Drug Detail:Gliadel (injection/implant) (Carmustine (injection/implant) [ kar-mus-teen ])
Drug Class: Alkylating agents
Highlights of Prescribing Information
GLIADEL® WAFER (carmustine implant), for intracranial use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1996
Indications and Usage for Gliadel
GLIADEL Wafer is an alkylating drug indicated for the treatment of:
- newly-diagnosed high-grade glioma as an adjunct to surgery and radiation (1) and
- recurrent glioblastoma as an adjunct to surgery (1)
Gliadel Dosage and Administration
- Recommended dose: Eight 7.7 mg wafers (61.6 mg total dose) implanted intracranially (2.1, 2.2)
- Follow preparation and handling recommendations (2.3).
Dosage Forms and Strengths
- Each GLIADEL Wafer contains 7.7 mg of carmustine (3).
Contraindications
None (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Seizures: Monitor patients for seizures following implantation (5.1).
- Intracranial hypertension: Monitor patients for signs of increased intracranial pressure (5.2).
- Impaired neurosurgical wound healing: Monitor patients for complications of craniotomy (5.3).
- Meningitis: Monitor patients for signs of bacterial or chemical meningitis (5.4).
- Wafer migration: Monitor patients for signs of obstructive hydrocephalus (5.5).
- Embryo-fetal toxicity: Can cause fetal harm. Advise patients of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise males and females of reproductive potential to use an effective method of contraception. (5.6, 8.1, 8.3).
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
- Newly-Diagnosed High-Grade Glioma: Most common adverse reactions (incidence >10% and between arm difference ≥4%) are cerebral edema, asthenia, nausea, vomiting, constipation, wound healing abnormalities and depression (6.1).
- Recurrent High-Grade Glioma: Most common adverse reactions (incidence >10% and between arm difference ≥4%) are urinary tract infection, wound healing abnormalities and fever (6.1).
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Arbor Pharmaceuticals, LLC at 1-866-516-4950 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Use In Specific Populations
- Lactation: Advise not to breastfeed (8.2).
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 12/2018
Related/similar drugs
Keytruda, Darzalex, Blenrep, Tecvayli, methotrexate, Avastin, rituximabFull Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Gliadel
GLIADEL Wafer is indicated for the treatment of patients with:
- newly-diagnosed high-grade glioma as an adjunct to surgery and radiation, and
- recurrent glioblastoma as an adjunct to surgery.
2. Gliadel Dosage and Administration
2.1 Recommended Dose
The recommended dose of GLIADEL Wafer is eight 7.7 mg wafers for a total of 61.6 mg implanted intracranially. The safety and effectiveness of repeat administration have not been studied.
2.2 Insertion Instructions
Following maximal tumor resection, confirmation of tumor pathology and establishment of hemostasis, place up to a maximum of eight GLIADEL Wafers to cover as much of the resection cavity as possible. Should the size and shape of the resected cavity not accommodate eight wafers, place the maximum number of wafers feasible within the cavity. Slight overlapping of the wafers is acceptable. Wafers broken in half may be used, but discard wafers broken in more than two pieces. Oxidized regenerated cellulose (Surgicel®) may be placed over the wafers to secure them against the cavity surface. After placement of the wafers, irrigate the resection cavity and close the dura in a water-tight fashion.
2.3 Preparation and Safe Handling
GLIADEL Wafers contain a cytotoxic drug. Follow applicable special handling and disposal procedures.1
Each wafer is packaged within two nested aluminum foil laminate pouches. The inner pouch is sterile and is designed to maintain product sterility and protect the product from moisture. The outside surface of the outer laminated aluminum foil pouch is a peelable overwrap and is not sterile.
Deliver GLIADEL Wafers to the operating room in their outer aluminum foil pouch, unopened. Do not open the pouch until the wafers are ready to be implanted. GLIADEL Wafers in unopened outer foil pouches are stable at room temperature for six hours at a time for up to three cycles within a 30-day period.
Exposure to carmustine can cause severe burning and hyperpigmentation of the skin. Use double gloves when handling GLIADEL Wafers. Discard the outer gloves into a biohazard waste container after use. Use a dedicated surgical instrument for wafer implantation. If repeat neurosurgical intervention is indicated, handle residual wafers or wafer remnants as potential cytotoxic agents.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
GLIADEL Wafer is an off-white to pale yellow round wafer. Each GLIADEL Wafer contains 7.7 mg of carmustine.
