Drug Detail:Elyxyb (Celecoxib)
Drug Class: Cox-2 inhibitors
Highlights of Prescribing Information
ELYXYB (celecoxib) oral solution
Initial U.S. Approval: 1998
WARNING: RISK OF SERIOUS CARDIOVASCULAR and GASTROINTESTINAL EVENTS
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) cause an increased risk of serious cardiovascular thrombotic events, including myocardial infarction and stroke, which can be fatal. This risk may occur early in the treatment and may increase with duration of use. (5.1)
- ELYXYB is contraindicated in the setting of coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery. (4, 5.1)
- NSAIDs cause an increased risk of serious gastrointestinal (GI) adverse events including bleeding, ulceration, and perforation of the stomach or intestines, which can be fatal. These events can occur at any time during use and without warning symptoms. Elderly patients and patients with a prior history of peptic ulcer disease and/or GI bleeding are at greater risk for serious GI events. (5.2)
Recent Major Changes
| Warnings and Precautions (5.10, 5.12) | 04/2021 |
Indications and Usage for Elyxyb
ELYXYB is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug indicated for the acute treatment of migraine with or without aura in adults (1)
Limitations of Use
ELYXYB is not indicated for the preventive treatment of migraine. (1)
Elyxyb Dosage and Administration
- The recommended dose of ELYXYB is 120 mg taken orally, with or without food. (2.1)
- The maximum dosage in a 24-hour period is 120 mg. (2.1)
- Use ELYXYB for the fewest number of days per month, as needed. (2.1)
- Hepatic Impairment: The recommended and maximum dose is 60 mg (2.4 mL) in patients with moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class B) (2.2, 8.6, 12.3)
- Poor Metabolizers of CYP2C9 Substrates: The recommended and maximum dose is 60 mg (2.4 mL) in patients who are known or suspected to be CYP2C9 poor metabolizers (2.3, 8.8, 12.5)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Oral solution, 120 mg/4.8 mL (25 mg/mL) (3)
Contraindications
- Known hypersensitivity to celecoxib, any components of the drug product, or sulfonamides (4)
- History of asthma, urticaria, or other allergic-type reactions after taking aspirin or other NSAIDs (4)
- In the setting of CABG surgery (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Hepatotoxicity: Inform patients of warning signs and symptoms of hepatotoxicity. Discontinue if abnormal liver tests persist or worsen or if clinical signs and symptoms of liver disease develop (5.3)
- Hypertension: Patients taking some antihypertensive medications may have impaired response to these therapies when taking NSAIDs. Monitor blood pressure (5.4, 7)
- Heart Failure and Edema: Avoid use of ELYXYB in patients with severe heart failure unless benefits are expected to outweigh risk of worsening heart failure (5.5)
- Renal Toxicity: Monitor renal function in patients with renal or hepatic impairment, heart failure, dehydration, or hypovolemia. Avoid use of ELYXYB in patients with severe renal impairment unless benefits are expected to outweigh risk of worsening renal function (5.6)
- Anaphylactic Reactions: Seek emergency help if an anaphylactic reaction occurs (5.7)
- Exacerbation of Asthma Related to Aspirin Sensitivity: ELYXYB is contraindicated in patients with aspirin-sensitive asthma. Monitor patients with preexisting asthma (without aspirin sensitivity) (5.8)
- Serious Skin Reactions: Discontinue ELYXYB at first appearance of skin rash or other signs of hypersensitivity (5.9)
- Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS): Discontinue and evaluate clinically (5.10)
- Medication Overuse Headache: Detoxification may be necessary (5.11)
- Fetal Toxicity: Limit use of NSAIDs, including Elyxyb, between about 20 to 30 weeks in pregnancy due to the risk of oligohydramnios/fetal renal dysfunction. Avoid use of NSAIDs in women at about 30 weeks gestation and later in pregnancy due to the risks of oligohydramnios/fetal renal dysfunction and premature closure of the fetal ductus arteriosus (5.12, 8.1)
- Hematologic Toxicity: Monitor hemoglobin or hematocrit in patients with any signs or symptoms of anemia (5.13, 7)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reaction (at least 3% and greater than placebo) is dysgeusia (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact BioDelivery Sciences International, Inc. at 1-800-469-0261or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch
Drug Interactions
- Drugs that Interfere with Hemostasis (e.g., warfarin, aspirin, SSRIs/SNRIs): Monitor patients for bleeding who are concomitantly taking ELYXYB with drugs that interfere with hemostasis. Concomitant use of ELYXYB and analgesic doses of aspirin is not generally recommended (7)
- ACE Inhibitors, Angiotensin Receptor Blockers (ARB), or Beta- Blockers: Concomitant use with ELYXYB may diminish the antihypertensive effect of these drugs. Monitor blood pressure (7)
- ACE Inhibitors and ARBs: Concomitant use with ELYXYB in elderly, volume depleted, or those with renal impairment may result in deterioration of renal function. In such high-risk patients, monitor for signs of worsening renal function (7)
- Diuretics: NSAIDs can reduce natriuretic effect of furosemide and thiazide diuretics. Monitor patients to assure diuretic efficacy including antihypertensive effects (7)
- Digoxin: Concomitant use with ELYXYB can increase serum concentration and prolong half-life of digoxin. Monitor serum digoxin levels (7)
Use In Specific Populations
- Infertility: NSAIDs are associated with reversible infertility. Consider withdrawal of ELYXYB in women who have difficulties conceiving (8.3)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 9/2021
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Elyxyb
ELYXYB is indicated for the acute treatment of migraine with or without aura in adults.
