Drug Detail:Mirapex er (Pramipexole [ pram-i-pex-ole ])
Drug Class: Dopaminergic antiparkinsonism agents
Highlights of Prescribing Information
MIRAPEX ER® (pramipexole dihydrochloride extended-release tablets), for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1997
Recent Major Changes
| Warnings and Precautions, | |
| Impulse Control/Compulsive Behaviors (5.3) | 7/2021 |
| Hallucinations and Psychotic-Like Behavior (5.4) | 7/2021 |
| Withdrawal Symptoms (5.11) | 7/2021 |
Indications and Usage for Mirapex ER
MIRAPEX ER is a non-ergot dopamine agonist indicated for the treatment of Parkinson's disease (PD) (1)
Mirapex ER Dosage and Administration
- MIRAPEX ER tablets are taken once daily, with or without food (2.1)
- Tablets must be swallowed whole and must not be chewed, crushed, or divided (2.1)
- Starting dose is 0.375 mg given once daily (2.2)
- Dose may be increased gradually, not more frequently than every 5 to 7 days, first to 0.75 mg per day and then by 0.75 mg increments up to a maximum recommended dose of 4.5 mg per day. Assess therapeutic response and tolerability at a minimal interval of 5 days or longer after each dose increment (2.2)
- Patients may be switched overnight from immediate-release pramipexole tablets to MIRAPEX ER tablets at the same daily dose. Dose adjustment may be needed in some patients (2.3)
- MIRAPEX ER tablets should be discontinued gradually (2.2)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Extended-release tablets: 0.375 mg, 0.75 mg, 1.5 mg, 2.25 mg, 3 mg, 3.75 mg, and 4.5 mg (3)
Contraindications
None (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Falling Asleep During Activities of Daily Living: Sudden onset of sleep may occur without warning; advise patients to report symptoms (5.1)
- Symptomatic Orthostatic Hypotension: Monitor closely especially during dose escalation (5.2)
- Impulse Control/Compulsive Behaviors: Patients may experience compulsive behaviors and other intense urges (5.3)
- Hallucinations and Psychotic-like Behavior: May occur; risk increases with age (5.4)
- Dyskinesia: May be caused or exacerbated by MIRAPEX ER (5.5)
- Postural Deformity: Consider reducing the dose or discontinuing MIRAPEX ER if postural deformity occurs (5.6)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥5% and greater than placebo):
- Early PD without levodopa: somnolence, nausea, constipation, dizziness, fatigue, hallucinations, dry mouth, muscle spasms, and peripheral edema (6.1)
- Advanced PD with levodopa: dyskinesia, nausea, constipation, hallucinations, headache, and anorexia (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc. at (800) 542-6257 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
Dopamine antagonists: May diminish the effectiveness of pramipexole (7.1)
Use In Specific Populations
Pregnancy: Based on animal data, may cause fetal harm (8.1)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 7/2021
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Mirapex ER
MIRAPEX ER® tablets are indicated for the treatment of Parkinson's disease.
2. Mirapex ER Dosage and Administration
2.1 General Dosing Considerations
MIRAPEX ER tablets are taken orally once daily, with or without food.
MIRAPEX ER tablets must be swallowed whole and must not be chewed, crushed, or divided.
If a significant interruption in therapy with MIRAPEX ER tablets has occurred, re-titration of therapy may be warranted.
2.2 Dosing for Parkinson's Disease
The starting dose is 0.375 mg given once per day. Based on efficacy and tolerability, dosages may be increased gradually, not more frequently than every 5 to 7 days, first to 0.75 mg per day and then by 0.75 mg increments up to a maximum recommended dose of 4.5 mg per day.
In clinical trials, dosage was initiated at 0.375 mg/day and gradually titrated based on individual therapeutic response and tolerability. Doses greater than 4.5 mg/day have not been studied in clinical trials. Patients should be assessed for therapeutic response and tolerability at a minimal interval of 5 days or longer after each dose increment [see Clinical Studies (14)].
Due to the flexible dose design used in clinical trials, specific dose-response information could not be determined [see Clinical Studies (14)].
MIRAPEX ER tablets may be tapered off at a rate of 0.75 mg per day until the daily dose has been reduced to 0.75 mg. Thereafter, the dose may be reduced by 0.375 mg per day [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10, 5.11)].
2.3 Switching from Immediate-Release Pramipexole Tablets to MIRAPEX ER
Patients with Parkinson's disease may be switched overnight from immediate-release pramipexole tablets to MIRAPEX ER tablets at the same daily dose. When switching between immediate-release pramipexole tablets and MIRAPEX ER tablets, patients should be monitored to determine if dosage adjustment is necessary.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
- 0.375 mg white to off-white, round, bevel-edged, extended-release tablets debossed with "ER" on one side and "0.375" on the other side. Each extended-release tablet contains 0.375 mg pramipexole dihydrochloride monohydrate equivalent to 0.352 mg pramipexole dihydrochloride.
