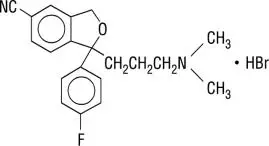
Drug Detail:Celexa (Citalopram [ si-tal-o-pram ])
Drug Class: Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors
Highlights of Prescribing Information
CELEXA (citalopram) tablets, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1998
WARNING: SUICIDAL THOUGHTS AND BEHAVIORS
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
-
Increased risk of suicidal thoughts and behavior in pediatric and young adult patients taking antidepressants. Closely monitor all antidepressant-treated patients for clinical worsening and emergence of suicidal thoughts and behaviors (5.1).
- CELEXA is not approved for use in pediatric patients (8.4).
Recent Major Changes
Warnings and Precautions (5.3, 5.4) 08/2023
Indications and Usage for Celexa
CELEXA is a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) indicated for the treatment of major depressive disorder (MDD) in adults (1).
Celexa Dosage and Administration
- Administer once daily with or without food (2).
- Initial dosage is 20 mg once daily; after one week may increase to maximum dosage of 40 mg once daily (2.1).
- Patients greater than 60 years of age, patients with hepatic impairment, and CYP2C19 poor metabolizers: maximum recommended dosage is 20 mg once daily (2.2).
- When discontinuing CELEXA, reduce dosage gradually (2.4, 5.6).
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Tablets: 10 mg; 20 mg, scored; and 40 mg, scored (3)
Contraindications
- Concomitant use of monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) or use within 14 days of discontinuing a MAOI (4).
- Concomitant use of pimozide (4).
- Known hypersensitivity to citalopram or any of the inactive ingredients of CELEXA (4).
Warnings and Precautions
-
QT-Prolongation and Torsade de Pointes: Dose-dependent QTc prolongation, Torsade de pointes, ventricular tachycardia, and sudden death have occurred. Avoid use of CELEXA in patients with congenital long QT syndrome, bradycardia, hypokalemia or hypomagnesemia, recent acute myocardial infarction, or uncompensated heart failure and patients taking other drugs that prolong the QTc interval. Monitor electrolytes in patients at high risk for hypokalemia or hypomagnesemia. Discontinue CELEXA in patients with persistent QTc measurements > 500 ms (5.2, 7).
-
Serotonin Syndrome: Increased risk when co-administered with other serotonergic agents, but also when taken alone. If occurs, discontinue CELEXA and serotonergic agents and initiate supportive measures (5.3).
-
Increased Risk of Bleeding: Concomitant use of aspirin, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, other antiplatelet drugs, warfarin and other anticoagulants may increase this risk (5.4).
-
Activation of Mania/Hypomania: Screen patients for bipolar disorder (5.5).
-
Seizures: Use with caution in patients with seizure disorder (5.7).
-
Angle-Closure Glaucoma: Avoid use of CELEXA in patients with untreated anatomically narrow angles (5.8).
-
Hyponatremia: Can occur in association with syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion (5.9).
- Sexual Dysfunction: CELEXA may cause symptoms of sexual dysfunction (5.10).
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reaction (incidence ≥ 5% and twice placebo) is ejaculation disorder (primarily ejaculation delay) (6.1).
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Allergan at 1-800-678-1605 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
CYP2C19 Inhibitors: CELEXA 20 mg daily is the maximum recommended dosage for patients taking concomitant CYP2C19 inhibitors (5.2, 7.1).
Use In Specific Populations
- Pregnancy: SSRI use, particularly late in pregnancy, may increase the risk for persistent pulmonary hypertension and symptoms of poor adaptation (respiratory distress, temperature instability, feeding difficulties, hypotonia, tremor, irritability) in the neonate (8.1).
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 8/2023
Related/similar drugs
sertraline, trazodone, fluoxetine, Lexapro, venlafaxine, citalopram, ZoloftFull Prescribing Information
WARNING: SUICIDAL THOUGHTS AND BEHAVIORS
Antidepressants increased the risk of suicidal thoughts and behaviors in pediatric and young adult patients in short-term studies. Closely monitor all antidepressant-treated patients for clinical worsening, and for emergence of suicidal thoughts and behaviors [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. CELEXA is not approved for use in pediatric patients [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
1. Indications and Usage for Celexa
CELEXA is indicated for the treatment of major depressive disorder (MDD) in adults [see Clinical Studies (14)].
2. Celexa Dosage and Administration
2.1 Recommended Dosage
Administer CELEXA once daily, with or without food, at an initial dosage of 20 mg once daily, with an increase to a maximum dosage of 40 mg once daily at an interval of no less than one week.
Dosages above 40 mg once daily are not recommended due to the risk of QT prolongation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
2.2 Screen for Bipolar Disorder Prior to Starting CELEXA
Prior to initiating treatment with CELEXA or another antidepressant, screen patients for a personal or family history of bipolar disorder, mania, or hypomania [See Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
2.3 Recommended Dosage for Specific Populations
The maximum recommended dosage of CELEXA for patients who are greater than 60 years of age, patients with hepatic impairment, and for CYP2C19 poor metabolizers is 20 mg once daily [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
2.4 Dosage Modifications with Concomitant Use of CYP2C19 Inhibitors
The maximum recommended dosage of CELEXA when used concomitantly with a CYP2C19 inhibitor is 20 mg once daily [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2), Drug Interactions (7)].
2.5 Switching Patients to or from a Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitor Antidepressant
At least 14 days must elapse between discontinuation of a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) antidepressant and initiation of therapy with CELEXA. Conversely, at least 14 days must elapse after stopping CELEXA before starting an MAOI antidepressant [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
CELEXA tablets are available as:
- 10 mg: beige, oval with “FP” imprinted on one side, “10 mg” imprinted on the other side
- 20 mg: pink, oval, scored with “F” imprinted on left side of score line and "P" imprinted on right side of score line, “20 mg” imprinted on non-scored side
- 40 mg: white, oval, scored with “F” imprinted on left side of score line and "P" imprinted on right side of score line, “40 mg” imprinted on non-scored side
4. Contraindications
CELEXA is contraindicated in patients:
- taking, or within 14 days of stopping, MAOIs (including MAOIs such as linezolid or intravenous methylene blue) because of an increased risk of serotonin syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3), Drug Interactions (7)].
- taking pimozide because of risk of QT prolongation [see Drug Interactions (7)].
