Drug Detail:Doxylamine and pyridoxine (Doxylamine and pyridoxine [ dox-il-a-meen-and-pir-i-dox-een ])
Drug Class: Miscellaneous antiemetics
Highlights of Prescribing Information
DOXYLAMINE SUCCINATE and PYRIDOXINE HYDROCHLORIDE delayed-release tablets, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1976
Recent Major Changes
Warnings and Precautions, Interference with Urine Screen for Methadone, Opiates and Phencyclidine Phosphate (PCP) (5.3) 06/2018
Indications and Usage for Doxylamine and Pyridoxine
Doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride delayed-release tablets are a fixed dose combination drug product of doxylamine succinate, an antihistamine, and pyridoxine hydrochloride, a Vitamin B6 analog, indicated for the treatment of nausea and vomiting of pregnancy in women who do not respond to conservative management. (1) (1)
Doxylamine and Pyridoxine Dosage and Administration
Take two tablets daily at bedtime. If symptoms are not adequately controlled, the dose can be increased to a maximum recommended dose of four tablets daily (one in the morning, one mid-afternoon and two at bedtime) as described in the full prescribing information. (2) (2)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Delayed-release tablets containing 10 mg doxylamine succinate and 10 mg pyridoxine hydrochloride. (3) (3)
Contraindications
- Known hypersensitivity to doxylamine succinate, other ethanolamine derivative antihistamines, pyridoxine hydrochloride or any inactive ingredient in the formulation (4)
- Monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors (4, 7)
Warnings and Precautions
- Activities requiring mental alertness: Avoid engaging in activities requiring complete mental alertness, such as driving or operating heavy machinery, while using doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride until cleared to do so by a healthcare provider (5.1)
- Central nervous system (CNS) depressants: Concurrent use with alcohol or other CNS depressants is not recommended (5.1)
- Anticholinergic actions: Use with caution in patients with asthma, increased intraocular pressure, narrow angle glaucoma, stenosing peptic ulcer, pyloroduodenal obstruction and urinary bladder-neck obstruction (5.2)
- Interference with urine drug screen: Doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride may interfere with urine screening for methadone, opiates and PCP (5.3)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The most common adverse reaction with doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride (≥5 percent and exceeding the rate in placebo) is somnolence. (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Par Pharmaceutical at 1-800-828-9393 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
- Severe drowsiness can occur when used in combination with alcohol or other sedating medications. (7)
Use In Specific Populations
Doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride is intended for use in pregnant women. (8)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 4/2019
Related/similar drugs
hydroxyzine, ondansetron, lorazepam, meclizine, Benadryl, promethazine, doxylamine / pyridoxineFull Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Doxylamine and Pyridoxine
Doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride delayed-release tablets are indicated for the treatment of nausea and vomiting of pregnancy in women who do not respond to conservative management.
Limitations of Use
Doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride delayed-release tablet has not been studied in women with hyperemesis gravidarum.
2. Doxylamine and Pyridoxine Dosage and Administration
2.1 Dosage Information
Initially, take two doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride delayed-release tablets orally at bedtime (Day 1). If this dose adequately controls symptoms the next day, continue taking two tablets daily at bedtime. However, if symptoms persist into the afternoon of Day 2, take the usual dose of two tablets at bedtime that night then take three tablets starting on Day 3 (one tablet in the morning and two tablets at bedtime). If these three tablets adequately control symptoms on Day 4, continue taking three tablets daily. Otherwise take four tablets starting on Day 4 (one tablet in the morning, one tablet mid-afternoon and two tablets at bedtime).
The maximum recommended dose is four tablets (one in the morning, one in the mid-afternoon and two at bedtime) daily.
Take on an empty stomach with a glass of water [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Swallow tablets whole. Do not crush, chew, or split doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride delayed-release tablets.