- 0.75 mg white to off-white, round, bevel-edged, extended-release tablets debossed with "ER" on one side and "0.75" on the other side. Each extended-release tablet contains 0.75 mg pramipexole dihydrochloride monohydrate equivalent to 0.705 mg pramipexole dihydrochloride.
- 1.5 mg white to off-white, oval, extended-release tablets debossed with "ER" on one side and "1.5" on the other side. Each extended-release tablet contains 1.5 mg pramipexole dihydrochloride monohydrate equivalent to 1.41 mg pramipexole dihydrochloride.
- 2.25 mg white to off-white, oval, extended-release tablets debossed with "ER" on one side and "2.25" on the other side. Each extended-release tablet contains 2.25 mg pramipexole dihydrochloride monohydrate equivalent to 2.12 mg pramipexole dihydrochloride.
- 3 mg white to off-white, oval, extended-release tablets debossed with "ER" on one side and "3.0" on the other side. Each extended-release tablet contains 3 mg pramipexole dihydrochloride monohydrate equivalent to 2.82 mg pramipexole dihydrochloride.
- 3.75 mg white to off-white, oval, extended-release tablets debossed with "ER" on one side and "3.75" on the other side. Each extended-release tablet contains 3.75 mg pramipexole dihydrochloride monohydrate equivalent to 3.53 mg pramipexole dihydrochloride.
- 4.5 mg white to off-white, oval, extended-release tablets debossed with "ER" on one side and "4.5" on the other side. Each extended-release tablet contains 4.5 mg pramipexole dihydrochloride monohydrate equivalent to 4.23 mg pramipexole dihydrochloride.
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Falling Asleep During Activities of Daily Living and Somnolence
Patients treated with pramipexole have reported falling asleep while engaged in activities of daily living, including the operation of motor vehicles, which sometimes resulted in accidents. Although many of these patients reported somnolence while on pramipexole tablets, some perceived that they had no warning signs (sleep attack) such as excessive drowsiness, and believed that they were alert immediately prior to the event. Some of these events had been reported as late as one year after the initiation of treatment. In placebo-controlled clinical trials in Parkinson's disease, the sudden onset of sleep or sleep attacks were reported in 8 of 387 (2%) patients treated with MIRAPEX ER tablets compared to 2 of 281 (1%) patients on placebo.
In early Parkinson's disease, somnolence was reported in 36% of 223 patients treated with MIRAPEX ER, median dose 3.0 mg/day, compared to 15% of 103 patients on placebo. In advanced Parkinson's disease, somnolence was reported in 15% of 164 patients treated with MIRAPEX ER tablets, median dose 3 mg/day, compared to 16% of 178 patients on placebo. It has been reported that falling asleep while engaged in activities of daily living usually occurs in a setting of preexisting somnolence, although patients may not give such a history. For this reason, prescribers should reassess patients for drowsiness or sleepiness, especially since some of the events occur well after the start of treatment. Prescribers should also be aware that patients may not acknowledge drowsiness or sleepiness until directly questioned about drowsiness or sleepiness during specific activities.
Before initiating treatment with MIRAPEX ER tablets, advise patients of the potential to develop drowsiness, and specifically ask about factors that may increase the risk for somnolence such as the use of concomitant sedating medications or alcohol, the presence of sleep disorders, and concomitant medications that increase pramipexole plasma levels (e.g., cimetidine) [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. If a patient develops significant daytime sleepiness or episodes of falling asleep during activities that require active participation (e.g., conversations, eating, etc.), MIRAPEX ER tablets should ordinarily be discontinued. If a decision is made to continue MIRAPEX ER tablets, advise patients not to drive and to avoid other potentially dangerous activities that might result in harm if the patients become somnolent. While dose reduction reduces the degree of somnolence, there is insufficient information to establish that dose reduction will eliminate episodes of falling asleep while engaged in activities of daily living.
5.2 Symptomatic Orthostatic Hypotension
Dopamine agonists, in clinical studies and clinical experience, appear to impair the systemic regulation of blood pressure, with resulting orthostatic hypotension, especially during dose escalation. Parkinson's disease patients, in addition, appear to have an impaired capacity to respond to an orthostatic challenge. For these reasons, Parkinson's disease patients being treated with dopaminergic agonists, including MIRAPEX ER, ordinarily require careful monitoring for signs and symptoms of orthostatic hypotension, especially during dose escalation, and should be informed of this risk. In placebo-controlled clinical trials in Parkinson's disease, symptomatic orthostatic hypotension was reported in 10 of 387 (3%) patients treated with MIRAPEX ER tablets compared to 3 of 281 (1%) patients on placebo. One patient of 387 on MIRAPEX ER tablets discontinued treatment due to hypotension.
