Drug Detail:Oleptro (Trazodone hydrochloride tablet, extended release)
Drug Class: Phenylpiperazine antidepressants
Highlights of Prescribing Information
OLEPTRO (trazodone hydrochloride) extended-release tablets
Initial U.S. Approval: 1981
WARNING: SUICIDALITY AND ANTIDEPRESSANT DRUGS
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
Increased risk of suicidal thinking and behavior in children, adolescents and young adults taking antidepressants for major depressive disorder (MDD) and other psychiatric disorders. Oleptro is not approved for use in pediatric patients (5.1).
Recent Major Changes
Warnings and Precautions, (5.3) 06/2014
Indications and Usage for Oleptro
Oleptro is indicated for the treatment of major depressive disorder (1).
- Efficacy was established in one 8-week trial of Oleptro as well as in trials of trazodone immediate release formulation in patients with major depressive disorder (14).
Oleptro Dosage and Administration
- Starting dose: 150 mg once daily. May be increased by 75 mg per day every three days. Maximum dose: 375 mg per day (2).
- Dosing at the same time every day in the late evening, preferably at bedtime, on an empty stomach (2).
- Tablets should be swallowed whole or broken in half along the score line, and should not be chewed or crushed (2).
- When discontinued, gradual dose reduction is recommended (2).
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Bisectable tablets of 150 mg or 300 mg (3).
Contraindications
- Serotonin Syndrome and MAOIs: Do not use MAOIs intended to treat psychiatric disorders with Oleptro or within 14 days of stopping treatment with Oleptro. Do not use Oleptro within 14 days of stopping an MAOI intended to treat psychiatric disorders. In addition, do not start Oleptro in a patient who is being treated with linezolid or intravenous methylene blue (4.1).
Warnings and Precautions
- Clinical Worsening/Suicide Risk: Monitor for clinical worsening and suicidal thinking and behavior (5.1).
-
Serotonin Syndrome: Serotonin syndrome has been reported with SSRIs and SNRIs, including Oleptro, both when taken alone, but especially when co-administered with other serotonergic agents (including triptans, tricyclic antidepressants, fentanyl, lithium, tramadol, tryptophan, buspirone and St. John's Wort). If such symptoms occur, discontinue Oleptro and initiate supportive treatment. If concomitant use of Oleptro with other serotonergic drugs is clinically warranted, patients should be made aware of a potential increased risk for serotonin syndrome, particularly during treatment initiation and dose increases (5.2).
- Angle Closure Glaucoma: Angle closure glaucoma has occurred in patients with untreated anatomically narrow angles treated with antidepressants. (5.3).
-
Activation of Mania/Hypomania: Screen for bipolar disorder and monitor for mania/hypomania (5.4).
- QT Prolongation: Increases the QT interval. Avoid use with drugs that also increase the QT interval and in patients with risk factors for prolonged QT interval (5.5).
- Use in Patients with Heart Disease: Use with caution in patients with cardiac disease (5.6).
- Orthostatic Hypotension and Syncope: Have occurred. Warn patients of risk and symptoms of hypotension (5.7).
- Abnormal Bleeding: May increase the risk of bleeding. Use with NSAIDs, aspirin, or other drugs that affect coagulation may compound this risk (5.8).
- Interaction with MAOIs: Do not use concomitantly or within 14 days of monoamine oxidase inhibitors (5.9).
- Priapism: Has occurred. Warn male patients of this risk and how/when to seek medical attention (5.10).
- Hyponatremia: Can occur in association with SIADH (5.11).
- Potential for Cognitive and Motor Impairment: Has potential to impair judgment, thinking, and motor skills. Advise patients to use caution when operating machinery (5.12).
- Discontinuation Symptoms: May occur with abrupt discontinuation and include anxiety and sleep disturbance. Upon discontinuation, taper Oleptro and monitor for symptoms (5.13).
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥5% and twice that of placebo) are: somnolence/sedation, dizziness, constipation, vision blurred (6).
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Angelini Pharma at 1-877-345-6177 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
- Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors: Should not be used concomitantly with Oleptro (5.9, 7).
- CNS Depressants: Trazodone may enhance effects of alcohol, barbiturates, or other CNS depressants (7).
- CYP3A4 Inhibitors: May necessitate lower dose of Oleptro (7).
- CYP3A4 Inducers (e.g., carbamazepine): May necessitate higher dose of Oleptro (7).
- Digoxin or Phenytoin: Monitor for increased serum levels (7).
- Warfarin: Monitor for increased or decreased prothrombin time (7).
- Serotonergic Medications: Serotonin syndrome has been reported (5.2, 7).
- NSAIDs, Aspirin or other Anticoagulants: Potential for increased risk of bleeding (5.8, 7).
Use In Specific Populations
- Pregnancy: Based on animal data, may cause fetal harm (8.1).
- Nursing Mothers: Use with caution (8.3).
- Pediatric Patients: Oleptro is not approved in pediatric patients (8.4).
- Renal or Hepatic Impairment: Use with caution (8.6, 8.7).
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 6/2014
Full Prescribing Information
WARNING: SUICIDALITY AND ANTIDEPRESSANT DRUGS
Antidepressants increased the risk compared to placebo of suicidal thinking and behavior (suicidality) in children, adolescents, and young adults in short-term studies of major depressive disorder (MDD) and other psychiatric disorders. Anyone considering the use of Oleptro or any other antidepressant in a child, adolescent, or young adult must balance this risk with the clinical need. Short-term studies did not show an increase in the risk of suicidality with antidepressants compared to placebo in adults beyond age 24; there was a reduction in risk with antidepressants compared to placebo in adults aged 65 and older. Depression and certain other psychiatric disorders are themselves associated with increases in the risk of suicide. Patients of all ages who are started on antidepressant therapy should be monitored appropriately and observed closely for clinical worsening, suicidality, or unusual changes in behavior. Families and caregivers should be advised of the need for close observation and communication with the prescriber. Oleptro is not approved for use in pediatric patients [see
Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Patient Counseling Information (17.1)].
1. Indications and Usage for Oleptro
Oleptro™ is indicated for the treatment of major depressive disorder (MDD) in adults. The efficacy of Oleptro has been established in a trial of outpatients with MDD as well as in trials with the immediate release formulation of trazodone [see Clinical Studies (14)].
