Drug Detail:Pegintron (Peginterferon alfa-2b [ peg-in-ter-feer-on-al-fa-too-bee ])
Drug Class: Antineoplastic interferons Antiviral interferons
Highlights of Prescribing Information
PEGINTRON® (peginterferon alfa-2b) injection, for subcutaneous use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2001
WARNING: RISK OF SERIOUS DISORDERS
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
- May cause or aggravate fatal or life-threatening neuropsychiatric, autoimmune, ischemic, and infectious disorders. Monitor closely and withdraw therapy with persistently severe or worsening signs or symptoms of the above disorders. (5)
Indications and Usage for Pegintron
PEGINTRON is an antiviral indicated for treatment of Chronic Hepatitis C (CHC) in patients with compensated liver disease. (1.1)
Pegintron Dosage and Administration
- PEGINTRON is administered by subcutaneous injection. (2)
PEGINTRON Dose (Adults)* PEGINTRON Dose (Pediatric Patients) PEGINTRON Combination Therapy (2.1) 1.5 mcg/kg/ week 60 mcg/m2/ week - PEGINTRON is used in combination with other products including ribavirin and HCV direct-acting antivirals. For further information on dosing and administration, refer to the respective prescribing information.
- Dose reduction is recommended in patients experiencing certain adverse reactions or renal dysfunction. (2.3, 2.5)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Injection: 50 mcg per 0.5 mL, 80 mcg per 0.5 mL, 120 mcg per 0.5 mL, 150 mcg per 0.5 mL in single-dose vial (with 5 mL diluent) and single-dose pre-filled pens (3)
Contraindications
- Known hypersensitivity reactions, such as urticaria, angioedema, bronchoconstriction, anaphylaxis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, and toxic epidermal necrolysis to interferon alpha or any other product component. (4)
- Autoimmune hepatitis. (4)
- Hepatic decompensation (Child-Pugh score greater than 6 [class B and C]) in cirrhotic CHC patients before or during treatment. (4)
- If PEGINTRON is administered with ribavirin, the contraindications to ribavirin also apply to this combination regimen. (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Risks Associated with Ribavirin Combination Treatment: If PEGINTRON is administered with ribavirin, the warnings and precautions for ribavirin also apply to this combination regimen (5.1)
Patients exhibiting the following conditions should be closely monitored and may require dose reduction or discontinuation of therapy:
- Neuropsychiatric events. (5.2)
- History of significant or unstable cardiac disease. (5.3)
- Hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, hyperglycemia, diabetes mellitus that cannot be effectively treated by medication. (5.4)
- New or worsening ophthalmologic disorders. (5.5)
- Ischemic and hemorrhagic cerebrovascular events. (5.6)
- Severe decreases in neutrophil or platelet counts. (5.7)
- History of autoimmune disorders. (5.8)
- Pancreatitis and ulcerative or hemorrhagic/ischemic colitis and pancreatitis. (5.9, 5.10)
- Pulmonary infiltrates or pulmonary function impairment. (5.11)
- Child-Pugh score greater than 6 (class B and C). (4, 5.12)
- Increased creatinine levels in patients with renal insufficiency. (5.13)
- Serious, acute hypersensitivity reactions and cutaneous eruptions. (5.14)
- Dental/periodontal disorders reported with combination therapy. (5.16)
- Hypertriglyceridemia may result in pancreatitis (e.g., triglycerides greater than 1000 mg/dL). (5.17)
- Weight loss and growth inhibition reported during combination therapy in pediatric patients. Long-term growth inhibition (height) reported in some patients. (5.18)
- Peripheral neuropathy when used in combination with telbivudine. (5.19)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions (greater than 40%) in adult patients receiving either PEGINTRON or PEGINTRON/REBETOL are injection site inflammation/reaction, fatigue/asthenia, headache, rigors, fevers, nausea, myalgia and anxiety/emotional lability/irritability (6.1). Most common adverse reactions (greater than 25%) in pediatric patients receiving PEGINTRON/REBETOL are pyrexia, headache, neutropenia, fatigue, anorexia, injection-site erythema, vomiting (6.1).
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp., a subsidiary of Merck & Co., Inc., at 1-877-888-4231 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
- Drugs metabolized by CYP450: Caution with drugs metabolized by CYP1A2 (e.g., caffeine) or CYP2D6 (e.g., thioridazine). (7.1)
- Methadone: Dosage reduction may be necessary. (7.1)
- Nucleoside analogues: Closely monitor for toxicities. Discontinue nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors or reduce dose or discontinue interferon, ribavirin, or both with worsening toxicities. (7.2)
- Didanosine: Concurrent use with ribavirin is not recommended. (7.2)
Use In Specific Populations
- Pregnancy: Based on animal data, may cause fetal harm (8.1).
- Pediatrics: safety and efficacy in pediatrics less than 3 years old have not been established. (8.4)
- Geriatrics: neuropsychiatric, cardiac, pulmonary, GI, and systemic (flu-like) adverse reactions may be more severe. (8.5)
- Organ transplant: safety and efficacy have not been studied. (8.6)
- HIV or HBV co-infection: safety and efficacy have not been established. (8.7)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 8/2019
Full Prescribing Information
WARNING: RISK OF SERIOUS DISORDERS
Alpha interferons, including PEGINTRON, may cause or aggravate fatal or life-threatening neuropsychiatric, autoimmune, ischemic, and infectious disorders. Patients should be monitored closely with periodic clinical and laboratory evaluations. Patients with persistently severe or worsening signs or symptoms of these conditions should be withdrawn from therapy. In many, but not all cases, these disorders resolve after stopping PEGINTRON therapy [see Warnings and Precautions (5) and Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
1. Indications and Usage for Pegintron
1.1 Chronic Hepatitis C (CHC)
PEGINTRON®, as part of a combination regimen, is indicated for the treatment of Chronic Hepatitis C (CHC) in patients with compensated liver disease.
- PEGINTRON in combination with ribavirin and an approved Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) NS3/4A protease inhibitor is indicated in adult patients with HCV genotype 1 infection (see labeling of the specific HCV NS3/4A protease inhibitor for further information).
- PEGINTRON in combination with ribavirin is indicated in patients with genotypes other than 1, pediatric patients (3-17 years of age), or in patients with genotype 1 infection where use of an HCV NS3/4A protease inhibitor is not warranted based on tolerability, contraindications or other clinical factors.
PEGINTRON monotherapy should only be used in the treatment of CHC in patients with compensated liver disease if there are contraindications to or significant intolerance of ribavirin and is indicated for use only in previously untreated adult patients. Combination therapy provides substantially better response rates than monotherapy [see Clinical Studies (14.1, 14.2)].
2. Pegintron Dosage and Administration
2.1 PEGINTRON Combination Therapy
Adults
The recommended dose of PEGINTRON is 1.5 mcg/kg/week. The volume of PEGINTRON to be injected depends on the strength of PEGINTRON and patient's body weight (see Table 1).
PEGINTRON is used in combination with other products including ribavirin and HCV direct acting antivirals. For further information on dosing and administration, refer to the respective prescribing information.
Duration of Treatment – Re-treatment with PEGINTRON/Ribavirin of Prior Treatment Failures
For patients with genotype 1 infection, PEGINTRON and ribavirin without an HCV NS3/4A protease inhibitor should only be used if there are contraindications, significant intolerance or other clinical factors that would not warrant use of an HCV NS3/4A protease inhibitor. The treatment duration for patients who previously failed therapy is 48 weeks, regardless of HCV genotype. Re-treated patients who fail to achieve undetectable HCV-RNA at Week 12 of therapy, or whose HCV-RNA remains detectable after 24 weeks of therapy, are highly unlikely to achieve SVR and discontinuation of therapy should be considered [see Clinical Studies (14.1)].
| Body Weight kg (lbs) | PEGINTRON REDIPEN Pre-filled pen or Vial Strength to Use | Amount of PEGINTRON to Administer (mcg) | Volume* of PEGINTRON to Administer (mL) |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|||
| <40 (<88) | 50 mcg per 0.5 mL | 50 | 0.5 |
| 40-50 (88-111) | 80 mcg per 0.5 mL | 64 | 0.4 |
| 51-60 (112-133) | 80 | 0.5 | |
| 61-65 (134-144) | 120 mcg per 0.5 mL | 96 | 0.4 |
| 66-75 (145-166) |
|||
| 76-80 (167-177) | 120 | 0.5 | |
| 81-85 (178-187) |
|||
| 86-105 (188-231) | 150 mcg per 0.5 mL | 150 | 0.5 |
| >105 (>231) | † | † | † |
2.2 PEGINTRON Monotherapy
The recommended dose of PEGINTRON regimen is 1 mcg/kg/week subcutaneously for 1 year administered on the same day of the week. Discontinuation of therapy should be considered in patients who do not achieve at least a 2 log10 drop or loss of HCV-RNA at 12 weeks of therapy, or whose HCV-RNA levels remain detectable after 24 weeks of therapy. The volume of PEGINTRON to be injected depends on patient weight (see Table 2).
| Body Weight kg (lbs) | PEGINTRON REDIPEN Pre-filled pen or Vial Strength to Use | Amount of PEGINTRON to Administer (mcg) | Volume of PEGINTRON to Administer (mL)* |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|||
| ≤45 (≤100) | 50 mcg per 0.5 mL | 40 | 0.4 |
| 46-56 (101-124) | 50 | 0.5 | |
| 57-72 (125-159) | 80 mcg per 0.5 mL | 64 | 0.4 |
| 73-88 (160-195) | 80 | 0.5 | |
| 89-106 (196-234) | 120 mcg per 0.5 mL | 96 | 0.4 |
| 107-136 (235-300) | 120 | 0.5 | |
| 137-160 (301-353) | 150 mcg per 0.5 mL | 150 | 0.5 |
2.3 Dosage Modifications
If a serious adverse reaction develops during the course of treatment, discontinue or modify the dosage of PEGINTRON and ribavirin until the adverse event abates or decreases in severity [see Warnings and Precautions (5)]. If persistent or recurrent serious adverse events develop despite adequate dosage adjustment, discontinue treatment. For guidelines for dose modifications and discontinuation based on depression or laboratory parameters see Tables 3 and 4. Dose reduction of PEGINTRON in adult patients on PEGINTRON/ribavirin combination therapy is accomplished in a two-step process from the original starting dose of 1.5 mcg/kg/week, to 1 mcg/kg/week, then to 0.5 mcg/kg/week, if needed. Dose reduction in patients on PEGINTRON monotherapy is accomplished by reducing the original starting dose of 1 mcg/kg/week to 0.5 mcg/kg/week. Instructions for dose reductions in adults are outlined in Tables 5 (Monotherapy: REDIPEN/Vial) and 6 (Combination therapy: REDIPEN/Vial).
Dose reduction in pediatric patients is accomplished by modifying the recommended dose in a 2-step process from the original starting dose of 60 mcg/m2/week, to 40 mcg/m2/week, then to 20 mcg/m2/week, if needed (see Tables 3 and 4).
