
|
Treatment* |
Budesonide and Formoterol Fumarate Dihydrate |
Budesonide |
Formoterol |
Placebo |
|
Adverse Event |
160/4.5 N = 771 % |
160 mcg N = 275 % |
4.5 mcg N = 779 % |
N = 781 % |
|
Nasopharyngitis |
7.3 |
3.3 |
5.8 |
4.9 |
|
Oral candidiasis |
6.0 |
4.4 |
1.2 |
1.8 |
|
Bronchitis |
5.4 |
4.7 |
4.5 |
3.5 |
|
Sinusitis |
3.5 |
1.5 |
3.1 |
1.8 |
|
Upper respiratory tract infection viral |
3.5 |
1.8 |
3.6 |
2.7 |
|
Average Duration of Exposure (days) |
255.2 |
157.1 |
240.3 |
223.7 |
Lung infections other than pneumonia (mostly bronchitis) occurred in a greater percentage of subjects treated with budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 160/4.5 compared with placebo (7.9% vs. 5.1%, respectively). There were no clinically important or unexpected patterns of abnormalities observed for up to 1 year in chemistry, hematology, ECG, ECG (Holter) monitoring, HPA-axis, bone mineral density and ophthalmology assessments.
The safety findings from the two double-blind, active-controlled exacerbations studies (6 and 12 months in duration) in which 1012 adult COPD patients (616 males and 396 females) 40 years of age and older were treated with budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 160/4.5, two inhalations twice daily were consistent with the lung function studies.
6.3 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure. Some of these adverse reactions may also have been observed in clinical studies with budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate.
Cardiac disorders: angina pectoris, tachycardia, atrial and ventricular tachyarrhythmias, atrial fibrillation, extrasystoles, palpitations
Endocrine disorders: hypercorticism, growth velocity reduction in pediatric patients
Eye disorders: cataract, glaucoma, increased intraocular pressure
Gastrointestinal disorders: oropharyngeal candidiasis, nausea
Immune system disorders: immediate and delayed hypersensitivity reactions, such as anaphylactic reaction, angioedema, bronchospasm, urticaria, exanthema, dermatitis, pruritus
Metabolic and nutrition disorders: hyperglycemia, hypokalemia
Musculoskeletal, connective tissue, and bone disorders: muscle cramps
Nervous system disorders: tremor, dizziness
Psychiatric disorders: behavior disturbances, sleep disturbances, nervousness, agitation, depression, restlessness
Respiratory, thoracic, and mediastinal disorders: dysphonia, cough, throat irritation
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: skin bruising
Vascular disorders: hypotension, hypertension
7. Drug Interactions
In clinical studies, concurrent administration of budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate and other drugs, such as short-acting beta2-agonists, intranasal corticosteroids, and antihistamines/decongestants has not resulted in an increased frequency of adverse reactions. No formal drug interaction studies have been performed with budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate.
7.1 Inhibitors of Cytochrome P4503A4
The main route of metabolism of corticosteroids, including budesonide, a component of budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate, is via cytochrome P450 (CYP) isoenzyme 3A4 (CYP3A4). After oral administration of ketoconazole, a strong inhibitor of CYP3A4, the mean plasma concentration of orally administered budesonide increased. Concomitant administration of CYP3A4 may inhibit the metabolism of, and increase the systemic exposure to, budesonide. Caution should be exercised when considering the coadministration of budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate with long-term ketoconazole and other known strong CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., ritonavir, atazanavir, clarithromycin, indinavir, itraconazole, nefazodone, nelfinavir, saquinavir, telithromycin) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)].
7.2 Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors and Tricyclic Antidepressants
Budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate should be administered with caution to patients being treated with monoamine oxidase inhibitors or tricyclic antidepressants, or within 2 weeks of discontinuation of such agents, because the action of formoterol, a component of budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate, on the vascular system may be potentiated by these agents. In clinical trials with budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate, a limited number of COPD and asthma patients received tricyclic antidepressants, and, therefore, no clinically meaningful conclusions on adverse events can be made.
7.3 Beta-Adrenergic Receptor Blocking Agents
Beta-blockers (including eye drops) may not only block the pulmonary effect of beta-agonists, such as formoterol, a component of budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate, but may produce severe bronchospasm in patients with asthma. Therefore, patients with asthma should not normally be treated with beta-blockers. However, under certain circumstances, there may be no acceptable alternatives to the use of beta-adrenergic blocking agents in patients with asthma. In this setting, cardioselective beta-blockers could be considered, although they should be administered with caution.
7.4 Diuretics
The ECG changes and/or hypokalemia that may result from the administration of non-potassium-sparing diuretics (such as loop or thiazide diuretics) can be acutely worsened by beta-agonists, especially when the recommended dose of the beta-agonist is exceeded. Although the clinical significance of these effects is not known, caution is advised in the coadministration of budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate with non-potassium-sparing diuretics.
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies of budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate or one of its individual components, formoterol fumarate, in pregnant women; however studies are available for the other component budesonide. In animal reproduction studies, budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate, administered by the inhalation route, was teratogenic, embryocidal, and reduced fetal weights in rats at less than the maximum recommended human daily inhalation dose (MRHDID) on a mcg/m2 basis. Budesonide alone, administered by the subcutaneous route, was teratogenic, embryocidal, and reduced fetal weights in rats and rabbits at less than the MRHDID, but these effects were not seen in rats that received inhaled doses up to 4 times the MRHDID. Studies of pregnant women have not shown that inhaled budesonide alone increases the risk of abnormalities when administered during pregnancy. Experience with oral corticosteroids suggests that rodents are more prone to teratogenic effects from corticosteroid exposure than humans. Formoterol fumarate alone, administered by the oral route, was teratogenic in rats and rabbits at 1600 and 65,000 times the MRHDID, respectively. Formoterol fumarate was also embryocidal, increased pup loss at birth and during lactation, and decreased pup weight in rats at 110 times the MRHDID. These adverse effects generally occurred at large multiples of the MRHDID when formoterol fumarate was administered by the oral route to achieve high systemic exposures. No teratogenic, embryocidal, or developmental effects were seen in rats that received inhalation doses up to 375 times the MRHDID.
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage of the indicated populations is unknown. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Disease-Associated Maternal and/or Embryo/Fetal risk
In women with poorly or moderately controlled asthma, there is an increased risk of several perinatal adverse outcomes such as preeclampsia in the mother and prematurity, low birth weight, and small for gestational age in the neonate. Pregnant women with asthma should be closely monitored and medication adjusted as necessary to maintain optimal asthma control.
Labor or Delivery
There are no well-controlled human studies that have investigated the effects of budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate during labor and delivery. Because of the potential for beta-agonist interference with uterine contractility, use of budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate during labor should be restricted to those patients in whom the benefits clearly outweigh the risk.
Data
Human Data
Studies of pregnant women have not shown that inhaled budesonide increases the risk of abnormalities when administered during pregnancy. The results from a large population-based prospective cohort epidemiological study reviewing data from three Swedish registries covering approximately 99% of the pregnancies from 1995-1997 (i.e., Swedish Medical Birth Registry; Registry of Congenital Malformations; Child Cardiology Registry) indicate no increased risk for congenital malformations from the use of inhaled budesonide during early pregnancy. Congenital malformations were studied in 2014 infants born to mothers reporting the use of inhaled budesonide for asthma in early pregnancy (usually 10-12 weeks after the last menstrual period), the period when most major organ malformations occur. The rate of recorded congenital malformations was similar compared to the general population rate (3.8% vs. 3.5%, respectively). In addition, after exposure to inhaled budesonide, the number of infants born with orofacial clefts was similar to the expected number in the normal population (4 children vs. 3.3, respectively).
These same data were utilized in a second study bringing the total to 2534 infants whose mothers were exposed to inhaled budesonide. In this study, the rate of congenital malformations among infants whose mothers were exposed to inhaled budesonide during early pregnancy was not different from the rate for all newborn babies during the same period (3.6%).
Animal Data
Budesonide and Formoterol Fumarate Dihydrate
In an embryo-fetal development study in pregnant rats dosed during the period of organogenesis from gestation days 6-16, budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate produced umbilical hernia in fetuses at doses less than the MRHDID (on a mcg/m2 basis at maternal inhaled doses of 12/0.66 mcg/kg/day and above). Fetal weights were reduced at approximately 5 and 3 times the MRHDID, respectively (on an AUC basis at a maternal inhaled dose of 80/4.4 mcg/kg (budesonide/formoterol)). No teratogenic or embryocidal effects were detected at doses less than the MRHDID (on a mcg/m2 basis at a maternal inhaled dose of 2.5/0.14 mcg/kg/day).
Budesonide
In a fertility and reproduction study, male rats were subcutaneously dosed for 9 weeks and females for 2 weeks prior to pairing and throughout the mating period. Females were dosed up until weaning of their offspring. Budesonide caused a decrease in prenatal viability and viability in the pups at birth and during lactation, along with a decrease in maternal body-weight gain, at doses less than the MRHDID (on a mcg/m2 basis at maternal subcutaneous doses of 20 mcg/kg/day and above). No such effects were noted at a dose less than the MRHDID (on a mcg/m2 basis at a maternal subcutaneous dose of 5 mcg/kg/day).
In an embryo-fetal development study in pregnant rabbits dosed during the period of organogenesis from gestation days 6-18, budesonide produced fetal loss, decreased fetal weight, and skeletal abnormalities at doses less than the MRHDID (on a mcg/m2 basis at a maternal subcutaneous dose of 25 mcg/kg/day). In an embryo-fetal development study in pregnant rats dosed during the period of organogenesis from gestation days 6-15, budesonide produced similar adverse fetal effects at doses approximately 8 times the MRHDID (on a mcg/m2 basis at a maternal subcutaneous dose of 500 mcg/kg/day). In another embryo-fetal development study in pregnant rats, no teratogenic or embryocidal effects were seen at doses up to 4 times the MRHDID (on a mcg/m2 basis at maternal inhalation doses up to 250 mcg/kg/day).
In a peri-and post-natal development study, rats dosed from gestation day 15 to postpartum day 21, budesonide had no effects on delivery, but did have an effect on growth and development of offspring. Offspring survival was reduced and surviving offspring had decreased mean body weights at birth and during lactation at doses less than the MRHDID and higher (on a mcg/m2 basis at maternal subcutaneous doses of 20 mcg/kg/day and higher). These findings occurred in the presence of maternal toxicity.
Formoterol
In a fertility and reproduction study, male rats were orally dosed for 9 weeks and females for 2 weeks prior to pairing and throughout the mating period. Females were either dosed up to gestation day 19 or up until weaning of their offspring. Males were dosed up to 25 weeks. Umbilical hernia was observed in rat fetuses at oral doses 1600 times and greater than the MRHDID (on a mcg/m2 basis at maternal oral doses of 3000 mcg/kg/day and higher). Brachygnathia was observed in rat fetuses at a dose 8000 times the MRHDID (on a mcg/m2 basis at a maternal oral dose of 15,000 mcg/kg/day). Pregnancy was prolonged at a dose 8000 times the MRHDID (on a mcg/m2 basis at a maternal oral dose of 15,000 mcg/kg/day). Fetal and pup deaths occurred at doses approximately 1600 times the MRHDID and higher (on a mcg/m2 basis at oral doses of 3000 mcg/kg/day and higher) during gestation.
