Drug Detail:Remeron (Mirtazapine [ mir-taz-a-peen ])
Drug Class: Tetracyclic antidepressants
Highlights of Prescribing Information
REMERON® (mirtazapine) tablets, for oral use
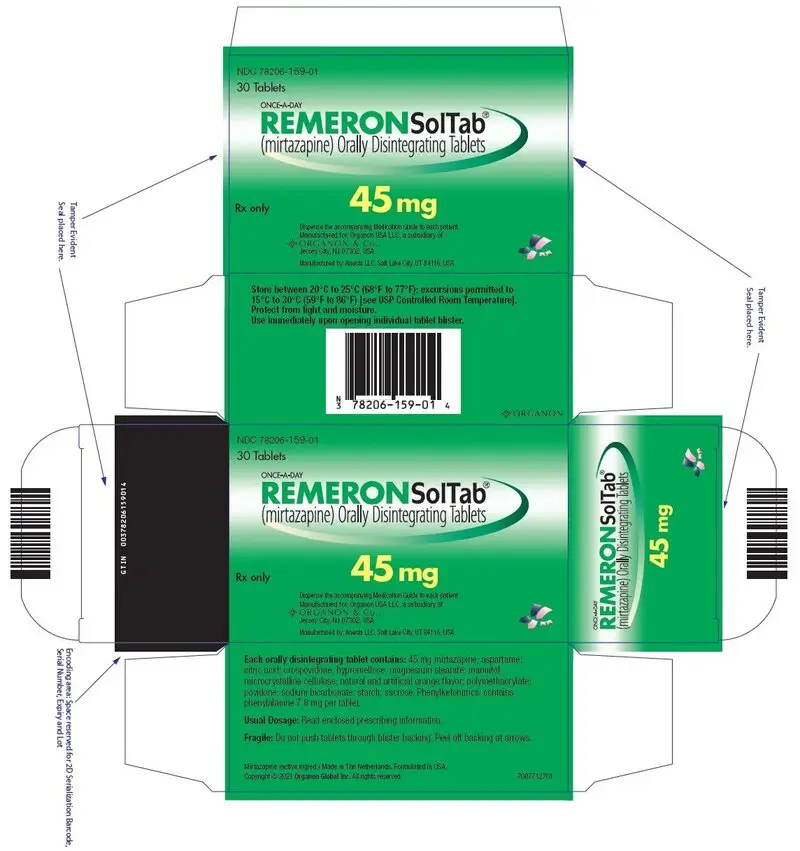
REMERONSolTab® (mirtazapine) orally disintegrating tablets
Initial U.S. Approval: 1996
WARNING: SUICIDAL THOUGHTS AND BEHAVIORS
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
Increased risk of suicidal thoughts and behavior in pediatric and young adult patients taking antidepressants. Closely monitor all antidepressant-treated patients for clinical worsening and emergence of suicidal thoughts and behaviors. REMERON/REMERONSolTab is not approved for use in pediatric patients. (5.1, 8.4)
Recent Major Changes
| Contraindications (4) | 11/2021 |
| Warnings and Precautions (5.6) | 11/2021 |
Indications and Usage for Remeron
REMERON/REMERONSolTab is indicated for the treatment of major depressive disorder (MDD) in adults. (1)
Remeron Dosage and Administration
- Starting dose: 15-mg once daily; may increase up to maximum recommended dose of 45 mg once daily. (2.1)
- Administer orally once daily, preferably in the evening prior to sleep. (2.1)
- Administer REMERONSolTab immediately after removal from blister pack. (2.2)
- Reduce dose gradually when discontinuing REMERON/REMERONSolTab. (2.6, 5.14)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
- Tablets: 15 mg scored and 30 mg scored. (3)
- Orally disintegrating tablets: 15 mg, 30 mg, and 45 mg. (3)
Contraindications
- Concomitant use of monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) or use within 14 days of stopping MAOIs. (2.4, 4, 7)
- Known hypersensitivity to mirtazapine or any of the excipients in REMERON/REMERONSolTab. (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Agranulocytosis: If sore throat, fever, stomatitis or signs of infection occur, along with a low white blood cell count, treatment with REMERON/REMERONSolTab should be discontinued and the patient should be closely monitored. (5.2)
- Serotonin Syndrome: Increased risk when co-administered with other serotonergic drugs (e.g., SSRI, SNRI, triptans), but also when taken alone. If it occurs, discontinue REMERON/REMERONSolTab and initiate supportive treatment. (2.4, 4, 5.3, 7)
- Angle-Closure Glaucoma: Angle closure glaucoma has occurred in patients with untreated anatomically narrow angles treated with antidepressants. (5.4)
- QT Prolongation: Use REMERON/REMERONSolTab with caution in patients with risk factors for QT prolongation. (5.5, 7)
- Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and System Symptoms (DRESS): Discontinue REMERON/REMERONSolTab if DRESS is suspected. (5.6)
- Increased Appetite/Weight Gain: REMERON/REMERONSolTab has been associated with increased appetite and weight gain. (5.7)
- Somnolence: May impair judgment, thinking and/or motor skills. Use with caution when engaging in activities requiring alertness, such as driving or operating machinery. (5.8, 7)
- Activation of Mania/Hypomania: Screen patients for bipolar disorder prior to initiating treatment. (2.3, 5.9)
- Seizures: Use with caution in patients with a seizure disorder. (5.10)
- Elevated Cholesterol/Triglycerides: Has been reported with REMERON use. (5.11)
- Hyponatremia: May occur as a result of treatment with serotonergic antidepressants, including REMERON/REMERONSolTab. (5.12)
- Transaminase Elevations: Clinically significant elevations have occurred. Use with caution in patients with impaired hepatic function. (5.13)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions (≥5% or greater and twice placebo) were somnolence, increased appetite, weight gain, and dizziness. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Organon USA LLC, a subsidiary of Organon & Co., at 1-844-674-3200 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
- Strong CYP3A inducers: Dosage increase may be needed for REMERON/REMERONSolTab with concomitant use of strong CYP3A inducers. (2.5, 7)
- Strong CYP3A inhibitors: Dosage decrease may be needed when REMERON/REMERONSolTab is coadministered with strong CYP3A inhibitors. (2.5, 7)
- Cimetidine: Dosage decrease may be needed when REMERON/REMERONSolTab is coadministered with cimetidine. (2.5, 7)
- Warfarin: Monitor INR during concomitant use. (7)
Use In Specific Populations
- Geriatric Use: Use with caution in elderly patients. (5.12, 5.15, 8.5)
- Renal impairment: Dosage decrease may be needed in patients with moderate to severe renal impairment. (8.6)
- Hepatic impairment: Dosage decrease may be needed in patients with hepatic impairment. (8.6)
- Patients with Phenylketonuria: REMERONSolTab contains phenylalanine. (5.16, 8.7)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 11/2021
Related/similar drugs
sertraline, trazodone, Lexapro, citalopram, Zoloft, Cymbalta, ProzacFull Prescribing Information
WARNING: SUICIDAL THOUGHTS AND BEHAVIORS
Antidepressants increased the risk of suicidal thoughts and behaviors in pediatric and young adult patients in short-term studies. Closely monitor all antidepressant-treated patients for clinical worsening, and for emergence of suicidal thoughts and behaviors [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. REMERON/REMERONSolTab is not approved for use in pediatric patients [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
1. Indications and Usage for Remeron
REMERON/REMERONSolTab are indicated for the treatment of major depressive disorder (MDD) in adults [see Clinical Studies (14)].