| Depression Severity* | Initial Management (4-8 weeks) | Depression Status | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dose Modification | Visit Schedule | Remains Stable | Improves | Worsens | |
|
|||||
| Mild | No change | Evaluate once weekly by visit or phone | Continue weekly visit schedule | Resume normal visit schedule | See moderate or severe depression |
| Moderate | Adults: Adjust Dose*
Pediatrics: Decrease dose to 40 mcg/m2/week, then to 20 mcg/m2/week, if needed | Evaluate once weekly (office visit at least every other week) | Consider psychiatric consultation. Continue reduced dosing | If symptoms improve and are stable for 4 weeks, may resume normal visit schedule. Continue reduced dosing or return to normal dose | See severe depression |
| Severe | Discontinue PEGINTRON/ribavirin permanently | Obtain immediate psychiatric consultation | Psychiatric therapy as necessary | ||
| Laboratory Parameters | Reduce PEGINTRON Dose (see note 1) if: | Reduce ribavirin Daily Dose (see note 2) if: | Discontinue Therapy if: |
|---|---|---|---|
| Note 1: Adult patients on combination therapy: 1st dose reduction of PEGINTRON is to 1 mcg/kg/week. If needed, 2nd dose reduction of PEGINTRON is to 0.5 mcg/kg/week. Adult patients on PEGINTRON monotherapy: decrease PEGINTRON dose to 0.5 mcg/kg/week. Pediatric patients: 1st dose reduction of PEGINTRON is to 40 mcg/m2/week, 2nd dose reduction of PEGINTRON is to 20 mcg/m2/week. |
|||
| Note 2: Adult patients: 1st dose reduction of ribavirin is by 200 mg/day (except in patients receiving the 1400 mg, dose reduction should be by 400 mg/day). If needed, 2nd dose reduction of ribavirin is by an additional 200 mg/day. Patients whose dose of ribavirin is reduced to 600 mg daily receive one 200 mg capsule in the morning and two 200 mg capsules in the evening. Pediatric patients: 1st dose reduction of ribavirin is to 12 mg/kg/day, 2nd dose reduction of ribavirin is to 8 mg/kg/day. |
|||
|
|||
| WBC | 1.0 to <1.5 × 109/L | N/A | <1.0 × 109/L |
| Neutrophils | 0.5 to <0.75 × 109/L | N/A | <0.5 × 109/L |
| Platelets | 25 to <50 × 109/L (adults) | N/A | <25 × 109/L (adults) |
| 50 to <70 × 109/L (pediatrics) | N/A | <50 × 109/L (pediatrics) | |
| Creatinine | N/A | N/A | >2 mg/dL (pediatrics) |
| Hemoglobin in patients without history of cardiac disease | N/A | 8.5 to <10 g/dL | <8.5 g/dL |
| Reduce PEGINTRON Dose by Half and the Ribavirin Dose by 200 mg/day if: | |||
| Hemoglobin in patients with history of cardiac disease*† | ≥2 g/dL decrease in hemoglobin during any four-week period during treatment | <8.5 g/dL or <12 g/dL after four weeks of dose reduction | |
| Body Weight kg (lbs) | PEGINTRON REDIPEN/Vial |
||
|---|---|---|---|
| Strength to Use | Amount to Administer (mcg) | Volume* to Administer (mL) |
|
|
|||
| ≤45 (≤100) | 50 mcg per 0.5 mL† | 20 | 0.2 |
| 46-56 (101-124) | 50 mcg per 0.5 mL† | 25 | 0.25 |
| 57-72 (125-159) | 50 mcg per 0.5 mL | 30 | 0.3 |
| 73-88 (160-195) | 50 mcg per 0.5 mL | 40 | 0.4 |
| 89-106 (196-234) | 50 mcg per 0.5 mL | 50 | 0.5 |
| 107-136 (235-300) | 80 mcg per 0.5 mL | 64 | 0.4 |
| ≥137 (≥301) | 80 mcg per 0.5 mL | 80 | 0.5 |
| First Dose Reduction to PEGINTRON 1 mcg/kg | Second Dose Reduction to PEGINTRON 0.5 mcg/kg | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Body weight kg (lbs) | PEGINTRON REDIPEN/Vial Strength to Use | Amount of PEGINTRON (mcg) to Administer | Volume (mL) * of PEGINTRON to Administer | Body weight kg (lbs) | PEGINTRON REDIPEN/Vial Strength to Use | Amount of PEGINTRON (mcg) to Administer | Volume (mL) * of PEGINTRON to Administer |
|
|||||||
| <40 (<88) | 50 mcg per 0.5 mL | 35 | 0.35 | <40 (<88) | 50 mcg per 0.5 mL† | 20 | 0.2 |
| 40-50 (88-111) | 45 | 0.45 | 40-50 (88-111) | 25 | 0.25 | ||
| 51-60 (112-133) | 50 | 0.5 | 51-60 (112-133) | 50 mcg per 0.5 mL | 30 | 0.3 | |
| 61-75 (134-166) | 80 mcg per 0.5 mL | 64 | 0.4 | 61-75 (134-166) | 35 | 0.35 | |
| 76-85 (167-187) | 80 | 0.5 | 76-85 (167-187) | 45 | 0.45 | ||
| 86-104 (188-230) | 120 mcg per 0.5 mL | 96 | 0.4 | 86-104 (188-230) | 50 | 0.5 | |
| 105-125 (231-275) | 108 | 0.45 | 105-125 (231-275) | 80 mcg per 0.5 mL | 64 | 0.4 | |
| >125 (>275) | 150 mcg per 0.5 mL | 135 | 0.45 | >125 (>275) | 72 | 0.45 | |
2.5 Renal Function
In patients with moderate renal dysfunction (creatinine clearance 30-50 mL/min), the PEGINTRON dose should be reduced by 25%. Patients with severe renal dysfunction (creatinine clearance 10-29 mL/min), including those on hemodialysis, should have the PEGINTRON dose reduced by 50%. If renal function decreases during treatment, PEGINTRON therapy should be discontinued. When PEGINTRON is administered in combination with ribavirin, subjects with impaired renal function or those over the age of 50 should be more carefully monitored with respect to the development of anemia. PEGINTRON/ribavirin should not be used in patients with creatinine clearance less than 50 mL/min.
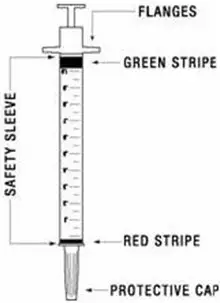
2.6 Preparation and Administration
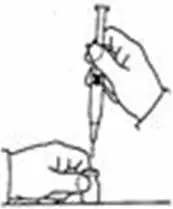
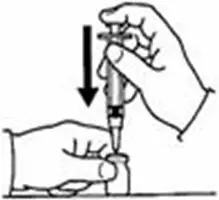
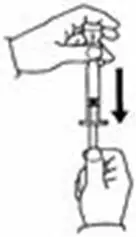
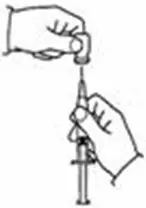
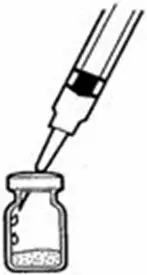
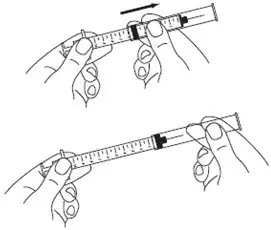
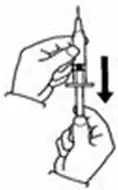
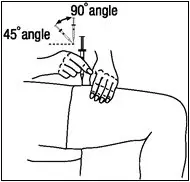
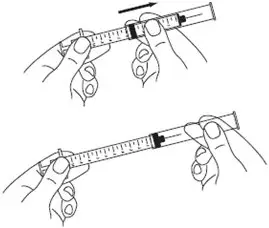
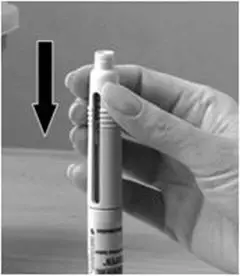
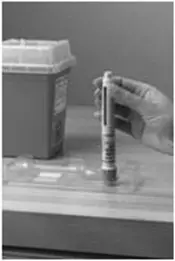
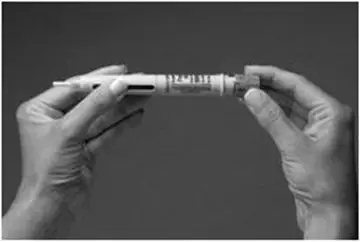
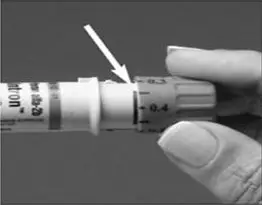
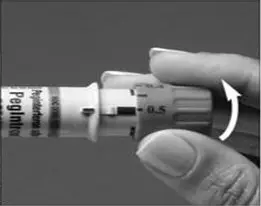
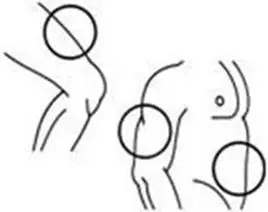
A patient should self-inject PEGINTRON only if a healthcare provider determines that it is appropriate and the patient agrees to medical follow-up as necessary and has been trained in proper injection technique [see illustrated FDA-approved Medication Guide and Instructions for Use for directions on injection site preparation and injection instructions].
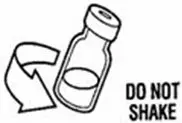
Reconstitute PEGINTRON Powder for Solution with 0.7 mL of Sterile Water for Injection, USP. The Sterile Water for Injection supplied contains 5 mL and is intended for single dose only. Discard the unused portion. The reconstituted solution should be visually inspected for discoloration and particulate matter prior to administration. Do not use the solution if it is discolored or not clear, or if particulates are present.
DO NOT REUSE THE VIAL OR PRE-FILLED PEN; DISCARD THE UNUSED PORTION. Pooling of unused portions of some medications has been linked to bacterial contamination and morbidity.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
- Single-dose vial: 5 mL diluent vial: 50 mcg per 0.5 mL, 80 mcg per 0.5 mL, 120 mcg per 0.5 mL, 150 mcg per 0.5 mL.
- REDIPEN® single-dose pre-filled pen: 50 mcg per 0.5 mL, 80 mcg per 0.5 mL, 120 mcg per 0.5 mL, 150 mcg per 0.5 mL.
4. Contraindications
PEGINTRON is contraindicated in patients with:
- known hypersensitivity reactions, such as urticaria, angioedema, bronchoconstriction, anaphylaxis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, and toxic epidermal necrolysis to interferon alpha or any other component of the product
- autoimmune hepatitis
- hepatic decompensation (Child-Pugh score greater than 6 [class B and C]) in cirrhotic CHC patients before or during treatment
If PEGINTRON is administered with ribavirin, the contraindications to ribavirin also apply to this combination regimen. Refer to the ribavirin prescribing information for a list of contraindications for ribavirin. PEGINTRON combination treatment with ribavirin is contraindicated in women who are or may become pregnant and men whose female partners are pregnant. Advise pregnant women about the potential risk to a fetus [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1), Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3), and Patient Counseling Information (17)].
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Risks Associated with Ribavirin Combination Treatment
If PEGINTRON is administered with ribavirin, the warnings and precautions for ribavirin, including the pregnancy avoidance warning and the association with hemolytic anemia, apply to this combination regimen. Refer to the ribavirin prescribing information for a full list of the warnings and precautions for ribavirin.
5.2 Neuropsychiatric Events
Life-threatening or fatal neuropsychiatric events, including suicide, suicidal and homicidal ideation, depression, relapse of drug addiction/overdose, and aggressive behavior sometimes directed towards others have occurred in patients with and without a previous psychiatric disorder during PEGINTRON treatment and follow-up. Psychoses, hallucinations, bipolar disorders, and mania have been observed in patients treated with interferon alpha.
PEGINTRON should be used with caution in patients with a history of psychiatric disorders. Treatment with interferons may be associated with exacerbated symptoms of psychiatric disorders in patients with co-occurring psychiatric and substance use disorders. If treatment with interferons is initiated in patients with prior history or existence of psychiatric condition or with a history of substance use disorders, treatment considerations should include the need for drug screening and periodic health evaluation, including psychiatric symptom monitoring. Early intervention for re-emergence or development of neuropsychiatric symptoms and substance use is recommended.
Patients should be advised to report immediately any symptoms of depression or suicidal ideation to their healthcare provider. Healthcare providers should monitor all patients for evidence of depression and other psychiatric symptoms. If patients develop psychiatric problems, including clinical depression, it is recommended that the patients be carefully monitored during treatment and in the 6-month follow-up period. If psychiatric symptoms persist or worsen, or suicidal or homicidal ideation or aggressive behavior towards others is identified, discontinue treatment with PEGINTRON and follow the patient closely, with psychiatric intervention as appropriate. In severe cases, PEGINTRON should be stopped immediately and psychiatric intervention instituted [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)]. Cases of encephalopathy have been observed in some patients, usually elderly, treated at higher doses of PEGINTRON.
5.3 Cardiovascular Events
Cardiovascular events, which include hypotension, arrhythmia, tachycardia, cardiomyopathy, angina pectoris, and myocardial infarction, have been observed in patients treated with PEGINTRON. PEGINTRON should be used cautiously in patients with cardiovascular disease. Patients with a history of myocardial infarction and arrhythmic disorder who require PEGINTRON therapy should be closely monitored [see Warnings and Precautions (5.15)]. Patients with a history of significant or unstable cardiac disease should not be treated with PEGINTRON/ribavirin combination therapy [see ribavirin labeling].
5.4 Endocrine Disorders
PEGINTRON causes or aggravates hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism. Hyperglycemia has been observed in patients treated with PEGINTRON. Diabetes mellitus, including cases of new onset Type 1 diabetes, has been observed in patients treated with alpha interferons, including PEGINTRON. Patients with these conditions who cannot be effectively treated by medication should not begin PEGINTRON therapy. Patients who develop these conditions during treatment and cannot be controlled with medication should not continue PEGINTRON therapy.
5.5 Ophthalmologic Disorders
Decrease or loss of vision, retinopathy including macular edema, retinal artery or vein thrombosis, retinal hemorrhages and cotton wool spots, optic neuritis, papilledema, and serous retinal detachment may be induced or aggravated by treatment with peginterferon alfa-2b or other alpha interferons. All patients should receive an eye examination at baseline. Patients with preexisting ophthalmologic disorders (e.g., diabetic or hypertensive retinopathy) should receive periodic ophthalmologic exams during interferon alpha treatment. Any patient who develops ocular symptoms should receive a prompt and complete eye examination. Peginterferon alfa-2b treatment should be discontinued in patients who develop new or worsening ophthalmologic disorders.
5.6 Cerebrovascular Disorders
Ischemic and hemorrhagic cerebrovascular events have been observed in patients treated with interferon alfa-based therapies, including PEGINTRON. Events occurred in patients with few or no reported risk factors for stroke, including patients less than 45 years of age. Because these are spontaneous reports, estimates of frequency cannot be made, and a causal relationship between interferon alfa-based therapies and these events is difficult to establish.
5.7 Bone Marrow Toxicity
PEGINTRON suppresses bone marrow function, sometimes resulting in severe cytopenias. PEGINTRON should be discontinued in patients who develop severe decreases in neutrophil or platelet counts [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)]. Ribavirin may potentiate the neutropenia induced by interferon alpha. Very rarely alpha interferons may be associated with aplastic anemia.