In an embryo-fetal development study in pregnant rats dosed during the period of organogenesis from gestation days 6-15, no teratogenic, embryocidal or developmental effects were seen at doses up to 375 times the MRHDID (on a mcg/m2 basis with maternal inhalation doses up to 690 mcg/kg/day).
In an embryo-fetal development study in pregnant rabbits dosed during the period of organogenesis from gestation days 6-18, subcapsular cysts on the liver were observed in the fetuses at a dose 65,000 times the MRHDID (on a mcg/m2 basis with a maternal oral dose of 60,000 mcg/kg/day). No teratogenic effects were observed at doses up to 3800 times the MRHDID (on a mcg/m2 basis at maternal oral doses up to 3500 mcg/kg/day).
In a pre- and post-natal development study, pregnant female rats received formoterol at oral doses of 0, 210, 840, and 3400 mcg/kg/day from gestation day 6 through the lactation period. Pup survival was decreased from birth to postpartum day 26 at doses 110 times the MRHDID and higher (on a mcg/m2 basis at maternal oral doses of 210 mcg/kg/day and higher), although there was no evidence of a dose- response relationship. There were no treatment-related effects on the physical, functional, and behavioral development of rat pups.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no available data on the effects of budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate, budesonide or formoterol fumarate on the breastfed child or on milk production. Budesonide, like other inhaled corticosteroids, is present in human milk [see Data]. There are no available data on the presence of formoterol fumarate in human milk. Formoterol fumarate is present in rat milk [see Data]. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate or from the underlying maternal condition.
Data
Human data with budesonide delivered via dry powder inhaler indicates that the total daily oral dose of budesonide available in breast milk to the infant is approximately 0.3% to 1% of the dose inhaled by the mother [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. For budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate, the dose of budesonide available to the infant in breast milk, as a percentage of the maternal dose, would be expected to be similar.
In the fertility and reproduction study in rats, plasma levels of formoterol were measured in pups on post-natal day 15 [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)]. It was estimated that the maximum plasma concentration that the pups received from the maternal animal, at the highest dose of 15 mg/kg, after nursing was 4.4% (0.24 nmol/L for a litter vs. 5.5 nmol/L for the mother).
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate in asthma patients 12 years of age and older have been established in studies up to 12 months. In the two 12-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled US pivotal studies 25 patients 12 to 17 years of age were treated with budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate twice daily [see Clinical Studies (14.1)]. Efficacy results in this age group were similar to those observed in patients 18 years and older. There were no obvious differences in the type or frequency of adverse events reported in this age group compared with patients 18 years of age and older.
The safety and effectiveness of budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 80/4.5 in asthma patients 6 to less than 12 years of age have been established in studies of up to 12-week duration [see Clinical Studies (14.1)]. The safety profile in these patients was consistent to that observed in patients 12 years of age and older who also received budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
The safety and effectiveness of budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate in asthma patients less than 6 years of age have not been established.
Controlled clinical studies have shown that orally inhaled corticosteroids including budesonide, a component of budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate, may cause a reduction in growth velocity in pediatric patients. This effect has been observed in the absence of laboratory evidence of HPA-axis suppression, suggesting that growth velocity is a more sensitive indicator of systemic corticosteroid exposure in pediatric patients than some commonly used tests of HPA-axis function. The long-term effect of this reduction in growth velocity associated with orally inhaled corticosteroids, including the impact on final height are unknown. The potential for “catch-up” growth following discontinuation of treatment with orally inhaled corticosteroids has not been adequately studied.
In a study of asthmatic children 5 to 12 years of age, those treated with budesonide DPI 200 mcg twice daily (n=311) had a 1.1 centimeter reduction in growth compared with those receiving placebo (n=418) at the end of one year; the difference between these two treatment groups did not increase further over three years of additional treatment. By the end of 4 years, children treated with budesonide DPI and children treated with placebo had similar growth velocities. Conclusions drawn from this study may be confounded by the unequal use of corticosteroids in the treatment groups and inclusion of data from patients attaining puberty during the course of the study.
The growth of pediatric patients receiving orally inhaled corticosteroids, including budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate, should be monitored. If a child or adolescent on any corticosteroid appears to have growth suppression, the possibility that he/she is particularly sensitive to this effect should be considered. The potential growth effects of prolonged treatment should be weighed against the clinical benefits obtained. To minimize the systemic effects of orally inhaled corticosteroids, including budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate, each patient should be titrated to the lowest strength that effectively controls his/her asthma [see Dosage and Administration (2)].
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the total number of asthma patients treated with budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate twice daily in two 12-week studies and a 26-week postmarketing study, 791 were 65 years of age or older, of whom 141 were 75 years of age or older.
In the COPD studies of 6 to 12 months duration, 810 patients treated with budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 160/4.5, two inhalations twice daily were 65 years old and above and of those, 177 patients were 75 years of age and older. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these patients and younger patients, and other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients.
As with other products containing beta2-agonists, special caution should be observed when using budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate in geriatric patients who have concomitant cardiovascular disease that could be adversely affected by beta2-agonists.
Based on available data for budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate or its active components, no adjustment of dosage of budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate in geriatric patients is warranted.
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
Formal pharmacokinetic studies using budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate have not been conducted in patients with hepatic impairment. However, since both budesonide and formoterol fumarate are predominantly cleared by hepatic metabolism, impairment of liver function may lead to accumulation of budesonide and formoterol fumarate in plasma. Therefore, patients with hepatic disease should be closely monitored.
10. Overdosage
BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL
BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL contains both budesonide and formoterol; therefore, the risks associated with overdosage for the individual components described below apply to BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL. In pharmacokinetic studies, single doses of 960/54 mcg (12 actuations of budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 80/4.5) and 1280/36 mcg (8 actuations of 160/4.5), were administered to patients with COPD. A total of 1920/54 mcg (12 actuations of budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 160/4.5) was administered as a single dose to both healthy subjects and patients with asthma. In a long-term active-controlled safety study in adolescent and adult asthma patients 12 years of age and older, budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 160/4.5 was administered for up to 12 months at doses up to twice the highest recommended daily dose. There were no clinically significant adverse reactions observed in any of these studies.
Budesonide
The potential for acute toxic effects following overdose of budesonide is low. If used at excessive doses for prolonged periods, systemic corticosteroid effects such as hypercorticism may occur [see Warnings and Precautions (5)]. Budesonide at five times the highest recommended dose (3200 mcg daily) administered to humans for 6 weeks caused a significant reduction (27%) in the plasma cortisol response to a 6-hour infusion of ACTH compared with placebo (+1%). The corresponding effect of 10 mg prednisone daily was a 35% reduction in the plasma cortisol response to ACTH.
Formoterol
An overdose of formoterol would likely lead to an exaggeration of effects that are typical for beta2-agonists: seizures, angina, hypertension, hypotension, tachycardia, atrial and ventricular tachyarrhythmias, nervousness, headache, tremor, palpitations, muscle cramps, nausea, dizziness, sleep disturbances, metabolic acidosis, hyperglycemia, hypokalemia. As with all sympathomimetic medications, cardiac arrest and even death may be associated with abuse of formoterol. No clinically significant adverse reactions were seen when formoterol was delivered to adult patients with acute bronchoconstriction at a dose of 90 mcg/day over 3 hours or to stable asthmatics 3 times a day at a total dose of 54 mcg/day for 3 days.
Treatment of formoterol overdosage consists of discontinuation of the medication together with institution of appropriate symptomatic and/or supportive therapy. The judicious use of a cardioselective beta-receptor blocker may be considered, bearing in mind that such medication can produce bronchospasm. There is insufficient evidence to determine if dialysis is beneficial for overdosage of formoterol. Cardiac monitoring is recommended in cases of overdosage.
11. Budesonide and Formoterol Aerosol Description
BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL 80/4.5 and BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL 160/4.5 each contain micronized budesonide and micronized formoterol fumarate dihydrate for oral inhalation only.
Each BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL 80/4.5 and BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL 160/4.5 canister is formulated as a hydrofluoroalkane (HFA 227; 1,1,1,2,3,3,3-heptafluoropropane)-propelled pressurized metered dose inhaler containing 120 actuations [see Dosage Forms and Strengths (3) and How Supplied/Storage and Handling (16)]. After priming, each actuation meters either 91/5.1 mcg or 181/5.1 mcg from the valve and delivers either 80/4.5 mcg, or 160/4.5 mcg (budesonide micronized/formoterol fumarate dihydrate micronized) from the actuator. The actual amount of drug delivered to the lung may depend on patient factors, such as the coordination between actuation of the device and inspiration through the delivery system. BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL also contains povidone K25 USP as a suspending agent and polyethylene glycol 1000 NF as a lubricant.
BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL should be primed before using for the first time by releasing two test sprays into the air away from the face, shaking well for 5 seconds before each spray. In cases where the inhaler has not been used for more than 7 days or when it has been dropped, prime the inhaler again by shaking well for 5 seconds before each spray and releasing two test sprays into the air away from the face.
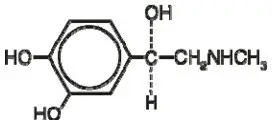
One active component of BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL is budesonide, a corticosteroid designated chemically as (RS)-11β, 16α, 17,21-Tetrahydroxypregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione cyclic 16,17-acetal with butyraldehyde. Budesonide is provided as a mixture of two epimers (22R and 22S). The empirical formula of budesonide is C25H34O6 and its molecular weight is 430.5. Its structural formula is:
Budesonide is a white to off-white, tasteless, odorless powder which is practically insoluble in water and in heptane, sparingly soluble in ethanol, and freely soluble in chloroform. Its partition coefficient between octanol and water at pH 7.4 is 1.6 x 103.
The other active component of BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL is formoterol fumarate dihydrate, a selective beta2-agonist designated chemically as (R*,R*)-(±)-N-[2-hydroxy-5-[1-hydroxy-2-[[2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1-methylethyl]amino]ethyl]phenyl]formamide, (E)-2-butendioate(2:1), dihydrate. The empirical formula of formoterol is C42H56N4O14 and its molecular weight is 840.9. Its structural formula is:
Formoterol fumarate dihydrate is a powder which is slightly soluble in water. Its octanol-water partition coefficient at pH 7.4 is 2.6. The pKa of formoterol fumarate dihydrate at 25°C is 7.9 for the phenolic group and 9.2 for the amino group.
12. Budesonide and Formoterol Aerosol - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL
BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL contains both budesonide and formoterol; therefore, the mechanisms of action described below for the individual components apply to BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL. These drugs represent two classes of medications (a synthetic corticosteroid and a long-acting selective beta2-adrenoceptor agonist) that have different effects on clinical, physiological, and inflammatory indices of COPD and asthma.
