Drug Detail:Herzuma (Trastuzumab [ tras-too-zoo-mab ])
Drug Class: HER2 inhibitors
Highlights of Prescribing Information
HERZUMA® (trastuzumab-pkrb) for injection, for intravenous use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2018
HERZUMA (trastuzumab-pkrb) is biosimilar* to HERCEPTIN (trastuzumab).
WARNING: CARDIOMYOPATHY, INFUSION REACTIONS, EMBRYO-FETAL TOXICITY, and PULMONARY TOXICITY
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning
Cardiomyopathy: Trastuzumab products can result in subclinical and clinical cardiac failure manifesting as CHF, and decreased LVEF, with greatest risk when administered concurrently with anthracyclines. Evaluate cardiac function prior to and during treatment. Discontinue HERZUMA for cardiomyopathy. (2.3, 5.1)
Infusion Reactions, Pulmonary Toxicity: Discontinue HERZUMA for anaphylaxis, angioedema, interstitial pneumonitis, or acute respiratory distress syndrome. (5.2, 5.4)
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: Exposure to trastuzumab products during pregnancy can result in oligohydramnios, in some cases complicated by pulmonary hypoplasia and neonatal death. Advise patients of these risks and the need for effective contraception. (5.3, 8.1, 8.3)
Recent Major Changes
| Indications and Usage, Adjuvant Breast Cancer (1.1) | 05/2019 |
| Indications and Usage, Metastatic Gastric Cancer (1.3) | 05/2019 |
| Dosage and Administration (2) | 05/2019 |
| Warnings and Precautions, Cardiomyopathy (5.1) | 05/2019 |
Indications and Usage for Herzuma
HERZUMA is a HER2/neu receptor antagonist indicated for:
- the treatment of HER2-overexpressing breast cancer. (1.1, 1.2)
- the treatment of HER2-overexpressing metastatic gastric or gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma. (1.3)
Select patients for therapy based on an FDA-approved companion diagnostic for a trastuzumab product. (1, 2.1)
Herzuma Dosage and Administration
For intravenous (IV) infusion only. Do not administer as an IV push or bolus. (2.2)
Do not substitute HERZUMA (trastuzumab-pkrb) for or with ado-trastuzumab emtansine. (2.2)
Perform HER2 testing using FDA-approved tests by laboratories with demonstrated proficiency. (1, 2.1)
Adjuvant Treatment of HER2-Overexpressing Breast Cancer (2.2)
Administer at either:
- Initial dose of 4 mg/kg over 90 minute IV infusion, then 2 mg/kg over 30 minute IV infusion weekly for 12 weeks (with paclitaxel or docetaxel) or 18 weeks (with docetaxel and carboplatin). One week after the last weekly dose of HERZUMA, administer 6 mg/kg as an IV infusion over 30−90 minutes every three weeks to complete a total of 52 weeks of therapy, or
- Initial dose of 8 mg/kg over 90 minute IV infusion, then 6 mg/kg over 30-90 minute IV infusion every three weeks for 52 weeks.
Metastatic HER2-Overexpressing Breast Cancer (2.2)
- Initial dose of 4 mg/kg as a 90 minute IV infusion followed by subsequent weekly doses of 2 mg/kg as 30 minute IV infusions.
Metastatic HER2-Overexpressing Gastric Cancer (2.2)
- Initial dose of 8 mg/kg over 90 minute IV infusion, followed by 6 mg/kg over 30 to 90 minute IV infusion every 3 weeks.
Dosage Forms and Strengths
- For Injection: 150 mg lyophilized powder in a single-dose vial for reconstitution. (3)
- For Injection: 420 mg lyophilized powder in a multiple-dose vial for reconstitution. (3)
Contraindications
- None. (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Exacerbation of Chemotherapy-Induced Neutropenia. (5.5, 6.1)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Adjuvant Breast Cancer
- Most common adverse reactions (≥ 5%) are headache, diarrhea, nausea, and chills. (6.1)
Metastatic Breast Cancer
- Most common adverse reactions (≥ 10%) are fever, chills, headache, infection, congestive heart failure, insomnia, cough, and rash. (6.1)
Metastatic Gastric Cancer
- Most common adverse reactions (≥ 10%) are neutropenia, diarrhea, fatigue, anemia, stomatitis, weight loss, upper respiratory tract infections, fever, thrombocytopenia, mucosal inflammation, nasopharyngitis, and dysgeusia. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Teva Pharmaceuticals at 1-888-483-8279 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Use In Specific Populations
Females and Males of Reproductive Potential: Verify the pregnancy status of females prior to initiation of HERZUMA. (8.3)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
- *
- Biosimilar means that the biological product is approved based on data demonstrating that it is highly similar to an FDA-approved biological product, known as a reference product, and that there are no clinically meaningful differences between the biosimilar product and the reference product. Biosimilarity of HERZUMA has been demonstrated for the condition(s) of use (e.g. indication(s), dosing regimen(s)), strength(s), dosage form(s), and route(s) of administration described in its Full Prescribing Information.
Revised: 5/2019
Full Prescribing Information
WARNING: CARDIOMYOPATHY, INFUSION REACTIONS, EMBRYO-FETAL TOXICITY, and PULMONARY TOXICITY
Cardiomyopathy
Administration of trastuzumab products can result in sub-clinical and clinical cardiac failure. The incidence and severity was highest in patients receiving trastuzumab with anthracycline-containing chemotherapy regimens.
Evaluate left ventricular function in all patients prior to and during treatment with HERZUMA. Discontinue HERZUMA treatment in patients receiving adjuvant therapy and withhold HERZUMA in patients with metastatic disease for clinically significant decrease in left ventricular function [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
1. Indications and Usage for Herzuma
1.1 Adjuvant Breast Cancer
HERZUMA is indicated for adjuvant treatment of HER2 overexpressing node positive or node negative (ER/PR negative or with one high risk feature [see Clinical Studies (14.1)]) breast cancer
- as part of a treatment regimen consisting of doxorubicin, cyclophosphamide, and either paclitaxel or docetaxel
- as part of a treatment regimen with docetaxel and carboplatin
- as a single agent following multi-modality anthracycline based therapy.
