Drug Detail:Lescol xl (Fluvastatin [ floo-va-sta-tin ])
Drug Class: Statins
Highlights of Prescribing Information
Lescol® XL (fluvastatin sodium) extended-release tablets for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2000
Recent Major Changes
| Warnings and Precautions (5.2) |
9/2020 |
Indications and Usage for Lescol XL
LESCOL XL is an HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor (statin) indicated as an adjunctive therapy to diet to:
- Reduce elevated TC, LDL-C, Apo B, and TG, and to increase HDL-C in adult patients with primary hypercholesterolemia and mixed dyslipidemia (1.1)
- Reduce elevated TC, LDL-C, and Apo B levels in boys and post-menarchal girls, 10 to 16 years of age, with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia after failing an adequate trial of diet therapy (1.1)
- Reduce the risk of undergoing revascularization procedures in patients with clinically evident Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) (1.2)
- Slow the progression of atherosclerosis in patients with CHD (1.2)
Limitations of Use:
- LESCOL XL has not been studied in conditions where the major abnormality is elevation of chylomicrons, VLDL, or IDL (i.e., hyperlipoproteinemia Types I, III, IV, or V) (1.3)
Lescol XL Dosage and Administration
- Dose range: 20 mg to 80 mg/day (2.1)
- LESCOL XL can be taken with or without food and may be taken at any time of the day (2.1)
- Do not break, crush or chew LESCOL XL tablets prior to administration (2.1)
- Adults: the recommended starting dose is 80 mg (administered as one 80 mg LESCOL XL once daily) (2.2)
- Children with Heterozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia (ages 10 to 16, inclusive): the recommended starting dose is fluvastatin capsule 20 mg once daily (2.3)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
LESCOL XL Tablets: 80 mg (3)
Contraindications
- Hypersensitivity to any component of this medication (4.1)
- Active liver disease or unexplained, persistent elevations in serum transaminases (4.2, 5.3)
- Women who are pregnant or may become pregnant (4.3, 8.1)
- Nursing mothers (4.4, 8.3)
Warnings and Precautions
- Skeletal muscle effects (e.g., myopathy and rhabdomyolysis): Risks increase with advanced age (≥ 65), uncontrolled hypothyroidism, renal impairment, and combination use with cyclosporine, or gemfibrozil. Advise patients to promptly report to their physician unexplained and/or persistent muscle pain, tenderness, or weakness and discontinue LESCOL XL if myopathy is diagnosed or suspected (5.1, 8.5, 8.7)
- Patients should be advised to report promptly any symptoms of myopathy. LESCOL XL therapy should be discontinued if myopathy is diagnosed or suspected (5.1)
- Immune-Mediated Necrotizing Myopathy (IMNM): There have been rare reports of IMNM, an autoimmune myopathy, associated with statin use. IMNM is characterized by proximal muscle weakness and elevated serum creatine kinase, which persist despite discontinuation of statin treatment; positive anti-HMG CoA reductase antibody; muscle biopsy showing necrotizing myopathy; and improvement with imunosuppressive agents (5.2)
- Liver enzyme abnormalities: Persistent elevations in hepatic transaminases can occur. Check liver enzyme tests before initiating therapy and as clinically indicated thereafter (5.3)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most frequent adverse reactions (rate ≥ 2% and > placebo) are headache, dyspepsia, myalgia, abdominal pain, and nausea (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation at 1-888-669-6682 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
- Cyclosporine: Combination increases fluvastatin exposure. Limit fluvastatin dose to 20 mg (2.4, 7.1)
- Fluconazole: Combination increases fluvastatin exposure. Limit fluvastatin dose to 20 mg (2.5, 7.2)
- Concomitant lipid-lowering therapies: Use with fibrates or lipid-modifying doses (≥ 1 g/day) of niacin increases the risk of adverse skeletal muscle effects. Caution should be used when prescribing with LESCOL XL (5.1, 7.3, 7.4)
- Glyburide: Monitor blood glucose levels when fluvastatin dose is changed (7.6)
- Phenytoin: Monitor plasma phenytoin levels when fluvastatin treatment is initiated or when the dosage is changed (7.7)
- Warfarin and coumarin derivates: Monitor prothrombin times when fluvastatin coadministration is initiated, discontinued, or the dosage changed (7.8)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 9/2020
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Lescol XL
Therapy with lipid-altering agents should be only one component of multiple risk factor intervention in individuals at significantly increased risk for atherosclerotic vascular disease due to hypercholesterolemia. Drug therapy is indicated as an adjunct to diet when the response to a diet restricted in saturated fat and cholesterol and other non-pharmacologic measures alone has been inadequate.
1.1 Hypercholesterolemia (Heterozygous Familial and Nonfamilial) and Mixed Dyslipidemia
LESCOL XL is indicated
- as an adjunct to diet to reduce elevated total cholesterol (Total-C), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), triglyceride (TG) and apolipoprotein B (Apo B) levels, and to increase high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) in patients with primary hypercholesterolemia and mixed dyslipidemia (Fredrickson Type IIa and IIb).