2. Elyxyb Dosage and Administration
2.1 Recommended Dosage
The recommended dose of ELYXYB is 120 mg taken orally, with or without food [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
The maximum dosage in a 24-hour period is 120 mg. The safety and effectiveness of a second dose in a 24-hour period have not been established.
Use ELYXYB for the fewest number of days per month, as needed.
2.2 Dosage Modification in Patients with Hepatic Impairment
The recommended and maximum dose in patients with moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class B) is 60 mg (2.4 mL) [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. A calibrated measuring device is recommended to measure and deliver the prescribed dose accurately. A household teaspoon or tablespoon is not an adequate measuring device. Use of ELYXYB in patients with severe hepatic impairment is not recommended.
2.3 Dosage Modification in CYP2C9 Poor Metabolizers
The recommended and maximum dose in patients who are known or suspected to be CYP2C9 poor metabolizers is 60 mg (2.4 mL) [see Use in Specific Populations (8.8) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.5)]. A calibrated measuring device is recommended to measure and deliver the prescribed dose accurately. A household teaspoon or tablespoon is not an adequate measuring device.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
Dosage form: Clear colorless oral solution
Strength: 120 mg/4.8 mL (25 mg/mL)
4. Contraindications
ELYXYB is contraindicated in the following patients:
- Known hypersensitivity (e.g., anaphylactic reactions and serious skin reactions) to celecoxib, any components of the drug product [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7, 5.9)].
- History of asthma, urticaria, or other allergic-type reactions after taking aspirin or other NSAIDs. Severe, sometimes fatal, anaphylactic reactions to NSAIDs have been reported in such patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7, 5.8)].
- In the setting of coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- In patients who have demonstrated allergic-type reactions to sulfonamides [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Cardiovascular Thrombotic Events
Clinical trials of several cyclooxygenase (COX-2) selective and nonselective NSAIDs of up to three years duration have shown an increased risk of serious cardiovascular (CV) thrombotic events, including myocardial infarction (MI) and stroke, which can be fatal. Based on available data, it is unclear that the risk for CV thrombotic events is similar for all NSAIDs. The relative increase in serious CV thrombotic events over baseline conferred by NSAID use appears to be similar in those with and without known CV disease or risk factors for CV disease. However, patients with known CV disease or risk factors had a higher absolute incidence of excess serious CV thrombotic events, due to their increased baseline rate. Some observational studies found that this increased risk of serious CV thrombotic events began as early as the first weeks of treatment. The increase in CV thrombotic risk has been observed most consistently at higher doses.
In a trial with celecoxib capsules, there was about a threefold increased risk of the composite endpoint of cardiovascular death, MI, or stroke for the celecoxib 400 mg twice daily and celecoxib 200 mg twice daily treatment arms compared to placebo. The increases in both celecoxib dose groups versus placebo-treated patients were mainly due to an increased incidence of myocardial infarction.
To minimize the potential risk for an adverse CV event in NSAID-treated patients, use ELYXYB for the fewest number of days per month as needed, based on individual treatment goals. Physicians and patients should remain alert for the development of such events, throughout the entire treatment course, even in the absence of previous CV symptoms. Patients should be informed about the symptoms of serious CV events and the steps to take if they occur.
There is no consistent evidence that concurrent use of aspirin mitigates the increased risk of serious CV thrombotic events associated with NSAID use. The concurrent use of aspirin and an NSAID, such as ELYXYB, increases the risk of serious gastrointestinal (GI) events [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
5.2 Gastrointestinal Bleeding, Ulceration and Perforation
NSAIDs, including ELYXYB, can cause serious gastrointestinal (GI) adverse events including inflammation, bleeding, ulceration, and perforation of the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, or large intestine, which can be fatal. These serious adverse events can occur at any time, with or without warning symptoms, in patients treated with celecoxib. Only one in five patients who develop a serious upper GI adverse event on NSAID therapy is symptomatic. Upper GI ulcers, gross bleeding, or perforation caused by NSAIDs occurred in approximately 1% of patients treated for 3 to 6 months, and in about 2% to 4% of patients treated for one year. However, even short-term NSAID therapy is not without risk.