Budesonide
Budesonide is an anti-inflammatory corticosteroid that exhibits potent glucocorticoid activity and weak mineralocorticoid activity. In standard in vitro and animal models, budesonide has approximately a 200-fold higher affinity for the glucocorticoid receptor and a 1000-fold higher topical anti-inflammatory potency than cortisol (rat croton oil ear edema assay). As a measure of systemic activity, budesonide is 40 times more potent than cortisol when administered subcutaneously and 25 times more potent when administered orally in the rat thymus involution assay.
In glucocorticoid receptor affinity studies, the 22R form of budesonide was two times as active as the 22S epimer. In vitro studies indicated that the two forms of budesonide do not interconvert.
Inflammation is an important component in the pathogenesis of COPD and asthma. Corticosteroids have a wide range of inhibitory activities against multiple cell types (e.g., mast cells, eosinophils, neutrophils, macrophages, and lymphocytes) and mediators (e.g., histamine, eicosanoids, leukotrienes, and cytokines) involved in allergic and non–allergic-mediated inflammation. These anti-inflammatory actions of corticosteroids may contribute to their efficacy in COPD and asthma.
Studies in asthmatic patients have shown a favorable ratio between topical anti-inflammatory activity and systemic corticosteroid effects over a wide range of doses of budesonide. This is explained by a combination of a relatively high local anti-inflammatory effect, extensive first pass hepatic degradation of orally absorbed drug (85%-95%), and the low potency of formed metabolites.
Formoterol
Formoterol fumarate is a long-acting selective beta2-adrenergic agonist (beta2-agonist) with a rapid onset of action. Inhaled formoterol fumarate acts locally in the lung as a bronchodilator. In vitro studies have shown that formoterol has more than 200-fold greater agonist activity at beta2-receptors than at beta1-receptors. The in vitro binding selectivity to beta2- over beta1-adrenoceptors is higher for formoterol than for albuterol (5 times), whereas salmeterol has a higher (3 times) beta2-selectivity ratio than formoterol.
Although beta2-receptors are the predominant adrenergic receptors in bronchial smooth muscle and beta1-receptors are the predominant receptors in the heart, there are also beta2-receptors in the human heart comprising 10% to 50% of the total beta-adrenergic receptors. The precise function of these receptors has not been established, but they raise the possibility that even highly selective beta2-agonists may have cardiac effects.
The pharmacologic effects of beta2-adrenoceptor agonist drugs, including formoterol, are at least in part attributable to stimulation of intracellular adenyl cyclase, the enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to cyclic-3', 5'-adenosine monophosphate (cyclic AMP). Increased cyclic AMP levels cause relaxation of bronchial smooth muscle and inhibition of release of mediators of immediate hypersensitivity from cells, especially from mast cells.
In vitro tests show that formoterol is an inhibitor of the release of mast cell mediators, such as histamine and leukotrienes, from the human lung. Formoterol also inhibits histamine-induced plasma albumin extravasation in anesthetized guinea pigs and inhibits allergen-induced eosinophil influx in dogs with airway hyper-responsiveness. The relevance of these in vitro and animal findings to humans is unknown.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Asthma
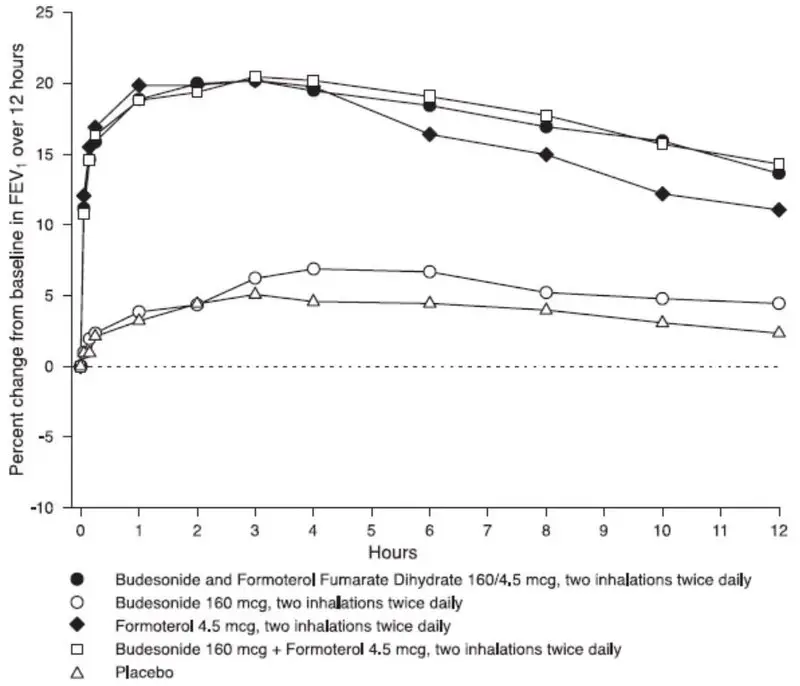
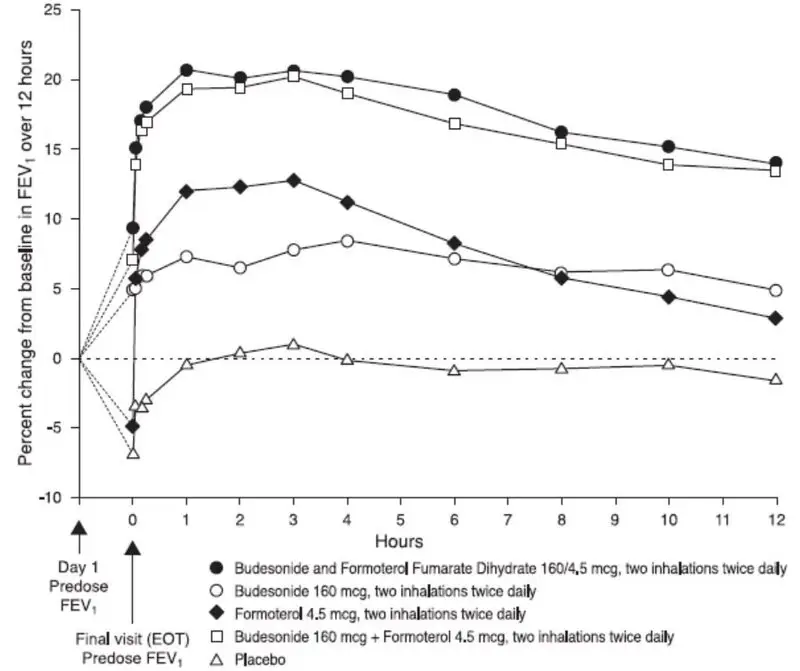
Cardiovascular effects: In a single-dose cross-over study involving 201 patients with persistent asthma, single-dose treatments of 4.5, 9, and 18 mcg of formoterol in combination with 320 mcg of budesonide delivered via BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL were compared to budesonide 320 mcg alone. Dose-ordered improvements in FEV1 were demonstrated when compared with budesonide. ECGs and blood samples for glucose and potassium were obtained post-dose. For budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate, small mean increases in serum glucose and decreases in serum potassium (+0.44 mmol/L and -0.18 mmol/L at the highest dose, respectively) were observed with increasing doses of formoterol, compared to budesonide. In ECGs, budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate produced small dose-related mean increases in heart rate (approximately 3 bpm at the highest dose), and QTc intervals (3-6 msec) compared to budesonide alone. No subject had a QT or QTc value ≥500 msec.
In the United States, five 12-week, active- and placebo-controlled studies and one 6-month active-controlled study evaluated 2976 patients aged 6 years and older with asthma. Systemic pharmacodynamic effects of formoterol (heart/pulse rate, blood pressure, QTc interval, potassium, and glucose) were similar in patients treated with budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate, compared with patients treated with formoterol dry inhalation powder 4.5 mcg, 2 inhalations twice daily. No patient had a QT or QTc value ≥500 msec during treatment.
In three placebo-controlled studies in adolescents and adults with asthma, aged 12 years and older, a total of 1232 patients (553 patients in the budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate group) had evaluable continuous 24-hour electrocardiographic monitoring. Overall, there were no important differences in the occurrence of ventricular or supraventricular ectopy and no evidence of increased risk for clinically significant dysrhythmia in the budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate group compared to placebo.
HPA-axis effects: Overall, no clinically important effects on HPA-axis, as measured by 24-hour urinary cortisol, were observed for budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate treated adult or adolescent patients at doses up to 640/18 mcg/day compared to budesonide.
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Cardiovascular effects: In two COPD lung function studies, 6 months and 12 months in duration including 3668 COPD patients, no clinically important differences were seen in pulse rate, blood pressure, potassium, and glucose between budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate, the individual components of BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL, and placebo [see Clinical Studies (14.2)].
ECGs recorded at multiple clinic visits on treatment in both studies showed no clinically important differences for heart rate, PR interval, QRS duration, heart rate, signs of cardiac ischemia or arrhythmias between budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 160/4.5 the monoproducts and placebo, all administered as 2 inhalations twice daily. Based on ECGs, 6 patients treated with budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 160/4.5, 6 patients treated with formoterol 4.5 mcg, and 6 patients in the placebo group experienced atrial fibrillation or flutter that was not present at baseline. There were no cases of nonsustained ventricular tachycardia in the budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 160/4.5, formoterol 4.5 mcg, or placebo groups.
In the 12-month study, 520 patients had evaluable continuous 24-hour ECG (Holter) monitoring prior to the first dose and after approximately 1 and 4 months on treatment. No clinically important differences in ventricular or supraventricular arrhythmias, ventricular or supraventricular ectopic beats, or heart rate were observed among the groups treated with budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 160/4.5, formoterol or placebo taken as 2 inhalations twice daily. Based on ECG (Holter) monitoring, one patient on budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 160/4.5, no patients on formoterol 4.5 mcg, and three patients in the placebo group experienced atrial fibrillation or flutter that was not present at baseline.
HPA-axis effects: Twenty-four hour urinary cortisol measurements were collected in a pooled subset (n=616) of patients from two COPD lung function studies. The data indicated approximately 30% lower mean 24-hour urinary free cortisol values following chronic administration (> 6 months) of budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate, relative to placebo. Budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate appeared to exhibit comparable cortisol suppression to budesonide 160 mcg alone or coadministration of budesonide 160 mcg and formoterol 4.5 mcg. For patients treated with budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate, or placebo for up to 12 months, the percentage of patients who shifted from normal to low for this measure were generally comparable.
Other Budesonide Products
To confirm that systemic absorption is not a significant factor in the clinical efficacy of inhaled budesonide, a clinical study in patients with asthma was performed comparing 400 mcg budesonide administered via a pressurized metered dose inhaler with a tube spacer to 1400 mcg of oral budesonide and placebo. The study demonstrated the efficacy of inhaled budesonide but not orally ingested budesonide, despite comparable systemic levels. Thus, the therapeutic effect of conventional doses of orally inhaled budesonide are largely explained by its direct action on the respiratory tract.
Inhaled budesonide has been shown to decrease airway reactivity to various challenge models, including histamine, methacholine, sodium metabisulfite, and adenosine monophosphate in patients with hyperreactive airways. The clinical relevance of these models is not certain.
