Drug Class: Antiviral combinations
Highlights of Prescribing Information
ODEFSEY® (emtricitabine, rilpivirine, and tenofovir alafenamide) tablets, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2016
WARNING: POST TREATMENT ACUTE EXACERBATION OF HEPATITIS B
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
Severe acute exacerbations of hepatitis B have been reported in patients who are coinfected with HIV-1 and HBV and have discontinued products containing emtricitabine (FTC) and/or tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF), and may occur with discontinuation of ODEFSEY. Hepatic function should be monitored closely in these patients. If appropriate, anti-hepatitis B therapy may be warranted. (5.1)
Recent Major Changes
| Warnings and Precautions, New Onset or Worsening Renal Impairment (5.5) | 03/2021 |
Indications and Usage for Odefsey
ODEFSEY is a three-drug combination of emtricitabine (FTC) and tenofovir alafenamide (TAF), both HIV nucleoside analog reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs), and rilpivirine (RPV), a non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI), and is indicated as a complete regimen for the treatment of HIV-1 infection in patients weighing at least 35kg as initial therapy in those with no antiretroviral treatment history with HIV-1 RNA less than or equal to 100,000 copies per mL; or to replace a stable antiretroviral regimen in those who are virologically-suppressed (HIV-1 RNA less than 50 copies per mL) for at least 6 months with no history of treatment failure and no known substitutions associated with resistance to the individual components of ODEFSEY. (1)
Limitations of Use:
- More rilpivirine-treated subjects with HIV-1 RNA greater than 100,000 copies/mL at the start of therapy experienced virologic failure (HIV-1 RNA ≥ 50 copies/mL) compared to rilpivirine-treated subjects with HIV-1 RNA less than or equal to 100,000 copies/mL. (14.2,14.3)
Odefsey Dosage and Administration
- Testing: Prior to or when initiating ODEFSEY, test for hepatitis B virus infection. Prior to or when initiating ODEFSEY, and during treatment on a clinically appropriate schedule, assess serum creatinine, estimated creatinine clearance, urine glucose, and urine protein in all patients. In patients with chronic kidney disease, also assess serum phosphorus (2.1)
- Recommended dosage: one tablet taken orally once daily with a meal. (2.2)
- For pregnant patients who are already on ODEFSEY prior to pregnancy and who are virologically suppressed (HIV-1 RNA less than 50 copies per mL), one tablet taken once daily may be continued. Lower exposures of rilpivirine were observed during pregnancy, therefore viral load should be monitored closely. (2.3)
- Renal impairment: ODEFSEY is not recommended in patients with estimated creatinine clearance of 15 to below 30 mL per minute, or below 15 mL per minute who are not receiving chronic hemodialysis. (2.4)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Tablets: 200 mg of FTC, 25 mg of RPV and 25 mg of TAF. (3)
Contraindications
ODEFSEY is contraindicated when coadministered with drugs where significant decreases in RPV plasma concentrations may occur, which may result in loss of virologic response and possible resistance and cross-resistance. (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Skin and Hypersensitivity Reactions: Severe skin and hypersensitivity reactions have been reported during postmarketing experience with RPV-containing regimens, including cases of Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS). Immediately discontinue treatment if hypersensitivity or rash with systemic symptoms or elevations in hepatic serum biochemistries develops and closely monitor clinical status, including hepatic serum biochemistries. (5.2)
- Hepatotoxicity: Hepatic adverse events have been reported in patients receiving an RPV-containing regimen. Monitor liver-associated tests before and during treatment with ODEFSEY in patients with underlying hepatic disease or marked elevations in liver-associated tests. Also consider monitoring liver-associated tests in patients without risk factors. (5.3)
- Depressive disorders: Severe depressive disorders have been reported. Immediate medical evaluation is recommended for severe depressive disorders. (5.4)
- New onset or worsening renal impairment: Assessment of serum creatinine, estimated creatinine clearance, urine glucose, and urine protein when initiating ODEFSEY and during therapy on a clinically appropriate schedule in all patients. Also assess serum phosphorus in patients with chronic kidney disease. (5.5)
- Concomitant use of ODEFSEY with drugs with a known risk to prolong the QTc interval of the electrocardiogram may increase the risk of Torsade de Pointes. (5.6)
- Lactic acidosis/severe hepatomegaly with steatosis: Discontinue treatment in patients who develop symptoms or laboratory findings suggestive of lactic acidosis or pronounced hepatotoxicity. (5.7)
- Immune reconstitution syndrome: May necessitate further evaluation and treatment. (5.8)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions (incidence greater than or equal to 2%, all grades) are headache and sleep disturbances. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Gilead Sciences, Inc. at 1-800-GILEAD-5 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
- ODEFSEY is a complete regimen for the treatment of HIV-1 infection; therefore, coadministration with other antiretroviral medications for the treatment of HIV-1 infection is not recommended. (7.1)
- Consult the Full Prescribing Information prior to and during treatment for important drug interactions. (4, 5.6, 7)
Use In Specific Populations
- Pregnancy: Total rilpivirine exposures were generally lower during pregnancy compared to the postpartum period. (2.3, 8.1, 12.3).
- Lactation: Breastfeeding not recommended due to the potential for HIV-1 transmission. (8.2)
- Pediatrics: Not recommended for patients weighing less than 35 kg. (8.4)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 9/2021
Related/similar drugs
Biktarvy, Descovy, Truvada, tenofovir, Atripla, Complera, StribildFull Prescribing Information
WARNING: POST TREATMENT ACUTE EXACERBATION OF HEPATITIS B
Severe acute exacerbations of hepatitis B have been reported in patients who are coinfected with HIV-1 and HBV and have discontinued products containing emtricitabine (FTC) and/or tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF), and may occur with discontinuation of ODEFSEY.
Hepatic function should be monitored closely with both clinical and laboratory follow-up for at least several months in patients who are coinfected with HIV-1 and HBV and discontinue ODEFSEY. If appropriate, anti-hepatitis B therapy may be warranted [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
1. Indications and Usage for Odefsey
ODEFSEY is indicated as a complete regimen for the treatment of HIV-1 infection in adult and pediatric patients weighing at least 35 kg:
- as initial therapy in those with no antiretroviral treatment history with HIV-1 RNA less than or equal to 100,000 copies per mL or
- to replace a stable antiretroviral regimen in those who are virologically-suppressed (HIV-1 RNA less than 50 copies per mL) for at least 6 months with no history of treatment failure and no known substitutions associated with resistance to the individual components of ODEFSEY [see Microbiology (12.4) and Clinical Studies (14)].
