Drug Detail:Firdapse (Amifampridine phosphate)
Drug Class: Cholinergic muscle stimulants
Highlights of Prescribing Information
FIRDAPSE® (amifampridine) tablets, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2018
Recent Major Changes
Indications and Usage (1) 9/2022
Dosage and Administration (2.1, 2.2, 2.3, 2.4, 2.5) 9/2022
Indications and Usage for Firdapse
FIRDAPSE is a potassium channel blocker indicated for the treatment of Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome (LEMS) in adults and pediatric patients 6 years of age and older. (1)
Firdapse Dosage and Administration
- Administer orally in divided doses (3 to 4 times daily). (2.1)
- The recommended starting dosage for adults (any weight) and pediatric patients weighing 45 kg or more is 15 mg to 30 mg daily, in divided doses. (2.1)
- Dosage can be increased by 5 mg daily every 3 to 4 days. (2.1)
- The maximum single dose is 20 mg. (2.1)
- Dosage is not to exceed a maximum of 80 mg daily. (2.1)
- The recommended starting dosage for pediatric patients weighing less than 45 kg is 5 mg to 15 mg daily, in divided doses. (2.1)
- Dosage can be increased by 2.5 mg daily every 3 to 4 days. (2.1)
- The maximum single dose is 10 mg. (2.1)
- Dosage is not to exceed a maximum of 40 mg daily. (2.1)
- The recommended starting dosage for adult and pediatric patients with renal impairment, hepatic impairment, and in known N-acetyltransferase 2 (NAT2) poor metabolizers is the lowest recommended initial daily dosage (2.1, 2.2, 2.3, 2.4)
- For patients with a dosage adjustment of less than 5 mg increments, or who have difficulty swallowing, or require feeding tube, a l mg/mL suspension can be prepared. (2.5)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
- Tablets: 10 mg, functionally scored. (3)
Contraindications
FIRDAPSE is contraindicated in patients with:
- A history of seizures (4)
- Hypersensitivity to amifampridine or another aminopyridine (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Seizures: FIRDAPSE can cause seizures. Consider discontinuation or dose-reduction of FIRDAPSE in patients who have a seizure while on treatment. (5.1)
- Hypersensitivity reactions: If a hypersensitivity reaction such as anaphylaxis occurs, FIRDAPSE should be discontinued and appropriate therapy initiated. (5.2)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The most common (> 10%) adverse reactions are: paresthesia, upper respiratory tract infection, abdominal pain, nausea, diarrhea, headache, elevated liver enzymes, back pain, hypertension, and muscle spasms. (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Catalyst Pharmaceuticals at 1-844-347-3277 (1-844-FIRDAPSE) or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
- Drugs that lower seizure threshold: Concomitant use may lead to an increased risk of seizures. (7.1)
- Drugs with cholinergic effects (e.g., direct or indirect cholinesterase inhibitors): Concomitant use may increase the cholinergic effects of FIRDAPSE and of those drugs and increase the risk of adverse reactions. (7.2)
Use In Specific Populations
- Pregnancy: Based on animal data, may cause fetal harm. (8.1)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 5/2023
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Firdapse
FIRDAPSE® is indicated for the treatment of Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome (LEMS) in adults and pediatric patients 6 years of age and older.
2. Firdapse Dosage and Administration
2.1 Dosage Information
The recommended dosage regimen of FIRDAPSE for adults and pediatric patients 6 years of age and older is included in Table 1. For pediatric patients, the recommended dosing regimen is dependent on body weight. Dosage should be increased every 3 to 4 days based on clinical response and tolerability. Titration increments should not exceed those shown in Table 1.
| *See Dosage and Administration (2.5) for a method to achieve these doses | ||||
| Age and Body Weight | Initial Daily Dosage* | Titration Regimen | Maximum Single
Dose | Maximum Total Daily
Maintenance Dosage |
|
15 mg to 30 mg daily, in 3 to 4 divided doses |
Increase total daily dosage by 5 mg every 3 or 4 days | 20 mg | 80 mg Given in divided doses |
| 5 mg to 15 mg daily, in 3 to 4 divided doses |
Increase total daily dosage by 2.5 mg every 3 or 4 days | 10 mg | 40 mg Given in divided doses |
Missed Dose
If a dose is missed, patients should not take double or extra doses.
