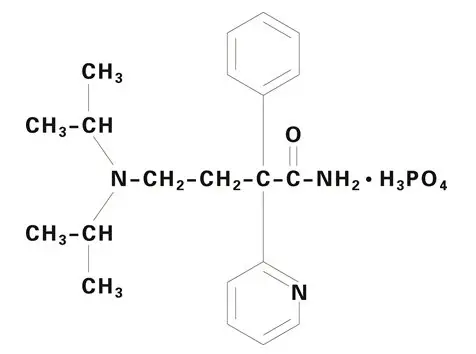
Drug Detail:Norpace (Disopyramide [ dye-soe-pir-a-mide ])
Drug Class: Group I antiarrhythmics
Related/similar drugs
amiodarone, lidocaine, verapamil, dofetilide, Pacerone, mexiletineNorpace - Clinical Pharmacology
Warnings
Negative Inotropic Properties
Anticholinergic Activity
Because of its anticholinergic activity, disopyramide phosphate should not be used in patients with glaucoma, myasthenia gravis, or urinary retention unless adequate overriding measures are taken; these consist of the topical application of potent miotics (e.g., pilocarpine) for patients with glaucoma, and catheter drainage or operative relief for patients with urinary retention. Urinary retention may occur in patients of either sex as a consequence of Norpace or Norpace CR administration, but males with benign prostatic hypertrophy are at particular risk. In patients with a family history of glaucoma, intraocular pressure should be measured before initiating Norpace or Norpace CR therapy. Disopyramide phosphate should be used with special care in patients with myasthenia gravis since its anticholinergic properties could precipitate a myasthenic crisis in such patients.
Precautions
General
Renal Impairment
More than 50% of disopyramide is excreted in the urine unchanged. Therefore Norpace dosage should be reduced in patients with impaired renal function (see Dosage and Administration). The electrocardiogram should be carefully monitored for prolongation of PR interval, evidence of QRS widening, or other signs of overdosage (see Overdosage).
Norpace CR is not recommended for patients with severe renal insufficiency (creatinine clearance 40 ml/min or less).
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The adverse reactions which were reported in Norpace clinical trials encompass observations in 1,500 patients, including 90 patients studied for at least 4 years. The most serious adverse reactions are hypotension and congestive heart failure. The most common adverse reactions, which are dose dependent, are associated with the anticholinergic properties of the drug. These may be transitory, but may be persistent or can be severe. Urinary retention is the most serious anticholinergic effect.
The following reactions were reported in 10% to 40% of patients:
Anticholinergic: dry mouth (32%), urinary hesitancy (14%), constipation (11%)
The following reactions were reported in 3% to 9% of patients:
Anticholinergic: blurred vision, dry nose/eyes/throat
Genitourinary: urinary retention, urinary frequency and urgency
Gastrointestinal: nausea, pain/bloating/gas
General: dizziness, general fatigue/muscle weakness, headache, malaise, aches/pains
The following reactions were reported in 1% to 3% of patients:
Genitourinary: impotence
Cardiovascular: hypotension with or without congestive heart failure, increased congestive heart failure (see Warnings), cardiac conduction disturbances (see Warnings), edema/weight gain, shortness of breath, syncope, chest pain
Gastrointestinal: anorexia, diarrhea, vomiting
Dermatologic: generalized rash/dermatoses, itching
Central nervous system: nervousness
Other: hypokalemia, elevated cholesterol/triglycerides
The following reactions were reported in less than 1%:
Depression, insomnia, dysuria, numbness/tingling, elevated liver enzymes, AV block, elevated BUN, elevated creatinine, decreased hemoglobin/hematocrit
Hypoglycemia has been reported in association with Norpace administration (see Warnings).
Infrequent occurrences of reversible cholestatic jaundice, fever, and respiratory difficulty have been reported in association with disopyramide therapy, as have rare instances of thrombocytopenia, reversible agranulocytosis, and gynecomastia. Some cases of LE (lupus erythematosus) symptoms have been reported; most cases occurred in patients who had been switched to disopyramide from procainamide following the development of LE symptoms. Rarely, acute psychosis has been reported following Norpace therapy, with prompt return to normal mental status when therapy was stopped. The physician should be aware of these possible reactions and should discontinue Norpace or Norpace CR therapy promptly if they occur.