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Seizures
Seizures occurred in 37% of patients treated with GLIADEL Wafers for recurrent glioma in Study 2. New or worsening (treatment emergent) seizures occurred in 20% of patients; 54% of treatment emergent seizures occurred within the first 5 post-operative days [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. The median time to onset of the first new or worsened post-operative seizure was four days. Institute optimal anti-seizure therapy prior to surgery. Monitor patients for seizures postoperatively.
5.2 Intracranial Hypertension
Brain edema occurred in 23% of patients with newly diagnosed glioma treated with GLIADEL Wafers in Study 1. Additionally, one GLIADEL-treated patient experienced intracerebral mass effect unresponsive to corticosteroids which led to brain herniation [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Monitor patients closely for intracranial hypertension related to brain edema, inflammation, or necrosis of the brain tissue surrounding the resection. In refractory cases, consider re-operation and removal of GLIADEL Wafers or Wafer remnants.
5.3 Impaired Neurosurgical Wound Healing
Impaired neurosurgical wound healing including wound dehiscence, delayed wound healing, and subdural, subgleal, or wound effusions occur with GLIADEL Wafer treatment. In Study 1, 16% of GLIADEL Wafer-treated patients with newly diagnosed glioma experienced impaired intracranial wound healing and 5% had cerebrospinal fluid leaks. In Study 2, 14% of GLIADEL Wafer-treated patients with recurrent high-grade glioma experienced wound healing abnormalities [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Monitor patients post-operatively for impaired neurosurgical wound healing.
5.4 Meningitis
Meningitis occurred in 4% of patients with recurrent glioma receiving GLIADEL Wafers in Study 2. Two cases of meningitis were bacterial; one patient required removal of the Wafers four days after implantation; the other developed meningitis following reoperation for recurrent tumor. One case was diagnosed as chemical meningitis and resolved following steroid treatment. In one case the cause was unspecified, but meningitis resolved following antibiotic treatment. Monitor postoperatively for signs of meningitis and central nervous system infection.
5.5 Wafer Migration
GLIADEL Wafer migration can occur. To reduce the risk of obstructive hydrocephalus due to wafer migration into the ventricular system, close any communication larger than the diameter of a Wafer between the surgical resection cavity and the ventricular system prior to Wafer implantation. Monitor patients for signs of obstructive hydrocephalus.
5.6 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
GLIADEL Wafers can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Carmustine, the active component of GLIADEL Wafer, is embryotoxic and teratogenic in rats at exposures less than the exposure at the recommended human dose based on body surface area (BSA) and embryotoxic in rabbits at exposures similar to the exposure at the recommended human dose based on BSA.
Advise patients of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception for 6 months after implantation of GLIADEL Wafer. Advise males with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception for 3 months following implantation of GLIADEL Wafers [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3), Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following serious adverse reactions are discussed elsewhere in the labeling:
- Seizures [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Intracranial Hypertension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Impaired Neurosurgical Wound Healing [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Meningitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
11. Gliadel Description
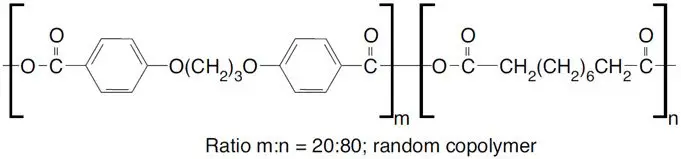
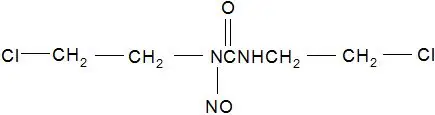
GLIADEL Wafer is an implant for intracranial use, containing carmustine, a nitrosourea alkylating agent, and polifeprosan, a biodegradable copolymer used to control the release of carmustine. It is a sterile, off-white to pale yellow wafer approximately 1.45 cm in diameter and 1 mm thick. Each wafer contains 7.7 mg of carmustine [1, 3-bis (2-chloroethyl)-1-nitrosourea, or BCNU] and 192.3 mg of a biodegradable polyanhydride copolymer. The copolymer, polifeprosan 20, consists of poly [bis (p-carboxyphenoxy)] propane and sebacic acid in a 20:80 molar ratio. Carmustine is homogeneously distributed in the copolymer matrix.
The structural formula for polifeprosan 20 is:
The structural formula for carmustine is:
12. Gliadel - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
The activity of GLIADEL Wafer is due to release of cytotoxic concentrations of carmustine, a DNA and RNA alkylating agent, into the tumor resection cavity. On exposure to the aqueous environment of the resection cavity, the anhydride bonds in the copolymer are hydrolyzed, releasing carmustine, carboxyphenoxypropane, and sebacic acid into the surrounding brain tissue.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Carmustine concentrations delivered by GLIADEL Wafer in human brain tissue have not been determined. Following wafer insertion, the mean whole blood Cmax (± SD) is 10.2 ng/mL ± 4.8 ng/mL.