- with known hypersensitivity to citalopram or any of the inactive ingredients in CELEXA. Reactions have included angioedema and anaphylaxis [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Suicidal Thoughts and Behavior in Adolescents and Young Adults
In pooled analyses of placebo-controlled trials of antidepressant drugs (SSRIs and other antidepressant classes) that included approximately 77,000 adult patients, and 4,500 pediatric patients, the incidence of suicidal thoughts and behaviors in antidepressant-treated patients age 24 years and younger was greater than in placebo-treated patients. There was considerable variation in risk of suicidal thoughts and behaviors among drugs, but there was an increased risk identified in young patients for most drugs studied. There were differences in absolute risk of suicidal thoughts and behaviors across the different indications, with the highest incidence in patients with MDD. The drug-placebo differences in the number of cases of suicidal thoughts and behaviors per 1000 patients treated are provided in Table 1.
| Age Range* | Drug-Placebo Difference in Number of Patients with Suicidal Thoughts or Behaviors per 1000 Patients Treated |
| Increases Compared to Placebo | |
| <18 years old | 14 additional patients |
| 18-24 years old | 5 additional patients |
| Decreases Compared to Placebo | |
| 25-64 years old | 1 fewer patient |
| ≥65 years old | 6 fewer patients |
*CELEXA is not approved for use in pediatric patients.
It is unknown whether the risk of suicidal thoughts and behaviors in children, adolescents, and young adults extends to longer-term use, i.e., beyond four months. However, there is substantial evidence from placebo-controlled maintenance trials in adults with MDD that antidepressants delay the recurrence of depression and that depression itself is a risk factor for suicidal thoughts and behaviors.
Monitor all antidepressant-treated patients for clinical worsening and emergence of suicidal thoughts and behaviors, especially during the initial few months of drug therapy and at times of dosage changes. Counsel family members or caregivers of patients to monitor for changes in behavior and to alert the healthcare provider. Consider changing the therapeutic regimen, including possibly discontinuing CELEXA, in patients whose depression is persistently worse, or who are experiencing emergent suicidal thoughts or behaviors.
5.2 QT-Prolongation and Torsade de Pointes
CELEXA causes dose-dependent QTc prolongation an ECG abnormality that has been associated with Torsade de Pointes (TdP), ventricular tachycardia, and sudden death, all of which have been observed in postmarketing reports for citalopram [see Adverse Reactions 6.2)].
Because of the risk of QTc prolongation at higher CELEXA doses, it is recommended that CELEXA not be given at doses above 40 mg once daily [see Dosage and Administration (2.1), Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)].
CELEXA should be avoided in patients with congenital long QT syndrome, bradycardia, hypokalemia or hypomagnesemia, recent acute myocardial infarction, or uncompensated heart failure unless the benefits outweigh the risks for a particular patient. CELEXA should also be avoided in patients who are taking other drugs that prolong the QTc interval [see Drug Interactions (7)]. Such drugs include Class 1A (e.g., quinidine, procainamide) or Class III (e.g., amiodarone, sotalol) antiarrhythmic medications, antipsychotic medications (e.g., chlorpromazine, thioridazine), antibiotics (e.g., gatifloxacin, moxifloxacin), or any other class of medications known to prolong the QTc interval (e.g., pentamidine, levomethadyl acetate, methadone).
The citalopram dose should be limited in certain populations. The maximum dose should be limited to 20 mg once daily in patients who are CYP2C19 poor metabolizers or those patients receiving concomitant cimetidine or another CYP2C19 inhibitor, since higher citalopram exposures would be expected. The maximum dose should also be limited to 20 mg once daily in patients with hepatic impairment and in patients who are greater than 60 years of age because of expected higher exposures [see Dosage and Administration (2.3, 2.4), Drug Interactions (7), Use in Specific Populations (8.5), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Electrolyte and/or ECG monitoring is recommended in certain circumstances. Patients being considered for treatment with CELEXA who are at risk for significant electrolyte disturbances should have baseline serum potassium and magnesium measurements with periodic monitoring. Hypokalemia (and/or hypomagnesemia) may increase the risk of QTc prolongation and arrhythmia, and should be corrected prior to initiation of treatment and periodically monitored. ECG monitoring is recommended in patients for whom CELEXA use is not recommended unless the benefits clearly outweigh the risks for a particular patient (see above). These include those patients with the cardiac conditions noted above, and those taking other drugs that may prolong the QTc interval.
Discontinue CELEXA in patients who are found to have persistent QTc measurements >500 ms. If patients taking CELEXA experience symptoms that could indicate the occurrence of cardiac arrhythmias, e.g., dizziness, palpitations, or syncope, the prescriber should initiate further evaluation, including cardiac monitoring.
5.3 Serotonin Syndrome
SSRIs, including CELEXA, can precipitate serotonin syndrome, a potentially life-threatening condition. The risk is increased with concomitant use of other serotonergic drugs (including triptans, tricyclic antidepressants, fentanyl, lithium, tramadol, meperidine, methadone, tryptophan, buspirone, amphetamines, and St. John’s Wort) and with drugs that impair metabolism of serotonin, i.e., MAOIs [see Contraindications (4), Drug Interactions (7)]. Serotonin syndrome can also occur when these drugs are used alone. Symptoms of serotonin syndrome were noted in 0.1% of MDD patients treated with CELEXA in premarketing clinical trials.
Serotonin syndrome signs and symptoms may include mental status changes (e.g., agitation, hallucinations, delirium, and coma), autonomic instability (e.g., tachycardia, labile blood pressure, dizziness, diaphoresis, flushing, hyperthermia), neuromuscular symptoms (e.g., tremor, rigidity, myoclonus, hyperreflexia, incoordination), seizures, and gastrointestinal symptoms (e.g., nausea, vomiting, diarrhea).
The concomitant use of CELEXA with MAOIs is contraindicated. In addition, do not initiate CELEXA in a patient being treated with MAOIs such as linezolid or intravenous methylene blue. No reports involved the administration of methylene blue by other routes (such as oral tablets or local tissue injection). If it is necessary to initiate treatment with an MAOI such as linezolid or intravenous methylene blue in a patient taking CELEXA, discontinue CELEXA before initiating treatment with the MAOI [see Contraindications (4), Drug Interactions (7)].
Monitor all patients taking CELEXA for the emergence of serotonin syndrome. Discontinue treatment with CELEXA and any concomitant serotonergic agents immediately if the above symptoms occur, and initiate supportive symptomatic treatment. If concomitant use of CELEXA with other serotonergic drugs is clinically warranted, inform patients of the increased risk for serotonin syndrome and monitor for symptoms.