Norpace Dosage and Administration
The dosage of Norpace or Norpace CR must be individualized for each patient on the basis of response and tolerance. The usual adult dosage of Norpace or Norpace CR is 400 to 800 mg per day given in divided doses. The recommended dosage for most adults is 600 mg/day given in divided doses (either 150 mg every 6 hours for immediate-release Norpace or 300 mg every 12 hours for Norpace CR). For patients whose body weight is less than 110 pounds (50 kg), the recommended dosage is 400 mg/day given in divided doses (either 100 mg every 6 hours for immediate-release Norpace or 200 mg every 12 hours for Norpace CR). In the event of increased anticholinergic side effects, plasma levels of disopyramide should be monitored and the dose of the drug adjusted accordingly. A reduction of the dose by one third, from the recommended 600 mg/day to 400 mg/day, would be reasonable, without changing the dosing interval.
For patients with cardiomyopathy or possible cardiac decompensation, a loading dose, as discussed below, should not be given, and initial dosage should be limited to 100 mg of immediate-release Norpace every 6 to 8 hours. Subsequent dosage adjustments should be made gradually, with close monitoring for the possible development of hypotension and/or congestive heart failure (see Warnings).
For patients with moderate renal insufficiency (creatinine clearance greater than 40 ml/min) or hepatic insufficiency, the recommended dosage is 400 mg/day given in divided doses (either 100 mg every 6 hours for immediate-release Norpace or 200 mg every 12 hours for Norpace CR).
For patients with severe renal insufficiency (Ccr 40 ml/min or less), the recommended dosage regimen of immediate-release Norpace is 100 mg at intervals shown in the table below, with or without an initial loading dose of 150 mg.
| Creatinine Clearance (ml/min) | 40–30 | 30–15 | Less than 15 |
| Approximate Maintenance-dosing interval | q 8 hr | q 12 hr | Q 24 hr |
The above dosing schedules are for Norpace immediate-release capsules; Norpace CR is not recommended for patients with severe renal insufficiency.
For patients in whom rapid control of ventricular arrhythmia is essential, an initial loading dose of 300 mg of immediate-release Norpace (200 mg for patients whose body weight is less than 110 pounds) is recommended, followed by the appropriate maintenance dosage. Therapeutic effects are usually attained 30 minutes to 3 hours after administration of a 300-mg loading dose. If there is no response or evidence of toxicity within 6 hours of the loading dose, 200 mg of immediate-release Norpace every 6 hours may be prescribed instead of the usual 150 mg. If there is no response to this dosage within 48 hours, either Norpace should then be discontinued or the physician should consider hospitalizing the patient for careful monitoring while subsequent immediate-release Norpace doses of 250 mg or 300 mg every 6 hours are given. A limited number of patients with severe refractory ventricular tachycardia have tolerated daily doses of Norpace up to 1600 mg per day (400 mg every 6 hours), resulting in disopyramide plasma levels up to 9 mcg/ml. If such treatment is warranted, it is essential that patients be hospitalized for close evaluation and continuous monitoring.
Norpace CR should not be used initially if rapid establishment of disopyramide plasma levels is desired.
| NORPACE
disopyramide phosphate capsule, gelatin coated |
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
| NORPACE
disopyramide phosphate capsule, gelatin coated |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| NORPACE CR
disopyramide phosphate capsule, extended release |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| NORPACE CR
disopyramide phosphate capsule, extended release |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Pfizer Laboratories Div Pfizer Inc (134489525) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pfizer Pharmaceuticals LLC | 829084552 | ANALYSIS(0025-2732, 0025-2742, 0025-2752, 0025-2762) , MANUFACTURE(0025-2732, 0025-2742, 0025-2752, 0025-2762) , PACK(0025-2732, 0025-2742, 0025-2752, 0025-2762) , LABEL(0025-2732, 0025-2742, 0025-2752, 0025-2762) | |