2. Oleptro Dosage and Administration
2.1 Dose Selection
The recommended starting dose of Oleptro is 150 mg once daily in adults. The dose may be increased by 75 mg/day every three days (i.e., start 225 mg on Day 4 of therapy). The maximum daily dose should not exceed 375 mg.
-
Oleptro tablets should be taken orally at the same time every day, in the late evening preferably at bedtime, on an empty stomach.
-
Once an adequate response has been achieved, dosage may be gradually reduced, with subsequent adjustment depending on therapeutic response.
-
Patients should be monitored for withdrawal symptoms when discontinuing treatment with trazodone hydrochloride. The dose should be gradually reduced whenever possible [see Warnings and Precautions (5.13)].
2.2 Maintenance Treatment
The efficacy of Oleptro for the maintenance treatment of MDD has not been evaluated. While there is no body of evidence available to answer the question of how long a patient treated with Oleptro should continue the drug, it is generally recommended that treatment be continued for several months after an initial response. Patients should be maintained on the lowest effective dose and be periodically reassessed to determine the continued need for maintenance treatment.
2.3 Switching a Patient To or From a Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitor (MAOI) Intended to Treat Psychiatric Disorders
At least 14 days should elapse between discontinuation of an MAOI intended to treat psychiatric disorders and initiation of therapy with Oleptro. Conversely, at least 14 days should be allowed after stopping Oleptro before starting an MAOI intended to treat psychiatric disorders [see CONTRAINDICATIONS (4.1)].
2.4 Use of Oleptro with Other MAOIs such as Linezolid or Methylene Blue
Do not start Oleptro in a patient who is being treated with linezolid or intravenous methylene blue because there is an increased risk of serotonin syndrome. In a patient who requires more urgent treatment of a psychiatric condition, other interventions, including hospitalization, should be considered [see CONTRAINDICATIONS (4.1)].
In some cases, a patient already receiving Oleptro therapy may require urgent treatment with linezolid or intravenous methylene blue. If acceptable alternatives to linezolid or intravenous methylene blue treatment are not available and the potential benefits of linezolid or intravenous methylene blue treatment are judged to outweigh the risks of serotonin syndrome in a particular patient, Oleptro should be stopped promptly, and linezolid or intravenous methylene blue can be administered. The patient should be monitored for symptoms of serotonin syndrome for two weeks or until 24 hours after the last dose of linezolid or intravenous methylene blue, whichever comes first. Therapy with Oleptro may be resumed 24 hours after the last dose of linezolid or intravenous methylene blue [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.2, 5.9)].
The risk of administering methylene blue by non-intravenous routes (such as oral tablets or by local injection) or in intravenous doses much lower than 1 mg/kg with Oleptro is unclear. The clinician should, nevertheless, be aware of the possibility of emergent symptoms of serotonin syndrome with such use [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.2)].
2.5 Important Administration Instructions
Oleptro tablets are scored to provide flexibility in dosing.
Oleptro can be swallowed whole or administered as a half tablet by breaking the tablet along the score line. Breaking the tablet in half does not affect the controlled-release properties of the tablet.
In order to maintain its controlled-release properties, Oleptro should not be chewed or crushed.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
Oleptro tablets are available in the following strengths:
- Oleptro bisectable tablets containing 150 mg of trazodone hydrochloride (yellowish-beige, capsule-shaped tablet, coated and scored on both sides with DDS 080 printed on one side)
- Oleptro bisectable tablets containing 300 mg of trazodone hydrochloride (beige-orange, capsule-shaped tablet, coated and scored on both sides with DDS 081 printed on one side)
4. Contraindications
4.1 Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs)
The use of MAOI’s intended to treat psychiatric disorders with Oleptro or within 14 days of stopping treatment with Oleptro is contraindicated because of an increased risk of serotonin syndrome. The use of Oleptro within 14 days of stopping an MAOI intended to treat psychiatric disorders is also contraindicated. [see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION (2.3) and WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.9)].
Starting Oleptro in a patient who is being treated with MAOIs such as linezolid or intravenous methylene blue is also contraindicated because of an increased risk of serotonin syndrome [see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION (2.4) and WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.2)].
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Clinical Worsening and Suicide Risk
Patients with major depressive disorder (MDD), both adult and pediatric, may experience worsening of their depression and/or the emergence of suicidal ideation and behavior (suicidality) or unusual changes in behavior, whether or not they are taking antidepressant medications, and this risk may persist until significant remission occurs. Suicide is a known risk of depression and certain other psychiatric disorders and these disorders themselves are the strongest predictors of suicide. There has been a long standing concern, however, that antidepressants may have a role in inducing worsening of depression and the emergence of suicidality in certain patients during the early phases of treatment. Pooled analyses of short-term placebo-controlled trials of antidepressant drugs (SSRIs and others) showed that these drugs increase the risk of suicidal thinking and behavior (suicidality) in children, adolescents, and young adults (ages 18 – 24) with MDD and other psychiatric disorders. Short-term studies did not show an increase in the risk of suicidality with antidepressants compared to placebo in adults beyond age 24; there was a reduction with antidepressants compared to placebo in adults aged 65 and older.
The pooled analyses of placebo-controlled trials in children and adolescents with MDD, obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD), or other psychiatric disorders included a total of 24 short-term trials of 9 antidepressant drugs in over 4,400 patients. The pooled analyses of placebo-controlled trials in adults with MDD or other psychiatric disorders included a total of 295 short-term trials (median duration of 2 months) of 11 antidepressant drugs in over 77,000 patients. There was considerable variation in risk of suicidality among drugs, but a tendency toward an increase in the younger patients for almost all drugs studied. There were differences in absolute risk of suicidality across the different indications, with the highest incidence in MDD. The risk differences (drug vs. placebo), however, were relatively stable within age strata and across indications. These risk differences (drug-placebo difference in the number of cases of suicidality per 1,000 patients treated) are provided in Table 1.
| Age Range | Drug-Placebo Difference in Number of Cases of Suicidality per 1,000 Patients Treated |
| Increases Compared to Placebo | |
| < 18 | 14 additional cases |
| 18 – 24 | 5 additional cases |
| Decreases Compared to Placebo | |
| 25 – 64 | 1 fewer case |
| ≥ 65 | 6 fewer cases |
No suicides occurred in any of the pediatric trials. There were suicides in the adult trials, but the number was not sufficient to reach any conclusion about drug effect on suicide.
