Drug Class: Antiviral combinations
Highlights of Prescribing Information
DELSTRIGO™ (doravirine, lamivudine, and tenofovir disoproxil fumarate) tablets, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2018
WARNING: POSTTREATMENT ACUTE EXACERBATION OF HEPATITIS B
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
Severe acute exacerbations of hepatitis B (HBV) have been reported in patients coinfected with HIV-1 and HBV who have discontinued lamivudine or tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF), two of the components of DELSTRIGO. Closely monitor hepatic function in these patients. If appropriate, initiation of anti-hepatitis B therapy may be warranted. (5.1)
Recent Major Changes
| Indications and Usage (1) | 01/2022 |
| Dosage and Administration (2), Recommended Dosage (2.2) | 01/2022 |
Indications and Usage for Delstrigo
DELSTRIGO is a three-drug combination of doravirine (a non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor [NNRTI]), lamivudine, and tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (both nucleoside analogue reverse transcriptase inhibitors) and is indicated as a complete regimen for the treatment of HIV-1 infection in adults and pediatric patients weighing at least 35 kg:
- with no antiretroviral treatment history, OR
- to replace the current antiretroviral regimen in those who are virologically-suppressed (HIV-1 RNA less than 50 copies per mL) on a stable antiretroviral regimen with no history of treatment failure and no known substitutions associated with resistance to the individual components of DELSTRIGO. (1)
Delstrigo Dosage and Administration
- Testing: Prior to or when initiating DELSTRIGO, test for HBV infection. Prior to or when initiating DELSTRIGO, and during treatment with DELSTRIGO, on a clinically appropriate schedule, assess serum creatinine, estimated creatinine clearance, urine glucose and urine protein in all patients. In patients with chronic kidney disease, also assess serum phosphorus. (2.1)
- Recommended dosage: One tablet taken orally once daily with or without food in adults and pediatric patients weighing at least 35 kg. (2.2)
- Renal impairment: Not recommended in patients with estimated creatinine clearance below 50 mL per minute. (2.3)
- Dosage adjustment with rifabutin: Take one tablet of DELSTRIGO once daily, followed by one tablet of doravirine 100 mg (PIFELTRO) approximately 12 hours after the dose of DELSTRIGO. (2.4)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
- Tablets: 100 mg of doravirine, 300 mg of lamivudine, and 300 mg of tenofovir disoproxil fumarate. (3)
Contraindications
- DELSTRIGO is contraindicated when co-administered with drugs that are strong cytochrome P450 (CYP)3A enzyme inducers as significant decreases in doravirine plasma concentrations may occur, which may decrease the effectiveness of DELSTRIGO. (4)
- DELSTRIGO is contraindicated in patients with a previous hypersensitivity reaction to lamivudine.
Warnings and Precautions
- New onset or worsening renal impairment: Prior to or when initiating DELSTRIGO, and during treatment with DELSTRIGO, on a clinically appropriate schedule, assess serum creatinine, estimated creatinine clearance, urine glucose, and urine protein in all patients. Avoid administering DELSTRIGO with concurrent or recent use of nephrotoxic drugs. (5.2)
- Bone loss and mineralization defects: Consider monitoring BMD in patients with a history of pathologic fracture or other risk factors of osteoporosis or bone loss. (5.4)
- Monitor for Immune Reconstitution Syndrome. (5.5)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions (incidence greater than or equal to 5%, all grades) are dizziness, nausea, and abnormal dreams. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Merck Sharp & Dohme LLC at 1-877-888-4231 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch .
Drug Interactions
- Because DELSTRIGO is a complete regimen, co-administration with other antiretroviral medications for treatment of HIV-1 infection is not recommended. (7.1)
- Consult the full prescribing information prior to and during treatment for important potential drug-drug interactions. (4, 5.3, 7)
Use In Specific Populations
- Lactation: Breastfeeding is not recommended due to the potential for HIV-1 transmission. (8.2)
- Pediatrics: Not recommended for patients weighing less than 35 kg. (8.4)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 6/2022
Related/similar drugs
Biktarvy, Truvada, tenofovir, Atripla, Complera, Stribild, EpzicomFull Prescribing Information
WARNING: POSTTREATMENT ACUTE EXACERBATION OF HEPATITIS B
Severe acute exacerbations of hepatitis B (HBV) have been reported in patients who are coinfected with HIV-1 and HBV and have discontinued lamivudine or tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF), which are components of DELSTRIGO. Hepatic function should be monitored closely with both clinical and laboratory follow-up for at least several months in patients who are coinfected with HIV-1 and HBV and discontinue DELSTRIGO. If appropriate, initiation of anti-hepatitis B therapy may be warranted [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
1. Indications and Usage for Delstrigo
DELSTRIGO™ is indicated as a complete regimen for the treatment of HIV-1 infection in adults and pediatric patients weighing at least 35 kg:
- with no prior antiretroviral treatment history, OR
- to replace the current antiretroviral regimen in those who are virologically-suppressed (HIV-1 RNA less than 50 copies per mL) on a stable antiretroviral regimen with no history of treatment failure and no known substitutions associated with resistance to the individual components of DELSTRIGO [see Clinical Studies (14)].
2. Delstrigo Dosage and Administration
2.1 Testing When Initiating and During Treatment with DELSTRIGO
Prior to or when initiating DELSTRIGO, test patients for HBV infection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Prior to or when initiating DELSTRIGO, and during treatment with DELSTRIGO, on a clinically appropriate schedule, assess serum creatinine, estimated creatinine clearance, urine glucose, and urine protein in all patients. In patients with chronic kidney disease, also assess serum phosphorus [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
2.2 Recommended Dosage
DELSTRIGO is a fixed-dose combination product containing 100 mg of doravirine (DOR), 300 mg of lamivudine (3TC), and 300 mg of TDF. The recommended dosage of DELSTRIGO in adults and pediatric patients weighing at least 35 kg is one tablet taken orally once daily with or without food [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
2.3 Renal Impairment
Because DELSTRIGO is a fixed-dose combination tablet and the dosage of lamivudine and TDF cannot be adjusted, DELSTRIGO is not recommended in patients with estimated creatinine clearance less than 50 mL/min [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
2.4 Dosage Adjustment with Rifabutin
If DELSTRIGO is co-administered with rifabutin, take one tablet of DELSTRIGO once daily, followed by one tablet of doravirine 100 mg (PIFELTRO) approximately 12 hours after the dose of DELSTRIGO for the duration of rifabutin co-administration [see Drug Interactions (7.2) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
DELSTRIGO film-coated tablets are yellow, oval-shaped tablets, debossed with the corporate logo and 776 on one side and plain on the other side. Each tablet contains 100 mg doravirine, 300 mg lamivudine, and 300 mg tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (equivalent to 245 mg of tenofovir disoproxil).