5.4 Increased Risk of Bleeding
Drugs that interfere with serotonin reuptake inhibition, including CELEXA, increase the risk of bleeding events. Concomitant use of aspirin, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS), other antiplatelet drugs, warfarin, and other anticoagulants may add to this risk. Case reports and epidemiological studies (case-control and cohort design) have demonstrated an association between use of drugs that interfere with serotonin reuptake and the occurrence of gastrointestinal bleeding. Based on data from the published observational studies, exposure to SSRIs, particularly in the month before delivery, has been associated with a less than 2-fold increase in the risk of postpartum hemorrhage [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)]. Bleeding events related to drugs that interfere with serotonin reuptake have ranged from ecchymosis, hematoma, epistaxis, and petechiae to life-threatening hemorrhages.
Inform patients about the increased risk of bleeding associated with the concomitant use of CELEXA and antiplatelet agents or anticoagulants. For patients taking warfarin, carefully monitor the international normalized ratio [see Drug Interactions (7)].
5.5 Activation of Mania or Hypomania
In patients with bipolar disorder, treating a depressive episode with CELEXA or another antidepressant may precipitate a mixed/manic episode. In controlled clinical trials, patients with bipolar disorder were excluded; however, symptoms of mania or hypomania were reported in 0.1% of undiagnosed patients treated with CELEXA. Prior to initiating treatment with CELEXA, screen patients for any personal or family history of bipolar disorder, mania, or hypomania [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
5.6 Discontinuation Syndrome
Adverse reactions after discontinuation of serotonergic antidepressants, particularly after abrupt discontinuation, include: nausea, sweating, dysphoric mood, irritability, agitation, dizziness, sensory disturbances (e.g., paresthesia, such as electric shock sensations), tremor, anxiety, confusion, headache, lethargy, emotional lability, insomnia, hypomania, tinnitus, and seizures. A gradual reduction in dosage rather than abrupt cessation is recommended whenever possible [see Dosage and Administration (2.6)].
5.7 Seizures
CELEXA has not been systematically evaluated in patients with seizure disorders. Patients with a history of seizures were excluded from clinical studies. In clinical trials of CELEXA, seizures occurred in 0.3% of patients treated with CELEXA (a rate of one patient per 98 years of exposure) and 0.5% of patients treated with placebo (a rate of one patient per 50 years of exposure). CELEXA should be prescribed with caution in patients with a seizure disorder.
5.8 Angle-closure Glaucoma
The pupillary dilation that occurs following use of many antidepressant drugs, including CELEXA, may trigger an angle closure attack in a patient with anatomically narrow angles who does not have a patent iridectomy. Avoid use of antidepressants, including CELEXA, in patients with untreated anatomically narrow angles.
5.9 Hyponatremia
Hyponatremia may occur as a result of treatment with SSRIs, including CELEXA. Cases of serum sodium lower than 110 mmol/L have been reported. Signs and symptoms of hyponatremia include headache, difficulty concentrating, memory impairment, confusion, weakness, and unsteadiness, which may lead to falls. Signs and symptoms associated with more severe and/or acute cases have included hallucination, syncope, seizure, coma, respiratory arrest, and death. In many cases, this hyponatremia appears to be the result of the syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion (SIADH).
In patients with symptomatic hyponatremia, discontinue CELEXA and institute appropriate medical intervention. Elderly patients, patients taking diuretics, and those who are volume-depleted may be at greater risk of developing hyponatremia with SSRIs [see Use in Specific Populations (8.5)].
5.10 Sexual Dysfunction
Use of SSRIs, including CELEXA, may cause symptoms of sexual dysfunction [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. In male patients, SSRI use may result in ejaculatory delay or failure, decreased libido, and erectile dysfunction. In female patients, SSRI use may result in decreased libido and delayed or absent orgasm.
It is important for prescribers to inquire about sexual function prior to initiation of CELEXA and to inquire specifically about changes in sexual function during treatment, because sexual function may not be spontaneously reported. When evaluating changes in sexual function, obtaining a detailed history (including timing of symptom onset) is important because sexual symptoms may have other causes, including the underlying psychiatric disorder. Discuss potential management strategies to support patients in making informed decisions about treatment.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the labeling:
- Hypersensitivity reactions [see Contraindications (4)]
- Suicidal thoughts and behaviors in adolescents and young adults [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- QT-prolongation and torsade de pointes [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Serotonin syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Increased risk of bleeding [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Activation of mania or hypomania [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Discontinuation syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Seizures [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- Angle-closure glaucoma [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
- Hyponatremia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]
- Sexual Dysfunction [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical studies of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
The safety for CELEXA included citalopram exposures in patients and/or healthy subjects from 3 different groups of studies: 429 healthy subjects in clinical pharmacology/pharmacokinetic studies; 4,422 exposures from patients in controlled and uncontrolled clinical trials, corresponding to approximately 1,370 patient-exposure years. There were, in addition, over 19,000 exposures from mostly open-label, European postmarketing studies. The conditions and duration of treatment with CELEXA varied greatly and included (in overlapping categories) open-label and double-blind studies, inpatient and outpatient studies, fixed-dose and dose-titration studies, and short-term and long-term exposure.
Adverse Reactions Associated with Discontinuation of Treatment
Among 1,063 patients with MDD who received CELEXA at doses ranging from 10 mg to 80 mg once daily in placebo-controlled trials of up to 6 weeks duration, 16% discontinued treatment due to an adverse reaction, as compared to 8% of 446 patients receiving placebo. The adverse reactions associated with discontinuation (i.e., associated with discontinuation in at least 1% of CELEXA-treated patients at a rate at least twice that of placebo) are shown in Table 2.
| Body System/Adverse Reaction | CELEXA | Placebo |
| (N=1,063)
% | (N=446)
% |
|
| General | ||
| Asthenia | 1 | <1 |
| Gastrointestinal Disorders | ||
| Nausea | 4 | 0 |
| Dry Mouth | 1 | <1 |
| Vomiting | 1 | 0 |
| Central and Peripheral Nervous System Disorders | ||
| Dizziness | 2 | <1 |
| Psychiatric Disorders | ||
| Insomnia | 3 | 1 |
| Somnolence | 2 | 1 |
| Agitation | 1 | <1 |
* A patient can report more than one reason for discontinuation and be counted more than once in this table.
Table 3 enumerates the incidence of adverse reactions that occurred among 1,063 patients with MDD who received CELEXA at doses ranging from 10 mg to 80 mg once daily in placebo-controlled trials of up to 6 weeks duration.
