Drug Detail:Ryplazim ( plasminogen, human-tvmh)
Drug Class: Miscellaneous uncategorized agents
Highlights of Prescribing Information
RYPLAZIM® (plasminogen, human-tvmh)
lyophilized powder for reconstitution, for intravenous use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2021
Indications and Usage for Ryplazim
RYPLAZIM® (plasminogen, human-tvmh) is plasma-derived human plasminogen indicated for the treatment of patients with plasminogen deficiency type 1 (hypoplasminogenemia). (1)
Ryplazim Dosage and Administration
For intravenous use after reconstitution only.
The recommended dosage of RYPLAZIM is 6.6 mg/kg body weight given every 2 to 4 days. (2.1)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
RYPLAZIM is available in a single-dose 50-mL vial containing 68.8 mg of plasminogen as a lyophilized powder for reconstitution with 12.5 mL of Sterile Water for Injection, USP (SWFI). After reconstitution, each vial will contain 5.5 mg/mL of plasminogen. (3)
Contraindications
RYPLAZIM is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to plasminogen, or other components of RYPLAZIM. (4) (11)
Warnings and Precautions
- Bleeding: RYPLAZIM administration may lead to bleeding at lesion sites or worsen active bleeding. Discontinue RYPLAZIM if serious bleeding occurs. Monitor patients during and for 4 hours after infusion when administering RYPLAZIM to patients with bleeding diatheses and patients taking anticoagulants, antiplatelet drugs, and other agents which may interfere with normal coagulation. (5.1)
- Tissue Sloughing: Respiratory distress due to tissue sloughing may occur in patients with mucosal lesions in the tracheobronchial tree following RYPLAZIM administration. Please monitor appropriately. (5.2)
- Transmission of Infectious Agents: RYPLAZIM is made from human blood and therefore carries a risk of transmitting infectious agents, e.g., viruses, the variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (vCJD) agent, and theoretically, the Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease (CJD) agent. (5.3)
- Hypersensitivity Reactions: Hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, may occur with RYPLAZIM. If symptoms occur, discontinue RYPLAZIM and administer appropriate treatment. (5.4)
- Neutralizing Antibodies: Neutralizing antibodies (inhibitors) may develop, although were not observed in clinical trials. If clinical efficacy is not maintained (e.g., development of new or recurrent lesions), then determine plasminogen activity levels in plasma. (5.5)
- Laboratory Abnormalities: Patients receiving RYPLAZIM may have elevated blood levels of D-dimer. D-dimer levels will lack interpretability in patients being screened for venous thromboembolism (VTE). (5.6)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The most frequent (incidence ≥ 10%) adverse reactions in clinical trials were abdominal pain, bloating, nausea, fatigue, extremity pain, hemorrhage, constipation, dry mouth, headache, dizziness, arthralgia, and back pain. (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Prometic at +1(855)-353-7466 and [email protected] or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 6/2023
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Ryplazim
RYPLAZIM® (plasminogen, human-tvmh) is plasma-derived human plasminogen indicated for the treatment of patients with plasminogen deficiency type 1 (hypoplasminogenemia).
2. Ryplazim Dosage and Administration
For intravenous use after reconstitution only.
2.2 Preparation and Reconstitution
Prepare RYPLAZIM within 3 hours of administration. Gather the following additional supplies before performing reconstitution and administration:
- One 20-mL syringe per vial of RYPLAZIM for product reconstitution
- 18- to 22-gauge needles for reconstitution and administration
- Sterile Water for Injection, USP (SWFI) (10-mL, 20-mL or 50-mL vials)
- One syringe disc filter per infusion (Baxter Supor® 5micron Syringe Filter or equivalent)
- One (or more) administration syringe(s) (20-mL, 30-mL or 60-mL)
- Alcohol wipes
- Antiseptic surface wipes
- Medical tape
- Butterfly needle or sterile infusion set
- 10 mL normal saline
- Sterile gauze pad
- Bandage
2.3 Administration
For intravenous use only through a syringe disc filter.
