Drug Detail:Cayston inhalation (Aztreonam (inhalation) [ az-tree-oh-nam ])
Drug Class: Miscellaneous antibiotics
Highlights of Prescribing Information
CAYSTON® (aztreonam for inhalation solution), for oral inhalation use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1986
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of CAYSTON and other antibacterial drugs, CAYSTON should be used only to treat patients with cystic fibrosis (CF) known to have Pseudomonas aeruginosa in the lungs. (1)
Indications and Usage for Cayston
CAYSTON is a monobactam antibacterial indicated to improve respiratory symptoms in cystic fibrosis (CF) patients with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Safety and effectiveness have not been established in pediatric patients below the age of 7 years, patients with FEV1 <25% or >75% predicted, or patients colonized with Burkholderia cepacia. (1)
Cayston Dosage and Administration
- Administer one dose (one single use vial and one ampule of diluent) 3 times a day for 28 days. (2.1)
- Use dose immediately after reconstitution. (2.2)
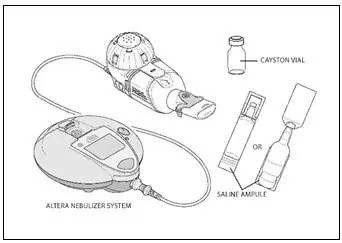
- Administer only with the Altera® Nebulizer System. Do not administer with any other type of nebulizer. (2.3)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
- Lyophilized aztreonam (75 mg/vial) (3)
- Diluent (0.17% sodium chloride): 1 mL/ampule (3)
Contraindications
Contraindicated in patients with a known allergy to aztreonam. (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Allergic reaction to CAYSTON was seen in clinical trials. Stop treatment if an allergic reaction occurs. Use caution when CAYSTON is administered to patients with a known allergic reaction to beta-lactams. (5.1)
- Bronchospasm has been reported with CAYSTON. Stop treatment if chest tightness develops during nebulizer use. (5.2)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Common adverse reactions (more than 5%) occurring more frequently in CAYSTON patients are cough, nasal congestion, wheezing, pharyngolaryngeal pain, pyrexia, chest discomfort, abdominal pain and vomiting. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Gilead Sciences, Inc. at 1-800-GILEAD5, option 3 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 11/2019
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Cayston
CAYSTON® is indicated to improve respiratory symptoms in cystic fibrosis (CF) patients with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Safety and effectiveness have not been established in pediatric patients below the age of 7 years, patients with FEV1 <25% or >75% predicted, or patients colonized with Burkholderia cepacia [see Clinical Studies (14)].
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of CAYSTON and other antibacterial drugs, CAYSTON should be used only to treat patients with CF known to have Pseudomonas aeruginosa in the lungs.
2. Cayston Dosage and Administration
2.1 Dosing Information
The recommended dose of CAYSTON for both adults and pediatric patients 7 years of age and older is one single-use vial (75 mg of aztreonam) reconstituted with 1 mL of sterile diluent administered 3 times a day for a 28-day course (followed by 28 days off CAYSTON therapy). Dosage is not based on weight or adjusted for age. Doses should be taken at least 4 hours apart.
CAYSTON is administered by inhalation using an Altera® Nebulizer System. Patients should use a bronchodilator before administration of CAYSTON.
2.2 Instructions for CAYSTON Reconstitution
CAYSTON should be administered immediately after reconstitution. Do not reconstitute CAYSTON until ready to administer a dose.
