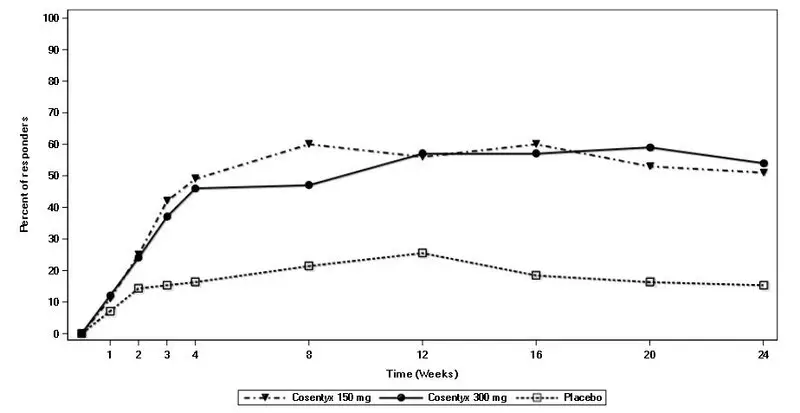
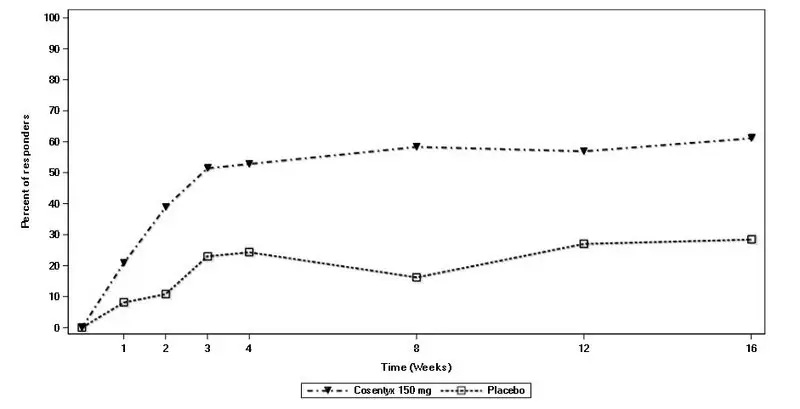
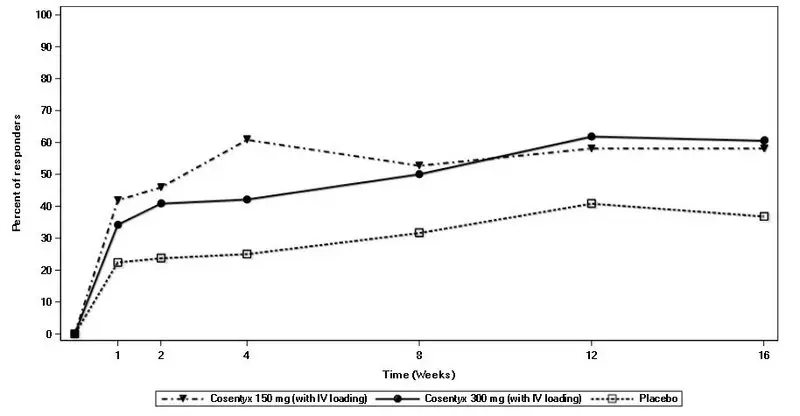
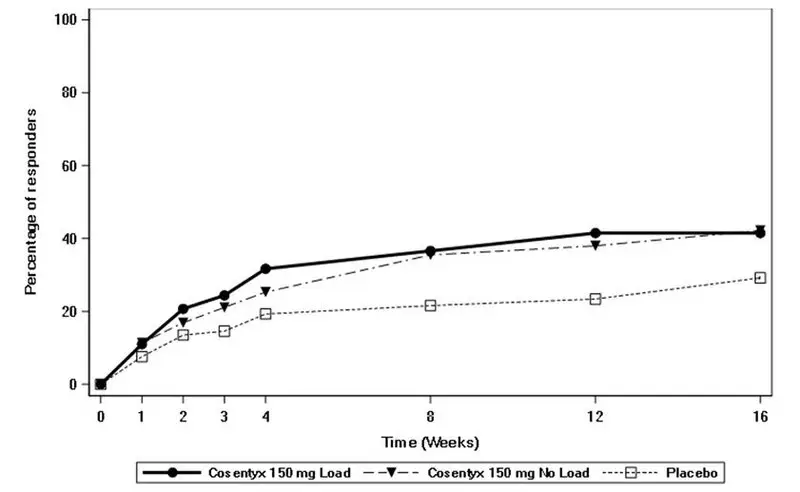
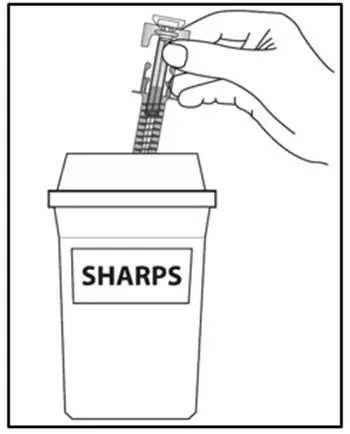
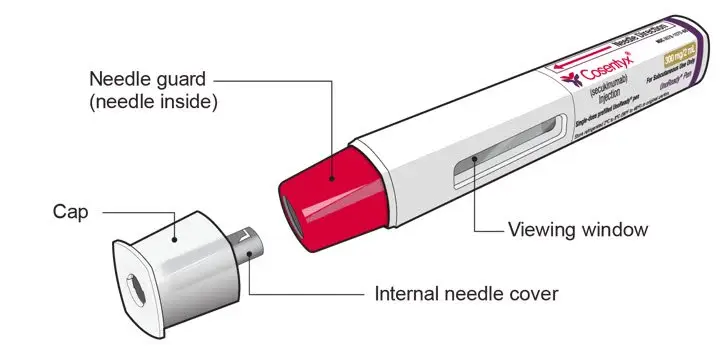
Drug Detail:Cosentyx (Secukinumab [ sek-ue-kin-ue-mab ])
Drug Class: Interleukin inhibitors
Highlights of Prescribing Information
COSENTYX® (secukinumab) injection, for subcutaneous use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2015
Recent Major Changes
| Dosage and Administration (2.2, 2.3, 2.4, 2.7, 2.8) | 5/2023 |
| Warnings and Precautions (5.5) | 7/2023 |
Indications and Usage for Cosentyx
COSENTYX is a human interleukin-17A antagonist indicated for the treatment of:
- moderate to severe plaque psoriasis in patients 6 years and older who are candidates for systemic therapy or phototherapy. (1.1)
- active psoriatic arthritis (PsA) in patients 2 years of age and older. (1.2)
- adults with active ankylosing spondylitis (AS). (1.3)
- adults with active non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis (nr-axSpA) with objective signs of inflammation. (1.4)
- active enthesitis-related arthritis (ERA) in patients 4 years of age and older. (1.5)
Cosentyx Dosage and Administration
- Prior to COSENTYX initiation, complete all age-appropriate vaccinations, evaluate patients for tuberculosis (TB). (2.1). See Full Prescribing Information for instructions on preparation and administration of COSENTYX. (2.7, 2.8, 2.9)
-
Plaque Psoriasis:
- Adults: Recommended dosage is 300 mg by subcutaneous injection at Weeks 0, 1, 2, 3, and 4 followed by 300 mg every 4 weeks. For some patients, a dose of 150 mg may be acceptable. (2.2)
-
Pediatric Patients 6 Years and Older: Recommended weight-based dosage is administered by subcutaneous injection at Weeks 0, 1, 2, 3, and 4 and every 4 weeks thereafter.