2. Odefsey Dosage and Administration
2.1 Testing Prior to Initiation and During Treatment with ODEFSEY
Prior to or when initiating ODEFSEY, test patients for hepatitis B virus infection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Prior to or when initiating ODEFSEY, and during treatment with ODEFSEY, on a clinically appropriate schedule, assess serum creatinine, estimated creatinine clearance, urine glucose, and urine protein in all patients. In patients with chronic kidney disease, also assess serum phosphorus [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
2.2 Recommended Dosage
ODEFSEY is a three-drug fixed dose combination product containing 200 mg of emtricitabine (FTC), 25 mg of rilpivirine (RPV), and 25 mg of tenofovir alafenamide (TAF). The recommended dosage of ODEFSEY is one tablet taken orally once daily with a meal in adults and pediatric patients with body weight at least 35 kg and creatinine clearance greater than or equal to 30 mL per minute [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
2.3 Recommended Dosage During Pregnancy
For pregnant patients who are already on ODEFSEY prior to pregnancy and are virologically suppressed (HIV-1 RNA less than 50 copies per mL), one tablet of ODEFSEY taken once daily may be continued. Lower exposures of rilpivirine, a component of ODEFSEY, were observed during pregnancy, therefore viral load should be monitored closely [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
2.4 Not Recommended in Patients with Severe Renal Impairment
ODEFSEY is not recommended in patients with:
- severe renal impairment (estimated creatinine clearance of 15 to below 30 mL per minute); or
- end stage renal disease (ESRD; estimated creatinine clearance below 15 mL per minute) who are not receiving chronic hemodialysis [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Warnings and Precautions (5.5), and Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
Each ODEFSEY tablet contains 200 mg of emtricitabine (FTC), 25 mg of rilpivirine (RPV) (equivalent to 27.5 mg of rilpivirine hydrochloride), and 25 mg of tenofovir alafenamide (TAF) (equivalent to 28 mg of tenofovir alafenamide fumarate).
The tablets are gray, capsule-shaped, film-coated and debossed with "GSI" on one side and "255" on the other side.
4. Contraindications
ODEFSEY is contraindicated when coadministered with the following drugs; coadministration may result in loss of virologic response and possible resistance to ODEFSEY or to the class of NNRTIs [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6), Drug Interactions (7) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]:
- Anticonvulsants: carbamazepine, oxcarbazepine, phenobarbital, phenytoin
- Antimycobacterials: rifampin, rifapentine
- Glucocorticoid (systemic): dexamethasone (more than a single-dose)
- Herbal Products: St. John's wort (Hypericum perforatum)
- Proton Pump Inhibitors: e.g., dexlansoprazole, esomeprazole, lansoprazole, omeprazole, pantoprazole, rabeprazole
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Severe Acute Exacerbation of Hepatitis B in Patients Coinfected with HIV-1 and HBV
Test patients with HIV-1 for the presence of hepatitis B virus (HBV) before or when initiating antiretroviral therapy [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
Severe acute exacerbations of hepatitis B (e.g., liver decompensation and liver failure) have been reported in patients who are coinfected with HIV-1 and HBV and have discontinued products containing FTC and/or TDF, and may occur with discontinuation of ODEFSEY. Patients coinfected with HIV-1 and HBV who discontinue ODEFSEY should be closely monitored with both clinical and laboratory follow-up for at least several months after stopping treatment with ODEFSEY. If appropriate, anti-hepatitis B therapy may be warranted, especially in patients with advanced liver disease or cirrhosis, since post treatment exacerbation of hepatitis may lead to hepatic decompensation and liver failure.
5.2 Skin and Hypersensitivity Reactions
Severe skin and hypersensitivity reactions, including cases of Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS), have been reported during postmarketing experience with RPV-containing regimens. While some skin reactions were accompanied by constitutional symptoms such as fever, other skin reactions were associated with organ dysfunction, including elevations in hepatic serum biochemistries. During Phase 3 clinical trials of RPV, treatment-related rashes with at least Grade 2 severity were reported in 1% of subjects. Overall, most rashes were Grade 1 or 2 and occurred in the first four to six weeks of therapy [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
Discontinue ODEFSEY immediately if signs or symptoms of severe skin or hypersensitivity reactions develop, including but not limited to, severe rash or rash accompanied by fever, blisters, mucosal involvement, conjunctivitis, facial edema, angioedema, hepatitis, or eosinophilia. Clinical status including laboratory parameters should be monitored and appropriate therapy should be initiated.
5.3 Hepatotoxicity
Hepatic adverse events have been reported in patients receiving an RPV-containing regimen. Patients with underlying hepatitis B or C virus infection, or marked elevations in liver-associated tests prior to treatment, may be at increased risk for worsening or development of liver-associated test elevations with use of ODEFSEY. A few cases of hepatic toxicity have been reported in adult patients receiving an RPV-containing regimen who had no preexisting hepatic disease or other identifiable risk factors. Appropriate laboratory testing prior to initiating therapy and monitoring for hepatotoxicity during therapy with ODEFSEY is recommended in patients with underlying hepatic disease such as hepatitis B or C, or in patients with marked elevations in liver-associated tests prior to treatment initiation. Liver-associated test monitoring should also be considered for patients without preexisting hepatic dysfunction or other risk factors.
5.4 Depressive Disorders
Depressive disorders (including depressed mood, depression, dysphoria, major depression, mood altered, negative thoughts, suicide attempt, suicidal ideation) have been reported with RPV. Promptly evaluate patients with severe depressive symptoms to assess whether the symptoms are related to ODEFSEY, and to determine whether the risks of continued therapy outweigh the benefits.
In Phase 3 trials of RPV in adult subjects (N=1368) through 96 weeks, the incidence of depressive disorders (regardless of causality, severity) reported among RPV-treated subjects (n=686) was 9%. Most events were mild or moderate in severity. In RPV-treated subjects, the incidence of Grades 3 and 4 depressive disorders (regardless of causality) was 1%, the incidence of discontinuation due to depressive disorders was 1%, and suicidal ideation and suicide attempt was reported in 4 and 2 subjects, respectively.
During the Phase 2 trial in RPV-treated pediatric subjects 12 to less than 18 years of age (N=36), the incidence of depressive disorders (regardless of causality, severity) was 19% (7/36) through 48 weeks. Most events were mild or moderate in severity. The incidence of Grades 3 and 4 depressive disorders (regardless of causality) was 6% (2/36). None of the subjects discontinued due to depressive disorders. Suicidal ideation and suicide attempt were reported in 1 subject.
5.5 New Onset or Worsening Renal Impairment
Postmarketing case of renal impairment, including acute renal failure, proximal renal tubulopathy (PRT), and Fanconi syndrome have been reported with TAF-containing products; while most of these cases were characterized by potential confounders that may have contributed to the reported renal events, it is also possible these factors may have predisposed patients to tenofovir-related adverse events [see Adverse Reactions (6.1, 6.2)]. ODEFSEY is not recommended in patients with estimated creatinine clearance of 15 to below 30 mL per minute, or in patients with estimated creatinine clearance below 15 mL per minute who are not receiving chronic hemodialysis.
Patients taking tenofovir prodrugs who have impaired renal function and those taking nephrotoxic agents, including nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are at increased risk of developing renal-related adverse reactions.
Prior to or when initiating ODEFSEY, and during treatment with ODEFSEY, on a clinically appropriate schedule, assess serum creatinine, estimated creatinine clearance, urine glucose and urine protein in all patients. In patients with chronic kidney disease, also assess serum phosphorus. Discontinue ODEFSEY in patients who develop clinically significant decreases in renal function or evidence of Fanconi syndrome.
5.6 Risk of Adverse Reactions or Loss of Virologic Response Due to Drug Interactions
The concomitant use of ODEFSEY and other drugs may result in potentially significant drug interactions, some of which may lead to [see Contraindications (4), and Drug Interactions (7)]:
- Loss of therapeutic effect of ODEFSEY and possible development of resistance due to reduced exposure of RPV.