4. Contraindications
- DELSTRIGO is contraindicated when co-administered with drugs that are strong cytochrome P450 (CYP)3A enzyme inducers as significant decreases in doravirine plasma concentrations may occur, which may decrease the effectiveness of DELSTRIGO [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3), Drug Interactions (7.2), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. These drugs include, but are not limited to, the following:
- -
- the anticonvulsants carbamazepine, oxcarbazepine, phenobarbital, phenytoin
- -
- the androgen receptor inhibitor enzalutamide
- -
- the antimycobacterials rifampin, rifapentine
- -
- the cytotoxic agent mitotane
- -
- St. John's wort (Hypericum perforatum)
- DELSTRIGO is contraindicated in patients with a previous hypersensitivity reaction to lamivudine.
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Severe Acute Exacerbation of Hepatitis B in Patients Coinfected with HIV-1 and HBV
All patients with HIV-1 should be tested for the presence of HBV before initiating antiretroviral therapy.
Severe acute exacerbations of hepatitis B (e.g., liver decompensated and liver failure) have been reported in patients who are coinfected with HIV-1 and HBV and have discontinued products containing lamivudine and/or TDF, and may occur with discontinuation of DELSTRIGO. Patients who are coinfected with HIV-1 and HBV who discontinue DELSTRIGO should be closely monitored with both clinical and laboratory follow-up for at least several months after stopping treatment with DELSTRIGO. If appropriate, initiation of anti-hepatitis B therapy may be warranted, especially in patients with advanced liver disease or cirrhosis, since post-treatment exacerbation of hepatitis may lead to hepatic decompensation and liver failure.
5.2 New Onset or Worsening Renal Impairment
Renal impairment, including cases of acute renal failure and Fanconi syndrome (renal tubular injury with severe hypophosphatemia), has been reported with the use of TDF, a component of DELSTRIGO.
DELSTRIGO should be avoided with concurrent or recent use of a nephrotoxic agent (e.g., high-dose or multiple nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs [NSAIDs]) [see Drug Interactions (7.1)]. Cases of acute renal failure after initiation of high-dose or multiple NSAIDs have been reported in HIV-infected patients with risk factors for renal dysfunction who appeared stable on TDF. Some patients required hospitalization and renal replacement therapy. Alternatives to NSAIDs should be considered, if needed, in patients at risk for renal dysfunction.
Persistent or worsening bone pain, pain in extremities, fractures, and/or muscular pain or weakness may be manifestations of proximal renal tubulopathy and should prompt an evaluation of renal function in at-risk patients.
Prior to or when initiating DELSTRIGO, and during treatment with DELSTRIGO, on a clinically appropriate schedule, assess serum creatinine, estimated creatinine clearance, urine glucose and urine protein in all patients. In patients with chronic kidney disease, also assess serum phosphorus. Discontinue DELSTRIGO in patients who develop clinically significant decreases in renal function or evidence of Fanconi syndrome.
The lamivudine and TDF components of DELSTRIGO are primarily excreted by the kidney. Discontinue DELSTRIGO if estimated creatinine clearance declines below 50 mL/min as dose interval adjustment required for lamivudine and TDF cannot be achieved with the fixed-dose combination tablet [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
5.3 Risk of Adverse Reactions or Loss of Virologic Response Due to Drug Interactions
The concomitant use of DELSTRIGO and certain other drugs may result in known or potentially significant drug interactions, some of which may lead to [see Dosage and Administration (2.4), Contraindications (4), and Drug Interactions (7.2)]:
- Loss of therapeutic effect of DELSTRIGO and possible development of resistance.
- Possible clinically significant adverse reactions from greater exposures of a component of DELSTRIGO.
See Table 6 for steps to prevent or manage these possible and known significant drug interactions, including dosing recommendations. Consider the potential for drug interactions prior to and during DELSTRIGO therapy, review concomitant medications during DELSTRIGO therapy, and monitor for adverse reactions.
5.5 Immune Reconstitution Syndrome
Immune reconstitution syndrome has been reported in patients treated with combination antiretroviral therapy. During the initial phase of combination antiretroviral treatment, patients whose immune system responds may develop an inflammatory response to indolent or residual opportunistic infections (such as Mycobacterium avium infection, cytomegalovirus, Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia (PCP), or tuberculosis), which may necessitate further evaluation and treatment.
Autoimmune disorders (such as Graves' disease, polymyositis, Guillain-Barré syndrome, and autoimmune hepatitis) have also been reported to occur in the setting of immune reconstitution; however, the time to onset is more variable and can occur many months after initiation of treatment.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following adverse reactions are discussed in other sections of the labeling:
- Severe Acute Exacerbation of Hepatitis B in Patients Coinfected with HIV-1 and HBV [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- New Onset or Worsening Renal Impairment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Bone Loss and Mineralization Defects [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Immune Reconstitution Syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Adverse Reactions in Adults with No Antiretroviral Treatment History
The safety assessment of DELSTRIGO is based on Week 96 data from two Phase 3, randomized, international, multicenter, double-blind, active-controlled trials. A total of 747 subjects received doravirine either as the single entity in combination with other antiretroviral drugs as background regimens (n=383) or as the fixed-dose DELSTRIGO (n=364), and a total of 747 subjects were randomized to control arms.
In DRIVE-AHEAD (Protocol 021), 728 adult subjects received either DELSTRIGO (n=364) or EFV/FTC/TDF once daily (n=364). By Week 96, 3% in the DELSTRIGO group and 7% in the EFV/FTC/TDF group had adverse events leading to discontinuation of study medication.
Adverse reactions reported in greater than or equal to 5% of subjects in any treatment group in DRIVE-AHEAD are presented in Table 1.
| DELSTRIGO Once Daily N=364 | EFV/FTC/TDF Once Daily N=364 |
|
|---|---|---|
|
||
| Dizziness | 7% | 32% |
| Nausea | 5% | 7% |
| Abnormal Dreams | 5% | 10% |
| Headache | 4% | 5% |
| Insomnia | 4% | 5% |
| Diarrhea | 4% | 6% |
| Somnolence | 3% | 7% |
| Rash‡ | 2% | 12% |
The majority (66%) of adverse reactions associated with DELSTRIGO occurred at severity Grade 1 (mild).