2. Remeron Dosage and Administration
2.1 Recommended Dosage
The recommended starting dose of REMERON/REMERONSolTab is 15 mg once daily, administered orally, preferably in the evening prior to sleep. If patients do not have an adequate response to the initial 15 mg dose, increase the dose up to a maximum of 45 mg per day. Dose changes should not be made in intervals of less than 1 to 2 weeks to allow sufficient time for evaluation of response to a given dose [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
2.2 Administration of REMERONSolTab
- The tablet should remain in the blister pack until the patient is ready to take it.
- The patient or caregiver should use dry hands to open the blister.
- As soon as the blister is opened, the tablet should be removed and placed on the patient's tongue.
- Use REMERONSolTab immediately after removal from its blister; once removed, it cannot be stored.
- The whole tablet should be placed on the tongue and allowed to disintegrate without chewing or crushing. Do not attempt to split the tablet.
- The tablet will disintegrate in saliva so that it can be swallowed.
2.3 Screen for Bipolar Disorder Prior to Starting REMERON/REMERONSolTab
Prior to initiating treatment with REMERON/REMERONSolTab or another antidepressant, screen patients for a personal or family history of bipolar disorder, mania, or hypomania [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)].
2.4 Switching Patients to or from a Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitor Antidepressant
At least 14 days must elapse between discontinuation of a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) antidepressant and initiation of REMERON/REMERONSolTab. In addition, at least 14 days must elapse after stopping REMERON/REMERONSolTab before starting an MAOI antidepressant [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
REMERON is supplied as:
- 15 mg tablets: Oval, scored, yellow, with "MSD" debossed on one side and "T3Z" on the other side, on both sides of the score line
- 30 mg tablets: Oval, scored, red-brown, with "MSD" debossed on one side and "T5Z" on the other side, on both sides of the score line
REMERONSolTab is supplied as:
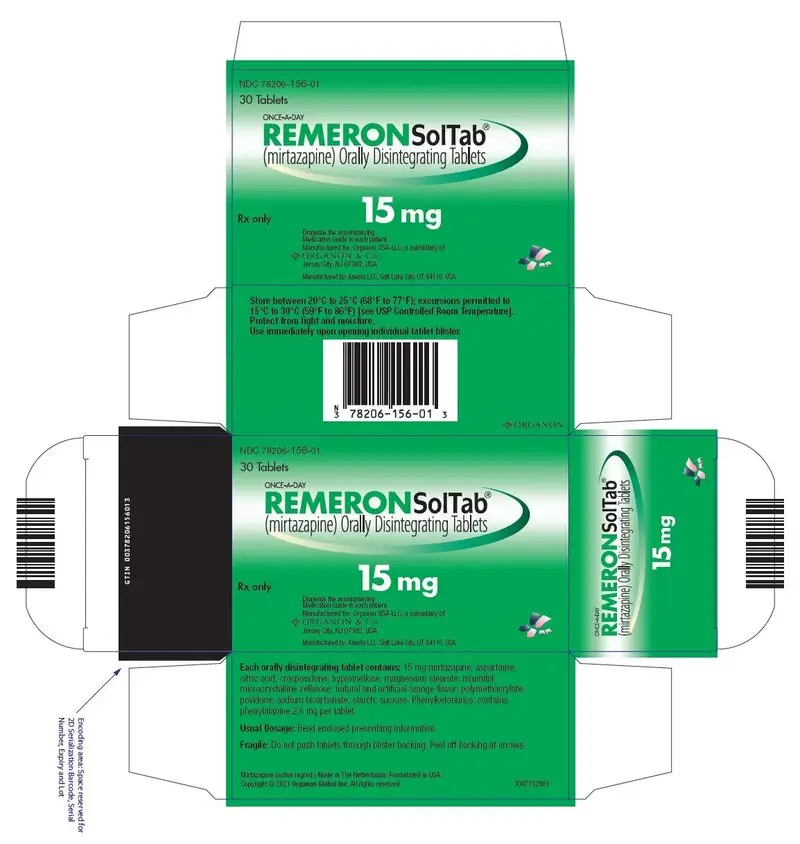
- 15 mg orally disintegrating tablets: Round, white, with "T1Z" debossed on one side
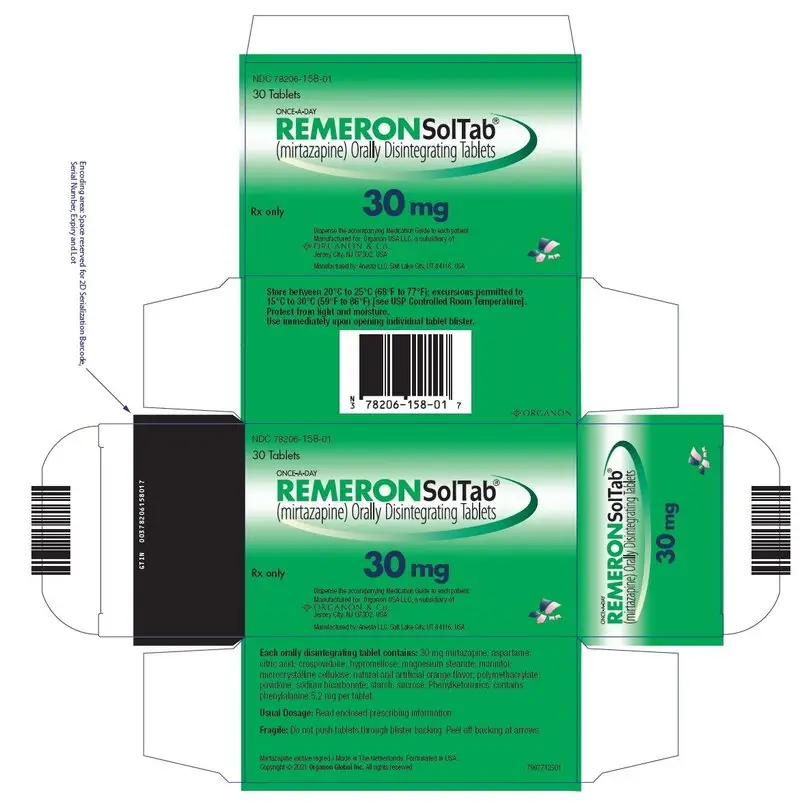
- 30 mg orally disintegrating tablets: Round, white, with "T2Z" debossed on one side
- 45 mg orally disintegrating tablets: Round, white, with "T4Z" debossed on one side
4. Contraindications
REMERON/REMERONSolTab is contraindicated in patients:
- Taking, or within 14 days of stopping, MAOIs (including the MAOIs linezolid and intravenous methylene blue) because of an increased risk of serotonin syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3), Drug Interactions (7)].