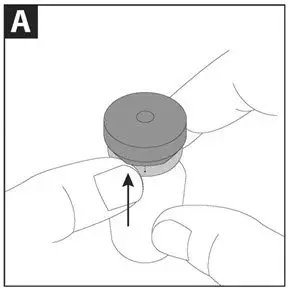
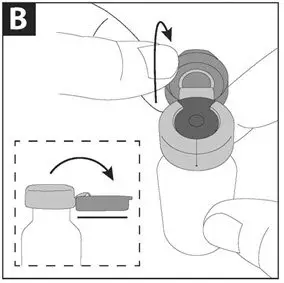
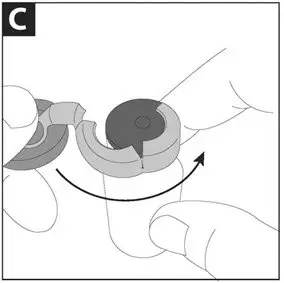
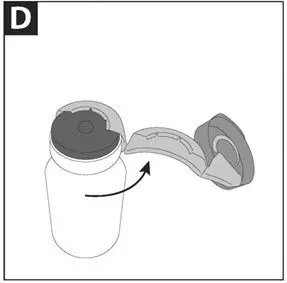
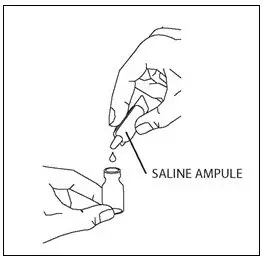
Take one amber glass vial containing CAYSTON and one diluent ampule from the carton. To open the glass vial, carefully remove the blue cap and metal ring and remove the gray rubber stopper. Twist the tip off the diluent ampule and squeeze the liquid into the glass vial. Replace the rubber stopper, then gently swirl the vial until contents have completely dissolved.
The empty vial, stopper, and diluent ampule should be disposed of properly upon completion of dosing.
2.3 Instructions for CAYSTON Administration
CAYSTON is administered by inhalation using an Altera Nebulizer System. CAYSTON should not be administered with any other nebulizer. CAYSTON should not be mixed with any other drugs in the Altera Nebulizer Handset.
CAYSTON is not for intravenous or intramuscular administration.
Patients should use a bronchodilator before administration of CAYSTON. Short-acting bronchodilators can be taken between 15 minutes and 4 hours prior to each dose of CAYSTON. Alternatively, long-acting bronchodilators can be taken between 30 minutes and 12 hours prior to administration of CAYSTON. For patients taking multiple inhaled therapies, the recommended order of administration is as follows: bronchodilator, mucolytics, and lastly, CAYSTON.
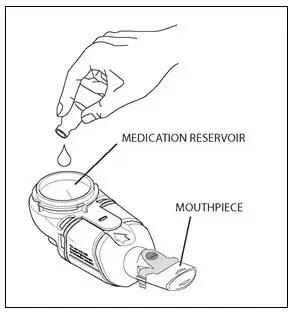
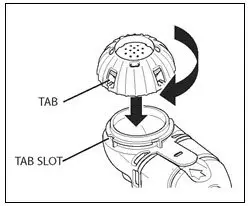
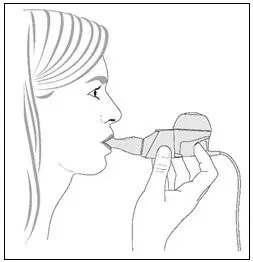
To administer CAYSTON, pour the reconstituted solution into the handset of the nebulizer system. Turn the unit on. Place the mouthpiece of the handset in your mouth and breathe normally only through your mouth. Administration typically takes between 2 and 3 minutes. Further patient instructions on how to administer CAYSTON are provided in the FDA-approved patient labeling. Instructions on testing nebulizer functionality and cleaning the handset are provided in the Instructions for Use included with the nebulizer system.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
A dose of CAYSTON consists of a single-use vial of sterile, lyophilized aztreonam (75 mg) reconstituted with a 1 mL ampule of sterile diluent (0.17% sodium chloride). Reconstituted CAYSTON is administered by inhalation.
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Allergic Reactions
Severe allergic reactions have been reported following administration of aztreonam for injection to patients with no known history of exposure to aztreonam. In addition, allergic reaction with facial rash, facial swelling, and throat tightness was reported with CAYSTON in clinical trials. If an allergic reaction to CAYSTON occurs, stop administration of CAYSTON and initiate treatment as appropriate.