Neuropsychiatric Adverse Events
For DRIVE-AHEAD, the analysis of subjects with neuropsychiatric adverse events by Week 48 is presented in Table 2. The proportion of subjects who reported one or more neuropsychiatric adverse events was 24% and 57% in the DELSTRIGO and EFV/FTC/TDF groups, respectively.
A statistically significantly lower proportion of DELSTRIGO-treated subjects compared to EFV/FTC/TDF-treated subjects reported neuropsychiatric adverse events by Week 48 in the three pre-specified categories of dizziness, sleep disorders and disturbances, and altered sensorium.
| DELSTRIGO Once Daily N=364 | EFV/FTC/TDF Once Daily N=364 | Treatment Difference (DELSTRIGO - EFV/FTC/TDF) Estimate (95% CI)† |
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
|||
| Sleep disorders and disturbances‡ | 12% | 26% | -13.5 (-19.1, -7.9) |
| Dizziness | 9% | 37% | -28.3 (-34.0, -22.5) |
| Altered sensorium§ | 4% | 8% | -3.8 (-7.6, -0.3) |
Neuropsychiatric adverse events in the pre-defined category of depression and suicide/self-injury were reported in 4% and 7% of subjects, in the DELSTRIGO and EFV/FTC/TDF groups, respectively.
In DRIVE-AHEAD through 48 weeks of treatment, the majority of subjects who reported neuropsychiatric adverse events reported events that were mild to moderate in severity (97% [83/86] and 96% [198/207], in the DELSTRIGO and EFV/FTC/TDF groups, respectively) and the majority of subjects reported these events in the first 4 weeks of treatment (72% [62/86] in the DELSTRIGO group and 86% [177/207] in the EFV/FTC/TDF group).
Neuropsychiatric adverse events led to treatment discontinuation in 1% (2/364) and 1% (5/364) of subjects in the DELSTRIGO and EFV/FTC/TDF groups, respectively. The proportion of subjects who reported neuropsychiatric adverse events through Week 4 was 17% (62/364) in the DELSTRIGO group and 49% (177/364) in the EFV/FTC/TDF group. At Week 48, the prevalence of neuropsychiatric adverse events was 12% (44/364) in the DELSTRIGO group and 22% (81/364) in the EFV/FTC/TDF group. At Week 96, the prevalence of neuropsychiatric adverse events was 13% (47/364) in the DELSTRIGO group and 23% (82/364) in the EFV/FTC/TDF group.
Laboratory Abnormalities
The percentages of subjects with selected laboratory abnormalities (that represent a worsening from baseline) who were treated with DELSTRIGO or EFV/FTC/TDF in DRIVE-AHEAD are presented in Table 3.
| Laboratory Parameter Preferred Term (Unit)/Limit | DELSTRIGO Once Daily N=364 | EFV/FTC/TDF Once Daily N=364 |
|---|---|---|
| Blood Chemistry | ||
| Each subject is only counted once per parameter at the highest toxicity grade. Only subjects with a baseline value and at least one on-treatment value for a given laboratory parameter are included. | ||
| ULN = Upper limit of normal range. | ||
| Total bilirubin | ||
| 1.1 - <1.6 × ULN | 5% | 0% |
| 1.6 - <2.6 × ULN | 2% | 0% |
| ≥2.6 × ULN | 1% | <1% |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | ||
| >1.3 - 1.8 × ULN or Increase of >0.3 mg/dL above baseline | 3% | 2% |
| >1.8 × ULN or Increase of ≥1.5 × above baseline | 3% | 2% |
| Aspartate aminotransferase (IU/L) | ||
| 2.5 - <5.0 × ULN | 3% | 3% |
| ≥5.0 × ULN | 1% | 4% |
| Alanine aminotransferase (IU/L) | ||
| 2.5 - <5.0 × ULN | 4% | 4% |
| ≥5.0 × ULN | 1% | 3% |
| Alkaline phosphatase (IU/L) | ||
| 2.5 - <5.0 × ULN | <1% | 1% |
| ≥5.0 × ULN | 0% | <1% |
| Lipase | ||
| 1.5 - <3.0 × ULN | 6% | 4% |
| ≥3.0 × ULN | 2% | 3% |
| Creatine kinase (IU/L) | ||
| 6.0 - <10.0 × ULN | 3% | 3% |
| ≥10.0 × ULN | 4% | 6% |
| Cholesterol, fasted (mg/dL) | ||
| ≥300 mg/dL | 1% | <1% |
| LDL cholesterol, fasted (mg/dL) | ||
| ≥190 mg/dL | <1% | 2% |
| Triglycerides, fasted (mg/dL) | ||
| >500 mg/dL | 1% | 3% |
Change in Lipids from Baseline
For DRIVE-AHEAD, changes from baseline at Week 48 in LDL-cholesterol, non-HDL-cholesterol, total cholesterol, triglycerides, and HDL-cholesterol are shown in Table 4. Changes from baseline at Week 96 were similar to findings at Week 48.
The LDL and non-HDL comparisons were pre-specified and are summarized in Table 4. The differences were statistically significant, showing superiority of DELSTRIGO for both parameters. The clinical benefit of these findings has not been demonstrated.