Select patients for therapy based on an FDA-approved companion diagnostic for a trastuzumab product [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
1.2 Metastatic Breast Cancer
HERZUMA is indicated:
- In combination with paclitaxel for first-line treatment of HER2-overexpressing metastatic breast cancer
- As a single agent for treatment of HER2-overexpressing breast cancer in patients who have received one or more chemotherapy regimens for metastatic disease.
Select patients for therapy based on an FDA-approved companion diagnostic for a trastuzumab product [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
1.3 Metastatic Gastric Cancer
HERZUMA is indicated, in combination with cisplatin and capecitabine or 5-fluorouracil, for the treatment of patients with HER2 overexpressing metastatic gastric or gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma who have not received prior treatment for metastatic disease.
Select patients for therapy based on an FDA-approved companion diagnostic for a trastuzumab product [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
2. Herzuma Dosage and Administration
2.1 Patient Selection
Select patients based on HER2 protein overexpression or HER2 gene amplification in tumor specimens [see Indications and Usage (1) and Clinical Studies (14)]. Assessment of HER2 protein overexpression and HER2 gene amplification should be performed using FDA-approved tests specific for breast or gastric cancers by laboratories with demonstrated proficiency. Information on the FDA-approved tests for the detection of HER2 protein overexpression and HER2 gene amplification is available at: http://www.fda.gov/CompanionDiagnostics.
Assessment of HER2 protein overexpression and HER2 gene amplification in metastatic gastric cancer should be performed using FDA-approved tests specifically for gastric cancers due to differences in gastric vs. breast histopathology, including incomplete membrane staining and more frequent heterogeneous expression of HER2 seen in gastric cancers.
Improper assay performance, including use of suboptimally fixed tissue, failure to utilize specified reagents, deviation from specific assay instructions, and failure to include appropriate controls for assay validation, can lead to unreliable results.
2.2 Recommended Doses and Schedules
- Do not administer as an intravenous push or bolus. Do not mix HERZUMA with other drugs.
- Do not substitute HERZUMA (trastuzumab-pkrb) for or with ado-trastuzumab emtansine.
2.3 Important Dosing Considerations
If the patient has missed a dose of HERZUMA by one week or less, then the usual maintenance dose (weekly schedule: 2 mg/kg; three-weekly schedule: 6 mg/kg) should be administered as soon as possible. Do not wait until the next planned cycle. Subsequent HERZUMA maintenance doses should be administered 7 days or 21 days later according to the weekly or three-weekly schedules, respectively.
If the patient has missed a dose of HERZUMA by more than one week, a re-loading dose of HERZUMA should be administered over approximately 90 minutes (weekly schedule: 4 mg/kg; three-weekly schedule: 8 mg/kg) as soon as possible. Subsequent HERZUMA maintenance doses (weekly schedule: 2 mg/kg; three-weekly schedule 6 mg/kg) should be administered 7 days or 21 days later according to the weekly or three-weekly schedules, respectively.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
- For injection: 150 mg of HERZUMA as a white to pale yellow lyophilized powder in a single-dose vial
- For injection: 420 mg of HERZUMA as a white to pale yellow lyophilized powder in a multiple-dose vial.
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Cardiomyopathy
Trastuzumab products can cause left ventricular cardiac dysfunction, arrhythmias, hypertension, disabling cardiac failure, cardiomyopathy, and cardiac death [see Boxed Warning: Cardiomyopathy]. Trastuzumab products can also cause asymptomatic decline in left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF).
There is a 4–6 fold increase in the incidence of symptomatic myocardial dysfunction among patients receiving trastuzumab products as a single agent or in combination therapy compared with those not receiving trastuzumab products. The highest absolute incidence occurs when a trastuzumab product is administered with an anthracycline.
Withhold HERZUMA for ≥ 16% absolute decrease in LVEF from pre-treatment values or an LVEF value below institutional limits of normal and ≥ 10% absolute decrease in LVEF from pretreatment values [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)]. The safety of continuation or resumption of HERZUMA in patients with trastuzumab product-induced left ventricular cardiac dysfunction has not been studied.
Patients who receive anthracycline after stopping HERZUMA may also be at increased risk of cardiac dysfunction [see Drug Interactions (7) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Cardiac Monitoring
Conduct thorough cardiac assessment, including history, physical examination, and determination of LVEF by echocardiogram or MUGA scan. The following schedule is recommended:
- Baseline LVEF measurement immediately prior to initiation of HERZUMA
- LVEF measurements every 3 months during and upon completion of HERZUMA
- Repeat LVEF measurement at 4 week intervals if HERZUMA is withheld for significant left ventricular cardiac dysfunction [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)]
- LVEF measurements every 6 months for at least 2 years following completion of HERZUMA as a component of adjuvant therapy.
In Study 1, 15% (158/1031) of patients discontinued trastuzumab due to clinical evidence of myocardial dysfunction or significant decline in LVEF after a median follow-up duration of 8.7 years in the AC-TH (anthracycline, cyclophosphamide, paclitaxel, and trastuzumab) arm. In Study 3 (one-year trastuzumab treatment), the number of patients who discontinued trastuzumab due to cardiac toxicity at 12.6 months median duration of follow-up was 2.6% (44/1678). In Study 4, a total of 2.9% (31/1056) of patients in the TCH (docetaxel, carboplatin, trastuzumab) arm (1.5% during the chemotherapy phase and 1.4% during the monotherapy phase) and 5.7% (61/1068) of patients in the AC-TH arm (1.5% during the chemotherapy phase and 4.2% during the monotherapy phase) discontinued trastuzumab due to cardiac toxicity.