- With a known hypersensitivity to mirtazapine or to any of the excipients in REMERON/REMERONSolTab. Severe skin reactions, including drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS), Stevens-Johnson syndrome, bullous dermatitis, erythema multiforme and toxic epidermal necrolysis have been reported following the use of REMERON/REMERONSolTab [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6), Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Suicidal Thoughts and Behaviors in Adolescents and Young Adults
In pooled analyses of placebo-controlled trials of antidepressant drugs (SSRIs and other antidepressant classes) that included approximately 77,000 adult patients and 4,500 pediatric patients, the incidence of suicidal thoughts and behaviors in antidepressant-treated patients age 24 years and younger was greater than in placebo-treated patients. There was considerable variation in risk of suicidal thoughts and behaviors among drugs, but there was an increased risk identified in young patients for most drugs studied. There were differences in absolute risk of suicidal thoughts and behaviors across the different indications, with the highest incidence in patients with MDD. The drug-placebo differences in the number of cases of suicidal thoughts and behaviors per 1000 patients treated are provided in Table 1.
| Age Range | Drug-Placebo Difference in Number of Patients with Suicidal Thoughts or Behaviors per 1000 Patients Treated |
|---|---|
| Increases Compared to Placebo | |
| <18 years old | 14 additional patients |
| 18–24 years old | 5 additional patients |
| Decreases Compared to Placebo | |
| 25–64 years old | 1 fewer patient |
| ≥65 years old | 6 fewer patients |
It is unknown whether the risk of suicidal thoughts and behaviors in children, adolescents, and young adults extends to longer-term use, i.e., beyond four months. However, there is substantial evidence from placebo-controlled maintenance trials in adults with MDD that antidepressants delay the recurrence of depression and that depression itself is a risk factor for suicidal thoughts and behaviors.
Monitor all antidepressant-treated patients for any indication of clinical worsening and emergence of suicidal thoughts and behaviors, especially during the initial few months of drug therapy, and at times of dosage changes. Counsel family members or caregivers of patients to monitor for changes in behavior and to alert the healthcare provider. Consider changing the therapeutic regimen, including possibly discontinuing REMERON/REMERONSolTab, in patients whose depression is persistently worse, or who are experiencing emergent suicidal thoughts or behaviors.
5.2 Agranulocytosis
In premarketing clinical trials, 2 (1 with Sjögren's Syndrome) out of 2796 patients treated with REMERON developed agranulocytosis [absolute neutrophil count (ANC) <500/mm3 with associated signs and symptoms, e.g., fever, infection, etc.] and a third patient developed severe neutropenia (ANC <500/mm3 without any associated symptoms). For these 3 patients, onset of severe neutropenia was detected on days 61, 9, and 14 of treatment, respectively. All 3 patients recovered after REMERON was stopped. If a patient develops a sore throat, fever, stomatitis, or other signs of infection, along with a low white blood cell (WBC) count, treatment with REMERON/REMERONSolTab should be discontinued and the patient should be closely monitored.
5.3 Serotonin Syndrome
Serotonergic antidepressants, including REMERON/REMERONSolTab, can precipitate serotonin syndrome, a potentially life-threatening condition. The risk is increased with concomitant use of other serotonergic drugs (including triptans, tricyclic antidepressants, fentanyl, lithium, tramadol, tryptophan, buspirone, amphetamines, and St. John's Wort) and with drugs that impair metabolism of serotonin, i.e., MAOIs [see Contraindications (4), Drug Interactions (7)]. Serotonin syndrome can also occur when these drugs are used alone.
Serotonin syndrome signs and symptoms may include mental status changes (e.g., agitation, hallucinations, delirium, and coma), autonomic instability (e.g., tachycardia, labile blood pressure, dizziness, diaphoresis, flushing, hyperthermia), neuromuscular symptoms (e.g., tremor, rigidity, myoclonus, hyperreflexia, incoordination), seizures, and gastrointestinal symptoms (e.g., nausea, vomiting, diarrhea).
The concomitant use of REMERON/REMERONSolTab with MAOIs is contraindicated. In addition, do not initiate REMERON/REMERONSolTab in a patient being treated with MAOIs such as linezolid or intravenous methylene blue. No reports involved the administration of methylene blue by other routes (such as oral tablets or local tissue injection). If it is necessary to initiate treatment with an MAOI such as linezolid or intravenous methylene blue in a patient taking REMERON/REMERONSolTab, discontinue REMERON/REMERONSolTab before initiating treatment with the MAOI [see Contraindications (4), Drug Interactions (7)].
Monitor all patients taking REMERON/REMERONSolTab for the emergence of serotonin syndrome. Discontinue treatment with REMERON/REMERONSolTab and any concomitant serotonergic agents immediately if the above symptoms occur, and initiate supportive symptomatic treatment. If concomitant use of REMERON/REMERONSolTab with other serotonergic drugs is clinically warranted, inform patients of the increased risk for serotonin syndrome and monitor for symptoms.
5.4 Angle-Closure Glaucoma
The pupillary dilation that occurs following use of many antidepressant drugs, including REMERON/REMERONSolTab, may trigger an angle-closure attack in a patient with anatomically narrow angles who does not have a patent iridectomy.
5.5 QT Prolongation and Torsades de Pointes
The effect of REMERON (mirtazapine) on QTc interval was assessed in a clinical randomized trial with placebo and positive (moxifloxacin) controls involving 54 healthy volunteers using exposure response analysis. This trial showed a positive relationship between mirtazapine concentrations and prolongation of the QTc interval. However, the degree of QT prolongation observed with both 45 mg and 75 mg (1.67 times the maximum recommended daily dose) doses of mirtazapine was not at a level generally considered to be clinically meaningful. During postmarketing use of mirtazapine, cases of QT prolongation, Torsades de Pointes, ventricular tachycardia, and sudden death, have been reported [see Adverse Reactions (6.1, 6.2)]. The majority of reports occurred in association with overdose or in patients with other risk factors for QT prolongation, including concomitant use of QTc-prolonging medicines [see Drug Interactions (7) and Overdosage (10)]. Exercise caution when REMERON/REMERONSolTab is prescribed in patients with known cardiovascular disease or family history of QT prolongation, and in concomitant use with other drugs thought to prolong the QTc interval.