Take as a daily prescription and not on an as needed basis. Reassess the woman for continued need for doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride delayed-release tablets as her pregnancy progresses.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
Doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride delayed-release tablets are white, round, biconvex, film-coated, delayed-release tablets containing 10 mg doxylamine succinate and 10 mg pyridoxine hydrochloride. The tablets are imprinted on one side with “186” in black color.
4. Contraindications
Doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride is contraindicated in women with any of the following conditions:
- Known hypersensitivity to doxylamine succinate, other ethanolamine derivative antihistamines, pyridoxine hydrochloride or any inactive ingredient in the formulation
Monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors intensify and prolong the adverse central nervous system effects of doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Activities Requiring Mental Alertness
Doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride may cause somnolence due to the anticholinergic properties of doxylamine succinate, an antihistamine. Women should avoid engaging in activities requiring complete mental alertness, such as driving or operating heavy machinery, while using doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride until cleared to do so by their healthcare provider.
Doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride use is not recommended if a woman is concurrently using central nervous system (CNS) depressants including alcohol. The combination may result in severe drowsiness leading to falls or accidents [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
5.2 Concomitant Medical Conditions
Doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride has anticholinergic properties and, therefore, should be used with caution in women with: asthma, increased intraocular pressure, narrow angle glaucoma, stenosing peptic ulcer, pyloroduodenal obstruction and urinary bladder-neck obstruction.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following adverse reactions are discussed elsewhere in the labeling:
- Somnolence [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Falls or other accidents resulting from the effect of the combined use of doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride with CNS depressants including alcohol [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
6.1 Clinical Trial Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
The safety and efficacy of doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride were compared to placebo in a double-blind, randomized, multi-center trial in 261 women with nausea and vomiting of pregnancy. The mean gestational age at enrollment was 9.3 weeks, range 7 to 14 weeks gestation [see Clinical Studies (14)]. Adverse reactions for doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride that occurred at an incidence ≥5 percent and exceeded the incidence for placebo are summarized in Table 1.
Table 1: Number (Percent) of Subjects with ≥ 5 Percent Adverse Reactions in a 15-Day Placebo-Controlled Study of Doxylamine Succinate and Pyridoxine Hydrochloride (Only Those Adverse Reactions Occurring at an Incidence ≥ 5 Percent and at a Higher Incidence with Doxylamine Succinate and Pyridoxine Hydrochloridethan Placebo are Shown)
|
Doxylamine Succinate and Pyridoxine Hydrochloride (N = 133) |
Placebo (n = 128) |
|
|
Somnolence |
19 (14.3%) |
15 (11.7%) |
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse events, listed alphabetically, have been identified during post-approval use of the combination of 10 mg doxylamine succinate and 10 mg pyridoxine hydrochloride. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Cardiac disorders: dyspnea, palpitation, tachycardia
Ear and labyrinth disorders: vertigo
Eye disorders: vision blurred, visual disturbances
Gastrointestinal disorders: abdominal distension, abdominal pain, constipation, diarrhea
General disorders and administration site conditions: chest discomfort, fatigue, irritability, malaise
Immune system disorders: hypersensitivity
Nervous system disorders: dizziness, headache, migraines, paresthesia, psychomotor hyperactivity
Psychiatric disorders: anxiety, disorientation, insomnia, nightmares
Renal and urinary disorders: dysuria, urinary retention
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: hyperhidrosis, pruritus, rash, rash maculo-papular
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 Drug Interactions
Use of doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride is contraindicated in women who are taking monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs), which prolong and intensify the anticholinergic (drying) effects of antihistamines. Concurrent use of alcohol and other CNS depressants (such as hypnotic sedatives and tranquilizers) with doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride is not recommended.
7.2 Drug-Food Interactions
A food-effect study demonstrated that the delay in the onset of action of doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride may be further delayed, and a reduction in absorption may occur when tablets are taken with food [see Dosage and Administration (2), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Therefore, doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride should be taken on an empty stomach with a glass of water [see Dosage and Administration (2)].