Among 64 patients receiving adjuvant chemotherapy (Studies 1 and 2) who developed congestive heart failure, one patient died of cardiomyopathy, one patient died suddenly without documented etiology and 33 patients were receiving cardiac medication at last follow-up. Approximately 24% of the surviving patients had recovery to a normal LVEF (defined as ≥ 50%) and no symptoms on continuing medical management at the time of last follow-up. Incidence of congestive heart failure (CHF) is presented in Table 1. The safety of continuation or resumption of HERZUMA in patients with trastuzumab product-induced left ventricular cardiac dysfunction has not been studied.
| Incidence of CHF | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Study | Regimen | Trastuzumab | Control |
|
|||
| 1 & 2* | AC†→Paclitaxel+Trastuzumab | 3.2% (64/2000)‡ | 1.3% (21/1655) |
| 3§ | Chemo → Trastuzumab | 2% (30/1678) | 0.3% (5/1708) |
| 4 | AC†→Docetaxel+Trastuzumab | 2% (20/1068) | 0.3% (3/1050) |
| 4 | Docetaxel+Carbo+Trastuzumab | 0.4% (4/1056) | 0.3% (3/1050) |
In Study 3 (one-year trastuzumab treatment), at a median follow-up duration of 8 years, the incidence of severe CHF (NYHA III & IV) was 0.8%, and the rate of mild symptomatic and asymptomatic left ventricular dysfunction was 4.6%.
| Incidence | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NYHA I-IV | NYHA III-IV | ||||
| Study | Event | Trastuzumab | Control | Trastuzumab | Control |
|
|||||
| 5 (AC)† | Cardiac Dysfunction | 28% | 7% | 19% | 3% |
| 5 (paclitaxel) | Cardiac Dysfunction | 11% | 1% | 4% | 1% |
| 6 | Cardiac Dysfunction‡ | 7% | N/A | 5% | N/A |
In Study 4, the incidence of NCI-CTC Grade 3/4 cardiac ischemia/infarction was higher in the trastuzumab containing regimens (AC-TH: 0.3% (3/1068) and TCH: 0.2% (2/1056)) as compared to none in AC-T.
5.2 Infusion Reactions
Infusion reactions consist of a symptom complex characterized by fever and chills, and on occasion included nausea, vomiting, pain (in some cases at tumor sites), headache, dizziness, dyspnea, hypotension, rash, and asthenia [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
In post-marketing reports, serious and fatal infusion reactions have been reported. Severe reactions, which include bronchospasm, anaphylaxis, angioedema, hypoxia, and severe hypotension, were usually reported during or immediately following the initial infusion. However, the onset and clinical course were variable, including progressive worsening, initial improvement followed by clinical deterioration, or delayed post-infusion events with rapid clinical deterioration. For fatal events, death occurred within hours to days following a serious infusion reaction.
Interrupt HERZUMA infusion in all patients experiencing dyspnea, clinically significant hypotension, and intervention of medical therapy administered (which may include epinephrine, corticosteroids, diphenhydramine, bronchodilators, and oxygen). Patients should be evaluated and carefully monitored until complete resolution of signs and symptoms. Permanent discontinuation should be strongly considered in all patients with severe infusion reactions.
There are no data regarding the most appropriate method of identification of patients who may safely be retreated with trastuzumab products after experiencing a severe infusion reaction. Prior to resumption of trastuzumab infusion, the majority of patients who experienced a severe infusion reaction were pre-medicated with antihistamines and/or corticosteroids. While some patients tolerated trastuzumab infusions, others had recurrent severe infusion reactions despite pre-medications.
5.3 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Trastuzumab products can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. In post marketing reports, use of trastuzumab during pregnancy resulted in cases of oligohydramnios and oligohydramnios sequence manifesting as pulmonary hypoplasia, skeletal abnormalities, and neonatal death.
Verify the pregnancy status of females of reproductive potential prior to the initiation of HERZUMA. Advise pregnant women and females of reproductive potential that exposure to HERZUMA during pregnancy or within 7 months prior to conception can result in fetal harm. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment and for 7 months following the last dose of HERZUMA [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
5.4 Pulmonary Toxicity
Trastuzumab product use can result in serious and fatal pulmonary toxicity. Pulmonary toxicity includes dyspnea, interstitial pneumonitis, pulmonary infiltrates, pleural effusions, non-cardiogenic pulmonary edema, pulmonary insufficiency and hypoxia, acute respiratory distress syndrome, and pulmonary fibrosis. Such events can occur as sequelae of infusion reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. Patients with symptomatic intrinsic lung disease or with extensive tumor involvement of the lungs, resulting in dyspnea at rest, appear to have more severe toxicity.
5.5 Exacerbation of Chemotherapy-Induced Neutropenia
In randomized, controlled clinical trials, the per-patient incidences of NCI-CTC Grade 3 to 4 neutropenia and of febrile neutropenia were higher in patients receiving trastuzumab in combination with myelosuppressive chemotherapy as compared to those who received chemotherapy alone. The incidence of septic death was similar among patients who received trastuzumab and those who did not [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the label:
- Cardiomyopathy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Infusion Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Pulmonary Toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Exacerbation of Chemotherapy-induced Neutropenia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
The most common adverse reactions in patients receiving trastuzumab products in the adjuvant and metastatic breast cancer setting are fever, nausea, vomiting, infusion reactions, diarrhea, infections, increased cough, headache, fatigue, dyspnea, rash, neutropenia, anemia, and myalgia. Adverse reactions requiring interruption or discontinuation of trastuzumab product treatment include CHF, significant decline in left ventricular cardiac function, severe infusion reactions, and pulmonary toxicity [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
In the metastatic gastric cancer setting, the most common adverse reactions (≥ 10%) that were increased (≥ 5% difference) in patients receiving trastuzumab as compared to patients receiving chemotherapy alone were neutropenia, diarrhea, fatigue, anemia, stomatitis, weight loss, upper respiratory tract infections, fever, thrombocytopenia, mucosal inflammation, nasopharyngitis, and dysgeusia. The most common adverse reactions which resulted in discontinuation of trastuzumab treatment in the absence of disease progression were infection, diarrhea, and febrile neutropenia.
