Drug Detail:Kaletra (Lopinavir and ritonavir [ loe-pin-a-vir-and-ri-toe-na-veer ])
Drug Class: Protease inhibitors
Highlights of Prescribing Information
KALETRA (lopinavir and ritonavir) tablet, for oral use
KALETRA (lopinavir and ritonavir) oral solution
Initial U.S. Approval: 2000
Recent Major Changes
Indications and Usage for Kaletra
KALETRA is an HIV-1 protease inhibitor indicated in combination with other antiretroviral agents for the treatment of HIV-1 infection in adults and pediatric patients (14 days and older). (1)
Kaletra Dosage and Administration
Tablets: May be taken with or without food, swallowed whole and not chewed, broken, or crushed. (2.1)
Oral solution: must be taken with food. (2.1)
KALETRA oral solution is not recommended for use with polyurethane feeding tubes due to potential incompatibility. Feeding tubes composed of silicone or polyvinyl chloride (PVC) can be used. (2.2)
Adults (2.3):
- Total recommended daily dosage is 800/200 mg given once or twice daily.
- KALETRA can be given as once daily or twice daily regimen. See Full Prescribing Information for details.
- KALETRA once daily dosing regimen is not recommended in:
- Adult patients with three or more of the following lopinavir resistance-associated substitutions: L10F/I/R/V, K20M/N/R, L24I, L33F, M36I, I47V, G48V, I54L/T/V, V82A/C/F/S/T, and I84V. (12.4)
- In combination with carbamazepine, phenobarbital, or phenytoin. (7.3)
- In combination with efavirenz, nevirapine, or nelfinavir. (12.3)
- In pregnant women. (2.5, 8.1, 12.3)
Pediatric Patients (14 days and older) (2.4):
- KALETRA once daily dosing regimen is not recommended in pediatric patients.
- Twice daily dose is based on body weight or body surface area.
Concomitant Therapy in Adults and Pediatric Patients:
- Dose adjustments of KALETRA may be needed when co-administering with efavirenz, nevirapine, or nelfinavir. (2.3, 2.4, 7.3)
- KALETRA oral solution should not be administered to neonates before a postmenstrual age (first day of the mother’s last menstrual period to birth plus the time elapsed after birth) of 42 weeks and a postnatal age of at least 14 days has been attained (2.4, 5.2)
Pregnancy (2.5):
- 400/100 mg twice daily in pregnant patients with no documented lopinavir-associated resistance substitutions.
- There are insufficient data to recommend a KALETRA dose for pregnant patients with any documented KALETRA-associated resistance substitutions.
- No dose adjustment of KALETRA is required for patients during the postpartum period.
Dosage Forms and Strengths
- Tablets: 200 mg lopinavir and 50 mg ritonavir (3)
- Tablets: 100 mg lopinavir and 25 mg ritonavir (3)
- Oral solution: 80 mg lopinavir and 20 mg ritonavir per milliliter (3)
Contraindications
- Hypersensitivity to KALETRA (e.g., toxic epidermal necrolysis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, erythema multiforme, urticaria, angioedema) or any of its ingredients, including ritonavir. (4)
- Co-administration with drugs highly dependent on CYP3A for clearance and for which elevated plasma levels may result in serious and/or life-threatening events. (4)
- Co-administration with potent CYP3A inducers where significantly reduced lopinavir plasma concentrations may be associated with the potential for loss of virologic response and possible resistance and cross resistance. (4)
Warnings and Precautions
The following have been observed in patients receiving KALETRA:
- The concomitant use of KALETRA and certain other drugs may result in known or potentially significant drug interactions. Consult the full prescribing information prior to and during treatment for potential drug interactions. (5.1, 7.3)
- Toxicity in preterm neonates: KALETRA oral solution should not be used in preterm neonates in the immediate postnatal period because of possible toxicities. A safe and effective dose of KALETRA oral solution in this patient population has not been established. (2.4, 5.2)
- Pancreatitis: Fatalities have occurred; suspend therapy as clinically appropriate. (5.3)
- Hepatotoxicity: Fatalities have occurred. Monitor liver function before and during therapy, especially in patients with underlying hepatic disease, including hepatitis B and hepatitis C, or marked transaminase elevations. (5.4, 8.6)
- QT interval prolongation and isolated cases of torsade de pointes have been reported although causality could not be established. Avoid use in patients with congenital long QT syndrome, those with hypokalemia, and with other drugs that prolong the QT interval. (5.1, 5.5, 12.3)
- PR interval prolongation may occur in some patients. Cases of second and third degree heart block have been reported. Use with caution in patients with pre-existing conduction system disease, ischemic heart disease, cardiomyopathy, underlying structural heart disease or when administering with other drugs that may prolong the PR interval. (5.1, 5.6, 12.3)
- Patients may develop new onset or exacerbations of diabetes mellitus, hyperglycemia (5.7), immune reconstitution syndrome. (5.8), redistribution/accumulation of body fat. (5.10)
- Total cholesterol and triglycerides elevations. Monitor prior to therapy and periodically thereafter. (5.9)
- Hemophilia: Spontaneous bleeding may occur, and additional factor VIII may be required. (5.11)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Commonly reported adverse reactions to KALETRA included diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, hypertriglyceridemia and hypercholesterolemia. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact AbbVie Inc. at 1-800-633-9110 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch
Drug Interactions
Co-administration of KALETRA can alter the plasma concentrations of other drugs and other drugs may alter the plasma concentrations of lopinavir. The potential for drug-drug interactions must be considered prior to and during therapy. (4, 5.1, 7, 12.3)
Use In Specific Populations
Lactation: Breastfeeding not recommended. (8.2)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 12/2019
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Kaletra
- Genotypic or phenotypic testing and/or treatment history should guide the use of KALETRA. The number of baseline lopinavir resistance-associated substitutions affects the virologic response to KALETRA [see Microbiology (12.4)].
2. Kaletra Dosage and Administration
2.3 Dosage Recommendations in Adults
- Adult patients with three or more of the following lopinavir resistance-associated substitutions: L10F/I/R/V, K20M/N/R, L24I, L33F, M36I, I47V, G48V, I54L/T/V, V82A/C/F/S/T, and I84V [see Microbiology (12.4)].
- In combination with carbamazepine, phenobarbital, or phenytoin [see Drug Interactions (7.3)].
- In combination with efavirenz, nevirapine, or nelfinavir [see Drug Interactions (7.3) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
- In pediatric patients younger than 18 years of age [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
- In pregnant women [see Dosage and Administration (2.5), Use in Specific Populations (8.1) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
| KALETRA Dosage Form | Recommended Dosage |
| 200 mg/50 mg Tablets | 800 mg/200 mg (4 tablets) once daily |
| 80 mg/20 mg per mL Oral Solution | 800 mg/200 mg (10 mL) once daily |
| KALETRA Dosage Form | Recommended Dosage |
| 200 mg/50 mg Tablets | 400 mg/100 mg (2 tablets) twice daily |
| 80 mg/20 mg per mL Oral Solution | 400 mg/100 mg (5 mL) twice daily |
| KALETRA Dosage Form | Recommended Dosage |
| 200 mg/50 mg Tablets and 100 mg/25 mg Tablets | 500 mg/125 mg (2 tablets of 200 mg/50 mg + 1 tablet of 100 mg/25 mg) twice daily |
| 80 mg/20 mg per mL Oral Solution | 520 mg/130 mg (6.5 mL) twice daily |
2.4 Dosage Recommendations in Pediatric Patients
Body surface area (BSA) can be calculated as follows:
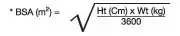
The KALETRA dose can be calculated based on weight or BSA:
Patient Weight (kg) × Prescribed lopinavir dose (mg/kg) = Administered lopinavir dose (mg)
Patient BSA (m2) × Prescribed lopinavir dose (mg/m2) = Administered lopinavir dose (mg)
If KALETRA oral solution is used, the volume (mL) of KALETRA solution can be determined as follows:
Volume of KALETRA solution (mL) = Administered lopinavir dose (mg) ÷ 80 (mg/mL)
Oral Solution Dosage Recommendation in Pediatric Patients 14 Days to Less Than 18 Years:
| Patient Age | Based on Weight (mg/kg) | Based on BSA (mg/m2) | Frequency | |
| 14 days to 6 months | 16/4 | 300/75 | Given twice daily |
|
| Older than 6 months to less than 18 years | Less than15 kg | 12/3 | 230/57.5 | Given twice daily |
| 15 kg to 40 kg | 10/2.5 | |||
Tablet Dosage Recommendation in Pediatric Patients Older than 6 Months to Less than 18 Years:
| Body Weight (kg) | Body Surface Area (m2)* | Recommended number of 100/25 mg Tablets Twice Daily |
| ≥15 to 25 | ≥0.6 to < 0.9 | 2 |
| >25 to 35 | ≥0.9 to < 1.4 | 3 |
| >35 | ≥1.4 | 4 |
| * KALETRA oral solution is available for children with a BSA less than 0.6 m2 or those who are unable to reliably swallow a tablet. | ||
Concomitant Therapy: Efavirenz, Nevirapine, or Nelfinavir
| Patient Age | Based on Weight (mg/kg) | Based on BSA (mg/m2) | Frequency | |
| > 6 months to < 18 years | <15 kg | 13/3.25 | 300/75 | Given twice daily |
| ≥15 kg to 45 kg | 11/2.75 | |||
| Body Weight (kg) | Body Surface Area (m2)* | Recommended number of
100/25 mg Tablets Twice Daily |
| ≥15 to 20 | ≥0.6 to < 0.8 | 2 |
| >20 to 30 | ≥0.8 to < 1.2 | 3 |
| >30 to 45 | ≥1.2 to <1.7 | 4 |
| >45 | ≥1.7 | 5 [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)] |
| * KALETRA oral solution is available for children with a BSA less than 0.6 m2 or those who are unable to reliably swallow a tablet. † Please refer to the individual product labels for appropriate dosing in children. |
||
2.5 Dosage Recommendations in Pregnancy
- Once daily KALETRA dosing is not recommended in pregnancy [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
- There are insufficient data to recommend dosing in pregnant women with any documented lopinavir-associated resistance substitutions.