Follow the steps below for infusion:
- One filter is needed per infusion.
- Only administer RYPLAZIM by infusing it into a vein through a syringe disc filter.
- Inspect the solution in the syringe. Do not use if discoloration or particulate matter are observed.
- Administer RYPLAZIM by a separate infusion line. Do not administer RYPLAZIM with other medications.
- Draw 10 mL of normal saline into a different syringe. Push the plunger down to remove any air bubbles.
- Attach a syringe disc filter to the pre-filled syringe of normal saline (from previous step) and the infusion tubing with the butterfly needle. (Figure 3)
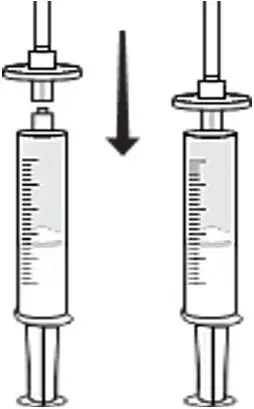
Figure 3
- Inject the normal saline through the syringe disc filter and butterfly needle tubing to remove any air bubbles.
- Remove the normal saline syringe. The syringe disc filter must remain attached to the tubing, as it is required for administration of the RYPLAZIM. Discard the normal saline syringe.
- Attach the administration syringe containing RYPLAZIM to the syringe disc filter that is connected to the butterfly needle tubing.
- Choose a peripheral vein (e.g., antecubital or dorsum of hand). Clean the injection site with a sterile alcohol wipe and allow to dry. Do not blow on it.
- Insert the butterfly infusion set needle in the peripheral vein, and tape in place.
- Infuse the total dose of RYPLAZIM slowly over 10-30 minutes (approximately 5 mL/min). Using a timer (e.g., watch or clock), push the plunger of the syringe approximately 1 mL every 12 seconds. (Figure 4)
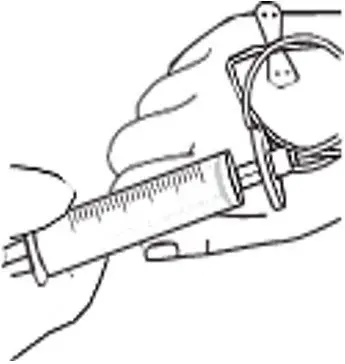
Figure 4
- Discard any open vials, unused solution, and administration equipment following administration.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
RYPLAZIM is available in a single-dose 50 mL vial containing 68.8 mg of plasminogen as a lyophilized powder for reconstitution with 12.5 mL of sterile water for injection (SWFI). After reconstitution, each vial will contain 5.5 mg/mL of plasminogen in a colorless and clear to slightly opalescent solution.
4. Contraindications
RYPLAZIM is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to plasminogen or other components of RYPLAZIM [See Hypersensitivity Reactions (5.4)].
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Bleeding
Patients with plasminogen deficiency type 1 may bleed from active mucosal disease-related lesions during RYPLAZIM therapy. Depending on the lesion sites, this may manifest as gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding, hemoptysis, epistaxis, vaginal bleeding, or hematuria.
RYPLAZIM may worsen active bleeding not related to disease lesions. One patient with a recent history of GI bleeding due to gastric ulcers experienced GI bleeding two days after receiving the second dose of RYPLAZIM. The patient received RYPLAZIM through a compassionate use program and the dose was 6.6 mg/kg body weight every 2 days. Endoscopy showed multiple ulcers with one actively bleeding ulcer near the pylorus. Given the mechanism of action of plasminogen in fibrinolysis, it is possible that RYPLAZIM played a role in either prolonging or worsening the active bleeding. RYPLAZIM has not been studied in patients at increased risk for bleeding due to disease or injury.