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Cardiomyopathy
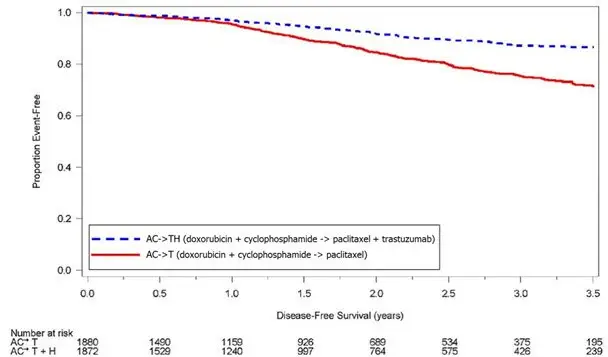
Serial measurement of cardiac function (LVEF) was obtained in clinical trials in the adjuvant treatment of breast cancer. In Study 3, the median duration of follow-up was 12.6 months (12.4 months in the observation arm; 12.6 months in the 1-year trastuzumab arm); and in Studies 1 and 2, 7.9 years in the AC-T arm, 8.3 years in the AC-TH arm. In Studies 1 and 2, 6% of all randomized patients with post-AC LVEF evaluation were not permitted to initiate trastuzumab following completion of AC chemotherapy due to cardiac dysfunction (LVEF < LLN or ≥ 16 point decline in LVEF from baseline to end of AC). Following initiation of trastuzumab therapy, the incidence of new-onset dose-limiting myocardial dysfunction was higher among patients receiving trastuzumab and paclitaxel as compared to those receiving paclitaxel alone in Studies 1 and 2, and in patients receiving one-year trastuzumab monotherapy compared to observation in Study 3 (see Table 6, Figures 1 and 2). The per-patient incidence of new-onset cardiac dysfunction, as measured by LVEF, remained similar when compared to the analysis performed at a median follow-up of 2.0 years in the AC-TH arm. This analysis also showed evidence of reversibility of left ventricular dysfunction, with 64.5% of patients who experienced symptomatic CHF in the AC-TH group being asymptomatic at latest follow-up, and 90.3% having full or partial LVEF recovery.
| LVEF < 50% and Absolute Decrease from Baseline | Absolute LVEF Decrease | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LVEF < 50% | ≥ 10% decrease | ≥ 16% decrease | < 20% and ≥ 10% | ≥ 20% | |
|
|||||
| Studies 1 & 2†, ‡ | |||||
| AC→TH (n = 1856) | 23.1% (428) | 18.5% (344) | 11.2% (208) | 37.9% (703) | 8.9% (166) |
| AC→T (n = 1170) | 11.7% (137) | 7.0% (82) | 3.0% (35) | 22.1% (259) | 3.4% (40) |
| Study 3§ | |||||
| Trastuzumab (n = 1678) | 8.6% (144) | 7.0% (118) | 3.8% (64) | 22.4% (376) | 3.5% (59) |
| Observation (n = 1708) | 2.7% (46) | 2.0% (35) | 1.2% (20) | 11.9% (204) | 1.2% (21) |
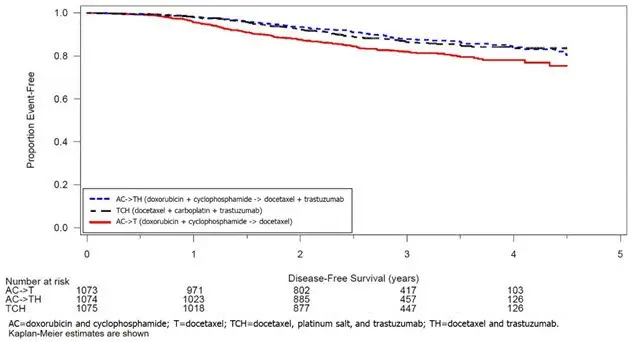
| Study 4¶ | |||||
| TCH (n = 1056) | 8.5% (90) | 5.9% (62) | 3.3% (35) | 34.5% (364) | 6.3% (67) |
| AC→TH (n = 1068) | 17% (182) | 13.3% (142) | 9.8% (105) | 44.3% (473) | 13.2% (141) |
| AC→T (n = 1050) | 9.5% (100) | 6.6% (69) | 3.3% (35) | 34% (357) | 5.5% (58) |
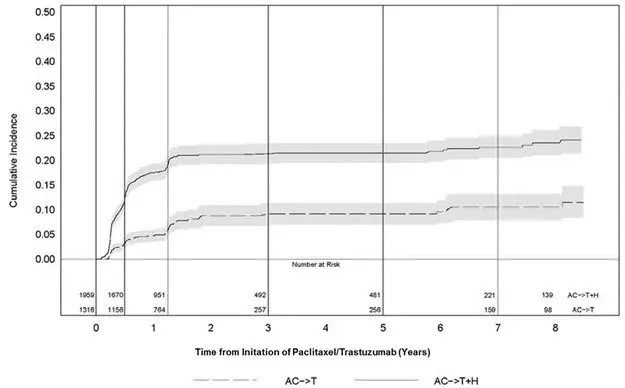
Time 0 is initiation of paclitaxel or trastuzumab + paclitaxel therapy.
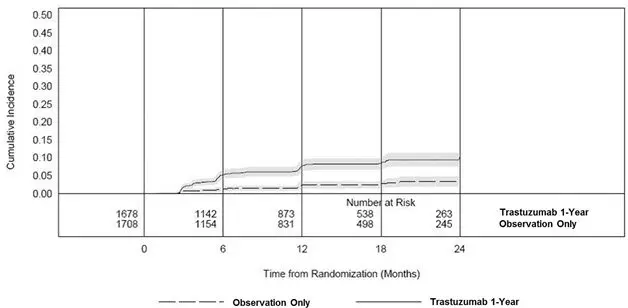
Time 0 is the date of randomization.
