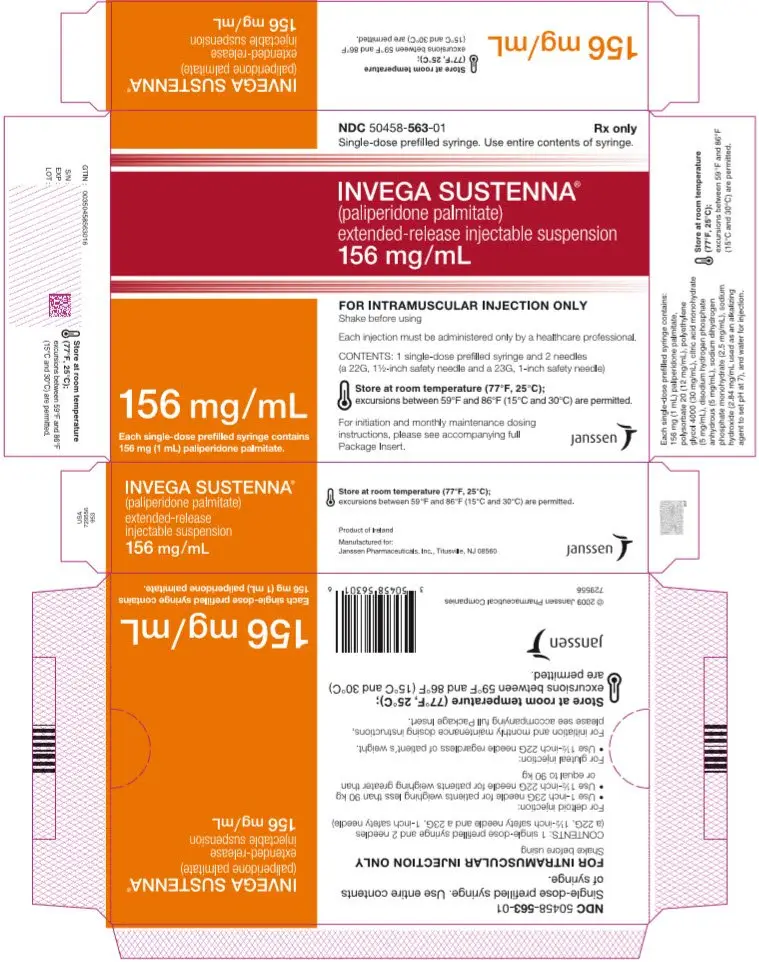
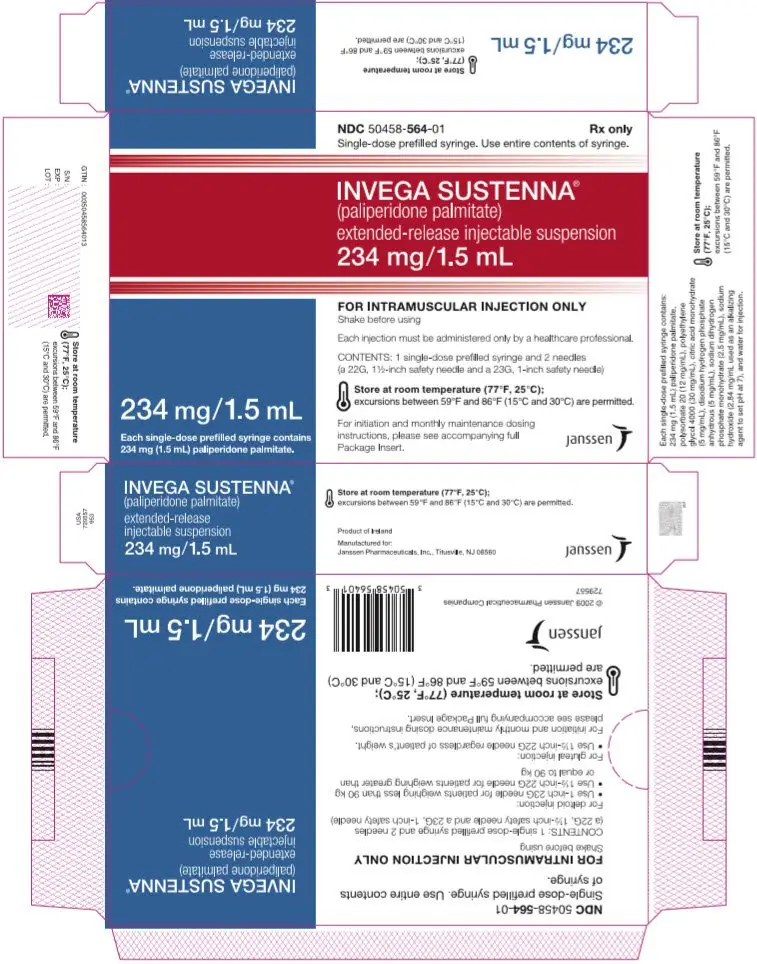
Drug Detail:Invega sustenna (Paliperidone (injection) [ pal-ee-per-i-done ])
Drug Class: Atypical antipsychotics
Highlights of Prescribing Information
INVEGA SUSTENNA® (paliperidone palmitate) extended-release injectable suspension, for intramuscular use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2006
WARNING: INCREASED MORTALITY IN ELDERLY PATIENTS WITH DEMENTIA-RELATED PSYCHOSIS
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
Elderly patients with dementia-related psychosis treated with antipsychotic drugs are at an increased risk of death. INVEGA SUSTENNA® is not approved for use in patients with dementia-related psychosis. (5.1)
Recent Major Changes
| Dosage and Administration (2.5) | 7/2022 |
Indications and Usage for Invega Sustenna
INVEGA SUSTENNA® is an atypical antipsychotic indicated for
- Treatment of schizophrenia in adults. (1)
- Treatment of schizoaffective disorder in adults as monotherapy and as an adjunct to mood stabilizers or antidepressants. (1)
Invega Sustenna Dosage and Administration
- For intramuscular injection only. (2.1)
- Each injection must be administered only by a healthcare professional. (2.1)
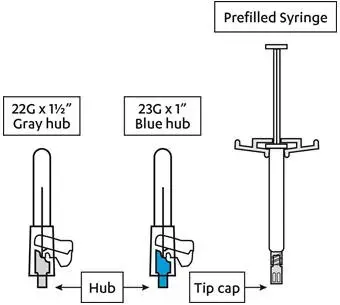
- For deltoid injection, use 1-inch 23G needle for patients weighing less than 90 kg or 1½-inch 22G needle for patients weighing 90 kg or more. For gluteal injection, use 1½-inch 22G needle regardless of patient weight. (2.1)
| Indication | Initiation Dosing (deltoid) | Monthly Maintenance Dose*
(deltoid or gluteal) | Maximum Monthly Dose | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day 1 | Day 8 | |||
|
||||
| Schizophrenia (2.2) | 234 mg | 156 mg | 39–234 mg† | 234 mg |
| Schizoaffective disorder (2.2) | 234 mg | 156 mg | 78–234 mg‡ | 234 mg |
- For patients naïve to oral paliperidone or oral or injectable risperidone, establish tolerability with oral paliperidone or oral risperidone prior to initiating treatment with INVEGA SUSTENNA®. (2.2)
- Missed Doses: To manage either a missed second initiation dose or a missed monthly maintenance dose, refer to the Full Prescribing Information. (2.3)
- Moderate to severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance < 50 mL/min): INVEGA SUSTENNA® is not recommended. (2.5)
- Mild renal impairment (creatinine clearance ≥ 50 mL/min to < 80 mL/min): Administer 156 mg on treatment Day 1 and 117 mg on Day 8, both in the deltoid muscle. Follow with the recommended monthly maintenance dose of 78 mg, administered in the deltoid or gluteal muscle. Adjust monthly maintenance dose based on tolerability and/or efficacy within the strengths of 39 mg, 78 mg, 117 mg, or 156 mg. The maximum monthly dose is 156 mg for patients with mild renal impairment. (2.5)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