The most common adverse reaction that occurred in CELEXA-treated patients with an incidence of 5% or greater and at least twice the incidence in placebo patients was ejaculation disorder (primarily ejaculatory delay) in male patients (see Table 3).
|
| CELEXA | Placebo |
| Body System/Adverse Reaction | (N=1,063)
% | (N=446)
% |
| Gastrointestinal Disorders | ||
| Nausea | 21 | 14 |
| Diarrhea | 8 | 5 |
| Dyspepsia | 5 | 4 |
| Vomiting | 4 | 3 |
| Abdominal Pain | 3 | 2 |
| Autonomic Nervous System Disorders | ||
| Dry Mouth | 20 | 14 |
| Sweating Increased | 11 | 9 |
| Psychiatric Disorders | ||
| Somnolence | 18 | 10 |
| Insomnia | 15 | 14 |
| Anxiety | 4 | 3 |
| Anorexia | 4 | 2 |
| Agitation | 3 | 1 |
| Dysmenorrhea1 | 3 | 2 |
| Libido Decreased | 2 | <1 |
| Yawning | 2 | <1 |
| Central & Peripheral Nervous System Disorders | ||
| Tremor | 8 | 6 |
| Urogenital | ||
| Ejaculation Disorder2,3 | 6 | 1 |
| Impotence3 | 3 | <1 |
| Respiratory System Disorders | ||
| Upper Respiratory Tract Infection | 5 | 4 |
| Rhinitis | 5 | 3 |
| Sinusitis | 3 | <1 |
| General | ||
| Fatigue | 5 | 3 |
| Fever | 2 | <1 |
| Musculoskeletal System Disorders | ||
| Arthralgia | 2 | 1 |
| Myalgia | 2 | 1 |
*Adverse reactions reported by at least 2% of patients treated with CELEXA are reported, except for the following adverse reactions which had an incidence on placebo ≥ CELEXA: headache, asthenia, dizziness, constipation, palpitation, vision abnormal, sleep disorder, nervousness, pharyngitis, micturition disorder, back pain.
1Denominator used was for females only (N=638 CELEXA; N=252 placebo).
2Primarily ejaculatory delay.
3Denominator used was for males only (N=425 CELEXA; N=194 placebo).
Dose Dependent Adverse Reactions
The potential relationship between the dosage of CELEXA and the incidence of adverse reactions was examined in a fixed-dose study in patients with MDD receiving placebo or CELEXA 10 mg, 20 mg 40 mg, or 60 mg (1.5 times the maximum recommended dosage). A positive dose response (p<0.05) was revealed for the following adverse reactions: fatigue, impotence, insomnia, increased sweating, somnolence, and yawning.
Male and Female Sexual Dysfunction with SSRIs
Although changes in sexual desire, sexual performance, and sexual satisfaction often occur as manifestations of a psychiatric disorder, they may also be a consequence of SSRI treatment. However, reliable estimates of the incidence and severity of untoward experiences involving sexual desire, performance, and satisfaction are difficult to obtain, in part because patients and healthcare providers may be reluctant to discuss them. Accordingly, estimates of the incidence of untoward sexual experience and performance cited in labeling may underestimate their actual incidence.
Table 4 displays the incidence of sexual adverse reactions reported by at least 2% of male patients taking CELEXA in a pool of placebo-controlled clinical trials in patients with depression.
| CELEXA
| Placebo
|
|
| n (males) | 425
(%) | 194
(%) |
| Abnormal ejaculation (mostly ejaculatory delay) | 6.1 | 1 |
| Decreased libido | 3.8 | <1 |
| Impotence | 2.8 | <1 |
In female depressed patients receiving CELEXA, the reported incidence of decreased libido and anorgasmia was 1.3% (n=638 females) and 1.1% (n=252 females), respectively.
Weight Changes
Patients treated with CELEXA in controlled trials experienced a weight loss of about 0.5 kg compared to no change for placebo patients.
ECG Changes
In a thorough QT study, CELEXA was found to be associated with a dose-dependent increase in the QTc interval.
Electrocardiograms from CELEXA (N=802) and placebo (N=241) groups were compared with respect to outliers defined as subjects with QTc changes over 60 msec from baseline or absolute values over 500 msec post-dose, and subjects with heart rate increases to over 100 bpm or decreases to less than 50 bpm with a 25% change from baseline (tachycardic or bradycardic outliers, respectively). In the CELEXA group 1.9% of the patients had a change from baseline in QTcF >60 msec compared to 1.2% of the patients in the placebo group. None of the patients in the placebo group had a post-dose QTcF >500 msec compared to 0.5% of the patients in the CELEXA group. The incidence of tachycardic outliers was 0.5% in the CELEXA group and 0.4% in the placebo group. The incidence of bradycardic outliers was 0.9% in the CELEXA group and 0.4% in the placebo group.
Other Adverse Reactions Observed During the Premarketing Evaluation of CELEXA
The following list of adverse reactions does not include reactions that are: 1) included in Table 3 or elsewhere in labeling, 2) for which a drug cause was remote, 3) which were so general as to be uninformative, and those occurring in only one patient.
Adverse reactions are categorized by body system and listed in order of decreasing frequency according to the following definitions: frequent adverse reactions are those occurring on one or more occasions in at least 1/100 patients; infrequent adverse reactions are those occurring in less than 1/100 patients to 1/1000 patients; rare adverse reactions are those occurring in fewer than 1/1000 patients.
Cardiovascular - Frequent: tachycardia, postural hypotension, hypotension. Infrequent: hypertension, bradycardia, edema (extremities), angina pectoris, extrasystoles, cardiac failure, flushing, myocardial infarction, cerebrovascular accident, myocardial ischemia. Rare: transient ischemic attack, phlebitis, atrial fibrillation, cardiac arrest, bundle branch block.
Central and Peripheral Nervous System Disorders - Frequent: paresthesia, migraine. Infrequent: hyperkinesia, vertigo, hypertonia, extrapyramidal disorder, leg cramps, involuntary muscle contractions, hypokinesia, neuralgia, dystonia, abnormal gait, hypoesthesia, ataxia. Rare: abnormal coordination, hyperesthesia, ptosis, stupor.
Endocrine Disorders - Rare: hypothyroidism, goiter, gynecomastia.
Gastrointestinal Disorders - Frequent: saliva increased, flatulence. Infrequent: gastritis, gastroenteritis, stomatitis, eructation, hemorrhoids, dysphagia, teeth grinding, gingivitis, esophagitis. Rare: colitis, gastric ulcer, cholecystitis, cholelithiasis, duodenal ulcer, gastroesophageal reflux, glossitis, jaundice, diverticulitis, rectal hemorrhage, hiccups.
