Drug Detail:Lamisil (Terbinafine [ ter-bin-na-feen ])
Drug Class: Miscellaneous antifungals
Highlights of Prescribing Information
See full prescribing information for LAMISIL Tablets.
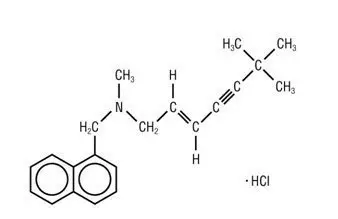
LAMISIL® (terbinafine hydrochloride) Tablets, 250 mg, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1992
Recent Major Changes
| Dosage and Administration: Assessment Prior to Initiation (2.1) | 8/2016 |
| Contraindications (4) | 8/2016 |
| Warnings and Precautions: Hepatotoxicty (5.1) | 8/2016 |
| Warnings and Precautions: Thrombotic Microangiopathy (5.8) | 1/2017 |
Indications and Usage for Lamisil
LAMISIL Tablets are an allylamine antifungal indicated for the treatment of onychomycosis of the toenail or fingernail due to dermatophytes (tinea unguium). (1)
Lamisil Dosage and Administration
- Prior to administering, evaluate patients for evidence of chronic or active liver disease. (2.1)
- Fingernail onychomycosis: One 250 mg tablet, once daily for 6 weeks. (2.2)
- Toenail onychomycosis: One 250 mg tablet, once daily for 12 weeks. (2.2)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Tablet, 250 mg (3)
Contraindications
- History of allergic reaction to oral terbinafine because of the risk of anaphylaxis. (4)
- Chronic or active liver disease. (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Liver failure, sometimes leading to liver transplant or death, has occurred with the use of oral terbinafine. Obtain pretreatment serum transaminases. Prior to initiating treatment and periodically during therapy, assess liver function tests. Discontinue LAMISIL Tablets if liver injury develops. (5.1)
- Taste disturbance, including taste loss, has been reported with the use of LAMISIL Tablets. Taste disturbance can be severe, may be prolonged, or may be permanent. Discontinue LAMISIL Tablets if taste disturbance occurs. (5.2)
- Smell disturbance, including loss of smell, has been reported with the use of LAMISIL Tablets. Smell disturbance may be prolonged, or may be permanent. Discontinue LAMISIL Tablets if smell disturbance occurs. (5.3)
- Depressive symptoms have been reported with terbinafine use. Prescribers should be alert to the development of depressive symptoms. (5.4)
- Severe neutropenia has been reported. If the neutrophil count is less than or equal to 1000 cells/mm3, LAMISIL Tablets should be discontinued. (5.5)
- Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, erythema multiforme, exfoliative dermatitis, bullous dermatitis, and drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) syndrome have been reported with oral terbinafine use. If signs or symptoms of drug reaction occur, treatment with LAMISIL Tablets should be discontinued. (5.6)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Common (greater than 2% of patients treated with LAMISIL Tablets) reported adverse events include headache, diarrhea, rash, dyspepsia, liver enzyme abnormalities, pruritus, taste disturbance, nausea, abdominal pain, and flatulence. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation at 1-888-669-6682 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
Terbinafine is an inhibitor of CYP450 2D6 isozyme and has an effect on metabolism of desipramine. Drug interactions have also been noted with cimetidine, fluconazole, cyclosporine, rifampin, and caffeine. (7.1)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 1/2017
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Lamisil
LAMISIL (terbinafine hydrochloride) Tablets are indicated for the treatment of onychomycosis of the toenail or fingernail due to dermatophytes (tinea unguium).
Prior to initiating treatment, appropriate nail specimens for laboratory testing [potassium hydroxide (KOH) preparation, fungal culture, or nail biopsy] should be obtained to confirm the diagnosis of onychomycosis.
2. Lamisil Dosage and Administration
2.1 Assessment Prior to Initiation
Before administering LAMISIL Tablets, evaluate patients for evidence of chronic or active liver disease [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
2.2 Dosage
Fingernail onychomycosis: One 250 mg tablet once daily for 6 weeks.
Toenail onychomycosis: One 250 mg tablet once daily for 12 weeks.
The optimal clinical effect is seen some months after mycological cure and cessation of treatment. This is related to the period required for outgrowth of healthy nail.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
Tablet, 250 mg white to yellow-tinged white circular, biconvex, beveled tablets imprinted with “LAMISIL” in circular form on one side and code “250” on the other side.