7.3 False Positive Urine Tests for Methadone, Opiates and PCP
False positive drug screens for methadone, opiates, and PCP can occur with doxylamine succinate/pyridoxine hydrochloride use. Confirmatory tests, such as Gas Chromatography Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS), should be used to confirm the identity of the substance in the event of a positive immunoassay result.
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride is intended for the treatment of nausea and vomiting of pregnancy in women who do not respond to conservative management. Maternal risks are discussed throughout the labeling. No increased risk for congenital malformations has been reported in epidemiologic studies in pregnant women.
In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risks for major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies are 2-4% and 15-20%, respectively.
Data
Human Data
The combination of doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride has been the subject of many epidemiological studies (cohort, case control and meta-analyses) designed to detect possible teratogenicity. A meta-analysis of 16 cohort and 11 case-control studies published between 1963 and 1991 reported no increased risk for malformations from first trimester exposures to doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride, with or without dicyclomine hydrochloride. A second meta-analysis of 12 cohort and 5 case-control studies published between 1963 and 1985 reported no statistically significant relationships between fetal abnormalities and the first trimester use of the combination doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride with or without dicyclomine hydrochloride.
8.3 Lactation
Women should not breastfeed while using doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride.
The molecular weight of doxylamine succinate is low enough that passage into breast milk can be expected. Excitement, irritability and sedation have been reported in nursing infants presumably exposed to doxylamine succinate through breast milk. Infants with apnea or other respiratory syndromes may be particularly vulnerable to the sedative effects of doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride resulting in worsening of their apnea or respiratory conditions.
Pyridoxine hydrochloride is excreted into breast milk. There have been no reports of adverse events in infants presumably exposed to pyridoxine hydrochloride through breast milk.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride in children under 18 years of age have not been established.
Fatalities have been reported from doxylamine overdose in children. The overdose cases have been characterized by coma, grand mal seizures and cardiorespiratory arrest. Children appear to be at a high risk for cardiorespiratory arrest. A toxic dose for children of more than 1.8 mg/kg has been reported. A 3 year old child died 18 hours after ingesting 1,000 mg doxylamine succinate. However, there is no correlation between the amount of doxylamine ingested, the doxylamine plasma level and clinical symptomatology.
10. Overdosage
10.1 Signs and Symptoms of Overdose
Doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride is a delayed-release formulation, therefore, signs and symptoms of intoxication may not be apparent immediately.
Signs and symptoms of overdose may include restlessness, dryness of mouth, dilated pupils, sleepiness, vertigo, mental confusion and tachycardia.
At toxic doses, doxylamine exhibits anticholinergic effects, including seizures, rhabdomyolysis, acute renal failure and death.
11. Doxylamine and Pyridoxine Description
Doxylamine Succinate and Pyridoxine Hydrochloride Delayed-Release Tablets 10 mg/10 mg are white, round, biconvex, film-coated, delayed-release tablet imprinted on one side with “186” in black color.
Inactive ingredients are as follows: ammonium hydroxide, black iron oxide, colloidal anhydrous silica, colloidal silicon dioxide, croscarmellose sodium, dicalcium phosphate anhydrous, hypromellose, isopropyl alcohol, magnesium stearate, magnesium trisilicate, methacrylic acid copolymer type C, microcrystalline cellulose, n-butanol, polyethylene glycol/macrogol, polysorbate 80, propylene glycol, shellac glaze, sodium bicarbonate, sodium lauryl sulphate, talc, titanium dioxide and triethyl citrate.
Doxylamine Succinate
Doxylamine succinate is classified as an antihistamine. The chemical name for doxylamine succinate is ethanamine, N,N-dimethyl-2-[1-phenyl-1-(2-pyridinyl)ethoxy]-, butanedioate (1:1). The empirical formula is C17H22N2O • C4H6O4 and the molecular mass is 388.46. The structural formula is:
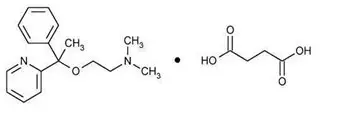
Doxylamine succinate is a white or almost white powder that is very soluble in water and alcohol, freely soluble in chloroform and very slightly soluble in ether and benzene.