General - Infrequent: hot flushes, rigors, alcohol intolerance, syncope, influenza-like symptoms. Rare: hay fever.
Hemic and Lymphatic Disorders - Infrequent: purpura, anemia, epistaxis, leukocytosis, leucopenia, lymphadenopathy. Rare: pulmonary embolism, granulocytopenia, lymphocytosis, lymphopenia, hypochromic anemia, coagulation disorder, gingival bleeding.
Metabolic and Nutritional Disorders - Frequent: decreased weight, increased weight. Infrequent: increased hepatic enzymes, thirst, dry eyes, increased alkaline phosphatase, abnormal glucose tolerance. Rare: bilirubinemia, hypokalemia, obesity, hypoglycemia, hepatitis, dehydration.
Musculoskeletal System Disorders - Infrequent: arthritis, muscle weakness, skeletal pain. Rare: bursitis, osteoporosis.
Psychiatric Disorders - Frequent: impaired concentration, amnesia, apathy, depression, increased appetite, aggravated depression, suicide attempt, confusion. Infrequent: increased libido, aggressive reaction, paroniria, drug dependence, depersonalization, hallucination, euphoria, psychotic depression, delusion, paranoid reaction, emotional lability, panic reaction, psychosis. Rare: catatonic reaction, melancholia.
Reproductive Disorders/Female* - Frequent: amenorrhea. Infrequent: galactorrhea, breast pain, breast enlargement, vaginal hemorrhage. (*% based on female subjects only: 2955)
Respiratory System Disorders - Frequent: coughing. Infrequent: bronchitis, dyspnea, pneumonia. Rare: asthma, laryngitis, bronchospasm, pneumonitis, sputum increased.
Skin and Appendages Disorders - Frequent: rash, pruritus. Infrequent: photosensitivity reaction, urticaria, acne, skin discoloration, eczema, alopecia, dermatitis, skin dry, psoriasis. Rare: hypertrichosis, decreased sweating, melanosis, keratitis, cellulitis, pruritus ani.
Special Senses - Frequent: abnormal accommodation, taste perversion. Infrequent: tinnitus, conjunctivitis, eye pain. Rare: mydriasis, photophobia, diplopia, abnormal lacrimation, cataract, taste loss.
Urinary System Disorders - Frequent: polyuria. Infrequent: micturition frequency, urinary incontinence, urinary retention, dysuria. Rare: facial edema, hematuria, oliguria, pyelonephritis, renal calculus, renal pain.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval use of citalopram, the racemate, or escitalopram, the S-enantiomer of citalopram. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Blood and Lymphatic System Disorders: hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, prothrombin decreased
Cardiac Disorders: torsade de pointes, ventricular arrhythmia, QT prolonged
Endocrine Disorders: hyperprolactinemia
Eye Disorders: angle-closure glaucoma
Gastrointestinal Disorders: gastrointestinal hemorrhage, pancreatitis
General Disorders and Administrative Site Conditions: withdrawal syndrome
Hepatobiliary Disorders: hepatic necrosis
Immune System Disorders: anaphylaxis, allergic reaction
Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders: rhabdomyolysis
Nervous System Disorders: grand mal convulsion(s), myoclonus, choreoathetosis, dyskinesia, akathisia, nystagmus
Pregnancy, Puerperium and Perinatal Conditions: spontaneous abortion
Psychiatric Disorders: delirium
Renal and Urinary Disorders: acute renal failure
Reproductive System and Breast Disorders: priapism
Respiratory, Thoracic and Mediastinal Disorders: anosmia, hyposmia
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders: Stevens Johnson Syndrome, epidermal necrolysis, angioedema, erythema multiforme, ecchymosis
Vascular Disorders: thrombosis
7. Drug Interactions
Table 5 presents clinically important drug interactions with CELEXA.
| Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs) | |
| Clinical Impact | Concomitant use of SSRIs, including CELEXA, and MAOIs increases the risk of serotonin syndrome. |
| Intervention | CELEXA is contraindicated in patients taking MAOIs, including MAOIs such as linezolid or intravenous methylene blue [see Dosage and Administration (2.5), Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]. |
| Pimozide | |
| Clinical Impact: | Concomitant use of CELEXA with pimozide increases plasma concentrations of pimozide, a drug with a narrow therapeutic index, and may increase the risk of QT prolongation and/or ventricular arrhythmias compared to use of CELEXA alone [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)]. |
| Intervention: | CELEXA is contraindicated in patients taking pimozide [see Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. |
| Drugs that Prolong the QTc Interval | |
| Clinical Impact: | Concomitant use of CELEXA with drugs that prolong QT can cause additional QT prolongation compared to the use of CELEXA alone [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)]. |
| Intervention: | Avoid concomitant use of CELEXA with drugs that prolong the QT interval (CELEXA is contraindicated in patients taking pimozide)[see Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. |
| CYP2C19 Inhibitors | |
| Clinical Impact: | Concomitant use of CELEXA with CYP2C19 inhibitors increases the risk of QT prolongation and/or ventricular arrhythmias compared to the use of CELEXA alone [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)]. |
| Intervention:
| The maximum recommended dosage of CELEXA is 20 mg daily when used concomitantly with a CYP2C19 inhibitor [see Dosage and Administration (2.4), Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. |
| Other Serotonergic Drugs | |
| Clinical Impact: | Concomitant use of CELEXA and other serotonergic drugs (including other SSRIs, SNRIs, triptans, tricyclic antidepressants, opioids, lithium, buspirone, amphetamines, tryptophan, and St. John's Wort) increases the risk of serotonin syndrome. |
| Intervention:
| Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of serotonin syndrome, particularly during CELEXA initiation and dosage increases. If serotonin syndrome occurs, consider discontinuation of CELEXA and/or concomitant serotonergic drugs [see Warning and Precautions (5.3)]. |
| Drugs That Interfere With Hemostasis (antiplatelet agents and anticoagulants) | |
| Clinical Impact: | Concomitant use of CELEXA and an antiplatelet or anticoagulant may potentiate the risk of bleeding. |
| Intervention:
| Inform patients of the increased risk of bleeding associated with the concomitant use of CELEXA and antiplatelet agents and anticoagulants. For patients taking warfarin, carefully monitor the international normalized ratio [see Warning and Precautions (5.4)]. |
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Exposure Registry
There is a pregnancy exposure registry that monitors pregnancy outcomes in women exposed to antidepressants during pregnancy. Healthcare providers are encouraged to register patients by calling the National Pregnancy Registry for Antidepressants at 1-844-405-6185 or visiting online at
https://womensmentalhealth.org/research/pregnancyregistry/antidepressants.