5.8 Autoimmune Disorders
Development or exacerbation of autoimmune disorders (e.g., thyroiditis, thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura, idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, rheumatoid arthritis, interstitial nephritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, and psoriasis) has been observed in patients receiving PEGINTRON.
PEGINTRON should be used with caution in patients with autoimmune disorders.
5.9 Pancreatitis
Fatal and nonfatal pancreatitis has been observed in patients treated with alpha interferon. PEGINTRON therapy should be suspended in patients with signs and symptoms suggestive of pancreatitis and discontinued in patients diagnosed with pancreatitis.
5.10 Colitis
Fatal and nonfatal ulcerative or hemorrhagic/ischemic colitis have been observed within 12 weeks of the start of alpha interferon treatment. Abdominal pain, bloody diarrhea, and fever are the typical manifestations. PEGINTRON treatment should be discontinued immediately in patients who develop these signs and symptoms. The colitis usually resolves within 1 to 3 weeks of discontinuation of alpha interferons.
5.11 Pulmonary Disorders
Dyspnea, pulmonary infiltrates, pneumonia, bronchiolitis obliterans, interstitial pneumonitis, pulmonary hypertension, and sarcoidosis, some resulting in respiratory failure or patient deaths, may be induced or aggravated by PEGINTRON or alpha interferon therapy. Recurrence of respiratory failure has been observed with interferon rechallenge. PEGINTRON combination treatment should be suspended in patients who develop pulmonary infiltrates or pulmonary function impairment. Patients who resume interferon treatment should be closely monitored.
Because of the fever and other "flu-like" symptoms associated with PEGINTRON administration, it should be used cautiously in patients with debilitating medical conditions, such as those with a history of pulmonary disease (e.g., chronic obstructive pulmonary disease).
5.12 Hepatic Failure
Chronic Hepatitis C (CHC) patients with cirrhosis may be at risk of hepatic decompensation and death when treated with alpha interferons, including PEGINTRON. Cirrhotic CHC patients co-infected with HIV receiving highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) and alpha interferons with or without ribavirin appear to be at increased risk for the development of hepatic decompensation compared to patients not receiving HAART. During treatment, patients' clinical status and hepatic function should be closely monitored, and PEGINTRON treatment should be immediately discontinued if decompensation (Child-Pugh score greater than 6) is observed [see Contraindications (4)].
5.13 Patients with Renal Insufficiency
Increases in serum creatinine levels have been observed in patients with renal insufficiency receiving interferon alpha products, including PEGINTRON. Patients with impaired renal function should be closely monitored for signs and symptoms of interferon toxicity, including increases in serum creatinine, and PEGINTRON dosing should be adjusted accordingly or discontinued [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) and Dosage and Administration (2.3)]. PEGINTRON monotherapy should be used with caution in patients with creatinine clearance less than 50 mL/min; the potential risks should be weighed against the potential benefits in these patients. Combination therapy with ribavirin must not be used in patients with creatinine clearance less than 50 mL/min [see ribavirin labeling].
5.14 Hypersensitivity
Serious, acute hypersensitivity reactions (e.g., urticaria, angioedema, bronchoconstriction, anaphylaxis) and cutaneous eruptions (Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis) have been rarely observed during alpha interferon therapy. If such a reaction develops during treatment with PEGINTRON, discontinue treatment and institute appropriate medical therapy immediately. Transient rashes do not necessitate interruption of treatment.
5.15 Laboratory Tests
PEGINTRON alone or in combination with ribavirin may cause severe decreases in neutrophil and platelet counts, and hematologic, endocrine (e.g., TSH), and hepatic abnormalities. Transient elevations in ALT (2- to 5-fold above baseline) were observed in 10% of subjects treated with PEGINTRON, and were not associated with deterioration of other liver functions. Triglyceride levels are frequently elevated in patients receiving alpha interferon therapy including PEGINTRON and should be periodically monitored.
Patients treated with PEGINTRON alone or in combination with ribavirin should have hematology and blood chemistry testing before the start of treatment and then periodically while on treatment. In the adult clinical trial, complete blood counts (including hemoglobin, neutrophil, and platelet counts) and chemistries (including AST, ALT, bilirubin, and uric acid) were measured during the treatment period at Weeks 2, 4, 8, and 12, and then at 6-week intervals, or more frequently if abnormalities developed. In pediatric subjects, the same laboratory parameters were evaluated with additional assessment of hemoglobin at treatment Week 6. TSH levels were measured every 12 weeks during the treatment period. HCV-RNA should be measured periodically during treatment [see Dosage and Administration (2.1, 2.2, 2.4)].
Patients who have pre-existing cardiac abnormalities should have electrocardiograms done before treatment with PEGINTRON/ribavirin.
5.16 Dental and Periodontal Disorders
Dental and periodontal disorders have been reported in patients receiving PEGINTRON/ribavirin combination therapy. In addition, dry mouth could have a damaging effect on teeth and mucous membranes of the mouth during long-term treatment with the combination of PEGINTRON and ribavirin. Patients should brush their teeth thoroughly twice daily and have regular dental examinations. If vomiting occurs, patients should be advised to rinse out their mouth thoroughly afterwards.
5.17 Triglycerides
Elevated triglyceride levels have been observed in patients treated with interferon alpha, including PEGINTRON therapy. Hypertriglyceridemia may result in pancreatitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]. Elevated triglyceride levels should be managed as clinically appropriate. Discontinuation of PEGINTRON therapy should be considered for patients with symptoms of potential pancreatitis, such as abdominal pain, nausea, or vomiting, and persistently elevated triglycerides (e.g., triglycerides greater than 1000 mg/dL).
5.18 Impact on Growth — Pediatric Use
Data on the effects of PEGINTRON plus ribavirin on growth come from an open-label trial in 107 subjects, 3 through 17 years of age, in which weight and height changes are compared to US normative population data. In general, the weight and height gain of pediatric subjects treated with PEGINTRON plus ribavirin lags behind that predicted by normative population data for the entire length of treatment. Severely inhibited growth velocity (less than 3rd percentile) was observed in 70% of the subjects while on treatment. Following treatment, rebound growth and weight gain occurred in most subjects. Long-term follow-up data in pediatric subjects, however, indicates that PEGINTRON in combination therapy with ribavirin may induce a growth inhibition that results in reduced adult height in some patients [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
5.19 Peripheral Neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy has been reported when alpha interferons were given in combination with telbivudine. In one clinical trial, an increased risk and severity of peripheral neuropathy was observed with the combination use of telbivudine and pegylated interferon alfa-2a as compared to telbivudine alone. The safety and efficacy of telbivudine in combination with interferons for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B has not been demonstrated.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
Clinical trials with PEGINTRON alone or in combination with REBETOL® (ribavirin) have been conducted in over 6,900 subjects from 3 to 75 years of age.
Serious adverse reactions have occurred in approximately 12% of subjects in clinical trials with PEGINTRON with or without REBETOL [see Warnings and Precautions (5)]. The most common serious events occurring in subjects treated with PEGINTRON and REBETOL were depression and suicidal ideation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)], each occurring at a frequency of less than 1%. The most common fatal events occurring in subjects treated with PEGINTRON and REBETOL were cardiac arrest, suicidal ideation, and suicide attempt [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2, 5.3)], all occurring in less than 1% of subjects.
Greater than 96% of all subjects in clinical trials experienced one or more adverse events. The most commonly reported adverse reactions in adult subjects receiving either PEGINTRON or PEGINTRON/REBETOL were injection-site inflammation/reaction, fatigue/asthenia, headache, rigors, fevers, nausea, myalgia, and emotional lability/irritability. The most common adverse events in pediatric subjects, ages 3 and older, were pyrexia, headache, vomiting, neutropenia, fatigue, anorexia, injection-site erythema, and abdominal pain.
Adults
Study 1 compared PEGINTRON monotherapy with INTRON® A monotherapy. Study 2 compared combination therapy of PEGINTRON/REBETOL with combination therapy with INTRON A/REBETOL. In these clinical trials, nearly all subjects experienced one or more adverse reactions. Study 3 compared a PEGINTRON/weight-based REBETOL combination to a PEGINTRON/flat dose REBETOL regimen. Study 4 compared two PEGINTRON doses (1.5 mcg/kg/week and 1 mcg/kg/week) in combination with REBETOL and a third treatment group receiving Pegasys® (180 mcg/week)/Copegus® (1000-1200 mg/day).
Adverse reactions that occurred in Studies 1 and 2 at greater than 5% incidence are provided in Table 7 by treatment group. Due to potential differences in ascertainment procedures, adverse reaction rate comparisons across trials should not be made. Table 8 summarizes the treatment-related adverse reactions in Study 4 that occurred at a greater than or equal to 10% incidence.
| Percentage of Subjects Reporting Adverse Reactions* | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study 1 | Study 2 | |||
| Adverse Reactions | PEGINTRON 1 mcg/kg | INTRON A 3 MIU | PEGINTRON 1.5 mcg/kg/ REBETOL | INTRON A/ REBETOL |
| (N=297) | (N=303) | (N=511) | (N=505) | |
|
||||
| Application Site | ||||
| Injection Site Inflammation/Reaction | 47 | 20 | 75 | 49 |
| Autonomic Nervous System | ||||
| Dry Mouth | 6 | 7 | 12 | 8 |
| Increased Sweating | 6 | 7 | 11 | 7 |
| Flushing | 6 | 3 | 4 | 3 |
| Body as a Whole | ||||
| Fatigue/Asthenia | 52 | 54 | 66 | 63 |
| Headache | 56 | 52 | 62 | 58 |
| Rigors | 23 | 19 | 48 | 41 |
| Fever | 22 | 12 | 46 | 33 |
| Weight Loss | 11 | 13 | 29 | 20 |
| Right Upper Quadrant Pain | 8 | 8 | 12 | 6 |
| Chest Pain | 6 | 4 | 8 | 7 |
| Malaise | 7 | 6 | 4 | 6 |
| Central/Peripheral Nervous System | ||||
| Dizziness | 12 | 10 | 21 | 17 |
| Endocrine | ||||
| Hypothyroidism | 5 | 3 | 5 | 4 |
| Gastrointestinal | ||||
| Nausea | 26 | 20 | 43 | 33 |
| Anorexia | 20 | 17 | 32 | 27 |
| Diarrhea | 18 | 16 | 22 | 17 |
| Vomiting | 7 | 6 | 14 | 12 |
| Abdominal Pain | 15 | 11 | 13 | 13 |
| Dyspepsia | 6 | 7 | 9 | 8 |
| Constipation | 1 | 3 | 5 | 5 |
| Hematologic Disorders | ||||
| Neutropenia | 6 | 2 | 26 | 14 |
| Anemia | 0 | 0 | 12 | 17 |
| Leukopenia | <1 | 0 | 6 | 5 |
| Thrombocytopenia | 7 | <1 | 5 | 2 |
| Liver and Biliary System | ||||
| Hepatomegaly | 6 | 5 | 4 | 4 |
| Musculoskeletal | ||||
| Myalgia | 54 | 53 | 56 | 50 |
| Arthralgia | 23 | 27 | 34 | 28 |
| Musculoskeletal Pain | 28 | 22 | 21 | 19 |
| Psychiatric | ||||
| Insomnia | 23 | 23 | 40 | 41 |
| Depression | 29 | 25 | 31 | 34 |
| Anxiety/Emotional Lability/Irritability | 28 | 34 | 47 | 47 |
| Concentration Impaired | 10 | 8 | 17 | 21 |
| Agitation | 2 | 2 | 8 | 5 |
| Nervousness | 4 | 3 | 6 | 6 |
| Reproductive, Female | ||||
| Menstrual Disorder | 4 | 3 | 7 | 6 |
| Resistance Mechanism | ||||
| Viral Infection | 11 | 10 | 12 | 12 |
| Fungal Infection | <1 | 3 | 6 | 1 |
| Respiratory System | ||||
| Dyspnea | 4 | 2 | 26 | 24 |
| Coughing | 8 | 5 | 23 | 16 |
| Pharyngitis | 10 | 7 | 12 | 13 |
| Rhinitis | 2 | 2 | 8 | 6 |
| Sinusitis | 7 | 7 | 6 | 5 |
| Skin and Appendages | ||||
| Alopecia | 22 | 22 | 36 | 32 |
| Pruritus | 12 | 8 | 29 | 28 |
| Rash | 6 | 7 | 24 | 23 |
| Skin Dry | 11 | 9 | 24 | 23 |
| Special Senses, Other | ||||
| Taste Perversion | <1 | 2 | 9 | 4 |
| Vision Disorders | ||||
| Vision Blurred | 2 | 3 | 5 | 6 |
| Conjunctivitis | 4 | 2 | 4 | 5 |
| Percentage of Subjects Reporting Treatment-Related Adverse Reactions | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Study 4 | |||
| Adverse Reactions | PEGINTRON 1.5 mcg/kg with REBETOL | PEGINTRON 1 mcg/kg with REBETOL | Pegasys 180 mcg with Copegus |
| (N=1019) | (N=1016) | (N=1035) | |
| Fatigue | 67 | 68 | 64 |
| Headache | 50 | 47 | 41 |
| Nausea | 40 | 35 | 34 |
| Chills | 39 | 36 | 23 |
| Insomnia | 38 | 37 | 41 |
| Anemia | 35 | 30 | 34 |
| Pyrexia | 35 | 32 | 21 |
| Injection Site Reactions | 34 | 35 | 23 |
| Anorexia | 29 | 25 | 21 |
| Rash | 29 | 25 | 34 |
| Myalgia | 27 | 26 | 22 |
| Neutropenia | 26 | 19 | 31 |
| Irritability | 25 | 25 | 25 |
| Depression | 25 | 19 | 20 |
| Alopecia | 23 | 20 | 17 |
| Dyspnea | 21 | 20 | 22 |
| Arthralgia | 21 | 22 | 22 |
| Pruritus | 18 | 15 | 19 |
| Influenza-like Illness | 16 | 15 | 15 |
| Dizziness | 16 | 14 | 13 |
| Diarrhea | 15 | 16 | 14 |
| Cough | 15 | 16 | 17 |
| Weight Decreased | 13 | 10 | 10 |
| Vomiting | 12 | 10 | 9 |
| Unspecified Pain | 12 | 13 | 9 |
| Dry Skin | 11 | 11 | 12 |
| Anxiety | 11 | 11 | 10 |
| Abdominal Pain | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| Leukopenia | 9 | 7 | 10 |
The adverse reaction profile in Study 3, which compared PEGINTRON/weight-based REBETOL combination to a PEGINTRON/flat-dose REBETOL regimen, revealed an increased rate of anemia with weight-based dosing (29% vs. 19% for weight-based vs. flat-dose regimens, respectively). However, the majority of cases of anemia were mild and responded to dose reductions.