12.6 Wafer Biodegradation
GLIADEL Wafers are biodegradable when implanted into the human brain. Wafer remnants were visible on CT scans obtained 49 days after implantation of GLIADEL Wafer. More than 70% of the copolymer degrades within three weeks. Wafer remnants have been present at re-operation and autopsy up to 7.8 months after GLIADEL Wafer implantation and consisted mostly of water and monomeric components with minimal detectable carmustine present.
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
No carcinogenicity, mutagenicity, or impairment of fertility studies have been conducted with GLIADEL Wafer. Carcinogenicity, mutagenicity, and impairment of fertility studies have been conducted with carmustine, the active component of GLIADEL Wafer. Carmustine was carcinogenic in rats and mice when delivered by intraperitoneal injection at doses lower than those delivered by GLIADEL Wafer at the recommended dose. There were increases in tumor incidence in all treated animals. Carmustine was mutagenic in vitro (Ames assay, human lymphoblast HGPRT assay) and clastogenic both in vitro (V79 hamster cell micronucleus assay) and in vivo (SCE assay in rodent brain tumors, mouse bone marrow micronucleus assay).
In male rats carmustine caused testicular degeneration at intraperitoneal doses of 8 mg/kg/week for eight weeks (about 1.3 times the recommended human dose based on body surface area).
14. Clinical Studies
14.1 Newly-Diagnosed High-Grade Glioma
Study 1 was a multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled, clinical trial in adult patients with newly-diagnosed high-grade glioma. A total of 240 patients were randomized (1:1) to receive up to eight GLIADEL Wafers or matched placebo wafers following maximal tumor resection. Patients received post-operative radiation therapy (55-60 Gy delivered in 28 to 30 fractions over six weeks) starting three weeks after surgery. Patients with anaplastic oligodendroglioma also received systemic chemotherapy (6 cycles of PCV- lomustine 110 mg/m2 day 1, procarbazine 60 mg/m2 days 8-21, vincristine 1.4 mg/m2 days 8 and 29).
The population in Study 1 was 67% male and 97% White, and the median age was 53 years (range: 21-72). Eighty-seven percent had a Karnofsky performance status ≥ 70% and 71% had a Karnofsky performance status of ≥ 80%. Seventy-eight percent had a histologic subtype of glioblastoma as determined by central pathology review. Thirty-eight percent of patients received 8 wafers and 78% received ≥ 6 wafers. Starting three weeks after surgery, 80% of patients received standard limited field radiation therapy (RT) described as 55-60 Gy delivered in 28 to 30 fractions over six weeks; 11% received no radiotherapy and the remainder received non-standard radiotherapy or a combination of standard and non-standard radiotherapy. At the time of progression, 12% received systemic chemotherapy. Patients were followed for at least three years or until death.
Efficacy results for patients randomized in Study 1 are summarized in Table 6 and Figure 6. Overall survival among all patients with newly diagnosed high-grade glioma, the primary outcome measure, was prolonged in the GLIADEL arm. Overall survival in the subset of patients with glioblastoma, a secondary outcome measure, was not significantly prolonged.
| Overall Survival – ITT* | Gliadel Wafer (n=120) | Placebo Wafer (n=120) |
|---|---|---|
|
||
| Number of deaths, n (%) | 111 (93%) | 117(98%) |
| Median overall survival, months (95% CI) | 13.9 (12.1, 15.1) | 11.6 (10.2, 12.7) |
| Hazard ratio (95% CI) | 0.73 (0.56, 0.95) | |
| Log-Rank test p-value | <0.02† | |
Figure 6: Kaplan-Meier Curves of Overall Survival in Patients with Newly Diagnosed High-Grade Glioma, Study 1.1
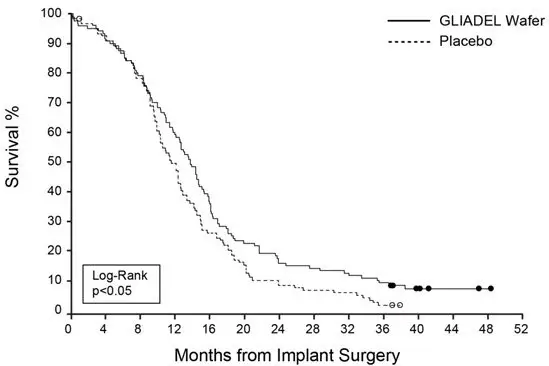
- 1
- Based on a post-final analysis, protocol specified non-stratified log-rank test; p-value not adjusted for multiple comparisons
14.2 Recurrent Glioblastoma
Study 2 was a multicenter, double-blind, placebo controlled, clinical trial in adult patients with recurrent high-grade glioma. Patients were required to have had prior definitive external beam radiation therapy sufficient to disqualify them from additional radiation therapy. Following maximal tumor resection and confirmation of high-grade glioma, a total of 222 patients were randomized (1:1) to receive a maximum of eight GLIADEL Wafers (n=110) or matched placebo wafers (n=112) positioned to cover the entire resection surface. All patients were eligible to receive chemotherapy which was withheld at least four weeks (six weeks for nitrosoureas) prior to and two weeks after surgery. Patients were followed for up to 71 months.