Pyridoxine Hydrochloride
Pyridoxine hydrochloride is a vitamin B6 analog. The chemical name for pyridoxine hydrochloride is 3,4-pyridinedimethanol, 5-hydroxy-6-methyl-, hydrochloride. The empirical formula is C8H11NO3 • HCl and the molecular mass is 205.64. The structural formula is:
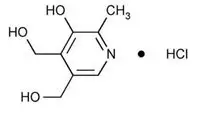
Pyridoxine hydrochloride is a white to practically white crystals or crystalline powder that is freely soluble in water, slightly soluble in alcohol and acetone, soluble in chloroform, insoluble in ether.
12. Doxylamine and Pyridoxine - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
The mechanism of action of doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride is unknown.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics of doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride has been characterized in healthy non-pregnant adult women. Pharmacokinetic results for doxylamine and pyridoxine, including its vitamin B6 metabolites, pyridoxal, pyridoxal 5’-phosphate, pyridoxamine and pyridoxamine 5’-phosphate, are summarized in Tables 2 to 5.
Absorption
A single-dose (two tablets) and multiple-dose (four tablets daily), open-label study was conducted to assess the safety and pharmacokinetic profile of doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride administered in healthy non-pregnant adult women. Single-doses (two tablets at bedtime) were administered on Days 1 and 2. Multiple-doses (one tablet in the morning, one tablet in the afternoon and two tablets at bedtime) were administered on Days 3-18.
Blood samples for pharmacokinetic analysis were collected pre-and post-dose on Days 2 and 18 as well as pre-dose prior to bedtime dose only (trough) on Days 9, 10, 11, 16, 17, and 18.
Doxylamine and pyridoxine are absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract, mainly in the jejunum.
The Cmax of doxylamine and pyridoxine are achieved within 7.5 and 5.5 hours, respectively (see Table 2).
Table 2 – Single-Dose and Multiple-Dose Pharmacokinetics of Doxylamine Succinate and Pyridoxine Hydrochloride in Healthy Non-Pregnant Adult Women
|
Single Dose |
Multiple Dose |
|||||
|
AUC0-inf (ng•h/mL) |
Cmax (ng/mL) |
Tmax (h) |
AUC0-inf (ng•h/mL) |
Cmax (ng/mL) |
Tmax (h) |
|
|
Doxylamine |
1,280.9 ± 369.3 |
83.3 ± 20.6 |
7.2 ± 1.9 |
3,721.5 ± 1,318.5 |
168.6 ± 38.5 |
7.8 ± 1.6 |
|
Pyridoxine |
43.4 ± 16.5 |
32.6 ± 15.0 |
5.7 ± 1.5 |
64.5 ± 36.4 |
46.1 ± 28.3 |
5.6 ± 1.3 |
|
Pyridoxal |
211.6 ± 46.1 |
74.3 ± 21.8 |
6.5 ± 1.4 |
1,587.2 ± 550.0 |
210.0 ± 54.4 |
6.8 ± 1.2 |
|
Pyridoxal 5’Phosphate |
1,536.4 ± 721.5 |
30.0 ± 10.0 |
11.7 ± 5.3 |
6,099.7 ± 1,383.7 |
84.9 ± 16.9 |
6.3 ± 6.6 |
|
Pyridoxamine |
4.1 ± 2.7 |
0.5 ± 0.7 |
5.9 ± 2.1 |
2.6 ± 0.8 |
0.5 ± 0.2 |
6.6 ± 1.4 |
|
Pyridoxamine 5’-phosphate |
5.2 ± 3.8 |
0.7 ± 0.5 |
14.8 ± 6.6 |
94.5 ± 58.0 |
2.3 ± 1.7 |
12.4 ± 11.2 |
Multiple-dose administration of doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride results in increased concentrations of doxylamine as well as increases in doxylamine Cmax and AUC0-last of absorption. The time to reach the maximum concentration is not affected by multiple doses. The mean accumulation index is more than 1.0 suggesting that doxylamine accumulates following multiple dosing (see Table 3).