The incidence of serious adverse reactions was comparable in all trials. In the PEGINTRON monotherapy trial (Study 1) the incidence of serious adverse reactions was similar (about 12%) in all treatment groups. In Study 2, the incidence of serious adverse reactions was 17% in the PEGINTRON/REBETOL groups compared to 14% in the INTRON A/REBETOL group. In Study 3, there was a similar incidence of serious adverse reactions reported for the weight-based REBETOL group (12%) and for the flat-dose REBETOL regimen.
In many but not all cases, adverse reactions resolved after dose reduction or discontinuation of therapy. Some subjects experienced ongoing or new serious adverse reactions during the 6-month follow-up period.
There have been 31 subject deaths that occurred during treatment or during follow-up in these clinical trials. In Study 1, there was 1 suicide in a subject receiving PEGINTRON monotherapy and 2 deaths among subjects receiving INTRON A monotherapy (1 murder/suicide and 1 sudden death). In Study 2, there was 1 suicide in a subject receiving PEGINTRON/REBETOL combination therapy, and 1 subject death in the INTRON A/REBETOL group (motor vehicle accident). In Study 3, there were 14 deaths, 2 of which were probable suicides, and 1 was an unexplained death in a person with a relevant medical history of depression. In Study 4, there were 12 deaths, 6 of which occurred in subjects receiving PEGINTRON/REBETOL combination therapy; 5 in the PEGINTRON 1.5 mcg/REBETOL arm (N=1019) and 1 in the PEGINTRON 1 mcg/REBETOL arm (n=1016); and 6 of which occurred in subjects receiving Pegasys/Copegus (N=1035). There were 3 suicides that occurred during the off-treatment follow-up period in subjects who received PEGINTRON (1.5 mcg/kg)/REBETOL combination therapy.
In Studies 1 and 2, 10% to 14% of subjects receiving PEGINTRON, alone or in combination with REBETOL, discontinued therapy compared with 6% treated with INTRON A alone and 13% treated with INTRON A in combination with REBETOL. Similarly in Study 3, 15% of subjects receiving PEGINTRON in combination with weight-based REBETOL and 14% of subjects receiving PEGINTRON and flat-dose REBETOL discontinued therapy due to an adverse reaction. The most common reasons for discontinuation of therapy were related to known interferon effects of psychiatric, systemic (e.g., fatigue, headache), or gastrointestinal adverse reactions. In Study 4, 13% of subjects in the PEGINTRON 1.5 mcg/REBETOL arm, 10% in the PEGINTRON 1 mcg/REBETOL arm, and 13% in the Pegasys 180 mcg/Copegus arm discontinued therapy due to adverse events.
In Study 2, dose reductions due to adverse reactions occurred in 42% of subjects receiving PEGINTRON (1.5 mcg/kg)/REBETOL and in 34% of those receiving INTRON A/REBETOL. The majority of subjects (57%) weighing 60 kg or less receiving PEGINTRON (1.5 mcg/kg)/REBETOL required dose reduction. Reduction of interferon was dose-related (PEGINTRON 1.5 mcg/kg more than PEGINTRON 0.5 mcg/kg or INTRON A), 40%, 27%, 28%, respectively. Dose reduction for REBETOL was similar across all three groups, 33% to 35%. The most common reasons for dose modifications were neutropenia (18%) or anemia (9%). Other common reasons included depression, fatigue, nausea, and thrombocytopenia. In Study 3, dose modifications due to adverse reactions occurred more frequently with weight-based dosing (WBD) compared to flat dosing (29% and 23%, respectively). In Study 4, 16% of subjects had a dose reduction of PEGINTRON to 1 mcg/kg in combination with REBETOL, with an additional 4% requiring the second dose reduction of PEGINTRON to 0.5 mcg/kg due to adverse events, compared to 15% of subjects in the Pegasys/Copegus arm, who required a dose reduction to 135 mcg/week with Pegasys, with an additional 7% requiring a second dose reduction to 90 mcg/week with Pegasys.
In the PEGINTRON/REBETOL combination trials the most common adverse reactions were psychiatric, which occurred among 77% of subjects in Study 2 and 68% to 69% of subjects in Study 3. These psychiatric adverse reactions included most commonly depression, irritability, and insomnia, each reported by approximately 30% to 40% of subjects in all treatment groups. Suicidal behavior (ideation, attempts, and suicides) occurred in 2% of all subjects during treatment or during follow-up after treatment cessation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. In Study 4, psychiatric adverse reactions occurred in 58% of subjects in the PEGINTRON 1.5 mcg/REBETOL arm, 55% of subjects in the PEGINTRON 1 mcg/REBETOL arm, and 57% of subjects in the Pegasys 180 mcg/Copegus arm.
PEGINTRON induced fatigue or headache in approximately two-thirds of subjects, with fever or rigors in approximately half of the subjects. The severity of some of these systemic symptoms (e.g., fever and headache) tended to decrease as treatment continued. In Studies 1 and 2, application site inflammation and reaction (e.g., bruise, itchiness, and irritation) occurred at approximately twice the incidence with PEGINTRON therapies (in up to 75% of subjects) compared with INTRON A. However, injection-site pain was infrequent (2-3%) in all groups. In Study 3, there was a 23% to 24% incidence overall for injection-site reactions or inflammation.
In Study 2, many subjects continued to experience adverse reactions several months after discontinuation of therapy. By the end of the 6-month follow-up period, the incidence of ongoing adverse reactions by body class in the PEGINTRON 1.5/REBETOL group was 33% (psychiatric), 20% (musculoskeletal), and 10% (for endocrine and for GI). In approximately 10% to 15% of subjects, weight loss, fatigue, and headache had not resolved.
Individual serious adverse reactions in Study 2 occurred at a frequency less than or equal to 1% and included suicide attempt, suicidal ideation, severe depression; psychosis, aggressive reaction, relapse of drug addiction/overdose; nerve palsy (facial, oculomotor); cardiomyopathy, myocardial infarction, angina, pericardial effusion, retinal ischemia, retinal artery or vein thrombosis, blindness, decreased visual acuity, optic neuritis, transient ischemic attack, supraventricular arrhythmias, loss of consciousness; neutropenia, infection (sepsis, pneumonia, abscess, cellulitis); emphysema, bronchiolitis obliterans, pleural effusion, gastroenteritis, pancreatitis, gout, hyperglycemia, hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism, autoimmune thrombocytopenia with or without purpura, rheumatoid arthritis, interstitial nephritis, lupus-like syndrome, sarcoidosis, aggravated psoriasis; urticaria, injection-site necrosis, vasculitis, and phototoxicity.
Subjects receiving PEGINTRON/REBETOL as re-treatment after failing a previous interferon combination regimen reported adverse reactions similar to those previously associated with this regimen during clinical trials of treatment-naïve subjects.
Pediatric Subjects
In general, the adverse-reaction profile in the pediatric population was similar to that observed in adults. In the pediatric trial, the most prevalent adverse reactions in all subjects were pyrexia (80%), headache (62%), neutropenia (33%), fatigue (30%), anorexia (29%), injection-site erythema (29%), and vomiting (27%). The majority of adverse reactions reported in the trial were mild or moderate in severity. Severe adverse reactions were reported in 7% (8/107) of all subjects and included injection-site pain (1%), pain in extremity (1%), headache (1%), neutropenia (1%), and pyrexia (4%). Important adverse reactions that occurred in this subject population were nervousness (7%; 7/107), aggression (3%; 3/107), anger (2%; 2/107), and depression (1%; 1/107). Five subjects received levothyroxine treatment; three with clinical hypothyroidism and two with asymptomatic TSH elevations. Weight and height gain of pediatric subjects treated with PEGINTRON plus REBETOL lagged behind that predicted by normative population data for the entire length of treatment. Severely inhibited growth velocity (less than 3rd percentile) was observed in 70% of the subjects while on treatment.
Dose modifications were required in 25% of subjects, most commonly for anemia, neutropenia, and weight loss. Two subjects (2%; 2/107) discontinued therapy as the result of an adverse reaction.
Adverse reactions that occurred with a greater than or equal to 10% incidence in the pediatric trial subjects are provided in Table 9.
| System Organ Class Preferred Term | All Subjects N=107 |
|---|---|
| Blood and Lymphatic System Disorders | |
| Neutropenia | 33% |
| Anemia | 11% |
| Leukopenia | 10% |
| Gastrointestinal Disorders | |
| Abdominal Pain | 21% |
| Abdominal Pain Upper | 12% |
| Vomiting | 27% |
| Nausea | 18% |
| General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions | |
| Pyrexia | 80% |
| Fatigue | 30% |
| Injection-site Erythema | 29% |
| Chills | 21% |
| Asthenia | 15% |
| Irritability | 14% |
| Investigations | |
| Weight Decreased | 19% |
| Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders | |
| Anorexia | 29% |
| Decreased Appetite | 22% |
| Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders | |
| Arthralgia | 17% |
| Myalgia | 17% |
| Nervous System Disorders | |
| Headache | 62% |
| Dizziness | 14% |
| Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders | |
| Alopecia | 17% |
Ninety-four of 107 subjects enrolled in a 5-year long-term follow-up trial. The long-term effects on growth were less in those subjects treated for 24 weeks than those treated for 48 weeks. Twenty-four percent of subjects (11/46) treated for 24 weeks and 40% of subjects (19/48) treated for 48 weeks had a >15 percentile height-for-age decrease from pre-treatment to the end of the 5-year long-term follow-up compared to pre-treatment baseline percentiles. Eleven percent of subjects (5/46) treated for 24 weeks and 13% of subjects (6/48) treated for 48 weeks were observed to have a decrease from pre-treatment baseline of >30 height-for-age percentiles to the end of the 5-year long-term follow-up. While observed across all age groups, the highest risk for reduced height at the end of long-term follow-up appeared to correlate with initiation of combination therapy during the years of expected peak growth velocity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.18)].
Laboratory Values
Pediatric Subjects
Decreases in hemoglobin, white blood cells, platelets, and neutrophils may require dose reduction or permanent discontinuation from therapy [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)]. Changes in selected laboratory values during treatment of 107 pediatric subjects with PEGINTRON/REBETOL combination therapy are described in Table 10. Most of the changes in laboratory values in this trial were mild or moderate.
| Laboratory Parameter* | All Subjects (N=107) |
|---|---|
|
|
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | |
| 9.5 to <11.0 | 30% |
| 8.0 to <9.5 | 2% |
| WBC (× 109/L) | |
| 2.0-2.9 | 39% |
| 1.5 to <2.0 | 3% |
| Platelets (× 109/L) | |
| 70-100 | 1% |
| 50 to <70 | — |
| 25 to <50 | 1% |
| Neutrophils (× 109/L) | |
| 1.0-1.5 | 35% |
| 0.75 to <1.0 | 26% |
| 0.5 to <0.75 | 13% |
| <0.5 | 3% |
| Total Bilirubin | |
| 1.26-2.59 × ULN† | 7% |
| Evidence of Hepatic Failure | — |
6.2 Immunogenicity
As with all therapeutic proteins, there is potential for immunogenicity. Approximately 2% of subjects receiving PEGINTRON (32/1759) or INTRON A (11/728) with or without REBETOL developed low-titer (less than or equal to 160) neutralizing antibodies to PEGINTRON or INTRON A. The clinical and pathological significance of the appearance of serum-neutralizing antibodies is unknown. The incidence of antibody formation is highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assay. Additionally, the observed incidence of antibody (including neutralizing antibody) positivity in an assay may be influenced by several factors, including assay methodology, sample handling, timing of sample collection, concomitant medications, and underlying disease. For these reasons, comparison of the incidence of antibodies to PEGINTRON with the incidence of antibodies to other products may be misleading.