Pretreatment with inhaled budesonide, 1600 mcg daily (800 mcg twice daily) for 2 weeks reduced the acute (early-phase reaction) and delayed (late-phase reaction) decrease in FEV1 following inhaled allergen challenge.
The systemic effects of inhaled corticosteroids are related to the systemic exposure to such drugs. Pharmacokinetic studies have demonstrated that in both adults and children with asthma the systemic exposure to budesonide is lower with budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate, compared with inhaled budesonide administered at the same delivered dose via a dry powder inhaler [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Therefore, the systemic effects (HPA-axis and growth) of budesonide delivered from budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate, would be expected to be no greater than what is reported for inhaled budesonide when administered at comparable doses via the dry powder inhaler [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
HPA-axis effects: The effects of inhaled budesonide administered via a dry powder inhaler on the HPA-axis were studied in 905 adults and 404 pediatric patients with asthma. For most patients, the ability to increase cortisol production in response to stress, as assessed by cosyntropin (ACTH) stimulation test, remained intact with budesonide treatment at recommended doses. For adult patients treated with 100, 200, 400, or 800 mcg twice daily for 12 weeks, 4%, 2%, 6%, and 13%, respectively, had an abnormal stimulated cortisol response (peak cortisol <14.5 mcg/dL assessed by liquid chromatography following short-cosyntropin test) as compared to 8% of patients treated with placebo. Similar results were obtained in pediatric patients. In another study in adults, doses of 400, 800, and 1600 mcg of inhaled budesonide twice daily for 6 weeks were examined; 1600 mcg twice daily (twice the maximum recommended dose) resulted in a 27% reduction in stimulated cortisol (6-hour ACTH infusion) while 10-mg prednisone resulted in a 35% reduction. In this study, no patient on budesonide at doses of 400 and 800 mcg twice daily met the criterion for an abnormal stimulated-cortisol response (peak cortisol <14.5 mcg/dL assessed by liquid chromatography) following ACTH infusion. An open-label, long-term follow-up of 1133 patients for up to 52 weeks confirmed the minimal effect on the HPA-axis (both basal- and stimulated-plasma cortisol) of budesonide when administered at recommended doses. In patients who had previously been oral-steroid-dependent, use of budesonide in recommended doses was associated with higher stimulated-cortisol response compared to baseline following 1 year of therapy.
Other Formoterol Products
While the pharmacodynamic effect is via stimulation of beta-adrenergic receptors, excessive activation of these receptors commonly leads to skeletal muscle tremor and cramps, insomnia, tachycardia, decreases in plasma potassium, and increases in plasma glucose. Inhaled formoterol, like other beta2-adrenergic agonist drugs, can produce dose-related cardiovascular effects and effects on blood glucose and/or serum potassium [see Warnings and Precautions (5)]. For budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate, these effects are detailed in the Clinical Pharmacology, Pharmacodynamics, BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL (12.2) section.
Use of LABA drugs can result in tolerance to bronchoprotective and bronchodilatory effects.
Rebound bronchial hyperresponsiveness after cessation of chronic long-acting beta-agonist therapy has not been observed.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL
Absorption
Budesonide
Healthy Subjects: Orally inhaled budesonide is rapidly absorbed in the lungs and peak concentration is typically reached within 20 minutes. After oral administration of budesonide peak plasma concentration was achieved in about 1 to 2 hours and the absolute systemic availability was 6%-13% due to extensive first pass metabolism. In contrast, most of the budesonide delivered to the lungs was systemically absorbed. In healthy subjects, 34% of the metered dose was deposited in the lung (as assessed by plasma concentration method and using a budesonide-containing dry powder inhaler) with an absolute systemic availability of 39% of the metered dose.
Following administration of budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 160/4.5, two or four inhalations twice daily for 5 days in healthy subjects, plasma concentration of budesonide generally increased in proportion to dose. The accumulation index for the group that received 2 inhalations twice daily was 1.32 for budesonide.
Asthma Patients: In a single-dose study, higher than recommended doses of budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate (12 inhalations of budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 160/4.5) were administered to patients with moderate asthma. Peak budesonide plasma concentration of 4.5 nmol/L occurred at 20 minutes following dosing. This study demonstrated that the total systemic exposure to budesonide from budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate was approximately 30% lower than from inhaled budesonide via a dry powder inhaler (DPI) at the same delivered dose. Following administration of budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate, the half-life of the budesonide component was 4.7 hours.
In a repeat dose study, the highest recommended dose of budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate (160/4.5, two inhalations twice daily) was administered to patients with moderate asthma and healthy subjects for 1 week. Peak budesonide plasma concentration of 1.2 nmol/L occurred at 21 minutes in asthma patients. Peak budesonide plasma concentration was 27% lower in asthma patients compared to that in healthy subjects. However, the total systemic exposure of budesonide was comparable to that in asthma patients.
Peak steady-state plasma concentrations of budesonide administered by DPI in adults with asthma averaged 0.6 and 1.6 nmol/L at doses of 180 mcg and 360 mcg twice daily, respectively. In asthmatic patients, budesonide showed a linear increase in AUC and Cmax with increasing dose after both single and repeated dosing of inhaled budesonide.
COPD Patients: In a single-dose study, 12 inhalations of budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 80/4.5 (total dose 960/54 mcg) were administered to patients with COPD. Mean budesonide peak plasma concentration of 3.3 nmol/L occurred at 30 minutes following dosing. Budesonide systemic exposure was comparable between budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate pMDI and coadministration of budesonide via a metered-dose inhaler and formoterol via a dry powder inhaler (budesonide 960 mcg and formoterol 54 mcg). In the same study, an open-label group of moderate asthma patients also received the same higher dose of budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate. For budesonide, COPD patients exhibited 12% greater AUC and 10% lower Cmax compared to asthma patients.
In the 6-month pivotal lung function clinical study, steady-state pharmacokinetic data of budesonide was obtained in a subset of COPD patients with treatment arms of budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate pMDI 160/4.5, budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate pMDI 80/4.5, budesonide 160 mcg, budesonide 160 mcg and formoterol 4.5 mcg given together, all administered as 2 inhalations twice daily. Budesonide systemic exposure (AUC and Cmax) increased proportionally with doses from 80 mcg to 160 mcg and was generally similar between the 3 treatment groups receiving the same dose of budesonide (budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate pMDI 160/4.5, budesonide 160 mcg, budesonide 160 mcg and formoterol 4.5 mcg administered together).
Formoterol
Inhaled formoterol is rapidly absorbed; peak plasma concentrations are typically reached at the first plasma sampling time, within 5-10 minutes after dosing. As with many drug products for oral inhalation, it is likely that the majority of the inhaled formoterol delivered is swallowed and then absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract.
Healthy Subjects: Following administration of budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate (160/4.5, two or four inhalations twice daily) for 5 days in healthy subjects, plasma concentration of formoterol generally increased in proportion to dose. The accumulation index for the group that received 2 inhalations twice daily was 1.77 for formoterol.
Asthma patients: In a single-dose study, higher than recommended doses of budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate (12 inhalations of budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 160/4.5) were administered to patients with moderate asthma. Peak plasma concentration for formoterol of 136 pmol occurred at 10 minutes following dosing. Approximately 8% of the delivered dose of formoterol was recovered in the urine as unchanged drug.
In a repeat dose study, the highest recommended dose of budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate (160/4.5, two inhalations twice daily) was administered to patients with moderate asthma and healthy subjects for 1 week. Peak formoterol plasma concentration of 28 pmol/L occurred at 10 minutes in asthma patients. Peak formoterol plasma concentration was about 42% lower in asthma patients compared to that in healthy subjects. However, the total systemic exposure of formoterol was comparable to that in asthma patients.
COPD patients: Following single-dose administration of 12 inhalations of budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 80/4.5, mean peak formoterol plasma concentration of 167 pmol/L was rapidly achieved at 15 minutes after dosing. Formoterol exposure was slightly greater (~16-18%) from budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate pMDI compared to coadministration of budesonide via a metered-dose inhaler and formoterol via a dry powder inhaler (total dose of budesonide 960 mcg and formoterol 54 mcg). In the same study, an open label group of moderate asthma patients received the same dose of budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate. COPD patients exhibited 12-15% greater AUC and Cmax for formoterol compared to asthma patients.
In the 6-month pivotal lung function clinical study, steady-state pharmacokinetic data of formoterol was obtained in a subset of COPD patients with treatment arms of budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate pMDI 160/4.5, budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate pMDI 80/4.5, formoterol 4.5 mcg, budesonide 160 mcg and formoterol 4.5 mcg given together, all administered as 2 inhalations twice daily. The systemic exposure of formoterol as evidenced by AUC, was about 30% and 16% higher from budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate pMDI compared to formoterol alone treatment arm and coadministration of individual components of budesonide and formoterol treatment arm, respectively.
Distribution
Budesonide: The volume of distribution of budesonide was approximately 3 L/kg. It was 85%-90% bound to plasma proteins. Protein binding was constant over the concentration range (1-100 nmol/L) achieved with, and exceeding, recommended inhaled doses. Budesonide showed little or no binding to corticosteroid binding globulin. Budesonide rapidly equilibrated with red blood cells in a concentration independent manner with a blood plasma ratio of about 0.8.
Formoterol: Over the concentration range of 10-500 nmol/L, plasma protein binding for the RR and SS enantiomers of formoterol was 46% and 58%, respectively. The concentrations of formoterol used to assess the plasma protein binding were higher than those achieved in plasma following inhalation of a single 54 mcg dose.
Metabolism
Budesonide: In vitro studies with human liver homogenates have shown that budesonide was rapidly and extensively metabolized. Two major metabolites formed via cytochrome P450 (CYP) isoenzyme 3A4 (CYP3A4) catalyzed biotransformation have been isolated and identified as 16α-hydroxyprednisolone and 6ß-hydroxybudesonide. The corticosteroid activity of each of these two metabolites was less than 1% of that of the parent compound. No qualitative differences between the in vitro and in vivo metabolic patterns were detected. Negligible metabolic inactivation was observed in human lung and serum preparations.
Formoterol: The primary metabolism of formoterol is by direct glucuronidation and by O-demethylation followed by conjugation to inactive metabolites. Secondary metabolic pathways include deformylation and sulfate conjugation. CYP2D6 and CYP2C have been identified as being primarily responsible for O-demethylation.
Elimination
Budesonide: Budesonide was excreted in urine and feces in the form of metabolites. Approximately 60% of an intravenous radiolabeled dose was recovered in the urine.
No unchanged budesonide was detected in the urine. The 22R form of budesonide was preferentially cleared by the liver with systemic clearance of 1.4 L/min vs. 1.0 L/min for the 22S form. The terminal half-life, 2 to 3 hours, was the same for both epimers and was independent of dose.
Formoterol: The excretion of formoterol was studied in four healthy subjects following simultaneous administration of radiolabeled formoterol via the oral and IV routes. In that study, 62% of the radiolabeled formoterol was excreted in the urine while 24% was eliminated in the feces.