5.3 Hepatotoxicity
Elevations of ALT or AST (three or more times the upper limit of normal [ULN]) have been reported in approximately 1% of NSAID-treated patients in clinical trials. In addition, rare, sometimes fatal, cases of severe hepatic injury, including fulminant hepatitis, liver necrosis, and hepatic failure have been reported.
Elevations of ALT or AST (less than three times ULN) may occur in up to 15% of patients treated with NSAIDs, including ELYXYB.
In controlled clinical trials of celecoxib capsules, the incidence of borderline elevations (greater than or equal to 1.2 times and less than 3 times the upper limit of normal) of liver associated enzymes was 6% for celecoxib and 5% for placebo, and approximately 0.2% of patients taking celecoxib and 0.3% of patients taking placebo had notable elevations of ALT and AST.
If clinical signs and symptoms consistent with liver disease develop, or if systemic manifestations occur (e.g., nausea, fatigue, pruritus, jaundice, right upper quadrant tenderness, and/or flu-like symptoms), discontinue ELYXYB immediately, and perform a clinical evaluation of the patient.
5.4 Hypertension
NSAIDs, including ELYXYB, can lead to new onset of hypertension or worsening of preexisting hypertension, either of which may contribute to the increased incidence of CV events. Use NSAIDS, including ELYXYB, with caution in patients with hypertension. Monitor blood pressure (BP) during the initiation of ELYXYB treatment and throughout the course of therapy.
Patients taking angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, thiazide diuretics, or loop diuretics may have impaired response to these therapies when taking NSAIDs [see Drug Interactions (7)].
5.5 Heart Failure and Edema
The Coxib and traditional NSAID Trialists' Collaboration meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials demonstrated an approximately two-fold increase in hospitalizations for heart failure in COX-2 selective-treated patients and nonselective NSAID-treated patients compared to placebo-treated patients. In a Danish National Registry study of patients with heart failure, NSAID use increased the risk of MI, hospitalization for heart failure, and death.
Additionally, fluid retention and edema have been observed in some patients treated with NSAIDs. Use of ELYXYB may blunt the CV effects of several therapeutic agents used to treat these medical conditions (e.g., diuretics, ACE inhibitors, or angiotensin receptor blockers [ARBs]) [see Drug Interactions (7)].
In a clinical study, the cumulative rates at 9 months of peripheral edema in patients on celecoxib capsules 400 mg twice daily, ibuprofen 800 mg three times daily, and diclofenac 75 mg twice daily were 4.5%, 6.9%, and 4.7%, respectively.
Avoid the use of ELYXYB in patients with severe heart failure unless the benefits are expected to outweigh the risk of worsening heart failure. If ELYXYB is used in patients with severe heart failure, monitor patients for signs of worsening heart failure.
5.7 Anaphylactic Reactions
Celecoxib has been associated with anaphylactic reactions in patients with and without known hypersensitivity to celecoxib and in patients with aspirin sensitive asthma. Celecoxib is a sulfonamide and both NSAIDs and sulfonamides may cause allergic type reactions including anaphylactic symptoms and life-threatening or less severe asthmatic episodes in certain susceptible people [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
5.8 Exacerbation of Asthma Related to Aspirin Sensitivity
A subpopulation of patients with asthma may have aspirin-sensitive asthma which may include chronic rhinosinusitis complicated by nasal polyps; severe, potentially fatal bronchospasm; and/or intolerance to aspirin and other NSAIDs. Because cross-reactivity between aspirin and other NSAIDs has been reported in such aspirin-sensitive patients, ELYXYB is contraindicated in patients with this form of aspirin sensitivity [see Contraindications (4)]. When ELYXYB is used in patients with preexisting asthma (without known aspirin sensitivity), monitor patients for changes in the signs and symptoms of asthma.
5.9 Serious Skin Reactions
Serious skin reactions have occurred following treatment with celecoxib, including erythema multiforme, exfoliative dermatitis, Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS), toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)], and acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP). These serious events may occur without warning and can be fatal.
Inform patients about the signs and symptoms of serious skin reactions, and to discontinue the use of ELYXYB at the first appearance of skin rash or any other sign of hypersensitivity. ELYXYB is contraindicated in patients with previous serious skin reactions to NSAIDs [see Contraindications (4)].