Caution is advised when administering CAYSTON to patients if they have a history of beta-lactam allergy, although patients with a known beta-lactam allergy have received CAYSTON in clinical trials and no severe allergic reactions were reported. A history of allergy to beta-lactam antibiotics, such as penicillins, cephalosporins, and/or carbapenems, may be a risk factor, since cross-reactivity may occur.
5.2 Bronchospasm
Bronchospasm is a complication associated with nebulized therapies, including CAYSTON. Reduction of 15% or more in forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) immediately following administration of study medication after pretreatment with a bronchodilator was observed in 3% of patients treated with CAYSTON.
5.3 Decreases in FEV1 After 28-Day Treatment Cycle
In clinical trials, patients with increases in FEV1 during a 28-day course of CAYSTON were sometimes treated for pulmonary exacerbations when FEV1 declined after the treatment period. Healthcare providers should consider a patient's baseline FEV1 measured prior to CAYSTON therapy and the presence of other symptoms when evaluating whether post-treatment changes in FEV1 are caused by a pulmonary exacerbation.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of drugs cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The safety of CAYSTON was evaluated in 344 patients from two placebo-controlled trials and one open-label follow-on trial. In controlled trials, 146 patients with CF received 75 mg CAYSTON 3 times a day for 28 days.
Table 1 displays adverse reactions reported in more than 5% of patients treated with CAYSTON 3 times a day in placebo-controlled trials. The listed adverse reactions occurred more frequently in CAYSTON-treated patients than in placebo-treated patients.
| Event (Preferred Term) | Placebo (N=160) n (%) | CAYSTON 75 mg 3 times a day (N=146) n (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Cough | 82 (51%) | 79 (54%) |
| Nasal congestion | 19 (12%) | 23 (16%) |
| Wheezing | 16 (10%) | 23 (16%) |
| Pharyngolaryngeal pain | 17 (11%) | 18 (12%) |
| Pyrexia | 9 (6%) | 19 (13%) |
| Chest discomfort | 10 (6%) | 11 (8%) |
| Abdominal Pain | 8 (5%) | 10 (7%) |
| Vomiting | 7 (4%) | 9 (6%) |
Adverse reactions that occurred in less than 5% of patients treated with CAYSTON were bronchospasm (3%) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] and rash (2%).
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
In addition to adverse reactions reported from clinical trials, the following possible adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of CAYSTON. Because these events have been reported voluntarily from a population of unknown size, estimates of frequency cannot be made.
MUSCULOSKELETAL AND CONNECTIVE TISSUE DISORDERS
Arthralgia, joint swelling
7. Drug Interactions
No formal clinical studies of drug interactions with CAYSTON have been conducted.
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.4 Pediatric Use
Patients 7 years and older were included in clinical trials with CAYSTON. Fifty-five patients under 18 years of age received CAYSTON in placebo-controlled trials. No dose adjustments were made for pediatric patients. Pyrexia was more commonly reported in pediatric patients than in adult patients. Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients below the age of 7 years have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical trials of CAYSTON did not include CAYSTON-treated patients aged 65 years of age and older to determine whether they respond differently from younger patients.
8.6 Use in Patients with Renal Impairment
Aztreonam is known to be excreted by the kidney. Placebo-controlled clinical trials with CAYSTON excluded patients with abnormal baseline renal function (defined as serum creatinine greater than 2 times the upper limit of normal range). Given the low systemic exposure of aztreonam following administration of CAYSTON, clinically relevant accumulation of aztreonam is unlikely to occur in patients with renal impairment. Therefore, CAYSTON may be administered to patients with mild, moderate and severe renal impairment with no dosage adjustment.
10. Overdosage
No overdoses have been reported with CAYSTON in clinical trials to date. In clinical trials, 225 mg doses of CAYSTON via inhalation were associated with higher rates of drug-related respiratory adverse reactions, particularly cough. Since the peak plasma concentration of aztreonam following administration of CAYSTON (75 mg) is approximately 0.6 mcg/mL, compared to a serum concentration of 54 mcg/mL following administration of aztreonam for injection (500 mg), no systemic safety issues associated with CAYSTON overdose are anticipated.