Special Populations
Geriatric
The pharmacokinetics of budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate in geriatric patients have not been specifically studied.
Pediatric
Plasma concentrations of budesonide were measured following administration of four inhalations of budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 160/4.5 in a single-dose study in pediatric patients with asthma, 6 to less than 12 years of age. Peak budesonide concentrations of 1.4 nmol/L occurred at 20 minutes post-dose. This study also demonstrated that the total systemic exposure to budesonide from budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate was approximately 30% lower than from inhaled budesonide via a dry powder inhaler that was also evaluated at the same delivered dose. The dose-normalized Cmax and AUC0-inf of budesonide following single dose inhalation in children 6 to less than 12 years of age were numerically lower than that observed in adults.
Following 2 inhalations of budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 160/4.5 twice daily treatment, formoterol Cmax and AUC0-6 at steady state in children 6 to less than 12 years of age were comparable to that observed in adults.
Gender/Race
Specific studies to examine the effects of gender and race on the pharmacokinetics of budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate have not been conducted. Population PK analysis of the budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate data indicates that gender does not affect the pharmacokinetics of budesonide and formoterol. No conclusions can be drawn on the effect of race due to the low number of non-Caucasians evaluated for PK.
Nursing Mothers
The disposition of budesonide when delivered by inhalation from a dry powder inhaler at doses of 200 or 400 mcg twice daily for at least 3 months was studied in eight lactating women with asthma from 1 to 6 months postpartum. Systemic exposure to budesonide in these women appears to be comparable to that in non-lactating women with asthma from other studies. Breast milk obtained over eight hours post-dose revealed that the maximum concentration of budesonide for the 400 and 800 mcg total daily doses was 0.39 and 0.78 nmol/L, respectively, and occurred within 45 minutes after dosing. The estimated oral daily dose of budesonide from breast milk to the infant is approximately 0.007 and 0.014 mcg/kg/day for the two dose regimens used in this study, which represents approximately 0.3% to 1% of the dose inhaled by the mother. Budesonide levels in plasma samples obtained from five infants at about 90 minutes after breastfeeding (and about 140 minutes after drug administration to the mother) were below quantifiable levels (<0.02 nmol/L in four infants and <0.04 nmol/L in one infant) [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
Renal or Hepatic Insufficiency
There are no data regarding the specific use of budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate in patients with hepatic or renal impairment. Reduced liver function may affect the elimination of corticosteroids. Budesonide pharmacokinetics was affected by compromised liver function as evidenced by a doubled systemic availability after oral ingestion. The intravenous budesonide pharmacokinetics was, however, similar in cirrhotic patients and in healthy subjects. Specific data with formoterol is not available, but because formoterol is primarily eliminated via hepatic metabolism, an increased exposure can be expected in patients with severe liver impairment.
Drug-Drug Interactions
A single-dose crossover study was conducted to compare the pharmacokinetics of eight inhalations of the following: budesonide, formoterol, and budesonide plus formoterol administered concurrently. The results of the study indicated that there was no evidence of a pharmacokinetic interaction between the two components of budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate.
Inhibitors of Cytochrome P450 Enzymes
Ketoconazole: Ketoconazole, a strong inhibitor of cytochrome P450 (CYP) isoenzyme 3A4 (CYP3A4), the main metabolic enzyme for corticosteroids, increased plasma levels of orally ingested budesonide.
Cimetidine: At recommended doses, cimetidine, a non-specific inhibitor of CYP enzymes, had a slight but clinically insignificant effect on the pharmacokinetics of oral budesonide.
Specific drug-drug interaction studies with formoterol have not been performed.
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Budesonide
Long-term studies were conducted in rats and mice using oral administration to evaluate the carcinogenic potential of budesonide.
In a 2-year study in Sprague-Dawley rats, budesonide caused a statistically significant increase in the incidence of gliomas in male rats at an oral dose of 50 mcg/kg (approximately equivalent to the MRHDID in adults and children on a mcg/m2 basis). No tumorigenicity was seen in male and female rats at respective oral doses up to 25 and 50 mcg/kg (approximately equivalent to the MRHDID in adults and children on a mcg/m2 basis). In two additional 2-year studies in male Fischer and Sprague-Dawley rats, budesonide caused no gliomas at an oral dose of 50 mcg/kg (approximately equivalent to the MRHDID in adults and children on a mcg/m2 basis). However, in the male Sprague-Dawley rats, budesonide caused a statistically significant increase in the incidence of hepatocellular tumors at an oral dose of 50 mcg/kg (approximately equivalent to the MRHDID in adults and children on a mcg/m2 basis). The concurrent reference corticosteroids (prednisolone and triamcinolone acetonide) in these two studies showed similar findings.
In a 91-week study in mice, budesonide caused no treatment-related carcinogenicity at oral doses up to 200 mcg/kg (approximately 2 times the MRHDID in adults and children on a mcg/m2 basis).
Budesonide was not mutagenic or clastogenic in six different test systems: Ames Salmonella/microsome plate test, mouse micronucleus test, mouse lymphoma test, chromosome aberration test in human lymphocytes, sex-linked recessive lethal test in Drosophila melanogaster, and DNA repair analysis in rat hepatocyte culture.
Fertility and reproductive performance were unaffected in rats at subcutaneous doses up to 80 mcg/kg (approximately equal to the MRHDID on a mcg/m2 basis). However, it caused a decrease in prenatal viability and viability in the pups at birth and during lactation, along with a decrease in maternal body-weight gain, at subcutaneous doses of 20 mcg/kg and above (less than the MRHDID on a mcg/m2 basis). No such effects were noted at 5 mcg/kg (less than the MRHDID on a mcg/m2 basis).
Formoterol
Long-term studies were conducted in mice using oral administration and rats using inhalation administration to evaluate the carcinogenic potential of formoterol fumarate.
In a 24-month carcinogenicity study in CD-1 mice, formoterol at oral doses of 100 mcg/kg and above (approximately 30 and 15 times the MRHDID in adults and children, respectively, on a mcg/m2 basis) caused a dose-related increase in the incidence of uterine leiomyomas.
In a 24-month carcinogenicity study in Sprague-Dawley rats, an increased incidence of mesovarian leiomyoma and uterine leiomyosarcoma were observed at the inhaled dose of 130 mcg/kg (approximately 70 and 35 times the MRHDID in adults and children, respectively, on a mcg/m2 basis). No tumors were seen at 22 mcg/kg (approximately 12 and 6 times the MRHDID in adults and children, respectively, on a mcg/m2 basis).
Other beta-agonist drugs have similarly demonstrated increases in leiomyomas of the genital tract in female rodents. The relevance of these findings to human use is unknown.
Formoterol was not mutagenic or clastogenic in Ames Salmonella/microsome plate test, mouse lymphoma test, chromosome aberration test in human lymphocytes, and rat micronucleus test.
A reduction in fertility and/or reproductive performance was identified in male rats treated with formoterol at an oral dose of 15,000 mcg/kg (approximately 2200 times the MRHDID on an AUC basis). No such effect was seen at 3000 mcg/kg (approximately 1600 times the MRHDID on a mcg/m2 basis). In a separate study with male rats treated with an oral dose of 15,000 mcg/kg (approximately 8000 times the MRHDID on a mcg/m2 basis), there were findings of testicular tubular atrophy and spermatic debris in the testes and oligospermia in the epididymides. No effect on fertility was detected in female rats at doses up to 15,000 mcg/kg (approximately 1100 times the MRHDID on an AUC basis).
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
Preclinical: Studies in laboratory animals (minipigs, rodents, and dogs) have demonstrated the occurrence of cardiac arrhythmias and sudden death (with histologic evidence of myocardial necrosis) when beta-agonists and methylxanthines are administered concurrently. The clinical significance of these findings is unknown.
14. Clinical Studies
14.1 Asthma
Patients with asthma 12 years of age and older
In two clinical studies comparing budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate with the individual components, improvements in most efficacy end points were greater with budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate than with the use of either budesonide or formoterol alone. In addition, one clinical study showed similar results between budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate and the concurrent use of budesonide and formoterol at corresponding doses from separate inhalers.
The safety and efficacy of budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate were demonstrated in two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled US clinical studies involving 1076 patients 12 years of age and older. Fixed budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate dosages of 160/9 mcg, and 320/9 mcg twice daily (each dose administered as 2 inhalations of the 80/4.5 and 160/4.5 mcg strengths, respectively) were compared with the monocomponents (budesonide and formoterol) and placebo to provide information about appropriate dosing to cover a range of asthma severity.
Study 1: Clinical Study with Budesonide and Formoterol Fumarate Dihydrate 160/4.5
This 12-week study evaluated 596 patients 12 years of age and older by comparing budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 160/4.5, the free combination of budesonide 160 mcg plus formoterol 4.5 mcg in separate inhalers, budesonide 160 mcg, formoterol 4.5 mcg, and placebo; each administered as 2 inhalations twice daily. The study included a 2-week run-in period with budesonide 80 mcg, 2 inhalations twice daily. Most patients had moderate to severe asthma and were using moderate to high doses of inhaled corticosteroids prior to study entry. Randomization was stratified by previous inhaled corticosteroid treatment (71.6% on moderate- and 28.4% on high-dose inhaled corticosteroid). Mean percent predicted FEV1 at baseline was 68.1% and was similar across treatment groups. The co-primary efficacy end points were 12-hour-average post-dose FEV1 at week 2, and pre-dose FEV1 averaged over the course of the study. The study also required that patients who satisfied a predefined asthma-worsening criterion be withdrawn. The predefined asthma-worsening criteria were a clinically important decrease in FEV1 or PEF, increase in rescue albuterol use, nighttime awakening due to asthma, emergency intervention or hospitalization due to asthma, or requirement for asthma medication not allowed by the protocol. For the criterion of nighttime awakening due to asthma, patients were allowed to remain in the study at the discretion of the investigator if none of the other asthma-worsening criteria were met. The percentage of patients withdrawing due to or meeting predefined criteria for worsening asthma is shown in Table 4.
|
|||||
|
Budesonide and Formoterol Fumarate Dihydrate 160/4.5 n = 124 |
Budesonide 160 mcg plus Formoterol 4.5 mcg n = 115 |
Budesonide 160 mcg n = 109 |
Formoterol 4.5 mcg n = 123 |
Placebo n = 125 |
|
|
Patients withdrawn due to predefined asthma event* |
13 (10.5) |
13 (11.3) |
22 (20.2) |
44 (35.8) |
62 (49.6) |
|
Patients with a predefined asthma event*,† |
37 (29.8) |
24 (20.9) |
48 (44.0) |
68 (55.3) |
84 (67.2) |
|
Decrease in FEV1 |
4 (3.2) |
8 (7.0) |
7 (6.4) |
15 (12.2) |
14 (11.2) |
|
Rescue medication use |
2 (1.6) |
0 |
3 (2.8) |
3 (2.4) |
7 (5.6) |
|
Decrease in AM PEF |
2 (1.6) |
5 (4.3) |
5 (4.6) |
17 (13.8) |
15 (12.0) |
|
Nighttime awakenings‡ |
24 (19.4) |
11 (9.6) |
29 (26.6) |
32 (26.0) |
49 (39.2) |
|
Clinical exacerbation |
7 (5.6) |
6 (5.2) |
5 (4.6) |
17 (13.8) |
16 (12.8) |
Mean percent change from baseline in FEV1 measured immediately prior to dosing (pre-dose) over 12 weeks is displayed in Figure 1. Because this study used predefined withdrawal criteria for worsening asthma, which caused a differential withdrawal rate in the treatment groups, pre-dose FEV1 results at the last available study visit (end of treatment, EOT) are also provided. Patients receiving budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 160/4.5 had significantly greater mean improvements from baseline in pre-dose FEV1 at the end of treatment (0.19 L, 9.4%), compared with budesonide 160 mcg (0.10 L, 4.9%), formoterol 4.5 mcg (-0.12 L, -4.8%), and placebo (-0.17 L, -6.9%).