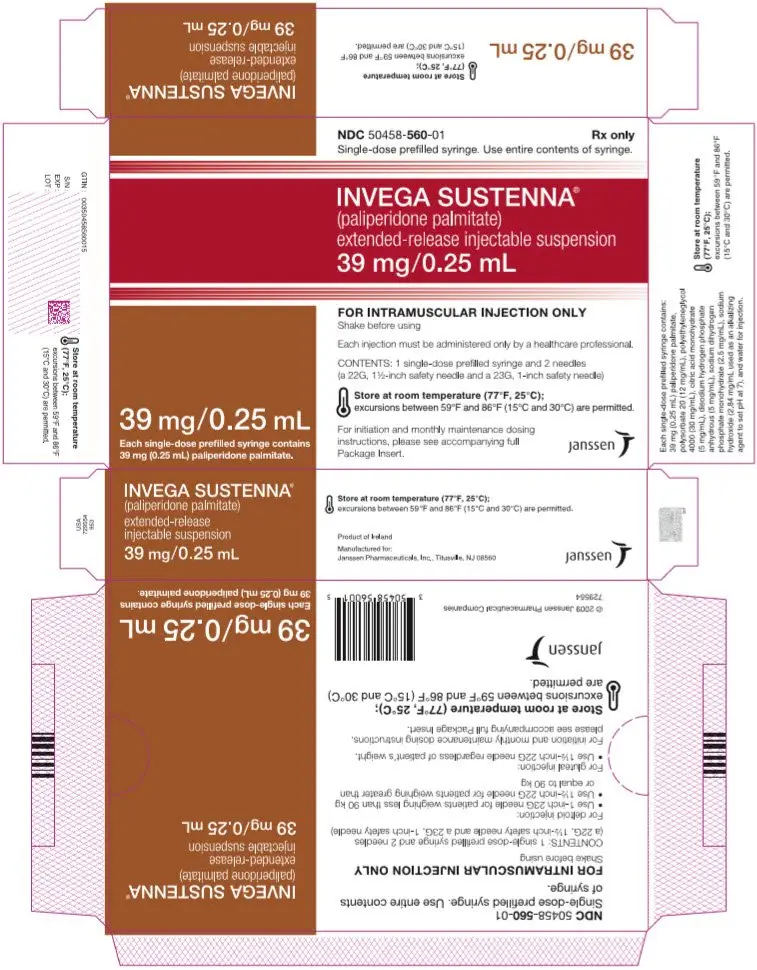
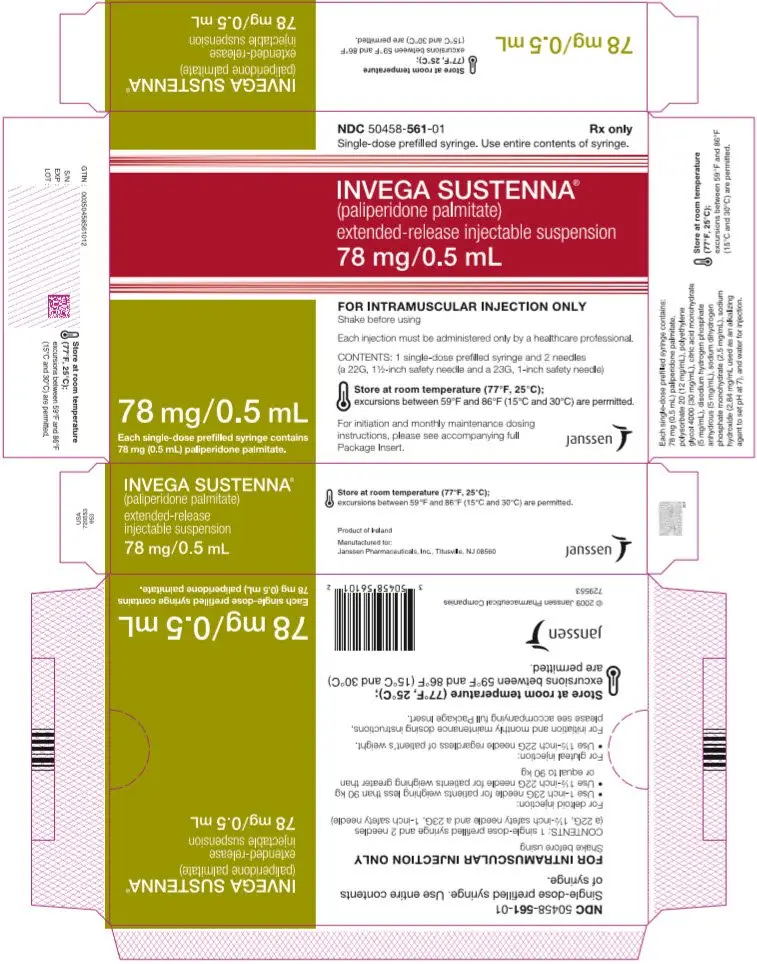
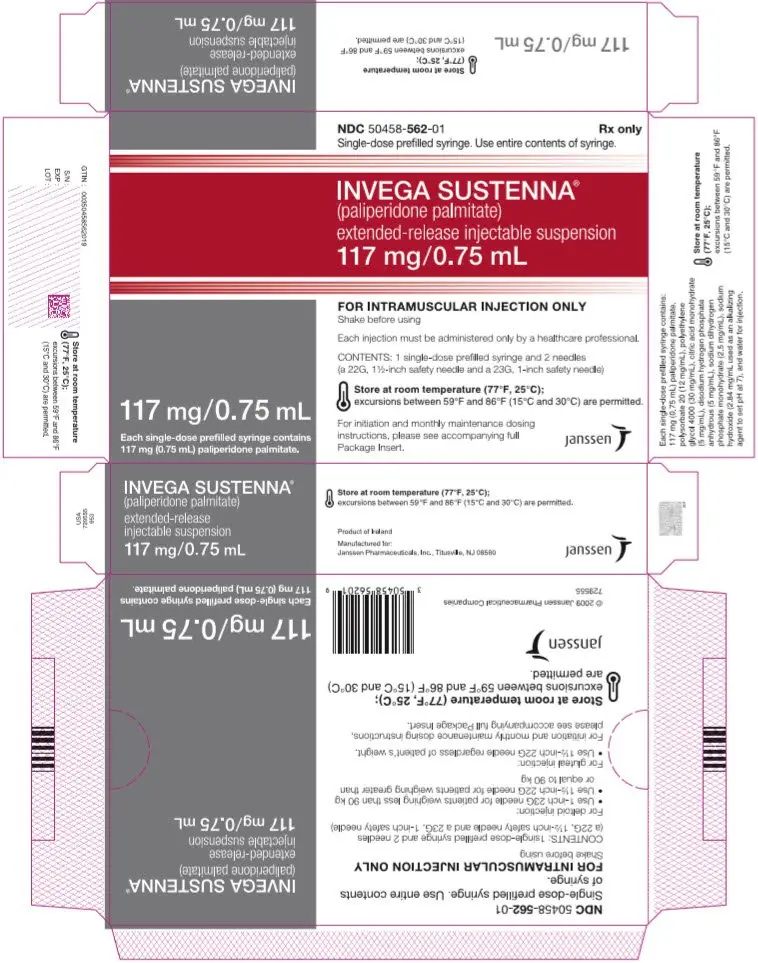
Extended-release injectable suspension: 39 mg/0.25 mL, 78 mg/0.5 mL, 117 mg/0.75 mL, 156 mg/mL, or 234 mg/1.5 mL (3)
Contraindications
Known hypersensitivity to paliperidone, risperidone, or to any excipients in INVEGA SUSTENNA®. (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Cerebrovascular Adverse Reactions, Including Stroke, in Elderly Patients with Dementia-Related Psychosis: Increased incidence of cerebrovascular adverse reactions (e.g. stroke, transient ischemic attack). (5.2)
- Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome: Manage with immediate discontinuation of drug and close monitoring. (5.3)
- QT Prolongation: Avoid use with drugs that also increase QT interval and in patients with risk factors for prolonged QT interval. (5.4)
- Tardive Dyskinesia: Discontinue drug if clinically appropriate. (5.5)
- Metabolic Changes: Monitor for hyperglycemia/diabetes mellitus, dyslipidemia and weight gain. (5.6)
- Orthostatic Hypotension and Syncope: Monitor heart rate and blood pressure and warn patients with known cardiovascular or cerebrovascular disease, and risk of dehydration or syncope. (5.7)
- Leukopenia, Neutropenia, and Agranulocytosis: Perform complete blood counts (CBC) in patients with pre-existing low white blood cell count (WBC) or history of leukopenia or neutropenia. Consider discontinuing INVEGA SUSTENNA® if clinically significant decline in WBC in the absence of other causative factors. (5.9)
- Hyperprolactinemia: Prolactin elevations occur and persist during chronic administration. (5.10)
- Potential for Cognitive and Motor Impairment: Use caution when operating machinery. (5.11)
- Seizures: Use cautiously in patients with a history of seizures or with conditions that lower the seizure threshold. (5.12)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥ 5% and occurring at least twice as often as placebo) were injection site reactions, somnolence/sedation, dizziness, akathisia, and extrapyramidal disorder. (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc. at 1-800-JANSSEN (1-800-526-7736) or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch
Drug Interactions
- Drugs that may cause orthostatic hypotension: An additive effect may occur when co-administered with INVEGA SUSTENNA®. (7.1)
- Strong CYP3A4/P-glycoprotein (P-gp) inducers: Avoid using a strong inducer of CYP3A4 and/or P-gp (e.g., carbamazepine, rifampin, St John's Wort) during a dosing interval for INVEGA SUSTENNA®. If administering a strong inducer is necessary, consider managing the patient using paliperidone extended release tablets. (2.5, 7.1, 12.3)
