Drug Detail:Haldol decanoate (injection) (Haloperidol (injection) [ hal-oh-per-i-dol ])
Drug Class: Miscellaneous antipsychotic agents
Haldol Decanoate - Clinical Pharmacology
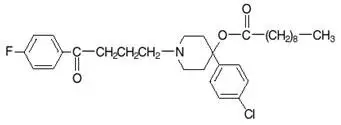
HALDOL decanoate 50 and HALDOL decanoate 100 are the long-acting forms of HALDOL (haloperidol), an antipsychotic. The mechanism of action of haloperidol for the treatment of schizophrenia is unclear. However, its efficacy could be mediated through its activity as an antagonist at central dopamine type 2 receptros. Haloperidol also binds to alpha-1 adrenergic receptors, but with lower affinity, and displays minimal binding to muscarinic cholinergic and histaminergic (H 1) receptors.
Administration of haloperidol decanoate in sesame oil results in slow and sustained release of haloperidol. The plasma concentrations of haloperidol gradually rise, reaching a peak at about 6 days after the injection, and falling thereafter, with an apparent half-life of about 3 weeks. Steady state plasma concentrations are achieved within 2 to 4 months in patient receiving monthly injections. The relationship between dose of haloperidol decanoate and plasma haloperidol concentration is roughly linear for doses below 450 mg. It should be noted, however, that the pharmacokinetics of haloperidol decanoate following intramuscular injections can be quite variable between subjects.
Contraindications
Since the pharmacologic and clinical actions of HALDOL decanoate 50 and HALDOL decanoate 100 are attributed to HALDOL (haloperidol) as the active medication, Contraindications, Warnings, and additional information are those of HALDOL, modified only to reflect the prolonged action.
HALDOL is contraindicated in patients with:
- Severe toxic central nervous system depression or comatose states from any cause.
- Hypersensitivity to this drug – hypersensitivity reactions have included anaphylactic reaction and angioedema (see WARNINGS, Hypersensitivity Reactions and ADVERSE REACTIONS).
- Parkinson's disease (see WARNINGS, Neurological Adverse Reactions in Patients with Parkinson's Disease or Dementia with Lewy Bodies).
- Dementia with Lewy bodies (see WARNINGS, Neurological Adverse Reactions in Patients with Parkinson's Disease or Dementia with Lewy Bodies).
Warnings
Cardiovascular Effects
Cases of sudden death, QTc interval-prolongation, and Torsades de Pointes have been reported in patients receiving haloperidol (see ADVERSE REACTIONS). Higher than recommended doses of any formulation and intravenous administration of haloperidol appear to be associated with a higher risk of QTc interval-prolongation and Torsades de Pointes. Also, a QTc interval that exceeds 500 msec is associated with an increased risk of Torsades de Pointes. Although cases have been reported even in the absence of predisposing factors, particular caution is advised in treating patients with other QTc-prolonging conditions (including electrolyte imbalance [particularly hypokalemia and hypomagnesemia], drugs known to prolong QTc, underlying cardiac abnormalities, hypothyroidism, and familial long QT-syndrome). HALDOL DECANOATE MUST NOT BE ADMINISTERED INTRAVENOUSLY.
Tachycardia and hypotension (including orthostatic hypotension) have also been reported in occasional patients (see ADVERSE REACTIONS).
Tardive Dyskinesia
A syndrome consisting of potentially irreversible, involuntary, dyskinetic movements may develop in patients treated with antipsychotic drugs (see ADVERSE REACTIONS). Although the prevalence of the syndrome appears to be highest among the elderly, especially elderly women, it is impossible to rely upon prevalence estimates to predict, at the inception of antipsychotic treatment, which patients are likely to develop the syndrome. Whether antipsychotic drug products differ in their potential to cause tardive dyskinesia is unknown.
Both the risk of developing tardive dyskinesia and the likelihood that it will become irreversible are believed to increase as the duration of treatment and the total cumulative dose of antipsychotic drugs administered to the patient increase. However, the syndrome can develop, although much less commonly, after relatively brief treatment periods at low doses.
Tardive dyskinesia, may remit, partially or completely, if antipsychotic treatment is discontinued. Antipsychotic treatment, itself, however, may suppress (or partially suppress) the signs and symptoms of the syndrome and thereby may possibly mask the underlying process. The effect that symptomatic suppression has upon the long-term course of the syndrome is unknown.