5.6 Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS)
Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) has been reported with postmarketing use of mirtazapine. DRESS may present with a cutaneous reaction (such as rash or exfoliative dermatitis), eosinophilia, fever, and/or lymphadenopathy with systemic complications such as hepatitis, nephritis, pneumonitis, myocarditis, and/or pericarditis. DRESS is sometimes fatal. Discontinue REMERON/REMERONSolTab immediately if DRESS is suspected and institute appropriate treatment [see Contraindications (4), Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
5.7 Increased Appetite and Weight Gain
In U.S. controlled clinical studies, appetite increase was reported in 17% of patients treated with REMERON, compared to 2% for placebo. In these same trials, weight gain of ≥7% of body weight was reported in 7.5% of patients treated with mirtazapine, compared to 0% for placebo. In a pool of premarketing U.S. clinical studies, including many patients for long-term, open-label treatment, 8% of patients receiving REMERON discontinued for weight gain.
In an 8-week-long pediatric clinical trial of doses between 15 to 45 mg/day, 49% of REMERON-treated pediatric patients had a weight gain of at least 7%, compared to 5.7% of placebo-treated patients. The safety and effectiveness of REMERON/REMERONSolTab in pediatric patients with MDD have not been established [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
5.8 Somnolence
In U.S. controlled studies, somnolence was reported in 54% of patients treated with REMERON, compared to 18% for placebo. In these studies, somnolence resulted in discontinuation for 10.4% of REMERON-treated patients, compared to 2.2% for placebo. It is unclear whether tolerance develops to the somnolent effects of REMERON/REMERONSolTab. Because of the potentially significant effects of REMERON/REMERONSolTab on impairment of performance, caution patients about engaging in activities that require alertness, including operating hazardous machinery and motor vehicles, until they are reasonably certain that REMERON/REMERONSolTab does not affect them adversely. The concomitant use of benzodiazepines and alcohol with REMERON/REMERONSolTab should be avoided [see Drug Interactions (7)].
5.9 Activation of Mania or Hypomania
In patients with bipolar disorder, treating a depressive episode with REMERON/REMERONSolTab or another antidepressant may precipitate a mixed/manic episode. In controlled clinical trials, patients with bipolar disorder were generally excluded; however, symptoms of mania or hypomania were reported in 0.2% of patients treated with REMERON. Prior to initiating treatment with REMERON/REMERONSolTab, screen patients for any personal or family history of bipolar disorder, mania, or hypomania.
5.10 Seizures
REMERON/REMERONSolTab has not been systematically evaluated in patients with seizure disorders. In premarketing clinical trials, 1 seizure was reported among the 2796 U.S. and non-U.S. patients treated with REMERON. REMERON/REMERONSolTab should be prescribed with caution in patients with a seizure disorder.
5.11 Elevated Cholesterol and Triglycerides
In U.S. controlled studies, nonfasting cholesterol increases to ≥20% above the upper limits of normal were observed in 15% of patients treated with REMERON, compared to 7% for placebo. In these same studies, nonfasting triglyceride increases to ≥500 mg/dL were observed in 6% of patients treated with REMERON, compared to 3% for placebo.
5.12 Hyponatremia
Hyponatremia may occur as a result of treatment with serotonergic antidepressants, including REMERON/REMERONSolTab. Cases with serum sodium lower than 110 mmol/L have been reported.
Signs and symptoms of hyponatremia include headache, difficulty concentrating, memory impairment, confusion, weakness, and unsteadiness, which may lead to falls. Signs and symptoms associated with more severe or acute cases have included hallucination, syncope, seizure, coma, respiratory arrest, and death. In many cases, this hyponatremia appears to be the result of the syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion (SIADH).
In patients with symptomatic hyponatremia, discontinue REMERON/REMERONSolTab and institute appropriate medical intervention. Elderly patients, patients taking diuretics, and those who are volume-depleted may be at greater risk of developing hyponatremia [see Use in Specific Populations (8.5)].
5.13 Transaminase Elevations
Clinically significant ALT (SGPT) elevations (≥3 times the upper limit of the normal range) were observed in 2.0% (8/424) of patients treated with REMERON in a pool of short-term, U.S. controlled trials, compared to 0.3% (1/328) of placebo patients. While some patients were discontinued for the ALT increases, in other cases, the enzyme levels returned to normal despite continued REMERON treatment. REMERON/REMERONSolTab should be used with caution in patients with impaired hepatic function [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
5.14 Discontinuation Syndrome
There have been reports of adverse reactions upon the discontinuation of REMERON/REMERONSolTab (particularly when abrupt), including but not limited to the following: dizziness, abnormal dreams, sensory disturbances (including paresthesia and electric shock sensations), agitation, anxiety, fatigue, confusion, headache, tremor, nausea, vomiting, and sweating, or other symptoms which may be of clinical significance.
A gradual reduction in the dosage, rather than an abrupt cessation, is recommended [see Dosage and Administration (2.6)].
5.15 Use in Patients with Concomitant Illness
REMERON/REMERONSolTab has not been systematically evaluated or used to any appreciable extent in patients with a recent history of myocardial infarction or other significant heart disease. REMERON was associated with significant orthostatic hypotension in early clinical pharmacology trials with normal volunteers. Orthostatic hypotension was infrequently observed in clinical trials with depressed patients [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. REMERON/REMERONSolTab should be used with caution in patients with known cardiovascular or cerebrovascular disease that could be exacerbated by hypotension (history of myocardial infarction, angina, or ischemic stroke) and conditions that would predispose patients to hypotension (dehydration, hypovolemia, and treatment with antihypertensive medication).
5.16 Risks in Patients with Phenylketonuria
Phenylalanine can be harmful to patients with phenylketonuria (PKU). REMERONSolTab contains phenylalanine, a component of aspartame. REMERONSolTab contains the following amount of phenylalanine: 2.6 mg in 15 mg orally disintegrating tablet, 5.2 mg in 30 mg orally disintegrating tablet, and 7.8 mg in 45 mg orally disintegrating tablet. Before prescribing REMERONSolTab to a patient with PKU, consider the combined daily amount of phenylalanine from all sources, including REMERONSolTab.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following adverse reactions are described in more detail in other sections of the prescribing information:
- Hypersensitivity [see Contraindications (4)]
- Suicidal Thoughts and Behaviors [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Agranulocytosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Serotonin Syndrome [see Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.3), Drug Interactions (7)]
- Angle-Closure Glaucoma [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- QT Prolongation and Torsades de Pointes [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Increased Appetite and Weight Gain [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- Somnolence [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
- Activation of Mania or Hypomania [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]
- Seizures [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)]
- Elevated Cholesterol and Triglycerides [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)]
- Hyponatremia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12)]
- Transaminase Elevations [see Warnings and Precautions (5.13)]
- Discontinuation Syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.14)]
- Use in Patients with Concomitant Illness [see Warnings and Precautions (5.15)]
6.1 Clinical Trial Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The data described below are from clinical trials in which REMERON/REMERONSolTab was administered to 2796 patients in phase 2 and 3 clinical studies. The trials consisted of double-blind controlled and open-label studies, inpatient and outpatient studies, fixed dose, and titration studies.