Use In Specific Populations
Pregnancy: May cause extrapyramidal and/or withdrawal symptoms in neonates with third trimester exposure. (8.1)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 7/2022
Related/similar drugs
fluoxetine, quetiapine, Abilify, Seroquel, Prozac, aripiprazole, olanzapineFull Prescribing Information
WARNING: INCREASED MORTALITY IN ELDERLY PATIENTS WITH DEMENTIA-RELATED PSYCHOSIS
Elderly patients with dementia-related psychosis treated with antipsychotic drugs are at an increased risk of death. INVEGA SUSTENNA® is not approved for use in patients with dementia-related psychosis. [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
1. Indications and Usage for Invega Sustenna
INVEGA SUSTENNA® (paliperidone palmitate) is indicated for the treatment of:
- Schizophrenia in adults [see Clinical Studies (14.1)].
- Schizoaffective disorder in adults as monotherapy and as an adjunct to mood stabilizers or antidepressants [see Clinical Studies (14.2)].
2. Invega Sustenna Dosage and Administration
2.1 Administration Instructions
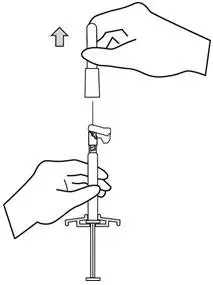
Each injection must be administered only by a healthcare professional.
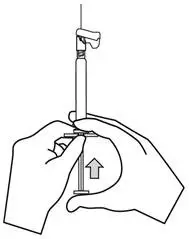
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for foreign matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever product and container permit.
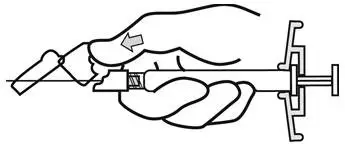
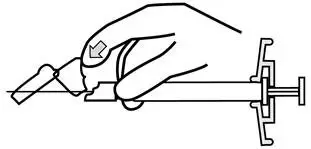
INVEGA SUSTENNA® is intended for intramuscular use only. Do not administer by any other route. Avoid inadvertent injection into a blood vessel. Administer the dose in a single injection; do not administer the dose in divided injections. Inject slowly, deep into the deltoid or gluteal muscle.
INVEGA SUSTENNA® must be administered using only the needles that are provided in the INVEGA SUSTENNA® kit.
The recommended needle size for administration of INVEGA SUSTENNA® into the deltoid muscle is determined by the patient's weight:
- For patients weighing less than 90 kg, the 1-inch, 23 gauge needle is recommended.
- For patients weighing 90 kg or more, the 1½-inch, 22 gauge needle is recommended.
Deltoid injections should be alternated between the two deltoid muscles.
The recommended needle size for administration of INVEGA SUSTENNA® into the gluteal muscle is the 1½-inch, 22 gauge needle regardless of patient weight.
Administer into the upper-outer quadrant of the gluteal muscle. Gluteal injections should be alternated between the two gluteal muscles.
2.2 Schizophrenia and Schizoaffective Disorder
For patients who have never taken oral paliperidone or oral or injectable risperidone, it is recommended to establish tolerability with oral paliperidone or oral risperidone prior to initiating treatment with INVEGA SUSTENNA®.