2.2 Patients with Renal Impairment
The recommended starting dosage of FIRDAPSE in patients with renal impairment [creatinine clearance (CLcr) 15 to 90 mL/min] is the lowest recommended initial daily dosage (i.e., 15 mg daily for pediatric patients weighing 45 kg or more and for adults, and 5 mg daily for pediatric patients weighing less than 45 kg) taken orally in divided doses. No dosage recommendation for FIRDAPSE can be made for patients with end-stage renal disease [see Dosage and Administration (2.1), Use in Specific Populations (8.6), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
2.3 Patients with Hepatic Impairment
The recommended starting dosage of FIRDAPSE in patients with any degree of hepatic impairment is the lowest recommended initial daily dosage (i.e., 15 mg daily for pediatric patients weighing 45 kg or more and for adults, and 5 mg daily for pediatric patients weighting less than 45 kg) taken orally in divided doses [see Dosage and Administration (2.1), Use in Specific Populations (8.7), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
2.4 Known N-acetyltransferase 2 (NAT2) Poor Metabolizers
The recommended starting dosage of FIRDAPSE in known N-acetyltransferase 2 (NAT2) poor metabolizers is the lowest recommended initial daily dosage (i.e., 15 mg daily for pediatric patients weighing 45 kg or more and for adults, and 5 mg daily for pediatric patients weighing less than 45 kg) taken orally in divided doses [see Dosage and Administration (2.1), Use in Specific Populations (8.8), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.5)].
2.5 Administration Instructions
FIRDAPSE can be taken without regard to food.
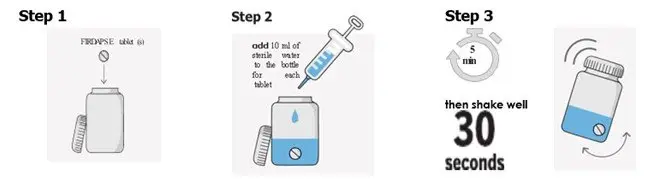
Preparation of a 1mg/mL Suspension (see the Instructions for Use for full instructions on how to prepare the 1mg/mL suspension)
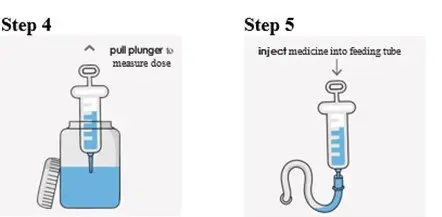
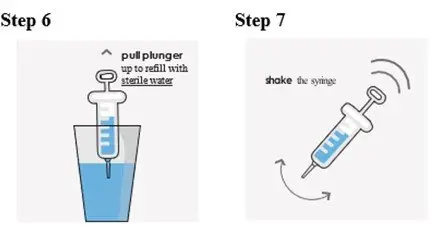
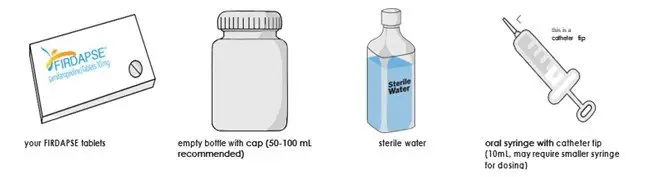
When patients require a dosage in less than 5 mg increments, have difficulty swallowing tablets, or require feeding tubes, a 1 mg/mL suspension can be prepared (e.g., by placing the required number of tablets in a 50 to 100 mL container, adding 10 mL of sterile water for each tablet, waiting for 5 minutes, and shaking well for 30 seconds).
Crushing the tablets prior to making the suspension is not necessary. After preparation of the suspension, an oral syringe can be used to draw up and administer the correct dose by mouth or by feeding tube.