- For patients < 50 kg (at the time of dosing), the dose is 75 mg.
- For patients ≥ 50 kg (at the time of dosing), the dose is 150 mg. (2.2)
-
Psoriatic Arthritis:
Adults: Recommended dosages are:
- For PsA patients with coexistent moderate to severe plaque psoriasis, use the dosage and administration for plaque psoriasis. (2.2)
- For other PsA patients, administer with or without a loading dosage.
- With a loading dosage: 150 mg at Weeks 0, 1, 2, 3, and 4 and every 4 weeks thereafter
- Without a loading dosage: 150 mg every 4 weeks
- If a patient continues to have active PsA, consider a dosage of 300 mg every 4 weeks. (2.3)
Pediatric Patients 2 years and older: Recommended weight-based dosage is administered by subcutaneous injection at Weeks 0, 1, 2, 3, and 4 and every 4 weeks thereafter.
- For patients ≥ 15 kg and < 50 kg the dose is 75 mg.
- For patients ≥ 50 kg the dose is 150 mg. (2.3)
-
Ankylosing Spondylitis: Administer with or without a loading dosage.
The recommended dosages are:- With a loading dosage: 150 mg at Weeks 0, 1, 2, 3, and 4 and every 4 weeks thereafter.
- Without a loading dosage: 150 mg every 4 weeks.
- If a patient continues to have active ankylosing spondylitis, consider a dosage of 300 mg every 4 weeks. (2.4)
-
Non-Radiographic Axial Spondyloarthritis: Administer with or without a loading dosage. The recommended dosage is:
- With a loading dosage: 150 mg at Weeks 0, 1, 2, 3, and 4 and every 4 weeks thereafter. (2.5)
- Without a loading dosage: 150 mg every 4 weeks. (2.5)
-
Enthesitis-Related Arthritis: Recommended weight-based dosage is administered by subcutaneous injection at Weeks 0, 1, 2, 3, and 4 and every 4 weeks thereafter.
- For patients ≥ 15 kg and < 50 kg the dose is 75 mg.
- For patients ≥ 50 kg the dose is 150 mg. (2.6)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
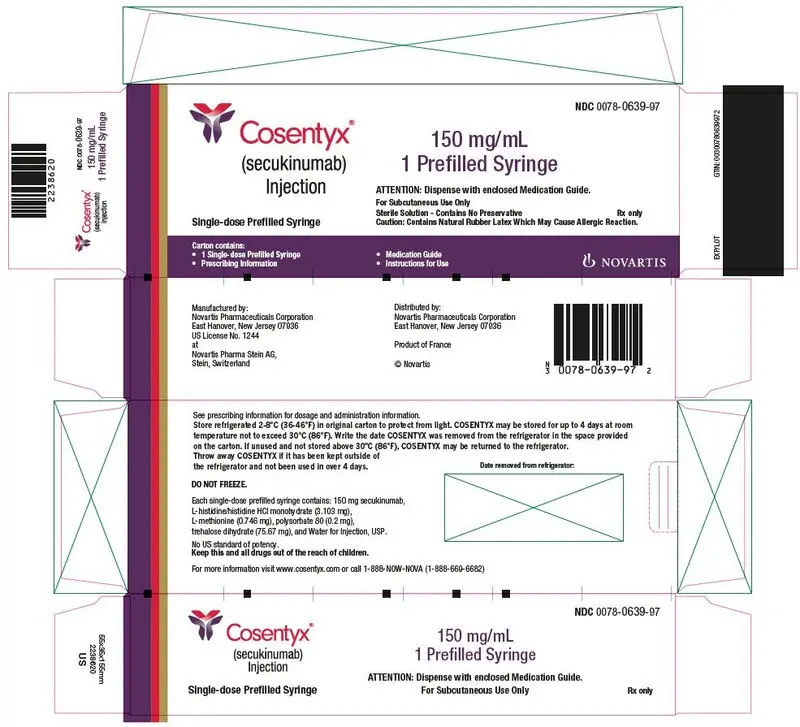
- Injection: 300 mg/2 mL solution in a single-dose UnoReady® pen and in a single-dose prefilled syringe. (3)
- Injection: 150 mg/mL solution in a single-dose Sensoready® pen and in a single-dose prefilled syringe. (3)
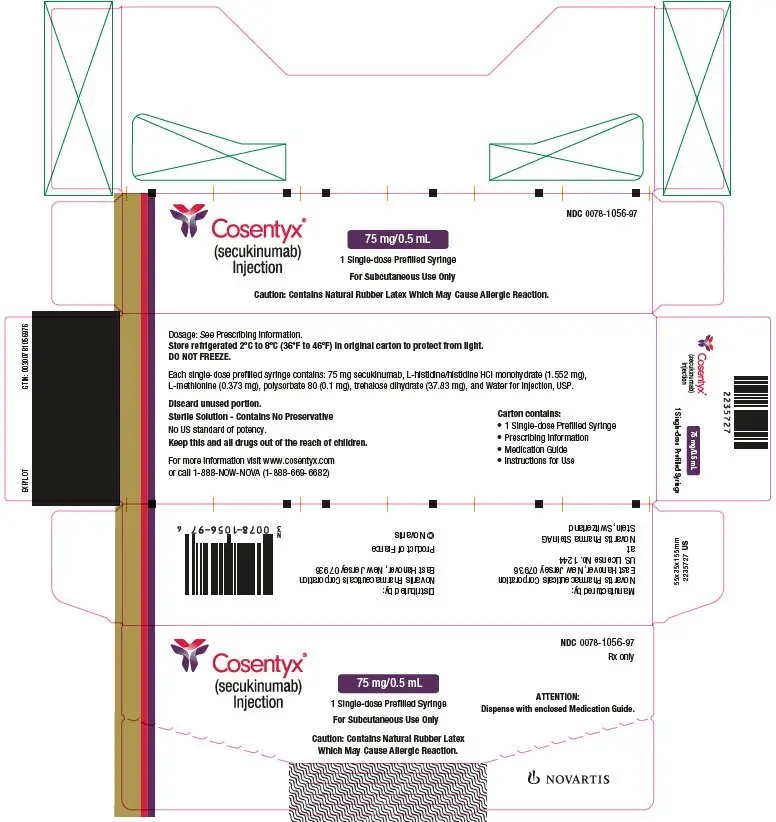
- Injection: 75 mg/0.5 mL solution in a single-dose prefilled syringe (for pediatric patients). (3)
Contraindications
Serious hypersensitivity to secukinumab or any excipients in COSENTYX. (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Infections: Serious infections have occurred. Caution should be exercised when considering the use of COSENTYX in patients with a chronic infection or a history of recurrent infection. If a serious infection develops, discontinue COSENTYX until the infection resolves. (5.1)
- Hypersensitivity Reactions: If an anaphylactic reaction or other serious allergic reaction occurs, discontinue COSENTYX immediately and initiate appropriate therapy. (5.2)
- Tuberculosis (TB): Prior to initiating treatment with COSENTYX, evaluate for TB. (5.3)
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Cases of inflammatory bowel disease were observed in clinical trials. Caution should be exercised when prescribing COSENTYX to patients with inflammatory bowel disease. (5.4)
- Eczematous Eruptions: Cases of severe eczematous eruptions have occurred in patients receiving COSENTYX. (5.5)
- Immunizations: Avoid use of live vaccines in patients treated with COSENTYX. (5.7)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions (> 1%) are nasopharyngitis, diarrhea, and upper respiratory tract infection. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation at 1-888-669-6682 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 7/2023
Related/similar drugs
Otezla, Sotyktu, prednisone, naproxen, methotrexate, Humira, EnbrelFull Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Cosentyx
1.1 Plaque Psoriasis
COSENTYX® is indicated for the treatment of moderate to severe plaque psoriasis in patients 6 years and older who are candidates for systemic therapy or phototherapy.