- No dosage adjustment of KALETRA is required for patients during the postpartum period.
- Avoid use of KALETRA oral solution in pregnant women [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
- Tablets:
- 200 mg lopinavir, 50 mg ritonavir: Yellow, film-coated, ovaloid, debossed with the “a” logo and the code KA containing 200 mg lopinavir and 50 mg ritonavir.
- Tablets, 100 mg lopinavir, 25 mg ritonavir: Pale yellow, film-coated, ovaloid, debossed with the “a” logo and the code KC containing 100 mg lopinavir and 25 mg ritonavir.
- Oral Solution: Light yellow to orange colored liquid containing 400 mg lopinavir and 100 mg ritonavir per 5 mL (80 mg lopinavir and 20 mg ritonavir per mL).
4. Contraindications
- KALETRA is contraindicated in patients with previously demonstrated clinically significant hypersensitivity (e.g., toxic epidermal necrolysis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, erythema multiforme, urticaria, angioedema) to any of its ingredients, including ritonavir.
- KALETRA is contraindicated with drugs that are highly dependent on CYP3A for clearance and for which elevated plasma concentrations are associated with serious and/or life-threatening reactions [see Drug Interactions (7.1) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
- Alpha 1- Adrenoreceptor Antagonist : alfuzosin
- Antianginal: ranolazine
- Antiarrhythmic: dronedarone
- Anti-gout: colchicine
- Antipsychotics: lurasidone, pimozide
- Ergot Derivatives: dihydroergotamine, ergotamine, methylergonovine
- GI Motility Agent: cisapride
- Hepatitis C direct acting antiviral: elbasvir/grazoprevir
- HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitors: lovastatin, simvastatin
- Microsomal triglyceride transfer protein (MTTP) Inhibitor: lomitapide
- PDE5 Inhibitor: sildenafil (Revatio®) when used for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension
- Sedative/Hypnotics: triazolam, orally administered midazolam
- KALETRA is contraindicated with drugs that are potent CYP3A inducers where significantly reduced lopinavir plasma concentrations may be associated with the potential for loss of virologic response and possible resistance and cross-resistance [see Drug Interactions (7.2) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
- Anticancer Agents: apalutamide
- Antimycobacterial: rifampin
- Herbal Products: St. John's Wort (hypericum perforatum)
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Risk of Serious Adverse Reactions Due to Drug Interactions
- Clinically significant adverse reactions, potentially leading to severe, life-threatening, or fatal events from greater exposures of concomitant medications.
- Clinically significant adverse reactions from greater exposures of KALETRA.
- Loss of therapeutic effect of KALETRA and possible development of resistance.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the labeling.
- QT Interval Prolongation, PR Interval Prolongation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5, 5.6)]
- Drug Interactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Pancreatitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
| System Organ Class (SOC) and Adverse Reaction | n | % | |
| BLOOD AND LYMPHATIC SYSTEM DISORDERS | |||
| anemia* | 54 | 2.1 | |
| leukopenia and neutropenia* | 44 | 1.7 | |
| lymphadenopathy* | 35 | 1.3 | |
| CARDIAC DISORDERS | |||
| atherosclerosis such as myocardial infarction* | 10 | 0.4 | |
| atrioventricular block* | 3 | 0.1 | |
| tricuspid valve incompetence* | 3 | 0.1 | |
| EAR AND LABYRINTH DISORDERS | |||
| vertigo* | 7 | 0.3 | |
| tinnitus | 6 | 0.2 | |
| ENDOCRINE DISORDERS | |||
| hypogonadism* | 16 | 0.81 | |
| EYE DISORDERS | |||
| visual impairment* | 8 | 0.3 | |
| GASTROINTESTINAL DISORDERS | |||
| diarrhea* | 510 | 19.5 | |
| nausea | 269 | 10.3 | |
| vomiting* | 177 | 6.8 | |
| abdominal pain (upper and lower)* | 160 | 6.1 | |
| gastroenteritis and colitis* | 66 | 2.5 | |
| dyspepsia | 53 | 2.0 | |
| pancreatitis* | 45 | 1.7 | |
| Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)* | 40 | 1.5 | |
| hemorrhoids | 39 | 1.5 | |
| flatulence | 36 | 1.4 | |
| abdominal distension | 34 | 1.3 | |
| constipation* | 26 | 1.0 | |
| stomatitis and oral ulcers* | 24 | 0.9 | |
| duodenitis and gastritis* | 20 | 0.8 | |
| gastrointestinal hemorrhage including rectal hemorrhage* | 13 | 0.5 | |
| dry mouth | 9 | 0.3 | |
| gastrointestinal ulcer* | 6 | 0.2 | |
| fecal incontinence | 5 | 0.2 | |
| GENERAL DISORDERS AND ADMINISTRATION SITE CONDITIONS | |||
| fatigue including asthenia* | 198 | 7.6 | |
| HEPATOBILIARY DISORDERS | |||
| hepatitis including AST, ALT, and GGT increases* | 91 | 3.5 | |
| hepatomegaly | 5 | 0.2 | |
| cholangitis | 3 | 0.1 | |
| hepatic steatosis | 3 | 0.1 | |
| IMMUNE SYSTEM DISORDERS | |||
| hypersensitivity including urticaria and angioedema* | 70 | 2.7 | |
| immune reconstitution syndrome | 3 | 0.1 | |
| INFECTIONS AND INFESTATIONS | |||
| upper respiratory tract infection* | 363 | 13.9 | |
| lower respiratory tract infection* | 202 | 7.7 | |
| skin infections including cellulitis, folliculitis, and furuncle* | 86 | 3.3 | |
| METABOLISM AND NUTRITION DISORDERS | |||
| hypercholesterolemia* | 192 | 7.4 | |
| hypertriglyceridemia* | 161 | 6.2 | |
| weight decreased* | 61 | 2.3 | |
| decreased appetite | 52 | 2.0 | |
| blood glucose disorders including diabetes mellitus* | 30 | 1.1 | |
| weight increased* | 20 | 0.8 | |
| lactic acidosis* | 11 | 0.4 | |
| increased appetite | 5 | 0.2 | |
| MUSCULOSKELETAL AND CONNECTIVE TISSUE DISORDERS | |||
| musculoskeletal pain including arthralgia and back pain* | 166 | 6.4 | |
| myalgia* | 46 | 1.8 | |
| muscle disorders such as weakness and spasms* | 34 | 1.3 | |
| rhabdomyolysis* | 18 | 0.7 | |
| osteonecrosis | 3 | 0.1 | |
| NERVOUS SYSTEM DISORDERS | |||
| headache including migraine* | 165 | 6.3 | |
| insomnia* | 99 | 3.8 | |
| neuropathy and peripheral neuropathy* | 51 | 2.0 | |
| dizziness* | 45 | 1.7 | |
| ageusia* | 19 | 0.7 | |
| convulsion* | 9 | 0.3 | |
| tremor* | 9 | 0.3 | |
| cerebral vascular event* | 6 | 0.2 | |
| PSYCHIATRIC DISORDERS | |||
| anxiety* | 101 | 3.9 | |
| abnormal dreams* | 19 | 0.7 | |
| libido decreased | 19 | 0.7 | |
| RENAL AND URINARY DISORDERS | |||
| renal failure* | 31 | 1.2 | |
| hematuria* | 20 | 0.8 | |
| nephritis* | 3 | 0.1 | |
| REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM AND BREAST DISORDERS | |||
| erectile dysfunction* | 34 | 1.71 | |
| menstrual disorders - amenorrhea, menorrhagia* | 10 | 1.72 | |
| SKIN AND SUBCUTANEOUS TISSUE DISORDERS | |||
| rash including maculopapular rash* | 99 | 3.8 | |
| lipodystrophy acquired including facial wasting* | 58 | 2.2 | |
| dermatitis/rash including eczema and seborrheic dermatitis* | 50 | 1.9 | |
| night sweats* | 42 | 1.6 | |
| pruritus* | 29 | 1.1 | |
| alopecia | 10 | 0.4 | |
| capillaritis and vasculitis* | 3 | 0.1 | |
| VASCULAR DISORDERS | |||
| hypertension* | 47 | 1.8 | |
| deep vein thrombosis* | 17 | 0.7 | |
| *Represents a medical concept including several similar MedDRA PTs 1. Percentage of male population (N=2,038) 2. Percentage of female population (N=574) |
|||
| Study 863
(48 Weeks) | Study 720
(360 Weeks) | Study 730
(48 Weeks) |
||||
| Variable | Limit1 | KALETRA
400/100 mg Twice Daily + d4T +3TC (N = 326) | Nelfinavir
750 mg Three Times Daily + d4T + 3TC (N = 327) | KALETRA
Twice Daily + d4T + 3TC (N = 100) | KALETRA
Once Daily + TDF +FTC (N=333) | KALETRA
Twice Daily + TDF +FTC (N=331) |
| Chemistry | High | |||||