5.3 Impulse Control/Compulsive Behaviors
Case reports and the results of cross-sectional studies suggest that patients can experience intense urges to gamble, increased sexual urges, intense urges to spend money, binge eating, and/or other intense urges, and the inability to control these urges while taking one or more of the medications, including MIRAPEX ER, that increase central dopaminergic tone. In some cases, although not all, these urges were reported to have stopped when the dose was reduced or the medication was discontinued. Because patients may not recognize these behaviors as abnormal, it is important for prescribers to specifically ask patients or their caregivers about the development of new or increased gambling urges, sexual urges, uncontrolled spending or other urges while being treated with MIRAPEX ER for Parkinson's disease. Physicians should consider dose reduction or stopping the medication if a patient develops such urges while taking MIRAPEX ER.
A total of 1056 patients with Parkinson's disease who participated in two MIRAPEX ER placebo-controlled studies of up to 33 weeks duration were specifically asked at each visit about the occurrence of these symptoms. A total of 14 of 387 (4%) treated with MIRAPEX ER tablets, 12 of 388 (3%) treated with immediate-release pramipexole tablets, and 4 of 281 (1%) treated with placebo reported compulsive behaviors, including pathological gambling, hypersexuality, and/or compulsive buying.
5.4 Hallucinations and Psychotic-like Behavior
In placebo-controlled clinical trials in Parkinson's disease, hallucinations (visual or auditory or mixed) were reported in 25 of 387 (6%) patients treated with MIRAPEX ER tablets compared to 5 of 281 (2%) patients receiving placebo. Hallucinations led to discontinuation of treatment in 5 of 387 (1%) patients on MIRAPEX ER tablets.
Age appears to increase the risk of hallucinations attributable to pramipexole. In placebo-controlled clinical trials in Parkinson's disease, hallucinations were reported in 15 of 162 (9%) patients ≥65 years of age taking MIRAPEX ER tablets compared to 10 of 225 (4%) patients <65 years of age taking MIRAPEX ER tablets.
Postmarketing reports with dopamine agonists, including MIRAPEX ER, indicate that patients with Parkinson's disease may experience new or worsening mental status and behavioral changes, which may be severe, including psychotic-like behavior during treatment with MIRAPEX ER or after starting or increasing the dose of MIRAPEX ER. Other drugs prescribed to improve the symptoms of Parkinson's disease can have similar effects on thinking and behavior. This abnormal thinking and behavior can consist of one or more of a variety of manifestations including paranoid ideation, delusions, hallucinations, confusion, psychotic-like behavior, symptoms of mania (e.g., insomnia, psychomotor agitation), disorientation, aggressive behavior, agitation, and delirium.
Patients with a major psychotic disorder should ordinarily not be treated with dopamine agonists, including MIRAPEX ER, because of the risk of exacerbating the psychosis. In addition, certain medications used to treat psychosis may exacerbate the symptoms of Parkinson's disease and may decrease the effectiveness of MIRAPEX ER [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
5.6 Postural Deformity
Postural deformities, including antecollis, camptocormia (Bent Spine Syndrome), and pleurothotonus (Pisa Syndrome), have been reported in patients after starting or increasing the dose of MIRAPEX ER. Postural deformity may occur several months after starting treatment or increasing the dose. Reducing the dose or discontinuing MIRAPEX ER has been reported to improve postural deformity in some patients, and should be considered if postural deformity occurs.
5.7 Renal Impairment
The elimination of pramipexole is dependent on renal function [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Patients with mild renal impairment (a creatinine clearance above 50 mL/min) require no reduction in daily dose. MIRAPEX ER tablets have not been studied in patients with moderate to severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance <50 mL/min) or on hemodialysis [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Use in Specific Populations (8.6), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
5.8 Rhabdomyolysis
In the clinical development program for immediate-release pramipexole tablets, a single case of rhabdomyolysis occurred in a 49-year-old male with advanced Parkinson's disease. The patient was hospitalized with an elevated CPK (10,631 IU/L). The symptoms resolved with discontinuation of the medication.
Advise patients to contact a physician if they experience any unexplained muscle pain, tenderness, or weakness, as these may be symptoms of rhabdomyolysis.
5.10 Events Reported with Dopaminergic Therapy
Although the events enumerated below may not have been reported with the use of pramipexole in its development program, they are associated with the use of other dopaminergic drugs. The expected incidence of these events, however, is so low that even if pramipexole caused these events at rates similar to those attributable to other dopaminergic therapies, it would be unlikely that even a single case would have occurred in a cohort of the size exposed to pramipexole in studies to date.