5.10 Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS)
Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS) has been reported in patients taking NSAIDs such as ELYXYB. Some of these events have been fatal or life-threatening. DRESS typically, although not exclusively, presents with fever, rash, lymphadenopathy, and/or facial swelling. Other clinical manifestations may include hepatitis, nephritis, hematological abnormalities, myocarditis, or myositis. Sometimes symptoms of DRESS may resemble an acute viral infection. Eosinophilia is often present. Because this disorder is variable in its presentation, other organ systems not noted here may be involved. It is important to note that early manifestations of hypersensitivity, such as fever or lymphadenopathy, may be present even though rash is not evident. If such signs or symptoms are present, discontinue ELYXYB and evaluate the patient immediately.
5.11 Medication Overuse Headache
Overuse of acute migraine drugs (e.g., ergotamine, triptans, opioids, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or combination of these drugs for 10 or more days per month), including ELYXYB, may lead to exacerbation of headache (medication overuse headache). Medication overuse headache may present as migraine-like daily headaches or as a marked increase in frequency of migraine attacks. Detoxification of patients, including withdrawal of the overused drugs and treatment of withdrawal symptoms (which often includes a transient worsening of headache) may be necessary.
5.13 Hematological Toxicity
Anemia has occurred in NSAID-treated patients. This may be due to occult or gross blood loss, fluid retention, or an incompletely described effect on erythropoiesis. If a patient treated with ELYXYB has any signs or symptoms of anemia, monitor hemoglobin or hematocrit.
In controlled clinical trials of celecoxib capsules, the incidence of anemia was 0.6% with celecoxib and 0.4% with placebo. Patients on long-term treatment with ELYXYB should have their hemoglobin or hematocrit checked if they exhibit any signs or symptoms of anemia or blood loss.
NSAIDs, including ELYXYB, may increase the risk of bleeding events. Co-morbid conditions such as coagulation disorders or concomitant use of warfarin, other anticoagulants, antiplatelet drugs (e.g., aspirin), SSRIs, and serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) may increase this risk. Monitor these patients for signs of bleeding [see Drug Interactions (7)].
5.14 Masking of Inflammation and Fever
The pharmacological activity of celecoxib in reducing inflammation, and possibly fever, may diminish the utility of diagnostic signs in detecting infections.
5.15 Laboratory Monitoring
Because serious GI bleeding, hepatotoxicity, and renal injury can occur without warning symptoms or signs, consider monitoring patients on long-term NSAID, including ELYXYB, treatment with a CBC and a chemistry profile periodically [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2, 5.3, 5.6)].
In controlled clinical trials with celecoxib capsules, elevated BUN occurred more frequently in patients receiving celecoxib compared with patients on placebo. This laboratory abnormality was also seen in patients who received comparator NSAIDs in these studies. The clinical significance of this abnormality has not been established.
5.16 Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC)
ELYXYB is not indicated in pediatric patients or for the treatment of juvenile rheumatoid arthritis (JRA). Disseminated intravascular coagulation has occurred with use of celecoxib capsules in pediatric patients with systemic onset JRA, which required monitoring for signs and symptoms of abnormal clotting or bleeding.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the labeling:
- Cardiovascular Thrombotic Events [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- GI Bleeding, Ulceration, and Perforation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Hypertension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Heart Failure and Edema [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Renal Toxicity and Hyperkalemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Anaphylactic Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- Exacerbation of Asthma Related to Aspirin Sensitivity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
- Serious Skin Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]
- Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)]
- Medication Overuse Headache [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)]
- Fetal Toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12)]
- Hematologic Toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.13)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to the rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The safety of ELYXYB was evaluated in 815 patients who received at least one dose of ELYXYB in two, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials (Study 1 and 2) in adult patients with migraine [see Clinical Studies (14)].
The most common (at least 2% of patients who received ELYXYB and greater than placebo) adverse reaction in Study 1 and Study 2 was dysgeusia, which occurred in 3% of patients who received ELYXB compared to 1% of patients who received placebo.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of celecoxib. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Cardiovascular: Vasculitis, deep venous thrombosis
General: Anaphylactic reaction, angioedema
Liver and biliary: Liver necrosis, hepatitis, jaundice, hepatic failure
Hemic and lymphatic: Agranulocytosis, aplastic anemia, pancytopenia, leucopenia
Metabolic: Hypoglycemia, hyponatremia
Nervous: Aseptic meningitis, ageusia, anosmia, fatal intracranial hemorrhage
Renal: Interstitial nephritis
7. Drug Interactions
See Table 1 for clinically significant drug interactions with celecoxib.
| Drugs That Interfere with Hemostasis | |
| Clinical Impact |
|
| Intervention | Monitor patients with concomitant use of ELYXYB with anticoagulants (e.g., warfarin), antiplatelet drugs (e.g., aspirin), SSRIs, and SNRIs for signs of bleeding [see Warnings and Precautions (5.13)]. |
| Aspirin | |
| Clinical Impact |
|
| Intervention | Concomitant use of ELYXYB and analgesic doses of aspirin is not generally recommended because of the increased risk of bleeding [see Warnings and Precautions (5.13)].