In healthy subjects, higher than recommended doses of RPV (75 mg once daily and 300 mg once daily –3 and 12 times the recommended dosages in ODEFSEY, respectively) have been shown to prolong the QTc interval of the electrocardiogram. Consider alternatives to ODEFSEY when coadministered with a drug that is known to have a risk of Torsade de Pointes [see Drug Interactions (7.2) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)].
See Table 3 for steps to prevent or manage these possible and known significant drug interactions, including dosing recommendations [see Contraindications (4) and Drug Interactions (7)]. Consider the potential for drug interactions prior to and during ODEFSEY therapy and review concomitant medications during ODEFSEY therapy.
5.7 Lactic Acidosis/Severe Hepatomegaly with Steatosis
Lactic acidosis and severe hepatomegaly with steatosis, including fatal cases, have been reported with the use of nucleoside analogs, including emtricitabine, a component of ODEFSEY, and tenofovir DF, another prodrug of tenofovir, alone or in combination with other antiretrovirals. Treatment with ODEFSEY should be suspended in any patient who develops clinical or laboratory findings suggestive of lactic acidosis or pronounced hepatotoxicity (which may include hepatomegaly and steatosis even in the absence of marked transaminase elevations).
5.8 Immune Reconstitution Syndrome
Immune reconstitution syndrome has been reported in patients treated with combination antiretroviral therapy, including FTC and RPV, both components of ODEFSEY. During the initial phase of combination antiretroviral treatment, patients whose immune system responds may develop an inflammatory response to indolent or residual opportunistic infections [such as Mycobacterium avium infection, cytomegalovirus, Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia (PCP), or tuberculosis], which may necessitate further evaluation and treatment.
Autoimmune disorders (such as Graves' disease, polymyositis, Guillain-Barré syndrome, and autoimmune hepatitis) have also been reported to occur in the setting of immune reconstitution, however, the time to onset is more variable, and can occur many months after initiation of treatment.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following adverse reactions are discussed in other sections of the labeling:
- Severe Acute Exacerbations of Hepatitis B [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Skin and Hypersensitivity Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Depressive Disorders [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- New Onset or Worsening Renal Impairment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Lactic Acidosis/Severe Hepatomegaly with Steatosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- Immune Reconstitution Syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug (or a drug given in various combinations with other concomitant therapy) cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug (or drug given in the same or different combination therapy) and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Adverse Reactions in Clinical Trials of ODEFSEY in Virologically-Suppressed Adult Subjects with HIV-1 Infection
The safety of ODEFSEY in virologically-suppressed adults is based on Week 48 data from two randomized, double-blinded, active-controlled clinical trials, 1160 and 1216, that enrolled 1505 adult subjects who were virologically-suppressed for at least 6 months. Both trials were designed to compare switching to ODEFSEY to maintaining efavirenz/emtricitabine/tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (EFV/FTC/TDF) or emtricitabine/rilpivirine/tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (FTC/RPV/TDF) in Trials 1160 and 1216, respectively. A total of 754 subjects received one tablet of ODEFSEY daily [see Clinical Studies (14.1)].
The most common adverse reactions (all Grades) reported in at least 2% of subjects in the ODEFSEY group across Trials 1216 and 1160 were headache and sleep disturbances (Table 1). Over 98% of the adverse reactions in the ODEFSEY group were of mild to moderate intensity. The proportion of subjects who discontinued treatment with ODEFSEY due to adverse events, regardless of severity, was 2% compared to 1% for FTC/RPV/TDF and 2% for EFV/FTC/TDF.
| Adverse Reaction | Trial 1160 | Trial 1216 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ODEFSEY (N=438) | EFV/FTC/TDF (N=437)† | ODEFSEY (N=316) | FTC/RPV/TDF (N=313)† |
|
|
||||
| Headache | 2% | 1% | 0 | 1% |
| Sleep Disturbances | 2% | 1% | 0 | <1% |
| Flatulence | 1% | <1% | <1% | 1% |
| Abnormal Dreams | 1% | 1% | 0 | 2% |
| Diarrhea | 1% | 3% | 1% | 2% |
| Nausea | 1% | 1% | 1% | 1% |
Serum Lipids
Changes from baseline in total cholesterol, HDL-cholesterol, LDL-cholesterol, triglycerides, and total cholesterol to HDL ratio for Trials 1216 and 1160 are presented in Table 2.
| Trial 1216 | Trial 1160 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ODEFSEY N=316 [n=235] | FTC/RPV/TDF N=314 [n=245] | ODEFSEY N=438 [n=295] | EFV/FTC/TDF N=437 [n=308] |
|||||
| Baseline | Week 48 | Baseline | Week 48 | Baseline | Week 48 | Baseline | Week 48 | |
| mg/dL | Change*,† | mg/dL | Change*,† | mg/dL | Change*,† | mg/dL | Change*,† | |
|
||||||||
| Total Cholesterol (fasted) | 176 | +17 | 171 | 0 | 193 | -7 | 192 | -3 |
| HDL-Cholesterol (fasted) | 50 | +3 | 48 | 0 | 56 | -4 | 55 | -2 |
| LDL-Cholesterol (fasted) | 111 | +13 | 108 | +1 | 118‡ | -1‡ | 119 | -1 |
| Triglycerides (fasted) |
116 | +12 | 119 | -9 | 139 | -12 | 133 | +3 |
| Total Cholesterol to HDL Ratio | 3.7 | +0.2 | 3.8 | +0.1 | 3.7 | +0.2 | 3.8 | 0 |
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during postmarketing experience in patients receiving RPV or TAF-containing regimens. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 Not Recommended with Other Antiretroviral Medications
Because ODEFSEY is a complete regimen, coadministration with other antiretroviral medications for the treatment of HIV-1 infection is not recommended.
7.2 Drugs Inducing or Inhibiting CYP3A Enzymes
RPV is primarily metabolized by CYP3A, and drugs that induce or inhibit CYP3A may affect the clearance of RPV [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Coadministration of RPV and drugs that induce CYP3A may result in decreased plasma concentrations of RPV and loss of virologic response and possible resistance to RPV or to the class of NNRTIs [see Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.6), and Table 3].
Coadministration of RPV and drugs that inhibit CYP3A may result in increased plasma concentrations of RPV and possible adverse events.
7.3 Drugs Inducing or Inhibiting P-glycoprotein
TAF, a component of ODEFSEY, is a substrate of P-gp, BCRP, OATP1B1, and OATP1B3. Drugs that strongly affect P-gp and BCRP activity may lead to changes in TAF absorption (see Table 3). Drugs that induce P-gp activity are expected to decrease the absorption of TAF, resulting in decreased plasma concentration of TAF, which may lead to loss of therapeutic effect of ODEFSEY and development of resistance. Coadministration of ODEFSEY with other drugs that inhibit P-gp and BCRP may increase the absorption and plasma concentration of TAF.
7.4 Drugs Increasing Gastric pH
Coadministration of RPV with drugs that increase gastric pH may decrease plasma concentrations of RPV and lead to loss of virologic response and possible resistance to RPV or to the class of NNRTIs. Use of RPV with proton pump inhibitors is contraindicated and use of RPV with H2-receptor antagonists requires staggered administration [see Contraindications (4) and Table 3].
7.5 QT Prolonging Drugs
There is limited information available on the potential for a pharmacodynamic interaction between RPV and drugs that prolong the QTc interval. In a study of healthy subjects, higher than recommended doses of RPV, 75 mg once daily and 300 mg once daily (3 times and 12 times recommended daily dose in ODEFSEY) prolonged the QTc interval [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)]. Consider alternative medications to ODEFSEY in patients taking a drug with a known risk of Torsade de Pointes.