Although no accumulation was observed for pyridoxine, the mean accumulation index for each metabolite (pyridoxal, pyridoxal 5’-phosphate, and pyridoxamine 5’-phosphate) is more than 1.0 following multiple-dose administration of doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride. The time to reach the maximum concentration is not affected by multiple doses (see Table 2).
Table 3 – Pharmacokinetics of Doxylamine and Pyridoxine Following Single Dose and Multiple Dose Administration of Doxylamine Succinate and Pyridoxine Hydrochloride to Healthy Non-Pregnant Adult Women
|
AUC0-last (ng•h/mL) |
AUC0-inf (ng•h/mL) |
Cmax (ng/mL) |
Tmax (h) |
T½el (h) |
||
|
Doxylamine Mean±SD N=18 |
Single |
911.4 ± 205.6 |
1,280.9 ± 369.3 |
83.3 ± 20.6 |
7.2 ± 1.9 |
10.1 ± 2.1 |
|
Multiple |
3,661.3 ± 1,279.2 |
3,721.5 ± 1,318.5 |
168.6 ± 38.5 |
7.8 ± 1.6 |
11.9 ± 3.3 |
|
|
Pyridoxine Mean±SD N=18 |
Single |
39.3 ± 16.5 |
43.4 ± 16.5 |
32.6 ± 15.0 |
5.7 ± 1.5 |
0.5 ± 0.2 |
|
Multiple |
59.3 ± 33.9 |
64.5 ± 36.4 |
46.1 ± 28.3 |
5.6 ± 1.3 |
0.5 ± 0.1 |
|
Food Effect
The administration of food delays the absorption of both doxylamine and pyridoxine. This delay is associated with a lower peak concentration of doxylamine, but the extent of absorption is not affected (see Table 4).
The effect of food on the peak concentration and the extent of absorption of the pyridoxine component is more complex because the pyridoxal, pyridoxamine, pyridoxal 5’-phosphate and pyridoxamine 5’-phosphate metabolites also contribute to the biological activity. Food significantly reduces the bioavailability of pyridoxine, lowering its Cmax and AUC by approximately 50% compared to fasting conditions. Similarly, food significantly reduces pyridoxal AUC and reduces its Cmax by 50% compared to fasting conditions. In contrast, food slightly increases pyridoxal 5’-phosphate Cmax and extent of absorption. As for pyridoxamine and pyridoxamine 5’-phosphate, the rate and extent of absorption seem to decrease under fed conditions.
Table 4 – Pharmacokinetics of Doxylamine and Pyridoxine Following Administration of Doxylamine Succinate and Pyridoxine Hydrochloride Under Fed and Fasted Conditions in Healthy Non-Pregnant Adult Women
|
AUC0-t (ng•h/mL) |
AUC0-inf (ng•h/mL) |
Cmax (ng/mL) |
Tmax (h) |
T½el (h) |
||
|
Doxylamine Mean±SD N=42 |
Fasted |
1,407.2 ± 336.9 |
1,447.9 ± 332.2 |
94.9 ± 18.4 |
5.1 ± 3.4 |
12.6 ± 3.4 |
|
Fed |
1,488.0 ± 463.2 |
1,579.0 ± 422.7a |
75.7 ± 16.6 |
14.9 ± 7.4 |
12.5 ± 2.9a |
|
|
Pyridoxine Mean±SD N=42 |
Fasted |
33.8 ± 13.7 |
39.5 ± 12.9c |
35.5 ± 21.4 |
2.5 ± 0.9 |
0.4 ± 0.2c |
|
Fed |
18.3 ± 14.5 |
24.2 ±14.0b |
13.7 ± 10.8 |
9.3 ± 4.0 |
0.5 ± 0.2b |
|
aN=37; bN=18; cN=31
Distribution
Pyridoxine is highly protein bound, primarily to albumin. Its main active metabolite, pyridoxal 5’-phosphate (PLP) accounts for at least 60% of circulating vitamin B6 concentrations.