6.3 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of PEGINTRON therapy. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Blood and Lymphatic System Disorders
Pure red cell aplasia, thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura
Cardiac Disorders
Palpitations, pericarditis
Ear and Labyrinth Disorders
Hearing loss, vertigo, hearing impairment
Endocrine Disorders
Diabetic ketoacidosis, diabetes
Eye Disorders
Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada syndrome, serous retinal detachment
Gastrointestinal Disorders
Aphthous stomatitis, tongue pigmentation
General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions
Asthenic conditions (including asthenia, malaise, fatigue)
Immune System Disorders
Cases of acute hypersensitivity reactions (including anaphylaxis, angioedema, urticaria); Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, systemic lupus erythematosus, erythema multiforme
Infections and Infestations
Bacterial infection including sepsis, Hepatitis B virus reactivation in HCV/HBV co-infected patients
Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders
Dehydration, hypertriglyceridemia
Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders
Rhabdomyolysis, myositis
Nervous System Disorders
Seizures, memory loss, peripheral neuropathy, paraesthesia, migraine headache
Psychiatric Disorders
Homicidal ideation
Respiratory, Thoracic, and Mediastinal Disorders
Pulmonary hypertension, pulmonary fibrosis
Renal and Urinary Disorders
Renal failure, renal insufficiency
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders
Psoriasis
Vascular Disorders
Hypertension, hypotension
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 Drugs Metabolized by Cytochrome P-450
Peginterferon alfa-2b inhibits CYP1A2 and CYP2D6 activity. Drugs with a narrow therapeutic range metabolized by CYP1A2 (caffeine) or CYP2D6 (thioridazine) should be administered with caution when coadministered with PEGINTRON (Table 11). [See Clinical Pharmacology (12.3).]
| Drugs | Effect on Concentration | Clinical Comment |
|---|---|---|
| Antiretroviral Agents: Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors (NRTIs):
zidovudine | ↔ zidovudine | Monitor blood cell count and suppressive effect on bone marrow function when zidovudine is coadministered with PEGINTRON. |
| Immunosuppressants:
e.g., cyclosporine sirolimus tacrolimus | Effect on immunosuppressants unknown | Therapeutic monitoring of the immunosuppressive agents is recommended upon coadministration with PEGINTRON. |
| Narcotic Analgesics:
methadone | ↑ methadone | Methadone dosage may need to be reduced when coadministered with PEGINTRON. |
| Neuroleptics:
thioridazine | ↑ thioridazine | Monitor for thioridazine adverse events when coadministered with PEGINTRON. |
| Xanthines:
theophylline | ↑ theophylline | Monitor for theophylline adverse events when coadministered with PEGINTRON. |
7.2 Use with Ribavirin (Nucleoside Analogues)
Hepatic decompensation (some fatal) has occurred in cirrhotic HIV/HCV co-infected patients receiving combination antiretroviral therapy for HIV and interferon alpha and ribavirin. Adding treatment with alpha interferons alone or in combination with ribavirin may increase the risk in this patient subset. Patients receiving interferon with ribavirin and nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs) should be closely monitored for treatment- associated toxicities, especially hepatic decompensation and anemia. Discontinuation of NRTIs should be considered as medically appropriate [see labeling for individual NRTI product]. Dose reduction or discontinuation of interferon, ribavirin, or both should also be considered if worsening clinical toxicities are observed, including hepatic decompensation (e.g., Child-Pugh greater than 6).
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
PEGINTRON may be used in combination with ribavirin. If PEGINTRON is administered with ribavirin, the information for ribavirin regarding pregnancy testing, contraception, and infertility also applies to this combination regimen. Refer to ribavirin prescribing information for additional information.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of PEGINTRON in pediatric patients below the age of 3 years have not been established.
Long-term follow-up data in pediatric subjects indicates that PEGINTRON in combination with ribavirin may induce a growth inhibition that results in reduced height in some patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.18) and Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
8.5 Geriatric Use
In general, younger patients tend to respond better than older patients to interferon-based therapies. Clinical trials of PEGINTRON alone or in combination with ribavirin did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently than younger subjects. Treatment with alpha interferons, including PEGINTRON, is associated with neuropsychiatric, cardiac, pulmonary, GI, and systemic (flu-like) adverse effects. Because these adverse reactions may be more severe in the elderly, caution should be exercised in the use of PEGINTRON in this population. This drug is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, the risk of toxic reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. When using PEGINTRON/ ribavirin therapy, refer also to the ribavirin labeling.
8.6 Organ Transplant Recipients
The safety and efficacy of PEGINTRON alone or in combination with ribavirin for the treatment of hepatitis C in liver or other organ transplant recipients have not been studied. In a small (n=16) single-center, uncontrolled case experience, renal failure in renal allograft recipients receiving interferon alpha and ribavirin combination therapy was more frequent than expected from the center's previous experience with renal allograft recipients not receiving combination therapy. The relationship of the renal failure to renal allograft rejection is not clear.
10. Overdosage
There is limited experience with overdosage. In the clinical trials, a few subjects accidentally received a dose greater than that prescribed. There were no instances in which a participant in the monotherapy or combination therapy trials received more than 10.5 times the intended dose of PEGINTRON. The maximum dose received by any subject was 3.45 mcg/kg weekly over a period of approximately 12 weeks. The maximum known overdosage of ribavirin was an intentional ingestion of 10 g (fifty 200 mg capsules). There were no serious reactions attributed to these overdosages. In cases of overdosing, symptomatic treatment and close observation of the patient are recommended.
11. Pegintron Description
PEGINTRON, peginterferon alfa-2b, is a covalent conjugate of recombinant alfa-2b interferon with monomethoxy polyethylene glycol (PEG). The average molecular weight of the PEG portion of the molecule is 12,000 daltons. The average molecular weight of the PEGINTRON molecule is approximately 31,000 daltons. The specific activity of peginterferon alfa-2b is approximately 0.7 × 108 IU/mg protein.
Interferon alfa-2b is a water-soluble protein with a molecular weight of 19,271 daltons produced by recombinant DNA techniques. It is obtained from the bacterial fermentation of a strain of Escherichia coli bearing a genetically engineered plasmid containing an interferon gene from human leukocytes.
PEGINTRON is supplied in both vials and the REDIPEN single-dose pre-filled pen for subcutaneous use.
12. Pegintron - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Pegylated recombinant human interferon alfa-2b is an inducer of the innate anti-HCV immune response [see Microbiology (12.4)].
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
The pharmacodynamic effects of peginterferon alfa-2b include inhibition of viral replication in virus-infected cells, the suppression of cell cycle progression/cell proliferation, induction of apoptosis, anti-angiogenic activities, and numerous immunomodulating activities, such as enhancement of the phagocytic activity of macrophages, activation of NK cells, stimulation of cytotoxic T-lymphocytes, and the upregulation of the Th1 T-helper cell subset.
PEGINTRON raises concentrations of effector proteins such as serum neopterin and 2'5' oligoadenylate synthetase, raises body temperature, and causes reversible decreases in leukocyte and platelet counts. The correlation between the in vitro and in vivo pharmacologic and pharmacodynamic and clinical effects is unknown.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Following a single subcutaneous dose of PEGINTRON, the mean absorption half-life (t ½ ka) was 4.6 hours. Maximal serum concentrations (Cmax) occur between 15 and 44 hours postdose and are sustained for up to 48 to 72 hours. The Cmax and AUC measurements of PEGINTRON increase in a dose-related manner. After multiple dosing, there is an increase in bioavailability of PEGINTRON. Week 48 mean trough concentrations (320 pg/mL; range 0, 2960) are approximately 3-fold higher than Week 4 mean trough concentrations (94 pg/mL; range 0, 416). The mean PEGINTRON elimination half-life is approximately 40 hours (range 22-60 hours) in patients with HCV infection. The apparent clearance of PEGINTRON is estimated to be approximately 22 mL/hr∙kg. Renal elimination accounts for 30% of the clearance.
Pegylation of interferon alfa-2b produces a product (PEGINTRON) whose clearance is lower than that of nonpegylated interferon alfa-2b. When compared to INTRON A, PEGINTRON (1 mcg/kg) has approximately a 7-fold lower mean apparent clearance and a 5-fold greater mean half-life, permitting a reduced dosing frequency. At effective therapeutic doses, PEGINTRON has approximately 10-fold greater Cmax and 50-fold greater AUC than interferon alfa-2b.
Drug Interactions
| Geometric Mean Ratio (Ratio with/without PEGINTRON) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coadministered Drug | Dose of PEGINTRON | Study Population | AUC (90% CI) | Cmax
(90% CI) |
|
||||
| Caffeine (CYP1A2 substrate) | 1.5 mcg/kg/week (4 weeks) | Chronic Hepatitis C Subjects (N=22) | 1.39 (1.27, 1.51) | 1.02 (0.95, 1.09) |
| 1 mcg/kg/week (4 weeks) | Healthy Subjects (N=24) | 1.18 (1.07, 1.31) | 1.12 (1.05, 1.19) |
|
| 3 mcg/kg/week (2 weeks) | Healthy Subjects (N=13) | 1.36 (1.25-1.49) | 1.16 (1.10-1.24) |
|
| Tolbutamide (CYP2C9 substrate) | 1.5 mcg/kg/week (4 weeks) | Chronic Hepatitis C Subjects (N=22) | 1.1*
(0.94, 1.28) | NA |
| 1 mcg/kg/week (4 weeks) | Healthy Subjects (N=24) | 0.90*
(0.81, 1.00) | NA | |
| 3 mcg/kg/week (2 weeks) | Healthy Subjects (N=13) | 0.95 (0.89-1.01) | 0.99 (0.92-1.07) |
|
| Dextromethorphan hydrobromide (CYP2D6 and CYP3A substrate) | 1.5 mcg/kg/week (4 weeks) | Chronic Hepatitis C Subjects (N=22) | 0.96†
(0.73, 1.26) | NA |
| 1 mcg/kg/week (4 weeks) | Healthy Subjects (N=24) | 2.03*
(1.55, 2.67) | NA | |
| Desipramine (CYP2D6 substrate) | 3 mcg/kg/week (2 weeks) | Healthy Subjects (N=13) | 1.30 (1.18-1.43) | 1.08 (1.00-1.16) |
| Midazolam (CYP3A4 substrate) | 1.5 mcg/kg/week (4 weeks) | Chronic Hepatitis C Subjects (N=24) | 1.07 (0.91, 1.25) | 1.12 (0.94, 1.33) |
| 1 mcg/kg/week (4 weeks) | Healthy Subjects (N=24) | 1.07 (0.99, 1.16) | 1.33 (1.15, 1.53) |
|
| 3 mcg/kg/week (2 weeks) | Healthy Subjects (N=13) | 1.18 (1.06-1.32) | 1.24 (1.07-1.43) |
|
| Dapsone (N-acetyltransferase substrate) | 1.5 mcg/kg/week (4 weeks) | Chronic Hepatitis C Subjects (N=24) | 1.05 (1.02, 1.08) | 1.03 (1.00, 1.06) |
12.5 Pharmacogenomics
A retrospective genome-wide association analysis1,2 of 1671 subjects (1604 subjects from Study 4 [see Clinical Studies (14.1)] and 67 subjects from another clinical trial) was performed to identify human genetic contributions to anti-HCV treatment response in previously untreated HCV genotype 1 subjects. A single nucleotide polymorphism near the gene encoding interferon-lambda-3 (IL28B rs12979860) was associated with variable SVR rates. The rs12979860 genotype was categorized as CC, CT and TT. In the pooled analysis of Caucasian, African-American, and Hispanic subjects from these trials (n=1587), SVR rates by rs12979860 genotype were as follows: CC 66% vs. CT 30% vs. TT 22%. The genotype frequencies differed depending on racial/ethnic background, but the relationship of SVR to IL28B genotype was consistent across various racial/ethnic groups (see Table 13). Other variants near the IL28B gene (e.g., rs8099917 and rs8103142) have been identified; however, they have not been shown to independently influence SVR rates during treatment with pegylated interferon alpha therapies combined with ribavirin.1
| Population | CC | CT | TT |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|||
| Caucasian | 69% (301/436) | 33% (196/596) | 27% (38/139) |
| African-American | 48% (20/42) | 15% (22/146) | 13% (15/112) |
| Hispanic | 56% (19/34) | 38% (21/56) | 27% (7/26) |
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14. Clinical Studies
14.1 Chronic Hepatitis C in Adults
PEGINTRON Monotherapy — Study 1
A randomized trial compared treatment with PEGINTRON (0.5, 1, or 1.5 mcg/kg once weekly subcutaneously) to treatment with INTRON A (3 million units 3 times weekly subcutaneously) in 1219 adults with chronic hepatitis from HCV infection. The subjects were not previously treated with interferon alpha, had compensated liver disease, detectable HCV-RNA, elevated ALT, and liver histopathology consistent with chronic hepatitis. Subjects were treated for 48 weeks and were followed for 24 weeks post-treatment.
Seventy percent of all subjects were infected with HCV genotype 1, and 74 percent of all subjects had high baseline levels of HCV-RNA (more than 2 million copies per mL of serum), two factors known to predict poor response to treatment.