5.11 Withdrawal Symptoms
Symptoms including apathy, anxiety, depression, fatigue, insomnia, sweating, and pain have been reported during taper or after discontinuation of dopamine agonists, including MIRAPEX ER. These symptoms generally do not respond to levodopa.
Prior to discontinuation of MIRAPEX ER, patients should be informed about potential withdrawal symptoms, and monitored during and after discontinuation. In case of severe withdrawal symptoms, a trial re-administration of a dopamine agonist at the lowest effective dose may be considered.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the labeling:
- Falling Asleep During Activities of Daily Living and Somnolence [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Symptomatic Orthostatic Hypotension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Impulse Control/Compulsive Behaviors [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Hallucinations and Psychotic-like Behavior [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Dyskinesia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Postural Deformity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Rhabdomyolysis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
- Retinal Pathology [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]
- Events Reported with Dopaminergic Therapy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)]
- Withdrawal Symptoms [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug (or of another development program of a different formulation of the same drug) and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
During the premarketing development of MIRAPEX ER tablets, patients with early Parkinson's disease were treated with MIRAPEX ER tablets, placebo, or immediate-release pramipexole tablets. In addition, a randomized, double-blind, parallel group trial was conducted in 156 early Parkinson's disease patients (Hoehn & Yahr Stages I-III) to assess overnight switching of immediate-release pramipexole tablets to MIRAPEX ER tablets. In this latter study, concomitant treatment with stable doses of levodopa, monoamine oxidase B inhibitor (MAOB-I) drugs, anticholinergics, or amantadine, individually or in combination, was allowed. In a third trial, advanced Parkinson's disease patients received MIRAPEX ER tablets, placebo, or immediate-release pramipexole tablets as adjunctive therapy to levodopa.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of MIRAPEX immediate-release or MIRAPEX ER tablets, primarily in Parkinson's disease patients. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure. Decisions to include these reactions in labeling are typically based on one or more of the following factors: (1) seriousness of the reaction, (2) frequency of reporting, or (3) strength of causal connection to pramipexole tablets.
Cardiac Disorders: cardiac failure
Gastrointestinal Disorders: vomiting
General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions: withdrawal symptoms [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)]
Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders: syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion (SIADH), weight increase
Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders: postural deformity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
Nervous System Disorders: syncope
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders: skin reactions (including erythema, rash, pruritus, urticaria)
There are postmarketing reports of patients noticing tablet residue in their stool that resembles a swollen MIRAPEX ER whole tablet or swollen pieces of the tablet. Some patients have reported worsening of their Parkinson's disease symptoms when tablet residue was observed. If a patient reports tablet residue with worsening of their Parkinson's symptoms, prescribers may need to re-evaluate their medications.
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of MIRAPEX ER tablets in pediatric patients have not been evaluated.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Pramipexole total oral clearance is approximately 30% lower in subjects older than 65 years compared with younger subjects, because of a decline in pramipexole renal clearance due to an age-related reduction in renal function. This resulted in an increase in elimination half-life from approximately 8.5 hours to 12 hours. In a placebo-controlled clinical trial of MIRAPEX ER tablets in early Parkinson's disease, 47% of the 259 patients were ≥65 years of age. Among patients receiving MIRAPEX ER tablets, hallucinations were more common in the elderly, occurring in 13% of the patients ≥65 years of age compared to 2% of the patients <65 years of age.
8.6 Renal Impairment
The elimination of pramipexole is dependent upon renal function. Pramipexole clearance is extremely low in dialysis patients, as a negligible amount of pramipexole is removed by dialysis [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Warnings and Precautions (5.7), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
10. Overdosage
There is no clinical experience with significant overdosage. One patient took 11 mg/day of pramipexole for 2 days in a clinical trial for an investigational use. Blood pressure remained stable, although pulse rate increased to between 100 and 120 beats/minute. No other adverse reactions were reported related to the increased dose.
There is no known antidote for overdosage of a dopamine agonist. If signs of central nervous system stimulation are present, a phenothiazine or other butyrophenone neuroleptic agent may be indicated; the efficacy of such drugs in reversing the effects of overdosage has not been assessed. Management of overdose may require general supportive measures along with gastric lavage, intravenous fluids, and electrocardiogram monitoring.
11. Mirapex ER Description
MIRAPEX ER tablets contain pramipexole dihydrochloride (as a monohydrate). Pramipexole is a non-ergot dopamine agonist. The chemical name of pramipexole dihydrochloride monohydrate is (S)-2-amino-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-6-(propylamino)benzothiazole dihydrochloride monohydrate. Its empirical formula is C10 H17 N3 S ∙ 2HCl ∙ H2O, and its molecular weight is 302.26.