ELYXYB is not a substitute for low dose aspirin for cardiovascular protection. |
| ACE Inhibitors, Angiotensin Receptor Blockers, and Beta-Blockers | |
| Clinical Impact |
|
| Intervention |
|
| Diuretics | |
| Clinical Impact | Clinical studies, as well as postmarketing observations, showed that NSAIDs reduced the natriuretic effect of loop diuretics (e.g., furosemide) and thiazide diuretics in some patients. This effect has been attributed to the NSAID inhibition of renal prostaglandin synthesis. |
| Intervention | During concomitant use of ELYXYB with diuretics, observe patients for signs of worsening renal function, in addition to assuring diuretic efficacy including antihypertensive effects [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]. |
| Digoxin | |
| Clinical Impact | The concomitant use of celecoxib with digoxin has been reported to increase the serum concentration and prolong the half-life of digoxin. |
| Intervention | During concomitant use of ELYXYB and digoxin, monitor serum digoxin levels. |
| Lithium | |
| Clinical Impact | NSAIDs have produced elevations in plasma lithium levels and reductions in renal lithium clearance. The mean minimum lithium concentration increased 15%, and the renal clearance decreased by approximately 20%. This effect has been attributed to NSAID inhibition of renal prostaglandin synthesis. |
| Intervention | During concomitant use of ELYXYB and lithium, monitor patients for signs of lithium toxicity. |
| Methotrexate | |
| Clinical Impact | Concomitant use of NSAIDs and methotrexate may increase the risk for methotrexate toxicity (e.g., neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, renal dysfunction). Celecoxib has no effect on methotrexate pharmacokinetics. |
| Intervention | During concomitant use of ELYXYB and methotrexate, monitor patients for methotrexate toxicity. |
| Cyclosporine | |
| Clinical Impact | Concomitant use of celecoxib and cyclosporine may increase cyclosporine's nephrotoxicity. |
| Intervention | During concomitant use of ELYXYB and cyclosporine, monitor patients for signs of worsening renal function. |
| NSAIDs and Salicylates | |
| Clinical Impact | Concomitant use of celecoxib with other NSAIDs or salicylates (e.g., diflunisal, salsalate) increases the risk of GI toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. |
| Intervention | The concomitant use of ELYXYB with other NSAIDs or salicylates is not recommended. |
| Pemetrexed | |
| Clinical Impact | Concomitant use of celecoxib and pemetrexed may increase the risk of pemetrexed-associated myelosuppression, renal, and GI toxicity (see the pemetrexed prescribing information). |
| Intervention |
|
| CYP2C9 Inhibitors or inducers | |
| Clinical Impact | Celecoxib metabolism is predominantly mediated via cytochrome P450 (CYP) 2C9 in the liver. Co-administration of ELYXYB with drugs that are known to inhibit CYP2C9 (e.g., fluconazole) may enhance the exposure and toxicity of celecoxib whereas co-administration with CYP2C9 inducers (e.g., rifampin) may lead to compromised efficacy of ELYXYB. |
| Intervention | Evaluate each patient's medical history when consideration is given to prescribing ELYXYB. A dosage adjustment may be warranted when ELYXYB is administered with CYP2C9 inhibitors or inducers. |
| CYP2D6 substrates | |
| Clinical Impact | In vitro studies indicate that celecoxib, although not a substrate, is an inhibitor of CYP2D6. Therefore, there is a potential for an in vivo drug interaction with drugs that are metabolized by CYP2D6 (e.g., atomoxetine), and celecoxib may enhance the exposure and toxicity of these drugs. |
| Intervention | Evaluate each patient's medical history when consideration is given to prescribing ELYXYB. A dosage adjustment may be warranted when ELYXYB is administered with CYP2D6 substrates. |
| Corticosteroids | |
| Clinical Impact | Concomitant use of corticosteroids with celecoxib may increase the risk of GI ulceration or bleeding. |
| Intervention | Monitor patients with concomitant use of ELYXYB with corticosteroids for signs of bleeding [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. |
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established. Disseminated intravascular coagulation has occurred in pediatric patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.16)].
8.5 Geriatric Use
Elderly patients, compared to younger patients, are at greater risk for NSAID-associated serious cardiovascular, gastrointestinal, and/or renal adverse reactions. If the anticipated benefit for the elderly patient outweighs these potential risks, treat for the fewest number of days per month, as needed, and monitor patients for adverse effects [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.6, 5.15)].