| Laboratory Parameter Preferred Term | DELSTRIGO Once Daily N=320 | EFV/FTC/TDF Once Daily N=307 | Difference Estimates (DELSTRIGO - EFV/FTC/TDF) |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | Change | Baseline | Change | Difference (95% CI) | |
| Subjects on lipid-lowering agents at baseline were excluded from these analyses (DELSTRIGO n=15 and EFV/FTC/TDF n=10). Subjects initiating a lipid-lowering agent post-baseline had their last fasted on-treatment value (prior to starting the agent) carried forward (DELSTRIGO n=3 and EFV/FTC/TDF n=8). |
|||||
|
|||||
| LDL-Cholesterol (mg/dL)* | 91.7 | -2.1 | 91.3 | 8.3 | -10.2 (-13.8, -6.7) |
| Non-HDL Cholesterol (mg/dL)* | 114.7 | -4.1 | 115.3 | 12.7 | -16.9 (-20.8, -13.0) |
| Total Cholesterol (mg/dL)† | 156.8 | -2.2 | 156.8 | 21.1 | - |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL)† | 118.7 | -12.0 | 122.6 | 21.6 | - |
| HDL-Cholesterol (mg/dL)† | 42.1 | 1.8 | 41.6 | 8.4 | - |
Adverse Reactions in Virologically-Suppressed Adults
The safety of DELSTRIGO in virologically-suppressed adults was based on Week 48 data from 670 subjects in the DRIVE-SHIFT trial (Protocol 024), a randomized, international, multicenter, open-label trial in which virologically-suppressed subjects were switched from a baseline regimen consisting of two nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs) in combination with a protease inhibitor (PI) plus either ritonavir or cobicistat, or elvitegravir plus cobicistat, or an NNRTI to DELSTRIGO. Overall, the safety profile in virologically-suppressed adult subjects was similar to that in subjects with no antiretroviral treatment history.
Change in Lipids from Baseline
Changes from baseline at Week 24 in LDL-cholesterol, non-HDL-cholesterol, total cholesterol, triglycerides, and HDL-cholesterol in subjects on a PI plus ritonavir-based regimen at baseline are shown in Table 5. The LDL and non-HDL comparisons were pre-specified, and the differences were statistically significant, showing superiority for an immediate switch to DELSTRIGO for both parameters. The clinical benefit of these findings has not been demonstrated.
| Laboratory Parameter Preferred Term | DELSTRIGO (Week 0-24) Once Daily N=244 | PI+ritonavir (Week 0-24) Once Daily N=124 | Difference Estimates | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | Change | Baseline | Change | Difference (95% CI) | |
| Subjects on lipid-lowering agents at baseline were excluded from these analyses (DELSTRIGO n=26 and PI+ritonavir n=13). Subjects initiating a lipid-lowering agent post-baseline had their last fasted on-treatment value (prior to starting the agent) carried forward (DELSTRIGO n=4 and PI+ritonavir n=2). |
|||||
|
|||||
| LDL-Cholesterol (mg/dL)* | 108.7 | -16.3 | 110.5 | -2.6 | -14.5 (-18.9, -10.1) |
| Non-HDL Cholesterol (mg/dL)* | 138.6 | -24.8 | 138.8 | -2.1 | -22.8 (-27.9, -17.7) |
| Total Cholesterol (mg/dL)† | 188.5 | -26.1 | 187.4 | -0.2 | - |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL)† | 153.1 | -44.4 | 151.4 | -0.4 | - |
| HDL-Cholesterol (mg/dL)† | 50.0 | -1.3 | 48.5 | 1.9 | - |
Adverse Reactions in Pediatric Patients
The safety of DELSTRIGO was evaluated in 45 HIV-1-infected virologically-suppressed or treatment-naïve pediatric patients 12 to less than 18 years of age through Week 24 in an open-label trial (IMPAACT 2014 (Protocol 027)) [see Clinical Studies (14.3)]. The safety profile in pediatric subjects was similar to that in adults. There were no serious or Grade 3 or 4 adverse reactions. No subjects discontinued due to an adverse event.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during postmarketing experience in patients receiving lamivudine- or TDF-containing regimens. Because postmarketing reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 Concomitant Use with Other Antiretroviral Medications
Because DELSTRIGO is a complete regimen for the treatment of HIV-1 infection, co-administration with other antiretroviral medications for treatment of HIV-1 infection is not recommended. Information regarding potential drug-drug interactions with other antiretroviral medications is not provided.
7.2 Effect of Other Drugs on DELSTRIGO
Co-administration of DELSTRIGO with a CYP3A inducer decreases doravirine plasma concentrations, which may reduce DELSTRIGO efficacy [see Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.3), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Co-administration of DELSTRIGO and drugs that are inhibitors of CYP3A may result in increased plasma concentrations of doravirine.
Table 6 shows the significant drug interactions with the components of DELSTRIGO. The drug interactions described are based on studies conducted with either DELSTRIGO or the components of DELSTRIGO as individual agents.
| Concomitant Drug Class: Drug Name | Effect on Concentration | Clinical Comment |
|---|---|---|
| ↑ = increase, ↓ = decrease | ||
| All other drug-drug interactions shown are anticipated based on the known metabolic and elimination pathways. | ||
|
||
| Androgen Receptors | ||
| enzalutamide | ↓ doravirine | Co-administration is contraindicated with enzalutamide. At least a 4-week cessation period is recommended prior to initiation of DELSTRIGO. |
| Anticonvulsants | ||
| carbamazepine oxcarbazepine phenobarbital phenytoin | ↓ doravirine | Co-administration is contraindicated with these anticonvulsants. At least a 4-week cessation period is recommended prior to initiation of DELSTRIGO. |
| Antimycobacterials | ||
| rifampin†
rifapentine | ↓ doravirine | Co-administration is contraindicated with rifampin or rifapentine. At least a 4-week cessation period is recommended prior to initiation of DELSTRIGO. |
| rifabutin† | ↓ doravirine | If DELSTRIGO is co-administered with rifabutin, one tablet of doravirine (PIFELTRO) should be taken approximately 12 hours after the dose of DELSTRIGO [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)]. |
| Cytotoxic Agents | ||
| mitotane | ↓ doravirine | Co-administration is contraindicated with mitotane. At least a 4-week cessation period is recommended prior to initiation of DELSTRIGO. |
| Hepatitis C Antiviral Agents | ||
| ledipasvir/sofosbuvir sofosbuvir/velpatasvir | ↑ tenofovir | Monitor for adverse reactions associated with TDF. |
| Herbal Products | ||
| St. John's wort | ↓ doravirine | Co-administration is contraindicated with St. John's wort. At least a 4-week cessation period is recommended prior to initiation of DELSTRIGO. |
| Other Agents | ||
| sorbitol | ↓ lamivudine | Co-administration of single doses of lamivudine and sorbitol resulted in a sorbitol dose-dependent reduction in lamivudine exposures. When possible, avoid use of sorbitol-containing medicines with lamivudine-containing medicines. |
Co-administration of DELSTRIGO with drugs that reduce renal function or compete for active tubular secretion may increase serum concentrations of lamivudine, tenofovir, and/or other renally eliminated drugs. Some examples of drugs that are eliminated by active tubular secretion include, but are not limited to, acyclovir, cidofovir, ganciclovir, valacyclovir, valganciclovir, aminoglycosides (e.g., gentamicin), and high-dose or multiple NSAIDs [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
No clinically significant changes in concentration were observed for doravirine when co-administered with the following agents: TDF, lamivudine, elbasvir and grazoprevir, ledipasvir and sofosbuvir, ritonavir, ketoconazole, aluminum hydroxide/magnesium hydroxide/simethicone containing antacid, pantoprazole, or methadone [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
No clinically significant changes in concentration were observed for tenofovir when co-administered with tacrolimus or entecavir [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
7.3 Effect of DELSTRIGO on Other Drugs
No clinically significant changes in concentration were observed for the following agents when co-administered with doravirine: lamivudine, TDF, elbasvir and grazoprevir, ledipasvir and sofosbuvir, atorvastatin, an oral contraceptive containing ethinyl estradiol and levonorgestrel, metformin, methadone, or midazolam.