1.2 Psoriatic Arthritis
COSENTYX is indicated for the treatment of active psoriatic arthritis (PsA) in patients 2 years of age and older.
1.3 Ankylosing Spondylitis
COSENTYX is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with active ankylosing spondylitis (AS).
2. Cosentyx Dosage and Administration
2.1 Testing and Procedures Prior to Treatment Initiation
Perform the following evaluations prior to COSENTYX initiation:
- Evaluate patients for tuberculosis (TB) infection. COSENTYX initiation is not recommended in patients with active TB infection. Initiate treatment of latent TB prior to initiation of COSENTYX [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
- Complete all age-appropriate vaccinations as recommended by current immunization guidelines prior to initiating treatment with COSENTYX [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
2.2 Recommended Dosage Plaque Psoriasis
Adults
The recommended dosage in adults with plaque psoriasis is 300 mg by subcutaneous injection at Weeks 0, 1, 2, 3, and 4 and every 4 weeks thereafter. Each 300 mg dosage is given as one subcutaneous injection of 300 mg or as two subcutaneous injections of 150 mg.
For some patients, a dosage of 150 mg by subcutaneous injection at Weeks 0, 1, 2, 3, and 4 and every 4 weeks thereafter may be acceptable.
Pediatric Patients 6 Years of Age and Older
The recommended weight-based dosage in pediatric patients 6 years of age and older with plaque psoriasis is administered by subcutaneous injection at Weeks 0, 1, 2, 3, and 4 and every 4 weeks thereafter.
- For patients < 50 kg (at the time of dosing), the recommended dose is 75 mg.
- For patients ≥ 50 kg (at the time of dosing), the recommended dose is 150 mg.
2.3 Recommended Dosage in Psoriatic Arthritis
Adults
For adult patients with PsA and with coexistent moderate to severe plaque psoriasis, use the dosage and administration recommendations in adults for plaque psoriasis [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
For other adult patients with PsA, administer COSENTYX with or without a loading dosage by subcutaneous injection.
The recommended dosage:
- With a loading dosage is 150 mg at Weeks 0, 1, 2, 3, and 4 and every 4 weeks thereafter.
- Without a loading dosage is 150 mg every 4 weeks.
- If a patient continues to have active PsA, consider a dosage of 300 mg by subcutaneous injection every 4 weeks. Each 300 mg dosage is given as one subcutaneous injection of 300 mg or as two subcutaneous injections of 150 mg.
Pediatric Patients 2 Years of Age and Older
The recommended weight-based dosage in pediatric patients 2 years of age and older with PsA is administered by subcutaneous injection at Weeks 0, 1, 2, 3, and 4 and every 4 weeks thereafter.
- For patients ≥ 15 kg and < 50 kg, the recommended dose is 75 mg.
- For patients ≥ 50 kg, the recommended dose is 150 mg.
COSENTYX may be administered with or without methotrexate.
2.4 Recommended Dosage in Ankylosing Spondylitis
Administer COSENTYX with or without a loading dosage by subcutaneous injection in adult patients with active AS.
The recommended dosage:
- With a loading dosage is 150 mg at Weeks 0, 1, 2, 3, and 4 and every 4 weeks thereafter.
- Without a loading dosage is 150 mg every 4 weeks.
- If a patient continues to have active AS, consider a dosage of 300 mg every 4 weeks by subcutaneous injection. Each 300 mg dosage is given as one subcutaneous injection of 300 mg or as two subcutaneous injections of 150 mg.
2.5 Recommended Dosage in Non-Radiographic Axial Spondyloarthritis
Administer COSENTYX with or without a loading dosage by subcutaneous injection in adult patients with active nr-axSpA.
The recommended dosage:
- With a loading dosage is 150 mg at Weeks 0, 1, 2, 3, and 4 and every 4 weeks thereafter.
- Without a loading dosage is 150 mg every 4 weeks.
2.6 Recommended Dosage in Enthesitis-Related Arthritis
The recommended weight-based dosage in pediatric patients 4 years of age and older with ERA is administered by subcutaneous injection at Weeks 0, 1, 2, 3, and 4 and every 4 weeks thereafter.
- For patients ≥ 15 kg and < 50 kg, the recommended dose is 75 mg.
- For patients ≥ 50 kg, the recommended dose is 150 mg.
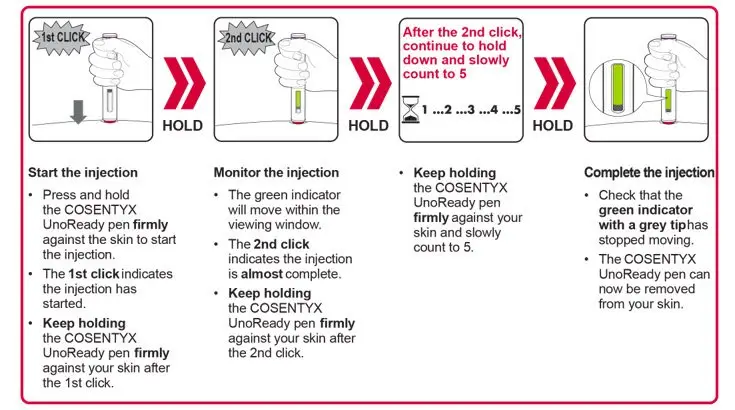
2.7 Important Administration Instructions
COSENTYX is intended for use under the guidance and supervision of a physician.
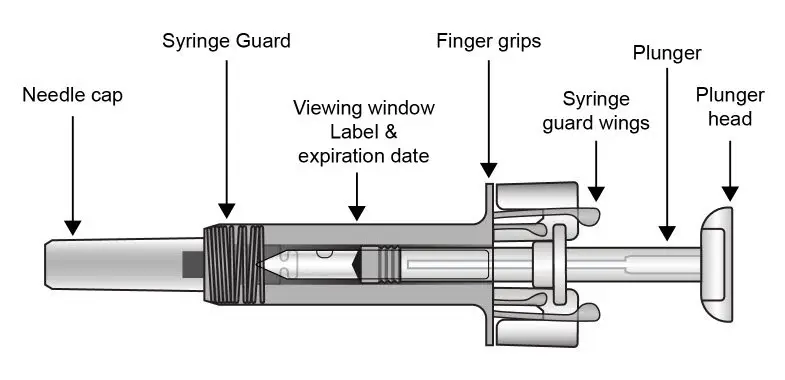
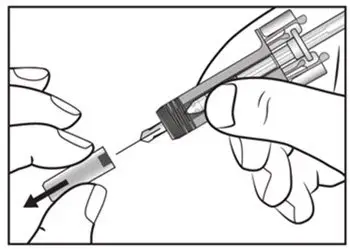
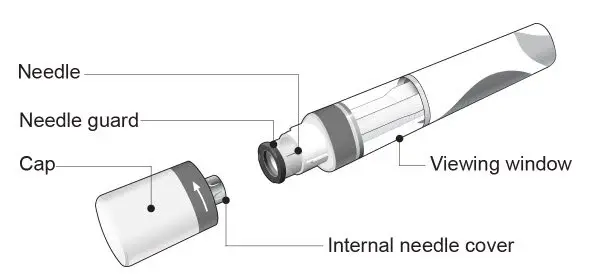
The COSENTYX “Instructions for Use” for each dosage form contains more detailed instructions on the preparation and administration of COSENTYX [see Instructions for Use].