Prior to initiation of treatment with RYPLAZIM, confirm healing of lesions or wounds suspected as a source of a recent bleeding event. RYPLAZIM may prolong or worsen bleeding in patients with bleeding diatheses or in patients taking anticoagulants and/or antiplatelet drugs and other agents which may interfere with normal coagulation. Monitor patients during and for 4 hours after infusion when administering RYPLAZIM to patients with bleeding diatheses and patients taking anticoagulants, antiplatelet drugs, or other agents which may interfere with normal coagulation. If a patient develops uncontrolled bleeding (defined as any gastrointestinal bleeding or bleeding from any other site that persists longer than 30 minutes), seek emergency care and discontinue RYPLAZIM immediately.
5.2 Tissue Sloughing
Tissue sloughing at mucosal sites may occur after initiation of treatment with RYPLAZIM as plasminogen activity levels are restored to physiological levels and fibrinolysis occurs. Lesions in the respiratory, gastrointestinal and genitourinary systems may slough following treatment resulting in bleeding or organ obstruction. Patients with tracheobronchial lesions may develop airway obstruction or hemoptysis. Closely monitor patients with either confirmed or suspected airway disease as manifested by cough, wheezing, shortness of breath, or changes in speech (dysphonia). Initiate the treatment with RYPLAZIM in an appropriate clinical setting with personnel trained in airway management and readily-available respiratory support equipment. Monitor at-risk patients in such a settting for a minimum of 4 hours after receiving their first dose of RYPLAZIM.
Patients with gastrointestinal and genitourinary lesions may experience tissue sloughing that causes pain, bleeding, or passage of tissue from affected organ systems. Patients should report persistent abdominal, flank, or pelvic pain to their physicians.
5.3 Transmission of Infectious Agents
Because RYPLAZIM is derived from human plasma, it carries a risk of transmitting infectious agents. Based on effective donor screening and product manufacturing processes, RYPLAZIM carries a remote risk for transmission of viral diseases and variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (vCJD). There is a theoretical risk for transmission of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD), but if that risk actually exists, the risk of transmission would also be considered extremely low. It is also possible that unknown infectious agents may be present in RYPLAZIM. The risk of infectious agent transmission has been reduced by screening plasma donors for prior exposure to certain viruses, testing for the presence of certain current virus infections, and including virus inactivation/removal steps in the manufacturing process for RYPLAZIM [see Description (11)].
Report any infection thought to be possibly transmitted by RYPLAZIM to Prometic at +1(855)-353-7466 and [email protected] or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
5.4 Hypersensitivity Reactions
Hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, may occur with RYPLAZIM [see Contraindications (4)]. In case of a hypersensitivity reaction, discontinue RYPLAZIM immediately and treat according to standard medical practice.
5.5 Neutralizing Antibodies
Formation of neutralizing antibodies (inhibitors) to plasminogen following the administration of RYPLAZIM has not been reported to date [See Immunogenicity (6.2)]. Monitor patients for the loss of clinical efficacy as manifested by the development of new or recurrent lesions while on RYPLAZIM therapy, and obtain plasminogen activity trough levels to confirm that adequate plasminogen activity levels have been achieved and are being maintained [see Dosage and Administration (2)].
5.6 Laboratory Abnormalities
Patients receiving RYPLAZIM may have elevated levels of D-dimer in blood. Intepret D-dimer levels with caution in patients being screened for venous thromboembolism (VTE), as elevated levels may be associated with the physiological activity of RYPLAZIM (fibrinolysis of ligneous lesions) and not indicative of VTE. Consider other tests to screen for VTE in patients receiving RYPLAZIM, as D-dimer levels will lack interpretability.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The most frequent (incidence ≥ 10%) adverse reactions were abdominal pain, bloating, nausea, fatigue, extremity pain, hemorrhage, constipation, dry mouth, headache, dizziness, arthralgia, and back pain.