No clinically significant drug interactions have been observed between TDF and the following medications: entecavir, methadone, oral contraceptives, sofosbuvir, or tacrolimus in studies conducted in healthy subjects.
Lamivudine is not significantly metabolized by CYP enzymes nor does it inhibit or induce this enzyme system; therefore, it is unlikely that clinically significant drug interactions will occur through these pathways [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and efficacy of DELSTRIGO for the treatment of HIV-1 infection have been established in pediatric patients weighing at least 35 kg [see Indications and Usage (1) and Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
Use of DELSTRIGO in this group is supported by evidence from adequate and well-controlled trials in adults with additional pharmacokinetic, safety, and efficacy data from an open-label trial in virologically-suppressed or treatment-naïve pediatric subjects 12 to less than 18 years of age. The safety and efficacy of DELSTRIGO in these pediatric subjects were similar to that in adults, and there was no clinically significant difference in exposure for the components of DELSTRIGO. [see Adverse Reactions (6.1), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3), and Clinical Studies (14.3).]
Safety and efficacy of DELSTRIGO in pediatric patients weighing less than 35 kg have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical trials of doravirine, lamivudine, or TDF did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 years and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. In general, caution should be exercised in the administration of DELSTRIGO in elderly patients reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.6 Renal Impairment
Because DELSTRIGO is a fixed-dose combination tablet and the dosage of lamivudine and TDF, both components of DELSTRIGO, cannot be altered, DELSTRIGO is not recommended in patients with estimated creatinine clearance less than 50 mL/min [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
10. Overdosage
No data are available on overdose of DELSTRIGO in patients and there is no known specific treatment for overdose with DELSTRIGO. If overdose occurs, the patient should be monitored and standard supportive treatment applied as required.
11. Delstrigo Description
DELSTRIGO is a fixed-dose combination, film-coated tablet, containing doravirine, lamivudine, and TDF for oral administration.
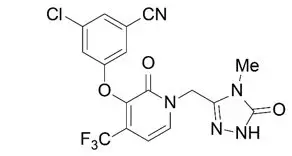
Doravirine is an HIV-1 non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI).
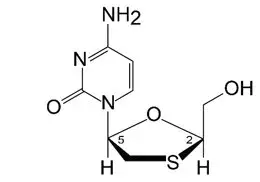
Lamivudine is the (-)enantiomer of a dideoxy analogue of cytidine and is an HIV-1 nucleoside analogue reverse transcriptase inhibitor.
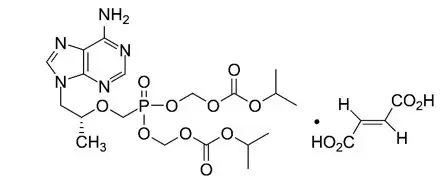
TDF (a prodrug of tenofovir) is a fumaric acid salt of the bis-isopropoxycarbonyloxymethyl ester derivative of tenofovir. In vivo TDF is converted to tenofovir, an acyclic nucleoside phosphonate (nucleotide) analog of adenosine 5'-monophosphate. Tenofovir is an HIV-1 reverse transcriptase inhibitor.
Each tablet contains 100 mg of doravirine, 300 mg of lamivudine, and 300 mg of TDF (equivalent to 245 mg of tenofovir disoproxil) as active ingredients. The tablets include the following inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, croscarmellose sodium, hypromellose acetate succinate, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, and sodium stearyl fumarate. The tablets are film coated with a coating material containing the following inactive ingredients: hypromellose, iron oxide yellow, lactose monohydrate, titanium dioxide, and triacetin. The coated tablets are polished with carnauba wax.
12. Delstrigo - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
DELSTRIGO is a fixed-dose combination of the antiretroviral drugs doravirine, lamivudine, and TDF [see Microbiology (12.4)].
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
In a Phase 2 trial evaluating doravirine over a dose range of 0.25 to 2 times the recommended dose of doravirine in DELSTRIGO (in combination with FTC/TDF) in HIV-1-infected subjects with no antiretroviral treatment history, no exposure-response relationship for efficacy was identified for doravirine.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Single-dose administration of one DELSTRIGO tablet to healthy subjects provided comparable exposures of doravirine, lamivudine, and tenofovir to administration of doravirine tablets (100 mg) plus lamivudine tablets (300 mg) plus TDF tablets (300 mg). Doravirine pharmacokinetics are similar in healthy subjects and HIV-1-infected subjects. Pharmacokinetic properties of the components of DELSTRIGO are provided in Table 7.