| Glucose | > 250 mg/dL | 2% | 2% | 4% | 0% | <1% |
| Uric Acid | > 12 mg/dL | 2% | 2% | 5% | <1% | 1% |
| SGOT/ AST2 | > 180 U/L | 2% | 4% | 10% | 1% | 2% |
| SGPT/ ALT2 | >215 U/L | 4% | 4% | 11% | 1% | 1% |
| GGT | >300 U/L | N/A | N/A | 10% | N/A | N/A |
| Total Cholesterol | >300 mg/dL | 9% | 5% | 27% | 4% | 3% |
| Triglycerides | >750 mg/dL | 9% | 1% | 29% | 3% | 6% |
| Amylase | >2 x ULN | 3% | 2% | 4% | N/A | N/A |
| Lipase | >2 x ULN | N/A | N/A | N/A | 3% | 5% |
| Chemistry | Low | |||||
| Calculated Creatinine Clearance | <50 mL/min | N/A | N/A | N/A | 2% | 2% |
| Hematology | Low | |||||
| Neutrophils | <0.75 x 109/L | 1% | 3% | 5% | 2% | 1% |
| 1 ULN = upper limit of the normal range; N/A = Not Applicable. 2 Criterion for Study 730 was >5x ULN (AST/ALT). |
||||||
| Study 888
(48 Weeks) | Study 9572 and Study 7653
(84-144 Weeks) | Study 802
(48 Weeks) |
||||
| Variable | Limit1 | KALETRA 400/100 mg Twice Daily + NVP + NRTIs (N = 148) | Investigator-Selected Protease Inhibitor(s) + NVP + NRTIs
(N = 140) | KALETRA
Twice Daily + NNRTI + NRTIs (N = 127) | KALETRA
800/200 mg Once Daily +NRTIs (N=300) | KALETRA
400/100 mg Twice Daily +NRTIs (N=299) |
| Chemistry | High | |||||
| Glucose | >250 mg/dL | 1% | 2% | 5% | 2% | 2% |
| Total Bilirubin | >3.48 mg/dL | 1% | 3% | 1% | 1% | 1% |
| SGOT/AST4 | >180 U/L | 5% | 11% | 8% | 3% | 2% |
| SGPT/ALT4 | >215 U/L | 6% | 13% | 10% | 2% | 2% |
| GGT | >300 U/L | N/A | N/A | 29% | N/A | N/A |
| Total Cholesterol | >300 mg/dL | 20% | 21% | 39% | 6% | 7% |
| Triglycerides | >750 mg/dL | 25% | 21% | 36% | 5% | 6% |
| Amylase | >2 x ULN | 4% | 8% | 8% | 4% | 4% |
| Lipase | >2 x ULN | N/A | N/A | N/A | 4% | 1% |
| Creatine Phosphokinase | >4 x ULN | N/A | N/A | N/A | 4% | 5% |
| Chemistry | Low | |||||
| Calculated Creatinine Clearance | <50 mL/min | N/A | N/A | N/A | 3% | 3% |
| Inorganic Phosphorus | <1.5 mg/dL | 1% | 0% | 2% | 1% | <1% |
| Hematology | Low | |||||
| Neutrophils | <0.75 x 109/L | 1% | 2% | 4% | 3% | 4% |
| Hemoglobin | <80 g/L | 1% | 1% | 1% | 1% | 2% |
| 1 ULN = upper limit of the normal range; N/A = Not Applicable. 2 Includes clinical laboratory data from patients receiving 400/100 mg twice daily (n = 29) or 533/133 mg twice daily (n = 28) for 84 weeks. Patients received KALETRA in combination with NRTIs and efavirenz. 3 Includes clinical laboratory data from patients receiving 400/100 mg twice daily (n = 36) or 400/200 mg twice daily (n = 34) for 144 weeks. Patients received KALETRA in combination with NRTIs and nevirapine. 4 Criterion for Study 802 was >5x ULN (AST/ALT). |
||||||
Adverse Reactions in Pediatric Patients
| Variable | Limit1 | KALETRA Twice Daily + RTIs
(N = 100) |
| Chemistry | High | |
| Sodium | > 149 mEq/L | 3% |
| Total Bilirubin | ≥ 3.0 x ULN | 3% |
| SGOT/AST | > 180 U/L | 8% |
| SGPT/ALT | > 215 U/L | 7% |
| Total Cholesterol | > 300 mg/dL | 3% |
| Amylase | > 2.5 x ULN | 7%2 |
| Chemistry | Low | |
| Sodium | < 130 mEq/L | 3% |
| Hematology | Low | |
| Platelet Count | < 50 x 109/L | 4% |
| Neutrophils | < 0.40 x 109/L | 2% |
| 1 ULN = upper limit of the normal range. 2 Subjects with Grade 3-4 amylase confirmed by elevations in pancreatic amylase. |
||
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 Potential for KALETRA to Affect Other Drugs
Additionally, KALETRA induces glucuronidation.
Published data suggest that lopinavir is an inhibitor of OATP1B1.
7.3 Established and Other Potentially Significant Drug Interactions
| Concomitant Drug Class:
Drug Name | Effect on Concentration of Lopinavir or Concomitant Drug | Clinical Comments |
| HIV-1 Antiviral Agents | ||
| HIV-1 Protease Inhibitor: fosamprenavir/ritonavir | ↓ amprenavir ↓ lopinavir | An increased rate of adverse reactions has been observed with co-administration of these medications. Appropriate doses of the combinations with respect to safety and efficacy have not been established. |
| HIV-1 Protease Inhibitor: indinavir* | ↑ indinavir | Decrease indinavir dose to 600 mg twice daily, when co-administered with KALETRA 400/100 mg twice daily. KALETRA once daily has not been studied in combination with indinavir. |
| HIV-1 Protease Inhibitor: nelfinavir* | ↑ nelfinavir ↑ M8 metabolite of nelfinavir ↓ lopinavir | KALETRA once daily in combination with nelfinavir is not recommended [see Dosage and Administration (2)]. |
| HIV-1 Protease Inhibitor: ritonavir* | ↑ lopinavir | Appropriate doses of additional ritonavir in combination with KALETRA with respect to safety and efficacy have not been established. |
| HIV-1 Protease Inhibitor: saquinavir | ↑ saquinavir | The saquinavir dose is 1000 mg twice daily, when co-administered with KALETRA 400/100 mg twice daily. KALETRA once daily has not been studied in combination with saquinavir. |
| HIV-1 Protease Inhibitor: tipranavir* | ↓ lopinavir | Co-administration with tipranavir (500 mg twice daily) and ritonavir (200 mg twice daily) is not recommended. |
| HIV CCR5 – Antagonist: maraviroc* | ↑ maraviroc | When co-administered, patients should receive 150 mg twice daily of maraviroc. For further details see complete prescribing information for maraviroc. |
| Non-nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors: efavirenz*, nevirapine* | ↓ lopinavir | Increase the dose of KALETRA tablets to 500/125 mg when KALETRA tablet is co-administered with efavirenz or nevirapine. KALETRA once daily in combination with efavirenz or nevirapine is not recommended [see Dosage and Administration (2)]. |
| Non-nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitor: delavirdine | ↑ lopinavir | Appropriate doses of the combination with respect to safety and efficacy have not been established. |
| Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitor: didanosine | KALETRA tablets can be administered simultaneously with didanosine without food. For KALETRA oral solution, it is recommended that didanosine be administered on an empty stomach; therefore, didanosine should be given one hour before or two hours after KALETRA oral solution (given with food). |
|
| Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitor: tenofovir disoproxil fumarate* | ↑ tenofovir | Patients receiving KALETRA and tenofovir should be monitored for adverse reactions associated with tenofovir. |
| Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors: abacavir zidovudine | ↓ abacavir ↓ zidovudine | The clinical significance of this potential interaction is unknown. |
| Other Agents | ||
| Alpha 1- Adrenoreceptor Antagonist: alfuzosin | ↑ alfuzosin | Contraindicated due to potential hypotension [see Contraindications (4)]. |
| Antianginal: ranolazine | ↑ ranolazine | Contraindicated due to potential for serious and/or life-threatening reactions [see Contraindications (4)]. |
| Antiarrhythmics: dronedarone | ↑ dronedarone | Contraindicated due to potential for cardiac arrhythmias [see Contraindications (4)]. |
| Antiarrhythmics e.g. amiodarone, bepridil, lidocaine (systemic), quinidine | ↑ antiarrhythmics | Caution is warranted and therapeutic concentration monitoring (if available) is recommended for antiarrhythmics when co-administered with KALETRA. |