Metabolism
Doxylamine is biotransformed in the liver by N-dealkylation to its principle metabolites N-desmethyl-doxylamine and N, N-didesmethyldoxylamine.
Pyridoxine is a prodrug primarily metabolized in the liver.
Excretion
The principle metabolites of doxylamine, N-desmethyl-doxylamine and N, N-didesmethyldoxylamine, are excreted by the kidney.
The terminal elimination half-life of doxylamine and pyridoxine are 12.5 hours and 0.5 hours, respectively (see Table 5).
Table 5 – Terminal Elimination Half-Life (T1/2el) for Doxylamine Succinate and Pyridoxine Hydrochloride Administered as a Single Dose of Two Tablets under Fasting Conditions in Healthy Non-Pregnant Adult Women
|
T½el (h) |
|
|
Doxylamine |
12.6 ± 3.4 |
|
Pyridoxine |
0.4 ± 0.2 |
|
Pyridoxal |
2.1 ± 2.2 |
|
Pyridoxal 5’-Phosphate |
81.6 ± 42.2 |
|
Pyridoxamine |
3.1 ± 2.5 |
|
Pyridoxamine 5’-Phosphate |
66.5 ± 51.3 |
Use in Specific Populations
Race: No pharmacokinetic studies have been conducted related to race.
Hepatic Impairment: No pharmacokinetic studies have been conducted in hepatic impaired patients.
Renal Impairment: No pharmacokinetic studies have been conducted in renal impaired patients.
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis and Mutagenesis and Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenicity
Two-year carcinogenicity studies in rats and mice have been conducted with doxylamine succinate.
Doxylamine succinate is not likely to have human carcinogenic potential. The carcinogenic potential of pyridoxine hydrochloride has not been evaluated.
14. Clinical Studies
A double-blind, randomized, multi-center, placebo-controlled study was conducted to support the safety and efficacy of doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride in the treatment of nausea and vomiting of pregnancy. Adult women 18 years of age or older and 7 to 14 weeks gestation (median 9 weeks of gestation) with nausea and vomiting of pregnancy were randomized to 14 days of doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride or placebo. Two tablets of doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride were administered at bedtime on Day 1. If symptoms of nausea and vomiting persisted into the afternoon hours of Day 2, the woman was directed to take her usual dose of two tablets at bedtime that night and, beginning on Day 3, to take one tablet in the morning and two tablets at bedtime. Based upon assessment of remaining symptoms at her clinic visit on Day 4 (± 1 day), the woman may have been directed to take an additional tablet mid-afternoon. A maximum of four tablets (one in the morning, one in the mid-afternoon and two at bedtime) were taken daily.
Over the treatment period, 19% of doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride-treated patients remained on 2 tablets daily, 21% received 3 tablets daily, and 60% received 4 tablets daily.
The primary efficacy endpoint was the change from baseline at Day 15 in the Pregnancy Unique-Quantification of Emesis (PUQE) score. The PUQE score incorporates the number of daily vomiting episodes, number of daily heaves, and length of daily nausea in hours, for an overall score of symptoms rated from 3 (no symptoms) to 15 (most severe).
At baseline, the mean PUQE score was 9.0 in the doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride arm and 8.8 in the placebo arm. There was a 0.7 (95% confidence interval 0.2 to 1.2 with p-value 0.006) mean decrease (improvement in nausea and vomiting symptoms) from baseline in PUQE score at Day 15 with doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride compared to placebo (see Table 6).