- as an adjunct to diet to reduce Total-C, LDL-C, and Apo B levels in adolescent boys and adolescent girls who are at least one year post-menarche, 10-16 years of age, with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia and the following findings are present:
- LDL-C remains ≥ 190 mg/dL or
- LDL-C remains ≥ 160 mg/dL and:
- there is a positive family history of premature cardiovascular disease or
- two or more other cardiovascular disease risk factors are present
- there is a positive family history of premature cardiovascular disease or
- LDL-C remains ≥ 190 mg/dL or
The NCEP classification of cholesterol levels in pediatric patients with a familial history of hypercholesterolemia or premature CVD is summarized below.
| Category | Total-C (mg/dL) | LDL-C (mg/dL) |
| Acceptable | < 170 | < 110 |
| Borderline | 170-199 | 110-129 |
| High | ≥ 200 | ≥ 130 |
Children treated with fluvastatin in adolescence should be reevaluated in adulthood and appropriate changes made to their cholesterol-lowering regimen to achieve adult treatment goals.
2. Lescol XL Dosage and Administration
2.1 General Dosing Information
Dose range: 20 mg to 80 mg/day.
LESCOL XL can be administered orally as a single dose, with or without food.
Do not break, crush or chew LESCOL XL tablets prior to administration.
Since the maximal effect of a given dose is seen within 4 weeks, periodic lipid determinations should be performed at this time and dosage adjusted according to the patient’s response to therapy and established treatment guidelines.
For patients requiring LDL-C reduction to a goal of ≥ 25%, the recommended starting dose is 80 mg as one LESCOL XL tablet administered as a single dose at any time of the day. For patients requiring LDL-C reduction to a goal of < 25%, a starting dose of 20 mg may be used.
2.2 Adult Patients With Hypercholesterolemia (Heterozygous Familial and Nonfamilial) and Mixed Dyslipidemia
The recommended starting dose for LESCOL XL is one 80 mg tablet administered as a single dose at any time of the day.
2.3 Pediatric Patients (10 to 16 years of age) With Heterozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia
The recommended starting dose is one 20 mg fluvastatin capsule. Dose adjustments, up to a maximum daily dose administered one LESCOL XL 80 mg tablet once daily should be made at 6-week intervals. Doses should be individualized according to the goal of therapy [see NCEP Pediatric Panel Guidelines and Clinical Studies (14)]1.
1National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP): Highlights of the Report of the Expert Panel on Blood Cholesterol Levels in Children and Adolescents. Pediatrics.89(3):495-501. 1992.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
LESCOL XL 80 mg tablets are yellow, round, slightly biconvex film-coated tablets with beveled edges debossed with “LESCOL XL” on one side and “80” on the other.
4. Contraindications
4.1 Hypersensitivity to Any Component of This Medication
LESCOL XL is contraindicated in patients with hypersensitivity to any component of this medication.
4.2 Active Liver Disease
LESCOL XL is contraindicated in patients with active liver disease or unexplained, persistent elevations in serum transaminases [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
4.3 Pregnancy
LESCOL XL is contraindicated in women who are pregnant or may become pregnant. Serum cholesterol and triglycerides increase during normal pregnancy, and cholesterol or cholesterol derivatives are essential for fetal development. LESCOL XL may cause fetal harm when administered to pregnant women. Atherosclerosis is a chronic process and the discontinuation of lipid-lowering drugs during pregnancy should have little impact on the outcome of long-term therapy of primary hypercholesterolemia.
LESCOL XL should be administered to women of childbearing age only when such patients are highly unlikely to conceive and have been informed of the potential hazards. If the patient becomes pregnant while taking this drug, LESCOL XL should be discontinued and the patient should be apprised of the potential hazard to the fetus [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
4.4 Nursing Mothers
Fluvastatin is secreted into the breast milk of animals and because HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors have the potential to cause serious adverse reactions in nursing infants, women who require treatment with LESCOL XL should be advised not to breastfeed their infants [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Skeletal Muscle
Rhabdomyolysis with acute renal failure secondary to myoglobinuria have been reported with LESCOL XL and other drugs in this class.
LESCOL XL should be prescribed with caution in patients with predisposing factors for myopathy. These factors include advanced age (> 65 years), renal impairment, and inadequately treated hypothyroidism.
The risk of myopathy and/or rhabdomyolysis with statins is increased with concurrent therapy with cyclosporine, erythromycin, fibrates or niacin. Myopathy was not observed in a clinical trial in 74 patients involving patients who were treated with LESCOL XL together with niacin. Isolated cases of myopathy have been reported during postmarketing experience with concomitant administration of LESCOL XL and colchicine. No information is available on the pharmacokinetic interaction between LESCOL XL and colchicine.
Uncomplicated myalgia has also been reported in fluvastatin-treated patients [see Adverse Reactions (6)]. In clinical trials, uncomplicated myalgia has been observed infrequently in patients treated with fluvastatin at rates indistinguishable from placebo. Myopathy, defined as muscle aching or muscle weakness in conjunction with increases in CPK values to greater than 10 times the upper limit of normal, was < 0.1% in fluvastatin clinical trials. Myopathy should be considered in any patient with diffuse myalgias, muscle tenderness or weakness, and/or marked elevation of CPK.
All patients should be advised to promptly report to their physician unexplained muscle pain, tenderness, or weakness, particularly if accompanied by malaise or fever or if muscle signs and symptoms persist after discontinuing LESCOL XL.
LESCOL XL therapy should be discontinued if markedly elevated CPK levels occur or myopathy is diagnosed or suspected. LESCOL XL therapy should also be temporarily withheld in any patient experiencing an acute or serious condition predisposing to the development of renal failure secondary to rhabdomyolysis, e.g., sepsis; hypotension; major surgery; trauma; severe metabolic, endocrine, or electrolyte disorders; or uncontrolled epilepsy.