7.6 Drugs Affecting Renal Function
Because FTC and tenofovir are primarily excreted by the kidneys by a combination of glomerular filtration and active tubular secretion, coadministration of ODEFSEY with drugs that reduce renal function or compete for active tubular secretion may increase concentrations of FTC, tenofovir, and other renally eliminated drugs and this may increase the risk of adverse reactions. Some examples of drugs that are eliminated by active tubular secretion include, but are not limited to, acyclovir, cidofovir, ganciclovir, valacyclovir, valganciclovir, aminoglycosides (e.g., gentamicin), and high-dose or multiple NSAIDs [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
7.7 Significant Drug Interactions
Table 3 provides a listing of established or potentially clinically significant drug interactions with recommended steps to prevent or manage the drug interaction (the table is not all inclusive). The drug interactions described are based on studies conducted with either ODEFSEY, the components of ODEFSEY (FTC, RPV and TAF) as individual agents, or are predicted drug interactions that may occur with ODEFSEY [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3), Tables 8–11]. For list of contraindicated drugs, [see Contraindications (4)].
| Concomitant Drug Class: Drug Name | Effect on Concentration† | Clinical Comment |
|---|---|---|
|
||
| Antacids:
antacids (e.g., aluminum, magnesium hydroxide, or calcium carbonate) | ↔ RPV (antacids taken at least 2 hours before or at least 4 hours after RPV) ↓ RPV (concomitant intake) | Administer antacids at least 2 hours before or at least 4 hours after ODEFSEY. |
| Anticonvulsants:
carbamazepine oxcarbazepine phenobarbital phenytoin | ↓ RPV | Coadministration is contraindicated due to potential for loss of virologic response and development of resistance. |
| Antimycobacterials:
rifampin rifapentine | ↓ RPV | Coadministration is contraindicated due to potential for loss of virologic response and development of resistance. |
| Antimycobacterials:
rifabutin | ↓ RPV‡
↓ TAF | Coadministration of ODEFSEY with rifabutin is not recommended. |
| Azole Antifungal Agents: fluconazole itraconazole ketoconazole posaconazole voriconazole | ↑ RPV‡,§
↑ TAF ↓ ketoconazole‡,§ | No dosage adjustment is required when ODEFSEY is coadministered with azole antifungal agents. Clinically monitor for breakthrough fungal infections when azole antifungals are coadministered with ODEFSEY. |
| Glucocorticoid (systemic):
dexamethasone (more than a single dose) | ↓ RPV | Coadministration is contraindicated due to potential for loss of virologic response and development of resistance. |
| H2-Receptor Antagonists:
cimetidine famotidine nizatidine ranitidine | ↔ RPV‡,§
(famotidine taken 12 hours before RPV or 4 hours after RPV) ↓ RPV‡,§ (famotidine taken 2 hours before RPV) | Administer H2-receptor antagonists at least 12 hours before or at least 4 hours after ODEFSEY. |
| Herbal Products:
St. John's wort (Hypericum perforatum) | ↓ RPV | Coadministration is contraindicated due to potential for loss of virologic response and development of resistance. |
| Macrolide or Ketolide Antibiotics:
clarithromycin erythromycin telithromycin | ↑ RPV ↔ clarithromycin ↔ erythromycin ↔ telithromycin | Where possible, alternatives such as azithromycin should be considered. |
| Narcotic Analgesics:
methadone | ↓ R(–) methadone‡
↓ S(+) methadone‡ ↔ RPV‡ ↔ methadone‡ (when used with tenofovir) | No dosage adjustments are required when initiating coadministration of methadone with ODEFSEY. However, clinical monitoring is recommended, as methadone maintenance therapy may need to be adjusted in some patients. |
| Proton Pump Inhibitors:
e.g., dexlansoprazole, esomeprazole, lansoprazole, omeprazole, pantoprazole, rabeprazole | ↓ RPV | Coadministration is contraindicated due to potential for loss of virologic response and development of resistance. |
7.8 Drugs Without Clinically Significant Interactions with ODEFSEY
Based on drug interaction studies conducted with the fixed dose combination or components of ODEFSEY, no clinically significant drug interactions have been observed when ODEFSEY is combined with the following drugs: acetaminophen, atorvastatin, chlorzoxazone, digoxin, ethinyl estradiol, ledipasvir, metformin, midazolam, norethindrone, norgestimate, sildenafil, simeprevir, sofosbuvir, velpatasvir, and voxilaprevir.
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Data
8.4 Pediatric Use
The efficacy and safety of ODEFSEY as a complete regimen for the treatment of HIV-1 infection was established in pediatric patients 12 years of age and older with body weight greater than or equal to 35 kg [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)]. Use of ODEFSEY in this age group is supported by adequate and well-controlled studies of RPV+FTC+TDF in adults with HIV-1 infection, adequate and well-controlled studies of FTC+TAF with EVG+COBI in adults with HIV-1 infection, and by the following pediatric studies [see Clinical Studies (14)]:
- 48-week open-label trial of 36 antiretroviral treatment-naïve HIV-1 infected pediatric subjects 12 to less than 18 years old weighing at least 32 kg treated with 25 mg per day of RPV and other antiretrovirals. The safety and efficacy of RPV administered with other antiretrovirals were similar to that of antiretroviral treatment-naïve HIV-1 infected adults on this regimen [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) and Clinical Studies (14)].
- 24-week open-label trial of 23 antiretroviral treatment-naïve HIV-1 infected pediatric subjects 12 to less than 18 years old (weighing at least 35 kg) treated with FTC+TAF with EVG+COBI. The safety and efficacy of FTC+TAF with EVG+COBI were similar to that of antiretroviral treatment-naïve HIV-1 infected adults on this regimen [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) and Clinical Studies (14)].
Because it is a fixed-dose combination tablet, the dose of ODEFSEY cannot be adjusted for patients of lower age and weight. The safety and efficacy of ODEFSEY have not been established in pediatric patients weighing less than 35 kg [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.5 Geriatric Use
In clinical trials, 80 of the 97 subjects enrolled aged 65 years and over received FTC+TAF with EVG+COBI. No differences in safety or efficacy have been observed between elderly subjects and those between 12 and less than 65 years of age. Clinical trials of RPV did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 years and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.6 Renal Impairment
No dosage adjustment of ODEFSEY is recommended in patients with estimated creatinine clearance greater than or equal to 30 mL per minute. ODEFSEY should be used with caution in adults patients with ESRD (estimated creatinine clearance below 15mL per minute) who are receiving chronic hemodialysis and increased monitoring is recommended for RPV-related adverse effects in patients with ESRD, as RPV concentrations may be increased due to alteration of drug absorption, distribution, and metabolism secondary to renal dysfunction. On days of hemodialysis, administer the daily dose of ODEFSEY after completion of hemodialysis treatment [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
ODEFSEY is not recommended in patients with severe renal impairment (estimated creatinine clearance of 15 to below 30 mL per minute), or in patients with ESRD who are not receiving chronic hemodialysis, as the safety of ODEFSEY has not been established in these populations [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
10. Overdosage
Limited data are available on overdose of the components of ODEFSEY in patients. If overdose occurs, monitor the patient for evidence of toxicity. Treatment of overdose with ODEFSEY consists of general supportive measures including monitoring of vital signs and ECG (QT interval) as well as observation of the clinical status of the patient.