Storage of 1mg/mL Prepared Suspension
Refrigerate the suspension between doses and shake well before drawing up each dose. The suspension can be stored under refrigeration
[between 2°C and 8°C (36°F and 46°F)] for up to 24 hours. Discard any unused portion of the suspension after 24 hours.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
FIRDAPSE tablets contain 10 mg amifampridine and are white to off-white, round, and functionally scored. Each tablet is debossed on the non-scored side with "CATALYST" and on the scored side with "211" above the score and "10" below the score.
4. Contraindications
FIRDAPSE is contraindicated in patients with:
- A history of seizures [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Hypersensitivity to amifampridine phosphate or another aminopyridine [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Seizures
FIRDAPSE can cause seizures. Seizures have been observed in patients without a history of seizures taking FIRDAPSE at the recommended doses, at various times after initiation of treatment, at an incidence of approximately 2%. Many of the patients were taking medications or had comorbid medical conditions that may have lowered the seizure threshold [see Drug Interactions (7.1)]. Seizures may be dose-dependent. Consider discontinuation or dose-reduction of FIRDAPSE in patients who have a seizure while on treatment. FIRDAPSE is contraindicated in patients with a history of seizures.
5.2 Hypersensitivity
In clinical trials, hypersensitivity reactions and anaphylaxis associated with FIRDAPSE administration have not been reported. Anaphylaxis has been reported in patients taking another aminopyridine; therefore, it may occur with FIRDAPSE. If anaphylaxis occurs, administration of FIRDAPSE should be discontinued and appropriate therapy initiated.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following serious adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Seizures [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Hypersensitivity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Adults
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
In controlled and uncontrolled clinical trials (Study 1 and 2) in patients with LEMS [see Clinical Studies (14)], 63 patients were treated with FIRDAPSE, including 40 patients treated for more than 6 months, and 39 patients treated for more than 12 months. In an expanded access program, 139 patients with LEMS were treated with FIRDAPSE, including 102 patients treated for more than 6 months, 77 patients treated for more than 12 months, and 53 patients treated for more than 18 months.
Study 1 was a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized discontinuation study in adults with LEMS. Following an initial open- label run-in phase (up to 90 days), patients were randomized to either continue FIRDAPSE treatment or transition to placebo, for a 14- day double-blind phase. Following final assessments, patients were allowed to resume FIRDAPSE treatment for up to 2 years (open- label long-term safety phase of the study).
During the open-label run-in phase of Study 1, 53 patients received FIRDAPSE for an average of 81 days at a mean daily dosage of
50.5 mg/day. The mean patient age was 52.1 years and 66% were female. There were 42 patients who had no prior exposure to FIRDAPSE at the initiation of this study. Table 2 shows adverse reactions with an incidence of 5% or greater occurring in the 42 LEMS patients newly initiated on treatment with FIRDAPSE during the run-in phase of the study.
|
Adverse Reaction |
FIRDAPSE % |
|
Paresthesia* |
62 |
|
Upper respiratory tract infection |
33 |
|
Abdominal pain |
14 |
|
Nausea |
14 |
|
Diarrhea |
14 |
|
Headache |
14 |
|
Elevated liver enzymes** |
14 |
|
Back pain |
14 |
|
Hypertension |
12 |
|
Muscle spasms |
12 |
|
Dizziness |
10 |
|
Asthenia |
10 |
|
Muscular weakness |
10 |
|
Pain in extremity |
10 |
|
Cataract |
10 |
|
Constipation |
7 |
|
Bronchitis |
7 |
|
Fall |
7 |
|
Lymphadenopathy |
7 |
*Includes paresthesia, oral paresthesia, oral hypoesthesia
**Includes elevated alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), and gamma- glutamyl transferase (GGT)
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 Drugs that Lower Seizure Threshold
The concomitant use of FIRDAPSE and drugs that lower seizure threshold may lead to an increased risk of seizures [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. The decision to administer FIRDAPSE concomitantly with drugs that lower the seizure threshold should be carefully considered in light of the severity of the associated risks.