5.2 Immune-Mediated Necrotizing Myopathy
There have been rare reports of immune-mediated necrotizing myopathy (IMNM), an autoimmune myopathy, associated with statin use. IMNM is characterized by proximal muscle weakness and elevated serum creatine kinase, which persist despite discontinuation of statin treatment; positive anti-HMG CoA reductase antibody; muscle biopsy showing necrotizing myopathy; and improvement with immunosuppressive agents. Additional neuromuscular and serologic testing may be necessary. Treatment with immunosuppressive agents may be required. Consider risk of IMNM carefully prior to initiation of a different statin. If therapy is initiated with a different statin, monitor for signs and symptoms of IMNM.
5.3 Liver Enzymes
Increases in serum transaminases (aspartate aminotransferase [AST]/serum glutamic-oxaloacetic transaminase, or alanine aminotransferase [ALT]/serum glutamic-pyruvic transaminase) have been reported with HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, including LESCOL XL. In most cases, the elevations were transient and resolved or improved on continued therapy or after a brief interruption in therapy.
Approximately 1.1% of patients treated with fluvastatin capsules in worldwide trials developed dose-related, persistent elevations of serum transaminase levels to more than 3 times the upper limit of normal (ULN). Fourteen of these patients (0.6%) were discontinued from therapy. In all clinical trials, a total of 33/2969 patients (1.1%) had persistent transaminase elevations with an average fluvastatin exposure of approximately 71.2 weeks; 19 of these patients (0.6%) were discontinued. The majority of patients with these abnormal biochemical findings were asymptomatic.
In a pooled analysis of all placebo-controlled studies in which LESCOL capsules were used, persistent transaminase elevations (> 3 times the ULN on two consecutive weekly measurements) occurred in 0.2%, 1.5%, and 2.7% of patients treated with daily doses of 20, 40, and 80 mg (titrated to 40 mg twice daily) fluvastatin capsules, respectively. Ninety-one percent of the cases of persistent liver function test abnormalities (20 of 22 patients) occurred within 12 weeks of therapy and in all patients with persistent liver function test abnormalities there was an abnormal liver function test present at baseline or by Week 8.
In the pooled analysis of the 24-week controlled trials, persistent transaminase elevation occurred in 1.9%, 1.8% and 4.9% of patients treated with LESCOL XL 80 mg, fluvastatin capsules 40 mg and fluvastatin capsules 40 mg twice daily, respectively. In 13 of 16 patients treated with LESCOL XL, the abnormality occurred within 12 weeks of initiation of treatment with LESCOL XL 80 mg.
It is recommended that liver enzyme tests be performed prior to the initiation of LESCOL XL, and if signs or symptoms of liver injury occur.
There have been rare postmarketing reports of fatal and non-fatal hepatic failure in patients taking statins, including fluvastatin. If serious liver injury with clinical symptoms and/or hyperbilirubinemia or jaundice occurs during treatment with LESCOL XL, promptly interrupt therapy. If an alternate etiology is not found, do not restart LESCOL XL.
In very rare cases, possibly drug-related hepatitis was observed that resolved upon discontinuation of treatment.1 Active liver disease or unexplained serum transaminase elevations are contraindications to the use of LESCOL XL [see Contraindications (4.2) and Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]. Caution should be exercised when fluvastatin is administered to patients with a history of liver disease or heavy alcohol ingestion [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Such patients should be closely monitored.
5.4 Endocrine Effects
Increases in HbA1c and fasting serum glucose levels have been reported with HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, including LESCOL XL.
Statins interfere with cholesterol synthesis and lower circulating cholesterol levels and, as such, might theoretically blunt adrenal or gonadal steroid hormone production.
LESCOL XL exhibited no effect upon non-stimulated cortisol levels and demonstrated no effect upon thyroid metabolism as assessed by measurement of thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH). Small declines in total serum testosterone have been noted in treated groups, but no commensurate elevation in LH occurred, suggesting that the observation was not due to a direct effect upon testosterone production. No effect upon FSH in males was noted. Due to the limited number of premenopausal females studied to date, no conclusions regarding the effect of LESCOL XL upon female sex hormones may be made.
Two clinical studies in patients receiving fluvastatin at doses up to 80 mg daily for periods of 24 to 28 weeks demonstrated no effect of treatment upon the adrenal response to ACTH stimulation. A clinical study evaluated the effect of fluvastatin at doses up to 80 mg daily for 28 weeks upon the gonadal response to HCG stimulation. Although the mean total testosterone response was significantly reduced (p < 0.05) relative to baseline in the 80 mg group, it was not significant in comparison to the changes noted in groups receiving either 40 mg of fluvastatin or placebo.
Patients treated with LESCOL XL who develop clinical evidence of endocrine dysfunction should be evaluated appropriately. Caution should be exercised if a statin or other agent used to lower cholesterol levels is administered to patients receiving other drugs (e.g., ketoconazole, spironolactone, cimetidine) that may decrease the levels of endogenous steroid hormones.