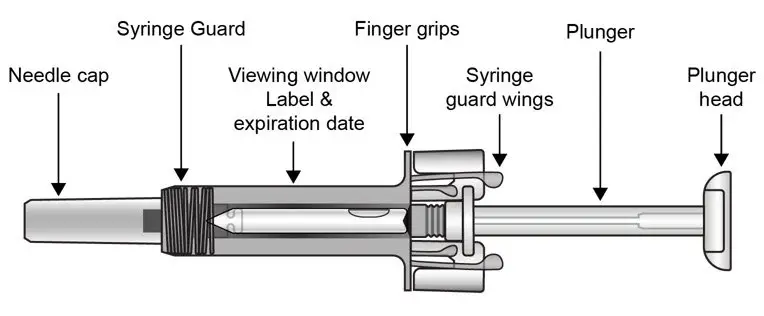
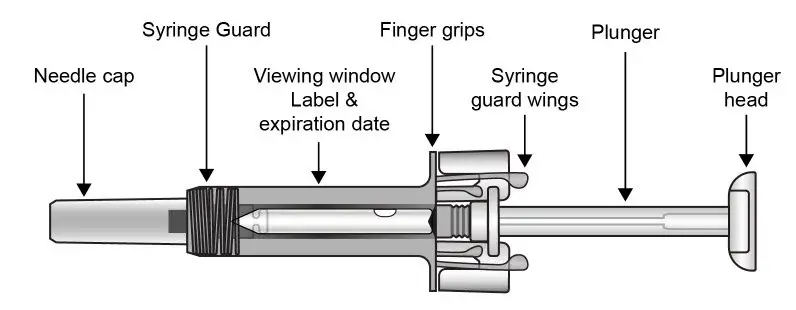
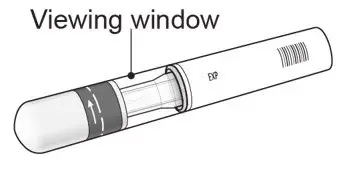
UnoReady Pen/Sensoready Pen/Prefilled Syringes
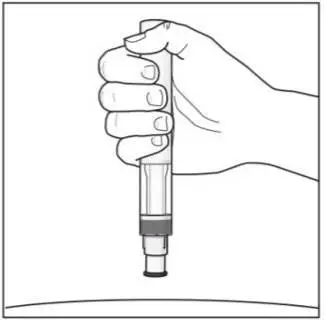
Adult patients may self-administer COSENTYX or be injected by a caregiver after proper training in subcutaneous injection technique.
Pediatric patients should not self-administer COSENTYX. An adult caregiver should prepare and inject COSENTYX after proper training in subcutaneous injection technique.
Administration Instructions
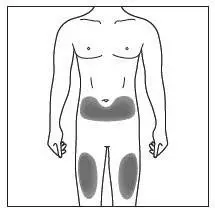
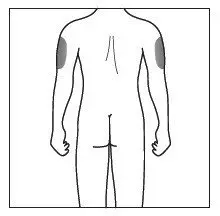
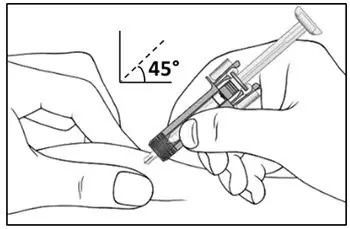
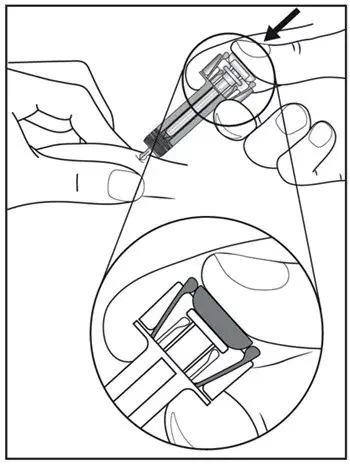
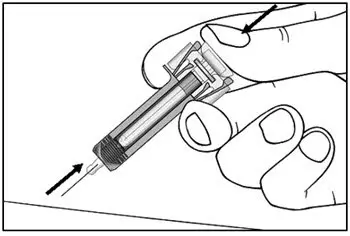
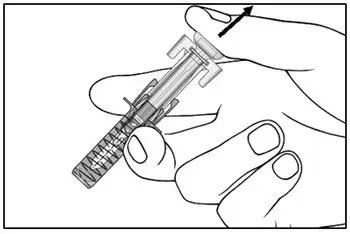
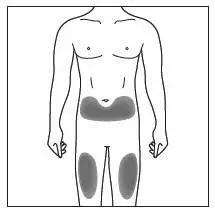
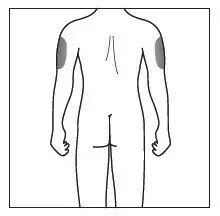
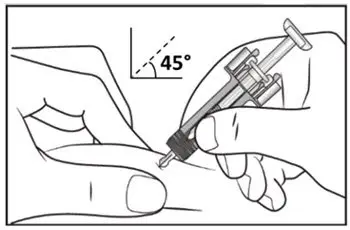
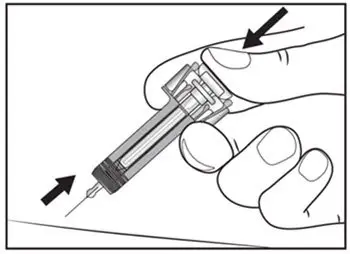
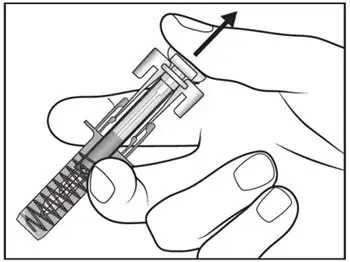
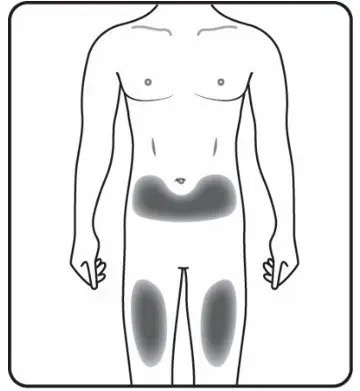
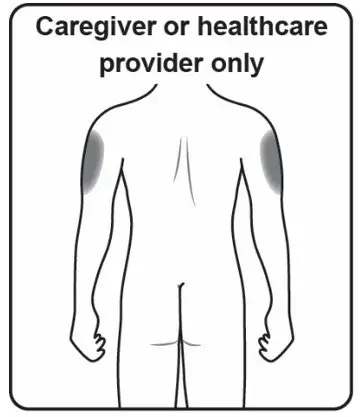
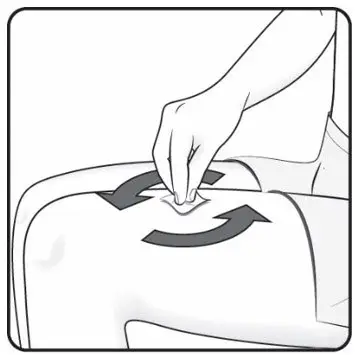
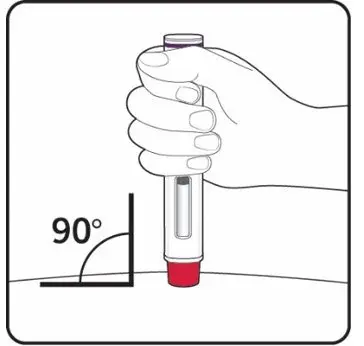
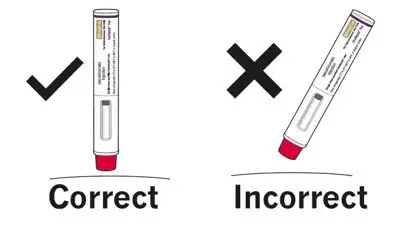
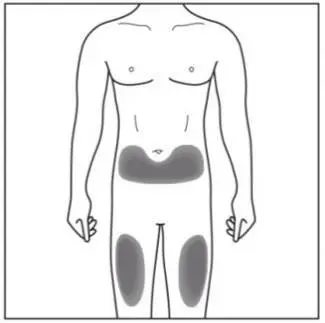
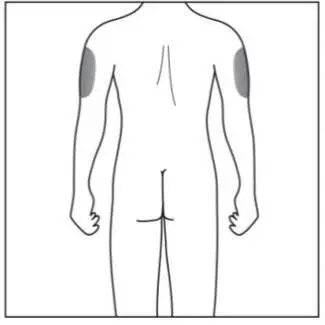
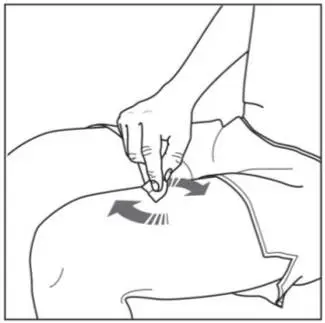
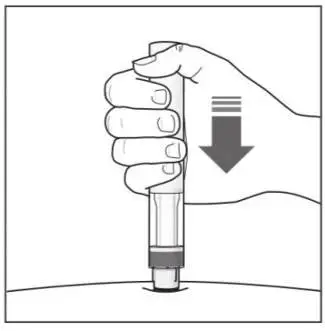
Administer each injection at a different anatomic location (such as upper arms, thighs, or any quadrant of abdomen) than the previous injection, and not into areas where the skin is tender, bruised, erythematous, indurated, or affected by psoriasis. Administration of COSENTYX in the upper, outer arm may be performed by a caregiver or healthcare provider.