The recommended dosing of INVEGA SUSTENNA® for each approved indication is displayed in Table 1. The recommended initiation of INVEGA SUSTENNA® is with a dose of 234 mg on treatment day 1 and 156 mg one week later, both administered in the deltoid muscle. Following the second initiation dose, monthly maintenance doses can be administered in either the deltoid or gluteal muscle.
| Indication | Initiation Dosing (deltoid) | Monthly Maintenance Dose*
(deltoid or gluteal) | Maximum Monthly Dose | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day 1 | Day 8 | |||
|
||||
| Schizophrenia | 234 mg | 156 mg | 39–234 mg† | 234 mg |
| Schizoaffective disorder | 234 mg | 156 mg | 78–234 mg‡ | 234 mg |
Adjustment of the maintenance dose may be made monthly. When making dose adjustments, the prolonged-release characteristics of INVEGA SUSTENNA® should be considered [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)], as the full effect of the dose adjustment may not be evident for several months.
2.3 Missed Doses
2.4 Use with Risperidone or with Oral Paliperidone
Since paliperidone is the major active metabolite of risperidone, caution should be exercised when INVEGA SUSTENNA® is coadministered with risperidone or with oral paliperidone for extended periods of time. Safety data involving concomitant use of INVEGA SUSTENNA® with other antipsychotics is limited.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
INVEGA SUSTENNA® is available as a white to off-white aqueous extended-release injectable suspension for intramuscular injection in dose strengths of 39 mg/0.25 mL, 78 mg/0.5 mL, 117 mg/0.75 mL, 156 mg/mL, and 234 mg/1.5 mL paliperidone palmitate in single-dose prefilled syringes.
4. Contraindications
INVEGA SUSTENNA® is contraindicated in patients with a known hypersensitivity to either paliperidone or risperidone, or to any of the excipients in the INVEGA SUSTENNA® formulation. Hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylactic reactions and angioedema, have been reported in patients treated with risperidone and in patients treated with paliperidone. Paliperidone palmitate is converted to paliperidone, which is a metabolite of risperidone.
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Increased Mortality in Elderly Patients with Dementia-Related Psychosis
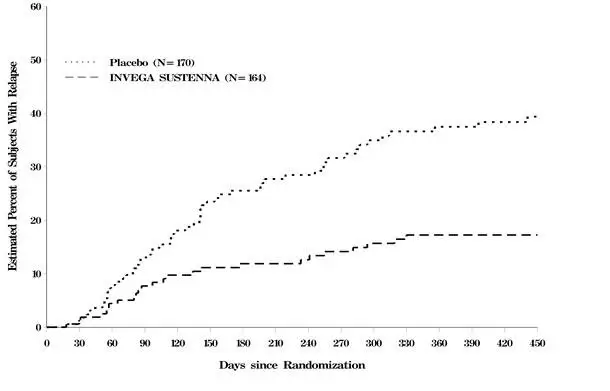
Elderly patients with dementia-related psychosis treated with antipsychotic drugs are at an increased risk of death. Analyses of 17 placebo-controlled trials (modal duration of 10 weeks), largely in patients taking atypical antipsychotic drugs, revealed a risk of death in drug-treated patients of between 1.6 to 1.7 times the risk of death in placebo-treated patients. Over the course of a typical 10-week controlled trial, the rate of death in drug-treated patients was about 4.5%, compared to a rate of about 2.6% in the placebo group. Although the causes of death were varied, most of the deaths appeared to be either cardiovascular (e.g., heart failure, sudden death) or infectious (e.g., pneumonia) in nature. Observational studies suggest that, similar to atypical antipsychotic drugs, treatment with conventional antipsychotic drugs may increase mortality. The extent to which the findings of increased mortality in observational studies may be attributed to the antipsychotic drug as opposed to some characteristic(s) of the patients is not clear. INVEGA SUSTENNA® is not approved for the treatment of patients with dementia-related psychosis [see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
5.2 Cerebrovascular Adverse Reactions, Including Stroke, in Elderly Patients with Dementia-Related Psychosis
In placebo-controlled trials with risperidone, aripiprazole, and olanzapine in elderly subjects with dementia, there was a higher incidence of cerebrovascular adverse reactions (cerebrovascular accidents and transient ischemic attacks) including fatalities compared to placebo-treated subjects. No studies have been conducted with oral paliperidone, INVEGA SUSTENNA®, or the 3-month paliperidone palmitate extended-release injectable suspension in elderly patients with dementia. These medicines are not approved for the treatment of patients with dementia-related psychosis [see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
5.3 Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome
Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS), a potentially fatal symptom complex, has been reported in association with antipsychotic drugs, including paliperidone.
Clinical manifestations of NMS are hyperpyrexia, muscle rigidity, altered mental status including delirium, and autonomic instability (irregular pulse or blood pressure, tachycardia, diaphoresis, and cardiac dysrhythmia). Additional signs may include elevated creatine phosphokinase, myoglobinuria (rhabdomyolysis), and acute renal failure.
If NMS is suspected, immediately discontinue INVEGA SUSTENNA® and provide symptomatic treatment and monitoring.
5.4 QT Prolongation
Paliperidone causes a modest increase in the corrected QT (QTc) interval. The use of paliperidone should be avoided in combination with other drugs that are known to prolong QTc including Class 1A (e.g., quinidine, procainamide) or Class III (e.g., amiodarone, sotalol) antiarrhythmic medications, antipsychotic medications (e.g., chlorpromazine, thioridazine), antibiotics (e.g., gatifloxacin, moxifloxacin), or any other class of medications known to prolong the QTc interval. Paliperidone should also be avoided in patients with congenital long QT syndrome and in patients with a history of cardiac arrhythmias.
Certain circumstances may increase the risk of the occurrence of Torsades de pointes and/or sudden death in association with the use of drugs that prolong the QTc interval, including (1) bradycardia; (2) hypokalemia or hypomagnesemia; (3) concomitant use of other drugs that prolong the QTc interval; and (4) presence of congenital prolongation of the QT interval.
The effects of oral paliperidone on the QT interval were evaluated in a double-blind, active-controlled (moxifloxacin 400 mg single dose), multicenter QT study in adults with schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder, and in three placebo- and active-controlled 6-week, fixed-dose efficacy trials in adults with schizophrenia.
In the QT study (n=141), the 8 mg dose of immediate-release oral paliperidone (n=50) showed a mean placebo-subtracted increase from baseline in QTcLD of 12.3 msec (90% CI: 8.9; 15.6) on day 8 at 1.5 hours post-dose. The mean steady-state peak plasma concentration for this 8 mg dose of paliperidone immediate release (Cmax ss = 113 ng/mL) was more than 2-fold the exposure observed with the maximum recommended 234 mg dose of INVEGA SUSTENNA® administered in the deltoid muscle (predicted median Cmax ss = 50 ng/mL). In this same study, a 4 mg dose of the immediate-release oral formulation of paliperidone, for which Cmax ss = 35 ng/mL, showed an increased placebo-subtracted QTcLD of 6.8 msec (90% CI: 3.6; 10.1) on day 2 at 1.5 hours post-dose.
In the three fixed-dose efficacy studies of oral paliperidone extended release in subjects with schizophrenia, electrocardiogram (ECG) measurements taken at various time points showed only one subject in the oral paliperidone 12 mg group had a change exceeding 60 msec at one time-point on Day 6 (increase of 62 msec).