Figure 1 Mean Percent Change From Baseline in Pre-dose FEV1 Over 12 Weeks (Study 1)
The effect of budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 160/4.5 two inhalations twice daily on selected secondary efficacy variables, including morning and evening PEF, albuterol rescue use, and asthma symptoms over 24 hours on a 0-3 scale is shown in Table 5.
| Efficacy Variable | Budesonide and Formoterol Fumarate Dihydrate
160/4.5 (n*=124) | Budesonide
160 mcg plus Formoterol 4.5 mcg (n*=115) | Budesonide
160 mcg (n*=109) | Formoterol
4.5 mcg (n*=123) | Placebo
(n*=125) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||
|
AM PEF (L/min) Baseline |
341 |
338 |
342 |
339 |
355 |
|
Change from Baseline |
35 |
28 |
9 |
-9 |
-18 |
|
PM PEF (L/min) Baseline |
351 |
348 |
357 |
354 |
369 |
|
Change from Baseline |
34 |
26 |
7 |
-7 |
-18 |
|
Albuterol rescue use Baseline |
2.1 |
2.3 |
2.7 |
.5 |
2.4 |
|
Change from Baseline |
-1.0 |
-1.5 |
-0.8 |
-0.3 |
0.8 |
|
Average symptom score/day (0–3 scale) Baseline |
0.99 |
1.03 |
1.04 |
1.04 |
1.08 |
|
Change from Baseline |
-0.28 |
-0.32 |
-0.14 |
-0.05 |
0.10 |
The subjective impact of asthma on patients’ health-related quality of life was evaluated through the use of the standardized Asthma Quality of Life Questionnaire (AQLQ(S)) (based on a 7-point scale where 1 = maximum impairment and 7 = no impairment). Patients receiving budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 160/4.5 had clinically meaningful improvement in overall asthma-specific quality of life, as defined by a mean difference between treatment groups of >0.5 points in change from baseline in overall AQLQ score (difference in AQLQ score of 0.70 [95% CI 0.47, 0.93], compared to placebo).
Study 2: Clinical Study with Budesonide and Formoterol Fumarate Dihydrate 80/4.5
This 12-week study was similar in design to Study 1, and included 480 patients 12 years of age and older. This study compared budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 80/4.5, budesonide 80 mcg, formoterol 4.5 mcg, and placebo; each administered as 2 inhalations twice daily. The study included a 2-week placebo run-in period. Most patients had mild to moderate asthma and were using low to moderate doses of inhaled corticosteroids prior to study entry. Mean percent predicted FEV1 at baseline was 71.3% and was similar across treatment groups. Efficacy variables and end points were identical to those in Study 1.
The percentage of patients withdrawing due to or meeting predefined criteria for worsening asthma is shown in Table 6. The method of assessment and criteria used were identical to that in Study 1.
|
||||
|
Budesonide and Formoterol Fumarate Dihydrate 80/4.5 (n=123) |
Budesonide 80 mcg (n=121) |
Formoterol 4.5 mcg (n=114) |
Placebo (n=122) |
|
|
Patients withdrawn due to predefined asthma event* |
9 (7.3) |
8 (6.6) |
21 (18.4) |
40 (32.8) |
|
Patients with a predefined asthma event*,† |
23 (18.7) |
26 (21.5) |
48 (42.1) |
69 (56.6) |
|
Decrease in FEV1 |
3 (2.4) |
3 (2.5) |
11 (9.6) |
9 (7.4) |
|
Rescue medication use |
1 (0.8) |
3 (2.5) |
1 (0.9) |
3 (2.5) |
|
Decrease in AM PEF |
3 (2.4) |
1 (0.8) |
8 (7.0) |
14 (11.5) |
|
Nighttime awakening‡ |
17 (13.8) |
20 (16.5) |
31 (27.2) |
52 (42.6) |
|
Clinical exacerbation |
1 (0.8) |
3 (2.5) |
5 (4.4) |
20 (16.4) |
Mean percent change from baseline in pre-dose FEV1 over 12 weeks is displayed in Figure 2.
Figure 2 Mean Percent Change From Baseline in Pre-dose FEV1 Over 12 Weeks (Study 2)
Efficacy results for other secondary end points, including quality of life, were similar to those observed in Study 1.
Onset and Duration of Action and Progression of Improvement in Asthma Control
The onset of action and progression of improvement in asthma control were evaluated in the two pivotal clinical studies. The median time to onset of clinically significant bronchodilation (>15% improvement in FEV1) was seen within 15 minutes. Maximum improvement in FEV1 occurred within 3 hours, and clinically significant improvement was maintained over 12 hours. Figures 3 and 4 show the percent change from baseline in post-dose FEV1 over 12 hours on the day of randomization and on the last day of treatment for Study 1.
Reduction in asthma symptoms and in albuterol rescue use, as well as improvement in morning and evening PEF, occurred within 1 day of the first dose of budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate; improvement in these variables was maintained over the 12 weeks of therapy.
Following the initial dose of budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate, FEV1 improved markedly during the first 2 weeks of treatment, continued to show improvement at the Week 6 assessment, and was maintained through Week 12 for both studies.
No diminution in the 12-hour bronchodilator effect was observed with either budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 80/4.5 or budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 160/4.5, as assessed by FEV1, following 12 weeks of therapy or at the last available visit.
FEV1 data from Study 1 evaluating budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 160/4.5 is displayed in Figures 3 and 4.
Figure 3 Mean Percent Change From Baseline in FEV1 on Day of Randomization (Study 1)
Figure 4 Mean Percent Change From Baseline in FEV1 at End of Treatment (Study 1)
Patients with asthma 6 to less than 12 years of age
The clinical program to support the efficacy of budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 80/4.5 in children 6 to less than 12 years of age included the following: 1) a budesonide dose confirmatory study, 2) a formoterol dose finding study, and 3) an efficacy and safety study of the budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate combination product.
The selection of budesonide 80 mcg is supported by a 6-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study in 304 pediatric patients (152 budesonide, 152 placebo) 6 to less than 12 years of age with asthma. Results showed that budesonide 80 mcg (2 inhalations twice daily) provided statistically significantly greater improvement compared to placebo for the primary endpoint of change from baseline to the treatment period average in pre-dose morning PEF and the key secondary endpoint of change in pre-dose morning FEV1. The selection of the formoterol dose is supported by a randomized, single dose, placebo-controlled, active-controlled (Foradil Aerolizer 12 mcg), 5-way cross-over study in which doses of 2.25, 4.5 and 9 mcg formoterol were administered in combination with budesonide in 54 pediatric patients 6 to less than 12 years of age with asthma. Results showed a dose response of formoterol compared to placebo for the primary endpoint of FEV1 averaged over 12 hours post-dose and the 9 mcg group showed numerically similar results compared to the active control.
The confirmatory efficacy study was a 12-week, randomized, double-blind, multicenter study in which budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 80/4.5 was compared with budesonide pMDI 80 mcg, each administered as 2 inhalations twice daily, in 184 pediatric patients 6 to less than 12 years of age with a documented clinical diagnosis of asthma. At trial entry, the children had a requirement for daily medium-dose range inhaled corticosteroid therapy or fixed combination of inhaled corticosteroid and LABA therapy, and exhibited symptoms despite treatment with a low-dose inhaled corticosteroid during a 2 to 4 week run-in period. The primary efficacy variable was change from baseline to Week 12 in clinic-measured 1-hour post-dose FEV1. In patients receiving budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 80/4.5, there was a statistically significant change compared to budesonide in 1-hour post-dose FEV1 which improved by 0.28 L from baseline to Week 12, as compared with 0.17 L for those receiving budesonide 80 mcg (mean difference 0.12 L; 95% CI: 0.03, 0.20) (see Figure 5).
Figure 5 Change From Baseline in Clinic-Measured 1-hour Post-dose FEV1 over 12 Weeks (Efficacy and Safety Study in Patients 6 to less than 12 years of age).
Similarly, improvement was noted in change from baseline to Week 12 for 1-hour post-dose clinic PEF (mean difference 25.5 L/min; 95% CI: 10.9, 40.0). Bronchodilatory effects were evident from the first assessment at 15 minutes on day 1 and were maintained at Week 12. The estimated mean difference between budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 80/4.5 and budesonide with respect to change from baseline to Week 12 in 15 minutes post-dose clinic FEV1 was 0.10 L (95% CI: 0.02, 0.18). No differences between budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate and budesonide were noted in nighttime awakenings, rescue albuterol use, or Pediatric Asthma Quality of Life Questionnaire (PAQLQ) scores. The proportion of patients with at least 0.5 points improvement from baseline to Week 12 in PAQLQ was 42% on budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 80/4.5 and 46% on budesonide 80 mcg.
Postmarketing Safety and Efficacy Study
A randomized, double-blind, parallel-group, safety study compared budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate with budesonide, each administered as 2 inhalations twice daily over 26 weeks (NCT01444430). The primary safety objective was to evaluate whether the addition of formoterol to budesonide therapy (budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate) was non-inferior to budesonide in terms of the risk of serious asthma-related events (asthma-related hospitalization, endotracheal intubation, and death). The study was designed to rule out a pre-defined risk margin of serious asthma-related events of 2.0. A blinded adjudication committee determined whether events were asthma-related.
This study enrolled patients who were 12 years of age and older, had a clinical diagnosis of asthma for at least 1 year, and had at least 1 asthma exacerbation requiring treatment with systemic corticosteroids or an asthma-related hospitalization in the previous year. Patients were stratified to one of the two dose levels of budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate or budesonide based on assessment of asthma control and ongoing asthma therapy. Patients with a history of life-threatening asthma were excluded. The study included 11,693 patients [5846 receiving budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate (80/4.5 or 160/4.5) and 5847 receiving budesonide (80 or 160 mcg)], whose mean age was 44 years, and of whom 66% were female and 69% were Caucasian.
Budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate was non-inferior to budesonide in terms of time to first serious asthma-related events based on the pre-specified risk margin, with an estimated hazard ratio of 1.07 [95% CI: 0.70, 1.65] (Table 7).
|
|||
|
Budesonide and Formoterol Fumarate Dihydrate (N*=5846) n† (%) |
Budesonide (N*=5847) n† (%) |
Budesonide and Formoterol Fumarate Dihydrate vs. Budesonide Hazard ratio (95% CI)‡ |
|
|
Serious asthma-related event§ |
43 (0.7) |
40 (0.7) |
1.07 (0.70, 1.65) |
|
Asthma-related death |
2 (<0.1) |
0 | |
|
Asthma-related endotracheal intubation |
1 (<0.1) |
0 | |
|
Asthma-related hospitalization |
42 (0.7) |
40 (0.7) | |
The primary efficacy endpoint was asthma exacerbations, defined as a deterioration of asthma that led to use of systemic corticosteroids for at least 3 days, or a hospitalization, or an emergency room visit that required systemic corticosteroids. The estimated hazard ratio for time to first asthma exacerbation rate for budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate relative to budesonide was 0.84 [95% CI: 0.75, 0.94]. This outcome was primarily driven by a reduction in systemic corticosteroid use.
14.2 Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Lung Function
The efficacy of budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 80/4.5 and budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 160/4.5 in the maintenance treatment of airflow obstruction in COPD patients was evaluated in two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled multinational studies, conducted over 6 months (Study 1) and 12 months (Study 2), in a total of 3668 patients (2416 males and 1252 females). The majority of patients (93%) were Caucasian. All patients were required to be at least 40 years of age, with a FEV1 of less than or equal to 50% predicted, a clinical diagnosis of COPD with symptoms for at least 2 years, and a smoking history of at least 10 pack years, prior to entering the trial. The mean prebronchodilator FEV1 at baseline of the patients enrolled in the study was 34% predicted. Forty-eight percent of the patients enrolled were on inhaled corticosteroids and 52.7% of patients were on short-acting anticholinergic bronchodilators during run-in. On randomization, inhaled corticosteroids were discontinued, and ipratropium bromide was allowed at a stable dose for those patients previously treated with short-acting anticholinergic bronchodilators. The co-primary efficacy variables in both studies were the change from baseline in average pre-dose and 1-hour post-dose FEV1 over the treatment period. The results of both studies 1 and 2 are described below.
Study 1
This was a 6-month, placebo-controlled study of 1704 COPD patients (mean % predicted FEV1 at baseline ranging from 33.5% -34.7%) conducted to demonstrate the efficacy and safety of budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate in the treatment of airflow obstruction in COPD. The patients were randomized to one of the following treatment groups: budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 160/4.5 (n=277), budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 80/4.5 (n=281), budesonide 160 mcg + formoterol 4.5 mcg (n=287), budesonide 160 mcg (n=275), formoterol 4.5 mcg (n=284), or placebo (n=300). Patients receiving budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 160/4.5, two inhalations twice daily, had significantly greater mean improvements from baseline in pre-dose FEV1 averaged over the treatment period [0.08 L, 10.7%] compared with formoterol 4.5 mcg [0.04 L, 6.9%] and placebo [0.01 L, 2.2%] (see Figure 6). Patients receiving budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 80/4.5, two inhalations twice daily, did not have significantly greater improvement from baseline in the pre-dose FEV1 averaged over the treatment period compared with formoterol 4.5 mcg.
Figure 6 Mean Percent Change From Baseline in Pre-dose FEV1 over 6 Months (Study 1)
Patients receiving budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 160/4.5, two inhalations twice daily, had significantly greater mean improvements from baseline in 1-hour post-dose FEV1 averaged over the treatment period [0.20 L, 22.6%], compared with budesonide 160 mcg [0.03 L, 4.9%] and placebo [0.03 L, 4.1%] (see Figure 7).
Figure 7 Mean Percent Change From Baseline in 1-hour Post-dose FEV1 Over 6 months (Study 1)
Study 2
This was a 12-month, placebo-controlled study of 1964 COPD patients (mean % predicted FEV1 at baseline ranging from 33.7% -35.5%) conducted to demonstrate the efficacy and safety of budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate in the treatment of airflow obstruction in COPD. The patients were randomized to one of the following treatment groups: budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 160/4.5 (n=494), budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 80/4.5 (n=494), formoterol 4.5 mcg (n=495), or placebo (n=481). Patients receiving budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 160/4.5, two inhalations twice daily, had significantly greater improvements from baseline in mean pre-dose FEV1 averaged over the treatment period [0.10 L, 10.8%] compared with formoterol 4.5 mcg [0.06 L, 7.2%] and placebo [0.01 L, 2.8%]. Patients receiving budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 80/4.5, two inhalations twice daily, did not have significantly greater improvements from baseline in the mean pre-dose FEV1 averaged over the treatment period compared to formoterol. Patients receiving budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 160/4.5, two inhalations twice daily, also had significantly greater mean improvements from baseline in 1-hour post-dose FEV1 averaged over the treatment period [0.21 L, 24.0%] compared with placebo [0.02 L, 5.2%].
Serial FEV1 measures over 12 hours were obtained in a subset of patients in Study 1 (n=99) and Study 2 (n=121). The median time to onset of bronchodilation, defined as an FEV1 increase of 15% or greater from baseline, occurred at 5 minutes post-dose. Maximum improvement (calculated as the average change from baseline at each timepoint) in FEV1 occurred at approximately 2 hours post-dose.
In both Studies 1 and 2, improvements in secondary endpoints of morning and evening peak expiratory flow and reduction in rescue medication use were supportive of the efficacy of budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 160/4.5.
Exacerbations
Studies 3 and 4 were primarily designed to evaluate the effect of budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 160/4.5 on COPD exacerbations.
Study 3
This was a 6-month, active-control study conducted to evaluate the effect of budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 160/4.5 compared to formoterol 4.5 mcg, each administered as 2 inhalations twice daily, on the rate of moderate and severe COPD exacerbations. COPD exacerbations were defined as worsening of 2 or more major symptoms (dyspnea, sputum volume, sputum color/purulence) or worsening of any 1 major symptom together with at least 1 of the minor symptoms: sore throat, colds (nasal discharge and/or nasal congestion), fever without other cause, increased cough or increased wheeze for at least 2 consecutive days. COPD exacerbations were considered of moderate severity if treatment of symptoms with systemic corticosteroids (≥3 days) and/or antibiotics were required, and were considered severe if hospitalization was required. The study randomized 1219 subjects to budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 160/4.5 (606) and formoterol 4.5 mcg (613) of which 57% were male and 92% were Caucasian. They had a mean age of 64 years and a median smoking history of 39 pack years, with 46% identified as current smokers. At run-in, the mean post-bronchodilator % predicted normal FEV1 was 48.7% (range: 16.0% to 78.1%), and patients had a history of at least 1 COPD exacerbation in the previous year treated with systemic corticosteroids and/or hospitalization. All subjects were treated with budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 160/4.5, two inhalations twice daily during a 4-week run-in period prior to being assigned trial treatment.
Study 4
This was a 12-month, active-control study which included 811 subjects treated with budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 160/4.5 or formoterol 4.5 mcg, each administered as 2 inhalations twice daily. The study was conducted to evaluate for COPD exacerbation reduction in patients with COPD. COPD exacerbations were defined as worsening of COPD that required a course of oral steroids for treatment and/or hospitalization. This study randomized 407 subjects to budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 160/4.5 and 404 to formoterol 4.5 mcg of which 61% were male and 83% were Caucasian. They had a mean age of 63 years and a median smoking history of 45 pack years, with 36% identified as current smokers. At run-in, the mean post-bronchodilator % predicted normal FEV1 was 37.8% (range: 11.75% to 76.50%), and a history of at least 1 COPD exacerbation in the previous year treated with systemic corticosteroids and/or antibiotics.
In Study 3, subjects treated with budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 160/4.5, two inhalations twice daily had a significantly lower annual rate of moderate/severe COPD exacerbations compared with formoterol 4.5 mcg with a reduction of 26% (95% CI: 9%, 39%). In Study 4, a significantly lower annual rate of exacerbations was also observed in subjects treated with budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 160/4.5 compared with formoterol 4.5 mcg with a reduction of 35% (95% CI: 20%, 47%) (Table 8).
| n | Annual Rate Estimate | Rate ratio Budesonide and Formoterol Fumarate Dihydrate 160/4.5 vs. Formoterol 4.5 mcg | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Treatment |
Estimate |
95% CI |
||
|
Study 3 | ||||
|
Budesonide and Formoterol Fumarate Dihydrate 160/4.5 |
606 |
0.94 |
0.74 |
0.61, 0.91 |
|
Formoterol 4.5 mcg |
613 |
1.27 | ||
|
Study 4 | ||||
|
Budesonide and Formoterol Fumarate Dihydrate 160/4.5 |
404 |
0.68 |
0.65 |
0.53, 0.80 |
|
Formoterol 4.5 mcg |
403 |
1.05 | ||
n – Number of patients included in efficacy analysis set.
Health-related quality of life was measured using the St. George’s Respiratory Questionnaire (SGRQ) in both COPD exacerbation clinical studies.
In Study 3, the SGRQ responder rates at 6-months (defined as an improvement in score of 4 or more as a threshold) were 40% and 33% for budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 160/4.5 and formoterol 4.5 mcg, respectively, with an odds ratio of 1.5 (95% CI: 1.0, 2.0) for budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 160/4.5 vs. formoterol 4.5 mcg. In Study 4, the responder rates at 12-months were 50% and 49% for budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 160/4.5 and formoterol 4.5 mcg, respectively, with an odds ratio of 1.0 (95% CI: 0.8, 1,4) for budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 160/4.5 vs. formoterol 4.5 mcg.
16. How is Budesonide and Formoterol Aerosol supplied
BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL is available in two strengths and is supplied in the following package sizes:
|
Package Size |
NDC |
||
|
BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL |
80/4.5 |
120 Inhalations |
0310-7372-20 |
|
BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL |
160/4.5 |
120 Inhalations |
0310-7370-20 |
Each strength is supplied as a pressurized aluminum canister with an attached counting device, a red plastic actuator body with a white mouthpiece, and attached gray dust cap. Each 120 inhalation canister has a net fill weight of 10.2 grams. Each canister is packaged in a foil overwrap pouch with desiccant sachet and placed into a carton. Each carton contains one canister and a Patient Information leaflet.
The BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL canister should only be used with the BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL actuator, and the BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL actuator should not be used with any other inhalation drug product.
The correct amount of medication in each inhalation cannot be ensured after the labeled number of inhalations from the canister have been used, even though the inhaler may not feel completely empty and may continue to operate. The inhaler should be discarded when the labeled number of inhalations have been used or within 3 months after removal from the foil pouch. Never immerse the canister into water to determine the amount remaining in the canister (“float test”).
Store at controlled room temperature 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F) [see USP]. Store the inhaler with the mouthpiece down.
For best results, the canister should be at room temperature before use. Shake well for 5 seconds before using.
Keep out of the reach of children. Avoid spraying in eyes.
CONTENTS UNDER PRESSURE.
Do not puncture or incinerate. Do not store near heat or open flame. Exposure to temperatures over 120ºF may cause bursting. Never throw container into fire or incinerator.
