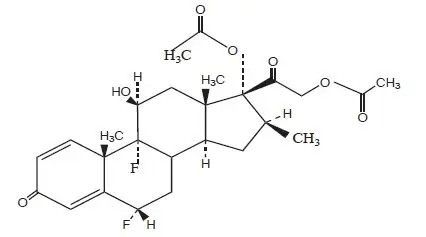
General
Systemic absorption of topical corticosteroids can produce reversible hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis suppression with the potential for glucocorticosteroid insufficiency after withdrawal of treatment. Manifestations of Cushing's syndrome, hyperglycemia, and glucosuria can also be produced in some patients by systemic absorption of topical corticosteroids while on treatment.
Patients receiving a large dose of a higher potency topical steroid applied to a large surface area or under an occlusive dressing should be evaluated periodically for evidence of HPA axis suppression. This may be done by using the ACTH-stimulation, A.M. plasma cortisol, and urinary free-cortisol tests.
This product has a greater ability to produce adrenal suppression than does diflorasone diacetate ointment USP, 0.05%. At 30 g per day (applied as 15 g twice daily) PSORCON® (diflorasone diacetate cream USP), 0.05% was shown to cause inhibition of the HPA axis in one of two patients following application for one week to psoriatic skin. At 15 g per day (applied as 7.5 g twice daily) PSORCON® (diflorasone diacetate cream USP), 0.05% was shown to cause mild inhibition of the HPA axis in one of five patients following application for one week to diseased skin (psoriasis or atopic dermatitis). These effects were reversible upon discontinuation of treatment. By comparison, diflorasone diacetate ointment USP, 0.05% did not produce significant HPA axis suppression when used in divided doses at 30 g per day for one week in patients with psoriasis or atopic dermatitis.
If HPA axis suppression is noted, an attempt should be made to withdraw the drug, to reduce the frequency of application, or to substitute a less potent corticosteroid. Recovery of HPA axis function is generally prompt and complete upon discontinuation of topical corticosteroids. Infrequently, signs and symptoms of glucocorticosteroid insufficiency may occur, requiring supplemental systemic corticosteroids. For information on systemic supplementation, see prescribing information for those products.
Pediatric patients may be more susceptible to systemic toxicity from equivalent doses due to their larger skin surface to body mass ratios (see PRECAUTIONS: Pediatric Use).
If irritation develops, diflorasone diacetate cream USP should be discontinued and appropriate therapy instituted. Allergic contact dermatitis with corticosteroids is usually diagnosed by observing failure to heal rather than noting a clinical exacerbation as with most topical products not containing corticosteroids. Such an observation should be corroborated with appropriate diagnostic patch testing.
If concomitant skin infections are present or develop, an appropriate antifungal or antibacterial agent should be used. If a favorable response does not occur promptly, use of PSORCON® (diflorasone diacetate cream USP), 0.05% should be discontinued until the infection has been adequately controlled. PSORCON® (diflorasone diacetate cream USP), 0.05% should not be used in the treatment of rosacea or perioral dermatitis, and it should not be used on the face, groin, or axillae.