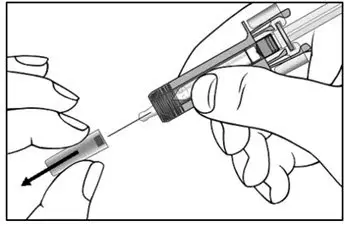
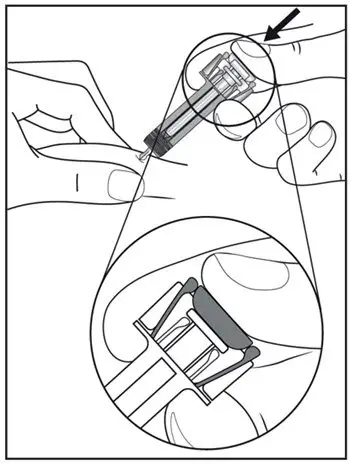
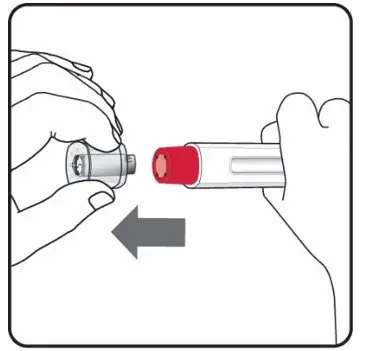
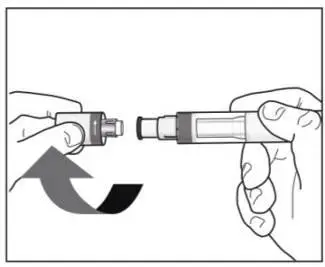
2.8 Preparation for Use of COSENTYX 300 mg/2 mL UnoReady Pen, 150 mg/mL Sensoready Pen and Prefilled Syringes (300 mg/2 mL, 150 mg/mL, 75 mg/0.5 mL)
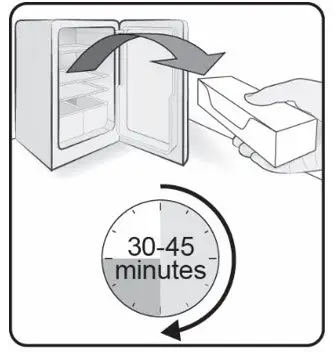
Before injection, remove COSENTYX from the refrigerator and allow COSENTYX to reach room temperature (15 to 30 minutes for the Sensoready pen, the 150 mg/mL and 75 mg/0.5 mL prefilled syringes; 30 to 45 minutes for the UnoReady pen and the 300 mg/2 mL prefilled syringe) without removing the needle cap.
The removable cap of the COSENTYX 150 mg/mL Sensoready pen and the COSENTYX prefilled syringes (150 mg/mL, 75 mg/0.5 mL) contain natural rubber latex and should not be handled by latex-sensitive individuals [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
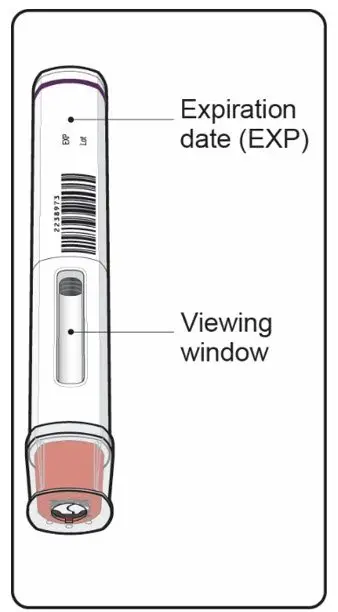
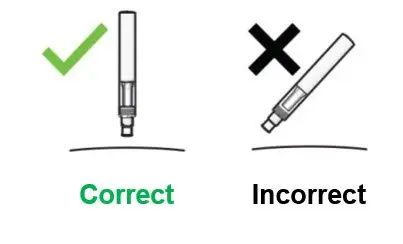
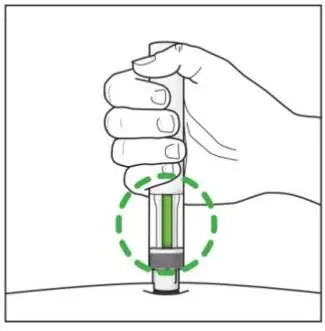
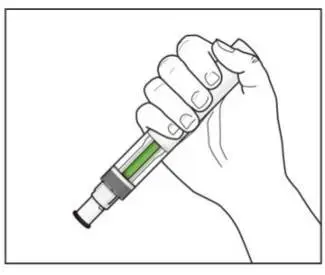
Inspect COSENTYX visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration. COSENTYX injection is a clear to slightly opalescent, colorless to slightly yellow solution. Do not use if the liquid contains visible particles, is discolored or cloudy. Discard any unused product.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
- Injection: 300 mg/2 mL as a clear to opalescent, colorless to slightly yellowish solution in a single-dose UnoReady pen
- Injection: 300 mg/2 mL as a clear to opalescent, colorless to slightly yellowish solution in a single-dose prefilled syringe
- Injection: 150 mg/mL as a clear to opalescent, colorless to slightly yellowish solution in a single-dose Sensoready pen
- Injection: 150 mg/mL as a clear to opalescent, colorless to slightly yellowish solution in a single-dose prefilled syringe
- Injection: 75 mg/0.5 mL as a clear to opalescent, colorless to slightly yellowish solution in a single-dose prefilled syringe (for pediatric patients less than 50 kg)
4. Contraindications
COSENTYX is contraindicated in patients with a previous serious hypersensitivity reaction to secukinumab or to any of the excipients in COSENTYX. Cases of anaphylaxis have been reported during treatment with COSENTYX [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Infections
COSENTYX may increase the risk of infections. In clinical trials, a higher rate of infections was observed in COSENTYX treated subjects compared to placebo-treated subjects. In placebo-controlled clinical trials in subjects with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis, higher rates of common infections, such as nasopharyngitis (11.4% versus 8.6%), upper respiratory tract infection (2.5% versus 0.7%) and mucocutaneous infections with candida (1.2% versus 0.3%) were observed with COSENTYX compared with placebo. A similar increase in risk of infection was seen in placebo-controlled trials in subjects with PsA, AS and nr-axSpA. The incidence of some types of infections appeared to be dose-dependent in clinical studies [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. In the postmarketing setting, serious and some fatal infections have been reported in patients receiving COSENTYX.