11. Cayston Description
A dose of CAYSTON consists of a 2 mL amber glass vial containing lyophilized aztreonam (75 mg) and lysine (46.7 mg), and a low-density polyethylene ampule containing 1 mL sterile diluent (0.17% sodium chloride). The reconstituted solution is for inhalation. The formulation contains no preservatives or arginine.
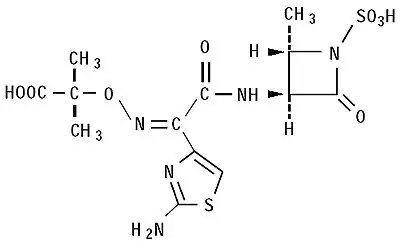
The active ingredient in CAYSTON is aztreonam, a monobactam antibacterial. The monobactams are structurally different from beta-lactam antibiotics (e.g., penicillins, cephalosporins, carbapenems) due to a monocyclic nucleus. This nucleus contains several side chains; sulfonic acid in the 1-position activates the nucleus, an aminothiazolyl oxime side chain in the 3-position confers specificity for aerobic Gram-negative bacteria including Pseudomonas spp., and a methyl group in the 4-position enhances beta-lactamase stability.
Aztreonam is designated chemically as (Z)-2-[[[(2-amino-4-thiazolyl)[[(2S,3S)-2-methyl-4-oxo-1-sulfo-3-azetidinyl]carbamoyl]methylene]amino]oxy]-2-methylpropionic acid. The structural formula is presented below:
CAYSTON is a white to off-white powder. CAYSTON is sterile, hygroscopic, and light sensitive. Once reconstituted with the supplied diluent, the pH range is 4.5 to 6.0.
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
A 104-week rat inhalation toxicology study to assess the carcinogenic potential of aztreonam demonstrated no drug-related increase in the incidence of tumors. Rats were exposed to aerosolized aztreonam for up to 4 hours per day. Peak plasma levels of aztreonam averaging approximately 6.8 mcg/mL were measured in rats at the highest dose level. This is approximately 12-fold higher than the average peak plasma level measured in humans following CAYSTON therapy.
Genetic toxicology studies performed in vitro demonstrated that aztreonam did not induce structural chromosome aberrations in CHO cells and did not induce mutations at the TK locus in mouse lymphoma L5178Y TK+/- cells. In vivo, aztreonam was not clastogenic in mouse bone marrow cells.
Aztreonam did not impair the fertility of rats when administered parenterally at doses up to 2400 mg/kg/day that would provide systemic exposures significantly higher than peak plasma levels measured in humans following CAYSTON therapy.
14. Clinical Studies
CAYSTON was evaluated over a period of 28 days of treatment in a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter trial that enrolled patients with CF and P. aeruginosa. This trial was designed to evaluate improvement in respiratory symptoms. Patients 7 years of age and older and with FEV1 of 25% to 75% predicted were enrolled. All patients received CAYSTON or placebo on an outpatient basis administered with the Altera Nebulizer System. All patients were required to take a dose of an inhaled bronchodilator (beta-agonist) prior to taking a dose of CAYSTON or placebo. Patients were receiving standard care for CF, including drugs for obstructive airway diseases.
The trial enrolled 164 patients with CF and P. aeruginosa. The mean age was 30 years, and the mean baseline FEV1 % predicted was 55%; 43% were females and 96% were Caucasian. These patients were randomized in a 1:1 ratio to receive either CAYSTON (75 mg) or volume-matched placebo administered by inhalation 3 times a day for 28 days. Patients were required to have been off antibiotics for at least 28 days before treatment with study drug. The primary efficacy endpoint was improvement in respiratory symptoms on the last day of treatment with CAYSTON or placebo. Respiratory symptoms were also assessed two weeks after the completion of treatment with CAYSTON or placebo. Changes in respiratory symptoms were assessed using a questionnaire that asks patients to report on symptoms like cough, wheezing, and sputum production.