It is unknown whether the suicidality risk extends to longer-term use, i.e., beyond several months. However, there is substantial evidence from placebo-controlled maintenance trials in adults with depression that the use of antidepressants can delay the recurrence of depression.
All patients being treated with antidepressants for any indication should be monitored appropriately and observed closely for clinical worsening, suicidality, and unusual changes in behavior, especially during the initial few months of a course of drug therapy, or at times of dose changes, either increases or decreases.
The following symptoms, anxiety, agitation, panic attacks, insomnia, irritability, hostility, aggressiveness, impulsivity, akathisia (psychomotor restlessness), hypomania, and mania, have been reported in adult and pediatric patients being treated with antidepressants for major depressive disorder as well as for other indications, both psychiatric and nonpsychiatric. Although a causal link between the emergence of such symptoms and either the worsening of depression and/or the emergence of suicidal impulses has not been established, there is concern that such symptoms may represent precursors to emerging suicidality.
Consideration should be given to changing the therapeutic regimen, including possibly discontinuing the medication, in patients whose depression is persistently worse, or who are experiencing emergent suicidality or symptoms that might be precursors to worsening depression or suicidality, especially if these symptoms are severe, abrupt in onset, or were not part of the patient's presenting symptoms.
Families and caregivers of patients being treated with antidepressants for major depressive disorder or other indications, both psychiatric and nonpsychiatric, should be alerted about the need to monitor patients for the emergence of agitation, irritability, unusual changes in behavior, and the other symptoms described above, as well as the emergence of suicidality, and to report such symptoms immediately to health care providers. Such monitoring should include daily observation by families and caregivers. Prescriptions for Oleptro should be written for the smallest quantity of tablets consistent with good patient management, in order to reduce the risk of overdose.
5.2 Serotonin Syndrome
The development of a potentially life-threatening serotonin syndrome has been reported with SNRIs and SSRIs, including Oleptro, alone but particularly with concomitant use of other serotonergic drugs (including triptans, tricyclic antidepressants, fentanyl, lithium, tramadol, tryptophan, buspirone, and St. John's Wort) and with drugs that impair metabolism of serotonin (in particular, MAOIs, both those intended to treat psychiatric disorders and also others, such as linezolid and intravenous methylene blue).
Serotonin syndrome symptoms may include mental status changes (e.g., agitation, hallucinations, delirium, and coma), autonomic instability (e.g., tachycardia, labile blood pressure, dizziness, diaphoresis, flushing, hyperthermia), neuromuscular symptoms (e.g., tremor, rigidity, myoclonus, hyperreflexia, incoordination), seizures, and/or gastrointestinal symptoms (e.g., nausea, vomiting, diarrhea). Patients should be monitored for the emergence of serotonin syndrome.
The concomitant use of Oleptro with MAOIs intended to treat psychiatric disorders is contraindicated. Oleptro should also not be started in a patient who is being treated with MAOIs such as linezolid or intravenous methylene blue. All reports with methylene blue that provided information on the route of administration involved intravenous administration in the dose range of 1 mg/kg to 8 mg/kg. No reports involved the administration of methylene blue by other routes (such as oral tablets or local tissue injection) or at lower doses. There may be circumstances when it is necessary to initiate treatment with an MAOI such as linezolid or intravenous methylene blue in a patient taking Oleptro. Oleptro should be discontinued before initiating treatment with the MAOI. [see Contraindications (4.1) and Dosage and Administration (2.3 and 2.4)].
If concomitant use of Oleptro with other serotonergic drugs, triptans, tricyclic antidepressants, fentanyl, lithium, tramadol, buspirone, tryptophan and St. John's Wort is clinically warranted, patients should be made aware of a potential increased risk for serotonin syndrome, particularly during treatment initiation and dose increases.
Treatment with Oleptro and any concomitant serotonergic agents, should be discontinued immediately if the above events occur and supportive symptomatic treatment should be initiated.
5.3 Angle Closure Glaucoma
The pupillary dilation that occurs following use of many antidepressant drugs including Oleptro may trigger an angle closure attack in a patient with anatomically narrow angles who does not have a patent iridectomy.
5.4 Screening Patients for Bipolar Disorder and Monitoring for Mania/Hypomania
A major depressive episode may be the initial presentation of bipolar disorder. It is generally believed (though not established in controlled trials) that treating such an episode with an antidepressant alone may increase the likelihood of precipitation of a mixed/manic episode in patients at risk for bipolar disorder. Whether any of the symptoms described for clinical worsening and suicide risk represent such a conversion is unknown. However, prior to initiating treatment with an antidepressant, patients with depressive symptoms should be adequately screened to determine if they are at risk for bipolar disorder; such screening should include a detailed psychiatric history, including a family history of suicide, bipolar disorder, and depression. It should be noted that Oleptro is not approved for use in treating bipolar depression.
5.5 QT Prolongation and Risk of Sudden Death
Trazodone is known to prolong the QT/QTc interval. Some drugs that prolong the QT/QTc interval can cause Torsades de Pointes with sudden, unexplained death. The relationship of QT prolongation is clearest for larger increases (20 msec and greater), but it is possible that smaller QT/QTc prolongations may also increase risk, especially in susceptible individuals, such as those with hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, or a genetic predisposition to prolonged QT/QTc.
Although Torsades de Pointes has not been observed with the use of Oleptro at recommended doses in premarketing trials, experience is too limited to rule out an increased risk. However, there have been postmarketing reports of Torsades de Pointes with the immediate-release form of trazodone (in the presence of multiple confounding factors), even at doses of 100 mg per day or less.
5.6 Use in Patients with Heart Disease
Trazodone hydrochloride is not recommended for use during the initial recovery phase of myocardial infarction.
Caution should be used when administering Oleptro to patients with cardiac disease and such patients should be closely monitored, since antidepressant drugs (including trazodone hydrochloride) may cause cardiac arrhythmias.
QT prolongation has been reported with trazodone therapy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]. Clinical studies in patients with pre-existing cardiac disease indicate that trazodone hydrochloride may be arrhythmogenic in some patients in that population. Arrhythmias identified include isolated PVCs, ventricular couplets, tachycardia with syncope, and Torsades de Pointes. Postmarketing events have been reported at doses of 100 mg or less with the immediate-release form of trazodone.