Given these considerations, antipsychotic drugs should be prescribed in a manner that is most likely to minimize the occurrence of tardive dyskinesia. Chronic antipsychotic treatment should generally be reserved for patients who suffer from a chronic illness that 1) is known to respond to antipsychotic drugs, and 2) for whom alternative, equally effective, but potentially less harmful treatments are not available or appropriate. In patients who do require chronic treatment, the smallest dose and the shortest duration of treatment producing a satisfactory clinical response should be sought. The need for continued treatment should be reassessed periodically.
If signs and symptoms of tardive dyskinesia appear in a patient on antipsychotics, drug discontinuation should be considered. However, some patients may require treatment despite the presence of the syndrome.
Neurological Adverse Reactions in Patients with Parkinson's Disease or Dementia with Lewy Bodies
Patients with Parkinson's Disease or Dementia with Lewy Bodies are reported to have an increased sensitivity to antipsychotic medication. Manifestations of this increased sensitivity with haloperidol treatment include severe extrapyramidal symptoms, confusion, sedation, and falls. In addition, haloperidol may impair the antiparkinson effects of levodopa and other dopamine agonists. HALDOL decanoate is contraindicated in patients with Parkinson's Disease or Dementia with Lewy Bodies (see CONTRAINDICATIONS).
Hypersensitivity Reactions
There have been postmarketing reports of hypersensitivity reactions with haloperidol. These include anaphylactic reaction, angioedema, dermatitis exfoliative, hypersensitivity vasculitis, rash, urticaria, face edema, laryngeal edema, bronchospasm, and laryngospasm (see ADVERSE REACTIONS). HALDOL decanoate is contraindicated in patients with hypersensitivity to this drug (see CONTRAINDICATIONS).
Precautions
Drug Interactions
Drug-drug interactions can be pharmacodynamic (combined pharmacologic effects) or pharmacokinetic (alteration of plasma levels). The risks of using haloperidol in combination with other drugs have been evaluated as described below.
Pharmacokinetic Interactions
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following adverse reactions are discussed in more detail in other sections of the labeling:
- WARNINGS, Increased mortality in Elderly Patients with Dementia-Related Psychosis
- WARNINGS, Cardiovascular Effects
- WARNINGS, Tardive Dyskinesia
- WARNINGS, Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome
- WARNINGS, Hypersensitivity Reactions
- WARNINGS, Falls
- WARNINGS, Combined Use of HALDOL and Lithium
- WARNINGS, General
- PRECAUTIONS, Leukopenia, Neutropenia, and Agranulocytosis
- PRECAUTIONS, Other
- PRECAUTIONS, Usage in Pregnancy
Haldol Decanoate Dosage and Administration
HALDOL decanoate 50 and HALDOL decanoate 100 should be administered by deep intramuscular injection. A 21 gauge needle is recommended. The maximum volume per injection site should not exceed 3 mL. DO NOT ADMINISTER INTRAVENOUSLY.
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit.
HALDOL decanoate 50 and HALDOL decanoate 100 are intended for use in schizophrenic patients who require prolonged parenteral antipsychotic therapy. These patients must be previously stabilized on antipsychotic medication before considering a conversion to haloperidol decanoate. Furthermore, it is recommended that patients being considered for haloperidol decanoate therapy have been treated with, and tolerate well, short-acting HALDOL (haloperidol) in order to reduce the possibility of an unexpected adverse sensitivity to haloperidol. Close clinical supervision is required during the initial period of dose adjustment in order to minimize the risk of overdosage or reappearance of psychotic symptoms before the next injection. During dose adjustment or episodes of exacerbation of symptoms of schizophrenia, haloperidol decanoate therapy can be supplemented with short-acting forms of haloperidol.
The dose of HALDOL decanoate 50 or HALDOL decanoate 100 should be expressed in terms of its haloperidol content. The starting dose of haloperidol decanoate should be based on the patient's age, clinical history, physical condition, and response to previous antipsychotic therapy. The preferred approach to determining the minimum effective dose is to begin with lower initial doses and to adjust the dose upward as needed. For patients previously maintained on low doses of antipsychotics (e.g. up to the equivalent of 10 mg/day oral haloperidol), it is recommended that the initial dose of haloperidol decanoate be 10–15 times the previous daily dose in oral haloperidol equivalents; limited clinical experience suggests that lower initial doses may be adequate.
| HALDOL DECANOATE
haloperidol decanoate injection |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HALDOL DECANOATE
haloperidol decanoate injection |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (063137772) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Janssen Pharmaceutica NV | 400345889 | api manufacture(50458-253, 50458-254) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Janssen Pharmaceutica NV | 370005019 | manufacture(50458-253, 50458-254) , analysis(50458-253, 50458-254) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| GlaxoSmithKline Manufacturing SpA | 338471078 | manufacture(50458-253, 50458-254) , analysis(50458-253, 50458-254) | |