| Anticancer Agents: abemaciclib, apalutamide, encorafenib, ibrutinib, ivosidenib, dasatinib, neratinib, nilotinib, venetoclax, vinblastine, vincristine | ↑ anticancer agents ↓lopinavir/ritonavir# | Apalutamide is contraindicated due to potential for loss of virologic response and possible resistance to KALETRA or to the class of protease inhibitors [see Contraindications (4)]. Avoid co-administration of encorafenib or ivosidenib with KALETRA due to potential risk of serious adverse events such as QT interval prolongation. If co-administration of encorafenib with KALETRA cannot be avoided, modify dose as recommended in encorafenib USPI. If co-administration of ivosidenib with KALETRA cannot be avoided, reduce ivosidenib dose to 250 mg once daily. Avoid use of neratinib, venetoclax or ibrutinib with KALETRA. For vincristine and vinblastine, consideration should be given to temporarily withholding the ritonavir-containing antiretroviral regimen in patients who develop significant hematologic or gastrointestinal side effects when KALETRA is administered concurrently with vincristine or vinblastine. If the antiretroviral regimen must be withheld for a prolonged period, consideration should be given to initiating a revised regimen that does not include a CYP3A or P-gp inhibitor. A decrease in the dosage or an adjustment of the dosing interval of nilotinib and dasatinib may be necessary for patients requiring co-administration with strong CYP3A inhibitors such as KALETRA. Please refer to the nilotinib and dasatinib prescribing information for dosing instructions. |
| Anticoagulants: warfarin, rivaroxaban | ↑↓ warfarin ↑ rivaroxaban | Concentrations of warfarin may be affected. Initial frequent monitoring of the INR during KALETRA and warfarin co-administration is recommended. Avoid concomitant use of rivaroxaban and KALETRA. Co-administration of KALETRA and rivaroxaban may lead to increased risk of bleeding. |
| Anticonvulsants: carbamazepine, phenobarbital, phenytoin | ↓ lopinavir ↓ phenytoin | KALETRA may be less effective due to decreased lopinavir plasma concentrations in patients taking these agents concomitantly and should be used with caution. KALETRA once daily in combination with carbamazepine, phenobarbital, or phenytoin is not recommended. In addition, co-administration of phenytoin and KALETRA may cause decreases in steady-state phenytoin concentrations. Phenytoin levels should be monitored when co-administering with KALETRA. |
| Anticonvulsants: lamotrigine, valproate | ↓ lamotrigine ↓ or ↔ valproate | A dose increase of lamotrigine or valproate may be needed when co-administered with KALETRA and therapeutic concentration monitoring for lamotrigine may be indicated; particularly during dosage adjustments. |
| Antidepressant: bupropion | ↓ bupropion ↓ active metabolite, hydroxybupropion | Patients receiving KALETRA and bupropion concurrently should be monitored for an adequate clinical response to bupropion. |
| Antidepressant: trazodone | ↑ trazodone | Adverse reactions of nausea, dizziness, hypotension and syncope have been observed following co-administration of trazodone and ritonavir. A lower dose of trazodone should be considered. |
| Anti-infective: clarithromycin | ↑ clarithromycin | For patients with renal impairment, adjust clarithromycin dose as follows:
|
| Antifungals: ketoconazole*, itraconazole, voriconazole isavuconazonium sulfate* | ↑ ketoconazole ↑ itraconazole ↓ voriconazole ↑ isavuconazonium | High doses of ketoconazole (>200 mg/day) or itraconazole (> 200 mg/day) are not recommended. The coadministration of voriconazole and KALETRA should be avoided unless an assessment of the benefit/risk to the patient justifies the use of voriconazole. Isavuconazonium and Kaletra should be coadministered with caution. Alternative antifungal therapies should be considered in these patients. |
| Anti-gout: colchicine | ↑ colchicine | Contraindicated due to potential for serious and/or life-threatening reactions in patients with renal and/or hepatic impairment [see Contraindications (4)]. For patients with normal renal or hepatic function: Treatment of gout flares-co-administration of colchicine in patients on KALETRA: 0.6 mg (1 tablet) x 1 dose, followed by 0.3 mg (half tablet) 1 hour later. Dose to be repeated no earlier than 3 days. Prophylaxis of gout flares-co-administration of colchicine in patients on KALETRA: If the original colchicine regimen was 0.6 mg twice a day, the regimen should be adjusted to 0.3 mg once a day. If the original colchicine regimen was 0.6 mg once a day, the regimen should be adjusted to 0.3 mg once every other day. Treatment of familial Mediterranean fever (FMF)-co-administration of colchicine in patients on KALETRA: Maximum daily dose of 0.6 mg (may be given as 0.3 mg twice a day). |
| Antimycobacterial: rifampin | ↓ lopinavir | Contraindicated due to potential loss of virologic response and possible resistance to KALETRA or to the class of protease inhibitors or other co-administered antiretroviral agents [see Contraindications (4)]. |
| Antimycobacterial: bedaquiline | ↑ bedaquiline | Bedaquiline should only be used with KALETRA if the benefit of co-administration outweighs the risk. |
| Antimycobacterial: rifabutin* | ↑ rifabutin and rifabutin metabolite | Dosage reduction of rifabutin by at least 75% of the usual dose of 300 mg/day is recommended (i.e., a maximum dose of 150 mg every other day or three times per week). Increased monitoring for adverse reactions is warranted in patients receiving the combination. Further dosage reduction of rifabutin may be necessary. |
| Antiparasitic: atovaquone | ↓ atovaquone | Clinical significance is unknown; however, increase in atovaquone doses may be needed. |
| Antipsychotics: lurasidone pimozide |
↑ lurasidone ↑ pimozide | Contraindicated due to potential for serious and/or life-threatening reactions [see Contraindications (4)]. Contraindicated due to potential for serious and/or life-threatening reactions such as cardiac arrhythmias [see Contraindications (4)]. |
| Antipsychotics: quetiapine | ↑ quetiapine | Initiation of KALETRA in patients taking quetiapine:
Consider alternative antiretroviral therapy to avoid increases in quetiapine exposures. If coadministration is necessary, reduce the quetiapine dose to 1/6 of the current dose and monitor for quetiapine-associated adverse reactions. Refer to the quetiapine prescribing information for recommendations on adverse reaction monitoring. Initiation of quetiapine in patients taking KALETRA: Refer to the quetiapine prescribing information for initial dosing and titration of quetiapine. |
| Contraceptive: ethinyl estradiol* | ↓ ethinyl estradiol | Because contraceptive steroid concentrations may be altered when KALETRA is co-administered with oral contraceptives or with the contraceptive patch, alternative methods of nonhormonal contraception are recommended. |
| Dihydropyridine Calcium Channel Blockers: e.g. felodipine, nifedipine, nicardipine | ↑ dihydropyridine calcium channel blockers | Clinical monitoring of patients is recommended and a dose reduction of the dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker may be considered. |
| Disulfiram/metronidazole | KALETRA oral solution contains ethanol, which can produce disulfiram-like reactions when co-administered with disulfiram or other drugs that produce this reaction (e.g., metronidazole). | |
| Endothelin Receptor Antagonists: bosentan | ↑ bosentan | Co-administration of bosentan in patients on KALETRA:
In patients who have been receiving KALETRA for at least 10 days, start bosentan at 62.5 mg once daily or every other day based upon individual tolerability. Co-administration of KALETRA in patients on bosentan: Discontinue use of bosentan at least 36 hours prior to initiation of KALETRA. After at least 10 days following the initiation of KALETRA, resume bosentan at 62.5 mg once daily or every other day based upon individual tolerability. |