Concomitant administration of drugs that prolong the QT interval or that are inhibitors of CYP3A4 may increase the risk of cardiac arrhythmia.
5.7 Orthostatic Hypotension and Syncope
Hypotension, including orthostatic hypotension and syncope has been reported in patients receiving trazodone hydrochloride. Concomitant use with an antihypertensive may require a reduction in the dose of the antihypertensive drug.
5.8 Abnormal Bleeding
Postmarketing data have shown an association between use of drugs that interfere with serotonin reuptake and the occurrence of gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding. While no association between trazodone and bleeding events, in particular GI bleeding, was shown, patients should be cautioned about potential risk of bleeding associated with the concomitant use of trazodone and NSAIDs, aspirin, or other drugs that affect coagulation or bleeding. Other bleeding events related to SSRIs and SNRIs have ranged from ecchymosis, hematoma, epistaxis, and petechiae to life-threatening hemorrhages.
5.9 Interaction with MAOIs
In patients receiving serotonergic drugs in combination with a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI), there have been reports of serious, sometimes fatal reactions including hyperthermia, rigidity, myoclonus, autonomic instability with rapid fluctuation in vital signs, and mental status changes that include extreme agitation progressing to delirium and coma. These reactions have also been reported in patients who have recently discontinued antidepressant treatment and have been started on an MAOI. Some cases presented with features resembling neuroleptic malignant syndrome. Furthermore, limited animal data on the effects of combined use of serotonergic antidepressants and MAOIs suggest that these drugs may act synergistically to elevate blood pressure and evoke behavioral excitation. Therefore, it is recommended that Oleptro should not be used in combination with an MAOI or within 14 days of discontinuing treatment with an MAOI. Similarly, at least 14 days should be allowed after stopping Oleptro before starting an MAOI.
5.10 Priapism
Rare cases of priapism (painful erections greater than 6 hours in duration) were reported in men receiving trazodone. Priapism, if not treated promptly, can result in irreversible damage to the erectile tissue. Men who have an erection lasting greater than 6 hours, whether painful or not, should immediately discontinue the drug and seek emergency medical attention [see Adverse Reactions (6.2) and Overdosage (10)].
Trazodone should be used with caution in men who have conditions that might predispose them to priapism (e.g., sickle cell anemia, multiple myeloma, or leukemia), or in men with anatomical deformation of the penis (e.g., angulation, cavernosal fibrosis, or Peyronie's disease).
5.11 Hyponatremia
Hyponatremia may occur as a result of treatment with antidepressants. In many cases, this hyponatremia appears to be the result of the syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion (SIADH). Cases with serum sodium lower than 110 mmol/L have been reported. Elderly patients may be at greater risk of developing hyponatremia with antidepressants. Also, patients taking diuretics or who are otherwise volume-depleted can be at greater risk. Discontinuation of Oleptro should be considered in patients with symptomatic hyponatremia and appropriate medical intervention should be instituted.
Signs and symptoms of hyponatremia include headache, difficulty concentrating, memory impairment, confusion, weakness, and unsteadiness, which can lead to falls. Signs and symptoms associated with more severe and/or acute cases have included hallucination, syncope, seizure, coma, respiratory arrest, and death.
5.12 Potential for Cognitive and Motor Impairment
Oleptro may cause somnolence or sedation and may impair the mental and/or physical ability required for the performance of potentially hazardous tasks. Patients should be cautioned about operating hazardous machinery, including automobiles, until they are reasonably certain that the drug treatment does not affect them adversely.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following serious adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Clinical Worsening and Suicide Risk [see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Serotonin Syndrome or NMS-like Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- QT Prolongation and Risk of Sudden Death [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Orthostatic Hypotension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- Abnormal bleeding events [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
- Priapism [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)]
- Hyponatremia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)]
- Cognitive and Motor Impairment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12)]
- Discontinuation symptoms [see Warnings and Precautions (5.13)]
The most common adverse reactions (reported in ≥5% and at twice the rate of placebo) are: somnolence/sedation, dizziness, constipation, vision blurred.
Table 2 presents the summary of adverse events (AEs) leading to discontinuation of Oleptro treatment with an incidence of at least 1% and at least twice that for placebo.
| Oleptro N = 202 |
|
| Somnolence/Sedation | 8 (4.0%) |
| Dizziness | 7 (3.5%) |
| Confusional state | 2 (1.0%) |
| Coordination abnormal | 2 (1.0%) |
| Headache | 2 (1.0%) |
| Nausea | 2 (1.0%) |
| Balance disorder / Gait disturbance | 2 (1.0%) |
6.1 Clinical Studies Experience
The data described below reflects exposure in a clinical trial of 406 patients, including 204 exposed to placebo and 202 exposed to Oleptro. Patients were between 18-80 years of age and 69.3% and 67.5% of patients had at least one previous episode of depression in the last 24 months in the placebo and active-treated group, respectively. In individual patients, doses were flexible and ranged from 150 to 375 mg per day. The mean daily dose during the 6-week treatment period was 310 mg. The tablets were administered orally and were given once a day for a total duration of 8 weeks, including the titration period.
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Table 3 presents the summary of all treatment emergent AEs that occurred at an incidence of ≥ 5% in the Oleptro group, whether considered by the clinical investigator to be related to the study drug or not.
| Preferred Term | Placebo N = 204 | Oleptro N = 202 |
| Somnolence/Sedation | 39 (19%) | 93 (46%) |
| Headache | 55 (27%) | 67 (33%) |
| Dry mouth | 26 (13%) | 51 (25%) |
| Dizziness | 25 (12%) | 50 (25%) |
| Nausea | 26 (13%) | 42 (21%) |
| Fatigue | 17 (8%) | 30 (15%) |
| Diarrhea | 23 (11%) | 19 (9%) |
| Constipation | 4 (2%) | 16 (8%) |
| Back pain | 7 (3%) | 11 (5%) |
| Vision blurred | 0 (0%) | 11 (5%) |
Sexual Dysfunction
Adverse events related to sexual dysfunction (regardless of causality) were reported by 4.9% and 1.5% of patients treated with Oleptro and placebo, respectively. In the Oleptro group, ejaculation disorders occurred in 1.5% of patients, decreased libido occurred in 1.5% of patients, and erectile dysfunction and abnormal orgasm < 1% of patients.