5.5 Central Nervous System Toxicity
Central Nervous System (CNS) effects, as evidenced by decreased activity, ataxia, loss of righting reflex, and ptosis were seen in the following animal studies: the 18-month mouse carcinogenicity study at 50 mg/kg/day, the 6-month dog study at 36 mg/kg/day, the 6-month hamster study at 40 mg/kg/day, and in acute, high-dose studies in rats and hamsters (50 mg/kg), rabbits (300 mg/kg) and mice (1,500 mg/kg). CNS toxicity in the acute high-dose studies was characterized (in mice) by conspicuous vacuolation in the ventral white columns of the spinal cord at a dose of 5,000 mg/kg and (in rats) by edema with separation of myelinated fibers of the ventral spinal tracts and sciatic nerve at a dose of 1,500 mg/kg. CNS toxicity, characterized by periaxonal vacuolation, was observed in the medulla of dogs that died after treatment for 5 weeks with 48 mg/kg/day; this finding was not observed in the remaining dogs when the dose level was lowered to 36 mg/kg/day. CNS vascular lesions, characterized by perivascular hemorrhages, edema, and mononuclear cell infiltration of perivascular spaces, have been observed in dogs treated with other members of this drug class. No CNS lesions have been observed after chronic treatment for up to 2 years with fluvastatin in the mouse (at doses up to 350 mg/kg/day), rat (up to 24 mg/kg/day), or dog (up to 16 mg/kg/day).
Prominent bilateral posterior Y suture lines in the ocular lens were seen in dogs after treatment with 1, 8, and 16 mg/kg/day for 2 years.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following serious adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the label:
- Rhabdomyolysis with myoglobinuria and acute renal failure and myopathy (including myositis) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- Liver Enzyme Abnormalities [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
6.1 Clinical Studies Experience in Adult Patients
Because clinical studies on fluvastatin capsules/LESCOL XL are conducted in varying study populations and study designs, the frequency of adverse reactions observed in the clinical studies of fluvastatin capsules/LESCOL XL cannot be directly compared with that in the clinical studies of other statins and may not reflect the frequency of adverse reactions observed in clinical practice.
In the fluvastatin capsule placebo-controlled clinical trials database of 2326 patients treated with fluvastatin1 (age range 18 to 75 years, 44% women, 94% Caucasians, 4% Blacks, 2% other ethnicities) with a median treatment duration of 24 weeks, 3.4% of patients on fluvastatin capsules and 2.3% patients on placebo discontinued due to adverse reactions regardless of causality. The most common adverse reactions that led to treatment discontinuation and occurred at an incidence greater than placebo were: transaminase increased (0.8%), upper abdominal pain (0.3%), dyspepsia (0.3%), fatigue (0.2%), and diarrhea (0.2%).
In the LESCOL XL database of controlled clinical trials of 912 patients treated with LESCOL XL (age range 21 to 87 years, 52% women, 91% Caucasians, 4% Blacks, 5% other ethnicities) with a median treatment duration of 24 weeks, 3.9% of patients on LESCOL XL discontinued due to adverse reactions regardless of causality. The most common adverse reactions that led to treatment discontinuation were abdominal pain (0.7%), diarrhea (0.5%), nausea (0.4%), dyspepsia (0.4%), and chest pain (0.3%).
Clinically relevant adverse experiences occurring in the fluvastatin capsules and LESCOL XL controlled studies with a frequency ≥ 2%, regardless of causality, included the following:
| Fluvastatin capsules1
N = 2326 (%) | Placebo1
N = 960 (%) | LESCOL XL2
N = 912 (%) |
||
| Musculoskeletal | Myalgia | 5.0 | 4.5 | 3.8 |
| Arthritis | 2.1 | 2.0 | 1.3 | |
| Arthropathy | NA | NA | 3.2 | |
| Respiratory | Sinusitis | 2.6 | 1.9 | 3.5 |
| Bronchitis | 1.8 | 1.0 | 2.6 | |
| Gastrointestinal | Dyspepsia | 7.9 | 3.2 | 3.5 |
| Diarrhea | 4.9 | 4.2 | 3.3 | |
| Abdominal pain | 4.9 | 3.8 | 3.7 | |
| Nausea | 3.2 | 2.0 | 2.5 | |
| Flatulence | 2.6 | 2.5 | 1.4 | |
| Tooth disorder | 2.1 | 1.7 | 1.4 | |
| Psychiatric | Insomnia | 2.7 | 1.4 | 0.8 |
| Genitourinary | Urinary tract infection | 1.6 | 1.1 | 2.7 |
| Miscellaneous | Headache | 8.9 | 7.8 | 4.7 |
| Influenza-like symptoms | 5.1 | 5.7 | 7.1 | |
| Accidental trauma | 5.1 | 4.8 | 4.2 | |
| Fatigue | 2.7 | 2.3 | 1.6 | |
| Allergy | 2.3 | 2.2 | 1.0 | |