In the controlled clinical trials for migraine, approximately 70 patients were ≥ 65 years of age. Of the total number of patients who received celecoxib (for indications other than migraine) in pre-approval clinical trials, more than 3,300 were 65-74 years of age, while approximately 1,300 additional patients were 75 years and over. No substantial differences in effectiveness were observed between these subjects and younger subjects. In clinical studies comparing renal function as measured by the GFR, BUN and creatinine, and platelet function as measured by bleeding time and platelet aggregation, the results were not different between elderly and young volunteers.
However, as with other NSAIDs, including those that selectively inhibit COX-2, there have been more spontaneous postmarketing reports of fatal GI events and acute renal failure in the elderly than in younger patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4, 5.6)].
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
No dosage adjustment is needed for patients with mild hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class A). Reduce the dose of ELYXYB in patients with moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class B) [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. The use of ELYXYB in patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class C) is not recommended.
8.7 Renal Impairment
No dosage adjustment is needed for patients with mild or moderate renal impairment. ELYXYB is not recommended in patients with severe renal impairment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.8 Poor Metabolizers of CYP2C9 Substrates
In patients who are known or suspected to be poor CYP2C9 metabolizers (i.e., CYP2C9*3/*3), based on genotype or previous history/experience with other CYP2C9 substrates (e.g., warfarin, phenytoin) reduce the dose of ELYXYB [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.5)].
10. Overdosage
Symptoms following acute NSAID overdosages have been typically limited to lethargy, drowsiness, nausea, vomiting, and epigastric pain, which have been generally reversible with supportive care. Gastrointestinal bleeding has occurred. Hypertension, acute renal failure, respiratory depression, and coma have occurred, but were rare [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2, 5.4, 5.6)].
No overdoses of celecoxib were reported during clinical trials. No information is available regarding the removal of celecoxib by hemodialysis, but based on its high degree of plasma protein binding (>97%), dialysis is unlikely to be useful in overdose.
Manage patients with symptomatic and supportive care following an NSAID overdosage. There are no specific antidotes. Consider emesis and/or activated charcoal (60 to 100 grams in adults, 1 to 2 grams per kg of body weight in pediatric patients) and/or osmotic cathartic in symptomatic patients seen within four hours of ingestion or in patients with a large overdosage (5 to 10 times the recommended dosage). Forced diuresis, alkalinization of urine, hemodialysis, or hemoperfusion may not be useful due to high protein binding.
For additional information about overdosage treatment contact a poison control center.
11. Elyxyb Description
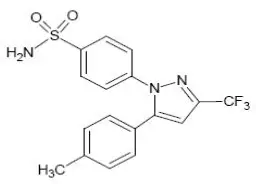
ELYXYB is an oral solution of celecoxib, a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug. Each unit dose of ELYXYB contains 120 mg of celecoxib. Celecoxib is a white or almost white, crystalline or amorphous powder with a pKa of 11. Celecoxib is hydrophobic (log P is 3.0) and practically insoluble in water. Celecoxib is chemically designated as p-[5-p-tolyl-3-(trifluoromethyl) pyrazol-1-yl] benzenesulfonamide. The empirical formula for celecoxib is C17H14 F3N3O2S, and the molecular weight is 381.37. It has the following chemical structure:
The inactive ingredients in ELYXYB include: acesulfame potassium, banana flavor, bubble gum flavor, ethyl alcohol, glycerin, glyceryl monocaprylate, L-menthol, lauroyl polyoxyl-32 glycerides, medium chain triglycerides, monoammonium glycyrrhizinate, peppermint flavor, polyoxyl 35 castor oil, polyoxyl 40 hydrogenated castor oil, propyl gallate, purified water, and sucralose.
12. Elyxyb - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Celecoxib is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug with analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and antipyretic properties.
The mechanism of action by which celecoxib exerts therapeutic effects in migraine patients is not fully understood but may involve inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis, primarily via inhibition of COX-2.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Celecoxib exhibits a dose-proportional increase in exposure after once daily oral administration of 120 to 240 mg doses (2 times the recommended dosage) of ELYXYB.
12.5 Pharmacogenomics
CYP2C9 activity is reduced in individuals with genetic polymorphisms that lead to reduced enzyme activity, such as those homozygous for the CYP2C9*2 and CYP2C9*3 polymorphisms. Limited data from 4 published reports that included a total of 8 subjects with the homozygous CYP2C9*3/*3 genotype showed celecoxib systemic levels that were 3- to 7-fold higher in these subjects compared to subjects with CYP2C9*1/*1 or *I/*3 genotypes. The pharmacokinetics of celecoxib have not been evaluated in subjects with other CYP2C9 polymorphisms, such as *2, *5, *6, *9, and *11. It is estimated that the frequency of the homozygous *3/*3 genotype is 0.3% to 1.0% in various ethnic groups [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) and Use in Specific Populations (8.8)].