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Exposure Registry
There is a pregnancy exposure registry that monitors pregnancy outcomes in women exposed to FIRDAPSE during pregnancy. Physicians are encouraged to enroll pregnant patients, or pregnant women may register themselves in the registry by calling 855-212-5856 (toll-free), using the Fax number 877-867-1874 (toll-free), by contacting the Pregnancy Coordinating Center at [email protected], or by visiting the study website www.firdapsepregnancystudy.com.
Data
Animal Data
Oral administration of amifampridine phosphate (0, 7.5, 22.5, or 75 mg/kg/day) to female rats prior to and during mating and continuing throughout organogenesis produced no adverse effects on embryofetal development. Plasma amifampridine exposure (AUC) at the highest dose tested is approximately 7 times that in humans at the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 80 mg amifampridine/day. Oral administration of amifampridine phosphate (0, 9, 30, or 57 mg/kg/day) to pregnant rabbits throughout organogenesis produced no adverse effects on embryofetal development. The highest dose tested is approximately 7 times the MRHD (80 mg/day amifampridine) on a body surface area (mg/m2) basis.
Oral administration of amifampridine phosphate (0, 7.5, 22.5, or 75 mg/kg/day) to female rats throughout pregnancy and lactation resulted in an increase in stillbirths and pup deaths, reduced pup weight, and delayed sexual development in female pups at the mid and high doses tested. The no-effect dose (7.5 mg/kg/day amifampridine phosphate) for adverse developmental effects is associated with a plasma amifampridine exposure (AUC) less than that in humans at the MRHD.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of FIRDAPSE for the treatment of LEMS have been established in pediatric patients 6 years of age and older. Use of FIRDAPSE for this indication is supported by evidence from adequate and well-controlled studies of FIRDAPSE in adults with LEMS, pharmacokinetic data in adult patients, pharmacokinetic modeling and simulation to identify the dosing regimen in pediatric patients, and safety data from pediatric patients aged 6 years and older [see Adverse Reactions (6.1), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3), and Clinical Studies (14)].
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients below the age of 6 years have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of FIRDAPSE did not include a sufficient number of subjects aged 65 and over (19 of 63 patients in Studies 1 and 2) to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy [see Dosage and Administration (2.2, 2.3) and Drug Interactions (7.2, 7.3)].
8.6 Renal Impairment
Renal clearance is an elimination pathway for amifampridine and the inactive metabolite, 3-N-acetyl amifampridine, and exposure of amifampridine is higher in subjects with renal impairment [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Therefore, in patients with renal impairment, FIRDAPSE should be initiated at the lowest recommended initial daily dosage, and patients should be closely monitored for adverse reactions [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)]. Consider dosage modification or discontinuation of FIRDAPSE for patients with renal impairment as needed based on clinical effect and tolerability. The safety, efficacy, and pharmacokinetics of amifampridine have not been studied in patients with end-stage renal disease (CLcr <15 mL/min or patients requiring dialysis). No dosage recommendation for FIRDAPSE can be made for patients with end-stage renal disease.
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
In patients with any degree of hepatic impairment, FIRDAPSE should be initiated at the lowest recommended initial daily dosage, and patients should be monitored for adverse reactions [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)]. Consider dosage modification or discontinuation of FIRDAPSE for patients with hepatic impairment as needed based on clinical effect and tolerability.
8.8 NAT2 Poor Metabolizers
Exposure of FIRDAPSE is increased in patients who are N-acetyltransferase 2 (NAT2) poor metabolizers [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.5)]. Therefore, initiate FIRDAPSE in patients who are known NAT2 poor metabolizers at the lowest recommended initial daily dosage and monitor for adverse reactions [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)]. Consider dosage modification of FIRDAPSE for patients who are known NAT2 poor metabolizers as needed based on clinical effect and tolerability.
10. Overdosage
Overdose with FIRDAPSE was not reported during clinical studies.