Vital Signs and Weight
There were no notable changes in vital signs (blood pressure, respiratory rate, pulse) or weight in either treatment group.
Following is a list of treatment-emergent adverse reactions with an incidence of ≥ 1% to < 5% (i.e., less common) in patients treated with Oleptro. This listing is not intended to include reactions (i) already listed in previous tables or elsewhere in the labeling (ii) for which the association with treatment is remote, (iii) which were so general as to be uninformative, and (iv) which were not considered to have significant clinical implications. Reactions are classified by body-system using the following definitions: frequent adverse reactions are those occurring in at least 1/100 patients; infrequent adverse reactions are those occurring in less than 1/100 patients.
Ear and Labyrinth Disorders— Infrequent: hypoacusis, tinnitus, vertigo
Eye Disorders— Frequent: visual disturbance; Infrequent: dry eye, eye pain, photophobia
Gastrointestinal Disorders— Frequent: abdominal pain, vomiting; Infrequent: reflux esophagitis
General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions— Frequent: edema; Infrequent: gait disturbance
Immune System Disorders— Infrequent: hypersensitivity
Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders— Frequent: musculoskeletal complaints, myalgia; Infrequent: muscle twitching
Nervous System Disorders— Frequent: coordination abnormal, dysgeusia, memory impairment, migraine, paraesthesia, tremor; Infrequent: amnesia, aphasia, hypoesthesia, speech disorder
Psychiatric Disorders— Frequent: agitation, confusional state, disorientation
Renal and Urinary Disorders— Frequent: micturition urgency; Infrequent: bladder pain, urinary incontinence
Respiratory, Thoracic and Mediastinal Disorders— Frequent: dyspnea
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders— Frequent: night sweats; Infrequent: acne, hyperhidrosis, photosensitivity reaction
Vascular Disorders— Infrequent: flushing
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
Spontaneous reports regarding trazodone hydrochloride received from postmarketing experience include the following: abnormal dreams, agitation, alopecia, anxiety, aphasia, apnea, ataxia, breast enlargement or engorgement, cardiospasm, cerebrovascular accident, chills, cholestasis, clitorism, congestive heart failure, diplopia, edema, extrapyramidal symptoms, grand mal seizures, hallucinations, hemolytic anemia, hirsutism, hyperbilirubinemia, increased amylase, increased salivation, insomnia, leukocytosis, leukonychia, jaundice, lactation, liver enzyme alterations, methemoglobinemia, nausea/vomiting (most frequently), paresthesia, paranoid reaction, priapism [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10) and Patient Counseling Information (17.1)], pruritus, psoriasis, psychosis, rash, stupor, inappropriate ADH syndrome, tardive dyskinesia, unexplained death, urinary incontinence, urinary retention, urticaria, vasodilation, vertigo, and weakness.
Cardiovascular system effects which have been reported include the following: conduction block, orthostatic hypotension and syncope, palpitations, bradycardia, atrial fibrillation, myocardial infarction, cardiac arrest, arrhythmia, ventricular ectopic activity, including ventricular tachycardia and QT prolongation. In postmarketing surveillance, prolonged QT interval, Torsades de Pointes, and ventricular tachycardia have been reported with the immediate-release form of trazodone at doses of 100 mg per day or less [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs)
[see Dosage and Administration (2.3 and 2.4), Contraindications (4.1), Warnings and Precautions (5.2 and 5.9)]
7.2 Serotonergic Drugs
[see Dosage and Administration (2.3 and 2.4), Contraindications (4.1), Warnings and Precautions (5.2 )]
7.3 Central Nervous System (CNS) Depressants
Trazodone may enhance the response to alcohol, barbiturates, and other CNS depressants.
7.4 Cytochrome P450 3A4 Inhibitors
In vitro drug metabolism studies suggest that there is a potential for drug interactions when trazodone is given with cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4) inhibitors. The effect of short-term administration of ritonavir (200 mg twice daily, 4 doses) on the pharmacokinetics of a single dose of trazodone (50 mg) has been studied in 10 healthy subjects. The Cmax of trazodone increased by 34%, the AUC increased 2.4-fold, the half-life increased by 2.2-fold, and the clearance decreased by 52%. Adverse effects including nausea, hypotension, and syncope were observed when ritonavir and trazodone were co-administered. It is likely that ketoconazole, indinavir, and other CYP3A4 inhibitors such as itraconazole may lead to substantial increases in trazodone plasma concentrations with the potential for adverse effects. If trazodone is used with a potent CYP3A4 inhibitor, the risk of cardiac arrhythmia may be increased [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)] and a lower dose of trazodone should be considered.
7.5 Cytochrome P450 Inducers (e.g., carbamazepine)
Carbamazepine induces CYP3A4. Following co-administration of carbamazepine 400 mg per day with trazodone 100 mg to 300 mg daily, carbamazepine reduced plasma concentrations of trazodone and mchlorophenlypiperazine (an active metabolite) by 76% and 60% respectively, compared to precarbamazepine values. Patients should be closely monitored to see if there is a need for an increased dose of trazodone when taking both drugs.
7.6 Digoxin and Phenytoin
Increased serum digoxin or phenytoin levels have been reported in patients receiving trazodone concurrently with either of these drugs. Monitor serum levels and adjust dosages as needed.
7.7 NSAIDs, Aspirin, or Other Drugs Affecting Coagulation or Bleeding
Due to a possible association between serotonin modulating drugs and gastrointestinal bleeding, patients should be monitored for and cautioned about the potential risk of bleeding associated with the concomitant use of trazodone and NSAIDs, aspirin, or other drugs that affect coagulation or bleeding [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category C
Trazodone hydrochloride has been shown to cause increased fetal resorption and other adverse effects on the fetus in two studies using the rat when given at dose levels approximately 30 - 50 times the proposed maximum human dose. There was also an increase in congenital anomalies in one of three rabbit studies at approximately 15 – 50 times the maximum human dose. There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Oleptro should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
Trazodone and/or its metabolites have been found in the milk of lactating rats, suggesting that the drug may be secreted in human milk. Caution should be exercised when Oleptro is administered to a nursing woman.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in the pediatric population have not been established [see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. Oleptro should not be used in children or adolescents.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of 202 patients treated with Oleptro in the clinical trial, there were 9 patients older than 65. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these subjects and younger subjects, and other reported clinical literature and experience with trazodone have not identified differences in responses between elderly and younger patients. However, as experience in the elderly with Oleptro is limited, it should be used with caution in geriatric patients.