| Ergot Derivatives: dihydroergotamine, ergotamine, methylergonovine | ↑ ergot derivatives | Contraindicated due to potential for acute ergot toxicity characterized by peripheral vasospasm and ischemia of the extremities and other tissues [see Contraindications (4)]. |
| GI Motility Agent: cisapride | ↑ cisapride | Contraindicated due to potential for cardiac arrhythmias [see Contraindications (4)]. |
| GnRH Receptor Antagonists: elagolix | ↑ elagolix ↓ lopinavir/ritonavir | Concomitant use of elagolix 200 mg twice daily and KALETRA for more than 1 month is not recommended due to potential risk of adverse events such as bone loss and hepatic transaminase elevations. Limit concomitant use of elagolix 150 mg once daily and KALETRA to 6 months. |
| Hepatitis C direct acting antiviral: elbasvir/grazoprevir | ↑ elbasvir/grazoprevir | Contraindicated due to increased risk of alanine transaminase (ALT) elevations [see Contraindications (4)]. |
| Hepatitis C direct acting antivirals: boceprevir* glecaprevir/pibrentasvir simeprevir sofosbuvir/velpatasvir/voxilaprevir ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ ritonavir and dasabuvir* | ↓ lopinavir ↓ boceprevir ↓ ritonavir ↑glecaprevir ↑ pibrentasvir ↑ simeprevir ↑ sofosbuvir ↑ velpatasvir ↑ voxilaprevir ↑ ombitasvir ↑ paritaprevir ↑ ritonavir ↔ dasabuvir | It is not recommended to co-administer KALETRA and boceprevir, glecaprevir/pibrentasvir, simeprevir, sofosbuvir/velpatasvir/voxilaprevir, or ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir and dasabuvir. |
| Herbal Products: St. John's Wort (hypericum perforatum) | ↓ lopinavir | Contraindicated due to potential for loss of virologic response and possible resistance to KALETRA or to the class of protease inhibitors [see Contraindications (4)]. |
| Lipid-modifying agents HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitors: lovastatin simvastatin atorvastatin rosuvastatin Microsomal triglyceride transfer protein (MTTP) Inhibitor: lomitapide |
↑ lovastatin ↑ simvastatin ↑ atorvastatin ↑ rosuvastatin ↑ lomitapide |
Contraindicated due to potential for myopathy including rhabdomyolysis [see Contraindications (4)]. Use atorvastatin with caution and at the lowest necessary dose. Titrate rosuvastatin dose carefully and use the lowest necessary dose; do not exceed rosuvastatin 10 mg/day. Lomitapide is a sensitive substrate for CYP3A4 metabolism. CYP3A4 inhibitors increase the exposure of lomitapide, with strong inhibitors increasing exposure approximately 27-fold. Concomitant use of moderate or strong CYP3A4 inhibitors with lomitapide is contraindicated due to potential for hepatotoxicity [see Contraindications (4)]. |
| Immunosuppressants: e.g. cyclosporine, tacrolimus, sirolimus | ↑ immunosuppressants | Therapeutic concentration monitoring is recommended for immunosuppressant agents when co-administered with KALETRA. |
| Kinase Inhibitors: fostamatinib (also see anticancer agents above) | ↑ fostamatinib metabolite R406 | Monitor for toxicities of R406 such as hepatotoxicity and neutropenia. Fostamatinib dose reduction may be required. |
| Long-acting beta-adrenoceptor Agonist: salmeterol | ↑ salmeterol | Concurrent administration of salmeterol and KALETRA is not recommended. The combination may result in increased risk of cardiovascular adverse events associated with salmeterol, including QT prolongation, palpitations and sinus tachycardia. |
| Narcotic Analgesics: methadone,* fentanyl | ↓ methadone ↑ fentanyl | Dosage of methadone may need to be increased when co-administered with KALETRA. Careful monitoring of therapeutic and adverse effects (including potentially fatal respiratory depression) is recommended when fentanyl is concomitantly administered with KALETRA. |
| PDE5 inhibitors: avanafil, sildenafil, tadalafil, vardenafil | ↑ avanafil ↑ sildenafil ↑ tadalafil ↑ vardenafil | Sildenafil when used for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension (Revatio®) is contraindicated due to the potential for sildenafil-associated adverse events, including visual abnormalities, hypotension, prolonged erection, and syncope [see Contraindications (4)]. Do not use KALETRA with avanafil because a safe and effective avanafil dosage regimen has not been established. Particular caution should be used when prescribing sildenafil, tadalafil, or vardenafil in patients receiving KALETRA. Co-administration of KALETRA with these drugs may result in an increase in PDE5 inhibitor associated adverse reactions including hypotension, syncope, visual changes and prolonged erection. Use of PDE5 inhibitors for pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH): Sildenafil (Revatio®) is contraindicated [see Contraindications (4)]. The following dose adjustments are recommended for use of tadalafil (Adcirca®) with KALETRA: Co-administration of ADCIRCA in patients on KALETRA: In patients receiving KALETRA for at least one week, start ADCIRCA at 20 mg once daily. Increase to 40 mg once daily based upon individual tolerability. Co-administration of KALETRA in patients on ADCIRCA: Avoid use of ADCIRCA during the initiation of KALETRA. Stop ADCIRCA at least 24 hours prior to starting KALETRA. After at least one week following the initiation of KALETRA, resume ADCIRCA at 20 mg once daily. Increase to 40 mg once daily based upon individual tolerability. Use of PDE5 inhibitors for erectile dysfunction: It is recommended not to exceed the following doses: • Sildenafil: 25 mg every 48 hours • Tadalafil: 10 mg every 72 hours • Vardenafil: 2.5 mg every 72 hours Use with increased monitoring for adverse events. |
| Sedative/Hypnotics: triazolam, orally administered midazolam | ↑ triazolam ↑ midazolam | Contraindicated due to potential for prolonged or increased sedation or respiratory depression [see Contraindications (4)]. |
| Sedative/Hypnotics: parenterally administered midazolam | ↑ midazolam | If KALETRA is co-administered with parenteral midazolam, close clinical monitoring for respiratory depression and/or prolonged sedation should be exercised and dosage adjustment should be considered. |
| Systemic/Inhaled/ Nasal/Ophthalmic Corticosteroids: e.g., betamethasone budesonide ciclesonide dexamethasone fluticasone methylprednisolone mometasone prednisone triamcinolone | ↓ lopinavir ↑ glucocorticoids | Coadministration with oral dexamethasone or other systemic corticosteroids that induce CYP3A may result in loss of therapeutic effect and development of resistance to lopinavir. Consider alternative corticosteroids. Coadministration with corticosteroids whose exposures are significantly increased by strong CYP3A inhibitors can increase the risk for Cushing’s syndrome and adrenal suppression. Alternative corticosteroids including beclomethasone and prednisolone (whose PK and/or PD are less affected by strong CYP3A inhibitors relative to other studied steroids) should be considered, particularly for long-term use. |
| * see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) for magnitude of interaction. # refers to interaction with apalutamide. |
||
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Dose Adjustments During Pregnancy and the Postpartum Period
11. Kaletra Description
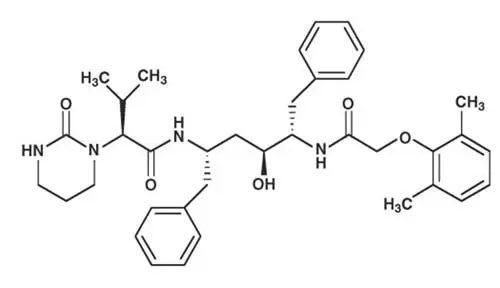
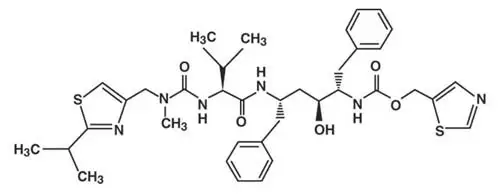
KALETRA tablets are available for oral administration in two strengths:
- Yellow tablets containing 200 mg of lopinavir and 50 mg of ritonavir
- Pale yellow tablets containing 100 mg of lopinavir and 25 mg of ritonavir.