Response to treatment was defined as undetectable HCV-RNA and normalization of ALT at 24 weeks post-treatment. The response rates to the 1 and 1.5 mcg/kg PEGINTRON doses were similar (approximately 24%) to each other and were both higher than the response rate to INTRON A (12%) (see Table 14).
| A PEGINTRON 0.5 mcg/kg (N=315) | B PEGINTRON 1 mcg/kg (N=298) | C INTRON A 3 MIU three times weekly (N=307) | B - C (95% CI) Difference between PEGINTRON 1 mcg/kg and INTRON A | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||
| Treatment Response (Combined Virologic Response and ALT Normalization) | 17% | 24% | 12% | 11 (5, 18) |
| Virologic Response* | 18% | 25% | 12% | 12 (6, 19) |
| ALT Normalization | 24% | 29% | 18% | 11 (5, 18) |
Subjects with both viral genotype 1 and high serum levels of HCV-RNA at baseline were less likely to respond to treatment with PEGINTRON. Among subjects with the two unfavorable prognostic variables, 8% (12/157) responded to PEGINTRON treatment and 2% (4/169) responded to INTRON A. Doses of PEGINTRON higher than the recommended dose did not result in higher response rates in these subjects. Subjects receiving PEGINTRON with viral genotype 1 had a response rate of 14% (28/199) while subjects with other viral genotypes had a 45% (43/96) response rate.
Ninety-six percent of the responders in the PEGINTRON groups and 100% of responders in the INTRON A group first cleared their viral RNA by Week 24 of treatment [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
The treatment response rates were similar in men and women. Response rates were lower in African-American and Hispanic subjects and higher in Asians compared to Caucasians. Although African Americans had a higher proportion of poor prognostic factors compared to Caucasians, the number of non-Caucasians studied (9% of the total) was insufficient to allow meaningful conclusions about differences in response rates after adjusting for prognostic factors.
Liver biopsies were obtained before and after treatment in 60% of subjects. A modest reduction in inflammation compared to baseline that was similar in all 4 treatment groups was observed.
PEGINTRON/REBETOL Combination Therapy — Study 2
A randomized trial compared treatment with two PEGINTRON/REBETOL regimens [PEGINTRON 1.5 mcg/kg subcutaneously once weekly/REBETOL 800 mg orally daily (in divided doses); PEGINTRON 1.5 mcg/kg subcutaneously once weekly for 4 weeks then 0.5 mcg/kg subcutaneously once weekly for 44 weeks/REBETOL 1000 or 1200 mg orally daily (in divided doses)] with INTRON A [3 MIU subcutaneously thrice weekly/REBETOL 1000 or 1200 mg orally daily (in divided doses)] in 1530 adults with chronic hepatitis C. Interferon-naïve subjects were treated for 48 weeks and followed for 24 weeks post-treatment. Eligible subjects had compensated liver disease, detectable HCV-RNA, elevated ALT, and liver histopathology consistent with chronic hepatitis.
Response to treatment was defined as undetectable HCV-RNA at 24 weeks post-treatment. The response rate to the PEGINTRON 1.5 mcg/kg plus REBETOL 800 mg dose was higher than the response rate to INTRON A/REBETOL (see Table 15). The response rate to PEGINTRON 1.5→0.5 mcg/kg/REBETOL was essentially the same as the response to INTRON A/REBETOL (data not shown).
| PEGINTRON 1.5 mcg/kg once weekly REBETOL 800 mg daily | INTRON A 3 MIU three times weekly REBETOL 1000/1200 mg daily | |
|---|---|---|
|
||
| Overall response * † | 52% (264/511) | 46% (231/505) |
| Genotype 1 | 41% (141/348) | 33% (112/343) |
| Genotype 2-6 | 75% (123/163) | 73% (119/162) |
Subjects with viral genotype 1, regardless of viral load, had a lower response rate to PEGINTRON (1.5 mcg/kg)/REBETOL (800 mg) compared to subjects with other viral genotypes. Subjects with both poor prognostic factors (genotype 1 and high viral load) had a response rate of 30% (78/256) compared to a response rate of 29% (71/247) with INTRON A/REBETOL.
Subjects with lower body weight tended to have higher adverse reaction rates [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] and higher response rates than subjects with higher body weights. Differences in response rates between treatment arms did not substantially vary with body weight.
Treatment response rates with PEGINTRON/REBETOL were 49% in men and 56% in women. Response rates were lower in African American and Hispanic subjects and higher in Asians compared to Caucasians. Although African Americans had a higher proportion of poor prognostic factors compared to Caucasians, the number of non-Caucasians studied (11% of the total) was insufficient to allow meaningful conclusions about differences in response rates after adjusting for prognostic factors in this trial.
Liver biopsies were obtained before and after treatment in 68% of subjects. Compared to baseline, approximately two-thirds of subjects in all treatment groups were observed to have a modest reduction in inflammation.
PEGINTRON/REBETOL Combination Therapy — Study 3
In a large United States community-based trial, 4913 subjects with chronic hepatitis C were randomized to receive PEGINTRON 1.5 mcg/kg subcutaneously once weekly in combination with a REBETOL dose of 800 to 1400 mg (weight-based dosing [WBD]) or 800 mg (flat) orally daily (in divided doses) for 24 or 48 weeks based on genotype. Response to treatment was defined as undetectable HCV-RNA (based on an assay with a lower limit of detection of 125 IU/mL) at 24 weeks post-treatment.
Treatment with PEGINTRON 1.5 mcg/kg and REBETOL 800 to 1400 mg resulted in a higher sustained virologic response compared to PEGINTRON in combination with a flat 800 mg daily dose of REBETOL. Subjects weighing greater than 105 kg obtained the greatest benefit with WBD, although a modest benefit was also observed in subjects weighing greater than 85 to 105 kg (see Table 16). The benefit of WBD in subjects weighing greater than 85 kg was observed with HCV genotypes 1-3. Insufficient data were available to reach conclusions regarding other genotypes. Use of WBD resulted in an increased incidence of anemia [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
| Treatment Group | Subject Baseline Weight | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| <65 kg (<143 lb) | 65-85 kg (143-188 lb) | >85-105 kg (>188-231 lb) | >105 kg (>231 lb) |
|
|
||||
| WBD* | 50% (173/348) | 45% (449/994) | 42% (351/835) | 47% (138/292) |
| Flat | 51% (173/342) | 44% (443/1011) | 39% (318/819) | 33% (91/272) |
A total of 1552 subjects weighing greater than 65 kg in Study 3 had genotype 2 or 3 and were randomized to 24 or 48 weeks of therapy. No additional benefit was observed with the longer treatment duration.
PEGINTRON/REBETOL Combination Therapy — Study 4
A large randomized trial compared the safety and efficacy of treatment for 48 weeks with two PEGINTRON/REBETOL regimens [PEGINTRON 1.5 mcg/kg and 1 mcg/kg subcutaneously once weekly both in combination with REBETOL 800 to 1400 mg PO daily (in two divided doses)] and Pegasys 180 mcg subcutaneously once weekly in combination with Copegus 1000 to 1200 mg PO daily (in two divided doses) in 3070 treatment-naïve adults with chronic hepatitis C genotype 1. In this trial, lack of early virologic response (undetectable HCV-RNA or greater than or equal to 2 log10 reduction from baseline) by treatment Week 12 was the criterion for discontinuation of treatment. SVR was defined as undetectable HCV-RNA (Roche COBAS TaqMan assay, a lower limit of quantitation of 27 IU/mL) at 24 weeks post-treatment (see Table 17).
| PEGINTRON 1.5 mcg/kg/ REBETOL | PEGINTRON 1 mcg/kg/ REBETOL | Pegasys 180 mcg/Copegus | |
|---|---|---|---|
| SVR | 40% (406/1019) | 38% (386/1016) | 41% (423/1035) |
Overall SVR rates were similar among the three treatment groups. Regardless of treatment group, SVR rates were lower in subjects with poor prognostic factors. Subjects with poor prognostic factors randomized to PEGINTRON (1.5 mcg/kg)/REBETOL or Pegasys/Copegus, however, achieved higher SVR rates compared to similar subjects randomized to PEGINTRON 1 mcg/kg/REBETOL. For the PEGINTRON 1.5 mcg/kg plus REBETOL dose, SVR rates for subjects with and without the following prognostic factors were as follows: cirrhosis (10% vs. 42%), normal ALT levels (32% vs. 42%), baseline viral load greater than 600,000 IU/mL (35% vs. 61%), 40 years of age and older (38% vs. 50%), and African American race (23% vs. 44%). In subjects with undetectable HCV-RNA at Week 12 who received PEGINTRON (1.5 mcg/kg)/REBETOL, the SVR rate was 81% (328/407).
PEGINTRON/REBETOL Combination Therapy in Prior Treatment Failures — Study 5
In a noncomparative trial, 2293 subjects with moderate to severe fibrosis who failed previous treatment with combination alpha interferon/ribavirin were re-treated with PEGINTRON, 1.5 mcg/kg subcutaneously, once weekly, in combination with weight adjusted ribavirin. Eligible subjects included prior nonresponders (subjects who were HCV-RNA positive at the end of a minimum 12 weeks of treatment) and prior relapsers (subjects who were HCV-RNA negative at the end of a minimum 12 weeks of treatment and subsequently relapsed after post-treatment follow-up). Subjects who were negative at Week 12 were treated for 48 weeks and followed for 24 weeks post-treatment. Response to treatment was defined as undetectable HCV-RNA at 24 weeks post-treatment (measured using a research-based test, limit of detection 125 IU/mL). The overall response rate was 22% (497/2293) (99% CI: 19.5, 23.9). Subjects with the following characteristics were less likely to benefit from re-treatment: previous nonresponse, previous pegylated interferon treatment, significant bridging fibrosis or cirrhosis, and genotype 1 infection.
The re-treatment sustained virologic response rates by baseline characteristics are summarized in Table 18.
| HCV Genotype/ Metavir Fibrosis Score | Overall SVR by Previous Response and Treatment | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nonresponder | Relapser | ||||||||
| alfa interferon/ribavirin % (number of subjects) | peginterferon (2a and 2b combined)/ribavirin % (number of subjects) | alfa interferon/ribavirin % (number of subjects) | peginterferon (2a and 2b combined)/ribavirin % (number of subjects) |
||||||
| Overall | 18 (158/903) | 6 (30/476) | 43 (130/300) | 35 (113/344) | |||||
| HCV 1 | 13 (98/761) | 4 (19/431) | 32 (67/208) | 23 (56/243) | |||||
| F2 | 18 (36/202) | 6 (7/117) | 42 (33/79) | 32 (23/72) | |||||
| F3 | 16 (38/233) | 4 (4/112) | 28 (16/58) | 21 (14/67) | |||||
| F4 | 7 (24/325) | 4 (8/202) | 26 (18/70) | 18 (19/104) | |||||
| HCV 2/3 | 49 (53/109) | 36 (10/28) | 67 (54/81) | 57 (52/92) | |||||
| F2 | 68 (23/34) | 56 (5/9) | 76 (19/25) | 61 (11/18) | |||||
| F3 | 39 (11/28) | 38 (3/8) | 67 (18/27) | 62 (18/29) | |||||
| F4 | 40 (19/47) | 18 (2/11) | 59 (17/29) | 51 (23/45) | |||||
| HCV 4 | 17 (5/29) | 7 (1/15) | 88 (7/8) | 50 (4/8) | |||||
Achievement of an undetectable HCV-RNA at treatment Week 12 was a strong predictor of SVR. In this trial, 1470 (64%) subjects did not achieve an undetectable HCV-RNA at treatment Week 12, and were offered enrollment into long-term treatment trials, due to an inadequate treatment response. Of the 823 (36%) subjects who were HCV-RNA undetectable at treatment Week 12, those infected with genotype 1 had an SVR of 48% (245/507), with a range of responses by fibrosis scores (F4-F2) of 39-55%. Subjects infected with genotype 2/3 who were HCV-RNA undetectable at treatment Week 12 had an overall SVR of 70% (196/281), with a range of responses by fibrosis scores (F4-F2) of 60-83%. For all genotypes, higher fibrosis scores were associated with a decreased likelihood of achieving SVR.
14.2 Chronic Hepatitis C in Pediatrics
PEGINTRON/REBETOL Combination Therapy — Pediatric Trial
Previously untreated pediatric subjects 3 to 17 years of age with compensated chronic hepatitis C and detectable HCV-RNA were treated with REBETOL 15 mg/kg/day plus PEGINTRON 60 mcg/m2 once weekly for 24 or 48 weeks based on HCV genotype and baseline viral load. All subjects were to be followed for 24 weeks post-treatment. A total of 107 subjects received treatment, of which 52% were female, 89% were Caucasian, and 67% were infected with HCV genotype 1. Subjects infected with genotype 1, 4 or genotype 3 with HCV-RNA greater than or equal to 600,000 IU/mL received 48 weeks of therapy while those infected with genotype 2 or genotype 3 with HCV-RNA less than 600,000 IU/mL received 24 weeks of therapy. The trial results are summarized in Table 19.
| All Subjects N=107 |
||
|---|---|---|
| 24 Weeks | 48 Weeks | |
| Virologic Response N* † (%) | Virologic Response N* † (%) |
|
| Genotype | ||
|
||
| All | 26/27 (96.3) | 44/80 (55.0) |
| 1 | — | 38/72 (52.8) |
| 2 | 14/15 (93.3) | — |
| 3‡ | 12/12 (100) | 2/3 (66.7) |
| 4 | — | 4/5 (80.0) |
15. References
- Ge, D., Fellay, J., Thompson, A.J., Simon, J.S., Shianna, K.V., Urban, T.J., Heinzen, E.L., Qiu, P., Bertelsen, A.H., Muir, A.J., Sulkowski, M., McHutchison, J.G., Goldstein, D.B., Genetic variation in IL28B predicts hepatitis C treatment-induced viral clearance, Nature 2009;461(7262):399-401.