Risk Summary
Based on data from published observational studies, exposure to SSRIs, particularly in the month before delivery, has been associated with a less than 2-fold increase in the risk of postpartum hemorrhage [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) and Clinical Considerations].
Available data from published epidemiologic studies and postmarketing reports with citalopram use in pregnancy have not established an increased risk of major birth defects or miscarriage. Published studies demonstrated that citalopram levels in both cord blood and amniotic fluid are similar to those observed in maternal serum. There are risks of persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn (PPHN) (see Data) and/or poor neonatal adaptation with exposure to selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), including CELEXA, during pregnancy. There also are risks associated with untreated depression in pregnancy (see Clinical Considerations).
In animal reproduction studies, citalopram caused adverse embryo/fetal effects at doses that caused maternal toxicity (see Data).
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in the clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Disease-Associated Maternal and/or Embryo/Fetal Risk
Women who discontinue antidepressants during pregnancy are more likely to experience a relapse of major depression than women who continue antidepressants. This finding is from a prospective longitudinal study of 201 pregnant women with a history of major depressive disorder who were euthymic and taking antidepressants at the beginning of pregnancy. Consider the risk of untreated depression when discontinuing or changing treatment with antidepressant medication during pregnancy and postpartum.
Maternal Adverse Reactions
Use of CELEXA in the month before delivery may be associated with an increased risk of postpartum hemorrhage [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Fetal/Neonatal Adverse Reactions
Neonates exposed to CELEXA and other SSRIs late in third trimester have developed complications requiring prolonged hospitalization, respiratory support, and tube feeding. Such complications can arise immediately upon delivery. Reported clinical findings have included respiratory distress, cyanosis, apnea, seizures, temperature instability, feeding difficulty, vomiting, hypoglycemia, hypotonia, hypertonia, hyperreflexia, tremor, jitteriness, irritability, and constant crying. These findings are consistent with either a direct toxic effect of SSRIs or possibly, a drug discontinuation syndrome. It should be noted that, in some cases, the clinical picture is consistent with serotonin syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Data
Human Data
Exposure during late pregnancy to SSRIs may have an increased risk for persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn (PPHN). PPHN occurs in 1- 2 per 1,000 live births in the general population and is associated with substantial neonatal morbidity and mortality.
Animal Data
Citalopram was administered orally to pregnant rats during the period of organogenesis at doses of 32, 56, and 112 mg/kg/day, which are approximately 8, 14, and 27 times the Maximum Recommended Human Dose (MRHD) of 40 mg, based on mg/m2 body surface area. Citalopram caused maternal toxicity of CNS clinical signs and decreased weight gain at 112 mg/kg/day, which is 27 times the MRHD. At this maternally toxic dose, citalopram decreased embryo/fetal growth and survival and increased fetal abnormalities (including cardiovascular and skeletal defects). The no observed adverse effect level (NOAEL) for maternal and embryofetal toxicity is 56 mg/kg/day, which is approximately 14 times the MRHD.
Citalopram was administered orally to pregnant rabbits during the period of organogenesis at doses up to 16 mg/kg/day, which is approximately 8 times the MRHD of 40 mg, based on mg/m2 body surface area. No maternal or embryofetal toxicity was observed. The NOAEL for maternal and embryofetal toxicity is 16 mg/kg/day, which is approximately 8 times the MRHD.
Citalopram was administered orally to pregnant rats during late gestation and lactation periods at doses of 4.8, 12.8, and 32 mg/kg/day, which are approximately 1, 3, and 8 times the MRHD of 40 mg, based on mg/m2 body surface area. Citalopram increased offspring mortality during the first 4 days of birth and decreased offspring growth at 32 mg/kg/day, which is approximately 8 times the MRHD. The NOAEL for developmental toxicity is 12.8 mg/kg/day, which is approximately 3 times the MRHD. In a separate study, similar effects on offspring mortality and growth were seen when dams were treated throughout gestation and early lactation at doses ≥ 24 mg/kg/day, which is approximately 6 times the MRHD. A NOAEL was not determined in that study.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
Data from the published literature report the presence of citalopram in human milk at relative infant doses ranging between 0.7 to 9.4% of the maternal weight-adjusted dosage and a milk/plasma ratio ranging between 0.78 to 4.3. There are reports of breastfed infants exposed to citalopram experiencing irritability, restlessness, excessive somnolence, decreased feeding, and weight loss (see Clinical Considerations). There is no information about effects of citalopram on milk production.
The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for CELEXA and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from CELEXA or from the underlying maternal condition.
Clinical Considerations
Monitor breastfeeding infants for adverse reactions, such as irritability, restlessness, excessive somnolence, decreased feeding, and weight loss.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of CELEXA have not been established in pediatric patients. Two placebo-controlled trials in 407 pediatric patients with MDD have been conducted with CELEXA, and the data were not sufficient to support use in pediatric patients.
Antidepressants increase the risk of suicidal thoughts and behaviors in pediatric patients [see Boxed Warning, Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. Decreased appetite and weight loss have been observed in association with the use of SSRIs in pediatric patients.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of 4422 patients in clinical studies of CELEXA, 1357 were 60 and over, 1034 were 65 and over, and 457 were 75 and over. In two pharmacokinetic studies, citalopram AUC was increased by 23% and 30%, respectively, in subjects ≥ 60 years of age as compared to younger subjects, and its half-life was increased by 30% and 50%, respectively [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Therefore, the maximum recommended dosage in patients 60 years of age and older is lower than younger patients [see Dosage and Administration (2.3),Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
SSRIs, including CELEXA, have been associated with cases of clinically significant hyponatremia in elderly patients, who may be at greater risk for this adverse reaction [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)].
12. Celexa - Clinical Pharmacology
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
In vitro and in vivo studies in animals suggest that citalopram is a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) with minimal effects on norepinephrine (NE) and dopamine (DA) neuronal reuptake.
Citalopram has no or very low affinity for 5-HT1A, 5-HT2A, dopamine D1 and D2, α1-, α2-, and β-adrenergic, histamine H1, gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA), muscarinic cholinergic, and benzodiazepine receptors.