11. Odefsey Description
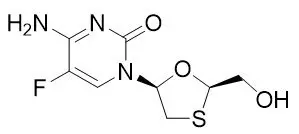
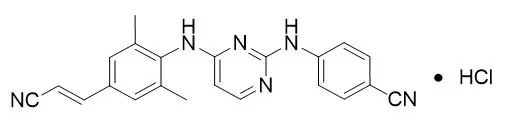
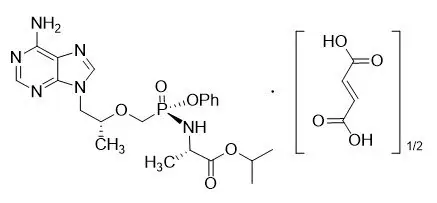
ODEFSEY (emtricitabine, rilpivirine, and tenofovir alafenamide) is a fixed-dose combination tablet containing emtricitabine (FTC), rilpivirine (RPV), and tenofovir alafenamide (TAF) for oral administration.
- FTC, a synthetic nucleoside analog of cytidine, is an HIV-1 nucleoside analog reverse transcriptase inhibitor (HIV-1 NRTI).
- RPV is an HIV-1 non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI).
- TAF, an HIV-1 NRTI, is converted in vivo to tenofovir, an acyclic nucleoside phosphonate (nucleotide) analog of adenosine 5′-monophosphate.
Each tablet contains 200 mg of FTC, 25 mg of RPV (equivalent to 27.5 of rilpivirine hydrochloride) and 25 mg of TAF (equivalent to 28 mg of tenofovir alafenamide fumarate) and the following inactive ingredients: croscarmellose sodium, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, polysorbate 20, and povidone. The tablets are film-coated with a coating material containing iron oxide black, polyethylene glycol, polyvinyl alcohol, talc, and titanium dioxide.
12. Odefsey - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
ODEFSEY is a fixed dose combination of antiretroviral drugs emtricitabine, rilpivirine, and tenofovir alafenamide [see Microbiology (12.4)].
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, and Excretion
The pharmacokinetic properties of the components of ODEFSEY are provided in Table 4. The multiple dose pharmacokinetic parameters of FTC, RPV and TAF and its metabolite tenofovir are provided in Table 5.
| Rilpivirine | Emtricitabine | Tenofovir Alafenamide | |
|---|---|---|---|
| PBMCs = peripheral blood mononuclear cells; CES1 = carboxylesterase 1. | |||
|
|||
| Absorption | |||
| Tmax (h) | 4 | 3 | 1 |
| Effect of moderate fat meal (relative to fasting)* | AUC Ratio = 1.13 (1.03, 1.23) | AUC Ratio = 0.91 (0.89, 0.93) | AUC Ratio = 1.45 (1.33, 1.58) |
| Effect of high fat meal (relative to fasting)* | AUC Ratio = 1.72 (1.49, 1.99) | AUC Ratio = 0.88 (0.85, 0.90) | AUC Ratio = 1.53 (1.39, 1.69) |
| Distribution | |||
| % Bound to human plasma proteins | ~99 | <4 | ~80 |
| Source of protein binding data | In vitro | In vitro | Ex vivo |
| Blood-to-plasma ratio | 0.7 | 0.6 | 1.0 |
| Metabolism | |||
| Metabolism | CYP3A | Not significantly metabolized | Cathepsin A† (PBMCs) CES1 (hepatocytes) CYP3A (minimal) |
| Elimination | |||
| Major route of elimination | Metabolism | Glomerular filtration and active tubular secretion | Metabolism (>80% of oral dose) |
| t1/2 (h)‡ | 50 | 10 | 0.51 |
| % Of dose excreted in urine§ | 6 | 70 | <1 |
| % Of dose excreted in feces§ | 85 | 13.7 | 31.7 |
| Parameter Mean (CV%) | Emtricitabine* | Rilpivirine† | Tenofovir Alafenamide‡ | Tenofovir§ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CV = Coefficient of Variation; NA = Not Applicable | ||||
|
||||
| Cmax
(microgram per mL) | 2.1 (20.2) | NA | 0.16 (51.1) | 0.02 (26.1) |
| AUCtau
(microgram∙hour per mL) | 11.7 (16.6) | 2.2 (38.1) | 0.21 (71.8) | 0.29 (27.4) |
| Ctrough
(microgram per mL) | 0.10 (46.7) | 0.08 (44.3) | NA | 0.01 (28.5) |
Specific Populations
Patients with Renal Impairment
Emtricitabine and Tenofovir Alafenamide: The pharmacokinetics of FTC+TAF with EVG+COBI in HIV-1 infected subjects with renal impairment (eGFR 30 to 69 mL per minute by Cockcroft-Gault method), and in HIV-1 infected subjects with ESRD (estimated creatinine clearance of less than 15 mL per minute by Cockcroft-Gault method) receiving chronic hemodialysis were evaluated in subsets of virologically-suppressed subjects in open-label trials. The pharmacokinetics of TAF were similar among healthy subjects, subjects with mild or moderate renal impairment, and subjects with ESRD receiving chronic hemodialysis; increases in FTC and TFV exposures in subjects with renal impairment were not considered clinically relevant (Table 6).
| AUCtau (microgram-hour per mL) Mean (CV%) |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Estimated Creatinine Clearance* | ≥90 mL per minute (N=18)† | 60–89 mL per minute (N=11)‡ | 30–59 mL per minute (N=18)§ | <15 mL per minute (N=12)¶ |
|
||||
| Emtricitabine | 11.4 (11.9) | 17.6 (18.2) | 23.0 (23.6) | 62.9 (48.0)# |
| Tenofovir | 0.32 (14.9) | 0.46 (31.5) | 0.61 (28.4) | 8.72 (39.4)Þ |
Pregnancy and Postpartum
Rilpivirine: The exposure (C0h and AUC24h) to total RPV after intake of RPV 25 mg once daily as part of an antiretroviral regimen was 30 to 40% lower during pregnancy (similar for the second and third trimester), compared with postpartum (see Table 7). However, the exposure during pregnancy was not significantly different from exposures obtained in Phase 3 trials of RPV-containing regimens. Based on the exposure-response relationship for RPV, this decrease is not considered clinically relevant in patients who are virologically suppressed. The protein binding of RPV was similar (>99%) during the second trimester, third trimester, and postpartum.
| Pharmacokinetics of total rilpivirine (mean ± SD, tmax: median [range]) | Postpartum (6–12 Weeks) (n=11) | 2nd Trimester of pregnancy (n=15) | 3rd Trimester of pregnancy (n=13) |
|---|---|---|---|
| C0h, ng/mL | 111 ± 69.2 | 65.0 ± 23.9 | 63.5 ± 26.2 |
| Cmin, ng/mL | 84.0 ± 58.8 | 54.3 ± 25.8 | 52.9 ± 24.4 |
| Cmax, ng/mL | 167 ± 101 | 121 ± 45.9 | 123 ± 47.5 |
| tmax, h | 4.00 (2.03–25.08) | 4.00 (1.00–9.00) | 4.00 (2.00–24.93) |
| AUC24h, ng.h/mL | 2714 ± 1535 | 1792 ± 711 | 1762 ± 662 |
Drug Interaction Studies
Rilpivirine: RPV is primarily metabolized by CYP3A, and drugs that induce or inhibit CYP3A may thus affect the clearance of RPV.