In a case report, a 65-year-old patient with LEMS inadvertently received a total daily amifampridine dose of 360 mg/day (more than 4 times the maximum recommended total daily dose) and was hospitalized for general weakness, paresthesia, nausea, vomiting, and palpitations. The patient developed convulsions and paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia, and four days after admission, experienced cardiac arrest. The patient was resuscitated and ultimately recovered following withdrawal of amifampridine.
Patients with suspected overdose with FIRDAPSE should be monitored for signs or symptoms of exaggerated FIRDAPSE adverse reactions or effects, and appropriate symptomatic treatment instituted immediately.
11. Firdapse Description
The active ingredient of FIRDAPSE is amifampridine phosphate, which is a voltage-gated potassium channel blocker. Amifampridine phosphate is described chemically as 3,4-diaminopyridine phosphate with a molecular weight of 207.1 and a molecular formula of C5H7N3 • H3PO4. The structural formula is:

Amifampridine phosphate is a white, crystalline powder that is freely soluble in water, and slightly soluble in solvents ethanol, methanol and acetic acid. A 1% aqueous solution of amifampridine phosphate has a pH of 4.4 at ambient conditions.
Each FIRDAPSE tablet contains 10 mg amifampridine (equivalent to 18.98 mg amifampridine phosphate). The tablet formulation includes the following inactive ingredients: calcium stearate, colloidal silicon dioxide, and microcrystalline cellulose.
FIRDAPSE tablets are intended for oral administration only.
12. Firdapse - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
The mechanism by which amifampridine exerts its therapeutic effect in LEMS patients has not been fully elucidated. Amifampridine is a broad-spectrum potassium channel blocker.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
The effect of FIRDAPSE on QTc interval prolongation was studied in a double blind, randomized, placebo and positive controlled study in 52 healthy individuals who are slow acetylators. At an exposure 2-fold the expected maximum therapeutic exposure of amifampridine, FIRDAPSE did not prolong QTc to any clinically relevant extent.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics of amifampridine are similar between healthy individuals and LEMS patients. Following single and multiple doses, AUC, Cmax and Cmin were highly variable between individuals. FIRDAPSE exposure increased proportionally with dose across the range of 20 mg to 80 mg single oral doses.
12.5 Pharmacogenomics
Genetic variants in the N-acetyltransferase gene 2 (NAT2) affect the rate and extent of FIRDAPSE metabolism. Poor metabolizers, also referred to as "slow acetylators" (i.e., carriers of two reduced function alleles), have 3.5- to 4.5-fold higher Cmax, and 5.6- to 9- fold higher AUC than normal metabolizers, also referred to as "fast/rapid acetylators" (i.e., carriers of two normal function alleles). Therefore, FIRDAPSE should be initiated at the lowest recommended initial daily dosage in known NAT2 poor metabolizers, and such patients should be closely monitored for adverse reactions [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) and Use in Specific Populations (8.8)]. In the general population, the NAT2 poor metabolizer phenotype prevalence is 40–60% in the White and African American populations, and in 10–30% in Asian ethnic populations (individuals of Japanese, Chinese, or Korean descent).
14. Clinical Studies
The efficacy of FIRDAPSE for the treatment of LEMS was demonstrated in two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled discontinuation studies. A total of 64 adults (age 21 to 88 years) with LEMS were enrolled (Study 1 and Study 2). The studies enrolled patients with a confirmed diagnosis of LEMS based on either neurophysiology studies or a positive anti-P/Q type voltage-gated calcium channel antibody test. Patients were required to be on an adequate and stable dosage (30 to 80 mg daily) of amifampridine phosphate prior to entering the randomized discontinuation phases of both studies.
The two co-primary measures of efficacy in both studies were the change from baseline to the end of the discontinuation period in the Quantitative Myasthenia Gravis (QMG) score and in the Subject Global Impression (SGI) score.
The QMG is a 13-item physician-rated categorical scale assessing muscle weakness. Each item is assessed on a 4 -point scale, where a score of 0 represents no weakness, and a score of 3 represents severe weakness (total score 0-39). Higher scores represent greater impairment.