Exercise caution when considering the use of COSENTYX in patients with a chronic infection or a history of recurrent infection.
Instruct patients to seek medical advice if signs or symptoms suggestive of an infection occur. If a patient develops a serious infection, monitor the patient closely and discontinue COSENTYX until the infection resolves.
5.2 Hypersensitivity Reactions
Anaphylaxis and cases of urticaria occurred in COSENTYX treated subjects in clinical trials. If an anaphylactic or other serious allergic reaction occurs, administration of COSENTYX should be discontinued immediately and appropriate therapy initiated [see Contraindications (4) and Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
5.3 Pre-Treatment Evaluation for Tuberculosis
Evaluate patients for tuberculosis (TB) infection prior to initiating treatment with COSENTYX. Avoid administration of COSENTYX to patients with active TB infection. Initiate treatment of latent TB prior to administering COSENTYX. Consider anti-TB therapy prior to initiation of COSENTYX in patients with a past history of latent or active TB in whom an adequate course of treatment cannot be confirmed. Monitor patients closely for signs and symptoms of active TB during and after treatment.
5.4 Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Caution should be used when prescribing COSENTYX to patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Exacerbations, in some cases serious, occurred in COSENTYX treated subjects during clinical trials in plaque psoriasis, PsA, AS and nr-axSpA. In addition, new onset inflammatory bowel disease cases occurred in clinical trials with COSENTYX. In an exploratory trial in 59 subjects with active Crohn’s disease, there were trends toward greater disease activity and increased adverse events in the secukinumab group as compared to the placebo group. Patients who are treated with COSENTYX should be monitored for signs and symptoms of inflammatory bowel disease [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
5.5 Eczematous Eruptions
In postmarketing reports, cases of severe eczematous eruptions, including atopic dermatitis-like eruptions, dyshidrotic eczema, and erythroderma, were reported in patients receiving COSENTYX; some cases resulted in hospitalization. The onset of eczematous eruptions was variable, ranging from days to months after the first dose of COSENTYX.
Treatment may need to be discontinued to resolve the eczematous eruption. Some patients were successfully treated for eczematous eruptions while continuing COSENTYX.
5.6 Risk of Hypersensitivity in Latex-Sensitive Individuals
The removable caps of the COSENTYX 150 mg/mL Sensoready pen and the COSENTYX 1 mL and 0.5 mL prefilled syringes contain natural rubber latex, which may cause an allergic reaction in latex-sensitive individuals. The safe use of COSENTYX 150 mg/mL Sensoready pen or 1 mL and 0.5 mL prefilled syringes in latex-sensitive individuals has not been studied.
5.7 Immunizations
Prior to initiating therapy with COSENTYX, consider completion of all age-appropriate immunizations according to current immunization guidelines. COSENTYX may alter a patient's immune response to live vaccines. Avoid use of live vaccines in patients treated with COSENTYX [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)].
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail elsewhere in the labeling:
- Infections [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Hypersensitivity Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Adult Plaque Psoriasis
A total of 3430 plaque psoriasis adult subjects were treated with COSENTYX in controlled and uncontrolled clinical trials. Of these, 1641 subjects were exposed for at least 1 year.
Four placebo-controlled Phase 3 trials in plaque psoriasis subjects were pooled to evaluate the safety of COSENTYX in comparison to placebo up to 12 weeks after treatment initiation, in Trials PsO1, PsO2, PsO3, and PsO4. In total, 2077 subjects were evaluated (691 to COSENTYX 300 mg group, 692 to COSENTYX 150 mg group, and 694 to placebo group). Subjects randomized to COSENTYX received 300 mg or 150 mg doses subcutaneously at Weeks 0, 1, 2, 3, and 4 followed by the same dose every 4 weeks [see Clinical Studies (14)].
Table 1 summarizes the adverse reactions that occurred at a rate of at least 1% and at a higher rate in the COSENTYX groups than the placebo group during the 12-week placebo-controlled period of the placebo-controlled trials.
| COSENTYX | |||
| Adverse reactions | 300 mg (N = 691) n (%) | 150 mg (N = 692) n (%) | Placebo (N = 694) n (%) |
| Nasopharyngitis | 79 (11.4) | 85 (12.3) | 60 (8.6) |
| Diarrhea | 28 (4.1) | 18 (2.6) | 10 (1.4) |
| Upper respiratory tract infection | 17 (2.5) | 22 (3.2) | 5 (0.7) |
| Rhinitis | 10 (1.4) | 10 (1.4) | 5 (0.7) |
| Oral herpes | 9 (1.3) | 1 (0.1) | 2 (0.3) |
| Pharyngitis | 8 (1.2) | 7 (1.0) | 0 (0) |
| Urticaria | 4 (0.6) | 8 (1.2) | 1 (0.1) |
| Rhinorrhea | 8 (1.2) | 2 (0.3) | 1 (0.1) |
Adverse reactions that occurred at rates less than 1% in the placebo-controlled period of Trials PsO1, PsO2, PsO3, and PsO4 through Week 12 included: sinusitis, tinea pedis, conjunctivitis, tonsillitis, oral candidiasis, impetigo, otitis media, otitis externa, inflammatory bowel disease, increased liver transaminases, and neutropenia.
Infections
In the placebo-controlled period of the clinical trials in plaque psoriasis (a total of 1382 subjects treated with COSENTYX and 694 subjects treated with placebo up to 12 weeks), infections were reported in 28.7% of subjects treated with COSENTYX compared with 18.9% of subjects treated with placebo. Serious infections occurred in 0.14% of subjects treated with COSENTYX and in 0.3% of subjects treated with placebo.
Over the entire treatment period (a total of 3430 plaque psoriasis subjects treated with COSENTYX for up to 52 weeks for the majority of subjects), infections were reported in 47.5% of subjects treated with COSENTYX (0.9 per patient-year of follow-up). Serious infections were reported in 1.2% of subjects treated with COSENTYX (0.015 per patient-year of follow-up).
Phase 3 data showed an increasing trend for some types of infection with increasing serum concentration of secukinumab. Candida infections, herpes viral infections, staphylococcal skin infections, and infections requiring treatment increased as serum concentration of secukinumab increased.
In the psoriasis open-label extension of Trials PsO1 and PsO2 (median follow-up of 3.9 years), representing 3582 subject-years of exposure, 74% of COSENTYX treated subjects reported infections (55 per 100 patient-years). Serious infections were reported in 4.5% of subjects (1.4 per 100 patient-years). Sepsis was reported in 5 subjects (0.2 per 100 patient-years).
Neutropenia was observed in controlled portion of clinical trials. Most cases of secukinumab-associated neutropenia were transient and reversible. No serious infections were associated with cases of neutropenia.
In the open-label extension of Trials PsO1 and PsO2, neutropenia (ANC < 1 x109/L) was reported in 1% of COSENTYX treated subjects (0.3 per 100 patient-years). Some cases of serious infections were associated with neutropenia; however, the causal relationship was not established.
Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Cases of inflammatory bowel disease, in some cases serious, were observed in clinical trials with COSENTYX. In the plaque psoriasis program, with 3430 subjects exposed to COSENTYX over the entire treatment period for up to 52 weeks (2725 patient-years), there were 3 cases (0.11 per 100 patient-years) of exacerbation of Crohn’s disease, 2 cases (0.08 per 100 patient-years) of exacerbation of ulcerative colitis, and 2 cases (0.08 per 100 patient-years) of new onset ulcerative colitis. There were no cases in placebo subjects (N = 793; 176 patient-years) during the 12-week placebo-controlled period.
One case of exacerbation of Crohn’s disease was reported in open-label portions of clinical trials in plaque psoriasis.
Hypersensitivity Reactions
Anaphylaxis and cases of urticaria occurred in COSENTYX treated subjects in clinical trials [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Pediatric Plaque Psoriasis
The safety of COSENTYX was assessed in two Phase 3 trials in pediatric subjects with plaque psoriasis.
The first was a randomized, double-blind, placebo and active-controlled, 236-week trial (Trial PsO6) that enrolled 162 pediatric subjects 6 years of age and older, with severe plaque psoriasis (defined by PASI score ≥ 20, an IGA modified 2011 score of 4, and involving ≥ 10% of the body surface area [BSA]) who were candidates for systemic therapy. The 162 subjects were randomized to receive placebo, a biologic active control, or COSENTYX. In the COSENTYX groups, subjects with body weight less than 25 kg received 75 mg, subjects with body weight 25 to less than 50 kg received either 75 mg or 150 mg (2 times the recommended dose), and subjects with body weight of at least 50 kg received either 150 mg or 300 mg (2 times the recommended dose).
The second trial was a randomized, open-label, 208-week trial (Trial PsO7; NCT03668613) of 84 subjects 6 years of age and older with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis (defined by a PASI score ≥ 12, IGA mod 2011 score of ≥ 3, and BSA involvement of ≥ 10% at randomization) who were randomized into two COSENTYX arms [Arm 1: 75 mg for body weight (BW) < 50 kg or 150 mg for ≥ 50 kg; and Arm 2: 75 mg for BW < 25 kg, 150 mg for BW ≥ 25 kg and < 50 kg, or 300 mg for BW ≥ 50 kg].
The safety profile reported in these trials was consistent with the safety profile reported in adult plaque psoriasis trials.
Infections
One case of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) toxic shock syndrome (TSS) was reported in a COSENTYX treated subject during the placebo-controlled period.
In the pediatric safety pool, which includes all subjects who took at least one dose of COSENTYX during the treatment periods [198 subjects (287 patient years)], 22 (11%) subjects reported ≥ Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) Grade 2 neutropenia (≥1,000 to < 1,500 cells/mm3) with 57% of subjects followed for one year or more and 30% of subjects followed for two years or more. During the placebo-controlled period which included a total of 80 subjects treated with secukinumab and 41 subjects treated with placebo up to 12 weeks, ≥ CTCAE Grade 2 neutropenia was reported in 3 (4%) of the subjects treated with secukinumab compared with no subjects treated with placebo. No serious infections were associated with cases of neutropenia.
Adult Psoriatic Arthritis
COSENTYX was studied in two placebo-controlled PsA trials with 1003 adult patients (703 patients on COSENTYX and 300 patients on placebo). Of the 703 patients who received COSENTYX, 299 patients received a subcutaneous loading dose of COSENTYX (PsA1) and 404 patients received an intravenous loading dose of secukinumab (PsA2) followed by COSENTYX administered by subcutaneous injection every four weeks. During the 16-week placebo-controlled period of the trials in patients with PsA, the overall proportion of patients with adverse events was similar in the secukinumab and placebo-treatment groups (59% and 58%, respectively). The adverse events that occurred at a proportion of at least 2% and at a higher proportion in the COSENTYX groups than the placebo groups during the 16-week placebo-controlled period were nasopharyngitis, upper respiratory tract infection, headache, nausea, and hypercholesterolemia. The safety profile observed in patients with PsA treated with COSENTYX is consistent with the safety profile in psoriasis.
Similar to the clinical trials in patients with psoriasis, there was an increased proportion of patients with infections in the COSENTYX groups (29%) compared to placebo group (26%).
There were cases of Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis that include patients who experienced either exacerbations or the development of new disease. There were three cases of inflammatory bowel disease, of which two patients received secukinumab and one received placebo.
Adult Ankylosing Spondylitis
COSENTYX was studied in two placebo-controlled AS trials with 590 adult patients (394 patients on COSENTYX and 196 patients on placebo). Of the 394 patients who received COSENTYX, 145 patients received a subcutaneous load of COSENTYX (study AS1), and 249 received an intravenous loading dose of secukinumab (study AS2) followed by COSENTYX administered by subcutaneous injection every four weeks. During the 16-week placebo-controlled period of the trials in patients with AS, the overall proportion of patients with adverse events was higher in the secukinumab groups than the placebo-treatment groups (66% and 59%, respectively). The adverse events that occurred at a proportion of at least 2% and at a higher proportion in the COSENTYX groups than the placebo groups during the 16-week placebo-controlled period were nasopharyngitis, nausea, and upper respiratory tract infection. The safety profile observed in patients with ankylosing spondylitis treated with COSENTYX is consistent with the safety profile in psoriasis. In a third controlled study of AS (study AS3), the safety profile of the 300 mg dose of COSENTYX was consistent with the safety profile of the 150 mg dose of COSENTYX.
Similar to clinical trials in patients with psoriasis, there was an increased proportion of patients with infections in the COSENTYX groups (31%) compared to the placebo group (18%).
In the original AS program, with 571 patients exposed to COSENTYX there were 8 cases of inflammatory bowel disease during the entire treatment period [5 Crohn’s (0.7 per 100 patient-years) and 3 ulcerative colitis (0.4 per 100 patient-years)]. During the placebo-controlled 16-week period, there were 2 Crohn’s disease exacerbations and 1 new onset ulcerative colitis case that was a serious adverse event in patients treated with COSENTYX compared to none of the patients treated with placebo. During the remainder of the study when all patients received COSENTYX, 1 patient developed Crohn’s disease, 2 patients had Crohn’s exacerbations, 1 patient developed ulcerative colitis, and 1 patient had an ulcerative colitis exacerbation.
Adult Non-Radiographic Axial Spondyloarthritis
COSENTYX was studied in one randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled nr-axSpA trial with 555 adult patients (185 patients on with load COSENTYX, 184 patients on without load COSENTYX and 186 patients on placebo). The safety profile for patients with nr-axSpA treated with COSENTYX was overall similar to the safety profile seen in patients with AS and other previous experience with COSENTYX. Patients in nr-axSpA1 study who received the loading dosing regimen compared to those without the loading regimen, had higher incidence of infections and infestations (92 per 100 patient-years vs 72 per 100 patient-years), including nasopharyngitis, upper respiratory tract infection and urinary tract infection, and gastrointestinal disorders (27 per 100 patient-years vs 22 per 100 patient-years), including gastritis, lower abdominal pain, colitis, diarrhea, and hematochezia.
Juvenile Psoriatic Arthritis and Enthesitis-Related Arthritis
COSENTYX was studied in one double-blind, placebo-controlled, event-driven, randomized trial in 86 pediatric patients aged 2 to less than 18 years old with Juvenile Psoriatic Arthritis (JPsA) and ERA. The safety profile reported in this study was consistent with the safety profile of secukinumab.