Improvement in respiratory symptoms was noted for CAYSTON-treated patients relative to placebo-treated patients on the last day of drug treatment. Statistically significant improvements were seen in both adult and pediatric patients but were substantially smaller in adult patients. Two weeks after completion of treatment, a difference in respiratory symptoms between treatment groups was still present, though the difference was smaller.
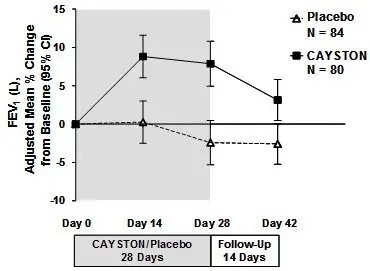
Pulmonary function, as measured by FEV1 (L), increased from baseline in patients treated with CAYSTON (see Figure 1). The treatment difference at Day 28 between CAYSTON-treated and placebo-treated patients for percent change in FEV1 (L) was statistically significant at 10% (95% CI: 6%, 14%). Improvements in FEV1 were comparable between adult and pediatric patients. Two weeks after completion of drug treatment, the difference in FEV1 between CAYSTON and placebo groups had decreased to 6% (95% CI: 2%, 9%).
Figure 1 Adjusted Mean Percent Change in FEV1 from Baseline to Study End (Days 0–42)
15. References
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria that Grow Aerobically—Eighth Edition; Approved Standard. CLSI Document M7-A8. CLSI, Wayne, PA 19087. January 2009.
16. How is Cayston supplied
Each kit for a 28-day course of CAYSTON contains 84 sterile vials of CAYSTON and 88 ampules of sterile diluent packed in 2 cartons, each carton containing a 14-day supply. The four additional diluent ampules are provided in case of spillage.
| Package Configuration | Dosage Strength | NDC |
|---|---|---|
| 28-Day Kit | 75 mg | 61958-0901-1 |
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information and Instructions for Use).
| This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration | Rev November 2019 |
| PATIENT INFORMATION CAYSTON® (kay-stun) (aztreonam for inhalation solution) for oral inhalation use |
|
| What is CAYSTON?
CAYSTON is a prescription medicine that is used to improve breathing symptoms in people with cystic fibrosis (CF) who have a lung infection caused by a bacterium called Pseudomonas aeruginosa. CAYSTON contains an antibacterial medicine called aztreonam. |
|
|
|
| It is not known if CAYSTON is safe and effective: | |
|
|
| Do not take CAYSTON if you are allergic to aztreonam, or any of the ingredients in CAYSTON. See the end of this Patient Information for a complete list of ingredients in CAYSTON. |
|
| Before you take CAYSTON, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you: | |
|
|
| Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. Some medicines may affect how CAYSTON works. |
|
| How should I take CAYSTON? | |
|
|
| What are the possible side effects of CAYSTON? CAYSTON may cause serious side effects, including: |
|
|
|
| The most common side effects of CAYSTON include: | |
|
|
| Other possible side effects of CAYSTON include swelling or pain in joints. Tell your healthcare provider if you have any new or worsening symptoms while taking CAYSTON. Tell your healthcare provider about any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away. |
|
| These are not all the possible side effects of CAYSTON. Call your healthcare provider for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. |
|
| How should I store CAYSTON? | |
|
|
| Keep CAYSTON and all medicines out of the reach of children. | |
| General information about the safe and effective use of CAYSTON
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use CAYSTON for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give CAYSTON to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about CAYSTON that is written for health professionals. |
|
| What are the ingredients in CAYSTON? Active ingredient: aztreonam Inactive ingredient: lysine, sodium chloride (diluent) Manufactured and distributed by: Gilead Sciences, Inc. Foster City, CA 94404 CAYSTON is a registered trademark of Gilead Sciences, Inc. ©2019 Gilead Sciences, Inc. All rights reserved. 50-814-GS-004 For more information, call 1-877-7CAYSTON (1-877-722-9786). |
|
| CAYSTON
aztreonam kit |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Gilead Sciences, Inc. (185049848) |