Adverse Reactions Leading to Discontinuation of Treatment
Approximately 16% of the 453 patients who received REMERON in U.S. 6-week placebo-controlled clinical trials discontinued treatment due to an adverse reaction, compared to 7% of the 361 placebo-treated patients in those studies. The most common reactions leading to discontinuation (≥1% and at a rate at least twice that of placebo) are included in Table 2.
| REMERON (n=453) | Placebo (n=361) |
|
|---|---|---|
| Somnolence | 10.4% | 2.2% |
| Nausea | 1.5% | 0% |
Common Adverse Reactions
The most common adverse reactions (≥5% and twice placebo) associated with the use of REMERON are listed in Table 3.
| REMERON (n=453) | Placebo (n=361) |
|
|---|---|---|
| Somnolence | 54% | 18% |
| Increased Appetite | 17% | 2% |
| Weight Gain | 12% | 2% |
| Dizziness | 7% | 3% |
Table 4 enumerates adverse reactions that occurred in ≥1% of REMERON-treated patients, and were more frequent than the placebo-treated patients, who participated in 6-week, U.S. placebo-controlled trials in which patients were dosed in a range of 5 to 60 mg/day. This table shows the percentage of patients in each group who had at least 1 episode of an adverse reaction at some time during their treatment.
| REMERON (n=453) | Placebo (n=361) |
|
|---|---|---|
| Body as a Whole | ||
| Asthenia | 8% | 5% |
| Flu Syndrome | 5% | 3% |
| Back Pain | 2% | 1% |
| Digestive System | ||
| Dry Mouth | 25% | 15% |
| Increased Appetite | 17% | 2% |
| Constipation | 13% | 7% |
| Metabolic and Nutritional Disorders | ||
| Weight Gain | 12% | 2% |
| Peripheral Edema | 2% | 1% |
| Edema | 1% | 0% |
| Musculoskeletal System | ||
| Myalgia | 2% | 1% |
| Nervous System | ||
| Somnolence | 54% | 18% |
| Dizziness | 7% | 3% |
| Abnormal Dreams | 4% | 1% |
| Thinking Abnormal | 3% | 1% |
| Tremor | 2% | 1% |
| Confusion | 2% | 0% |
| Respiratory System | ||
| Dyspnea | 1% | 0% |
| Urogenital System | ||
| Urinary Frequency | 2% | 1% |
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of REMERON. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Cardiac disorders: ventricular arrhythmia (Torsades de Pointes)
Endocrine disorders: hyperprolactinemia (and related symptoms, e.g., galactorrhea and gynecomastia)
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders: increased creatine kinase blood levels and rhabdomyolysis
Psychiatric disorders: somnambulism (ambulation and other complex behaviors out of bed)
Reproductive system and breast disorders: priapism
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: severe skin reactions, including DRESS, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, bullous dermatitis, erythema multiforme and toxic epidermal necrolysis
7. Drug Interactions
Table 5 includes clinically important drug interactions with REMERON/REMERONSolTab [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
| Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs) | |
| Clinical Impact | The concomitant use of serotonergic drugs, including REMERON/REMERONSolTab, and MAOIs increases the risk of serotonin syndrome. |
| Intervention | REMERON/REMERONSolTab is contraindicated in patients taking MAOIs, including MAOIs such as linezolid or intravenous methylene blue [see Dosage and Administration (2.4), Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]. |
| Examples | selegiline, tranylcypromine, isocarboxazid, phenelzine, linezolid, methylene blue |
| Other Serotonergic Drugs | |
| Clinical Impact | The concomitant use of serotonergic drugs with REMERON/REMERONSolTab increases the risk of serotonin syndrome. |
| Intervention | Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of serotonin syndrome, particularly during treatment initiation and dosage increases. If serotonin syndrome occurs, consider discontinuation of REMERON/REMERONSolTab and/or concomitant serotonergic drugs [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]. |
| Examples | SSRIs, SNRIs, triptans, tricyclic antidepressants, fentanyl, lithium, amphetamines, St. John's Wort, tramadol, tryptophan, buspirone |
| Strong CYP3A Inducers | |
| Clinical Impact | The concomitant use of strong CYP3A inducers with REMERON/REMERONSolTab decreases the plasma concentration of mirtazapine [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. |
| Intervention | Increase the dose of REMERON/REMERONSolTab if needed with concomitant CYP3A inducer use. Conversely, a decrease in dosage of REMERON/REMERONSolTab may be needed if the CYP3A inducer is discontinued [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)]. |
| Examples | phenytoin, carbamazepine, rifampin |
| Strong CYP3A Inhibitors | |
| Clinical Impact | The concomitant use of strong CYP3A inhibitors with REMERON/REMERONSolTab may increase the plasma concentration of mirtazapine [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. |
| Intervention | Decrease the dose of REMERON/REMERONSolTab if needed with concomitant strong CYP3A inhibitor use. Conversely, an increase in dosage of REMERON/REMERONSolTab may be needed if the CYP3A inhibitor is discontinued [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)]. |
| Examples | itraconazole, ritonavir, nefazodone |
| Cimetidine | |
| Clinical Impact | The concomitant use of cimetidine, a CYP1A2, CYP2D6, and CYP3A inhibitor, with REMERON/REMERONSolTab may increase the plasma concentration of mirtazapine [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. |
| Intervention | Decrease the dose of REMERON/REMERONSolTab if needed with concomitant cimetidine use. Conversely, an increase in dosage of REMERON/REMERONSolTab may be needed if cimetidine is discontinued [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)]. |
| Benzodiazepines and Alcohol | |
| Clinical Impact | The concomitant use of benzodiazepines or alcohol with REMERON/REMERONSolTab increases the impairment of cognitive and motor skills produced by REMERON/REMERONSolTab alone. |
| Intervention | Avoid concomitant use of benzodiazepines and alcohol with REMERON/REMERONSolTab [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. |
| Examples | diazepam, alprazolam, alcohol |
| Drugs that Prolong QTc Interval | |
| Clinical Impact | The concomitant use of other drugs which prolong the QTc interval with REMERON/REMERONSolTab, increase the risk of QT prolongation and/or ventricular arrhythmias (e.g., Torsades de Pointes). |
| Intervention | Use caution when using REMERON/REMERONSolTab concomitantly with drugs that prolong the QTc interval [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. |
| Warfarin | |
| Clinical Impact | The concomitant use of warfarin with REMERON/REMERONSolTab may result in an increase in INR [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. |
| Intervention | Monitor INR during concomitant use of warfarin with REMERON/REMERONSolTab. |
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Exposure Registry
There is a pregnancy exposure registry that monitors pregnancy outcomes in women exposed to antidepressants during pregnancy. Healthcare providers are encouraged to register patients by calling the National Pregnancy Registry for Antidepressants at 1-844-405-6185 or visiting online at https://womensmentalhealth.org/clinical-and-research-programs/pregnancyregistry/antidepressants/.