6.2 Immunogenicity
As with all therapeutic proteins, there is the potential for immunogenicity. The immunogenicity of COSENTYX was evaluated using an electrochemiluminescence-based bridging immunoassay. Less than 1% of subjects treated with COSENTYX developed antibodies to secukinumab in up to 52 weeks of treatment. However, this assay has limitations in detecting anti-secukinumab antibodies in the presence of secukinumab; therefore, the incidence of antibody development might not have been reliably determined. Of the subjects who developed antidrug antibodies, approximately one-half had antibodies that were classified as neutralizing. Neutralizing antibodies were not associated with loss of efficacy.
The detection of antibody formation is highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assay. Additionally, the observed incidence of antibody (including neutralizing antibody) positivity in an assay may be influenced by several factors, including assay methodology, sample handling, timing of sample collection, concomitant medications, and underlying disease. For these reasons, comparison of incidence of antibodies to COSENTYX with the incidences of antibodies to other products may be misleading.
6.3 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been reported during postapproval use of COSENTYX. Because they are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders: Eczematous eruptions (atopic dermatitis-like eruptions, dyshidrotic eczema, and erythroderma) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
7. Drug Interactions
CYP450 Substrates
The formation of CYP450 enzymes can be altered by increased levels of certain cytokines (e.g., IL-1, IL-6, IL-10, TNFα, IFN) during chronic inflammation.
Upon initiation or discontinuation of COSENTYX in patients who are receiving concomitant CYP450 substrates, particularly those with a narrow therapeutic index, consider monitoring for therapeutic effect or drug concentration and consider dosage adjustment of the CYP450 substrate as needed [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
It is not known whether secukinumab is excreted in human milk or absorbed systemically after ingestion. There are no data on the effects of COSENTYX on the breastfed child or the effects on milk production. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for COSENTYX and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from COSENTYX or from the underlying maternal condition.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Pediatric Plaque Psoriasis
The safety and effectiveness of COSENTYX have been established in pediatric patients aged 6 years and older with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) and Clinical Studies (14.2)]. Safety and effectiveness of COSENTYX in pediatric patients with plaque psoriasis below the age of 6 years have not been established.
Juvenile Psoriatic Arthritis and Enthesitis-Related Arthritis
The safety and effectiveness of COSENTYX have been established in pediatric patients weighing 15 kg or more with JPsA (2 years and older) and ERA (4 years and older) [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) and Clinical Studies (14.6)].
The safety and effectiveness of COSENTYX in pediatric patients with JPsA below the age of 2 years and with body weight less than 15 kg have not been established.
The safety and effectiveness of COSENTYX in pediatric patients with ERA below the age of 4 years and with body weight less than 15 kg have not been established.
12. Cosentyx - Clinical Pharmacology
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetic (PK) properties of secukinumab observed in PsA, AS and nr-axSpA patients were similar to the PK properties displayed in plaque psoriasis patients.
Absorption
Following a single subcutaneous dose of either 150 mg (one-half the recommended dose) or 300 mg (administered as two injections of 150 mg) in plaque psoriasis subjects, secukinumab reached peak mean (± SD) serum concentrations (Cmax) of 13.7 ± 4.8 mcg/mL and 27.3 ± 9.5 mcg/mL, respectively, by approximately 6 days post dose.
Following multiple subcutaneous doses of secukinumab (administered as one or two injections of 150 mg), the mean (± SD) serum trough concentrations of secukinumab ranged from 22.8 ± 10.2 mcg/mL (150 mg) to 45.4 ± 21.2 mcg/mL (300 mg) at Week 12. At the 300 mg dose at Week 4 and Week 12, the mean trough concentrations resulted from the 150 mg/mL Sensoready pen were 23% to 26% higher than those from the prefilled syringe based on cross-study comparisons. Following multiple subcutaneous doses of 300 mg administered via the 300 mg/2 mL UnoReady pen, the mean serum trough concentrations of secukinumab were generally consistent with those in the previous Sensoready pen study used to deliver 300 mg.
Steady-state concentrations of secukinumab were achieved by Week 24 following the every 4-week dosing regimens. The mean (± SD) steady-state trough concentrations ranged from 16.7 ± 8.2 mcg/mL (150 mg) to 34.4 ± 16.6 mcg/mL (300 mg administered as two injections of 150 mg).
In healthy subjects and subjects with plaque psoriasis, secukinumab bioavailability ranged from 55% to 77% following subcutaneous dose of 150 mg (one-half the recommended dose) or 300 mg (administered as two injections of 150 mg).
Distribution
The mean volume of distribution during the terminal phase (Vz) following a single intravenous administration ranged from 7.10 to 8.60 L in plaque psoriasis subjects. Intravenous use is not recommended [see Dosage and Administration (2)].
Secukinumab concentrations in interstitial fluid in lesional and non-lesional skin of plaque psoriasis subjects ranged from 27% to 40% of those in serum at 1 and 2 weeks after a single subcutaneous dose of secukinumab 300 mg (administered as two injections of 150 mg).
Elimination
Metabolism
The metabolic pathway of secukinumab has not been characterized. As a human IgG1κ monoclonal antibody secukinumab is expected to be degraded into small peptides and amino acids via catabolic pathways in the same manner as endogenous IgG.
Excretion
The mean systemic clearance (CL) ranged from 0.14 L/day to 0.22 L/day and the mean half-life ranged from 22 to 31 days in plaque psoriasis subjects following intravenous and subcutaneous administration across all psoriasis trials. Intravenous use is not recommended [see Dosage and Administration (2)].
Dose Linearity
Secukinumab exhibited dose-proportional pharmacokinetics in subjects with psoriasis over a dose range from 25 mg (approximately 0.083 times the recommended dose) to 300 mg following subcutaneous administrations.
Weight
Secukinumab clearance and volume of distribution increase as body weight increases.
Specific Populations
Patients with Hepatic or Renal Impairment
No formal trial of the effect of hepatic or renal impairment on the pharmacokinetics of secukinumab was conducted.
Geriatric Patients
Population pharmacokinetic analysis indicated that the clearance of secukinumab was not significantly influenced by age in adult subjects with plaque psoriasis, PsA and AS. Subjects who are 65 years or older had apparent clearance of secukinumab similar to subjects less than 65 years old.
Pediatric Patients
In a pool of the two pediatric trials, subjects with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis (6 years of age and older) were administered secukinumab at the recommended pediatric dosing regimen. At Week 24, secukinumab steady state mean ± SD serum trough concentrations were 32.6 ± 10.8 mcg/mL (n = 8), 19.8 ± 6.96 mcg/mL (n = 24), and 27.3 ± 10.1 mcg/mL (n = 36), in subjects weighing less than 25 kg and receiving 75 mg of secukinumab, subjects weighing at least 25 and less than 50 kg and receiving 75 mg of secukinumab, and subjects weighing at least 50 kg and receiving 150 mg of secukinumab, respectively.
In a pediatric study, JPsA and ERA patients (2 to less than 18 years of age) were administered secukinumab at the recommended pediatric dosing regimen. At Week 24, patients weighing at least 15 kg and less than 50 kg, and patients weighing at least 50 kg had a mean ± SD steady-state trough concentration of 25.2 ± 5.45 mcg/mL (n = 10) and 27.9 ± 9.57 mcg/mL (n = 19), respectively.
Drug Interactions
Cytochrome P450 Substrates
In adult subjects with plaque psoriasis, midazolam (CYP3A4 substrate) pharmacokinetics was similar when administered alone, or when administered following either a single or five weekly subcutaneous administrations of 300 mg secukinumab [see Drug Interactions (7.3)].
| COSENTYX
secukinumab injection |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| COSENTYX
secukinumab injection |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| COSENTYX
secukinumab injection |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation (002147023) |