4. Contraindications
LAMISIL Tablets are contraindicated in patients with:
• History of allergic reaction to oral terbinafine because of the risk of anaphylaxis [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)]
• Chronic or active liver disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Hepatotoxicity
LAMISIL Tablets are contraindicated for patients with chronic or active liver disease. Before prescribing LAMISIL Tablets, perform liver function tests because hepatotoxicity may occur in patients with and without preexisting liver disease. Cases of liver failure, some leading to liver transplant or death, have occurred with the use of LAMISIL Tablets in individuals with and without preexisting liver disease.
In the majority of liver cases reported in association with use of LAMISIL Tablets, the patients had serious underlying systemic conditions. The severity of hepatic events and/or their outcome may be worse in patients with active or chronic liver disease. Periodic monitoring of liver function tests is recommended. Discontinue LAMISIL Tablets if biochemical or clinical evidence of liver injury develops.
Warn patients prescribed LAMISIL Tablets and/or their caregivers to report immediately to their healthcare providers any symptoms or signs of persistent nausea, anorexia, fatigue, vomiting, right upper abdominal pain or jaundice, dark urine, or pale stools. Advise patients with these symptoms to discontinue taking oral terbinafine, and immediately evaluate the patient’s liver function.
5.2 Taste Disturbance Including Loss of Taste
Taste disturbance, including taste loss, has been reported with the use of LAMISIL Tablets. It can be severe enough to result in decreased food intake, weight loss, anxiety, and depressive symptoms. Taste disturbance may resolve within several weeks after discontinuation of treatment, but may be prolonged (greater than 1 year), or may be permanent. If symptoms of a taste disturbance occur, LAMISIL Tablets should be discontinued.
5.3 Smell Disturbance Including Loss of Smell
Smell disturbance, including loss of smell, has been reported with the use of LAMISIL Tablets. Smell disturbance may resolve after discontinuation of treatment, but may be prolonged (greater than 1 year), or may be permanent. If symptoms of a smell disturbance occur, LAMISIL Tablets should be discontinued.
5.4 Depressive Symptoms
Depressive symptoms have occurred during postmarketing use of LAMISIL Tablets. Prescribers should be alert to the development of depressive symptoms, and patients should be instructed to report depressive symptoms to their physician.
5.5 Hematologic Effects
Transient decreases in absolute lymphocyte counts (ALCs) have been observed in controlled clinical trials. In placebo-controlled trials, 8/465 subjects receiving LAMISIL Tablets (1.7%) and 3/137 subjects receiving placebo (2.2%) had decreases in ALC to below 1000/mm3 on 2 or more occasions. In patients with known or suspected immunodeficiency, physicians should consider monitoring complete blood counts if treatment continues for more than 6 weeks. Cases of severe neutropenia have been reported. These were reversible upon discontinuation of LAMISIL Tablets, with or without supportive therapy. If clinical signs and symptoms suggestive of secondary infection occur, a complete blood count should be obtained. If the neutrophil count is less than or equal to 1000 cells/mm3, LAMISIL Tablets should be discontinued and supportive management started.
5.6 Serious Skin/Hypersensitivity Reactions
There have been postmarketing reports of serious skin/hypersensitivity reactions [e.g., Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, erythema multiforme, exfoliative dermatitis, bullous dermatitis, and drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) syndrome]. Manifestations of DRESS syndrome may include cutaneous reaction (such as rash or exfoliative dermatitis), eosinophilia, and one or more organ complications such as hepatitis, pneumonitis, nephritis, myocarditis, and pericarditis. If progressive skin rash or signs/symptoms of the above drug reactions occur, treatment with LAMISIL Tablets should be discontinued.
5.8 Thrombotic Microangiopathy
Cases of thrombotic microangiopathy (TMA), including thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura and hemolytic uremic syndrome, some fatal, have been reported with terbinafine. Discontinue terbinafine if clinical symptoms and laboratory findings consistent with TMA occur. The findings of unexplained thrombocytopenia and anemia should prompt further evaluation and consideration of diagnosis of TMA.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The most frequently reported adverse events observed in the 3 US/Canadian placebo-controlled trials are listed in the table below. The adverse events reported encompass gastrointestinal symptoms (including diarrhea, dyspepsia, and abdominal pain), liver test abnormalities, rashes, urticaria, pruritus, and taste disturbances. Changes in the ocular lens and retina have been reported following the use of LAMISIL Tablets in controlled trials. The clinical significance of these changes is unknown. In general, the adverse events were mild, transient, and did not lead to discontinuation from study participation.