Risk Summary
Prolonged experience with mirtazapine in pregnant women, based on published observational studies and postmarketing reports, has not reliably identified a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. There are risks associated with untreated depression in pregnancy (see Clinical Considerations).
In animal reproduction studies, oral administration of mirtazapine to pregnant rats and rabbits during the period of organogenesis revealed no evidence of teratogenic effects up to 20 and 17 times the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 45 mg, respectively, based on mg/m2 body surface area. However, in rats, there was an increase in postimplantation loss at 20 times the MRHD based on mg/m2 body surface area. Oral administration of mirtazapine to pregnant rats during pregnancy and lactation resulted in an increase in pup deaths and a decrease in pup birth weights at doses 20 times the MRHD based on mg/m2 body surface area (see Data).
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4% and 15 to 20%, respectively.
Disease-Associated Maternal and/or Embryo/Fetal Risk
Women who discontinue antidepressants during pregnancy are more likely to experience a relapse of major depression than women who continue antidepressants. This finding is from a prospective, longitudinal study that followed 201 pregnant women with a history of major depressive disorder who were euthymic and taking antidepressants at the beginning of pregnancy. Consider the risk of untreated depression when discontinuing or changing treatment with antidepressant medication during pregnancy and postpartum.
Animal Data
Mirtazapine was administered orally to pregnant rats and rabbits during the period of organogenesis at doses of 2.5, 15, and 100 mg/kg/day and 2.5, 10, and 40 mg/kg/day, respectively, which are up to 20 and 17 times the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 45 mg based on mg/m2 body surface area, respectively. No evidence of teratogenic effects was observed. However, in rats, there was an increase in postimplantation loss in dams treated with mirtazapine at 100 mg/kg/day which is 20 times the MRHD based on mg/m2 body surface area. Oral administration of mirtazapine at doses of 2.5, 15, and 100 mg/kg/day to pregnant rats during pregnancy and lactation resulted in an increase in pup deaths during the first 3 days of lactation and a decrease in pup birth weights at 20 times the MRHD based on mg/m2 body surface area. The cause of these deaths is not known. The no effect dose level is 3 times the MRHD based on mg/m2 body surface area.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
Data from published literature report the presence of mirtazapine in human milk at low levels with relative infant doses for mirtazapine ranging between 0.6 and 2.8% of the maternal weight-adjusted dose (see Data). No adverse effects on the breastfed infant have been reported in most cases of maternal use of mirtazapine. There are no data on the effects of mirtazapine on milk production.
The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for mirtazapine and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from mirtazapine or from the underlying maternal condition.
In a published pooled analysis of 8 breastfeeding mother-infant pairs, the mean (min, max) total relative infant doses for mirtazapine and its desmethyl metabolite were 1.5% (0.6%, 2.8%) and 0.4% (0.1%, 0.7%) of the maternal weight-adjusted dose (median (min, max) dose of 38 mg (30 mg, 120 mg), respectively). No adverse drug effects were reported for any of the infants.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of REMERON/REMERONSolTab have not been established in pediatric patients with MDD. Two placebo-controlled trials in 258 pediatric patients with MDD have been conducted with REMERON, and the data were insufficient to establish the safety and effectiveness of REMERON/REMERONSolTab in pediatric patients with MDD.
Antidepressants increased the risk of suicidal thoughts and behaviors in pediatric patients [see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
In an 8-week-long clinical trial in pediatric patients receiving doses between 15 to 45 mg per day, 49% of REMERON-treated patients had a weight gain of at least 7%, compared to 5.7% of placebo-treated patients. The mean increase in weight was 4 kg (2 kg SD) for REMERON-treated patients versus 1 kg (2 kg SD) for placebo-treated patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
8.5 Geriatric Use
Approximately 190 patients ≥65 years of age participated in clinical studies with REMERON. REMERON/REMERONSolTab is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney (75%), and the risk of decreased clearance of this drug is greater in patients with impaired renal function. Pharmacokinetic studies revealed a decreased clearance of mirtazapine in the elderly [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Sedating drugs, including REMERON/REMERONSolTab, may cause confusion and over-sedation in the elderly. Elderly patients may be at greater risk of developing hyponatremia. Caution is indicated when administering REMERON/REMERONSolTab to elderly patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12), (5.15) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be conservative, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
8.6 Renal or Hepatic Impairment
The clearance of mirtazapine is reduced in patients with moderate to severe renal or hepatic impairment. Consequently, plasma mirtazapine levels may be increased in these patient groups, compared to levels observed in patients without renal or hepatic impairment. Dosage decrease may be necessary when administering REMERON/REMERONSolTab to patients with moderate to severe renal or hepatic impairment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.13), Use in Specific Populations (8.5), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.7 Patients with Phenylketonuria
REMERONSolTab contains phenylalanine, a component of aspartame. REMERONSolTab contains the following amount of phenylalanine: 2.6 mg in 15 mg orally disintegrating tablet, 5.2 mg in 30 mg orally disintegrating tablet, and 7.8 mg in 45 mg orally disintegrating tablet [see Warnings and Precautions (5.16)].
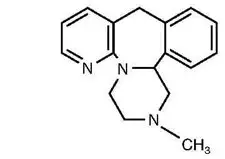
11. Remeron Description
REMERON and REMERONSolTab contain mirtazapine. Mirtazapine has a tetracyclic chemical structure and belongs to the piperazino-azepine group of compounds. It is designated 1,2,3,4,10,14b-hexahydro-2-methylpyrazino [2,1-a] pyrido [2,3-c][2] benzazepine and has the empirical formula of C17H19N3. Its molecular weight is 265.35. The structural formula is the following and it is the racemic mixture:
Mirtazapine is a white to creamy white crystalline powder which is practically insoluble in water.