The structural formula is:
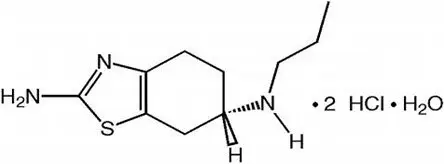
Pramipexole dihydrochloride is a white to off-white powder substance. Melting occurs in the range of 296°C to 301°C, with decomposition. Pramipexole dihydrochloride is more than 20% soluble in water, about 8% in methanol, about 0.5% in ethanol, and practically insoluble in dichloromethane.
MIRAPEX ER tablets 0.375 mg:
Each extended-release tablet contains 0.375 mg pramipexole dihydrochloride monohydrate equivalent to 0.352 mg pramipexole dihydrochloride.
MIRAPEX ER tablets 0.75 mg:
Each extended-release tablet contains 0.75 mg pramipexole dihydrochloride monohydrate equivalent to 0.705 mg pramipexole dihydrochloride.
MIRAPEX ER tablets 1.5 mg:
Each extended-release tablet contains 1.5 mg pramipexole dihydrochloride monohydrate equivalent to 1.41 mg pramipexole dihydrochloride.
MIRAPEX ER tablets 2.25 mg:
Each extended-release tablet contains 2.25 mg pramipexole dihydrochloride monohydrate equivalent to 2.12 mg pramipexole dihydrochloride.
MIRAPEX ER tablets 3 mg:
Each extended-release tablet contains 3 mg pramipexole dihydrochloride monohydrate equivalent to 2.82 mg pramipexole dihydrochloride.
MIRAPEX ER tablets 3.75 mg:
Each extended-release tablet contains 3.75 mg pramipexole dihydrochloride monohydrate equivalent to 3.53 mg pramipexole dihydrochloride.
MIRAPEX ER tablets 4.5 mg:
Each extended-release tablet contains 4.5 mg pramipexole dihydrochloride monohydrate equivalent to 4.23 mg pramipexole dihydrochloride.
Inactive ingredients for all strengths of MIRAPEX ER tablets consist of hypromellose, corn starch, carbomer homopolymer, colloidal silicon dioxide, and magnesium stearate.
12. Mirapex ER - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Pramipexole is a non-ergot dopamine agonist with high relative in vitro specificity and full intrinsic activity at the D2 subfamily of dopamine receptors, binding with higher affinity to D3 than to D2 or D4 receptor subtypes.
The precise mechanism of action of pramipexole as a treatment for Parkinson's disease is unknown, although it is believed to be related to its ability to stimulate dopamine receptors in the striatum. This conclusion is supported by electrophysiologic studies in animals that have demonstrated that pramipexole influences striatal neuronal firing rates via activation of dopamine receptors in the striatum and the substantia nigra, the site of neurons that send projections to the striatum. The relevance of D3 receptor binding in Parkinson's disease is unknown.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
The effect of pramipexole on the QT interval of the ECG was investigated in a clinical study in 60 healthy male and female volunteers. All subjects initiated treatment with 0.375 mg MIRAPEX ER tablets administered once daily, and were up-titrated every 3 days to 2.25 mg and 4.5 mg daily, a faster rate of titration than recommended in the label. No dose- or exposure-related effect on mean QT intervals was observed; however, the study did not have a valid assessment of assay sensitivity. The effect of pramipexole on QTc intervals at higher exposures achieved either due to drug interactions (e.g., with cimetidine), renal impairment, or at higher doses has not been systematically evaluated.
Although mean values remained within normal reference ranges throughout the study, supine systolic blood pressure (SBP), diastolic blood pressure (DBP), and pulse rate for subjects treated with pramipexole generally increased during the rapid up-titration phase, by 10 mmHg, 7 mmHg, and 10 bpm higher than placebo, respectively. Higher SBP, DBP, and pulse rates compared to placebo were maintained until the pramipexole doses were tapered; values on the last day of tapering were generally similar to baseline values. Such effects have not been observed in clinical studies with Parkinson's disease patients, who were titrated according to labeled recommendations.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
MIRAPEX ER tablets, like immediate-release pramipexole tablets, display linear pharmacokinetics over the entire clinical dosage range. Slow release of pramipexole from MIRAPEX ER tablets with once-daily administration results in the same daily maximum and minimum pramipexole plasma concentrations (Cmax, Cmin) as three times daily administration of immediate-release pramipexole tablets.
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Two-year carcinogenicity studies with pramipexole have been conducted in mice and rats. Pramipexole was administered in the diet to mice at doses up to 10 mg/kg/day [or approximately 10 times the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 1.5 mg TID on a mg/m2 basis]. Pramipexole was administered in the diet to rats at doses up to 8 mg/kg/day. These doses were associated with plasma AUCs up to approximately 12 times that in humans at the MRHD. No significant increases in tumors occurred in either species.