| Adverse Event | Discontinuation | |||
| LAMISIL Tablets | Placebo | LAMISIL Tablets | Placebo | |
| (%) | (%) | (%) | (%) | |
| n=465 | n=137 | n=465 | n=137 | |
| Headache | 12.9 | 9.5 | 0.2 | 0.0 |
| Gastrointestinal Symptoms: | ||||
| Diarrhea | 5.6 | 2.9 | 0.6 | 0.0 |
| Dyspepsia | 4.3 | 2.9 | 0.4 | 0.0 |
| Abdominal Pain | 2.4 | 1.5 | 0.4 | 0.0 |
| Nausea | 2.6 | 2.9 | 0.2 | 0.0 |
| Flatulence | 2.2 | 2.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Dermatological Symptoms: | ||||
| Rash | 5.6 | 2.2 | 0.9 | 0.7 |
| Pruritus | 2.8 | 1.5 | 0.2 | 0.0 |
| Urticaria | 1.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Liver Enzyme Abnormalities* | 3.3 | 1.4 | 0.2 | 0.0 |
| Taste Disturbance | 2.8 | 0.7 | 0.2 | 0.0 |
| Visual Disturbance | 1.1 | 1.5 | 0.9 | 0.0 |
* Liver enzyme abnormalities greater than or equal to 2x the upper limit of normal range.
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 Drug-Drug Interactions
In vivo studies have shown that terbinafine is an inhibitor of the CYP450 2D6 isozyme. Drugs predominantly metabolized by the CYP450 2D6 isozyme include the following drug classes: tricyclic antidepressants, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, beta-blockers, antiarrhythmics class 1C (e.g., flecainide and propafenone) and monoamine oxidase inhibitors Type B. Coadministration of LAMISIL Tablets should be done with careful monitoring and may require a reduction in dose of the 2D6-metabolized drug. In a study to assess the effects of terbinafine on desipramine in healthy volunteers characterized as normal metabolizers, the administration of terbinafine resulted in a 2-fold increase in Cmax and a 5-fold increase in area under the curve (AUC). In this study, these effects were shown to persist at the last observation at 4 weeks after discontinuation of LAMISIL Tablets. In studies in healthy subjects characterized as extensive metabolizers of dextromethorphan (antitussive drug and CYP2D6 probe substrate), terbinafine increases the dextromethorphan/ dextrorphan metabolite ratio in urine by 16- to 97-fold on average. Thus, terbinafine may convert extensive CYP2D6 metabolizers to poor metabolizer status.
In vitro studies with human liver microsomes showed that terbinafine does not inhibit the metabolism of tolbutamide, ethinylestradiol, ethoxycoumarin, cyclosporine, cisapride and fluvastatin. In vivo drug-drug interaction studies conducted in healthy volunteer subjects showed that terbinafine does not affect the clearance of antipyrine or digoxin. Terbinafine decreases the clearance of caffeine by 19%. Terbinafine increases the clearance of cyclosporine by 15%.
The influence of terbinafine on the pharmacokinetics of fluconazole, cotrimoxazole (trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole), zidovudine or theophylline was not considered to be clinically significant.
Coadministration of a single dose of fluconazole (100 mg) with a single dose of terbinafine resulted in a 52% and 69% increase in terbinafine Cmax and AUC, respectively. Fluconazole is an inhibitor of CYP2C9 and CYP3A enzymes. Based on this finding, it is likely that other inhibitors of both CYP2C9 and CYP3A4 (e.g., ketoconazole, amiodarone) may also lead to a substantial increase in the systemic exposure (Cmax and AUC) of terbinafine when concomitantly administered.
There have been spontaneous reports of increase or decrease in prothrombin times in patients concomitantly taking oral terbinafine and warfarin, however, a causal relationship between LAMISIL Tablets and these changes has not been established.
Terbinafine clearance is increased 100% by rifampin, a CYP450 enzyme inducer, and decreased 33% by cimetidine, a CYP450 enzyme inhibitor. Terbinafine clearance is unaffected by cyclosporine. There is no information available from adequate drug-drug interaction studies with the following classes of drugs: oral contraceptives, hormone replacement therapies, hypoglycemics, phenytoins, thiazide diuretics, and calcium channel blockers.
12. Lamisil - Clinical Pharmacology
| LAMISIL
terbinafine hydrochloride tablet |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation (002147023) |