RPV at a dose of 25 mg once daily is not likely to have a clinically relevant effect on the exposure of medicinal products metabolized by CYP enzymes.
TAF is not an inhibitor of CYP1A2, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, or UGT1A1. TAF is a weak inhibitor of CYP3A in vitro. TAF is not an inhibitor or inducer of CYP3A in vivo.
The drug interaction studies described in Tables 8–11 were conducted with ODEFSEY (FTC/RPV/TAF) or the components of ODEFSEY (FTC, RPV, or TAF) administered individually.
The effects of coadministered drugs on the exposures of RPV and TAF are shown in Tables 8 and 9, respectively. The effects of RPV and TAF on the exposure of coadministered drugs are shown in Tables 10 and 11, respectively. For information regarding clinical recommendations, see Drug Interactions (7).
| Coadministered Drug | Dose/Schedule | Mean Ratio of RPV Pharmacokinetic Parameters With/Without Coadministered Drug (90% CI); No Effect = 1.00 |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coadministered Drug (mg) | RPV (mg) | N | Cmax | AUC | Cmin | |
| CI=Confidence Interval; N=maximum number of subjects with data; NA=Not Available; ↔=no change | ||||||
|
||||||
| Acetaminophen | 500 single dose | 150 once daily* | 16 | 1.09 (1.01, 1.18) | 1.16 (1.10, 1.22) | 1.26 (1.16, 1.38) |
| Atorvastatin | 40 once daily | 150 once daily* | 16 | 0.91 (0.79, 1.06) | 0.90 (0.81, 0.99) | 0.90 (0.84, 0.96) |
| Chlorzoxazone | 500 single dose taken 2 hours after RPV | 150 once daily* | 16 | 1.17 (1.08, 1.27) | 1.25 (1.16, 1.35) | 1.18 (1.09, 1.28) |
| Ethinylestradiol/Norethindrone | 0.035 once daily /1 mg once daily | 25 once daily† | 15 | ↔‡ | ↔‡ | ↔‡ |
| Famotidine | 40 single dose taken 12 hours before RPV | 150 single dose* | 24 | 0.99 (0.84, 1.16) | 0.91 (0.78, 1.07) | NA |
| Famotidine | 40 single dose taken 2 hours before RPV | 150 single dose* | 23 | 0.15 (0.12, 0.19) | 0.24 (0.20, 0.28) | NA |
| Famotidine | 40 single dose taken 4 hours after RPV | 150 single dose* | 24 | 1.21 (1.06, 1.39) | 1.13 (1.01, 1.27) | NA |
| Ketoconazole | 400 once daily | 150 once daily* | 15 | 1.30 (1.13, 1.48) | 1.49 (1.31, 1.70) | 1.76 (1.57, 1.97) |
| Methadone | 60–100 once daily, individualized dose | 25 once daily† | 12 | ↔‡ | ↔‡ | ↔‡ |
| Ledipasvir/Sofosbuvir | 90/400 once daily | 25 once daily§ | 42 | 0.97 (0.92, 1.02) | 0.95 (0.91, 0.98) | 0.93 (0.89, 0.97) |
| Omeprazole | 20 once daily | 25 single dose† | 15 | 0.30 (0.24, 0.38) | 0.35 (0.28, 0.44) | NA |
| Rifabutin | 300 once daily | 25 once daily† | 18 | 0.69 (0.62, 0.76) | 0.58 (0.52, 0.65) | 0.52 (0.46, 0.59) |
| Rifampin | 600 once daily | 150 once daily* | 16 | 0.31 (0.27, 0.36) | 0.20 (0.18, 0.23) | 0.11 (0.10, 0.13) |
| Simeprevir | 25 once daily | 150 once daily† | 23 | 1.04 (0.95, 1.30) | 1.12 (1.05, 1.19) | 1.25 (1.16, 1.35) |
| Sildenafil | 50 single dose | 75 once daily* | 16 | 0.92 (0.85, 0.99) | 0.98 (0.92, 1.05) | 1.04 (0.98, 1.09) |
| Sofosbuvir/velpatasvir | 400/100 once daily | 10 once daily¶ | 24 | 0.93 (0.88,0.98) | 0.95 (0.90, 1.00) | 0.96 (0.90,1.03) |
| Sofosbuvir/velpatasvir/voxilaprevir | 400/100/100 + 100 voxilaprevir# once daily | 25 once daily§ | 30 | 0.79 (0.74, 0.84) | 0.80 (0.76, 0.85) | 0.82 (0.77, 0.87) |
| Coadministered Drug | Dose of Coadministered Drug (mg) | TAF (mg) | N | Mean Ratio of Tenofovir Alafenamide Pharmacokinetic Parameters (90% CI); No Effect = 1.00 |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cmax | AUC | Cmin | ||||
| CI=Confidence Interval; N=maximum number of subjects with data; NA=Not Available | ||||||
|
||||||
| Cobicistat† | 150 once daily | 8 once daily | 12 | 2.83 (2.20, 3.65) | 2.65 (2.29, 3.07) | NA |
| Ledipasvir/Sofosbuvir | 90/400 once daily | 25 once daily‡ | 42 | 1.03 (0.94, 1.14) | 1.32 (1.25, 1.40) | NA |
| Sofosbuvir/velpatasvir/voxilaprevir | 400/100/100 + 100 voxilaprevir§ once daily | 25 once daily‡ | 30 | 1.32 (1.17, 1.48) | 1.52 (1.43,1.61) | NA |
| Coadministered Drug | Dose/Schedule | Mean Ratio of Coadministered Drug Pharmacokinetic Parameters With/Without RPV (90% CI); No Effect = 1.00 |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coadministered Drug (mg) | RPV (mg) | N | Cmax | AUC | Cmin | |
| CI=Confidence Interval; N=maximum number of subjects with data; NA=Not Available | ||||||
|
||||||
| Acetaminophen | 500 single dose | 150 once daily* | 16 | 0.97 (0.86, 1.10) | 0.92 (0.85, 0.99) | NA |
| Atorvastatin | 40 once daily | 150 once daily* | 16 | 1.35 (1.08, 1.68) | 1.04 (0.97, 1.12) | 0.85 (0.69, 1.03) |
| 2-hydroxy-atorvastatin | 1.58 (1.33, 1.87) | 1.39 (1.29, 1.50) | 1.32 (1.10, 1.58) |
|||
| 4-hydroxy-atorvastatin | 1.28 (1.15, 1.43) | 1.23 (1.13, 1.33) | NA | |||
| Chlorzoxazone | 500 single dose taken 2 hours after RPV | 150 once daily* | 16 | 0.98 (0.85, 1.13) | 1.03 (0.95, 1.13) | NA |
| Digoxin | 0.5 single dose | 25 once daily† | 22 | 1.06 (0.97, 1.17) | 0.98 (0.93, 1.04)‡ | NA |
| Ethinylestradiol | 0.035 once daily | 25 once daily† | 17 | 1.17 (1.06, 1.30) | 1.14 (1.10, 1.19) | 1.09 (1.03, 1.16) |
| Norethindrone | 1 mg once daily | 0.94 (0.83, 1.06) | 0.89 (0.84, 0.94) | 0.99 (0.90, 1.08) |
||
| Ketoconazole | 400 once daily | 150 once daily* | 14 | 0.85 (0.80, 0.90) | 0.76 (0.70, 0.82) | 0.34 (0.25, 0.46) |
| Ledipasvir | 90 once daily | 25 once daily§ | 41 | 1.01 (0.97, 1.05) | 1.02 (0.97, 1.06) | 1.02 (0.98, 1.07) |