Table 6 – Change from Baseline in the Primary Endpoint, Pregnancy Unique-Quantification of Emesis (PUQE) Score at Day 15. (Intent-to-Treat Population with Last-Observation Carried Forward)
|
PUQE Score* |
Doxylamine Succinate + Pyridoxine Hydrochloride |
Placebo |
Treatment Difference [95% Confidence Interval] |
|
Baseline Change from baseline at Day 15 |
9.0 ± 2.1 |
8.8 ± 2.1 | |
|
-4.8 ± 2.7 |
-3.9 ± 2.6 |
-0.7 [-1.2, -0.2] |
*The Pregnancy-Unique Quantification of Emesis and Nausea (PUQE) score incorporated the number of daily vomiting episodes, number of daily heaves, and length of daily nausea in hours, for an overall score of symptoms rated from 3 (no symptoms) to 15 (most severe). Baseline was defined as the PUQE score completed at the enrollment visit.
16. How is Doxylamine and Pyridoxine supplied
16.1 How supplied
Doxylamine Succinate and Pyridoxine Hydrochloride Delayed-Release Tablets 10 mg/10 mg are supplied in a high-density polyethylene bottle with a polypropylene child-resistant cap and a silica gel desiccant canister. Each white, round, biconvex, film-coated, delayed-release tablet contains 10 mg doxylamine succinate and 10 mg pyridoxine hydrochloride, and is imprinted on one side with “186” in black color. Doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride tablets are provided as follows:
NDC 49884-186-01 Bottles of 100.
17. Patient Counseling Information
See FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information)
Somnolence and Severe Drowsiness
Inform women to avoid engaging in activities requiring complete mental alertness, such as driving or operating heavy machinery, while using doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride until cleared to do so.
Inform women of the importance of not taking doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride with alcohol or sedating medications, including other antihistamines (present in some cough and cold medications), opiates and sleep aids because somnolence could worsen leading to falls or other accidents.
Interference with urine drug screening
Inform women that use of doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride may result in false positive urine drug screening for methadone, opiates and PCP.
Patient Information
Doxylamine Succinate and Pyridoxine Hydrochloride Delayed-Release Tablets
(dok-sil′ă-mēn sŭk′si-nāt and peer-ih-DOX-een HIGH-droe-KLOR-ide)
What are doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride delayed-release tablets?
- Doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride delayed-release tablets are a prescription medicine used to treat nausea and vomiting of pregnancy in women who have not improved with change in diet or other non-medicine treatments.
- It is not known if doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride delayed-release tablets are safe and effective in women with severe nausea and vomiting of pregnancy, a condition called hyperemesis gravidarum. Women with this condition may need to be hospitalized.
- It is not known if doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride delayed-release tablets are safe and effective in children under 18 years of age.
Who should not take doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride delayed-release tablets?
Do not take doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride delayed-release tablets if you:
- are allergic to doxylamine succinate, other ethanolamine derivative antihistamines, pyridoxine hydrochloride or any of the ingredients in doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride delayed-release tablets. See the end of this leaflet for a complete list of ingredients in doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride delayed-release tablets.
- take monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs). Ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist if you are not sure if you take an MAOI, including Marplan, Nardil, Emsam, Eldepryl, Zelapar, and Parnate.
Before taking doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride delayed-release tablets, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
- have asthma.
- have eye problems called increased intraocular pressure or narrow angle glaucoma.
- have a stomach problem called stenosing peptic ulcer or pyloroduodenal obstruction.
- have a bladder problem called urinary bladder-neck obstruction.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. Doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride can pass into your breast milk and may harm your baby. You should not breastfeed while using doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride delayed-release tablets.
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription or over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, or herbal supplements.
How should I take doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride delayed-release tablets?
- Talk to your healthcare provider about how much doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride delayed-release tablets to take and when to take it.
- Take doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride delayed-release tablets everyday as prescribed by your healthcare provider. Do not stop taking doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride delayed-release tablets without talking to your healthcare provider first.
- See the following schedule for the usual way you should start taking doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride delayed-release tablets:
- Day 1- Take 2 tablets, by mouth at bedtime.
- Day 2- Take 2 tablets at bedtime. If your nausea and vomiting is better or controlled on Day 2, continueto take 2 tablets every night at bedtime. This will be your usual dose unless your healthcare provider tells you otherwise.