In the four fixed-dose efficacy studies of INVEGA SUSTENNA® in subjects with schizophrenia and in the long-term study in subjects with schizoaffective disorder, no subject experienced a change in QTcLD exceeding 60 msec and no subject had a QTcLD value of > 500 msec at any time point. In the maintenance study in subjects with schizophrenia, no subject had a QTcLD change > 60 msec, and one subject had a QTcLD value of 507 msec (Bazett's QT corrected interval [QTcB] value of 483 msec); this latter subject also had a heart rate of 45 beats per minute.
5.5 Tardive Dyskinesia
Tardive dyskinesia, a syndrome consisting of potentially irreversible, involuntary, dyskinetic movements, may develop in patients treated with antipsychotic drugs. Although the prevalence of the syndrome appears to be highest among the elderly, especially elderly women, it is impossible to predict which patients will develop the syndrome. Whether antipsychotic drug products differ in their potential to cause tardive dyskinesia is unknown.
The risk of developing tardive dyskinesia and the likelihood that it will become irreversible appear to increase with the duration of treatment and the cumulative dose. The syndrome can develop after relatively brief treatment periods, even at low doses. It may also occur after discontinuation of treatment.
Tardive dyskinesia may remit, partially or completely, if antipsychotic treatment is discontinued. Antipsychotic treatment, itself, however, may suppress (or partially suppress) the signs and symptoms of the syndrome, possibly masking the underlying process. The effect that symptomatic suppression has upon the long-term course of the syndrome is unknown.
Given these considerations, INVEGA SUSTENNA® should be prescribed in a manner that is most likely to minimize the occurrence of tardive dyskinesia. Chronic antipsychotic treatment should generally be reserved for patients: (1) who suffer from a chronic illness that is known to respond to antipsychotic drugs, and (2) for whom alternative, equally effective, but potentially less harmful treatments are not available or appropriate. In patients who do require chronic treatment, use the lowest dose and the shortest duration of treatment producing a satisfactory clinical response. Periodically reassess the need for continued treatment.
If signs and symptoms of tardive dyskinesia appear in a patient on INVEGA SUSTENNA®, drug discontinuation should be considered. However, some patients may require treatment with INVEGA SUSTENNA® despite the presence of the syndrome.
5.6 Metabolic Changes
Atypical antipsychotic drugs have been associated with metabolic changes that may increase cardiovascular/cerebrovascular risk. These metabolic changes include hyperglycemia, dyslipidemia, and body weight gain. While all of the drugs in the class have been shown to produce some metabolic changes, each drug has its own specific risk profile.
5.7 Orthostatic Hypotension and Syncope
Paliperidone can induce orthostatic hypotension and syncope in some patients because of its alpha-adrenergic blocking activity. Syncope was reported in < 1% (4/1293) of subjects treated with INVEGA SUSTENNA® in the recommended dose range of 39 mg to 234 mg in the four fixed-dose, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials compared with 0% (0/510) of subjects treated with placebo. In the four fixed-dose efficacy studies in subjects with schizophrenia, orthostatic hypotension was reported as an adverse event by < 1% (2/1293) of INVEGA SUSTENNA®-treated subjects compared to 0% (0/510) with placebo. Incidences of orthostatic hypotension and syncope in the long-term studies in subjects with schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder were similar to those observed in the short-term studies.
INVEGA SUSTENNA® should be used with caution in patients with known cardiovascular disease (e.g., heart failure, history of myocardial infarction or ischemia, conduction abnormalities), cerebrovascular disease, or conditions that predispose the patient to hypotension (e.g., dehydration, hypovolemia, and treatment with antihypertensive medications). Monitoring of orthostatic vital signs should be considered in patients who are vulnerable to hypotension.
5.8 Falls
Somnolence, postural hypotension, motor and sensory instability have been reported with the use of antipsychotics, including INVEGA SUSTENNA®, which may lead to falls and, consequently, fractures or other fall-related injuries. For patients, particularly the elderly, with diseases, conditions, or medications that could exacerbate these effects, assess the risk of falls when initiating antipsychotic treatment and recurrently for patients on long-term antipsychotic therapy.
5.9 Leukopenia, Neutropenia, and Agranulocytosis
In clinical trial and/or postmarketing experience, events of leukopenia and neutropenia have been reported temporally related to antipsychotic agents, including INVEGA SUSTENNA®. Agranulocytosis has also been reported.
Possible risk factors for leukopenia/neutropenia include pre-existing low white blood cell count (WBC)/absolute neutrophil count (ANC) and history of drug-induced leukopenia/neutropenia. In patients with a history of a clinically significant low WBC/ANC or a drug-induced leukopenia/neutropenia, perform a complete blood count (CBC) frequently during the first few months of therapy. In such patients, consider discontinuation of INVEGA SUSTENNA® at the first sign of a clinically significant decline in WBC in the absence of other causative factors.
Monitor patients with clinically significant neutropenia for fever or other symptoms or signs of infection and treat promptly if such symptoms or signs occur. Discontinue INVEGA SUSTENNA® in patients with severe neutropenia (absolute neutrophil count < 1000/mm3) and follow their WBC until recovery.
5.10 Hyperprolactinemia
Like other drugs that antagonize dopamine D2 receptors, paliperidone elevates prolactin levels and the elevation persists during chronic administration. Paliperidone has a prolactin-elevating effect similar to that seen with risperidone, a drug that is associated with higher levels of prolactin than other antipsychotic drugs.
Hyperprolactinemia, regardless of etiology, may suppress hypothalamic GnRH, resulting in reduced pituitary gonadotrophin secretion. This, in turn, may inhibit reproductive function by impairing gonadal steroidogenesis in both female and male patients. Galactorrhea, amenorrhea, gynecomastia, and impotence have been reported in patients receiving prolactin-elevating compounds. Long-standing hyperprolactinemia when associated with hypogonadism may lead to decreased bone density in both female and male subjects.
Tissue culture experiments indicate that approximately one-third of human breast cancers are prolactin dependent in vitro, a factor of potential importance if the prescription of these drugs is considered in a patient with previously detected breast cancer. An increase in the incidence of pituitary gland, mammary gland, and pancreatic islet cell neoplasia (mammary adenocarcinomas, pituitary and pancreatic adenomas) was observed in the risperidone carcinogenicity studies conducted in mice and rats [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)]. Neither clinical studies nor epidemiologic studies conducted to date have shown an association between chronic administration of this class of drugs and tumorigenesis in humans, but the available evidence is too limited to be conclusive.
Prolactin data from two long-term, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies with INVEGA SUSTENNA® are presented below; one study was in a population of patients with schizophrenia; the second study was in patients with schizoaffective disorder.
5.11 Potential for Cognitive and Motor Impairment
Somnolence, sedation, and dizziness were reported as adverse reactions in subjects treated with INVEGA SUSTENNA® [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Antipsychotics, including INVEGA SUSTENNA®, have the potential to impair judgment, thinking, or motor skills. Patients should be cautioned about performing activities requiring mental alertness, such as operating hazardous machinery or operating a motor vehicle, until they are reasonably certain that paliperidone therapy does not adversely affect them.