Pramipexole was not mutagenic or clastogenic in a battery of in vitro (bacterial reverse mutation, V79/HGPRT gene mutation, chromosomal aberration in CHO cells) and in vivo (mouse micronucleus) assays.
In rat fertility studies, pramipexole at a dose of 2.5 mg/kg/day (5 times the MRHD on a mg/m2 basis) prolonged estrus cycles and inhibited implantation. These effects were associated with reductions in serum levels of prolactin, a hormone necessary for implantation and maintenance of early pregnancy in rats.
14. Clinical Studies
The effectiveness of MIRAPEX ER tablets in the treatment of Parkinson's disease was supported by clinical pharmacokinetic data [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)] and two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter clinical trials in early and advanced Parkinson's disease. In both randomized studies, the Unified Parkinson's Disease Rating Scale (UPDRS) served as a primary outcome assessment measure. The UPDRS is a four-part multi-item rating scale intended to evaluate mentation (Part I), activities of daily living (Part II), motor performance (Part III), and complications of therapy (Part IV).
Part II of the UPDRS contains 13 questions related to activities of daily living, which are scored from 0 (normal) to 4 (maximal severity) for a maximum (worst) score of 52. Part III of the UPDRS contains 14 items designed to assess the severity of the cardinal motor findings in patients with Parkinson's disease (e.g., tremor, rigidity, bradykinesia, postural instability, etc.), scored for different body regions and has a maximum (worst) score of 108.
16. How is Mirapex ER supplied
16.1 How Supplied
MIRAPEX ER tablets are available as follows:
0.375 mg: white to off-white, round, bevel-edged, extended-release tablets debossed with "ER" on one side and "0.375" on the other side.
| Unit of Use Bottles of 7 | NDC 0597-0109-17 | |
| Unit of Use Bottles of 30 | NDC 0597-0109-30 |
0.75 mg: white to off-white, round, bevel-edged, extended-release tablets debossed with "ER" on one side and "0.75" on the other side.
| Unit of Use Bottles of 7 | NDC 0597-0285-17 | |
| Unit of Use Bottles of 30 | NDC 0597-0285-30 |
1.5 mg: white to off-white, oval, extended-release tablets debossed with "ER" on one side and "1.5" on the other side.
| Unit of Use Bottles of 7 | NDC 0597-0113-17 | |
| Unit of Use Bottles of 30 | NDC 0597-0113-30 |
2.25 mg: white to off-white, oval, extended-release tablets debossed with "ER" on one side and "2.25" on the other side.
| Unit of Use Bottles of 30 | NDC 0597-0286-30 |
3 mg: white to off-white, oval, extended-release tablets debossed with "ER" on one side and "3.0" on the other side.
| Unit of Use Bottles of 30 | NDC 0597-0115-30 |
3.75 mg: white to off-white, oval, extended-release tablets debossed with "ER" on one side and "3.75" on the other side.
| Unit of Use Bottles of 30 | NDC 0597-0287-30 |
4.5 mg: white to off-white, oval, extended-release tablets debossed with "ER" on one side and "4.5" on the other side.
| Unit of Use Bottles of 30 | NDC 0597-0116-30 |
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
Patient Information MIRAPEX ER® (mîr'-ah-pěx) (pramipexole dihydrochloride extended-release tablets)
Read this Patient Information before you start taking MIRAPEX ER and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking with your doctor about your medical condition or your treatment.
What is MIRAPEX ER?
MIRAPEX ER is a prescription medicine used to treat the signs and symptoms of Parkinson's disease.
It is not known if MIRAPEX ER is safe and effective in children.
What should I tell my doctor before taking MIRAPEX ER?
Before taking MIRAPEX ER, tell your doctor if you:
- feel sleepy during the day
- have low blood pressure, or if you feel dizzy or faint, especially when getting up from sitting or lying down.
- have trouble controlling your muscles (dyskinesia)
- have kidney problems
- drink alcohol. Alcohol can increase the chance that MIRAPEX ER will make you feel sleepy or fall asleep when you should be awake.
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if MIRAPEX ER will harm your unborn baby.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if MIRAPEX ER passes into your breast milk. You and your doctor should decide if you will take MIRAPEX ER or breastfeed. You should not do both.
Tell your doctor about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
MIRAPEX ER and other medicines may affect each other causing side effects. MIRAPEX ER may affect the way other medicines work, and other medicines may affect how MIRAPEX ER works.