| Parameter | Doravirine | Lamivudine | Tenofovir |
|---|---|---|---|
| Abbreviations: NA=not available; AUC=area under the time concentration curve; Cmax=maximum concentration; C24=concentration at 24 hours; Tmax=time to Cmax; Vdss=apparent volume of distribution at steady state; t1/2=elimination half-life; CL/F=apparent clearance; CLrenal = renal clearance | |||
|
|||
| General | |||
| Steady State Exposure* | |||
| AUC0-24
(mcg∙h/mL) | 16.1 (29)† | 8.87 ± 1.83‡ | 2.29 ± 0.69§ |
| Cmax
(mcg/mL) | 0.962 (19)† | 2.04 ± 0.54‡ | 0.30 ± 0.09§ |
| C24
(mcg/mL) | 0.396 (63)† | NA | NA |
| Absorption | |||
| Absolute Bioavailability | 64% | 86% | 25% |
| Tmax (h) | 2 | NA | 1 |
| Effect of Food¶ | |||
| AUC Ratio | 1.10 (1.01, 1.20) | 0.93 (0.84, 1.03) | 1.27 (1.17, 1.37) |
| Cmax Ratio | 0.95 (0.80, 1.12) | 0.81 (0.65, 1.01) | 0.88 (0.74, 1.04) |
| C24 Ratio | 1.26 (1.13, 1.41) | NA | NA |
| Distribution | |||
| Vdss# | 60.5 L | 1.3 L/kg | 1.3 L/kg |
| Plasma Protein Binding | 76% | < 36% | <0.7% |
| Elimination | |||
| t1/2 (h) | 15 | 5-7 | 17 |
| CL/F (mL/ min)* | 106 (35.2) | 398.5 ± 69.1 | 1,043.7 ± 115.4 |
| CLrenal (mL/ min)* | 9.3 (18.6) | 199.7 ± 56.9 | 243.5 ± 33.3 |
| Metabolism | |||
| Primary Pathway(s) | CYP3A | Minor | No CYP Metabolism |
| Excretion | |||
| Major route of elimination | Metabolism | Glomerular filtration and active tubular secretion | Glomerular filtration and active tubular secretion |
| Urine (unchanged) | 6% | 71% | 70-80% |
| Biliary/Fecal (unchanged) | Minor | NA | NA |
Specific Populations
In adults, no clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of certain DELSTRIGO components were observed based on age ≥65 years (for doravirine), sex (for doravirine, lamivudine, tenofovir), and race/ethnicity (for doravirine, lamivudine). The effects of age (≥65 years) on the pharmacokinetics of lamivudine and tenofovir, and the effect of race on the pharmacokinetics of tenofovir are unknown.
Pediatric Patients
Mean doravirine exposures were similar in 54 pediatric patients aged 12 to less than 18 years and weighing at least 35 kg who received doravirine or DELSTRIGO in IMPAACT 2014 (Protocol 027) relative to adults following administration of doravirine or DELSTRIGO. Exposures of lamivudine and tenofovir in pediatric patients following the administration of DELSTRIGO were similar to those in adults following administration of lamivudine and tenofovir (Table 8). For pediatric patients weighing ≥ 35 kg and < 45 kg who receive doravirine 100 mg or DELSTRIGO, the population pharmacokinetic model-predicted mean C24 of doravirine was comparable to that achieved in adults, whereas mean AUC0-24 and Cmax of doravirine were 25% and 36% higher than adult values, respectively. However, the predicted AUC0-24 and Cmax increases are not considered clinically significant.
| Parameter* | Doravirine† | Lamivudine‡ | Tenofovir‡ |
|---|---|---|---|
| Abbreviations: NA=not applicable; AUC=area under the time concentration curve; Cmax=maximum concentration; C24=concentration at 24 hours | |||
|
|||
| AUC0-24
(mcg•h/mL) | 16.4 (24) | 11.3 (28) | 2.55 (14) |
| Cmax
(mcg/mL) | 1.03 (16) | 2.1 (24) | 0.293 (37) |
| C24
(mcg/mL) | 0.379 (42) | NA | NA |
Drug Interaction Studies
DELSTRIGO is a complete regimen for the treatment of HIV-1 infection; therefore, DELSTRIGO is not recommended to be administered with other HIV-1 antiretroviral medications. Information regarding potential drug-drug interactions with other antiretroviral medications is not provided.
The drug interaction trials described were conducted with doravirine, lamivudine and/or TDF, as single entities; no drug interaction trials have been conducted using the combination of doravirine, lamivudine, and TDF. No clinically relevant drug interactions were observed between doravirine, lamivudine, and TDF.
Doravirine: Doravirine is primarily metabolized by CYP3A, and drugs that induce or inhibit CYP3A may affect the clearance of doravirine. Co-administration of doravirine and drugs that induce CYP3A may result in decreased plasma concentrations of doravirine. Co-administration of doravirine and drugs that inhibit CYP3A may result in increased plasma concentrations of doravirine.
Doravirine is not likely to have a clinically relevant effect on the exposure of medicinal products metabolized by CYP enzymes. Doravirine did not inhibit major drug metabolizing enzymes in vitro, including CYPs 1A2, 2B6, 2C8, 2C9, 2C19, 2D6, 3A4, and UGT1A1 and is not likely to be an inducer of CYP1A2, 2B6, or 3A4. Based on in vitro assays, doravirine is not likely to be an inhibitor of OATP1B1, OATP1B3, P-glycoprotein, BSEP, OAT1, OAT3, OCT2, MATE1, and MATE2K. Drug interaction studies were performed with doravirine and other drugs likely to be co-administered or commonly used as probes for pharmacokinetic interactions. The effects of co-administration with other drugs on the exposure (Cmax, AUC, and C24) of doravirine are summarized in Table 9. A single doravirine 100 mg dose was administered in these studies unless otherwise noted.
| Co-administered Drug | Regimen of Co-administered Drug | N | Geometric Mean Ratio (90% CI) of Doravirine Pharmacokinetics with/without Co-administered Drug (No Effect=1.00) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUC* | Cmax | C24 | |||
| CI = confidence interval; QD = once daily; BID = twice daily | |||||
|
|||||
| Azole Antifungal Agents | |||||
| ketoconazole† | 400 mg QD | 10 | 3.06 (2.85, 3.29) | 1.25 (1.05, 1.49) | 2.75 (2.54, 2.98) |
| Antimycobacterials | |||||
| rifampin | 600 mg QD | 10 | 0.12 (0.10, 0.15) | 0.43 (0.35, 0.52) | 0.03 (0.02, 0.04) |
| rifabutin | 300 mg QD | 12 | 0.50 (0.45, 0.55) | 0.99 (0.85, 1.15) | 0.32 (0.28, 0.35) |
| 300 mg QD‡ | 15 | 1.03 (0.94, 1.14) | 0.97 (0.87, 1.08) | 0.98 (0.88, 1.10) | |
| HIV Antiviral Agents | |||||
| ritonavir†,§ | 100 mg BID | 8 | 3.54 (3.04, 4.11) | 1.31 (1.17, 1.46) | 2.91 (2.33, 3.62) |
| efavirenz | 600 mg QD¶ | 17 | 0.38 (0.33, 0.45) | 0.65 (0.58, 0.73) | 0.15 (0.10, 0.23) |
| 600 mg QD# | 17 | 0.68 (0.58, 0.80) | 0.86 (0.77, 0.97) | 0.50 (0.39, 0.64) | |
Based on drug interaction studies conducted with doravirine, no clinically significant drug interactions have been observed following the co-administration of doravirine and the following drugs: dolutegravir, TDF, lamivudine, elbasvir and grazoprevir, ledipasvir and sofosbuvir, ketoconazole, ritonavir, aluminum hydroxide/magnesium hydroxide/simethicone containing antacid, pantoprazole, atorvastatin, an oral contraceptive containing ethinyl estradiol and levonorgestrel, metformin, methadone, and midazolam.