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
As clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
The safety data described in this section reflect exposure to RYPLAZIM in two single-arm, open-label clinical trials as well as expanded access and compassionate use programs for a total of 29 patients with plasminogen deficiency type 1 who received at least one dose of RYPLAZIM. Patients were between 11 months and 42 years of age. There were 18 pediatric patients and 11 adult patients. Fifteen patients were female. Twenty-eight patients were Caucasian, and one patient was Asian.
RYPLAZIM Trial 1 enrolled 7 patients (5 female) of whom 2 were pediatric patients (age 13 to 15 years) and 5 were adults. Five patients received two infusions: one 2 mg/kg infusion, and one 6 mg/kg infusion. Two patients received a single 6 mg/kg infusion. There were no adverse reactions in this trial.
RYPLAZIM Trial 2 enrolled 15 patients (11 female) of whom 6 were pediatric patients (age 4 to 16 years) and 9 were adults. Six of the 15 patients participated in RYPLAZIM Trial 1. Treatment duration ranged from 48 to 124 weeks. All patients received RYPLAZIM at a dose of 6.6 mg/kg administered every second, third or fourth day for 48 weeks.
A long-term treatment protocol enrolled 12 patients (8 female) of whom 8 were pediatric patients (age 16 months to 16 years) and 4 were adults. Eight patients in this treatment protocol continued from Trial 2 and 4 patients were from individual expanded access protocols in the US. All 12 patients continue to receive RYPLAZIM at the dose of 6.6 mg/kg every 2 to 4 days.
Fourteen patients (5 female) received RYPLAZIM through expanded access programs. There were 8 pediatric patients (age 11 months to 17 years) and 6 adults. Patients' dosage regimens were adjusted based on clinical response, and the regimens varied between 6.6 mg/kg every 1 to 7 days.
Table 1 shows the most frequent adverse reactions (incidence ≥ 10%) observed in the two trials and in the treatment protocols.
| Adverse Reactions | Number of Patients (%)(N = 19) |
|---|---|
|
|
| Abdominal pain | 3 (16%) |
| Gastric dilatation (bloating/feel bloated) | 3 (16%) |
| Nausea | 3 (16%) |
| Fatigue | 3 (16%) |
| Pain in extremity | 3 (16%) |
| Hemorrhage | 3 (16%) |
| Constipation | 2 (11%) |
| Dry mouth | 2 (11%) |
| Headache | 2 (11%) |
| Dizziness | 2 (11%) |
| Arthralgia | 2 (11%) |
| Back pain | 2 (11%) |
6.2 Immunogenicity
In RYPLAZIM Trial 2, three patients (20%) developed anti-plasminogen antibodies following RYPLAZIM treatment. Comparison of pharmacokinetic (PK) parameters and /or trough activity levels for those positive samples with the parameters assessed either at baseline or for negative samples suggest these antibodies are not neutralizing antibodies (inhibitors) to plasminogen.
The detection of anti-plasminogen antibodies depends on the sensitivity and specificity of the test methods used. Additionally, the observed incidence of antibody positivity in a test method may be influenced by several factors, including sample handling, timing of sample collection, drug interference, concomitant medication, and the underlying disease. For these reasons, comparison of the incidence of antibodies to RYPLAZIM with the incidence of antibodies to other products may be misleading.
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and efficacy of RYPLAZIM has been established in pediatric patients. Use of RYPLAZIM is supported by the two clinical trials, and expanded access and compassionate use programs that included 18 pediatric patients age 11 months to 17 years [see Clinical Studies (14), and Adverse Reactions (6)].
8.5 Geriatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of RYPLAZIM have not been established in geriatric patients. Clinical studies of RYPLAZIM for this indication did not include patients age 65 years and over. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
11. Ryplazim Description
RYPLAZIM is a Glu-plasminogen (> 95% purity) which is the native circulating form of plasminogen in the blood. RYPLAZIM is a sterile, white to off-white, lyophilized preparation of purified, plasma-derived plasminogen (human) to be reconstituted and administered by the intravenous route. Each vial of RYPLAZIM contains 68.8 mg of plasminogen. Following reconstitution with 12.5 mL of sterile water for injection (SWFI), the RYPLAZIM solution contains 5.5 mg/mL plasminogen and the following inactive ingredients: sodium citrate, sodium chloride, glycine, and sucrose. RYPLAZIM contains no preservatives. Biological potency of the plasminogen is determined by a chromogenic assay calibrated with a standard.