The SGI is a 7-point scale on which patients rated their global impression of the effects of the study treatment on their physical well- being. Lower scores on the SGI represent lower perceived benefit with the study treatment.
A key secondary efficacy endpoint was the clinical global impression improvement (CGI-I) score, a 7-point scale on which the treating physician rated the global impression of change in clinical symptoms. A higher CGI-I score indicates a perceived worsening of clinical symptoms.
16. How is Firdapse supplied
16.1 How Supplied
FIRDAPSE 10 mg tablets are white to off white, round, and functionally scored. Each tablet is debossed on the non-scored side with "CATALYST" and on the scored side with "211" above the score and "10" below the score. Tablets can be divided in half at the score. FIRDAPSE is supplied as follows:
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient and/or caregiver to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide and Instructions for Use).
| MEDICATION GUIDE FIRDAPSE® (FIR-dapse) (amifampridine) tablets, for oral use |
|
|---|---|
| This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration | Revised: 09/2022 |
| Read this Medication Guide before you start taking FIRDAPSE and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking with your doctor about your medical condition or your treatment. | |
| What is the most important information I should know about FIRDAPSE?
FIRDAPSE can cause seizures.
|
|
| What is FIRDAPSE?
FIRDAPSE is a prescription medicine used to treat Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome (LEMS) in people 6 years of age and older. It is not known if FIRDAPSE is safe or effective in children less than 6 years of age. |
|
Do not take FIRDAPSE if you:
|
|
|
Before you take FIRDAPSE, tell your doctor about all of your medical conditions. including if you:
|
|
|
How should I take FIRDAPSE?
|
|
| What are the possible side effects of FIRDAPSE? FIRDAPSE may cause serious side effects, including:
|
|
The most common side effects of FIRDAPSE include:
These are not all the possible side effects of FIRDAPSE. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. |
|
|
How should I store FIRDAPSE?
|
|
| General Information about the safe and effective use of FIRDAPSE
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use FIRDAPSE for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give FIRDAPSE to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. If you would like more information, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. You can ask your pharmacist or doctor for information about FIRDAPSE that is written for health professionals. |
|
| What are the ingredients in FIRDAPSE? Active ingredient: amifampridine Inactive ingredients: calcium stearate, colloidal silicon dioxide, and microcrystalline cellulose. Distributed by Catalyst Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Coral Gables, FL 33134 For more information, go to www.YourCatalystPathways.com or call 1-833-422-8259 |
|
| FIRDAPSE
amifampridine phosphate tablet |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Catalyst Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (053742248) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patheon API Manufacturing, Inc. | 962538372 | API MANUFACTURE(69616-211) , analysis(69616-211) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Catalent Micron Technologies, Inc. | 015966157 | particle size reduction(69616-211) , ANALYSIS(69616-211) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pharmaceutics International, Inc. | 878265586 | MANUFACTURE(69616-211) , analysis(69616-211) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCI Pharma Services Canada, Inc. | 204123822 | PACK(69616-211) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Quality Chemical Laboratories, LLC | 071344167 | ANALYSIS(69616-211) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patheon Inc. | 240769596 | ANALYSIS(69616-211) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patheon Pharmaceuticals Inc. | 005286822 | MANUFACTURE(69616-211) , PACK(69616-211) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patheon Softgels Inc. | 002193829 | ANALYSIS(69616-211) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Robertson-Microlit Laboratories Inc. | 177250289 | ANALYSIS(69616-211) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| SGS Canada Inc. | 203668041 | analysis(69616-211) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| SGS North America Inc. | 049859261 | analysis(69616-211) | |




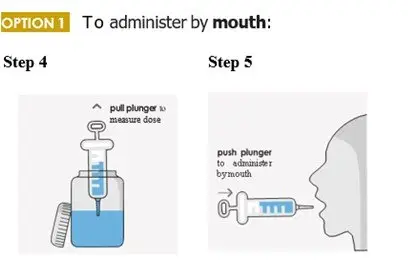
 To administer by
To administer by