12.4 Microbiology
Resistance
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
14. Clinical Studies
14.1 Clinical Trial Results in Adults with No Antiretroviral Treatment History
The efficacy of DELSTRIGO is based on the analyses of 96-week data from a randomized, multicenter, double-blind, active controlled Phase 3 trial (DRIVE-AHEAD, NCT02403674) in HIV-1-infected subjects with no antiretroviral treatment history (n=728).
Subjects were randomized and received at least 1 dose of either DELSTRIGO or EFV 600 mg/FTC 200 mg/TDF 300 mg once daily. At baseline, the median age of subjects was 31 years, 15% were female, 52% were non-white, 3% had hepatitis B or C coinfection, 14% had a history of AIDS, 21% had HIV-1 RNA greater than 100,000 copies/mL, and 88% had CD4+ T-cell count greater than 200 cells/mm3; these characteristics were similar between treatment groups. Week 96 outcomes for DRIVE-AHEAD are provided in Table 10.
Mean CD4+ T-cell counts in the DELSTRIGO and EFV/FTC/TDF groups increased from baseline by 238 and 223 cells/mm3, respectively.
| Outcome | DELSTRIGO Once Daily N=364 | EFV/FTC/TDF Once Daily N=364 |
|---|---|---|
|
||
| HIV-1 RNA <50 copies/mL | 77% | 74% |
| Treatment Difference (95% CI) * | 3.8% (-2.4%, 10.0%) | |
| HIV-1 RNA ≥ 50 copies/mL† | 15% | 12% |
| No Virologic Data at Week 96 Window | 7% | 14% |
| Discontinued study due to AE or Death‡ | 3% | 8% |
| Discontinued study for Other Reasons§ | 4% | 5% |
| On study but missing data in window | 1% | 1% |
| Proportion (%) of Subjects With HIV-1 RNA <50 copies/mL at Week 96 by Baseline and Demographic Category | ||
| Gender | ||
| Male | 78% (N = 305) | 73% (N = 311) |
| Female | 75% (N = 59) | 75% (N = 53) |
| Race | ||
| White | 80% (N = 176) | 74% (N = 170) |
| Non-White | 76% (N = 188) | 74% (N = 194) |
| Ethnicity¶ | ||
| Hispanic or Latino | 81% (N = 126) | 77% (N = 119) |
| Not Hispanic or Latino | 76% (N = 238) | 72% (N = 239) |
| Baseline HIV-1 RNA (copies/mL) | ||
| ≤100,000 copies/mL | 80% (N = 291) | 77% (N = 282) |
| >100,000 copies/mL | 67% (N = 73) | 62% (N = 82) |
| CD4+ T-cell Count (cells/mm3) | ||
| ≤200 cells/mm3 | 59% (N = 44) | 70% (N = 46) |
| >200 cells/mm3 | 80% (N = 320) | 74% (N = 318) |
| Viral Subtype¶ | ||
| Subtype B | 80% (N = 232) | 72% (N = 253) |
| Subtype Non-B | 73% (N = 130) | 77% (N = 111) |
14.2 Clinical Trial Results in Virologically-Suppressed Adults
The efficacy of switching from a baseline regimen consisting of two NRTIs in combination with a PI plus either ritonavir or cobicistat, or elvitegravir plus cobicistat, or an NNRTI to DELSTRIGO was evaluated in a randomized, open-label trial (DRIVE-SHIFT, NCT02397096), in virologically-suppressed HIV-1-infected adults. Subjects must have been virologically-suppressed (HIV-1 RNA <50 copies/mL) on their baseline regimen for at least 6 months prior to trial entry, with no history of virologic failure. Subjects were randomized to either switch to DELSTRIGO at baseline [n = 447, Immediate Switch Group (ISG)], or stay on their baseline regimen until Week 24, at which point they switched to DELSTRIGO [n = 223, Delayed Switch Group (DSG)].
At baseline, the median age of subjects was 43 years, 16% were female, and 24% were Non-White, 21% were of Hispanic or Latino ethnicity, 3% had hepatitis B and/or C virus co-infection, 17% had a history of AIDS, 96% had CD4+ T-cell count greater than or equal to 200 cells/mm3, 70% were on a regimen containing a PI plus ritonavir, 24% were on a regimen containing an NNRTI, 6% were on a regimen containing elvitegravir plus cobicistat, and 1% were on a regimen containing a PI plus cobicistat; these characteristics were similar between treatment groups.
Virologic outcome results are shown in Table 11.