The population in Study 2 was 64% male and 92% White, and the median age was 49 years (range: 19-80). Sixty-five percent had a histologic subtype of glioblastoma, 26% had anaplastic astrocytoma or another anaplastic variant, 73% had a Karnofsky performance status ≥ 70, 53% had a Karnofsky performance status of ≥ 80%, 73% had only one prior surgery, and 46% had prior treatment with nitrosourea. Eighty-one percent of patients received 8 wafers and 96% received ≥ 6 wafers.
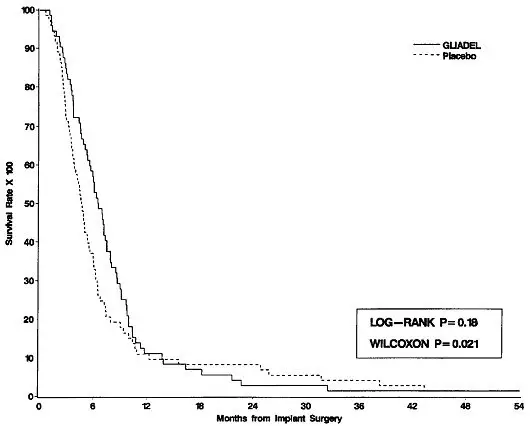
Survival and 6-month mortality rate in the subgroup of patients with recurrent glioblastoma, were exploratory outcome measures and are summarized in Table 7 and Figures 7 and 8. No survival prolongation was observed in patients with pathologic diagnoses other than glioblastoma.
| GLIADEL Wafer | Placebo Wafer | |
|---|---|---|
| GLIOBLASTOMA | n=72 | n=73 |
|
||
| 6-Month Survival | ||
| Number of deaths, n (%) | 32 | 47 |
| 6-month survival rate (%) | 56% | 36% |
| Log-Rank test p-value Gehan's generalized Wilcoxon Test p-value | 0.013*
0.015* |
|
| Overall Survival | ||
| Number of deaths, n (%) | 71 (99%) | 72 (99%) |
| Median overall survival (95% CI (months) | 6.51 (5.32, 7.49) | 4.63 (3.78, 5.52) |
| Log-Rank test p-value Gehan's generalized Wilcoxon Test p-value | 0.181*
0.021* |
|
Figure 7: Kaplan-Meier Curves of 6-Month Survival for Patients with Recurrent Glioblastoma, Study 2.
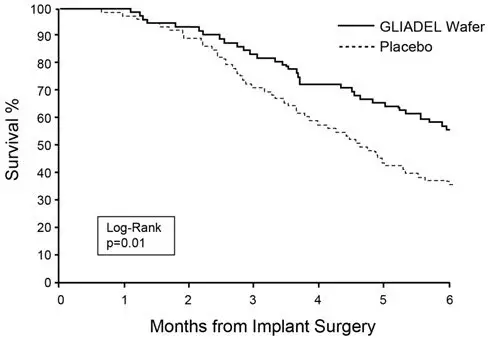
Figure 8: Kaplan-Meier Curves of Overall Survival for Patients with Recurrent Glioblastoma, Study 2.
16. How is Gliadel supplied
GLIADEL Wafer is supplied in a single dose treatment box containing eight individually pouched wafers. Each wafer contains 7.7 mg of carmustine and is packaged in two aluminum foil laminate pouches. The inner pouch is sterile and is designed to maintain product sterility and protect the product from moisture. The outer pouch is a peelable overwrap. The outside surface of the outer pouch is not sterile.
NDC for single dose treatment box: 24338-050-08
| GLIADEL
carmustine wafer |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Arbor Pharmaceuticals (781796417) |