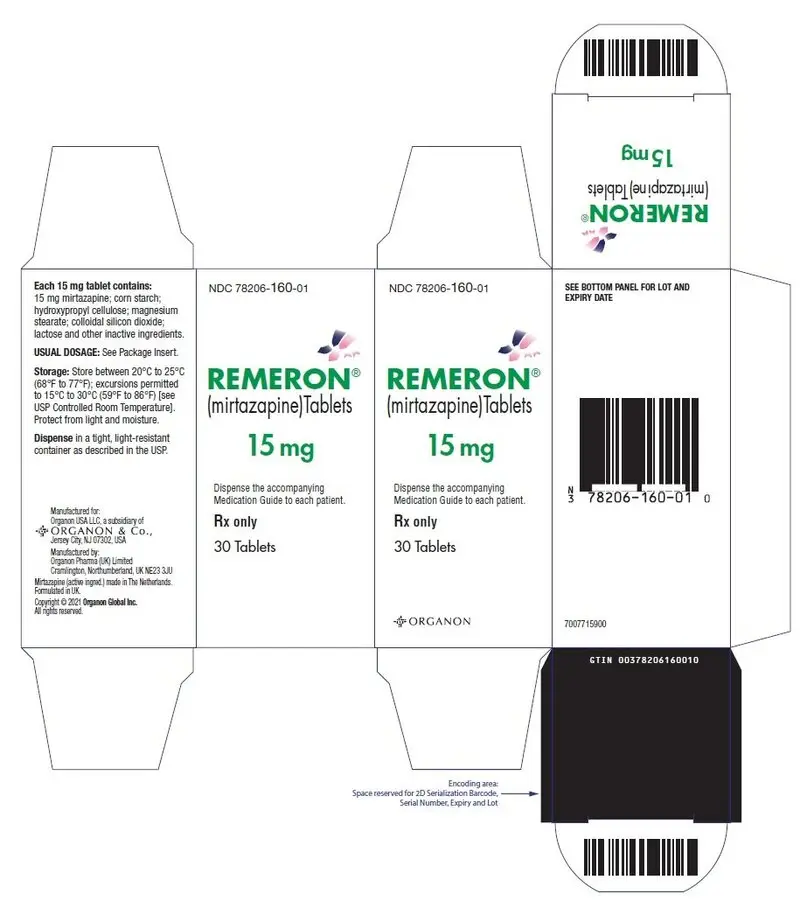
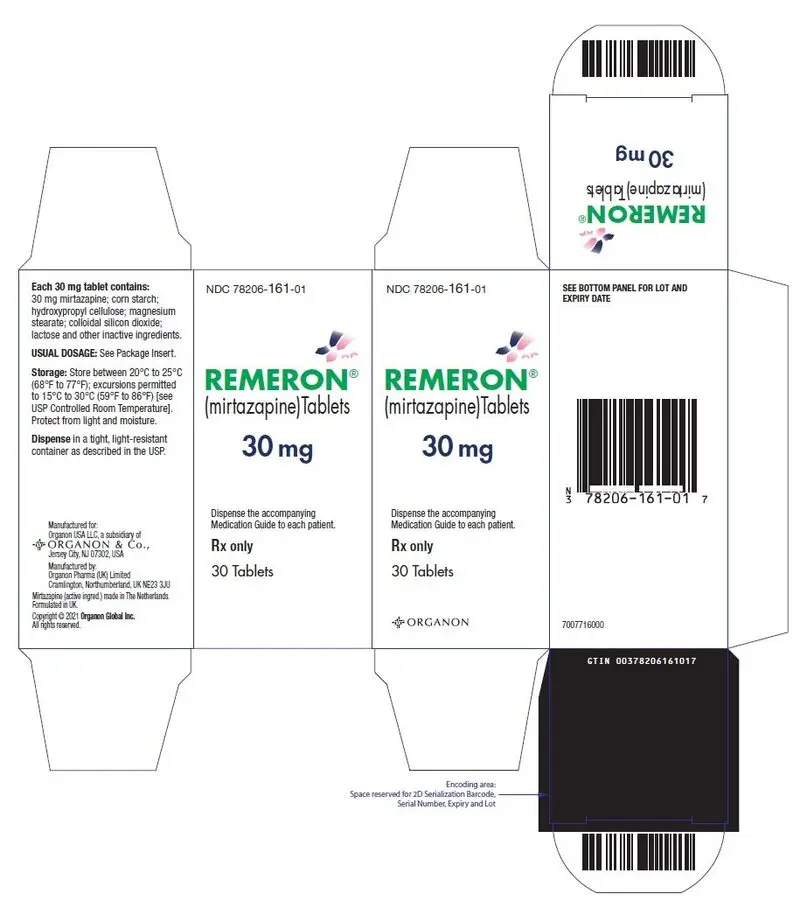
REMERON is available for oral administration as scored film-coated tablets containing 15 or 30 mg of mirtazapine Each tablet contains the following inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide anhydrous, corn starch, ferric oxide (yellow), hydroxypropyl cellulose, hypromellose, magnesium stearate, lactose monohydrate, polyethylene glycol 8000, and titanium dioxide. The 30 mg tablets also contain ferric oxide (red).
REMERONSolTab is available for oral administration as an orally disintegrating tablet containing 15, 30, or 45 mg of mirtazapine. REMERONSolTab also contains the following inactive ingredients: aspartame, citric acid anhydrous fine granular, crospovidone, hypromellose, magnesium stearate, mannitol, granular mannitol 2080, microcrystalline cellulose, natural and artificial orange flavor, polymethacrylate (Eudragit E100), povidone, sodium bicarbonate, and sugar spheres (composed of starch and sucrose).
12. Remeron - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
The mechanism of action of mirtazapine for the treatment of major depressive disorder, is unclear. However, its efficacy could be mediated through its activity as an antagonist at central presynaptic α2-adrenergic inhibitory autoreceptors and heteroreceptors and enhancing central noradrenergic and serotonergic activity.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
In preclinical studies, mirtazapine acts as an antagonist at α2-adrenergic inhibitory autoreceptors and heteroreceptors and as an antagonist at serotonin 5-HT2 and 5-HT3 receptors. Mirtazapine has no significant affinity for the 5-HT1A and 5-HT1B receptors.
Mirtazapine also acts as an antagonist of histamine (H1) receptors, peripheral α1-adrenergic receptors, and muscarinic receptors. Actions at these receptors may explain some of the other clinical effects of mirtazapine (e.g., its prominent somnolent effects and orthostatic hypotension may be explained by its inhibition of histamine (H1) receptors and peripheral α1-adrenergic receptors, respectively).
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Plasma levels of mirtazapine are linearly related to dose over a dose range of 15 to 80 mg (1.78 times the maximum recommended dose). Steady state plasma levels of mirtazapine are attained within 5 days, with about 50% accumulation (accumulation ratio=1.5). The (–) enantiomer has an elimination half-life that is approximately twice as long as the (+) enantiomer and therefore achieves plasma levels that are about 3 times as high as that of the (+) enantiomer.