Cardiac Electrophysiology
Individually corrected QTc (QTcNi) interval was evaluated in a randomized, placebo and active (moxifloxacin 400 mg) controlled cross-over, escalating multiple-dose study in 119 healthy subjects. The maximum mean (upper bound of the 95% one-sided confidence interval) difference from placebo were 8.5 (10.8) and 18.5 (21.0) msec for 20 mg and 60 mg (1.5 times the maximum recommended dosage) citalopram, respectively. Based on the established exposure-response relationship, the predicted QTcNi change from placebo (upper bound of the 95% one-sided confidence interval) under the Cmax for the dose of 40 mg is 12.6 (14.3) msec [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The single- and multiple-dose pharmacokinetics of citalopram are linear and dose-proportional in a dose range of 10 to 40 mg/day. Biotransformation of citalopram is mainly hepatic, with a mean terminal half-life of about 35 hours. With once daily dosing, steady state plasma concentrations are achieved within approximately one week. At steady state, the extent of accumulation of citalopram in plasma, based on the half-life, is expected to be 2.5 times the plasma concentrations observed after a single dose.
Absorption
Following a single oral dose (40 mg tablet) of citalopram, peak blood levels occur at about 4 hours. The absolute bioavailability of citalopram was about 80% relative to an intravenous dose, and absorption is not affected by food.
Distribution
The volume of distribution of citalopram is about 12 L/kg and the binding of citalopram (CT), demethylcitalopram (DCT) and didemethylcitalopram (DDCT) to human plasma proteins is about 80%.
Elimination
Metabolism
Citalopram is metabolized to demethylcitalopram (DCT), didemethylcitalopram (DDCT), citalopram-N-oxide, and a deaminated propionic acid derivative. In humans, unchanged citalopram is the predominant compound in plasma. At steady state, the concentrations of citalopram's metabolites, DCT and DDCT, in plasma are approximately one-half and one-tenth, respectively, that of the parent drug. In vitro studies show that citalopram is at least 8 times more potent than its metabolites in the inhibition of serotonin reuptake, suggesting that the metabolites evaluated do not likely contribute significantly to the antidepressant actions of citalopram.
In vitro studies using human liver microsomes indicated that CYP3A4 and CYP2C19 are the primary isozymes involved in the N-demethylation of citalopram.
Excretion
Following intravenous administrations of citalopram, the fraction of drug recovered in the urine as citalopram and DCT was about 10% and 5%, respectively. The systemic clearance of citalopram was 330 mL/min, with approximately 20% of that due to renal clearance.
Specific Populations
Geriatric Patients
Citalopram pharmacokinetics in subjects ≥ 60 years of age were compared to younger subjects in two normal volunteer studies. In a single-dose study, citalopram AUC and half-life were increased in the subjects ≥ 60 years old by 30% and 50%, respectively, whereas in a multiple-dose study they were increased by 23% and 30%, respectively[see Dosage and Administration (2.3), Warnings and Precautions (5.2), Use in Specific Populations (8.5)].
Male and Female Patients
In three pharmacokinetic studies (total N=32), citalopram AUC in women was one and a half to two times that in men. This difference was not observed in five other pharmacokinetic studies (total N=114). In clinical studies, no differences in steady state serum citalopram levels were seen between men (N=237) and women (N=388). There were no gender differences in the pharmacokinetics of DCT and DDCT.
Patients with Hepatic Impairment
Citalopram oral clearance was reduced by 37% and half-life was doubled in patients with reduced hepatic function compared to normal subjects [see Dosage and Administration (2.3), Warnings and Precautions (5.2), Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
Patients with Renal Impairment
In patients with mild to moderate renal impairment, oral clearance of citalopram was reduced by 17% compared to normal subjects. No adjustment of dosage for such patients is recommended. No information is available about the pharmacokinetics of citalopram in patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance < 20 mL/min).
CYP2C19 poor metabolizers
In CYP2C19 poor metabolizers, citalopram steady state Cmax and AUC was increased by 68% and 107%, respectively [see Dosage and Administration (2.3),Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
CYP2D6 poor metabolizers
Citalopram steady state levels were not significantly different in poor metabolizers and extensive metabolizers of CYP2D6.
Drug Interaction Studies
In vitro enzyme inhibition data did not reveal an inhibitory effect of citalopram on CYP3A4, -2C9, or -2E1, but did suggest that it is a weak inhibitor of CYP1A2, -2D6, and -2C19. Citalopram would be expected to have little inhibitory effect on in vivo metabolism mediated by these enzymes. However, in vivo data to address this question are limited.
CYP3A4 and CYP2C19 Inhibitors
Since CYP3A4 and CYP2C19 are the primary enzymes involved in the metabolism of citalopram, it is expected that potent inhibitors of CYP3A4 (e.g., ketoconazole, itraconazole, and macrolide antibiotics) and inhibitors of CYP2C19 (e.g., omeprazole, cimetidine) might decrease the clearance of citalopram. However, coadministration of citalopram and the potent CYP3A4 inhibitor ketoconazole did not significantly affect the pharmacokinetics of citalopram. 20 mg/day is the maximum recommended citalopram dose in patients taking concomitant cimetidine or another CYP2C19 inhibitor, because of the risk of QT prolongation [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Cimetidine
In subjects who had received 21 days of 40 mg/day CELEXA, combined administration of 400 mg twice a day cimetidine for 8 days resulted in an increase in citalopram AUC and Cmax of 43% and 39%, respectively [see Dosage and Administration (4),Warnings and Precautions (5.2), Drug Interactions (7)].
CYP2D6 Inhibitors
Coadministration of a drug that inhibits CYP2D6 with citalopram is unlikely to have clinically significant effects on citalopram metabolism, based on the study results in CYP2D6 poor metabolizers.
Digoxin
In subjects who had received 21 days of 40 mg/day CELEXA, combined administration of CELEXA and digoxin (single dose of 1 mg) did not significantly affect the pharmacokinetics of either citalopram or digoxin.
Lithium
Coadministration of CELEXA (40 mg/day for 10 days) and lithium (30 mmol/day for 5 days) had no significant effect on the pharmacokinetics of citalopram or lithium.
Pimozide
In a controlled study, a single dose of pimozide 2 mg co-administered with citalopram 40 mg given once daily for 11 days was associated with a mean increase in QTc values of approximately 10 msec compared to pimozide given alone. Citalopram did not alter the mean AUC or Cmax of pimozide. The mechanism of this pharmacodynamic interaction is not known [see Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Theophylline
Combined administration of CELEXA (40 mg/day for 21 days) and the CYP1A2 substrate theophylline (single dose of 300 mg) did not affect the pharmacokinetics of theophylline. The effect of theophylline on the pharmacokinetics of citalopram was not evaluated.
Warfarin
Administration of 40 mg/day CELEXA for 21 days did not affect the pharmacokinetics of warfarin, a CYP3A4 substrate. Prothrombin time was increased by 5%, the clinical significance of which is unknown.