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information and Instructions for Use).
Serious Asthma-Related Events: Inform patients with asthma that LABA when used alone increases the risk of asthma-related hospitalization or asthma-related death. Available data show that when ICS and LABA are used together, such as with budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate, there is not a significant increase in risk of these events.
Not for Acute Symptoms: Inform patients that budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate is not meant to relieve acute symptoms of asthma or COPD and extra doses should not be used for that purpose. Advise patients to treat acute symptoms with an inhaled, short-acting beta2-agonist such as albuterol. Provide patients with such medication and instruct the patient in how it should be used.
Instruct patients to seek medical attention immediately if they experience any of the following:
- •
- Decreasing effectiveness of inhaled, short-acting beta2-agonists
- •
- Need for more inhalations than usual of inhaled, short-acting beta2-agonists
- •
- Significant decrease in lung function as outlined by the physician
Tell patients they should not stop therapy with budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate without physician/provider guidance since symptoms may recur after discontinuation.
Do Not Use Additional Long-Acting Beta2-Agonists: Instruct patients not to use other LABA for asthma and COPD.
Local Effects: Inform patients that localized infections with Candida albicans occurred in the mouth and pharynx in some patients. If oropharyngeal candidiasis develops, it should be treated with appropriate local or systemic (i.e., oral) antifungal therapy while still continuing therapy with budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate, but at times therapy with budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate may need to be temporarily interrupted under close medical supervision. Rinsing the mouth with water without swallowing after inhalation is advised to reduce the risk of thrush.
Pneumonia: Patients with COPD have a higher risk of pneumonia; instruct them to contact their healthcare provider if they develop symptoms of pneumonia.
Immunosuppression: Warn patients who are on immunosuppressant doses of corticosteroids to avoid exposure to chicken pox or measles and, if exposed, to consult their physician without delay. Inform patients of potential worsening of existing tuberculosis, fungal, bacterial, viral, or parasitic infections, or ocular herpes simplex.
Hypercorticism and Adrenal Suppression: Advise patients that budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate may cause systemic corticosteroid effects of hypercorticism and adrenal suppression. Additionally, inform patients that deaths due to adrenal insufficiency have occurred during and after transfer from systemic corticosteroids. Patients should taper slowly from systemic corticosteroids if transferring to budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate.
Reduction in Bone Mineral Density: Advise patients who are at an increased risk for decreased BMD that the use of corticosteroids may pose an additional risk.
Reduced Growth Velocity: Inform patients that orally inhaled corticosteroids, a component of budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate, may cause a reduction in growth velocity when administered to pediatric patients. Physicians should closely follow the growth of children and adolescents taking corticosteroids by any route.
Ocular Effects: Long-term use of inhaled corticosteroids may increase the risk of some eye problems (cataracts or glaucoma); consider regular eye examinations.
Risks Associated With Beta-Agonist Therapy: Inform patients of adverse effects associated with beta2-agonists, such as palpitations, chest pain, rapid heart rate, tremor, or nervousness.
©AstraZeneca 2019
Manufactured for: AstraZeneca Pharmaceuticals LP, Wilmington, DE 19850
By: AstraZeneca Dunkerque Production, Dunkerque, France
Product of France
|
Patient Information
BUDESONIDE (bue-DES-oh-nide) AND FORMOTEROL (for-MOH-teh-rol) FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL
BUDESONIDE (bue-DES-oh-nide) AND FORMOTEROL (for-MOH-teh-rol) FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL
|
||
|
What is BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL? BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL combines an inhaled corticosteroid medicine (ICS), budesonide and a long-acting beta2-adrenergic agonist (LABA) medicine, formoterol.
BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL is not used to relieve sudden breathing problems and will not replace a rescue inhaler. BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL is used for asthma and COPD as follows:
|
||
|
Do not use BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL:
|
||
|
Before you use BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL and certain other medicines may interact with each other. This may cause serious side effects. Especially tell your healthcare provider if you take antifungal or anti-HIV medicines. Know all the medicines you take. Keep a list and show it to your healthcare provider and pharmacist each time you get a new medicine. |
||
|
How should I use BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL? See the step-by-step instructions for using BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL at the end of this Patient Information leaflet. Do not use BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL unless your healthcare provider has taught you and you understand everything. Ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist if you have any questions.
|
||
|
What are the possible side effects of BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL? BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL may cause serious side effects, including:
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
The most common side effects of BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL include:
|
||
|
|
|
|
People with COPD:
Tell your healthcare provider about any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away. These are not all the possible side effects of BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. You may also report side effects to AstraZeneca at 1-800-236-9933. |
||
|
How should I store BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL?
|
||
|
General Information about the safe and effective use of BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL. Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. You can ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for information about BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL that is written for health professionals. |
||
|
What are the ingredients in BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL? Active ingredients: micronized budesonide and micronized formoterol fumarate dihydrate Manufactured for: AstraZeneca Pharmaceuticals LP, Wilmington, DE 19850 By: AstraZeneca Dunkerque Production, Dunkerque, France Product of France For more information, call 1-800-236-9933. |
||
Revised: July 2019
Instructions for Use
BUDESONIDE (bue-DES-oh-nide) AND FORMOTEROL (for-MOH-teh-rol) FUMARATE DIHYDRATE
INHALATION AEROSOL
(budesonide 80 mcg and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 4.5 mcg)
BUDESONIDE (bue-DES-oh-nide) AND FORMOTEROL (for-MOH-teh-rol) FUMARATE DIHYDRATE
INHALATION AEROSOL
(budesonide 160 mcg and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 4.5 mcg)
Upright Position
How to Use BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL
Follow the instructions below for using BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL. You will breathe-in (inhale) the medicine. If you have any questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Preparing your BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL inhaler for use
- 1.
- Take your BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL out of the moisture-protective foil pouch before you use it for the first time and throw the foil away. Write the date that you open the foil pouch on the box.
- 2.
- A counter is attached to the top of the metal canister. The counter will count down each time you release a puff of BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL. The arrow points to the number of inhalations (puffs) left in the canister. The counter will stop counting at zero (“0”).
- 3.
- Use the BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL canister only with the red BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL inhaler supplied with the product. Parts of the BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL inhaler should not be used with parts from any other inhalation product.
- 4.
- Shake your BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL inhaler well for 5 seconds right before each use. Remove the mouthpiece cover by squeezing gently at both sides, then pulling out (see Figure 2). Check the mouthpiece for foreign objects before use.
- 1.
-
Priming your BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL inhaler
Before you use BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL for the first time, you will need to prime it. To prime BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL, hold it in the upright position. See Figure 1. Shake the BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL inhaler well for 5 seconds. Hold your BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL inhaler facing away from you and press down firmly and fully on the top of the counter on the BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL inhaler to release a test spray. Then shake it again for 5 seconds and release a second test spray. Your BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL inhaler is now primed and ready for use. After you have primed the BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL inhaler for the first time, the counter will read 120.
If you do not use your BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL inhaler for more than 7 days or if you drop it, you will need to prime again.
Ways to hold the BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL inhaler for use
OR
Using your BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL inhaler
- 1.
- Shake your BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL inhaler well for 5 seconds. Remove the mouthpiece cover. Check the mouthpiece for foreign objects.
- 2.
- Breathe out fully (exhale). Hold the BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL inhaler up to your mouth. Place the white mouthpiece fully into your mouth and close your lips around it. Make sure that the BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL inhaler is upright and that the opening of the mouthpiece is pointing towards the back of your throat (see Figure 5).
- 1.
- Breathe in (inhale) deeply and slowly through your mouth. Press down firmly and fully on the top of the counter on the BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL inhaler to release the medicine (see Figures 3 and 4).
- 2.
- Continue to breathe in (inhale) and hold your breath for about 10 seconds, or for as long as is comfortable. Before you breathe out (exhale), release your finger from the top of the counter. Keep the BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL inhaler upright and remove from your mouth.
- 3.
- Shake the BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL inhaler again for 5 seconds and repeat steps 7 to 9.
After using your BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL inhaler
- 1.
- After use, close the mouthpiece cover by pushing until it clicks in place.
- 2.
- After you finish taking BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL (2 puffs), rinse your mouth with water. Spit out the water. Do not swallow it.
Reading the counter
- •
- The arrow on the counter on the top of the BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL inhaler points to the number of inhalations (puffs) left in your inhaler.
COUNTER
- •
- The counter will count down each time you release a puff of medicine (either when priming your BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL inhaler or when taking the medicine).
- •
- When the arrow on the counter approaches 20, you will notice the beginning of a yellow area letting you know that it is time to call your healthcare provider for a refill.
COUNTER
- •
- It is important that you pay attention to the number of inhalations (puffs) left in your BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL inhaler by reading the counter. Throw away BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL when the counter shows zero (“0”) or 3 months after you take your BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL inhaler out of its foil pouch, whichever comes first. Your BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL inhaler may not feel empty and it may continue to operate, but you will not get the right amount of medicine if you keep using it. Use a new BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL inhaler and follow the instructions for priming (see instruction 5 above).
How to clean your BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL inhaler
Clean the white mouthpiece of your BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL inhaler every 7 days. To clean the mouthpiece:
- •
- Remove the grey mouthpiece cover
- •
- Wipe the inside and outside of the white mouthpiece opening with a clean, dry cloth
- •
- Replace the mouthpiece cover
- •
- Do not put the BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL inhaler into water
- •
- Do not try to take apart your BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE INHALATION AEROSOL inhaler
Manufactured for: AstraZeneca Pharmaceuticals LP, Wilmington, DE 19850
By: AstraZeneca Dunkerque Production, Dunkerque, France
Product of France
This Patient Information and Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
©AstraZeneca 2019
Revised: July 2019
PACKAGE/LABEL DISPLAY PANEL – 80/4.5
NDC 0310-7372-20
Store Upright
Budesonide and Formoterol
Fumarate Dihydrate
Inhalation Aerosol 80/4.5
budesonide 80 mcg/formoterol fumarate dihydrate 4.5 mcg
INHALATION AEROSOL
120 inhalations
For Oral Inhalation only
Rx only
Manufactured for:
AstraZeneca LP, Wilmington, DE 19850
By: AstraZeneca Dunkerque Production
Dunkerque, France
Product of France
© AstraZeneca 2019
PACKAGE/LABEL DISPLAY PANEL – 160/4.5
NDC 0310-7370-20
Store Upright
Budesonide and Formoterol
Fumarate Dihydrate
Inhalation Aerosol 160/4.5
budesonide 160 mcg/formoterol fumarate dihydrate 4.5 mcg
INHALATION AEROSOL
120 inhalations
For Oral Inhalation only
Rx only
Manufactured for:
AstraZeneca LP, Wilmington, DE 19850
By: AstraZeneca Dunkerque Production
Dunkerque, France
Product of France
© AstraZeneca 2019
| BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE
budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate aerosol |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BUDESONIDE AND FORMOTEROL FUMARATE DIHYDRATE
budesonide and formoterol fumarate dihydrate aerosol |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - AstraZeneca Pharmaceuticals LP (054743190) |
| Registrant - AstraZeneca PLC (230790719) |