| 1Controlled trials with fluvastatin capsules (20 and 40 mg daily and 40 mg twice daily) compared to placebo. 2Controlled trials with LESCOL XL 80 mg Tablets as compared to fluvastatin capsules. |
||||
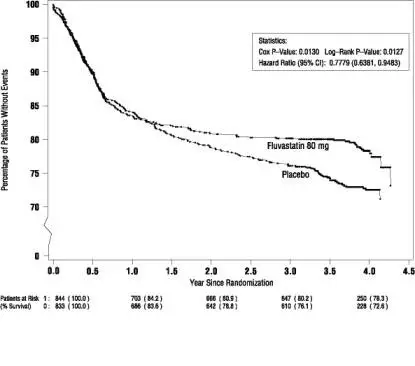
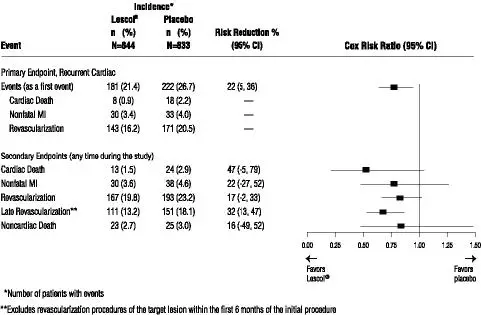
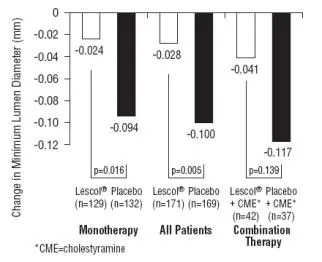
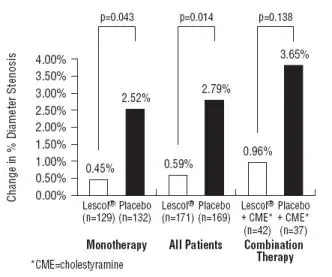
LESCOL Intervention Prevention Study
In the LESCOL Intervention Prevention Study (LIPS), the effect of LESCOL (fluvastatin capsules) 40 mg, administered twice daily on the risk of recurrent cardiac events was assessed in 1677 patients with CHD who had undergone a percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) procedure. This was a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study, patients were treated with dietary/lifestyle counseling and either fluvastatin capsules 40 mg (n = 844) or placebo (n = 833) given twice daily for a median of 3.9 years [see Clinical Studies (14.3)].
| Fluvastatin Capsules
40 mg twice daily N = 822 (%) | Placebo
N = 818 (%) |
||
| Cardiac disorders | Atrial fibrillation | 2.4 | 2.0 |
| Gastrointestinal disorders | Abdominal pain upper | 6.3 | 4.5 |
| Constipation | 3.3 | 2.1 | |
| Dyspepsia | 4.5 | 4.0 | |
| Gastric disorder | 2.7 | 2.1 | |
| Nausea | 2.7 | 2.3 | |
| General disorders | Fatigue | 4.7 | 3.8 |
| Edema peripheral | 4.4 | 2.9 | |
| Infections and infestations | Bronchitis | 2.3 | 2.0 |
| Nasopharyngitis | 2.8 | 2.1 | |
| Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders | Arthralgia | 2.1 | 1.8 |
| Myalgia | 2.2 | 1.6 | |
| Pain in extremity | 4.1 | 2.7 | |
| Nervous system disorders | Dizziness | 3.9 | 3.5 |
| Syncope | 2.4 | 2.2 | |
| Respiratory disorders | Dyspnea exertional | 2.8 | 2.4 |
| Vascular disorders | Hypertension | 5.8 | 4.2 |
| Intermittent claudication | 2.3 | 2.1 | |
6.2 Clinical Studies Experience in Pediatric Patients
In patients aged < 18 years, efficacy and safety have not been studied for treatment periods longer than two years.
In two open-label uncontrolled studies, 66 boys and 48 girls with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (9 to 16 years of age, 80% Caucasian, 19% Other [mixed ethnicity], 1% Asians) were treated with fluvastatin sodium administered as fluvastatin capsules 20 mg to 40 mg twice daily, or LESCOL XL 80 mg extended-release tablet [see Clinical Studies (14.2) and Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
6.3 Postmarketing Experience
Because adverse reactions from spontaneous reports are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is generally not possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure. The following effects have been reported with drugs in this class. Not all the effects listed below have necessarily been associated with fluvastatin sodium therapy.
Musculoskeletal: muscle cramps, myalgia, myopathy, rhabdomyolysis, arthralgias, muscle spasms, muscle weakness, myositis.
There have been rare reports of immune-mediated necrotizing myopathy associated with statin use [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Neurological: dysfunction of certain cranial nerves (including alteration of taste, impairment of extra-ocular movement, facial paresis), tremor, dizziness, vertigo, paresthesia, hypoesthesia, dysesthesia, peripheral neuropathy, peripheral nerve palsy.
There have been rare postmarketing reports of cognitive impairment (e.g., memory loss, forgetfulness, amnesia, memory impairment, confusion) associated with statin use. These cognitive issues have been reported for all statins. The reports are generally nonserious, and reversible upon statin discontinuation, with variable times to symptom onset (1 day to years) and symptom resolution (median of 3 weeks).
Psychiatric: anxiety, insomnia, depression, psychic disturbances
Respiratory: interstitial lung disease
Hypersensitivity Reactions: An apparent hypersensitivity syndrome has been reported rarely which has included one or more of the following features: anaphylaxis, angioedema, lupus erythematosus-like syndrome, polymyalgia rheumatica, vasculitis, purpura, thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, hemolytic anemia, positive ANA, ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate) increase, eosinophilia, arthritis, arthralgia, urticaria, asthenia, photosensitivity reaction, fever, chills, flushing, malaise, dyspnea, toxic epidermal necrolysis, erythema multiforme, including Stevens-Johnson syndrome.