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
An increase in the incidence of background findings of spermatocele with or without secondary changes such as epididymal hypospermia as well as minimal to slight dilation of the seminiferous tubules were seen in the juvenile rat. These reproductive findings while apparently treatment-related did not increase in incidence or severity with dose and may indicate an exacerbation of a spontaneous condition. Similar reproductive findings were not observed in studies of juvenile or adult dogs or in adult rats treated with celecoxib. The clinical significance of this observation is unknown.
14. Clinical Studies
14.1 Migraine
The efficacy of ELYXYB for the acute treatment of migraine with or without aura was demonstrated in two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trials [Study 1 (NCT03009019) and Study 2 (NCT03006276)]. In Study 1, patients were randomized to receive ELYXYB 120 mg (n=316) or placebo (n=315); in Study 2, patients were also randomized to receive ELYXYB 120 mg (n=311) or placebo (n=311). In both studies, patients were instructed to treat a migraine with moderate to severe pain intensity.
Patients enrolled in the trials were predominantly female (86%) and White (74%), with a mean age of 40.6 years (range 18 to 75 years).
The primary efficacy analyses were conducted in patients who treated a migraine with moderate to severe pain. The efficacy of ELYXYB was established by an effect on pain freedom at 2 hours post-dose and most bothersome symptom (MBS) freedom at 2 hours post-dose. Pain freedom was defined as a reduction of moderate or severe headache pain to no pain, and MBS freedom was defined as the absence of the self-identified MBS (photophobia, phonophobia, or nausea). Among patients who selected a MBS, the most commonly selected MBS was photophobia (56%), followed by nausea (25%), and phonophobia (18%).
In both studies, the percentage of patients achieving MBS freedom at 2 hours post-dose was significantly greater among patients receiving ELYXYB, compared to those receiving placebo. In Study 2, the percentage of patients achieving headache pain freedom at 2 hours post-dose was significantly greater among patients receiving ELYXYB, compared to those receiving placebo (see Table 2).
| Study 1 | Study 2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Placebo | ELYXYB 120 mg | Placebo | ELYXYB 120 mg |
|
|
||||
| Pain Free at 2 hours | ||||
| N | 273 | 284 | 271 | 279 |
| % Responders | 25.3 | 32.4 | 21.0 | 35.1 |
| Difference from placebo (%) | 7 | 14 | ||
| p-value | 0.076* | <0.001 | ||
| Most Bothersome Symptom Free at 2 hours | ||||
| N | 234 | 245 | 237 | 236 |
| % Responders | 44.4 | 58.0 | 43.9 | 56.8 |
| Difference from placebo (%) | 14 | 13 | ||
| p-value | 0.003 | 0.006 | ||
16. How is Elyxyb supplied
16.1 How Supplied
ELYXYB (celecoxib) oral solution, 120 mg/4.8 mL (25 mg/mL) is a clear colorless oral solution supplied in a disposable glass bottle with a child resistant cap.
Each carton (NDC 59385-055-06) contains six (6) glass bottles, a Full Prescribing Information, Medication Guide, and Instructions for Use.
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide and Instructions for Use).
| Medication Guide ELYXYB (ee-lix'-ib)) (celecoxib) oral solution |
||
|---|---|---|
| What is the most important information I should know about ELYXYB? ELYXYB contains celecoxib (a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug or NSAID). NSAIDs, including ELYXYB, can cause serious side effects, including:
Avoid taking NSAIDs, including ELYXYB, after a recent heart attack, unless your healthcare provider tells you to. You may have an increased risk of another heart attack if you take NSAIDs after a recent heart attack.
|
||
|
||
|
|
|
| ELYXYB should only be used: | ||
|
||
| What is ELYXYB?
ELYXYB is a prescription medicine used for the acute treatment of migraine attacks with or without aura in adults.
|
||
| Who should not take ELYXYB? Do not take ELYXYB:
|
||
Before taking ELYXYB, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
|
||
| How should I take ELYXYB? See the detailed "Instructions for Use" on how to take ELYXYB solution.
|
||
| What are the possible side effects of ELYXYB? ELYXYB can cause serious side effects, including: See "What is the most important information I should know about ELYXYB?
|
||
|
|
|
| Stop taking ELYXYB and call your healthcare provider right away if you get any of the following symptoms: | ||
|
|
|
| If you take too much ELYXYB, call your healthcare provider or get medical help right away.
These are not all the possible side effects of NSAIDs. For more information, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist about NSAIDs. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. |
||
Other information about NSAIDs
|
||
| General information about the safe and effective use of ELYXYB
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use ELYXYB for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give ELYXYB to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. If you would like more information about ELYXYB, talk with your healthcare provider. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about ELYXYB that is written for health professionals. |
||
| Manufactured for: BioDelivery Sciences International, Inc.ted | ||
| This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Revised: Sep 2021 | ||
Instructions For Use ELYXYB (ee-lix'-ib) (celecoxib) oral solution 25 mg/mL
Read this Instructions for Use before you start taking ELYXYB and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This leaflet does not take the place of talking to your healthcare provider about your medical condition or treatment. Take ELYXYB exactly how your healthcare provider tells you to.