Figure 3: Study 4: Cumulative Incidence of Time to First LVEF Decline of ≥ 10 Percentage Points from Baseline and to Below 50% with Death as a Competing Risk Event
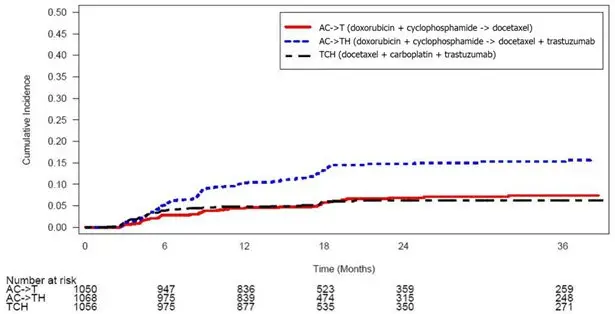
Time 0 is the date of randomization.
The incidence of treatment emergent congestive heart failure among patients in the metastatic breast cancer trials was classified for severity using the New York Heart Association classification system (I–IV, where IV is the most severe level of cardiac failure) (see Table 2). In the metastatic breast cancer trials, the probability of cardiac dysfunction was highest in patients who received trastuzumab concurrently with anthracyclines.
In Study 7, 5.0% of patients in the trastuzumab plus chemotherapy arm compared to 1.1% of patients in the chemotherapy alone arm had LVEF value below 50% with a ≥ 10% absolute decrease in LVEF from pretreatment values.
6.2 Immunogenicity
As with all therapeutic proteins, there is a potential for immunogenicity. The detection of antibody formation is highly dependent on the sensitivity and the specificity of the assay. Additionally, the observed incidence of antibody (including neutralizing antibody) positivity in an assay may be influenced by several factors including assay methodology, sample handling, timing of sample collection, concomitant medications, and underlying disease. For these reasons, comparison of the incidence of antibodies in the studies described below with the incidence of antibodies in other studies or to other trastuzumab products may be misleading.
Among 903 women with metastatic breast cancer, human anti-human antibody (HAHA) to trastuzumab was detected in one patient using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). This patient did not experience an allergic reaction. Samples for assessment of HAHA were not collected in studies of adjuvant breast cancer.
6.3 Post-Marketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of trastuzumab. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
- Infusion reaction [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Oligohydramnios or oligohydramnios sequence, including pulmonary hypoplasia, skeletal abnormalities, and neonatal death [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Glomerulopathy [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]
- Immune thrombocytopenia
- Tumor lysis syndrome (TLS): Cases of possible TLS have been reported in patients treated with trastuzumab. Patients with significant tumor burden (e.g. bulky metastases) may be at a higher risk. Patients could present with hyperuricemia, hyperphosphatemia, and acute renal failure which may represent possible TLS. Providers should consider additional monitoring and/or treatment as clinically indicated.
7. Drug Interactions
Patients who receive anthracycline after stopping trastuzumab products may be at increased risk of cardiac dysfunction because of trastuzumab's long washout period based on population PK analysis [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. If possible, physicians should avoid anthracycline-based therapy for up to 7 months after stopping trastuzumab products. If anthracyclines are used, the patient's cardiac function should be monitored carefully.
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.2 Lactation
Data
In lactating Cynomolgus monkeys, trastuzumab was present in breast milk at about 0.3% of maternal serum concentrations after pre- (beginning Gestation Day 120) and post-partum (through Post-partum Day 28) doses of 25 mg/kg administered twice weekly (25 times the recommended weekly human dose of 2 mg/kg of trastuzumab products). Infant monkeys with detectable serum levels of trastuzumab did not exhibit any adverse effects on growth or development from birth to 1 month of age.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of trastuzumab products in pediatric patients have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Trastuzumab has been administered to 386 patients who were 65 years of age or over (253 in the adjuvant treatment and 133 in metastatic breast cancer treatment settings). The risk of cardiac dysfunction was increased in geriatric patients as compared to younger patients in both those receiving treatment for metastatic disease in Studies 5 and 6, or adjuvant therapy in Studies 1 and 2. Limitations in data collection and differences in study design of the 4 studies of trastuzumab in adjuvant treatment of breast cancer preclude a determination of whether the toxicity profile of trastuzumab in older patients is different from younger patients. The reported clinical experience is not adequate to determine whether the efficacy improvements (ORR, TTP, OS, DFS) of trastuzumab treatment in older patients is different from that observed in patients < 65 years of age for metastatic disease and adjuvant treatment.
In Study 7 (metastatic gastric cancer), of the 294 patients treated with trastuzumab, 108 (37%) were 65 years of age or older, while 13 (4.4%) were 75 and over. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed.
10. Overdosage
There is no experience with overdosage in human clinical trials. Single doses higher than 8 mg/kg have not been tested.
11. Herzuma Description
Trastuzumab-pkrb is a humanized IgG1 kappa monoclonal antibody that selectively binds with high affinity to the extracellular domain of the human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 protein, HER2. Trastuzumab-pkrb is produced by recombinant DNA technology in a mammalian cell (Chinese Hamster Ovary) culture.
HERZUMA (trastuzumab-pkrb) for injection is a sterile, white to pale yellow, preservative-free lyophilized powder with a cake-like appearance, for intravenous administration.
Each multiple-dose vial of HERZUMA delivers 420 mg trastuzumab-pkrb, 839 mg α,α-trehalose dihydrate, 9.5 mg L-histidine HCl, 6.1 mg L-histidine, and 1.7 mg polysorbate 20. Reconstitution with 20 mL of the appropriate diluent (BWFI or SWFI) yields a solution containing 21 mg/mL trastuzumab-pkrb that delivers 20 mL (420 mg trastuzumab-pkrb), at a pH of approximately 6. If HERZUMA is reconstituted with SWFI without preservative, the reconstituted solution is considered single-dose.