- Thompson, A.J., Muir, A.J., Sulkowski, M.S., Ge, D., Fellay, J., Shianna, K.V., Urban, T., Afdhal, N.H., Jacobson, I.M., Esteban, R., Poordad, F., Lawitz, E.J., McCone, J., Shiffman, M.L., Galler, G.W., Lee, W.M., Reindollar, R., King, J.W., Kwo, P.Y., Ghalib, R.H., Freilich, B., Nyberg, L.M., Zeuzem, S., Poynard, T., Vock, D.M., Pieper, K.S., Patel, K., Tillmann, H.L., Noviello, S., Koury, K., Pedicone, L.D., Brass, C.A., Albrecht, J.K., Goldstein, D.B., McHutchison, J.G., Interlukin-28B polymorphism improves viral kinetics and is the strongest pretreatment predictor of sustained virologic response in genotype 1 hepatitis C virus, Gastroenterology 2010;139:120-129.
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide and Instructions for Use)
A patient should self-inject PEGINTRON only if it has been determined that it is appropriate, the patient agrees to medical follow-up as necessary, and training in proper injection technique has been given to him/her.
| This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. | Revised 08/2019 |
| MEDICATION GUIDE
PEGINTRON® (peg-In-tron) (Peginterferon alfa-2b) for injection, for subcutaneous use |
|
| Important: When taking PEGINTRON in combination with ribavirin, you should also read the ribavirin Medication Guide. If your healthcare provider also prescribes an approved hepatitis C virus (HCV) medicine for you, also read the Medication Guide that comes with that medicine. | |
| What is the most important information I should know about PEGINTRON? PEGINTRON can cause serious side effects that:
Mental health problems, including suicide. PEGINTRON may cause you to develop mood or behavior problems that may get worse during treatment with PEGINTRON or after your last dose, including:
Heart problems. Some people who take PEGINTRON may get heart problems, including:
New or worsening autoimmune problems. Some people taking PEGINTRON develop autoimmune problems (a condition where the body's immune cells attack other cells or organs in the body), including rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, and psoriasis. In some people who already have an autoimmune problem, it may get worse during your treatment with PEGINTRON. Infections. Some people who take PEGINTRON may get an infection. Symptoms may include:
During treatment with PEGINTRON, you should see a healthcare provider regularly for check-ups and blood tests to make sure that your treatment is working, and to check for side effects. |
|
| What is PEGINTRON?
PEGINTRON is a prescription medicine that is used:
It is not known if PEGINTRON use for longer than 1 year is safe and will work. It is not known if PEGINTRON use in children younger than 3 years old is safe and will work. |
|
| Who should not take PEGINTRON?
Do not take PEGINTRON:
When taking PEGINTRON in combination with ribavirin you should also read the Medication Guide for ribavirin for important pregnancy information. Talk to your healthcare provider before taking PEGINTRON if you have any of these conditions. |
|
| What should I tell my healthcare provider before taking PEGINTRON? Before you take PEGINTRON, see "What is the most important information I should know about PEGINTRON?", and tell your healthcare provider if you:
Especially tell your healthcare provider if you take the anti-hepatitis B medicine telbivudine (Tyzeka). Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them and show it to your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medicine. |
|
How should I take PEGINTRON?
|
|
| What are the possible side effects of PEGINTRON? PEGINTRON may cause serious side effects including: See "What is the most important information I should know about PEGINTRON?"
The most common side effects of PEGINTRON include:
Tell your healthcare provider if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away. These are not all of the possible side effects of PEGINTRON. For more information, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1–800–FDA–1088. |
|
How should I store PEGINTRON?
|
|
| General Information about the safe and effective use of PEGINTRON
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use PEGINTRON for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give PEGINTRON to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. You can ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for information about PEGINTRON that was written for healthcare professionals. |
|
| What are the ingredients in PEGINTRON? Active ingredients: peginterferon alfa-2b Inactive ingredients: dibasic sodium phosphate anhydrous, monobasic sodium phosphate dihydrate, sucrose, polysorbate 80. Sterile water for injection is supplied as a diluent. Manufactured by: Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp., a subsidiary of Merck & Co., Inc., Whitehouse Station, NJ 08889, USA U.S. License Number 0002 For patent information: www.merck.com/product/patent/home.html Copyright © 2001-2019 Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp., a subsidiary of Merck & Co., Inc. All rights reserved. usmg-mk4031-mf-1908r023 For more information call 1-800-526-4099. |
|
Instructions for Use
PEGINTRON® (peg-In-tron)
(peginterferon alfa-2b)
Powder for Injection
This Instructions for Use is only for use with the single-dose vials of Powder for injection. If your healthcare provider prescribes the REDIPEN Pre-filled Pen for you, use only those Instructions for Use.
Be sure that you read, understand and follow these instructions before injecting PEGINTRON. Your healthcare provider should show you how to prepare, measure, and inject PEGINTRON properly using a vial before you use it for the first time. Ask your healthcare provider if you have any questions.
Important:
- Make sure that you have:
- the correct strength of PEGINTRON vial prescribed by your healthcare provider.
- the correct syringe and needle to use with PEGINTRON. Your healthcare provider should tell you what syringes and needles to use to inject PEGINTRON.
- Throw away the syringe and needle after you use it. Do not re-use your syringes and needles. See "How should I dispose of the used syringes, needles, and vials?" at the end of this Instructions for Use.
- The vial of mixed PEGINTRON should be used right away. Do not mix more than 1 vial of PEGINTRON at a time. If you do not use the vial of the prepared solution right away, store it in a refrigerator and use within 24 hours. See the end of these Instructions for Use for information about "How should I store PEGINTRON?"
Before starting, collect all of the supplies that you will need to use for preparing and injecting PEGINTRON. For each injection you will need a PEGINTRON vial package that contains:
- 1 vial of PEGINTRON powder for injection
- 1 vial of sterile water for injection (diluent). The vial contains an excess amount of sterile water (5 mL). You will only need to withdraw 0.7 mL to prepare your single dose.
- 2 single-dose disposable syringes (BD Safety Lok syringes with a safety sleeve)
- 2 alcohol swabs
You will also need:
- 1 cotton ball or gauze
- 1 sharps disposal container for throwing away (dispose of) your used syringes, needles, and vials. See "How should I dispose of the used syringes, needles, and vials?" at the end of this Instructions for Use.
How should I prepare a dose of PEGINTRON?
Before you inject PEGINTRON, the powder must be mixed with 0.7 mL of the sterile water for injection (diluent) that comes in the PEGINTRON vial package.
- 1.
- Find a clean, well-lit, flat work surface.
- 2.
- Get 1 of your PEGINTRON vial packages. Check the date printed on the PEGINTRON carton. Make sure that the expiration date has not passed. Do not use your PEGINTRON vial packages if the expiration date has passed. The medicine in the PEGINTRON vial should look like a white to off-white tablet that is whole, or in pieces, or powdered.
If you have already mixed the PEGINTRON solution and stored it in the refrigerator, take it out of the refrigerator before use and allow the solution to come to room temperature. See the Medication Guide section "How should I store PEGINTRON?" - 3.
- Wash your hands well with soap and water, rinse and towel dry (See Figure A). Keep your work area, your hands, and injection site clean to decrease the risk of infection.
The disposable syringes have needles that are already attached and cannot be removed. Each syringe has a clear plastic safety sleeve that is pulled over the needle for disposal after use. The safety sleeve should remain tight against the flange while using the syringe and moved over the needle only when ready for disposal. (See Figure B)
- 4.
- Remove the protective wrapper from one of the syringes provided. Use the syringe for steps 4 through 15. Make sure that the syringe safety sleeve is sitting against the flange. (See Figure B)
- 5.
- Remove the protective plastic cap from the tops of both the sterile water for injection (diluent) and the PEGINTRON vials (See Figure C). Clean the rubber stopper on the top of both vials with an alcohol swab.
- 6.
- Carefully remove the protective cap straight off of the needle to avoid damaging the needle point.
- 7.
- Fill the syringe with air by pulling back on the plunger to 0.7 mL. (See Figure D)
- 8.
- Hold the diluent vial upright. Do not touch the cleaned top of the vial with your hands.
- Push the needle through the center of the rubber stopper of the diluent vial. (See Figure E)
- Slowly inject all the air from the syringe into the air space above the diluent in the vial. (See Figure F)
- 9.
- Turn the vial upside down and make sure the tip of the needle is in the liquid.
- Important: The sterile water for injection vial contains an excess amount of sterile water (5 mL). You will only need to withdraw 0.7 mL to prepare your single dose.
- 10.
- Withdraw only 0.7 mL of diluent by pulling the plunger back to the 0.7 mL mark on the side of the syringe. (See Figure G)
- 11.
- With the needle still inserted in the vial, check the syringe for air bubbles.
- If there are any air bubbles, gently tap the syringe with your finger until the air bubbles rise to the top of the syringe.
- Slowly push the plunger up to remove the air bubbles.
- If you push diluent back into the vial, slowly pull back on the plunger to draw the correct amount of diluent back into the syringe.
- 12.
- Remove the needle from the vial (See Figure H). Do not let the syringe touch anything.
- 13.
- Throw away the diluent that is left over in the vial. Do not save any leftover diluent or use it again. See "How should I dispose of the used syringes, needles, and vials?" at the end of this Instructions for Use.
- 14.
- Insert the needle through the center of the rubber stopper of the PEGINTRON powder vial. Do not touch the cleaned rubber stopper.
- Place the needle tip, at an angle, against the side of the vial. (See Figure I)
- Slowly push the plunger down to inject the 0.7 mL diluent. The stream of diluent should run down the side of the vial.
- To prevent bubbles from forming, do not aim the stream of diluent directly on the medicine in the bottom of the vial.
- 15.
- Remove the needle from the vial.
- Firmly grasp the safety sleeve and pull it over the exposed needle until you hear a click (See Figure J). The green stripe on the safety sleeve will completely cover the red stripe on the needle. Dispose of the syringe, needle, and vial in the sharps disposal container (See "How should I dispose of the used syringes, needles, and vials?").
- Firmly grasp the safety sleeve and pull it over the exposed needle until you hear a click (See Figure J). The green stripe on the safety sleeve will completely cover the red stripe on the needle. Dispose of the syringe, needle, and vial in the sharps disposal container (See "How should I dispose of the used syringes, needles, and vials?").
- 16.
- Gently swirl the vial in a gentle circular motion, until the PEGINTRON is completely dissolved (mixed together). (See Figure K)
- Do not shake the vial. If any powder remains undissolved in the vial, gently turn the vial upside down until all of the powder is dissolved.
- The solution may look cloudy or bubbly for a few minutes. If air bubbles form, wait until the solution settles and all bubbles rise to the top.
- 17.
- After the PEGINTRON completely dissolves, the solution should be clear, colorless and without particles. It is normal to see a ring of foam or bubbles on the surface.
Do not use the mixed solution if you see particles in it, or it is not clear and colorless. Dispose of the syringe, needle, and vial in the sharps disposal container (See "How should I dispose of the used syringes, needles, and vials?"). Then, repeat steps 1 through 17 with a new vial of PEGINTRON and diluent to prepare a new syringe. - 18.
- After the PEGINTRON powder completely dissolves, clean the rubber stopper again with an alcohol swab before you withdraw your dose.
- 19.
- Unwrap the second syringe provided. You will use it to give yourself the injection.
- Carefully remove the protective cap from the needle. Fill the syringe with air by pulling the plunger to the number on the side of the syringe (mL) that matches your prescribed dose. (See Figure L)
- Hold the PEGINTRON vial upright. Do not touch the cleaned top of the vial with your hands. (See Figure M)
- Insert the needle into the vial containing the PEGINTRON solution. Inject the air into the center of the vial. (See Figure N)
- Carefully remove the protective cap from the needle. Fill the syringe with air by pulling the plunger to the number on the side of the syringe (mL) that matches your prescribed dose. (See Figure L)
- 20.
- Turn the PEGINTRON vial upside down. Be sure the tip of the needle is in the PEGINTRON solution.
- Hold the vial and syringe with one hand. Be sure the tip of the needle is in the PEGINTRON solution. With the other hand, slowly pull the plunger back to fill the syringe with the exact amount of PEGINTRON into the syringe your healthcare provider told you to use. (See Figure O)
- Hold the vial and syringe with one hand. Be sure the tip of the needle is in the PEGINTRON solution. With the other hand, slowly pull the plunger back to fill the syringe with the exact amount of PEGINTRON into the syringe your healthcare provider told you to use. (See Figure O)
- 21.