Antidepressants have been associated with cases of clinically significant hyponatremia in elderly patients who may be at greater risk for this adverse reaction [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)].
9. Drug Abuse and Dependence
9.2 Abuse
Although trazodone hydrochloride has not been systematically studied in preclinical or clinical studies for its potential for abuse, no indication of drug-seeking behavior was seen in the clinical studies with Oleptro. However, it is difficult to predict the extent to which a CNS-active drug will be misused, diverted, and abused. Consequently, physicians should carefully evaluate patients for a history of drug abuse and follow such patients closely, observing them for signs of misuse or abuse of trazodone hydrochloride (e.g., development of tolerance, incrementation of dose, drug-seeking behavior).
10. Overdosage
10.1 Human Experience
It is expected that the health risks associated with overdose of Oleptro are most likely similar to those for trazodone immediate-release formulations.
Death from overdose has occurred in patients ingesting trazodone and other CNS depressant drugs concurrently (alcohol; alcohol and chloral hydrate and diazepam; amobarbital; chlordiazepoxide; or meprobamate).
The most severe reactions reported to have occurred with overdose of trazodone alone have been priapism, respiratory arrest, seizures, and ECG changes, including QT prolongation. The reactions reported most frequently have been drowsiness and vomiting. Overdosage may cause an increase in incidence or severity of any of the reported adverse reactions.
10.2 Management of Overdose
There is no specific antidote for Oleptro overdose.
Treatment should consist of those general measures employed in the management of overdosage with any drug effective in the treatment of major depressive disorder.
Ensure an adequate airway, oxygenation and ventilation. Monitor cardiac rhythm and vital signs.
General supportive and symptomatic measures are also recommended. Induction of emesis is not recommended. Gastric lavage with a large bore orogastric tube with appropriate airway protection, if needed, may be indicated if performed soon after ingestion, or in symptomatic patients. Activated charcoal should be administered. Forced diuresis may be useful in facilitating elimination of the drug.
In managing overdosage, consider the possibility of multiple drug involvement. The physician should consider contacting a poison control center for additional information on the treatment of any overdose.
11. Oleptro Description
Oleptro (trazodone hydrochloride) is a triazolopyridine. It is a white, odorless crystalline powder which is freely soluble in water.
Chemical Name: 2-[3-[4-(m-Chlorophenyl)-1-piperazinyl]propyl]-s-triazolo[4,3-a]pyridin-3(2H)-one monohydrochloride
Structural Formula:
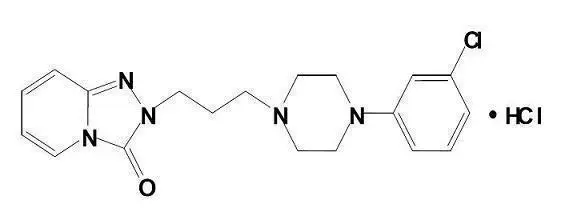
Molecular Formula: C19H22ClN5O•HCl
Molecular Weight: 408.32
Oleptro tablets containing 150 mg or 300 mg of trazodone hydrochloride are designed to release their drug content over a 24-hour period and are intended for once-a-day dosing.
Inactive Ingredients:
Hydroxypropyl distarch phosphate (Contramid®)
Hypromellose
Sodium stearyl fumarate
Colloidal silicon dioxide
Iron Oxide Yellow
Iron Oxide Red
Talc
Polyethylene Glycol 3350
Titanium Dioxide
Polyvinyl Alcohol
Black ink (food grade)
12. Oleptro - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
The mechanism of trazodone’s antidepressant action is not fully understood, but is thought to be related to its potentiation of serotonergic activity in the CNS.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Preclinical studies have shown that trazodone selectively inhibits neuronal reuptake of serotonin and acts as an antagonist at 5-HT-2A/2C serotonin receptors.
Trazodone is not a monoamine oxidase inhibitor and, unlike amphetamine-type drugs, does not stimulate the central nervous system.
Trazodone antagonizes alpha 1-adrenergic receptors, a property which may be associated with postural hypotension.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Steady state AUC of Trazodone is equivalent after administration of Trazodone 100 mg immediate release (IR) three (3) times a day (mean ± SD AUCss = 33058 ± 8006 ng*h/mL) and Oleptro 300 mg once daily (mean ± SD AUCss = 29131 ± 9931 ng*h/mL) for one week. Steady State Cmax and Cmin of trazodone were not equivalent after administration of trazodone 100 mg IR 3 times a day (mean ± SD Cmax,ss = 3118 ± 758 ng/mL, Cmin,ss = 843 ± 274 ng/mL) and Oleptro 300 mg once daily (mean ± SD Cmax,ss = 1812 ± 621 ng/mL, Cmin,ss = 674 ± 355 ng/mL) for one week.
Absorption
Trazodone is well absorbed after oral administration, without selective localization in any tissue. Following single-dose administration of Oleptro 300 mg tablets under fasting conditions, a mean peak trazodone plasma concentration (Cmax) of 1188 ± 362 ng/mL was reported at a median Tmax of 9 hours post-dose. When Oleptro 300 mg tablets are taken shortly after ingestion of a high-fat meal, Cmax increases by about 86% compared to taking it under fasting conditions. However, AUC0-∞ and Tmax are not significantly affected by food.
Oleptro tablets are dose proportional following single-dose administration of doses ranging from 75 mg to 375 mg as intact or bisected tablets.
Metabolism
In vitro studies in human liver microsomes show that trazodone is metabolized, via oxidative cleavage, to an active metabolite, m-chlorophenylpiperazine (mCPP) by CYP3A4. Other metabolic pathways that may be involved in the metabolism of trazodone have not been well characterized. Trazodone is extensively metabolized; less than 1% of an oral dose is excreted unchanged in the urine.
Elimination
Elimination is predominantly renal, with 70 to 75% of an oral dose being recovered in the urine within the first 72 hours of ingestion. Following single-dose administration of Oleptro 300 mg tablets, a mean apparent terminal half-life of 10 hours was reported.