All plasma used in the manufacturing of RYPLAZIM is tested using serological assays for hepatitis B virus (HBV) surface antigen and antibodies to human immunodeficiency virus-1/2 (HIV-1/2) and hepatitis C virus (HCV). The plasma is also tested via nucleic acid amplification testing for HBV, HCV, HIV-1, hepatitis A virus (HAV) and human parvovirus B19 virus. Only plasma pools negative for HIV-1, HCV, HBV, and HAV, and containing levels of human parvovirus B19 DNA ≤ 104 IU/mL are used for the manufacture of RYPLAZIM.
The RYPLAZIM manufacturing process encompasses a series of chromatography adsorbents to purify plasminogen and includes multiple steps and controls to ensure that the purified plasminogen is essentially free of known adventitious agents. First, three orthogonal viral removal/inactivation steps are included: affinity chromatography for removal of enveloped and non-enveloped viruses; solvent/detergent treatment for inactivation of enveloped viruses; and 20 nm nanofiltration for removal of both enveloped and non-enveloped viruses. Two independent studies demonstrated effective viral removal/inactivation afforded by these three steps using validated scaled-down models. The overall virus reduction achieved in these studies for enveloped viruses was ≥ 11.8 logs and for non-enveloped viruses was ≥ 9.7 logs (considering both contributing steps), as summarized in Table 2. Second, the plasma used in this process is Human Source Plasma from FDA-approved collection centers; thus, there is minimal risk of contamination that could cause transmissible spongiform encephalopathies. Lastly, the product is tested for microbial and endotoxin levels throughout the process.
| Enveloped Viruses | Non EnvelopedViruses | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Process Step | HIV-1 | BVDV | PRV | HAV | PPV | Reo-3 | EMCV |
|
|||||||
| Affinity chromatography | ≥ 5.22 | ND* | ND* | 3.64 | 2.64 | ND* | 3.55 |
| Solvent/Detergent treatment | > 6.09 | > 5.77 | > 6.54 | NA† | NA† | NA† | NA† |
| Nanofiltration | > 5.89 | > 6.02 | > 6.51 | > 7.08 | > 7.03 | > 7.08 | ND* |
| Total LRV | ≥ 17.2 | ≥ 11.8 | ≥ 13.1 | ≥ 10.7 | ≥ 9.7 | ≥ 7.1 | 3.6 |
12. Ryplazim - Clinical Pharmacology
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Plasminogen deficiency type 1 is characterized by decreased plasminogen levels that causes formation of fibrin-rich, ligneous pseudomembranous lesions on mucous membranes that can impair normal tissue and organ function. Replacemenq t therapy increases the plasma level of plasminogen enabling a temporary correction of the plasminogen deficiency and reduction or resolution of extravascular fibrinous lesions.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics of RYPLAZIM were assessed by plasminogen activity (chromogenic assay) in plasma. Plasminogen was measured as both absolute and baseline-adjustedlevels.
In RYPLAZIM Trial 2, pharmacokinetic analyses were conducted in 15 patients (9 adults) who completed at least 12 weeks of RYPLAZIM 6.6 mg/kg administered every second, third or fourth day and had sufficient plasma samples. Full pharmacokinetic profiles of plasminogen were measured over 96 hours after the first and Week 12 infusions, and trough levels of plasminogen were measured at baseline and at Weeks 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, and 12.