5.12 Seizures
In the four fixed-dose double-blind placebo-controlled studies in subjects with schizophrenia, <1% (1/1293) of subjects treated with INVEGA SUSTENNA® in the recommended dose range of 39 mg to 234 mg experienced an adverse event of convulsion compared with <1% (1/510) of placebo-treated subjects who experienced an adverse event of grand mal convulsion.
Like other antipsychotic drugs, INVEGA SUSTENNA® should be used cautiously in patients with a history of seizures or other conditions that potentially lower the seizure threshold. Conditions that lower the seizure threshold may be more prevalent in patients 65 years or older.
5.13 Dysphagia
Esophageal dysmotility and aspiration have been associated with antipsychotic drug use. INVEGA SUSTENNA® and other antipsychotic drugs should be used cautiously in patients at risk for aspiration pneumonia.
5.14 Priapism
Drugs with alpha-adrenergic blocking effects have been reported to induce priapism. Although no cases of priapism have been reported in clinical trials with INVEGA SUSTENNA®, priapism has been reported with oral paliperidone during postmarketing surveillance. Severe priapism may require surgical intervention.
5.15 Disruption of Body Temperature Regulation
Disruption of the body's ability to reduce core body temperature has been attributed to antipsychotic agents. Appropriate care is advised when prescribing INVEGA SUSTENNA® to patients who will be experiencing conditions which may contribute to an elevation in core body temperature, e.g., exercising strenuously, exposure to extreme heat, receiving concomitant medication with anticholinergic activity, or being subject to dehydration.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following are discussed in more detail in other sections of the labeling:
- Increased mortality in elderly patients with dementia-related psychosis [see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Cerebrovascular adverse reactions, including stroke, in elderly patients with dementia-related psychosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Neuroleptic malignant syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- QT prolongation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Tardive dyskinesia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Metabolic changes [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Orthostatic hypotension and syncope [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- Falls [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
- Leukopenia, neutropenia, and agranulocytosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]
- Hyperprolactinemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)]
- Potential for cognitive and motor impairment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)]
- Seizures [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12)]
- Dysphagia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.13)]
- Priapism [see Warnings and Precautions (5.14)]
- Disruption of body temperature regulation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.15)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval use of paliperidone; because these reactions were reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure: angioedema, catatonia, ileus, somnambulism, swollen tongue, thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura, urinary incontinence, and urinary retention.
Cases of anaphylactic reaction after injection with INVEGA SUSTENNA® have been reported during postmarketing experience in patients who have previously tolerated oral risperidone or oral paliperidone.
Paliperidone is the major active metabolite of risperidone. Adverse reactions reported with oral risperidone and risperidone long-acting injection can be found in the Adverse Reactions (6) sections of the package inserts for those products.
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 Drugs Having Clinically Important Interactions with INVEGA SUSTENNA®
Because paliperidone palmitate is hydrolyzed to paliperidone [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)], results from studies with oral paliperidone should be taken into consideration when assessing drug-drug interaction potential.
| Concomitant Drug Name or Drug Class | Clinical Rationale | Clinical Recommendation |
|---|---|---|
| Centrally Acting Drugs and Alcohol | Given the primary CNS effects of paliperidone, concomitant use of centrally acting drugs and alcohol may modulate the CNS effects of INVEGA SUSTENNA®. | INVEGA SUSTENNA® should be used with caution in combination with other centrally acting drugs and alcohol [see Adverse Reactions (6.1, 6.2)]. |
| Drugs with Potential for Inducing Orthostatic Hypotension | Because INVEGA SUSTENNA® has the potential for inducing orthostatic hypotension, an additive effect may occur when INVEGA SUSTENNA® is administered with other therapeutic agents that have this potential [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]. | Monitor orthostatic vital signs in patients who are vulnerable to hypotension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]. |
| Strong Inducers of CYP3A4 and P-gp (e.g., carbamazepine, rifampin, or St. John's Wort) | The concomitant use of paliperidone and strong inducers of CYP3A4 and P-gp may decrease the exposure of paliperidone [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. | Avoid using CYP3A4 and/or P-gp inducers with INVEGA SUSTENNA® during the 1-month dosing interval, if possible. If administering a strong inducer is necessary, consider managing the patient using paliperidone extended-release tablets [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)]. |
| Levodopa and Other Dopamine Agonists | Paliperidone may antagonize the effect of levodopa and other dopamine agonists. | Monitor and manage patient as clinically appropriate. |
7.2 Drugs Having No Clinically Important Interactions with INVEGA SUSTENNA®
Clinically meaningful pharmacokinetic interaction between INVEGA SUSTENNA® and valproate (including valproic acid and divalproex sodium) is not expected. Based on pharmacokinetic studies with oral paliperidone, no dosage adjustment of INVEGA SUSTENNA® is required when administered with valproate [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Additionally, no dosage adjustment is necessary for valproate when co-administered with INVEGA SUSTENNA® [See Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Pharmacokinetic interaction between lithium and INVEGA SUSTENNA® is also unlikely.
Paliperidone is not expected to cause clinically important pharmacokinetic interactions with drugs that are metabolized by cytochrome P450 isozymes. In vitro studies indicate that CYP2D6 and CYP3A4 may be involved in paliperidone metabolism; however, there is no evidence in vivo that inhibitors of these enzymes significantly affect the metabolism of paliperidone. Paliperidone is not a substrate of CYP1A2, CYP2A6, CYP2C9, and CYP2C19; an interaction with inhibitors or inducers of these isozymes is unlikely. [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Data
Animal Data
There were no treatment-related effects on the offspring when pregnant rats were injected intramuscularly with paliperidone palmitate extended-release injectable suspension during the period of organogenesis at doses up to 250 mg/kg, which is 10 times MRHD of 234 mg paliperidone based on mg/m2 body surface area.
In animal reproduction studies, there were no increases in fetal abnormalities when pregnant rats and rabbits were treated orally with paliperidone during the period of organogenesis with up to 8 times the MRHD of 12 mg based on mg/m2 body surface area.
Additional reproduction toxicity studies were conducted with orally administered risperidone, which is extensively converted to paliperidone. Cleft palate was observed in the offspring of pregnant mice treated with risperidone at 3 to 4 times the MRHD of 16 mg based on mg/m2 body surface area; maternal toxicity occurred at 4 times the MHRD. There was no evidence of teratogenicity in embryo-fetal developmental toxicity studies with risperidone in rats and rabbits at doses up to 6 times the MRHD of 16 mg/day risperidone based on mg/m2 body surface area. When the offspring of pregnant rats, treated with risperidone at 0.6 times the MRHD based on mg/m2 body surface area, reached adulthood, learning was impaired. Increased neuronal cell death occurred in the fetal brains of the offspring of pregnant rats treated at 0.5 to 1.2 times the MRHD; the postnatal development and growth of the offspring was delayed.
In rat reproduction studies with risperidone, pup deaths occurred at oral doses which are less than the MRHD of risperidone based on mg/m2 body surface area; it is not known whether these deaths were due to a direct effect on the fetuses or pups or, to effects on the dams (see RISPERDAL® package insert).