- Day 3- If you still had nausea and vomiting on Day 2, take 3 tablets on Day 3 (1 tablet in the morning and 2 tablets at bedtime).
- Day 4- If your nausea and vomiting was better or controlled on Day 3, continue to take 3 tablets each day (1 tablet in the morning and 2 tablets at bedtime). If you still had nausea and vomiting on Day 3, start taking 4 tablets each day (1 tablet in the morning, 1 tablet in the afternoon, and 2 tablets at bedtime).
- Do not take more than 4 tablets (1 in the morning, 1 in the mid-afternoon, and 2 at bedtime) in 1 day.
- Take doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride delayed-release tablets on an empty stomach with a glass of water.
- Take doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride delayed-release tablets whole. Do not crush, chew, or break doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride delayed-release tablets before swallowing. If you cannot swallow doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride delayed-release tablets whole, tell your healthcare provider.
- If you take too much doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride (overdose), you may have the following symptoms: restlessness, dry mouth, the pupils of your eyes become larger (dilated), sleepiness, dizziness, confusion, fast heart rate, seizures, muscle pain or weakness, and sudden and severe kidney problems. If you have these symptoms and they are severe, they may lead to death. Stop taking doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride delayed-release tablets, call your healthcare provider or go to the nearest hospital emergency room right away. For more information about overdose treatment, call your poison control center at 1-800-222-1222.
What are the possible side effects of doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride delayed-release tablets?
Doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride delayed-release tablets may cause serious side effects, including drowsiness.
Drowsiness is a common side effect when taking doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride delayed-release tablets, but can also be severe:
- Do not drive, operate heavy machinery, or other activities that need your full attention unless your healthcare provider says that you may do so.
- Do not drink alcohol, or take other central nervous system depressants such as cough and cold medicines, certain pain medicines, and medicines that help you sleep while you take doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride delayed-release tablets. Severe drowsiness can happen or become worse causing falls or accidents.
Doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride delayed-release tablets may cause false positive urine drug screening test for methadone, opiates and PCP.
These are not all the possible side effects of doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride delayed-release tablets.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride delayed-release tablets?
- Store doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride delayed-release tablets between 68° to 77°F (20° to 25°C).
- Keep doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride delayed-release tablets dry, in a tightly closed container, and out of the light.
- Safely throw away medicine that is out of date or no longer needed.
Keep doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride delayed-release tablets and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about the safe and effective use of doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride delayed-release tablets.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride delayed-release tablets that is written for health professionals. Do not use doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride delayed-release tablets for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride delayed-release tablets to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them.
What are the ingredients in doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride delayed-release tablets?
Active ingredient: doxylamine succinate (an antihistamine) and pyridoxine hydrochloride (vitamin B6).
Inactive ingredients: ammonium hydroxide, black iron oxide, colloidal anhydrous silica, colloidal silicon dioxide, croscarmellose sodium, dicalcium phosphate anhydrous, hypromellose, isopropyl alcohol, magnesium stearate, magnesium trisilicate, methacrylic acid copolymer type C, microcrystalline cellulose, n-butanol, polyethylene glycol/macrogol, polysorbate 80, propylene glycol, shellac glaze, sodium bicarbonate, sodium lauryl sulphate, talc, titanium dioxide and triethyl citrate.
This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
All brand names listed are the registered trademarks of their respective owners and are not trademarks of Par Pharmaceutical.
Dist. by:
Par Pharmaceutical
Chestnut Ridge, NY 10977 U.S.A.
Mfg. by:
Par Formulations Private Limited,
9/215, Pudupakkam, Kelambakkam - 603 103.
Made in India
Mfg. Lic. No.: TN00002122
OS186-01-74-01
Issued: 04/2019
| DOXYLAMINE SUCCINATE AND PYRIDOXINE HYDROCHLORIDE
doxylamine succinate and pyridoxine hydrochloride, delayed release tablets 10 mg/10 mg tablet, delayed release |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Par Pharmaceutical, Inc. (092733690) |