Mean absolute plasminogen activity in adult and pediatric patients reached physiological levels (70% to 130%) immediately after the first infusion, were sustained for approximately 24 hours, and remained an absolute 10% above baseline 72 hours after dosing. After 12 weeks, mean absolute plasminogen activity in adult and pediatric patients reached physiological levels (70% to 130%) immediately after dosing, were sustained for approximately 24 hours, and continued to maintain an absolute 10% above baseline 96 hours after dosing.
Although some inter-patient variability was observed, PK parameters for baseline-adjusted plasminogen activity levels were generally similar between adult and pediatric patients.
| PK Parameter | First Dose Adult (N=9) | Week 12 Adult (N=9) | First Dose Pediatric (N=6) | Week 12 Pediatric (N=6) | First Dose Total (N=15) | Week 12 Total (N=15) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUCLast = area under the time-concentration curve, from time 0 to the last measured time point; AUCInf = extrapolated area under the time-concentration curve, from time 0 to infinity; CL = clearance; Cmax = peak concentration; MRTLast = mean residence time from time 0 to the last measured time point; Vss = steady-state volume of distribution; T1/2 = half-life | ||||||
|
||||||
| AUCLast (hr*%) | 2860.9 (700.7) | 4665.6 (762.1) | 3367.6 (852.8) | 4641.6 (1393.4) | 3063.6 (778.7) | 4656.0 (1012.7) |
| AUCInf (hr*%) | 3317.3 (915.7) | 5676.0 (1186.6) | 4038.5 (1104.2) | 5815.5 (1863.5) | 3605.8 (1023.9) | 5731.8 (1431.7) |
| CL (mL/h/kg) | 1.5 (0.5) | 0.9 (0.2) | 1.3 (0.4) | 0.9 (0.3) | 1.4 (0.5) | 0.9 (0.3) |
| Cmax (%) | 90.9 (17.5) | 127.4 (17.4) | 102.0 (31.1) | 120.3 (31.6) | 95.3 (23.5) | 124.6 (23.3) |
| MRTLast (hr) | 29.7 (3.7) | 33.0 (1.6) | 31.8 (2.0) | 34.2 (1.5) | 30.6 (3.2) | 33.5 (1.6) |
| Vss (mL/kg) | 62.8 (11.2) | 47.2 (5.6) | 64.1 (12.9) | 52.5 (15.2) | 63.3 (11.4) | 49.3 (10.4) |
| T1/2 (hr) | 32.4 (13.1) | 38.5 (7.1) | 36.3 (10.0) | 40.3 (5.0) | 34.0 (11.7) | 39.2 (6.2) |
| Study Population | Baseline | Week 2 | Week 4 | Week 6 | Week 8 | Week 10 | Week 12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasminogen activity levels measured with a chromogenic assay. Normal range: 70%-130%, as determined by the laboratory. Individual plasminogen activity values reported as < 5% were set at 5% for mean calculation. There was no Week 2 plasminogen activity trough value for one adult patient; however, an unscheduled Week 3 value was obtained and used for mean calculation. Baseline value corresponds to endogenous plasminogen level. |
|||||||
| Adult (N = 9) | 20.3 (13.7) | 44.7 (18.6) | 50.8 (17.1) | 55.4 (12.0) | 50.3 (19.5) | 51.1 (15.5) | 51.7 (12.3) |
| Pediatric (N = 6) | 22.3 (5.1) | 47.7 (7.4) | 46.2 (10.5) | 47.8 (9.8) | 45.2 (14.8) | 48.8 (6.4) | 50.0 (12 6) |
| Combined (N = 15) | 21.1 (10.8) | 45.9 (14.8) | 48.9 (14.6) | 52.4 (11.5) | 48.3 (17.4) | 50.2 (12.4) | 51.0 (12.0) |
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
14. Clinical Studies
The efficacy of RYPLAZIM in pediatric and adult patients with plasminogen deficiency type 1 was evaluated in a single-arm, open-label clinical trial (RYPLAZIM Trial 2). A total of 15 patients with plasminogen deficiency type 1 were enrolled. All patients had a baseline plasminogen activity level between <5% and 45% of normal, and biallelic mutations in the plasminogen (PLG) gene. The age range of these patients was 4 to 42 years, including 6 pediatric patients age 4 to 16 years, and 9 adults. Eleven patients were female. All patients were White. All patients received RYPLAZIM at a dose of 6.6 mg/kg administered every 2 to 4 days for 48 weeks to achieve at least an increase of individual trough plasminogen activity by an absolute 10% above baseline and to treat the clinical manifestations of the disease.