Gastrointestinal: pancreatitis, hepatitis, including chronic active hepatitis, cholestatic jaundice, fatty change in liver, cirrhosis, fulminant hepatic necrosis, hepatoma, anorexia, vomiting, fatal, and non-fatal hepatic failure
Skin: rash, dermatitis, including bullous dermatitis, eczema, alopecia, pruritus, a variety of skin changes (e.g., nodules, discoloration, dryness of skin/mucous membranes, changes to hair/nails)
Reproductive: gynecomastia, loss of libido, erectile dysfunction
Eye: progression of cataracts (lens opacities), ophthalmoplegia
Laboratory abnormalities: elevated transaminases, alkaline phosphatase, gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase and bilirubin; thyroid function abnormalities
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 Cyclosporine
Cyclosporine coadministration increases fluvastatin exposure. Therefore, in patients taking cyclosporine, therapy should be limited to fluvastatin 20 mg twice daily [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
7.2 Fluconazole
Administration of fluvastatin 40 mg single dose to healthy volunteers pre-treated with fluconazole for 4 days results in an increase of fluvastatin exposure. Therefore, in patients taking fluconazole, therapy should be limited to fluvastatin 20 mg twice daily [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
7.3 Gemfibrozil
Due to an increased risk of myopathy/rhabdomyolysis when HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors are coadministered with gemfibrozil, concomitant administration of LESCOL XL with gemfibrozil should be avoided.
7.4 Other Fibrates
Because it is known that the risk of myopathy during treatment with HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors is increased with concurrent administration of other fibrates, LESCOL XL should be administered with caution when used concomitantly with other fibrates [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
7.5 Niacin
The risk of skeletal muscle effects may be enhanced when fluvastatin is used in combination with lipid-modifying doses (≥ 1 g/day) of niacin; a reduction in fluvastatin dosage should be considered in this setting [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
7.6 Glyburide
Concomitant administration of fluvastatin and glyburide increased glyburide exposures. Patients on concomitant therapy of glyburide and fluvastatin should continue to be monitored appropriately [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
7.7 Phenytoin
Concomitant administration of fluvastatin and phenytoin increased phenytoin exposures. Patients should continue to be monitored appropriately when fluvastatin therapy is initiated or when fluvastatin dose is changed [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
7.8 Warfarin
Bleeding and/or increased prothrombin times have been reported in patients taking coumarin anticoagulants concomitantly with other HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors. Therefore, patients receiving warfarin-type anticoagulants should have their prothrombin times closely monitored when fluvastatin sodium is initiated or the dosage of fluvastatin sodium is changed.
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category X
LESCOL XL is contraindicated in women who are or may become pregnant [see Contraindications (4.3)].
Lipid lowering drugs are contraindicated during pregnancy, because cholesterol and cholesterol derivatives are needed for normal fetal development. Serum cholesterol and triglycerides increase during normal pregnancy. Atherosclerosis is a chronic process, and discontinuation of lipid-lowering drugs during pregnancy should have little impact on long-term outcomes of primary hypercholesterolemia therapy.
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies of use with LESCOL XL during pregnancy. Rare reports of congenital anomalies have been received following intrauterine exposure to other statins. In a review2 of about 100 prospectively followed pregnancies in women exposed to other statins, the incidences of congenital anomalies, spontaneous abortions, and fetal deaths/stillbirths did not exceed the rate expected in the general population. The number of cases is adequate only to exclude a 3- to 4-fold increase in congenital anomalies over background incidence. In 89% of prospectively followed pregnancies, drug treatment was initiated prior to pregnancy and was discontinued at some point in the first trimester when pregnancy was identified.
Teratology studies with fluvastatin in rats and rabbits showed maternal toxicity at high dose levels, but there was no evidence of embryotoxic or teratogenic potential [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13)].
LESCOL XL should be administered to women of child-bearing potential only when such patients are highly unlikely to conceive and have been informed of the potential hazards. If a woman becomes pregnant while taking LESCOL XL, the drug should be discontinued and the patient advised again as to the potential hazards to the fetus.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
Based on animal data, fluvastatin is present in breast milk in a 2:1 ratio (milk:plasma). Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants, nursing women should not take LESCOL XL [see Contraindications (4.4)].
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and efficacy of LESCOL XL in children and adolescent patients 9 to 16 years of age with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia have been evaluated in open-label, uncontrolled clinical trials for a duration of two years. The most common adverse events observed were influenza and infections. In these limited uncontrolled studies, there was no detectable effect on growth or sexual maturation in the adolescent boys or on menstrual cycle length in girls [see Clinical Studies (14.2), Adverse Reactions (6.3), and Dosage and Administration (2.2)]. Adolescent females should be counseled on appropriate contraceptive methods while on fluvastatin therapy [see Contraindications (4)].
8.5 Geriatric Use
Fluvastatin exposures were not significantly different between the nonelderly and elderly populations (age ≥ 65 years) [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Since advanced age (> 65 years) is a predisposing factor for myopathy, LESCOL XL should be prescribed with caution in the elderly.
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
LESCOL XL are contraindicated in patients with active liver disease or unexplained, persistent elevations in serum transaminases [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.7 Renal Impairment
Dose adjustments for mild to moderate renal impairment are not necessary. Fluvastatin has not been studied at doses greater than 40 mg in patients with severe renal impairment; therefore, caution should be exercised when treating such patients at higher doses [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
10. Overdosage
To date, there has been limited experience with overdosage of fluvastatin. If an overdose occurs, it should be treated symptomatically with laboratory monitoring and supportive measures should be instituted as required. The dialyzability of fluvastatin sodium and of its metabolites in humans is not known at present [see Warnings and Precautions (5)].