- Check for air bubbles in the syringe. If you see any air bubbles, hold the syringe with the needle pointing up. Gently tap the syringe until the air bubbles rise. Then, slowly push the plunger up to remove any air bubbles. If you push solution into the vial, slowly pull back on the plunger again to draw the correct amount of PEGINTRON back into the syringe. When you are ready to inject the medicine, remove the needle from the vial. (See Figure P)
How should I choose a site for injection?
The best sites for giving yourself an injection are those areas with a layer of fat between the skin and muscle, like your thigh, the outer surface of your upper arm, and abdomen (See Figure Q). Do not inject yourself in the area near your belly-button (navel) or waistline. If you are very thin, you should only use the thigh or outer surface of the arm for injection.
You should use a different site each time you inject PEGINTRON to avoid soreness at any one site. Do not inject PEGINTRON solution into an area where the skin is irritated, red, bruised, infected or has scars, stretch marks, or lumps.
How should I inject a dose of PEGINTRON?
- 22.
- Clean the skin where the injection is to be given with an alcohol swab. Wait for the area to dry.
- Make sure the safety sleeve of the syringe is pushed firmly against the syringe flange so that the needle is fully exposed.
- 23.
- With one hand, pinch a fold of skin. With your other hand, pick up the syringe and hold it like a pencil.
- Insert the needle into the pinched skin at a 45- to 90-degree angle with a quick dart-like motion. (See Figure R)
- After the needle is inserted, remove the hand that you used to pinch your skin. Use it to hold the syringe barrel.
- Pull the plunger of the syringe back very slightly.
- If no blood is present in the syringe, inject the medicine by gently pressing the plunger all the way down the syringe barrel, until the syringe is empty.
-
If blood comes into the syringe, the needle has entered a blood vessel. Do not inject.
- Withdraw the needle and dispose of the syringe and needle in the sharps disposal container. (See "How should I dispose of the used syringes, needles, and vials?" at the end of this Instructions for Use.)
- If there is bleeding, cover the injection site with a bandage.
- Then, repeat steps 1 through 23 with a new vial of PEGINTRON and diluent to prepare a new syringe, and inject the medicine at a new site.
- Insert the needle into the pinched skin at a 45- to 90-degree angle with a quick dart-like motion. (See Figure R)
- 24.
- When the syringe is empty, pull the needle out of the skin.
- Place a cotton ball or gauze over the injection site and press for several seconds. Do not massage the injection site.
- If there is bleeding, cover it with a bandage.
- 25.
- After injecting your dose:
- Firmly grasp the safety sleeve and pull it over the exposed needle until you hear a click, and the green stripe on the safety sleeve covers the red stripe on the needle. (See Figure S)
- Firmly grasp the safety sleeve and pull it over the exposed needle until you hear a click, and the green stripe on the safety sleeve covers the red stripe on the needle. (See Figure S)
- 26.
- Dispose of used syringes, needles, and vials in the sharps disposal container. (See "How should I dispose of the used syringes, needles, and vials?" below).
How should I dispose of the used syringes, needles, and vials?
- Put your used needles, syringes and vials in a FDA-cleared sharps disposal container right away after use. Do not throw away (dispose of) loose needles, syringes and vials in your household trash.
- If you do not have a FDA-cleared sharps disposal container, you may use a household container that is:
- made of a heavy-duty plastic,
- can be closed with a tight-fitting, puncture-resistant lid, without sharps being able to come out,
- upright and stable during use,
- leak-resistant, and
- properly labeled to warn of hazardous waste inside the container.
- When your sharps disposal container is almost full, you will need to follow your community guidelines for the right way to dispose of your sharps disposal container. There may be state or local laws about how you should throw away used syringes and needles. For more information about safe sharps disposal, and for specific information about sharps disposal in the state that you live in, go to the FDA's website at: http://www.fda.gov/safesharpsdisposal.
- Do not dispose of your used sharps disposal container in your household trash unless your community guidelines permit this. Do not recycle your used sharps disposal container.
Always keep the sharps disposal container out of the reach of children.
- Before mixing, store PEGINTRON vials at room temperature, between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
- After mixing, use PEGINTRON right away or store it in the refrigerator for up to 24 hours between 36°F to 46°F (2°C to 8°C).
- Do not freeze PEGINTRON.
- Keep PEGINTRON away from heat.
Keep PEGINTRON and all medicines out of the reach of children.
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Instructions for Use
PEGINTRON® (peg-In-tron)
(Peginterferon alfa-2b)
REDIPEN® single-dose pre-filled pen
This Instructions for Use is only for use with the REDIPEN single-dose pre-filled pen.
Be sure that you read, understand, and follow these instructions before injecting PEGINTRON. Your healthcare provider should show you how to prepare and inject PEGINTRON properly using the REDIPEN single-dose pre-filled pen before you use it for the first time. Ask your healthcare provider if you have any questions.
Important:
- Make sure that you have the correct strength of REDIPEN pre-filled pen prescribed by your healthcare provider.
- Throw away REDIPEN after you use it. Do not re-use your pre-filled pen or needle. See "Disposal of used needles and pre-filled pens" in this Instructions for Use.
Before starting, collect all of the supplies that you will need to use for preparing and injecting PEGINTRON. For each injection you will need a package that contains:
- 1 PEGINTRON REDIPEN single-dose pre-filled pen
- 1 disposable needle
- 2 alcohol swabs
- dosing tray (the dosing tray is the bottom half of the REDIPEN package)
- You will need gauze or a cotton ball to press to the injection site after injecting. You will also need 1 sharps disposal container for throwing away your used pre-filled pen. See "Disposal of used needles and pre-filled pens" in this Instructions for Use.
The REDIPEN single-dose pre-filled pen should only be used with the injection needle that comes in the package. If you use other needles, the pen may not work the right way.
- Figures A and B below show the different parts of the REDIPEN single-dose pre-filled pen and the injection needle. Figure C below shows the dosing tray with the pre-filled pen. The parts of the pre-filled pen you need to know are:

Figure A
Figure B
Figure C
How should I prepare a dose of PEGINTRON using the REDIPEN single-dose pre-filled pen?
- 1.
- Find a clean, well-lit, flat work surface.
- 2.
- Take the pre-filled pen out of the refrigerator and allow the medicine to come to room temperature. Look at the date printed on the carton to make sure that the expiration date has not passed. Do not use if the expiration date has passed.
- 3.
- After taking the pre-filled pen out of the carton, look in the window of the pre-filled pen and make sure the PEGINTRON in the cartridge holder window is a white to off-white tablet that is whole, or in pieces, or powdered.
- 4.
- Wash your hands well with soap and water. It is important to keep your work area, your hands, and the injection site clean to decrease the risk of infection. See Figure D.
Mix the PEGINTRON
- 5.
-
Place the pre-filled pen upright in the dosing tray on a hard, flat, non-slip surface with the dosing button down. See Figure E. You may want to hold the pre-filled pen using the grip.
- 6.
- To mix the powder and the liquid, keep the pre-filled pen upright in the dosing tray and press the top half of the pre-filled pen downward toward the hard, flat, non-slip surface until you hear the "click" sound. See Figure F. When you hear the click, you will notice in the window that both dark stoppers are now touching. The dosing button should be flat with the pen body.
- 7.
- Wait several seconds for the powder to completely dissolve. Do not shake. If the solution does not dissolve, gently turn the pre-filled pen upside down two times. See Figure G.
- 8.
- Keep the pre-filled pen UPRIGHT, with the dosing button down. Look through the pre-filled pen window to see that the mixed PEGINTRON solution is completely dissolved. The solution should be clear and colorless before use. It is normal to see some small bubbles in the pre-filled pen window, near the top of the solution. Do not use the REDIPEN pre-filled pen if the solution is discolored, or is not clear, or if it has particles in it.
- 9.
- Place the pre-filled pen back into the dosing tray provided in the packaging. See Figure H. The dosing button will be on the bottom.
Attach the Needle
- 10.
- Before you attach the needle to the pre-filled pen, wipe the rubber membrane of the pre-filled pen with an alcohol swab.
- 11.
- Remove the protective paper tab from the injection needle, but do not remove either the outer cap or the yellow inner cap from the injection needle.
- 12.
- Keep the pre-filled pen upright in the dosing tray and push the injection needle straight into the pre-filled pen rubber membrane. Screw the needle onto the pre-filled pen by turning it in a clockwise direction. See Figure I.
- Remember to leave the needle caps in place when you attach the needle to the pre-filled pen. Pushing the needle through the rubber membrane "primes" the needle and allows the extra liquid and air in the pen to be removed.
- Remove the outer clear needle cap on the pre-filled pen, but leave the yellow cap on. See Figure J.
- Remember to leave the needle caps in place when you attach the needle to the pre-filled pen. Pushing the needle through the rubber membrane "primes" the needle and allows the extra liquid and air in the pen to be removed.
How should I set the dose prescribed by my healthcare provider?
Dial the Dose
- 13.
- Holding the pre-filled pen firmly, pull the dosing button out as far as it will go. See Figure K. You will see a dark band.
Do not push the dosing button in until you are ready to self-inject the PEGINTRON dose.
- 14.
- Turn the dosing button until your prescribed dose is lined up with the dosing tab. See Figure L. The dosing button will turn freely. If you have trouble dialing your dose, check to make sure the dosing button has been pulled out as far as it will go. See Figure M.
- 15.
- Carefully lay the pre-filled pen down on the dosing tray or on a hard, flat, non-slip surface. Do not remove the yellow needle cap and do not push the dosing button in until you are ready to self-inject the PEGINTRON dose.
Choosing an Injection Site
The best sites for giving yourself an injection are those areas with a layer of fat between the skin and muscle, like your thigh, the outer surface of your upper arm, and abdomen. See Figure N. Do not inject yourself in the area near your belly-button (navel) or waistline. If you are very thin, you should only use the thigh or outer surface of the arm for injection.
You should use a different site each time you inject PEGINTRON to avoid soreness at any one site. Do not inject PEGINTRON into an area where the skin is irritated, red, bruised, infected, or has scars, stretch marks, or lumps.
How should I Inject a dose of PEGINTRON?
- 16.
- Clean the skin where the injection is to be given with the second alcohol swab provided, and wait for the skin to dry.
- 17.
- There may be some liquid around the yellow inner needle cap. See Figure O. This is normal.
- 18.
- Remove the yellow inner needle cap when the injection site is dry. See Figure P. You are now ready to inject.
- 19.
- Hold the pre-filled pen with your fingers wrapped around the pen body barrel and your thumb on the dosing button. See Figure Q.
- 20.
- With your other hand, pinch the skin in the area you have cleaned for injection.
- 21.
- Insert the needle into the pinched skin at an angle of 45° to 90°. See Figure R.
- 22.
- Press the dosing button down slowly and firmly until you can not push it any further. Keep your thumb pressed down on the dosing button for an additional 5 seconds to make sure that you get the complete dose.
- 23.
- Slowly release the dosing button and remove the needle from your skin.
- 24.
- Gently press the injection site with a small bandage or sterile gauze if needed for a few seconds but do not massage the injection site. If there is bleeding, cover with an adhesive bandage. Do not recap the needle and do not reuse the pre-filled pen.
Disposal of the used needles and pre-filled pens
- Put your used needles and pre-filled pens in a FDA-cleared sharps disposal container right away after use. Do not throw away (dispose of) loose needles and pre-filled pens in your household trash.
- If you do not have a FDA-cleared sharps disposal container, you may use a household container that is:
- made of a heavy-duty plastic,
- can be closed with a tight-fitting, puncture-resistant lid, without sharps being able to come out,
- upright and stable during use,
- leak-resistant, and
- properly labeled to warn of hazardous waste inside the container.
- When your sharps disposal container is almost full, you will need to follow your community guidelines for the right way to dispose of your sharps disposal container. There may be state or local laws about how you should throw away used needles, syringes and pre-filled pens. For more information about safe sharps disposal, and for specific information about sharps disposal in the state that you live in, go to the FDA's website at: http://www.fda.gov/safesharpsdisposal.
- Do not dispose of your used sharps disposal container in your household trash unless your community guidelines permit this. Do not recycle your used sharps disposal container.
Always keep the sharps disposal container out of the reach of children.
How should I store PEGINTRON REDIPEN pre-filled pen?
- Before mixing, store PEGINTRON REDIPEN pre-filled pen in the refrigerator between 36°F to 46°F (2°C to 8°C).
- After mixing, use PEGINTRON right away or store it in the refrigerator for up to 24 hours between 36°F to 46°F (2°C to 8°C).
- Do not freeze PEGINTRON.
- Keep PEGINTRON away from heat.
Keep PEGINTRON and all medicines out of reach of children.
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
| PEGINTRON
peginterferon alfa-2b injection, powder, lyophilized, for solution |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PEGINTRON
peginterferon alfa-2b injection, powder, lyophilized, for solution |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PEGINTRON
peginterferon alfa-2b injection, powder, lyophilized, for solution |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PEGINTRON
peginterferon alfa-2b injection, powder, lyophilized, for solution |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PEGINTRON
peginterferon alfa-2b kit |
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
| PEGINTRON
peginterferon alfa-2b kit |
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
| PEGINTRON
peginterferon alfa-2b kit |
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
| PEGINTRON
peginterferon alfa-2b kit |
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp. (001317601) |