Protein Binding
Trazodone is 89 to 95% protein bound in vitro at concentrations attained with therapeutic doses in humans.
14. Clinical Studies
The efficacy and safety of Oleptro were established from trials of the immediate release formulation as well as a randomized, double-blind, two-arm study comparing the efficacy and safety of Oleptro and placebo in the treatment of unipolar major depressive disorder.
The Oleptro trial was a multi-center, parallel-design study of outpatients meeting DSM-IV criteria for major depressive disorder (MDD). This study consisted of a Baseline Phase (screening and washout) and a double-blind Randomized Phase (randomization to Oleptro (n=206) or placebo (n=206)). The total study duration, including washout of prohibited medications, was approximately 11 weeks; the total duration of the randomized treatment phase was 8 weeks (titration: 2 weeks and treatment: 6 weeks). Rescue medication for MDD was not allowed during the study.
Patients were between 18 and 80 years of age. Of this population, 25 patients were 65 years old or older. The mean age of the population was 44 years; 64% were female.
The primary efficacy endpoint in this study was change from baseline in HAMD-17 total score.
A statistically significant difference in the HAMD-17 score was demonstrated at 8 weeks between the Oleptro group and the placebo group.
16. How is Oleptro supplied
Oleptro 150 mg is a yellowish-beige, capsule-shaped extended-release tablet, coated and scored on both sides with DDS 080 printed on one side. It is supplied as follows:
Bottles of 30 tablets NDC 43595-080-03
Oleptro 300 mg is a beige-orange, capsule-shaped extended-release tablet, coated and scored on both sides with DDS 081 printed on one side. It is supplied as follows:
Bottles of 30 tablets NDC 43595-081-03
Store at room temperature (15 – 30ºC) in tight, light-resistant containers.
17. Patient Counseling Information
See Medication Guide (17.2).
17.1 Information for Patients
Prescribers or other health professionals should inform patients, their families, and their caregivers about the benefits and risks associated with treatment with Oleptro and should counsel them in its appropriate use.
Patients should be warned that:
- There is a potential for increased risk of suicidal thoughts especially in children, teenagers and young adults.
- The following symptoms should be reported to the physician: anxiety, agitation, panic attacks, insomnia, irritability, hostility, aggressiveness, impulsivity, akathisia, hypomania and mania.
- They should inform their physician if they have a history of bipolar disorder, cardiac disease or myocardial infarction.
- Serotonin syndrome could occur and symptoms may include changes in mental status (e.g., agitation, hallucinations, and coma), autonomic instability (e.g., tachycardia, labile blood pressure, and hyperthermia), neuromuscular aberrations (e.g., hyperreflexia, incoordination) and/or gastrointestinal symptoms (e.g., nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea).
- Patients should be advised that taking Oleptro can cause mild pupillary dilation, which in susceptible individuals, can lead to an episode of angle closure glaucoma. Pre-existing glaucoma is almost always open-angle glaucoma because angle closure glaucoma, when diagnosed, can be treated definitively with iridectomy. Open-angle glaucoma is not a risk factor for angle closure glaucoma. Patients may wish to be examined to determine whether they are susceptible to angle closure, and have a prophylactic procedure (e.g., iridectomy), if they are susceptible. [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Trazodone hydrochloride has been associated with the occurrence of priapism.
- There is a potential for hypotension, including orthostatic hypotension and syncope.
- There is a potential risk of bleeding (including life-threatening hemorrhages) and bleeding related events (including ecchymosis, hematoma, epistaxis, and petechiae) with the concomitant use of trazodone hydrochloride and NSAIDs, aspirin, or other drugs that affect coagulation or bleeding.
- Withdrawal symptoms including anxiety, agitation and sleep disturbances, have been reported with trazodone. Clinical experience suggests that the dose should be gradually reduced.
Patients should be counseled that:
- Oleptro may cause somnolence or sedation and may impair the mental and/or physical ability required for the performance of potentially hazardous tasks. Patients should be cautioned about operating hazardous machinery, including automobiles until they are reasonably certain that the drug treatment does not affect them.
- Trazodone may enhance the response to alcohol, barbiturates, and other CNS depressants.
- Women who intend to become pregnant or who are breastfeeding should discuss with a physician whether they should continue to use Oleptro, since use in pregnant and nursing women is not recommended.
Important Administration Instructions:
- Oleptro should be swallowed whole or broken in half along the score line.
- In order to maintain its controlled-release properties, it should not be chewed or crushed.
- Oleptro should be taken at the same time every day, in the late evening preferably at bedtime, on an empty stomach.
Angelini Pharma Inc.
Gaithersburg, MD 20877
© 2014, Angelini Pharma Inc.
All rights reserved.
U.S. Patent Nos. 6,607,748, 7,829,120 and 8,133,893
Oleptro™ is a trademark of Angelini Pharma Inc.
Contramid® is a registered trademark of Paladin Labs Inc.
[June 2014]
17.2. Medication Guide
Medication Guide
Oleptro™ (Oh-LEP-troe)
(trazodone hydrochloride)extended-release tablets
Read the Medication Guide that comes with Oleptro before you start taking it and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking to your healthcare provider about your medical condition or treatment. Talk to your healthcare provider or pharmacist if there is something you do not understand or you want to learn about Oleptro.
What is the most important information I should know about Oleptro?
Antidepressant medicines, depression or other serious mental illnesses, and suicidal thoughts or actions:
Talk to your healthcare provider about:
- All risks and benefits of treatment with antidepressant medicines
- All treatment choices for depression or other serious mental illnesses
- Antidepressant medicines may increase suicidal thoughts or actions in some children, teenagers, and young adults within the first few months of treatment.
- Depression and other serious mental illnesses are the most important causes of suicidal thoughts and actions. Some people may have a higher risk of having suicidal thoughts or actions. These include people who have or have a family history of bipolar illness (also called manic-depressive illness) or suicidal thoughts or actions.
- How can I watch for and try to prevent suicidal thoughts and actions?
- Pay close attention to any changes, especially sudden changes in mood, behaviors, thoughts, or feelings. This is very important when an antidepressant medicine is started or when the dose is changed.