Especially tell your doctor if you take:
- medicines called neuroleptics (phenothiazines, butyrophenones, thioxanthenes) or metoclopramide. MIRAPEX ER may not work as well if you take these medicines.
- pramipexole (MIRAPEX). Pramipexole is the active ingredient in both MIRAPEX ER and MIRAPEX. If you are taking MIRAPEX, you should not take MIRAPEX ER.
- any other medicines that make you sleepy or may increase the effects of MIRAPEX ER, such as cimetidine (Tagamet).
Ask your doctor for a list of these medicines if you are not sure.
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them and show it to your doctor and pharmacist when you get a new medicine.
How should I take MIRAPEX ER?
- MIRAPEX ER is taken once daily.
- Your doctor will tell you how much MIRAPEX ER to take and when to take it. Do not take more or less MIRAPEX ER than your doctor tells you to.
- Swallow MIRAPEX ER whole. Do not chew, crush, or cut MIRAPEX ER.
- MIRAPEX ER can be taken with or without food. Taking MIRAPEX ER with food may lower your chances of getting nausea.
- You may see something that looks like a swollen original tablet or swollen pieces of the original tablet in your stool. If this happens, tell your doctor.
- If you miss a dose of MIRAPEX ER it should be taken as soon as possible, but no later than 12 hours after your regularly scheduled time. If it is later than 12 hours, the missed dose should be skipped and the next dose should be taken on the following day at your regularly scheduled time. Do not double your next MIRAPEX ER dose.
- Do not stop taking MIRAPEX ER without talking to your doctor first. If your doctor tells you to stop taking MIRAPEX ER, you should ask your doctor for specific instructions on how to slowly and safely discontinue taking MIRAPEX ER. If you stop taking MIRAPEX ER you may have withdrawal symptoms (see "withdrawal symptoms" under "What are the possible side effects of MIRAPEX ER?").
What should I avoid while taking MIRAPEX ER?
- Do not drink alcohol while taking MIRAPEX ER. It can increase your chance of having serious side effects. See "What are the possible side effects of MIRAPEX ER?"
- Do not drive a car, operate a machine, or do other dangerous activities until you know how MIRAPEX ER affects you. Sleepiness caused by MIRAPEX ER can happen as late as 1 year after you start your treatment.
What are the possible side effects of MIRAPEX ER?
MIRAPEX ER may cause serious side effects, including:
-
falling asleep during normal daily activities. MIRAPEX ER may cause you to fall asleep while you are doing daily activities such as driving, talking with other people, or eating.
- Some people taking the medicine in MIRAPEX ER have had car accidents because they fell asleep while driving.
- Some people did not feel sleepy before they fell asleep while driving. You could fall asleep without any warning.
-
low blood pressure when you sit or stand up quickly. After you have been sitting or lying down, stand up slowly until you know how MIRAPEX ER affects you. This may help reduce the following symptoms while you are taking MIRAPEX ER:
- dizziness
- nausea
- fainting
- sweating
-
unusual urges. Some people who take certain medicines to treat Parkinson's disease, including MIRAPEX ER, have reported problems, such as gambling, compulsive eating, compulsive buying, and increased sex drive.
If you or your family members notice that you are developing unusual urges or behaviors, talk to your doctor. -
hallucinations and other psychotic-like behavior (seeing visions, hearing sounds or feeling sensations that are not real, confusion, excessive suspicion, aggressive behavior, agitation, delusional beliefs and disorganized thinking). The chances of having hallucinations or other psychotic-like changes are higher in people taking MIRAPEX ER for Parkinson's disease who are elderly (age 65 or older).
If you have hallucinations or other psychotic-like changes, talk with your doctor right away. - uncontrolled sudden movements (dyskinesia). If you have new dyskinesia, or your existing dyskinesia gets worse, tell your doctor.
- posture changes. Talk with your doctor if you have posture changes you cannot control. These may include your neck bending forward, bending forward at the waist, or tilting sideways when you sit, stand, or walk.
-
withdrawal symptoms. MIRAPEX ER is a dopamine agonist medicine. Dopamine agonist medicines, including MIRAPEX ER, can cause withdrawal symptoms as your dose is slowly lowered (tapered) or when treatment with MIRAPEX ER is stopped. Tell your doctor right away if you get any of the following withdrawal symptoms:
- fever
- confusion
- severe muscle stiffness
- feeling like you do not care about things you usually care about (apathy)
- anxiety
- depression
- fatigue
- insomnia
- sweating
- pain
After you have stopped taking MIRAPEX ER, your doctor may need to restart you at a low dose of MIRAPEX ER if you get severe withdrawal symptoms.