Each single-dose vial of HERZUMA delivers 150 mg trastuzumab-pkrb, 299.6 mg α,α-trehalose dihydrate, 3.4 mg L-histidine HCl, 2.2 mg L-histidine, and 0.6 mg polysorbate 20. Reconstitution with 7.4 mL of sterile water for injection (SWFI) yields a solution containing 21 mg/mL trastuzumab-pkrb that delivers 7.15 mL (150 mg trastuzumab-pkrb), at a pH of approximately 6.
12. Herzuma - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
The HER2 (or c-erbB2) proto-oncogene encodes a transmembrane receptor protein of 185 kDa, which is structurally related to the epidermal growth factor receptor. Trastuzumab products have been shown, in both in vitro assays and in animals, to inhibit the proliferation of human tumor cells that overexpress HER2.
Trastuzumab products are mediators of antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC). In vitro, trastuzumab product-mediated ADCC has been shown to be preferentially exerted on HER2 overexpressing cancer cells compared with cancer cells that do not overexpress HER2.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics of trastuzumab were evaluated in a pooled population pharmacokinetic (PK) model analysis of 1,582 subjects with primarily breast cancer and metastatic gastric cancer (MGC) receiving intravenous trastuzumab. Total trastuzumab clearance increases with decreasing concentrations due to parallel linear and non-linear elimination pathways.
Although the average trastuzumab exposure was higher following the first cycle in breast cancer patients receiving the three-weekly schedule compared to the weekly schedule of trastuzumab, the average steady-state exposure was essentially the same at both dosages. The average trastuzumab exposure following the first cycle and at steady state as well as the time to steady state was higher in breast cancer patients compared to MGC patients at the same dosage; however, the reason for this exposure difference is unknown. Additional predicted trastuzumab exposure and PK parameters following the first trastuzumab cycle and at steady state exposure are described in Tables 7 and 8, respectively.
Population PK based simulations indicate that following discontinuation of trastuzumab, concentrations in at least 95% of breast cancer patients and MGC patients will decrease to approximately 3% of the population predicted steady-state trough serum concentration (approximately 97% washout) by 7 months [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)].
| Schedule | Primary tumor type | N | Cmin
(µg/mL) | Cmax
(µg/mL) | AUC0-21days
(µg.day/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8 mg/kg + 6 mg/kg q3w | Breast cancer | 1195 | 29.4 (5.8 to 59.5) | 178 (117 to 291) | 1373 (736 to 2245) |
| MGC | 274 | 23.1 (6.1 to 50.3) | 132 (84.2 to 225) | 1109 (588 to 1938) |
|
| 4 mg/kg + 2 mg/kg qw | Breast cancer | 1195 | 37.7 (12.3 to 70.9) | 88.3 (58 to 144) | 1066 (586 to 1754) |
| Schedule | Primary tumor type | N | Cmin,ss*
(µg/mL) | Cmax,ss†
(µg/mL) | AUCss, 0-21 days
(µg.day/mL) | Time to steady-state (week) | Total CL range at steady-state (L/day) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||
| 8 mg/kg + 6 mg/kg q3w | Breast cancer | 1195 | 47.4 (5 to 115) | 179 (107 to 309) | 1794 (673 to 3618) | 12 | 0.173 to 0.283 |
| MGC | 274 | 32.9 (6.1 to 88.9) | 131 (72.5 to 251) | 1338 (557 to 2875) | 9 | 0.189 to 0.337 | |
| 4 mg/kg + 2 mg/kg qw | Breast cancer | 1195 | 66.1 (14.9 to 142) | 109 (51.0 to 209) | 1765 (647 to 3578) | 12 | 0.201 to 0.244 |
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Trastuzumab products have not been tested for carcinogenic potential.
No evidence of mutagenic activity was observed when trastuzumab was tested in the standard Ames bacterial and human peripheral blood lymphocyte mutagenicity assays, at concentrations of up to 5000 mcg/mL. In an in vivo micronucleus assay, no evidence of chromosomal damage to mouse bone marrow cells was observed following bolus intravenous doses of up to 118 mg/kg of trastuzumab.
A fertility study was conducted in female Cynomolgus monkeys at doses up to 25 times the weekly recommended human dose of 2 mg/kg of trastuzumab and has revealed no evidence of impaired fertility, as measured by menstrual cycle duration and female sex hormone levels.
14. Clinical Studies
14.1 Adjuvant Breast Cancer
The safety and efficacy of trastuzumab in women receiving adjuvant chemotherapy for HER2 overexpressing breast cancer were evaluated in an integrated analysis of two randomized, open-label, clinical trials (Studies 1 and 2) with a total of 4063 women at the protocol-specified final overall survival analysis, a third randomized, open-label, clinical trial (Study 3) with a total of 3386 women at definitive Disease-Free Survival analysis for one-year trastuzumab treatment versus observation, and a fourth randomized, open-label clinical trial with a total of 3222 patients (Study 4).
14.2 Metastatic Breast Cancer
The safety and efficacy of trastuzumab in treatment of women with metastatic breast cancer were studied in a randomized, controlled clinical trial in combination with chemotherapy (Study 5, n = 469 patients) and an open-label, single agent clinical trial (Study 6, n = 222 patients). Both trials studied patients with metastatic breast cancer whose tumors overexpress the HER2 protein. Patients were eligible if they had 2 or 3 levels of overexpression (based on a 0 to 3 scale) by immunohistochemical assessment of tumor tissue performed by a central testing lab.