| Sofosbuvir | 400 once daily | 25 once daily§ | 41 | 0.96 (0.89, 1.04) | 1.05 (1.01, 1.09) | NA |
| GS-331007¶ | 1.08 (1.05, 1.11) | 1.08 (1.06, 1.10) | 1.10 (1.07, 1.12) |
|||
| R(-) methadone | 60–100 once daily, individualized dose | 25 once daily† | 13 | 0.86 (0.78, 0.95) | 0.84 (0.74, 0.95) | 0.78 (0.67, 0.91) |
| S(+) methadone | 0.87 (0.78, 0.97) | 0.84 (0.74, 0.96) | 0.79 (0.67, 0.92) |
|||
| Metformin | 850 single dose | 25 once daily† | 20 | 1.02 (0.95, 1.10) | 0.97 (0.90,1.06)# | NA |
| Rifampin | 600 once daily | 150 once daily* | 16 | 1.02 (0.93, 1.12) | 0.99 (0.92, 1.07) | NA |
| 25-desacetylrifampin | 1.00 (0.87, 1.15) | 0.91 (0.77, 1.07) | NA | |||
| Simeprevir | 150 once daily | 25 once daily† | 21 | 1.10 (0.97, 1.26) | 1.06 (0.94, 1.19) | 0.96 (0.83, 1.11) |
| Sildenafil | 50 single dose | 75 once daily* | 16 | 0.93 (0.80, 1.08) | 0.97 (0.87, 1.08) | NA |
| N-desmethyl-sildenafil | 0.90 (0.80, 1.02) | 0.92 (0.85, 0.99)‡ | NA | |||
| Sofosbuvir GS-331007¶ | 400 once daily | 25 once dailyÞ | 24 | 1.09 (0.95, 1.25) 0.96 (0.90, 1.01) | 1.16 (1.10, 1.24) 1.04 (1.00, 1.07) |
NA 1.12 (1.07, 1.17) |
| Velpatasvir | 100 once daily | 25 once dailyÞ | 24 | 0.96 (0.85, 1.10) | 0.99 (0.88, 1.11) | 1.02 (0.91, 1.15) |
| Sofosbuvir | 400 once daily | 25 once daily§ | 30 | 0.95 (0.86, 1.05) | 1.01 (0.97, 1.06) | NA |
| GS-331007¶ | 1.02 (0.98, 1.06) | 1.04 (1.01, 1.06) | NA | |||
| Velpatasvir | 100 once daily | 25 once daily§ | 30 | 1.05 (0.96, 1.16) | 1.01 (0.94, 1.07) | 1.01 (0.95, 1.09) |
| Voxilaprevir | 100 + 100 once daily | 25 once daily§ | 30 | 0.96 (0.84, 1.11) | 0.94 (0.84, 1.05) | 1.02 (0.92, 1.12) |
| Coadministered Drug | Dose of Coadministered Drug (mg) | TAF (mg) | N | Mean Ratio of Coadministered Drug Pharmacokinetic Parameters (90% CI); No Effect = 1.00 |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cmax | AUC | Cmin | ||||
| CI=Confidence Interval; N=maximum number of subjects with data; NA=Not Available | ||||||
|
||||||
| Midazolam* | 2.5 single dose, orally | 25 once daily†
| 18 | 1.02 (0.92, 1.13) | 1.13 (1.04, 1.23) | NA |
| 1 single dose, IV | 0.99 (0.89, 1.11) | 1.08 (1.04, 1.13) | NA | |||
| Ledipasvir‡ | 90/400 once daily | 25 once daily‡
| 41 | 1.01 (0.97, 1.05) | 1.02 (0.97, 1.06) | 1.02 (0.98,1.07) |
| Sofosbuvir‡ | 0.96 (0.89, 1.04) | 1.05 (1.01, 1.09) | NA | |||
| GS-331007‡,§ | 1.08 (1.05, 1.11) | 1.08 (1.06, 1.10) | 1.10 (1.07, 1.12) | |||
| Norelgestromin | norgestimate 0.180/0.215/0.250 once daily/ethinyl estradiol 0.025 once daily | 25 once daily¶ | 29 | 1.17 (1.07,1.26) | 1.12 (1.07, 1.17) | 1.16 (1.08,1.24) |
| Norgestrel | 1.10 (1.02, 1.18) | 1.09 (1.01, 1.18) | 1.11 (1.03,1.20) |
|||
| Ethinyl estradiol | 1.22 (1.15, 1.29) | 1.11 (1.07, 1.16) | 1.02 (0.93,1.12) |
|||
| Sofosbuvir | 400 once daily | 25 once daily‡ | 30 | 0.95 (0.86, 1.05) | 1.01 (0.97, 1.06) | NA |
| GS-331007§ | 1.02 (0.98, 1.06) | 1.04 (1.01, 1.06) | NA | |||
| Velpatasvir | 100 once daily | 1.05 (0.96, 1.16) | 1.01 (0.94, 1.07) | 1.01 (0.95,1.09) |
||
| Voxilaprevir | 100 + 100 once daily | 0.96 (0.84, 1.11) | 0.94 (0.84, 1.05) | 1.02 (0.92,1.12) |
||
12.4 Microbiology
Antiviral Activity in Cell Culture
Resistance
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
Minimal to slight infiltration of mononuclear cells in the posterior uvea was observed in dogs with similar severity after three- and nine-month administration of TAF; reversibility was seen after a three-month recovery period. No eye toxicity was observed in the dog at systemic exposures of 5 (TAF) and 15 (tenofovir) times the exposure seen in humans at the recommended daily TAF dose in ODEFSEY.
14. Clinical Studies
14.1 Clinical Trial Results in HIV-1 Virologically-Suppressed Subjects Who Switched to ODEFSEY
In Trial 1216, the efficacy and safety of switching from emtricitabine/rilpivirine/tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (FTC/RPV/TDF) to ODEFSEY were evaluated in a randomized, double-blind study of virologically-suppressed HIV-1 infected adults. Subjects were suppressed (HIV-1 RNA <50 copies/mL) on their baseline regimen of FTC/RPV/TDF for at least 6 months and have no documented resistance mutations to FTC, TAF, or RPV prior to study entry. Subjects were randomized in a 1:1 ratio to either switch to ODEFSEY (N=316) once daily or stay on FTC/RPV/TDF (N=314) once daily. Subjects had a mean age of 45 years (range: 23–72), 90% were male, 75% were White, and 19% were Black. The mean baseline CD4+ cell count was 709 cells/mm3 (range: 104–2527).
In Trial 1160, the efficacy and safety of switching from efavirenz/emtricitabine/tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (EFV/FTC/TDF) to ODEFSEY were evaluated in a randomized, double-blind study of virologically-suppressed HIV-1 infected adults. Subjects must have been stably suppressed (HIV-1 RNA <50 copies/mL) on their baseline regimen of EFV/FTC/TDF for at least 6 months and have no documented resistance mutations to FTC, TAF, or RPV prior to study entry. Subjects were randomized in a 1:1 ratio to either switch to ODEFSEY (N=438) once daily or stay on EFV/FTC/TDF (N=437) once daily. Subjects had a mean age of 48 years (range: 19−76), 87% were male, 67% were White, and 27% were Black. The mean baseline CD4+ cell count was 700 cells/mm3 (range: 140–1862).