12. Kaletra - Clinical Pharmacology
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
| Absorption | |
| Tmax (hr)a | 4.4 ± 0.8 |
| Effect of meal (relative to fasting) Tablet Oral solution | ↑ 19%b
↑ 130%b |
| Distribution | |
| % Bound to human plasma proteins | > 98 |
| Vd/Fa (L) | 16.9 |
| Metabolism | |
| Metabolism | CYP3A |
| Elimination | |
| Major route of elimination | hepatic |
| t1/2 (h)a | 6.9 ± 2.2 |
| % of dose excreted in urine | 10.4 ± 2.3 |
| % of dose excreted in feces | 82.6 ± 2.5 |
| a. Kaletra tablet b. Changes in AUC values |
|
| Pharmacokinetic Parameter | Twice Dailya | Once Dailyb |
| Cmax (µg/mL) | 9.8 ± 3.7 | 11.8 ± 3.7 |
| Cmin (µg/mL) | 5.5 ± 2.7 | 1.7 ± 1.6 |
| AUCtau (µg•h/mL) | 92.6 ± 36.7 | 154.1 ± 61.4 |
|
||
| Cmax (μg/mL) | Cmin (μg/mL) | AUC12 (μg•hr/m) |
| Age ≥ 14 Days to < 6 Weeks Cohort (N = 9): | ||
| 5.17 ± 1.84a | 1.40 ± 0.48a | 43.39 ± 14.80a |
| Age ≥ 6 Weeks to < 6 Months Cohort (N = 18): | ||
| 9.39 ± 4.91a | 1.95 ± 1.80a | 74.50 ± 37.87a |
| Age ≥ 6 Months to ≤ 12 years Cohort (N = 24): | ||
| 8.2 ± 2.9b | 3.4 ± 2.1b | 72.6 ± 31.1b |
| 10.0 ± 3.3c | 3.6 ± 3.5c | 85.8 ± 36.9c |
|
||
| Co- administered Drug | Dose of Co- administered Drug (mg) | Dose of KALETRA (mg) | n | Ratio (in combination with Co-administered drug/alone) of Lopinavir Pharmacokinetic Parameters (90% CI); No Effect = 1.00 |
||
| Cmax | AUC | Cmin | ||||
| Efavirenz1 | 600 at bedtime | 400/100 capsule twice daily | 11, 73 | 0.97 (0.78, 1.22) | 0.81 (0.64, 1.03) | 0.61 (0.38, 0.97) |
| 600 at bedtime | 500/125 tablet twice daily | 19 | 1.12 (1.02, 1.23) | 1.06 (0.96, 1.17) | 0.90 (0.78, 1.04) |
|
| 600 at bedtime | 600/150 tablet twice daily | 23 | 1.36 (1.28, 1.44) | 1.36 (1.28, 1.44) | 1.32 (1.21, 1.44) |
|
| Etravirine | 200 twice daily | 400/100 mg twice day (tablets) | 16 | 0.89 (0.82-0.96) | 0.87 (0.83-0.92) | 0.80 (0.73-0.88) |
| Fosamprenavir2 | 700 twice daily plus ritonavir 100 twice daily | 400/100 capsule twice daily | 18 | 1.30 (0.85, 1.47) | 1.37 (0.80, 1.55) | 1.52 (0.72, 1.82) |
| Ketoconazole | 200 single dose | 400/100 capsule twice daily | 12 | 0.89 (0.80, 0.99) | 0.87 (0.75, 1.00) | 0.75 (0.55, 1.00) |
| Nelfinavir | 1000 twice daily | 400/100 capsule twice daily | 13 | 0.79 (0.70, 0.89) | 0.73 (0.63, 0.85) | 0.62 (0.49, 0.78) |
| Nevirapine | 200 twice daily steady-state | 400/100 capsule twice daily | 22, 193 | 0.81 (0.62, 1.05) | 0.73 (0.53, 0.98) | 0.49 (0.28, 0.74) |
| 7 mg/kg or 4 mg/kg once daily; twice daily 1 wk5 | (> 1 yr) 300/ 75 mg/m2 oral solution twice daily | 12, 153 | 0.86 (0.64, 1.16) | 0.78 (0.56, 1.09) | 0.45 (0.25, 0.81) |
|
| Ombitasvir/ paritaprevir/ ritonavir+ dasabuvir2 | 25/150/100 + dasabuvir 400 | 400/100 tablet twice daily | 6 | 0.87 (0.76, 0.99) | 0.94 (0.81, 1.10) | 1.15 (0.93, 1.42) |
| Omeprazole | 40 once daily, 5 d | 400/100 tablet twice daily, 10 d | 12 | 1.08 (0.99, 1.17) | 1.07 (0.99, 1.15) | 1.03 (0.90, 1.18) |
| 40 once daily, 5 d | 800/200 tablet once daily, 10 d | 12 | 0.94 (0.88, 1.00) | 0.92 (0.86, 0.99) | 0.71 (0.57, 0.89) |
|
| Pravastatin | 20 once daily, 4 d | 400/100 capsule twice daily, 14 d | 12 | 0.98 (0.89, 1.08) | 0.95 (0.85, 1.05) | 0.88 (0.77, 1.02) |
| Ranitidine | 150 single dose | 400/100 tablet twice daily, 10 d | 12 | 0.99 (0.95, 1.03) | 0.97 (0.93, 1.01) | 0.90 (0.85, 0.95) |
| 150 single dose | 800/200 tablet once daily, 10 d | 10 | 0.97 (0.95, 1.00) | 0.95 (0.91, 0.99) | 0.82 (0.74, 0.91) |
|
| Rifabutin | 150 once daily | 400/100 capsule twice daily | 14 | 1.08 (0.97, 1.19) | 1.17 (1.04, 1.31) | 1.20 (0.96, 1.65) |
| Rifampin | 600 once daily | 400/100 capsule twice daily | 22 | 0.45 (0.40, 0.51) | 0.25 (0.21, 0.29) | 0.01 (0.01, 0.02) |
| 600 once daily | 800/200 capsule twice daily | 10 | 1.02 (0.85, 1.23) | 0.84 (0.64, 1.10) | 0.43 (0.19, 0.96) |
|
| 600 once daily | 400/400 capsule twice daily | 9 | 0.93 (0.81, 1.07) | 0.98 (0.81, 1.17) | 1.03 (0.68, 1.56) |
|
| Rilpivirine | 150 once daily | 400/100 twice daily (capsules) | 15 | 0.96 (0.88-1.05) | 0.99 (0.89-1.10) | 0.89 (0.73-1.08) |
| Ritonavir | 100 twice daily | 400/100 capsule twice daily | 8, 213 | 1.28 (0.94, 1.76) | 1.46 (1.04, 2.06) | 2.16 (1.29, 3.62) |
| Tipranavir/ ritonavir | 500/200 twice daily | 400/100 capsule twice daily | 21 693 | 0.53 (0.40, 0.69) | 0.45 (0.32, 0.63) | 0.30 (0.17, 0.51) 0.484 (0.40, 0.58) |
| 1 Reference for comparison is lopinavir/ritonavir 400/100 mg twice daily without efavirenz. 2 Data extracted from the U.S. prescribing information of co-administered drugs. 3 Parallel group design 4 Drug levels obtained at 8-16 hours post dose N/A = Not available. |
||||||
| Co- administered Drug | Dose of Co- administered Drug (mg) | Dose of KALETRA (mg) | n | Ratio (in combination with KALETRA/alone) of Co- administered Drug Pharmacokinetic Parameters (90% CI); No Effect = 1.00 |
||
| Cmax | AUC | Cmin | ||||
| Bedaquiline1 | 400 single dose | 400/100 twice daily | N/A | N/A | 1.22 (1.11, 1.34) | N/A |
| Efavirenz | 600 at bedtime | 400/100 capsule twice daily | 11, 123 | 0.91 (0.72, 1.15) | 0.84 (0.62, 1.15) | 0.84 (0.58, 1.20) |
| Elbasvir/ grazoprevir1 | 50 once daily | 400/100 twice daily | 10 | 2.87 (2.29, 3.58) | 3.71 (3.05, 4.53) | 4.58 (3.72, 5.64) |
| 200 once daily | 13 | 7.31 (5.65, 9.45) | 12.86 (10.25, 16.13) | 21.70 (12.99, 36.25) |
||
| Ethinyl Estradiol | 35 µg once daily (Ortho Novum®) | 400/100 capsule twice daily | 12 | 0.59 (0.52, 0.66) | 0.58 (0.54, 0.62) | 0.42 (0.36, 0.49) |
| Etravirine | 200 twice daily | 400/100 tablet twice day | 16 | 0.70 (0.64-0.78) | 0.65 (0.59-0.71) | 0.55 (0.49-0.62) |
| Fosamprenavir1 | 700 twice daily plus ritonavir 100 twice daily | 400/100 capsule twice daily | 18 | 0.42 (0.30, 0.58) | 0.37 (0.28, 0.49) | 0.35 (0.27, 0.46) |
| Indinavir | 600 twice daily combo nonfasting vs. 800 three times daily alone fasting | 400/100 capsule twice daily | 13 | 0.71 (0.63, 0.81) | 0.91 (0.75, 1.10) | 3.47 (2.60, 4.64) |
| Ketoconazole | 200 single dose | 400/100 capsule twice daily | 12 | 1.13 (0.91, 1.40) | 3.04 (2.44, 3.79) | N/A |
| Maraviroc1 | 300 twice daily | 400/100 twice daily | 11 | 1.97 (1.66, 2.34) | 3.95 (3.43, 4.56) | 9.24 (7.98, 10.7) |
| Methadone | 5 single dose | 400/100 capsule twice daily | 11 | 0.55 (0.48, 0.64) | 0.47 (0.42, 0.53) | N/A |
| Nelfinavir | 1000 twice daily combo vs. 1250 twice daily alone | 400/100 capsule twice daily | 13 | 0.93 (0.82, 1.05) | 1.07 (0.95, 1.19) | 1.86 (1.57, 2.22) |
| M8 metabolite | 2.36 (1.91, 2.91) | 3.46 (2.78, 4.31) | 7.49 (5.85, 9.58) |
|||
| Nevirapine | 200 once daily twice daily | 400/100 capsule twice daily | 5, 63 | 1.05 (0.72, 1.52) | 1.08 (0.72, 1.64) | 1.15 (0.71, 1.86) |
| Norethindrone | 1 once daily (Ortho Novum®) | 400/100 capsule twice daily | 12 | 0.84 (0.75, 0.94) | 0.83 (0.73, 0.94) | 0.68 (0.54, 0.85) |
| Ombitasvir/ paritaprevir/ ritonavir+ dasabuvir1 | 25/150/100 + dasabuvir 400 | 400/100 tablet twice daily | 6 | 1.14 (1.01, 1.28) | 1.17 (1.07, 1.28) | 1.24 (1.14, 1.34) |
| 2.04 (1.30, 3.20) | 2.17 (1.63, 2.89) | 2.36 (1.00, 5.55) |
||||
| 1.55 (1.16, 2.09) | 2.05 (1.49, 2.81) | 5.25 (3.33, 8.28) |
||||
| 0.99 (0.75, 1.31) | 0.93 (0.75, 1.15) | 0.68 (0.57, 0.80) |