Previously Untreated Metastatic Breast Cancer (Study 5)
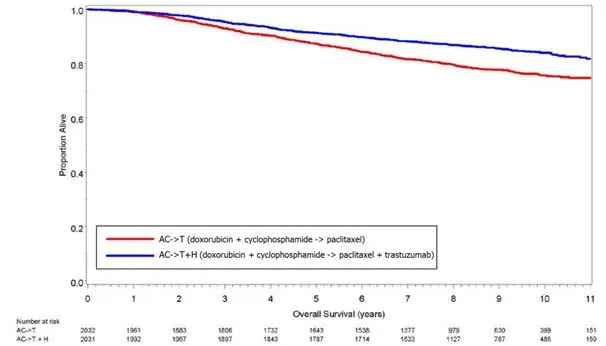
Study 5 was a multicenter, randomized, open-label clinical trial conducted in 469 women with metastatic breast cancer who had not been previously treated with chemotherapy for metastatic disease. Tumor specimens were tested by IHC (Clinical Trial Assay, CTA) and scored as 0, 1+, 2+, or 3+, with 3+ indicating the strongest positivity. Only patients with 2+ or 3+ positive tumors were eligible (about 33% of those screened). Patients were randomized to receive chemotherapy alone or in combination with trastuzumab given intravenously as a 4 mg/kg loading dose followed by weekly doses of trastuzumab at 2 mg/kg. For those who had received prior anthracycline therapy in the adjuvant setting, chemotherapy consisted of paclitaxel (175 mg/m2 over 3 hours every 21 days for at least six cycles); for all other patients, chemotherapy consisted of anthracycline plus cyclophosphamide (AC: doxorubicin 60 mg/m2 or epirubicin 75 mg/m2 plus 600 mg/m2 cyclophosphamide every 21 days for six cycles). Sixty-five percent of patients randomized to receive chemotherapy alone in this study received trastuzumab at the time of disease progression as part of a separate extension study.
Based upon the determination by an independent response evaluation committee, the patients randomized to trastuzumab and chemotherapy experienced a significantly longer median time to disease progression, a higher overall response rate (ORR), and a longer median duration of response, as compared with patients randomized to chemotherapy alone. Patients randomized to trastuzumab and chemotherapy also had a longer median survival (see Table 11). These treatment effects were observed both in patients who received trastuzumab plus paclitaxel and in those who received trastuzumab plus AC; however, the magnitude of the effects was greater in the paclitaxel subgroup.
| Combined Results | Paclitaxel Subgroup | AC Subgroup | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trastuzumab + All Chemotherapy (n = 235) | All Chemo-therapy (n = 234) | Trastuzumab + Paclitaxel (n = 92) | Paclitaxel (n = 96) | Trastuzumab + AC*
(n = 143) | AC (n = 138) |
|
|
||||||
| Primary Endpoint | ||||||
| Median TTP (mos)†, ‡ | 7.2 | 4.5 | 6.7 | 2.5 | 7.6 | 5.7 |
| 95% CI | 7, 8 | 4, 5 | 5, 10 | 2, 4 | 7, 9 | 5, 7 |
| p-value§ | < 0.0001 | < 0.0001 | 0.002 | |||
| Secondary Endpoints | ||||||
| Overall Response Rate† | 45 | 29 | 38 | 15 | 50 | 38 |
| 95% CI | 39, 51 | 23, 35 | 28, 48 | 8, 22 | 42, 58 | 30, 46 |
| p-value¶ | < 0.001 | < 0.001 | 0.10 | |||
| Median Resp Duration (mos)†, ‡ | 8.3 | 5.8 | 8.3 | 4.3 | 8.4 | 6.4 |
| 25%, 75% Quartile | 6, 15 | 4, 8 | 5, 11 | 4, 7 | 6, 15 | 4, 8 |
| Med Survival (mos)‡ | 25.1 | 20.3 | 22.1 | 18.4 | 26.8 | 21.4 |
| 95% CI | 22, 30 | 17, 24 | 17, 29 | 13, 24 | 23, 33 | 18, 27 |
| p-value§ | 0.05 | 0.17 | 0.16 | |||
Data from Study 5 suggest that the beneficial treatment effects were largely limited to patients with the highest level of HER2 protein overexpression (3+) (see Table 12).
| HER2 Assay Result | Number of Patients (N) | Relative Risk* for Time to Disease Progression (95% CI) | Relative Risk* for Mortality (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|||
| CTA 2+ or 3+ | 469 | 0.49 (0.40, 0.61) | 0.80 (0.64, 1.00) |
| FISH (+)† | 325 | 0.44 (0.34, 0.57) | 0.70 (0.53, 0.91) |
| FISH (−)† | 126 | 0.62 (0.42, 0.94) | 1.06 (0.70, 1.63) |
| CTA 2+ | 120 | 0.76 (0.50, 1.15) | 1.26 (0.82, 1.94) |
| FISH (+) | 32 | 0.54 (0.21, 1.35) | 1.31 (0.53, 3.27) |
| FISH (–) | 83 | 0.77 (0.48, 1.25) | 1.11 (0.68, 1.82) |
| CTA 3+ | 349 | 0.42 (0.33, 0.54) | 0.70 (0.51, 0.90) |
| FISH (+) | 293 | 0.42 (0.32, 0.55) | 0.67 (0.51, 0.89) |
| FISH (–) | 43 | 0.43 (0.20, 0.94) | 0.88 (0.39, 1.98) |
14.3 Metastatic Gastric Cancer
The safety and efficacy of trastuzumab in combination with cisplatin and a fluoropyrimidine (capecitabine or 5-fluorouracil) were studied in patients previously untreated for metastatic gastric or gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma (Study 7). In this open-label, multi-center trial, 594 patients were randomized 1:1 to trastuzumab in combination with cisplatin and a fluoropyrimidine (FC+H) or chemotherapy alone (FC). Randomization was stratified by extent of disease (metastatic vs. locally advanced), primary site (gastric vs. gastroesophageal junction), tumor measurability (yes vs. no), ECOG performance status (0, 1 vs. 2), and fluoropyrimidine (capecitabine vs. 5-fluorouracil). All patients were either HER2 gene amplified (FISH+) or HER2 overexpressing (IHC 3+). Patients were also required to have adequate cardiac function (e.g., LVEF > 50%).
On the trastuzumab-containing arm, trastuzumab was administered as an IV infusion at an initial dose of 8 mg/kg followed by 6 mg/kg every 3 weeks until disease progression. On both study arms, cisplatin was administered at a dose of 80 mg/m2 Day 1 every 3 weeks for 6 cycles as a 2 hour IV infusion. On both study arms, capecitabine was administered at 1000 mg/m2 dose orally twice daily (total daily dose 2000 mg/m2) for 14 days of each 21 day cycle for 6 cycles. Alternatively, continuous intravenous infusion (CIV) 5-fluorouracil was administered at a dose of 800 mg/m2/day from Day 1 through Day 5 every three weeks for 6 cycles.