The most common side effects in people taking MIRAPEX ER for early Parkinson's disease are:
- nausea and vomiting
- constipation
- dizziness
- fatigue
- dry mouth
- swelling of the feet and ankles
The most common side effects in people taking MIRAPEX ER who have later stage Parkinson's disease are nausea, constipation, headache and weight loss (anorexia).
These are not all the possible side effects of MIRAPEX ER. Tell your doctor if you have any side effect that bothers you.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store MIRAPEX ER?
- Store MIRAPEX ER at room temperature from 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
- Keep MIRAPEX ER away from high humidity or moisture.
- Keep MIRAPEX ER and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General Information about the safe and effective use of MIRAPEX ER.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use MIRAPEX ER for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give MIRAPEX ER to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them.
This Patient Information leaflet summarizes the most important information about MIRAPEX ER. If you would like more information, talk with your doctor. You can ask your pharmacist or doctor for more information about MIRAPEX ER tablets that is written for healthcare professionals.
For current Prescribing Information, scan the code or for additional information, you may also call Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc. at 1-800-542-6257.

What are the ingredients in MIRAPEX ER?
Active Ingredient: pramipexole dihydrochloride monohydrate.
Inactive Ingredients: hypromellose, corn starch, carbomer homopolymer, colloidal silicon dioxide, and magnesium stearate.
What does MIRAPEX ER look like?
These pictures show what MIRAPEX ER tablets look like. Notice that each strength tablet looks different. Immediately call your pharmacist if you receive a MIRAPEX ER tablet that does not look like one of the tablets shown below, as you may have received the wrong medication.
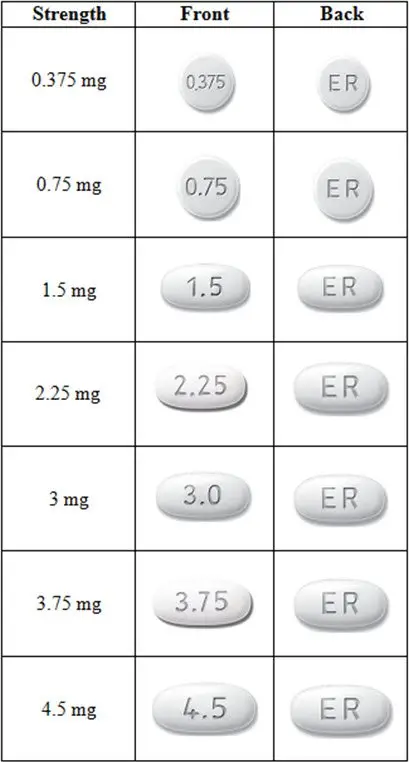
Tablets not actual size.
This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Distributed by:
Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Ridgefield, CT 06877 USA
Licensed from:
Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH
MIRAPEX is a registered trademark of and used under license from Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH.
Revised: 7/2021
COL9694AG162021
| MIRAPEX
ER
pramipexole dihydrochloride tablet, extended release |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MIRAPEX
ER
pramipexole dihydrochloride tablet, extended release |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MIRAPEX
ER
pramipexole dihydrochloride tablet, extended release |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MIRAPEX
ER
pramipexole dihydrochloride tablet, extended release |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| MIRAPEX
ER
pramipexole dihydrochloride tablet, extended release |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| MIRAPEX
ER
pramipexole dihydrochloride tablet, extended release |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| MIRAPEX
ER
pramipexole dihydrochloride tablet, extended release |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (603175944) |
| Registrant - Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals Inc. (603175944) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Boehringer Ingelheim Pharma GmbH and Co. KG | 551147440 | ANALYSIS(0597-0109, 0597-0113, 0597-0115, 0597-0116, 0597-0285, 0597-0286, 0597-0287) , API MANUFACTURE(0597-0109, 0597-0113, 0597-0115, 0597-0116, 0597-0285, 0597-0286, 0597-0287) , LABEL(0597-0109, 0597-0113, 0597-0115, 0597-0116, 0597-0285, 0597-0286, 0597-0287) , MANUFACTURE(0597-0109, 0597-0113, 0597-0115, 0597-0116, 0597-0285, 0597-0286, 0597-0287) , PACK(0597-0109, 0597-0113, 0597-0115, 0597-0116, 0597-0285, 0597-0286, 0597-0287) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| West-Ward Columbus Inc. | 058839929 | LABEL(0597-0109, 0597-0113, 0597-0115, 0597-0116, 0597-0285, 0597-0286, 0597-0287) , PACK(0597-0109, 0597-0113, 0597-0115, 0597-0116, 0597-0285, 0597-0286, 0597-0287) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Boehringer Ingelheim Pharma GmbH and Co. KG | 340700520 | ANALYSIS(0597-0109, 0597-0113, 0597-0115, 0597-0116, 0597-0285, 0597-0286, 0597-0287) | |