In the pediatric population, there have been reports of overdosage with fluvastatin sodium in children, including a 2 year-old and the other 3 years of age, either of whom may have possibly ingested fluvastatin sodium. The maximum amount of fluvastatin sodium that could have been ingested was 80 mg (4 x 20 mg capsules). Vomiting was induced by ipecac in both children and no capsules were noted in their emesis. Neither child experienced any adverse symptoms and both recovered from the incident without problems.
In the postmarketing experience there have been reports of accidental ingestion of fluvastatin capsules in infants up to 3 years of age. In one case, increased serum CPK values were noted. There have been reports of intentional overdose in adolescents with the development of hepatic enzyme elevations, convulsions and gastroenteritis/vomiting/diarrhea. One case of intentional overdose as suicide attempt in a 15 year-old female reported ingestion of 2,800 mg LESCOL XL with hepatic enzyme elevation.
11. Lescol XL Description
Fluvastatin sodium is a water-soluble cholesterol lowering agent which acts through the inhibition of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase.
Fluvastatin sodium is [R*,S*-(E)]-(±)-7-[3-(4-fluorophenyl)-1-(1-methylethyl)-1H-indol-2-yl]-3,5-dihydroxy-6-heptenoic acid, monosodium salt. The empirical formula of fluvastatin sodium is C24H25FNO4•Na, its molecular weight is 433.46 and its structural formula is:
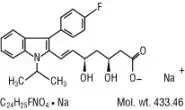
This molecular entity is the first entirely synthetic HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor, and is in part structurally distinct from the fungal derivatives of this therapeutic class.
Fluvastatin sodium is a white to pale yellow, hygroscopic powder soluble in water, ethanol and methanol. LESCOL XL is supplied as extended-release tablets containing fluvastatin sodium, equivalent to 80 mg of fluvastatin, for oral administration.
Active Ingredient: fluvastatin sodium
Inactive Ingredients in extended-release tablets: hydroxypropyl cellulose, hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, polyethylene glycol 8000, potassium bicarbonate, povidone, titanium dioxide, and yellow iron oxide.
12. Lescol XL - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Fluvastatin is a competitive inhibitor of HMG-CoA reductase, the rate limiting enzyme that converts 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) to mevalonate, a precursor of sterols, including cholesterol. The inhibition of cholesterol biosynthesis reduces the cholesterol in hepatic cells, which stimulates the synthesis of LDL receptors and thereby increases the uptake of LDL particles. The end result of these biochemical processes is a reduction of the plasma cholesterol concentration.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Following oral administration of the capsule, fluvastatin reaches peak concentrations in less than 1 hour. The absolute bioavailability is 24% (range 9% to 50%) after administration of a 10 mg dose.
At steady state, administration of fluvastatin with the evening meal results in a 50% decrease in Cmax, an 11% decrease in AUC, and a more than 2-fold increase in Tmax as compared to administration 4 hours after the evening meal. No significant differences in the lipid-lowering effects were observed between the two administrations. After single or multiple doses above 20 mg, fluvastatin exhibits saturable first-pass metabolism resulting in more than dose proportional plasma fluvastatin concentrations.
Fluvastatin administered as LESCOL XL 80 mg tablets reaches peak concentration in approximately 3 hours under fasting conditions, after a low-fat meal, or 2.5 hours after a low-fat meal. The mean relative bioavailability of the XL tablet is approximately 29% (range 9% to 66%) compared to that of the fluvastatin immediate-release capsule administered under fasting conditions. Administration of a high-fat meal delayed the absorption (Tmax 6h) and increased the bioavailability of the XL tablet by approximately 50%. However, the maximum concentration of LESCOL XL seen after a high-fat meal is less than the peak concentration following a single dose or twice daily dose of the 40 mg fluvastatin capsule.
Distribution
Fluvastatin is 98% bound to plasma proteins. The mean volume of distribution (VDss) is estimated at 0.35 L/kg. At therapeutic concentrations, the protein binding of fluvastatin is not affected by warfarin, salicylic acid and glyburide.
Metabolism
Fluvastatin is metabolized in the liver, primarily via hydroxylation of the indole ring at the 5- and 6-positions. N-dealkylation and beta-oxidation of the side-chain also occurs. The hydroxy metabolites have some pharmacologic activity, but do not circulate in the blood. Fluvastatin has two enantiomers. Both enantiomers of fluvastatin are metabolized in a similar manner.
In vitro data indicate that fluvastatin metabolism involves multiple Cytochrome P450 (CYP) isozymes. CYP2C9 isoenzyme is primarily involved in the metabolism of fluvastatin (approximately 75%), while CYP2C8 and CYP3A4 isoenzymes are involved to a much less extent, i.e., approximately 5% and approximately 20%, respectively.
Excretion
Following oral administration, fluvastatin is primarily (about 90%) excreted in the feces as metabolites, with less than 2% present as unchanged drug. Approximately 5% of a radiolabeled oral dose were recovered in urine. The elimination half-life (t1/2) of fluvastatin is approximately 3 hours.