The median age of the study population was 60 years (range: 21-83); 76% were male; 53% were Asian, 38% Caucasian, 5% Hispanic, 5% other racial/ethnic groups; 91% had ECOG PS of 0 or 1; 82% had primary gastric cancer and 18% had primary gastroesophageal adenocarcinoma. Of these patients, 23% had undergone prior gastrectomy, 7% had received prior neoadjuvant and/or adjuvant therapy, and 2% had received prior radiotherapy.
The main outcome measure of Study 7 was overall survival (OS), analyzed by the unstratified log-rank test. The final OS analysis based on 351 deaths was statistically significant (nominal significance level of 0.0193). An updated OS analysis was conducted at one year after the final analysis. The efficacy results of both the final and the updated analyses are summarized in Table 13 and Figure 7.
| FC Arm N = 296 | FC + H Arm N = 298 |
|
|---|---|---|
|
||
| Definitive (Second Interim) Overall Survival | ||
| No. Deaths (%) | 184 (62.2%) | 167 (56.0%) |
| Median | 11.0 | 13.5 |
| 95% CI (mos.) | (9.4, 12.5) | (11.7, 15.7) |
| Hazard Ratio | 0.73 | |
| 95% CI | (0.60, 0.91) | |
| p value*, two-sided | 0.0038 | |
| Updated Overall Survival | ||
| No. Deaths (%) | 227 (76.7%) | 221 (74.2%) |
| Median | 11.7 | 13.1 |
| 95% CI (mos.) | (10.3, 13.0) | (11.9, 15.1) |
| Hazard Ratio | 0.80 | |
| 95% CI | (0.67, 0.97) | |
Figure 7: Updated Overall Survival in Patients with Metastatic Gastric Cancer (Study 7)
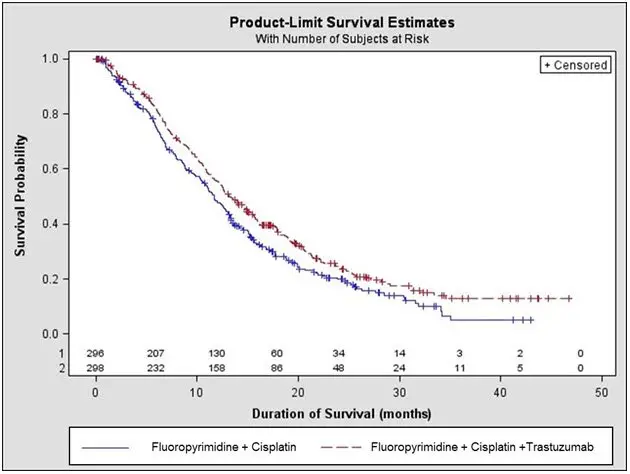
An exploratory analysis of OS in patients based on HER2 gene amplification (FISH) and protein overexpression (IHC) testing is summarized in Table 14.
| FC (N = 296)* | FC + H (N = 298)† |
|
|---|---|---|
|
||
| FISH+ / IHC 0, 1+ subgroup (N=133) | ||
| No. Deaths / n (%) | 57/71 (80%) | 56/62 (90%) |
| Median OS Duration (mos.) | 8.8 | 8.3 |
| 95% CI (mos.) | (6.4, 11.7) | (6.2, 10.7) |
| Hazard ratio (95% CI) | 1.33 (0.92, 1.92) | |
| FISH+ / IHC2+ subgroup (N=160) | ||
| No. Deaths / n (%) | 65/80 (81%) | 64/80 (80%) |
| Median OS Duration (mos.) | 10.8 | 12.3 |
| 95% CI (mos.) | (6.8, 12.8) | (9.5, 15.7) |
| Hazard ratio (95% CI) | 0.78 (0.55, 1.10) | |
| FISH+ or FISH- / IHC3+‡ subgroup (N=294) | ||
| No. Deaths / n (%) | 104/143 (73%) | 96/151 (64%) |
| Median OS Duration (mos.) | 13.2 | 18.0 |
| 95% CI (mos.) | (11.5, 15.2) | (15.5, 21.2) |
| Hazard ratio (95% CI) | 0.66 (0.50, 0.87) | |
| HERZUMA
trastuzumab kit |
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
| HERZUMA
trastuzumab injection, powder, lyophilized, for solution |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Cephalon, Inc. (183236314) |
| Registrant - CELLTRION, Inc. (688836030) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| CELLTRION, Inc. | 688836030 | analysis(63459-307, 63459-303, 63459-221) , api manufacture(63459-307, 63459-303) , manufacture(63459-307, 63459-303, 63459-221) , label(63459-307, 63459-303, 63459-221, 63459-305) , pack(63459-307, 63459-303, 63459-221, 63459-305) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| WuXi AppTec, Inc. | 032689593 | analysis(63459-307, 63459-303) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| WuXi AppTec, Inc. | 053506585 | analysis(63459-307, 63459-303) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| BioReliance Ltd. | 505004556 | analysis(63459-307, 63459-303) , manufacture(63459-307, 63459-303) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| BioReliance Ltd. | 217063511 | analysis(63459-307, 63459-303) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| BioReliance Ltd. | 217063514 | analysis(63459-307, 63459-303) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Andersonbrecon Inc. | 053217022 | LABEL(63459-303) , PACK(63459-303) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Andersonbrecon Limited | 762771269 | LABEL(63459-303) , PACK(63459-303) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| SGS Vitrology Limited | 516257446 | analysis(63459-303, 63459-307) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| WuXi Advanced Therapies Inc. | 117331245 | analysis(63459-303, 63459-307) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| WuXi Advanced Therapies Inc. | 117556312 | analysis(63459-303, 63459-307) | |