14. Clinical Studies
The efficacy of REMERON as a treatment for major depressive disorder was established in 4 placebo-controlled, 6-week trials in adult outpatients meeting DSM-III criteria for major depressive disorder. Patients were titrated with REMERON from a dose range of 5 mg to 35 mg/day. The mean mirtazapine dose for patients who completed these 4 studies ranged from 21 to 32 mg/day. Overall, these studies demonstrated REMERON to be superior to placebo on at least 3 of the following 4 measures: 21-Item Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HDRS) total score; HDRS Depressed Mood Item; CGI Severity score; and Montgomery and Asberg Depression Rating Scale (MADRS). Superiority of REMERON over placebo was also found for certain factors of the HDRS, including anxiety/somatization factor and sleep disturbance factor.
Examination of age and gender subsets of the population did not reveal any differential responsiveness on the basis of these subgroupings.
In a longer-term study, patients meeting (DSM-IV) criteria for major depressive disorder who had responded during an initial 8 to 12 weeks of acute treatment on REMERON were randomized to continuation of REMERON or placebo for up to 40 weeks of observation for relapse. Response during the open phase was defined as having achieved a HAM-D 17 total score of ≤8 and a CGI-Improvement score of 1 or 2 at 2 consecutive visits beginning with week 6 of the 8 to 12 weeks in the open-label phase of the study. Relapse during the double-blind phase was determined by the individual investigators. Patients receiving continued REMERON treatment experienced significantly lower relapse rates over the subsequent 40 weeks compared to those receiving placebo. This pattern was demonstrated in both male and female patients.
16. How is Remeron supplied
REMERON tablets are supplied as:
| Tablet Strength | Tablet Color/Shape | Tablet Markings | Package Configuration | NDC Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 mg | Yellow, oval tablet | Scored with "MSD" debossed on one side and "T3Z" on other side, on both sides of score line | Bottle / 30 count | 78206-160-01 |
| 30 mg | Red-brown, oval tablet | Scored with "MSD" debossed on one side and "T5Z" on other side, on both sides of score line | Bottle / 30 count | 78206-161-01 |
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide).
| MEDICATION GUIDE REMERON® (rĕm' - ĕ – rŏn) (mirtazapine) tablets, for oral use REMERONSolTab® (rĕm' - ĕ - rŏn - sŏl' – tăb) (mirtazapine) orally disintegrating tablets, for oral use |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration | Revised: 11/2021 | ||||
| What is the most important information I should know about REMERON and REMERONSolTab? | |||||
REMERON and REMERONSolTab may cause serious side effects, including:
|
|||||
|
|
||||
| What is REMERON and REMERONSolTab? | |||||
| REMERON and REMERONSolTab are prescription medicines used to treat a certain type of depression called Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) in adults. | |||||
| It is not known if REMERON and REMERONSolTab are safe and effective for use to treat MDD in children. | |||||
| Who should not take REMERON and REMERONSolTab? | |||||
Do not take REMERON or REMERONSolTab if you:
|
|||||
| Ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist if you are not sure if you take an MAOI, including the antibiotic linezolid or intravenous methylene blue. | |||||
| Do not start taking an MAOI for at least 14 days after you stop treatment with REMERON or REMERONSolTab. | |||||
Before taking REMERON or REMERONSolTab, tell your healthcare provider about all your medical conditions, including if you:
|
|||||
| Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. | |||||
| REMERON and REMERONSolTab and other medicines may affect each other causing possible serious side effects. | |||||
| REMERON and REMERONSolTab may affect the way other medicines work and other medicines may affect the way REMERON and REMERONSolTab work. | |||||
Especially tell your healthcare provider if you take:
|
|||||
| Ask your healthcare provider if you are not sure if you are taking any of these medicines. Your healthcare provider can tell you if it is safe to take REMERON and REMERONSolTab with your other medicines. | |||||
| Do not start or stop any other medicines during treatment with REMERON or REMERONSolTab without talking to your healthcare provider first. Stopping REMERON or REMERONSolTab suddenly may cause you to have serious side effects. See, "What are the possible side effects of REMERON and REMERONSolTab?" | |||||
| Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them to show to your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medicine. | |||||
How should I take REMERON or REMERONSolTab?
|
|||||
How to take REMERONSolTab:
|
|||||
What should I avoid while taking REMERON and REMERONSolTab?
|
|||||
| What are the possible side effects of REMERON and REMERONSolTab? | |||||
REMERON and REMERONSolTab may cause serious side effects, including:
|
|||||
|
|
||||
|
|||||
|
|
||||
|
|||||
|
|
||||
|
|||||
|
|
||||
| In severe or more sudden cases, signs and symptoms include: | |||||
|
| ||||
|
|||||
|
|
|
|||
The most common side effects of REMERON and REMERONSolTab include:
|
|||||
| These are not all the possible side effects of REMERON and REMERONSolTab. | |||||
| Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. | |||||
How should I store REMERON and REMERONSolTab?
|
|||||
| Keep REMERON, REMERONSolTab, and all medicines out of the reach of children. | |||||
| General information about the safe and effective use of REMERON and REMERONSolTab. | |||||
| Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use REMERON and REMERONSolTab for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give REMERON and REMERONSolTab to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. You can ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for information about REMERON and REMERONSolTab that is written for healthcare professionals. | |||||
| What are the ingredients in REMERON and REMERONSolTab? | |||||
| Active ingredient: mirtazapine | |||||
| Inactive ingredients: | |||||
| REMERON Tablets: Colloidal silicon dioxide anhydrous, corn starch, ferric oxide (yellow), hydroxypropyl cellulose, hypromellose, polyethylene glycol 8000, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, and titanium dioxide. The 30 mg tablets also contain ferric oxide (red). | |||||
| REMERONSolTab: Aspartame, citric acid anhydrous fine granular, crospovidone, hypromellose, magnesium stearate, mannitol, granular mannitol 2080, microcrystalline cellulose, natural and artificial orange flavor, polymethacrylate (Eudragit E100), povidone, sodium bicarbonate, sugar spheres (made of starch and sucrose). | |||||
| Distributed by: Organon USA LLC, a subsidiary of ORGANON & Co., Jersey City, NJ 07302, USA |
|||||
| For patent information: www.organon.com/our-solutions/patent/ © 2021 Organon group of companies. All rights reserved. For more information about REMERON/REMERONSolTab call 1-844-674-3200. |
|||||
| usmg-og8246-t-tod-2111r001 | |||||
| REMERON
mirtazapine tablet, film coated |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| REMERON
mirtazapine tablet, film coated |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| REMERONSOLTAB
mirtazapine tablet, orally disintegrating |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| REMERONSOLTAB
mirtazapine tablet, orally disintegrating |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| REMERONSOLTAB
mirtazapine tablet, orally disintegrating |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Organon LLC (117494753) |