Specific Populations
Renal Impairment
In patients with moderate to severe renal impairment (CLCr 10 to 40 mL/min), AUC and Cmax increased approximately 1.2-fold after administration of a single dose of 40 mg fluvastatin compared to healthy volunteers. In patients with end-stage renal disease on hemodialysis, the AUC increased by approximately 1.5-fold. LESCOL XL was not evaluated in patients with renal impairment. However, systemic exposures after administration of LESCOL XL are lower than after the 40 mg immediate release capsule.
Hepatic Impairment
In patients with hepatic impairment due to liver cirrhosis, fluvastatin AUC and Cmax increased approximately 2.5-fold compared to healthy subjects after administration of a single 40 mg dose. The enantiomer ratios of the two isomers of fluvastatin in hepatic impairment patients were comparable to those observed in healthy subjects.
Geriatric
Plasma levels of fluvastatin are not significantly different in patients age > 65 years compared to patients age 21 to 49 years.
Gender
In a study evaluating the effect of age and gender on fluvastatin pharmacokinetics, there were no significant differences in fluvastatin exposures between males and females, except between younger females and younger males (both ages 21 to 49 years), where there was an approximate 30% increase in AUC in females. Adjusting for body weight decreases the magnitude of the differences seen. For LESCOL XL, the AUC increases 67% and 77% for women compared to men under fasted and high- fat meal fed conditions, respectively.
Pediatric
Pharmacokinetic data in the pediatric population are not available.
Drug-Drug Interactions
Data from drug-drug interactions studies involving coadministration of gemfibrozil, niacin, itraconazole, erythromycin, tolbutamide or clopidogrel indicate that the PK disposition of fluvastatin is not significantly altered when fluvastatin is coadministered with any of these drugs.
The below listed drug interaction information is derived from studies using fluvastatin capsules. Similar studies have not been conducted using the LESCOL XL tablet.
| *Single dose unless otherwise noted. **Mean ratio (with/without coadministered drug and no change = 1-fold) or % change (with/without coadministered drug and no change = 0%); symbols of ↑ and ↓ indicate the exposure increase and decrease, respectively. †Considered clinically significant [see Dosage and Administration (2) and Drug Interactions (7)]. |
|||
| Coadministered Drug and Dosing Regimen | Fluvastatin | ||
| Dose (mg)* | Change in AUC** | Change in Cmax** | |
| Cyclosporine – stable dose (twice daily)† | 20 mg QD for 14 weeks | ↑ 90% | ↑ 30% |
| Fluconazole 400 mg QD Day 1, 200 mg b.i.d. Day 2-4† | 40 mg QD | ↑ 84% | ↑ 44% |
| Cholestyramine 8 g QD | 20 mg QD administered 4 hrs after a meal plus cholestyramine | ↓ 51% | ↓ 83% |
| Rifampicin 600 mg QD for 6 days | 20 mg QD | ↓ 53% | ↓ 42% |
| Cimetidine 400 mg twice daily for 5 days, QD on Day 6 | 20 mg QD | ↑ 30% | ↑ 40% |
| Ranitidine 150 mg twice daily for 5 days, QD on Day 6 | 20 mg QD | ↑ 10% | ↑ 50% |
| Omeprazole 40 mg QD for 6 days | 20 mg QD | ↑ 20% | ↑ 37% |
| Phenytoin 300 mg QD | 40 mg twice daily for 5 days | ↑ 40 % | ↑ 27% |
| Propranolol 40 mg twice daily for 3.5 days | 40 mg QD | ↓ 5% | No change |
| Digoxin 0.1 – 0.5 mg QD for 3 weeks | 40 mg QD | No change | ↑ 11% |
| Diclofenac 25 mg QD | 40 mg QD for 8 days | ↑50 % | ↑ 80% |
| Glyburide 5 – 20 mg QD for 22 days | 40 mg twice daily for 14 days | ↑ 51% | ↑ 44% |
| Warfarin 30 mg QD | 40 mg QD for 8 days | ↑ 30% | ↑ 67% |
| Clopidogrel 300 mg loading dose on Day 10, 75 mg QD on Days 11-19 | 80 mg XL QD for 19 days | ↓ 2% | ↑ 27% |
Data from drug-drug interaction studies involving fluvastatin and coadministration of either gemfibrozil, tolbutamide or losartan indicate that the PK disposition of either gemfibrozil, tolbutamide or losartan is not significantly altered when coadministered with fluvastatin.
| *Single dose unless otherwise noted. **Mean ratio (with/without coadministered drug and no change = 1-fold) or % change (with/without coadministered drug and no change = 0%); symbols of ↑ and ↓ indicate the exposure increase and decrease, respectively. †Considered clinically significant [see Dosage and Administration (2) and Drug Interactions (7)]. |
|||
| Fluvastatin Dosage Regimen | Coadministered Drug | ||
| Name and Dose (mg)* | Change in AUC** | Change in Cmax** | |
| 40 mg QD for 5 days | Phenytoin 300 mg QD†
| ↑ 20%
| ↑ 5% |
| 40 mg twice daily for 21 days | Glyburide 5 – 20 mg QD for 22 days† | ↑ 70% | ↑ 50% |
| 40 mg QD for 8 days | Diclofenac 25 mg QD | ↑ 25% | ↑ 60% |
| 40 mg QD for 8 days | Warfarin 30 mg QD | S-warfarin: ↑ 7% | S-warfarin: ↑ 10% |
| R-warfarin: no change | R-warfarin: ↑ 6% | ||
| LESCOL
XL
fluvastatin sodium tablet, extended release |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation (002147023) |