- Call your healthcare provider right away to report new or sudden changes in mood, behavior, thoughts or feelings.
- Keep all follow-up visits with your healthcare provider as scheduled. Call your healthcare provider between visits as needed, especially if you are worried about symptoms.
Call a healthcare provider right away if you have any of the following symptoms, especially if they are new, worse, or worry you:
- Thoughts about suicide or dying
- Attempts to commit suicide
- New or worse depression
- New or worse anxiety
- Feeling very agitated or restless
- Panic attacks
- Trouble sleeping (insomnia)
- New or worse irritability
- Acting aggressive, being angry or violent
- Acting on dangerous impulses
- An extreme increase in activity and talking (mania)
- Other unusual changes in behavior or mood
What else do I need to know about antidepressant medicines?
- Never stop an antidepressant medicine without first talking to a healthcare provider. Stopping an antidepressant medicine suddenly can cause other symptoms.
- Antidepressants are medicines used to treat depression and other illnesses. It is important to discuss all the risks of treating depression and also the risks of not treating it. You should discuss all treatment choices with your healthcare provider, not just the use of antidepressants.
- Antidepressant medicines have other side effects. Talk to your healthcare provider about the side effects of your medicines.
- Antidepressant medicines can interact with other medicines. Know all of the medicines that you take. Keep a list of all medicines to show your healthcare provider. Do not start new medicines without first checking with your healthcare provider.
4. Oleptro is not approved for use in children. Talk to your healthcare provider for more information.
What is Oleptro?
Oleptro is a prescription medicine taken 1 time a day to treat major depressive disorder in adults.
Who should not take Oleptro?
- If you take a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI). Ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist if you are not sure if you take an MAOI, including the antibiotic linezolid.
-
Do not take an MAOI within 2 weeks of stopping Oleptro unless directed to do so by your physician.
-
Do not start Oleptro if you stopped taking an MAOI in the last 2 weeks unless directed to do so by your physician.
What should I tell my healthcare provider before taking Oleptro?
Before you take Oleptro, tell your healthcare provider if you:
- Have heart problems, including QT prolongation or a family history of it
- Have ever had a heart attack
- Have bipolar disorder
- Have liver or kidney problems
- Have other serious medical conditions
- Are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. Oleptro may harm your unborn baby. Talk to your healthcare provider if you are pregnant or plan to become pregnant.
- Are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if Oleptro passes into your breast milk. You and your healthcare provider should decide if you will take Oleptro or breastfeed.
- Have taken a Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitor (MAOI) or if you have stopped taking an MAOI in the last 2 weeks.
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and non-prescription medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
Using Oleptro with certain other medicines can affect each other causing serious side effects.
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them and show it to your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medicine.
How should I take Oleptro?
- Take Oleptro exactly as your healthcare provider tells you.
- Oleptro should be taken 1 time a day.
- Oleptro should be taken at the same time each day in the late evening, if possible at bedtime, on an empty stomach.
- Do not stop taking Oleptro without talking to your healthcare provider.
- Oleptro should be swallowed whole or broken in half along the score line. Do not chew or crush Oleptro. Tell your healthcare provider if you cannot swallow Oleptro either whole or as a half tablet.
What should I avoid while taking Oleptro?
- Do not drive, operate heavy machinery, or do other dangerous activities until you know how Oleptro affects you. Oleptro can slow your thinking and motor skills.
- Do not drink alcohol or take other medicines that make you sleepy or dizzy while taking Oleptro until you talk with your healthcare provider. Oleptro may make your sleepiness or dizziness worse if you take it with alcohol or other medicines that cause sleepiness or dizziness.
What are the possible side effects of Oleptro?
Oleptro can cause serious side effects or death. See “What is the most important information I should know about Oleptro?”
Serious side effects include:
- Serotonin syndrome. Symptoms of serotonin syndrome include: agitation, hallucinations, problems with coordination, fast heartbeat, tight muscles, trouble walking, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea.
- Visual problems
- eye pain
- changes in vision
- swelling or redness in or around the eye
Only some people are at risk for these problems. You may want to undergo an eye examination to see if you are at risk and receive preventative treatment if you are.
- Feeling high or in a very good mood, then becoming irritable, or having too much energy, feeling like you have to keep talking or do not sleep (Mania).
- Irregular or fast heartbeat or faint (QT prolongation).
- Low blood pressure. You feel dizzy or faint when you change positions (go from sitting to standing).
- Unusual bruising or bleeding.
- Erection lasting for more than 6 hours (Priapism).
- Low sodium in your blood (Hyponatremia). Symptoms of hyponatremia include: headache, feeling weak, feeling confused, trouble concentrating, memory problems and feeling unsteady when you walk.
Get medical help right away, if you have any of the symptoms listed above.
The most common side effects of Oleptro include:
- Sleepiness
- Dizziness
- Constipation
- Blurry vision
Tell your healthcare provider if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away.
These are not all the possible side effects of Oleptro. For more information, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store Oleptro?
- Store Oleptro between 59°F to 86°F (15°C to 30°C)
- Keep in tight container
- Keep out of the light
Keep Oleptro and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about Oleptro.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use Oleptro for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give Oleptro to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them.
This Medication Guide summarizes the most important information about Oleptro. If you would like more information, talk with your healthcare provider. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about Oleptro that is written for health professionals.
For more information, go to www.oleptro.com or call 1-877-345-6177.
What are the ingredients in Oleptro?
Active ingredient: trazodone hydrochloride
Inactive ingredients: hydroxypropyl distarch phosphate (Contramid®), hypromellose, sodium stearyl fumarate, colloidal silicon dioxide, iron oxide yellow, iron oxide red, talc, polyethylene glycol 3350, titanium dioxide, polyvinyl alcohol, black ink (food grade).
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Angelini Pharma Inc.
Gaithersburg, MD 20877
© 2014, Angelini Pharma Inc.
All rights reserved.
U.S. Patent Nos. 6,607,748, 7,829,120 and 8,133,893
Oleptro™ is a trademark of Angelini Pharma Inc.
Contramid® is a registered trademark of Paladin Labs Inc.
[June 2014]
| OLEPTRO
trazodone hydrochloride tablet, extended release |
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
| OLEPTRO
trazodone hydrochloride tablet, extended release |
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Angelini Pharma Inc. (078843940) |