||||
| Pitavastatin1 | 4 once daily | 400/100 tablet twice daily | 23 | 0.96 (0.84-1.10) | 0.80 (0.73-0.87) | N/A |
| Pravastatin | 20 once daily | 400/100 capsule twice daily | 12 | 1.26 (0.87, 1.83) | 1.33 (0.91, 1.94) | N/A |
| Rifabutin | 150 once daily combo vs. 300 once daily alone | 400/100 capsule twice daily | 12 | 2.12 (1.89, 2.38) | 3.03 (2.79, 3.30) | 4.90 (3.18, 5.76) |
| 25-O-desacetyl rifabutin | 23.6 (13.7, 25.3) | 47.5 (29.3, 51.8) | 94.9 (74.0, 122) |
|||
| Rifabutin + 25- O-desacetyl rifabutin | 3.46 (3.07, 3.91) | 5.73 (5.08, 6.46) | 9.53 (7.56, 12.01) |
|||
| Rilpivirine | 150 once daily | 400/100 capsules twice daily | 15 | 1.29 (1.18-1.40) | 1.52 (1.36-1.70) | 1.74 (1.46-2.08) |
| Rosuvastatin2 | 20 once daily | 400/100 tablet twice daily | 15 | 4.66 (3.4, 6.4) | 2.08 (1.66, 2.6) | 1.04 (0.9, 1.2) |
| Tenofovir alafenamide1 | 10 once daily | 800/200 tablet once daily | 10 | 2.19 (1.72, 2.79) | 1.47 (1.17, 1.85) | N/A |
| Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate1 | 300 once daily | 400/100 capsule twice daily | 24 | No Change | 1.32 (1.26, 1.38) | 1.51 (1.32, 1.66) |
| 1 Data extracted from the U.S. prescribing information of co-administered drugs. 2 Kiser, et al. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2008 Apr 15; 47(5):570-8. 3 Parallel group design N/A = Not available. |
||||||
12.4 Microbiology
| Susceptibility reduced by >4 fold | Susceptibility reduced to LPV |
| Indinavir (n=16) | 5.7 fold |
| Nelfinavir (n=13) | <4 fold |
| Ritonavir (n=3) | 8.32 fold |
| Saquinavir (n=4) | <4 fold |
| Number of protease inhibitor substitutions at baseline1 | Study 888 (Single protease inhibitor-experienced2, NNRTI-naïve) n=130 | Study 765 (Single protease inhibitor-experienced3, NNRTI-naïve) n=56 | Study 957 (Multiple protease inhibitor-experienced4, NNRTI-naïve) n=50 |
| 0-2 | 76/103 (74%) | 34/45 (76%) | 19/20 (95%) |
| 3-5 | 13/26 (50%) | 8/11 (73%) | 18/26 (69%) |
| 6 or more | 0/1 (0%) | N/A | 1/4 (25%) |
| 1 Substitutions considered in the analysis included L10F/I/R/V, K20M/N/R, L24I, L33F, M36I, I47V, G48V, I54L/T/V, V82A/C/F/S/T, and I84V. 2 43% indinavir, 42% nelfinavir, 10% ritonavir, 15% saquinavir. 3 41% indinavir, 38% nelfinavir, 4% ritonavir, 16% saquinavir. 4 86% indinavir, 54% nelfinavir, 80% ritonavir, 70% saquinavir. |
|||
| Lopinavir susceptibility2 at baseline | HIV-1 RNA <400 copies/mL (%) | HIV-1 RNA <50 copies/mL (%) |
| < 10 fold | 25/27 (93%) | 22/27 (81%) |
| > 10 and < 40 fold | 11/15 (73%) | 9/15 (60%) |
| ≥ 40 fold | 2/8 (25%) | 2/8 (25%) |
| 1 Lopinavir susceptibility was determined by recombinant phenotypic technology performed by Virologic. 2 Fold change in susceptibility from wild type. |
||
14. Clinical Studies
14.1 Adult Patients without Prior Antiretroviral Therapy
Treatment response and outcomes of randomized treatment are presented in Table 21.
| Outcome | KALETRA+d4T+3TC
(N = 326) | Nelfinavir+d4T+3TC
(N = 327) |
| Responder1 | 75% | 62% |
| Virologic failure2
Rebound Never suppressed through Week 48 | 9% 7% 2% | 25% 15% 9% |
| Death | 2% | 1% |
| Discontinued due to adverse events | 4% | 4% |
| Discontinued for other reasons3 | 10% | 8% |
| 1 Patients achieved and maintained confirmed HIV-1 RNA < 400 copies/mL through Week 48. 2 Includes confirmed viral rebound and failure to achieve confirmed < 400 copies/mL through Week 48. 3 Includes lost to follow-up, patient's withdrawal, non-compliance, protocol violation and other reasons. Overall discontinuation through Week 48, including patients who discontinued subsequent to virologic failure, was 17% in the KALETRA arm and 24% in the nelfinavir arm. |
||
| Baseline Viral Load (HIV-1 RNA copies/mL) | KALETRA +d4T+3TC | Nelfinavir +d4T+3TC | ||||
| <400 copies/mL 1 | <50 copies/mL 2 | n | <400 copies/mL 1 | <50 copies/mL 2 | n | |
| < 30,000 | 74% | 71% | 82 | 79% | 72% | 87 |
| ≥ 30,000 to < 100,000 | 81% | 73% | 79 | 67% | 54% | 79 |
| ≥ 100,000 to < 250,000 | 75% | 64% | 83 | 60% | 47% | 72 |
| ≥ 250,000 | 72% | 60% | 82 | 44% | 33% | 89 |
| 1 Patients achieved and maintained confirmed HIV-1 RNA < 400 copies/mL through Week 48. 2 Patients achieved HIV-1 RNA < 50 copies/mL at Week 48. |
||||||
Treatment response and outcomes of randomized treatment through Week 48 are presented in Table 23.
| Outcome | KALETRA Once Daily + TDF + FTC
(n = 333) | KALETRA Twice Daily + TDF + FTC
(n = 331) |
| Responder1 | 78% | 77% |
| Virologic failure2
Rebound Never suppressed through Week 48 | 10% 5% 5% | 8% 5% 3% |
| Death | 1% | <1% |
| Discontinued due to adverse events | 4% | 3% |
| Discontinued for other reasons3 | 8% | 11% |
| 1 Patients achieved and maintained confirmed HIV-1 RNA < 50 copies/mL through Week 48. 2 Includes confirmed viral rebound and failure to achieve confirmed < 50 copies/mL through Week 48. 3 Includes lost to follow-up, patient's withdrawal, non-compliance, protocol violation and other reasons. |
||
14.2 Adult Patients with Prior Antiretroviral Therapy
Treatment response and outcomes of randomized treatment through Week 48 are presented in Table 24.
| Outcome | KALETRA + nevirapine + NRTIs
(n = 148) | Investigator-Selected Protease Inhibitor(s) + nevirapine + NRTIs
(n = 140) |
| Responder1 | 57% | 33% |
| Virologic failure2
Rebound Never suppressed through Week 48 | 24% 11% 13% | 41% 19% 23% |
| Death | 1% | 2% |
| Discontinued due to adverse events | 5% | 11% |
| Discontinued for other reasons3 | 14% | 13% |
| 1 Patients achieved and maintained confirmed HIV-1 RNA < 400 copies/mL through Week 48. 2 Includes confirmed viral rebound and failure to achieve confirmed < 400 copies/mL through Week 48. 3 Includes lost to follow-up, patient's withdrawal, non-compliance, protocol violation and other reasons. |
||
Treatment response and outcomes of randomized treatment through Week 48 are presented in Table 25.
| Outcome | KALETRA Once Daily + NRTIs
(n = 300) | KALETRA Twice Daily + NRTIs
(n = 299) |
| Virologic Success (HIV-1 RNA <50 copies/mL) | 57% | 54% |
| Virologic failure1 | 22% | 24% |
| No virologic data in Week 48 window | ||
| Discontinued study due to adverse event or death2 | 5% | 7% |
| Discontinued study for other reasons3 | 13% | 12% |
| Missing data during window but on study | 3% | 3% |
| 1 Includes patients who discontinued prior to Week 48 for lack or loss of efficacy and patients with HIV-1 RNA ≥ 50 copies/mL at Week 48. 2 Includes patients who discontinued due to adverse events or death at any time from Day 1 through Week 48 if this resulted in no virologic data on treatment at Week 48. 3 Includes withdrawal of consent, loss to follow-up, non-compliance, protocol violation and other reasons. |
||
14.3 Other Studies Supporting Approval in Adult Patients
Study 720: KALETRA twice daily + stavudine + lamivudine
14.4 Pediatric Studies
Dose selection in pediatric patients was based on the following:
- Among patients 14 days to 6 months of age receiving 300/75 mg/m2 twice daily without nevirapine, plasma concentrations were lower than those observed in adults or in older children. This dose resulted in HIV-1 RNA < 400 copies/mL in 55% of patients (70% in those initiating treatment at <6 weeks of age).