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of INVEGA SUSTENNA® in patients < 18 years of age have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of INVEGA SUSTENNA® did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients.
This drug is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney and clearance is decreased in patients with renal impairment [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)], who should be given reduced doses. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, adjust dose based on renal function [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)].
8.6 Renal Impairment
Use of INVEGA SUSTENNA® is not recommended in patients with moderate or severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance < 50 mL/min). Dose reduction is recommended for patients with mild renal impairment (creatinine clearance ≥ 50 mL/min to < 80 mL/min) [see Dosage and Administration (2.5) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
INVEGA SUSTENNA® has not been studied in patients with hepatic impairment. Based on a study with oral paliperidone, no dose adjustment is required in patients with mild or moderate hepatic impairment. Paliperidone has not been studied in patients with severe hepatic impairment [Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.8 Patients with Parkinson's Disease or Lewy Body Dementia
Patients with Parkinson's Disease or Dementia with Lewy Bodies can experience increased sensitivity to INVEGA SUSTENNA®. Manifestations can include confusion, obtundation, postural instability with frequent falls, extrapyramidal symptoms, and clinical features consistent with neuroleptic malignant syndrome.
9. Drug Abuse and Dependence
10. Overdosage
10.1 Human Experience
No cases of overdose were reported in premarketing studies with INVEGA SUSTENNA®. Because INVEGA SUSTENNA® is to be administered by healthcare professionals, the potential for overdosage by patients is low.
While experience with paliperidone overdose is limited, among the few cases of overdose reported in premarketing trials with oral paliperidone, the highest estimated ingestion was 405 mg. Observed signs and symptoms included extrapyramidal symptoms and gait unsteadiness. Other potential signs and symptoms include those resulting from an exaggeration of paliperidone's known pharmacological effects, i.e., drowsiness and sedation, tachycardia and hypotension, and QT prolongation. Torsades de pointes and ventricular fibrillation have been reported in a patient in the setting of overdose with oral paliperidone.
Paliperidone is the major active metabolite of risperidone. Overdose experience reported with risperidone can be found in the OVERDOSAGE section of the risperidone package insert.
10.2 Management of Overdosage
Contact a Certified Poison Control Center for the most up to date information on the management of INVEGA SUSTENNA® overdosage (1-800-222-1222 or www.poison.org). Provide supportive care, including close medical supervision and monitoring. Treatment should consist of general measures employed in the management of overdosage with any drug. Consider the possibility of multiple drug overdosage. Ensure an adequate airway, oxygenation, and ventilation. Monitor cardiac rhythm and vital signs. Use supportive and symptomatic measures. There is no specific antidote to paliperidone.
Consider the prolonged-release characteristics of INVEGA SUSTENNA® and the long apparent half-life of paliperidone when assessing treatment needs and recovery.
11. Invega Sustenna Description
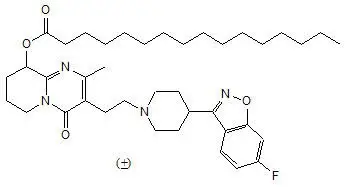
INVEGA SUSTENNA® contains paliperidone palmitate. The active ingredient, paliperidone, is an atypical antipsychotic belonging to the chemical class of benzisoxazole derivatives. INVEGA SUSTENNA® contains a racemic mixture of (+)- and (-)- paliperidone palmitate. The chemical name is (9RS)-3-[2-[4-(6-Fluoro-1,2-benzisoxazol-3-yl)piperidin-1-yl]ethyl]-2-methyl-4-oxo-6,7,8,9-tetrahydro-4H-pyrido[1,2-a]pyrimadin-9-yl hexadecanoate. Its molecular formula is C39H57FN4O4 and its molecular weight is 664.89. The structural formula is:
Paliperidone palmitate is very slightly soluble in ethanol and methanol, practically insoluble in polyethylene glycol 400 and propylene glycol, and slightly soluble in ethyl acetate.
INVEGA SUSTENNA® is available as a white to off-white sterile aqueous extended-release suspension for intramuscular injection in the following dose strengths of paliperidone palmitate (and deliverable volumes) of the single-dose prefilled syringes: 39 mg (0.25 mL), 78 mg (0.5 mL), 117 mg (0.75 mL), 156 mg (1.0 mL), and 234 mg (1.5 mL). The drug product hydrolyzes to the active moiety, paliperidone, resulting in dose strengths of 25 mg, 50 mg, 75 mg, 100 mg, and 150 mg of paliperidone, respectively. The inactive ingredients are polysorbate 20 (12 mg/mL), polyethylene glycol 4000 (30 mg/mL), citric acid monohydrate (5 mg/mL), disodium hydrogen phosphate anhydrous (5 mg/mL), sodium dihydrogen phosphate monohydrate (2.5 mg/mL), sodium hydroxide (2.84 mg/mL used as an alkalizing agent to set pH at 7), and water for injection.
INVEGA SUSTENNA® is provided in a single-dose prefilled syringe (cyclic-olefin-copolymer) with a plunger stopper and tip cap (bromobutyl rubber). The kit also contains 2 safety needles (a 1 ½-inch 22 gauge safety needle and a 1-inch 23 gauge safety needle).
12. Invega Sustenna - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Paliperidone palmitate is hydrolyzed to paliperidone [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Paliperidone is the major active metabolite of risperidone. The mechanism of action of paliperidone is unclear. However, the drug's therapeutic effect in schizophrenia could be mediated through a combination of central dopamine Type 2 (D2) and serotonin Type 2 (5HT2A) receptor antagonism.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
In vitro, paliperidone acts as an antagonist at the central dopamine Type 2 (D2) and serotonin Type 2 (5HT2A) receptors with binding affinities (Ki values) of 1.6–2.8 nM for D2 and 0.8–1.2 nM for 5HT2A receptors. Paliperidone is also active as an antagonist at the α1 and α2 adrenergic receptors and H1 histaminergic receptors, which may explain some of the other effects of the drug. Paliperidone has no affinity for cholinergic muscarinic or β1- and β2-adrenergic receptors. The pharmacological activity of the (+)- and (-)- paliperidone enantiomers is qualitatively and quantitatively similar in vitro.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Drug Interaction Studies
No specific drug interaction studies have been performed with INVEGA SUSTENNA®. The information below is obtained from studies with oral paliperidone.
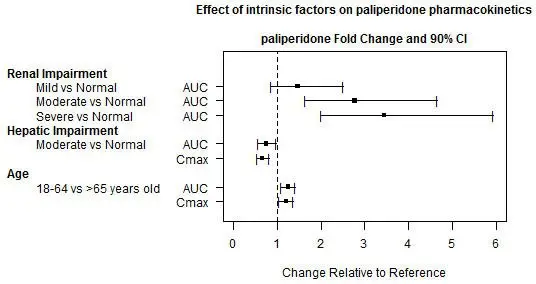
Effects of other drugs on the exposures of paliperidone are summarized in Figure 1. After oral administration of 20 mg/day of paroxetine (a potent CYP2D6 inhibitor), an increase in mean Cmax and AUC values at steady-state was observed (see Figure 1). Higher doses of paroxetine have not been studied. The clinical relevance is unknown. After oral administration, a decrease in mean Cmax and AUC values at steady state is expected when patients are treated with carbamazepine, a strong inducer of both CYP3A4 and P-gp [see Drug Interactions (7.1)]. This decrease is caused, to a substantial degree, by a 35% increase in renal clearance of paliperidone.