Carbamazepine
Combined administration of CELEXA (40 mg/day for 14 days) and carbamazepine (titrated to 400 mg/day for 35 days) did not significantly affect the pharmacokinetics of carbamazepine, a CYP3A4 substrate. Although trough citalopram plasma levels were unaffected, given the enzyme-inducing properties of carbamazepine, the possibility that carbamazepine might increase the clearance of citalopram should be considered if the two drugs are coadministered.
Triazolam
Combined administration of CELEXA (titrated to 40 mg/day for 28 days) and the CYP3A4 substrate triazolam (single dose of 0.25 mg) did not significantly affect the pharmacokinetics of either citalopram or triazolam.
Ketoconazole
Combined administration of CELEXA (40 mg) and ketoconazole (200 mg) decreased the Cmax and AUC of ketoconazole by 21% and 10%, respectively, and did not significantly affect the pharmacokinetics of citalopram.
Metoprolol
Administration of 40 mg/day CELEXA for 22 days resulted in a two-fold increase in the plasma levels of the beta-adrenergic blocker metoprolol. Increased metoprolol plasma levels have been associated with decreased cardioselectivity. Coadministration of CELEXA and metoprolol had no clinically significant effects on blood pressure or heart rate.
Imipramine and Other Tricyclic Antidepressants (TCAs)
In vitro studies suggest that citalopram is a relatively weak inhibitor of CYP2D6. Coadministration of CELEXA (40 mg/day for 10 days) with the TCA imipramine (single dose of 100 mg), a substrate for CYP2D6, did not significantly affect the plasma concentrations of imipramine or citalopram. However, the concentration of the imipramine metabolite desipramine was increased by approximately 50%. The clinical significance of the desipramine change is unknown.
14. Clinical Studies
The efficacy of CELEXA as a treatment for major depressive disorder was established in two placebo-controlled studies (of 4 to 6 weeks duration) in adult outpatients (ages 18-66) meeting DSM-III or DSM-III-R criteria for major depressive disorder (MDD) (Studies 1 and 2).
Study 1, a 6-week trial in which patients received fixed CELEXA doses of 10 mg, 20 mg, 40 mg, and 60 mg daily, showed that CELEXA 40 daily and 60 mg daily (1.5 times the maximum recommended daily dosage) was effective as measured by the Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HAMD) total score, the primary efficacy endpoint. The HAMD-17 is a 17-item, clinician-rated scale used to assess severity of depressive symptoms. Scores on the HAMD-17 range from 0 to 52, with higher scores indicating more severe depression. This study showed no clear effect of the 10 mg and 20 mg daily doses, and the 60 mg daily dose was not more effective than the 40 mg daily dose. Due to the risk of QTc prolongation and ventricular arrhythmias, the maximum recommended dosage of CELEXA is 40 mg once daily.
In study 2, a 4-week, placebo-controlled trial in patients with MDD, the initial dose was 20 mg daily, followed by titration to the maximum tolerated dose or a maximum dose of 80 mg daily (2 times the maximum recommended daily dosage). Patients treated with CELEXA showed statistically significantly greater improvement than placebo patients on the HAMD total score, the primary efficacy endpoint. In three additional placebo-controlled trials in patients with MDD, the difference in response to treatment between patients receiving CELEXA and patients receiving placebo was not statistically significant.
In two long-term studies, patients with MDD who had responded to CELEXA during an initial 6 or 8 weeks of acute treatment were randomized to continuation of CELEXA or placebo. In one study, patients received fixed doses of CELEXA 20 mg or 40 mg daily and in the second study, patients received flexible doses of CELEXA 20 mg daily to 60 mg daily (1.5 times the maximum recommended daily dosage). In both studies, patients receiving continued CELEXA treatment experienced statistically significantly lower relapse rates over the subsequent 6 months compared to those receiving placebo. In the fixed-dose study, the decreased rate of depression relapse was similar in patients receiving 20 mg or 40 mg daily of CELEXA. Due to the risk of QTc prolongation and ventricular arrhythmias, the maximum recommended dosage of CELEXA is 40 mg once daily.
Analyses of the relationship between treatment outcome and age, gender, and race did not suggest any differential responsiveness on the basis of these patient characteristics.
Medication Guide
| MEDICATION GUIDE
CELEXA® (Suh-leks-uh) (citalopram) Tablets, for oral use |
|||
| What is the most important information I should know about CELEXA?
CELEXA may cause serious side effects, including:
|
|||
|
|
||
| What is CELEXA?
CELEXA is a prescription medicine used to treat a certain type of depression called Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) in adults. It is not known if CELEXA is safe and effective for use in children. |
|||
| Who should not take CELEXA?
Do not take CELEXA if you:
Do not start taking an MAOI for at least 14 days after you stop treatment with CELEXA. |
|||
Before taking CELEXA, tell your healthcare provider about all your medical conditions, including if you:
CELEXA and other medicines may affect each other causing possible serious side effects. CELEXA may affect the way other medicines work and other medicines may affect the way CELEXA works. Especially tell your healthcare provider if you take:
Do not start or stop any other medicines during treatment with CELEXA without talking to your healthcare provider first. Stopping CELEXA suddenly may cause you to have serious side effects. See, “What are the possible side effects of CELEXA?” Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them to show to your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medicine. |
|||
How should I take CELEXA?
|
|||
| What are the possible side effects of CELEXA?
CELEXA may cause serious side effects, including:
|
|||
|
|
||
|
|||
|
|
||
|
|||
|
|
||
|
|||
|
|
||
| In severe or more sudden cases, signs and symptoms include: | |||
|
|
||
The most common side effect of CELEXA is delayed ejaculation. These are not all the possible side effects of CELEXA. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. |
|||
How should I store CELEXA?
|
|||
| General information about the safe and effective use of CELEXA
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use CELEXA for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give CELEXA to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. You may ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for information about CELEXA that is written for healthcare professionals. |
|||
| What are the ingredients in CELEXA?
Active ingredient: citalopram hydrobromide Inactive ingredients: copolyvidone, corn starch, crosscarmellose sodium, glycerin, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, hypromellose, microcrystalline cellulose, polyethylene glycol, titanium dioxide and iron dioxide for coloring. Distributed by: Allergan USA, Inc. Madison, NJ 07960 © 2023 Allergan. All rights reserved. Licensed from H. Lundbeck A/S For more information about CELEXA call 1-800-678-1605. |
|||
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Revised: 08/2023
V2.0MG4010
| CELEXA
citalopram tablet, film coated |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CELEXA
citalopram tablet, film coated |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CELEXA
citalopram tablet, film coated |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Allergan, Inc. (144796497) |