| Outcome | DELSTRIGO Once Daily ISG Week 48 N=447 | Baseline Regimen DSG Week 24 N=223 |
|---|---|---|
|
||
| HIV-1 RNA ≥ 50 copies/mL* | 2% | 1% |
| ISG-DSG, Difference (95% CI)†,‡ | 0.7% (-1.3%, 2.6%) | |
| HIV-1 RNA <50 copies/mL | 91% | 95% |
| No Virologic Data Within the Time Window | 8% | 4% |
| Discontinued study due to AE or Death§ | 3% | <1% |
| Discontinued study for Other Reasons¶ | 4% | 4% |
| On study but missing data in window | 0 | 0 |
| Proportion (%) of Subjects With HIV-1 RNA <50 copies/mL by Baseline and Demographic Category | ||
| Age (years) | ||
| <50 | 90% (N = 320) | 95% (N = 157) |
| ≥50 | 94% (N = 127) | 94% (N = 66) |
| Gender | ||
| Male | 91% (N = 372) | 94% (N = 194) |
| Female | 91% (N = 75) | 100% (N = 29) |
| Race | ||
| White | 90% (N = 344) | 95% (N = 168) |
| Non-White | 93% (N = 103) | 93% (N = 55) |
| Ethnicity | ||
| Hispanic or Latino | 88% (N = 99) | 91% (N = 45) |
| Not Hispanic or Latino | 91% (N = 341) | 95% (N = 175) |
| CD4+ T-cell Count (cells/mm3) | ||
| <200 cells/mm3 | 85% (N = 13) | 75% (N = 4) |
| ≥200 cells/mm3 | 91% (N = 426) | 95% (N = 216) |
| Baseline Regimen# | ||
| PI plus either ritonavir or cobicistat | 90% (N = 316) | 94% (N = 156) |
| elvitegravir plus cobicistat or NNRTI | 93% (N = 131) | 96% (N = 67) |
14.3 Clinical Trial Results in Pediatric Patients
The efficacy of DELSTRIGO was evaluated in cohort 2 of an open-label, single-arm 2-cohort trial in HIV-1-infected pediatric patients 12 to less than 18 years of age (IMPAACT 2014 (Protocol 027), NCT03332095). In cohort 1, virologically-suppressed subjects (n=9) received a single 100 mg dose of doravirine followed by intensive PK sampling. In cohort 2, virologically-suppressed subjects (n=43) were switched to DELSTRIGO and treatment-naïve subjects (n=2) were started on DELSTRIGO.
In cohort 2, at baseline the median age of subjects was 15 years (range: 12 to 17), the median weight was 52 kg (range: 45 to 80), 58% were female, 78% were Asian and 22% were Black, and the median CD4+ T-cell count was 713 cells per mm3 (range 84 to 1397). After switching to DELSTRIGO, 95% (41/43) of virologically-suppressed subjects remained suppressed (HIV-1 RNA <50 copies/mL) at Week 24. One of the two treatment-naïve subjects achieved HIV-1 RNA <50 copies/mL at Week 24. The other treatment-naïve subject met the protocol-defined virologic failure criteria (defined as 2 consecutive plasma HIV-1 RNA test results ≥200 copies/mL at or after Week 24) and was evaluated for the development of resistance; no emergence of genotypic or phenotypic resistance to doravirine, lamivudine, or tenofovir was detected.
16. How is Delstrigo supplied
Each DELSTRIGO tablet contains 100 mg of doravirine, 300 mg of lamivudine, and 300 mg of tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (equivalent to 245 mg of tenofovir disoproxil), is yellow, oval-shaped, film-coated, and is debossed with the corporate logo and 776 on one side and plain on the other side. Each bottle contains 30 tablets (NDC 0006-5007-01) and silica gel desiccants, and is closed with a child-resistant closure.
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
| Patient Information DELSTRIGO™ (del-STREE-go) (doravirine, lamivudine, and tenofovir disoproxil fumarate) tablets |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. | Revised: 06/2022 | ||
|
What is the most important information I should know about DELSTRIGO? |
|||
| DELSTRIGO can cause serious side effects, including: Worsening of hepatitis B virus infection (HBV). If you have Human Immunodeficiency Virus-1 (HIV-1) and HBV infection, your HBV infection may get worse (flare-up) if you stop taking DELSTRIGO. A "flare-up" is when your HBV infection suddenly returns in a worse way than before. Your healthcare provider will test you for HBV infection before you start treatment with DELSTRIGO.
|
|||
| For more information about side effects, see "What are the possible side effects of DELSTRIGO?" | |||
| What is DELSTRIGO? | |||
| DELSTRIGO is a prescription medicine that is used without other HIV-1 medicines to treat HIV-1 infection in adults and children who weigh at least 77 pounds (35 kg): | |||
|
|||
| HIV-1 is the virus that causes Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome (AIDS). | |||
| DELSTRIGO contains the prescription medicines doravirine, lamivudine and tenofovir disoproxil fumarate. | |||
| It is not known if DELSTRIGO is safe and effective in children who weigh less than 77 pounds (35 kg). | |||
| Who should not take DELSTRIGO? | |||
| Do not take DELSTRIGO if you take any of the following medicines: | |||
|
|
||
| Ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist if you are not sure if your medicine is one that is listed above. If you have taken any of the medicines in the past 4 weeks, talk to your healthcare provider or pharmacist before starting treatment with DELSTRIGO. | |||
| Do not take DELSTRIGO if you have ever had an allergic reaction to lamivudine. | |||
| What should I tell my healthcare provider before treatment with DELSTRIGO? | |||
Before treatment with DELSTRIGO, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
|
|||
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
|
|||
| How should I take DELSTRIGO? | |||
|
|||
DELSTRIGO may cause serious side effects, including:
|
|||
| Tell your healthcare provider if you have any of the following symptoms during treatment with DELSTRIGO: bone pain that does not go away or worsening bone pain, pain in your arms, legs, hands or feet, broken (fractured) bones or muscle pain or weakness. These may be symptoms of a bone or kidney problem. | |||
|
|||
| The most common side effects of DELSTRIGO include dizziness, nausea, and abnormal dreams. | |||
| These are not all the possible side effects of DELSTRIGO. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. |
|||
| How should I store DELSTRIGO? | |||
|
|||
| Keep DELSTRIGO and all medicines out of the reach of children. | |||
| General information about the safe and effective use of DELSTRIGO. | |||
| Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in the Patient Information leaflet. Do not use DELSTRIGO for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give DELSTRIGO to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about DELSTRIGO that is written for healthcare professionals. | |||
| What are the ingredients in DELSTRIGO? | |||
| Active ingredients: doravirine, lamivudine, and tenofovir disoproxil fumarate. | |||
| Inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, croscarmellose sodium, hypromellose acetate succinate, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, and sodium stearyl fumarate. The tablet film coating contains hypromellose, iron oxide yellow, lactose monohydrate, titanium dioxide, and triacetin. The coated tablets are polished with carnauba wax. | |||
|
Manufactured for: Merck Sharp & Dohme LLC Rahway, NJ 07065, USA |
|||
|
U.S. License No. 0002 For patent information: www.msd.com/research/patent The trademarks depicted herein are owned by their respective companies. Copyright © 2018-2022 Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA, and its affiliates. All rights reserved. usppi-mk1439a-t-2206r003 |
|||
| For more information, go to www.DELSTRIGO.com or call 1-877-888-4231. | |||
| DELSTRIGO
doravirine, lamivudine, and tenofovir disoproxil fumarate tablet, film coated |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Merck Sharp & Dohme LLC (118446553) |