If your healthcare provider has prescribed 120 mg of ELYXYB, take all of the medicine in the bottle as described below in Instructions-1.
If your healthcare provider has prescribed 60 mg of ELYXYB, take 2.4 mL of the medicine, as described in Instructions-2. You will need a dosing syringe from the pharmacy to give the right amount of medicine. Do not use a household teaspoon to measure ELYXYB.
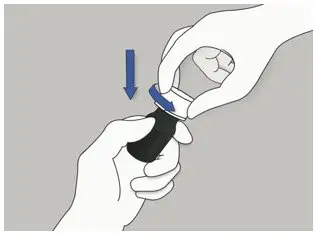 | Step 1: When you need to take ELYXYB, push down the cap and turn it to the left (counterclockwise) to open it. |
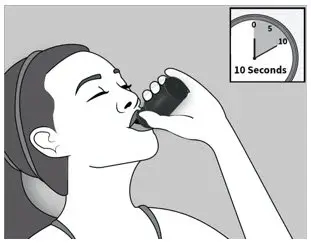 | Step 2: When taking 120 mg of ELYXYB, drink it directly from the bottle. Hold the bottle upside down for 10 seconds to make sure the full amount of medicine is taken. |
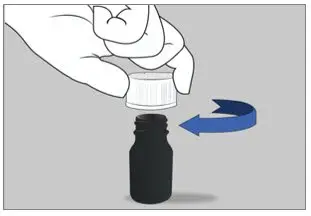 | Step 3: Close the bottle by turning the cap to the right (clockwise) right away after drinking the medicine. |
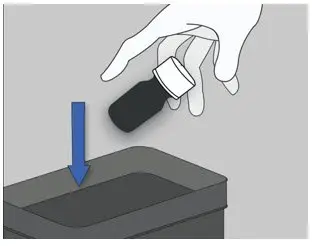 | Step 4: Throw away (discard) the bottle. |
 | Step 5: After you take ELYXYB, you may drink up to 8 ounces (240 mL) of water. |
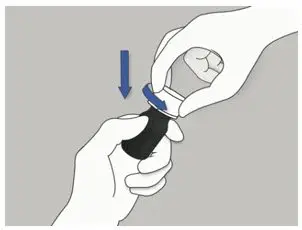 | Step 1: When you need to take ELYXYB, push down the cap and turn it to the left (counterclockwise to open it. |
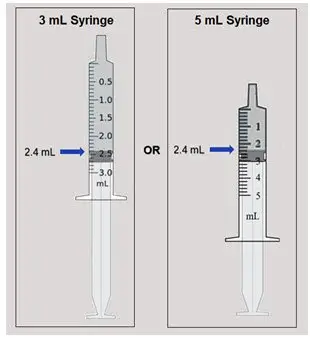 | Step 2: Use an oral dosing syringe (3 mL or 5 mL) from your pharmacy to withdraw 2.4 mL of ELYXYB. Insert the syringe through ELYXYB bottle opening and draw up 2.4 mL of ELYXYB directly from the bottle into the syringe. This 2.4 mL will be your 60 mg dose. Note: Do not use a household teaspoon to measure ELYXYB. |
| Step 3: Place the 2.4 mL of the ELYXYB that is in the dosing syringe in your mouth and swallow it right away. | |
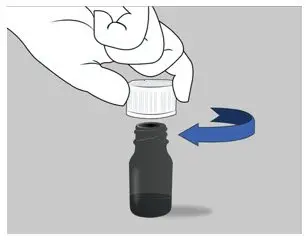 | Step 4: Close the bottle tightly by turning the cap to the right (clockwise) right away after taking the correct dose of ELYXYB. Note: Do not store the bottle to reuse the remaining medicine. |
 | Step 5: Throw away (discard) the bottle with the unused ELYXYB. |
 | Step 6: After you take ELYXYB, you may drink up to 8 ounces (240 mL) of water. |
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration
Revised: Sep 2021
For more information call BioDelivery Sciences International, Inc. at 1-800-469-0261.
Manufactured for:
BioDelivery Sciences International, Inc., Raleigh, NC 27612
ELYXYB is a trademark of BioDelivery Sciences International, Inc.
©2021 BioDelivery Sciences International, Inc. All rights reserved.
ELY-001-MGIFU-Sep2021
| ELYXYB - CELECOXIB
celecoxib liquid |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - BioDelivery Sciences International Inc (016058955) |