Figure 1: The effects of other drugs on paliperidone pharmacokinetics.
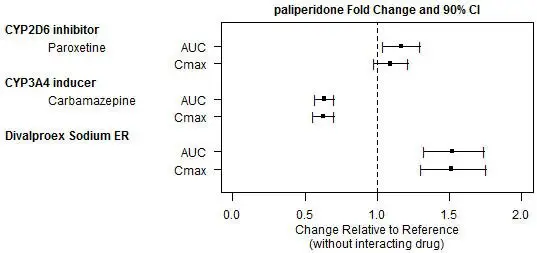
Clinically meaningful pharmacokinetic interaction between INVEGA SUSTENNA® and valproate (including valproic acid and divalproex sodium) is not expected. Oral administration of divalproex sodium extended-release tablets (two 500 mg tablets once daily at steady-state) with oral paliperidone extended-release tablets resulted in an increase of approximately 50% in the Cmax and AUC of paliperidone.
After oral administration of paliperidone, the steady-state Cmax and AUC of divalproex sodium extended-release tablets were not affected in 13 patients stabilized on divalproex sodium extended-release tablets. In a clinical study, subjects on stable doses of divalproex sodium extended-release tablets had comparable valproate average plasma concentrations when oral paliperidone extended-release tablets 3–15 mg/day was added to their existing divalproex sodium extended-release tablets treatment [see Drug Interactions (7.2)].
In vitro studies indicate that CYP2D6 and CYP3A4 may be involved in paliperidone metabolism, however, there is no evidence in vivo that inhibitors of these enzymes significantly affect the metabolism of paliperidone; they contribute to only a small fraction of total body clearance. In vitro studies demonstrated that paliperidone is a substrate of P-glycoprotein (P-gp) [see Drug Interactions (7.2)].
In vitro studies in human liver microsomes demonstrated that paliperidone does not substantially inhibit the metabolism of drugs metabolized by cytochrome P450 isozymes, including CYP1A2, CYP2A6, CYP2C8/9/10, CYP2D6, CYP2E1, CYP3A4, and CYP3A5. Therefore, paliperidone is not expected to inhibit clearance of drugs that are metabolized by these metabolic pathways in a clinically relevant manner. Paliperidone is also not expected to have enzyme inducing properties.
Paliperidone is a weak inhibitor of P-gp at high concentrations. No in vivo data are available, and the clinical relevance is unknown.
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
Injection site toxicity was assessed in minipigs injected intramuscularly with the 3-month paliperidone palmitate extended-release injectable suspension at doses up to 819 mg, which is equal to the MRHD. Injection site inflammatory reactions were greater and more advanced than reactions to the 1-month paliperidone palmitate extended-release injectable suspension. Reversibility of these findings was not examined.
16. How is Invega Sustenna supplied
INVEGA SUSTENNA® is available as a white to off-white sterile aqueous extended-release suspension for intramuscular injection in dose strengths of 39 mg/0.25 mL, 78 mg/0.5 mL, 117 mg/0.75 mL, 156 mg/mL, and 234 mg/1.5 mL paliperidone palmitate in single-dose prefilled syringes. The single-use kit contains a prefilled syringe and 2 safety needles (a 1 ½-inch 22 gauge safety needle and a 1-inch 23 gauge safety needle).
| 39 mg paliperidone palmitate kit | (NDC 50458-560-01) |
| 78 mg paliperidone palmitate kit | (NDC 50458-561-01) |
| 117 mg paliperidone palmitate kit | (NDC 50458-562-01) |
| 156 mg paliperidone palmitate kit | (NDC 50458-563-01) |
| 234 mg paliperidone palmitate kit | (NDC 50458-564-01) |
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
|
PATIENT INFORMATION |
|
|
What is the most important information I should know about INVEGA SUSTENNA®? INVEGA SUSTENNA® can cause serious side effects, including:
|
|
|
What is INVEGA SUSTENNA®? INVEGA SUSTENNA® is a prescription medicine given by injection by a healthcare professional and used to treat: |
|
|
|
|
It is not known if INVEGA SUSTENNA® is safe and effective in children under 18 years of age. |
|
|
Who should not receive INVEGA SUSTENNA®? Do not receive INVEGA SUSTENNA® if you:
|
|
|
What should I tell my healthcare provider before receiving INVEGA SUSTENNA®? Before you receive INVEGA SUSTENNA®, tell your healthcare provider about all your medical conditions, including if you:
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them to show to your healthcare provider or pharmacist when you get a new medicine. |
|
|
How will I receive INVEGA SUSTENNA®?
|
|
|
What should I avoid while receiving INVEGA SUSTENNA®?
|
|
|
What are the possible side effects of INVEGA SUSTENNA®? INVEGA SUSTENNA® may cause serious side effects, including:
|
|
|
The most common side effects of INVEGA SUSTENNA® include: injection site reactions, sleepiness or drowsiness, dizziness, feeling restlessness or needing to be constantly moving, abnormal muscle movements including tremor (shaking), shuffling, uncontrolled involuntary movements, and abnormal movements of your eyes. Tell your healthcare provider if you have any side effect that bothers you or does not go away. These are not all the possible side effects of INVEGA SUSTENNA®. For more information, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. |
|
|
General information about the safe and effective use of INVEGA SUSTENNA®. Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use INVEGA SUSTENNA® for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give INVEGA SUSTENNA® to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about INVEGA SUSTENNA® that is written for healthcare professionals. This Patient Information leaflet summarizes the most important information about INVEGA SUSTENNA®. If you would like more information, talk with your healthcare provider. You can ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for more information that is written for healthcare professionals. For more information, go to www.invegasustenna.com or call 1-800-526-7736. |
|
|
What are the ingredients in INVEGA SUSTENNA®? Active ingredient: paliperidone palmitate Inactive ingredients: polysorbate 20, polyethylene glycol 4000, citric acid monohydrate, sodium dihydrogen phosphate monohydrate, sodium hydroxide, and water for injection Revised: 07/2018 Manufactured by: Janssen Pharmaceutica NV, Beerse, Belgium |
|
| INVEGA SUSTENNA
paliperidone palmitate injection |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| INVEGA SUSTENNA
paliperidone palmitate injection |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| INVEGA SUSTENNA
paliperidone palmitate injection |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| INVEGA SUSTENNA
paliperidone palmitate injection |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| INVEGA SUSTENNA
paliperidone palmitate injection |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (063137772) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Janssen Pharmaceutical Sciences Unlimited Company | 985639841 | API MANUFACTURE(50458-560, 50458-561, 50458-562, 50458-563, 50458-564) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Janssen Pharmaceutica, NV | 370005019 | MANUFACTURE(50458-560, 50458-561, 50458-562, 50458-563, 50458-564) , ANALYSIS(50458-560, 50458-561, 50458-562, 50458-563, 50458-564) | |