Treatment outcomes of Trials 1216 and 1160 are presented in Table 12.
| Study 1216 | Study 1160 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ODEFSEY (N=316) | FTC/RPV/TDF (N=313)† | ODEFSEY (N=438) | EFV/FTC/TDF (N=437) |
|
|
||||
| HIV-1 RNA <50 copies/mL | 94% | 94% | 90% | 92% |
| HIV-1 RNA ≥50 copies/mL‡ | 1% | 0% | 1% | 1% |
| No Virologic Data at Week 48 Window | 6% | 6% | 9% | 7% |
| Discontinued Study Drug Due to AE or Death and Last Available HIV-1 RNA <50 copies/mL | 2% | 1% | 3% | 1% |
| Discontinued Study Drug Due to Other Reasons and Last Available HIV-1 RNA <50 copies/mL§ | 4% | 4% | 5% | 5% |
| Missing Data During Window but on Study Drug | <1% | 1% | 1% | 1% |
14.2 Clinical Trial Results for Adult Subjects with no Antiretroviral Treatment History and Adults with Renal Impairment for Components of ODEFSEY
The efficacy of RPV, FTC, and TAF in the treatment of HIV-1 infection in adults as initial therapy in those with no antiretroviral treatment history [see Indications and Usage (1)] was established in trials of:
- RPV+FTC/TDF in HIV-1 infected adults as initial therapy in those with no antiretroviral treatment history (n=550). The virologic response rate (i.e., HIV-1 RNA less than 50 copies per mL) was 77% at Week 96. The virologic response rate at 96 weeks was 83% in subjects with baseline HIV-1 RNA less than or equal to 100,000 copies per mL and 71% in subjects with baseline HIV-1 RNA greater than 100,000 copies per mL. Further, the virologic response rate at 96 weeks among subjects with baseline CD4+ cell counts less than 200 and greater than or equal to 200 cells/mm3 were 68% and 82%, respectively.
- FTC+TAF with EVG+COBI in HIV-1 infected adults as initial therapy in those with no antiretroviral treatment history (n=866). The virologic response rate (i.e., HIV-1 RNA less than 50 copies per mL) was 92% at Week 48.
In the clinical trial of 248 HIV-1 infected adults with estimated creatinine clearance greater than 30 mL per minute but less than 70 mL per minute, 95% (235/248) of the combined populations of treatment-naïve (N=6) begun on FTC+TAF with EVG+COBI and those previously virologically-suppressed on other regimens (N=242) and switched to FTC+TAF with EVG +COBI had HIV-1 RNA levels less than 50 copies per mL at Week 24.
14.3 Clinical Trial Results for Pediatric Subjects Aged 12 to Less than 18 Years Old with no Antiretroviral Treatment History for Components of ODEFSEY
The efficacy of RPV, FTC, and TAF in the treatment of HIV-1 infection in pediatric patients aged 12 to less than 18 years old and greater than 32–35 kg as initial therapy in those with no antiretroviral treatment history and to replace a stable antiretroviral regimen in those who are virologically-suppressed [see Indications and Usage (1)] was established in trials of antiretroviral treatment-naïve HIV-1 infected pediatric subjects 12 to less than 18 years old with:
- RPV in combination with other antiretroviral agents in 36 treatment-naïve HIV-1 infected adolescents weighing at least 32 kg. The majority of subjects (24/36) received RPV in combination with FTC and TDF. Of these 24 subjects, 20 had a baseline HIV-1 RNA less than or equal to 100,000 copies per mL. The virologic response rate in these 20 subjects (i.e., HIV-1 RNA less than 50 copies per mL) was 80% (16/20) at 48 weeks.
- FTC+TAF with EVG+COBI in 23 adolescents weighing at least 35 kg. The virologic response rate (i.e., HIV-1 RNA less than 50 copies per mL) was 91% at 24 weeks.
16. How is Odefsey supplied
ODEFSEY tablets are gray, capsule-shaped, and film coated with "GSI" debossed on one side and "255" on the other side. Each bottle contains 30 tablets (NDC 61958-2101-1), a silica gel desiccant, and a polyester coil, and is closed with a child-resistant closure.
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
| Patient Information ODEFSEY® (oh-DEF-see) (emtricitabine, rilpivirine and tenofovir alafenamide) tablets |
||
|---|---|---|
| This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration | Revised: 03/2021 | |
| Important: Ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist about medicines that should not be taken with ODEFSEY. For more information, see "What should I tell my healthcare provider before taking ODEFSEY?" | ||
| What is the most important information I should know about ODEFSEY? ODEFSEY can cause serious side effects, including:
|
||
| What is ODEFSEY?
ODEFSEY is a prescription medicine that is used to treat human immunodeficiency virus-1 (HIV-1) infection in adults and children who weigh at least 77 pounds (35 kg):
ODEFSEY contains the prescription medicines emtricitabine, rilpivirine and tenofovir alafenamide. It is not known if ODEFSEY is safe and effective in children under 12 years of age or who weigh less than 77 lb (35 kg). |
||
| Who should not take ODEFSEY? Do not take ODEFSEY if you also take a medicine that contains: |
||
|
|
|
| What should I tell my healthcare provider before taking ODEFSEY? Before taking ODEFSEY, tell your healthcare provider about all your medical conditions, including if you:
Some medicines may interact with ODEFSEY. Keep a list of your medicines and show it to your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medicine.
|
||
How should I take ODEFSEY?
|
||
| What are the possible side effects of ODEFSEY? ODEFSEY may cause serious side effects, including:
|
||
|
|
|
These are not all the possible side effects of ODEFSEY. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. |
||
How should I store ODEFSEY?
|
||
| General information about the safe and effective use of ODEFSEY.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use ODEFSEY for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give ODEFSEY to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them. You can ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for information about ODEFSEY that is written for health professionals. |
||
| What are the ingredients in ODEFSEY?
Active ingredients: emtricitabine, rilpivirine, and tenofovir alafenamide. Inactive ingredients: croscarmellose sodium, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, polysorbate 20, and povidone. The tablet film coating contains iron oxide black, polyethylene glycol, polyvinyl alcohol, talc, and titanium dioxide. Manufactured and distributed by: Gilead Sciences, Inc. Foster City, CA 94404 ODEFSEY is a trademark of Gilead Sciences, Inc., or its related companies. © 2021 Gilead Sciences, Inc. All rights reserved. 208351-GS-006 For more information, call 1-800-445-3235 or go to www.ODEFSEY.com. |
||
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 30 Tablet Bottle Label
NDC 61958- 2101-1
30 tablets
Odefsey ®
(emtricitabine, rilpivirine, and
tenofovir alafenamide) Tablets
200 mg/25 mg/25 mg
Note to pharmacist:
Do not cover ALERT box with pharmacy label.
ALERT: Find out about medicines that
should NOT be taken with Odefsey ®
| ODEFSEY
emtricitabine, rilpivirine hydrochloride, and tenofovir alafenamide tablet |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Gilead Sciences, Inc. (185049848) |