- Among patients 6 months to 12 years of age, the 230/57.5 mg/m2 oral solution twice daily regimen without nevirapine and the 300/75 mg/m2 oral solution twice daily regimen with nevirapine provided lopinavir plasma concentrations similar to those obtained in adult patients receiving the 400/100 mg twice daily regimen (without nevirapine). These doses resulted in treatment benefit (proportion of patients with HIV-1 RNA < 400 copies/mL) similar to that seen in the adult clinical trials.
- Among patients 12 to 18 years of age receiving 400/100 mg/m2 or 480/120 mg/m2 (with efavirenz) twice daily, plasma concentrations were 60-100% higher than among 6 to 12 year old patients receiving 230/57.5 mg/m2. Mean apparent clearance was similar to that observed in adult patients receiving standard dose and in patients 6 to 12 years of age. Although changes in HIV-1 RNA in patients with prior treatment failure were less than anticipated, the pharmacokinetic data supports use of similar dosing as in patients 6 to 12 years of age, not to exceed the recommended adult dose.
- For all age groups, the body surface area dosing was converted to body weight dosing using the patient’s prescribed lopinavir dose.
16. How is Kaletra supplied
| KALETRA Tablets, 200 mg lopinavir and 50 mg ritonavir | KALETRA Tablets, 100 mg lopinavir and 25 mg ritonavir | KALETRA Oral Solution, 80 mg lopinavir and 20 mg ritonavir per mL |
|
| Presentation | Yellow film-coated ovaloid tablets debossed with the “a” logo and the code KA | Pale yellow film-coated ovaloid tablets debossed with the “a” logo and the code KC | Light yellow to orange colored liquid supplied in amber-colored multiple-dose bottles containing 400 mg lopinavir and 100 mg ritonavir per 5 mL packaged with a marked dosing cup |
| Bottle Size and NDC Number | Bottles of 120 tablets (NDC 0074-6799-22) | Bottles of 60 tablets (NDC 0074-0522-60) | 160 mL bottle (NDC 0074-3956-46) |
| Recommended Storage | Store KALETRA tablets at 20°- 25°C (68°- 77°F); excursions permitted to 15°- 30°C (59°- 86°F) [see USP controlled room temperature]. Dispense in original container or USP equivalent tight container. For patient use: exposure of this product to high humidity outside the original container or USP equivalent tight container for longer than 2 weeks is not recommended. | Store KALETRA oral solution at 2°- 8°C (36°- 46°F) until dispensed. Avoid exposure to excessive heat. |
|
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide)
General Administration Information [see Dosage and Administration (2)]:
- Advise patients to pay special attention to accurate administration of their dose to minimize the risk of accidental overdose or underdose of KALETRA.
- Advise patients and caregivers that the oral solution should be administered using the calibrated dosing cup (supplied) or oral dosing syringe.
- Advise caregivers to inform their healthcare provider if the child’s weight changes in order to make sure that the child’s KALETRA dose is adjusted as needed.
- Inform patients and caregivers that KALETRA tablets may be taken with or without food but KALETRA oral solution should be taken with food to enhance absorption.
- Advise patients to remain under the care of a healthcare provider while using KALETRA and to take KALETRA in combination with other antiretroviral drugs as prescribed.
- Advise patients not to alter the dose or discontinue therapy without consulting with their healthcare provider. If a dose of KALETRA is missed patients should take the dose as soon as possible and then return to their normal schedule. However, if a dose is skipped the patient should not double the next dose.
- Inform patients that it is important to take KALETRA on a regular dosing schedule as directed and to avoid missing doses as that can result in development of resistance.
- Inform patients that there may be a greater chance of developing diarrhea with the once daily regimen as compared with the twice daily regimen.
- Inform patients that Kaletra is not a cure for HIV-1 infection and that they may continue to experience illnesses associated with HIV-1 infection, including opportunistic infections.
QT and PR Interval Prolongation
Diabetes Mellitus/Hyperglycemia
Immune Reconstitution Syndrome
KALETRA Tablets, 200 mg lopinavir and 50 mg ritonavir
Manufactured by AbbVie LTD, Barceloneta, PR 00617
for AbbVie Inc., North Chicago, IL 60064 USA
KALETRA Tablets, 100 mg lopinavir and 25 mg ritonavir and KALETRA Oral Solution
AbbVie Inc., North Chicago, IL 60064 USA
© 2019 AbbVie Inc. All rights reserved.
| MEDICATION GUIDE | |
| KALETRA® (kuh-LEE-tra)
(lopinavir and ritonavir) tablets | KALETRA® (kuh-LEE-tra)
(lopinavir and ritonavir) oral solution |
|
What is the most important information I should know about KALETRA? |
|
|
|
| ° nausea ° vomiting ° stomach-area (abdominal) pain | |
|
|
|
|
Tell your healthcare provider right away if you have any of these symptoms: |
|
|
|
| See “What are the possible side effects of KALETRA?” for more information about serious side effects. | |
| What is KALETRA?
KALETRA is a prescription medicine that is used with other antiretroviral medicines to treat Human Immunodeficiency Virus-1 (HIV-1) infection in adults and children 14 days of age and older. HIV is the virus that causes AIDS (Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome). It is not known if KALETRA is safe and effective in children under 14 days old. |
|
Do not take KALETRA if you:
|
|
Keep a list of your medicines to show your healthcare provider and pharmacist. |
|
|
|
| What are the possible side effects of KALETRA?
KALETRA can cause serious side effects, including:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| How should I store KALETRA?
KALETRA tablets:
Keep KALETRA and all medicines out of the reach of children. |
|
| General information about the safe and effective use of KALETRA.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use KALETRA for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give KALETRA to other people, even if they have the same condition you have. It may harm them. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about KALETRA that is written for health professionals. |
|
| What are the ingredients in KALETRA?
Active ingredients: lopinavir and ritonavir Inactive ingredients: KALETRA 200 mg lopinavir and 50 mg ritonavir tablets: colloidal silicon dioxide, copovidone, sodium stearyl fumarate, and sorbitan monolaurate. The film coating contains: colloidal silicone dioxide, hydroxypropyl cellulose, hypromellose, polyethylene glycol 400, polyethylene glycol 3350, polysorbate 80, talc, titanium dioxide, and yellow ferric oxide 172. KALETRA 100 mg lopinavir and 25 mg ritonavir tablets: colloidal silicon dioxide, copovidone, sodium stearyl fumarate, and sorbitan monolaurate. The film coating contains: polyethylene glycol 3350, polyvinyl alcohol, talc, titanium dioxide, and yellow ferric oxide E172. KALETRA oral solution: acesulfame potassium, artificial cotton candy flavor, citric acid, ethanol (a type of alcohol), glycerin, high fructose corn syrup, Magnasweet-110 flavor, menthol, natural and artificial vanilla flavor, peppermint oil, polyoxyl 40 hydrogenated castor oil, povidone, propylene glycol, saccharin sodium, sodium chloride, sodium citrate, and water. KALETRA oral solution contains approximately 42% ethanol (a type of alcohol) and approximately 15% propylene glycol. “See How should I take KALETRA?” For more information about KALETRA call 1-800-633-9110 or go to www.KALETRA.com KALETRA Tablets, 200 mg lopinavir and 50 mg ritonavir Manufactured by AbbVie LTD, Barceloneta, PR 00617 for AbbVie Inc., North Chicago, IL 60064 USA KALETRA Tablets, 100 mg lopinavir and 25 mg ritonavir and KALETRA Oral Solution AbbVie Inc., North Chicago, IL 60064 USA The brands listed are trademarks of their respective owners and are not trademarks of AbbVie Inc. The makers of these brands are not affiliated with and do not endorse AbbVie Inc. or its products. © 2019 AbbVie Inc. All rights reserved. 03-C068 |
|
Kaletra®(Lopinavir and Ritonavir) Tablets
ALERT: Find out about medicines that should NOT be taken with Kaletra®
Attention Pharmacist: Do not cover ALERT box with pharmacy label.
Dispense the accompanying Medication Guide to each patient

Kaletra®(Lopinavir and Ritonavir) Tablets
ALERT: Find out about medicines that should NOT be taken with Kaletra®
Attention Pharmacist: Do not cover ALERT box with pharmacy label.
Dispense the accompanying Medication Guide to each patient.

Lopinavir and Ritonavir Oral Solution
ALERT: Find out about medicines that should NOT be taken with KALETRA
Dispense the enclosed Medication Guide to each patient.

| KALETRA
lopinavir and ritonavir tablet, film coated |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| KALETRA
lopinavir and ritonavir solution |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KALETRA
lopinavir and ritonavir tablet, film coated |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - AbbVie Inc. (078458370) |