Efficacy was established on the basis of overall rate of clinical success at 48 weeks. Overall rate of clinical success is defined as 50% of patients with visible or other measurable non-visible lesions achieving at least 50% improvement in lesion number/size, or functionality impact from baseline. Spirometry was the only test of organ function used and one patient had abnormal spirometry at baseline. This patient had a history of ligneous airway disease with a severe obstructive ventilatory defect (FEV1: 46.7% of predicted normal) at baseline prior to treatment that corrected to normal (FEV1: 89.3% of predicted normal) after 12 weeks of treatment. All patients with any lesion at baseline had at least 50% improvement in the number/size of their lesions.
16. How is Ryplazim supplied
RYPLAZIM is supplied in a single-dose vial [NDC 70573-099-01] containing 68.8 mg of plasminogen (human) (5.5 mg/mL after reconstitution with 12.5 mL of SWFI), one vial per carton [NDC 70573-099-02]. The treating physician will provide reconstitution and administration supplies. RYPLAZIM contains no preservatives.
17. Patient Counseling Information
- Advise patients and/or caregiver to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information and Instructions for Use).
- Counsel patients and/or caregiver to discontinue RYPLAZIM and immediately contact their physicians if signs or symptoms of a possible hypersensitivity reaction occur, such as hives, generalized urticaria, angioedema, chest tightness, wheezing, tachycardia, and hypotension [see Contraindications (4)], Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
- Inform patients that bleeding from active mucosal disease-related lesions and worsening of active bleeding not related to those lesions during RYPLAZIM therapy may occur. Depending on the lesion sites, this may manifest as gastrointestinal bleeding, hemoptysis, epistaxis, vaginal bleeding, or hematuria. Prior to initiation of treatment with RYPLAZIM, lesions or wounds suspected as the source of recent bleeding events should be confirmed to have healed. RYPLAZIM may prolong or worsen bleeding in patients with bleeding diatheses and/or taking anticoagulants or antiplatelet drugs. If a patient develops serious bleeding, seek emergency care and discontinue RYPLAZIM immediately [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- Inform patients that tissue sloughing at mucosal sites may occur at initiation of RYPLAZIM therapy as lesions resolve. Patients with respiratory lesion are at risk for respiratory compromise and initial treatment with RYPLAZIM should be performed in a clinical setting with close monitoring. Patients with lesions in gastrointestinal and genitourinary systems may experience tissue sloughing that may cause pain, mucosal bleeding, or passage of tissue referable to those organ systems. Patients should report persistent abdominal, flank or pelvic pain to their physicians if not resolved. [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
- Inform patients and/or caregiver that RYPLAZIM is made from human plasma and may contain infectious agents that can cause disease (eg, viruses, the variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease [vCJD] agent and, theoretically the CJD agent). Explain that the risk that RYPLAZIM may transmit an infectious agent has been reduced by screening the plasma donors, by testing donated plasma for certain virus infections, and by inactivating or removing certain viruses during manufacturing. Counsel patients and/or caregiver to report any symptoms that concern them. [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
- Advise patients and/or caregivers that antibodies may develop during treatment that make RYPLAZIM less effective [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
- Advise female patients who are pregnant or may become pregnant that the potential effects of RYPLAZIM on pregnancy and breastfeeding are unknown. They should notify their physicians if they become or intend to become pregnant, or if they plan to breastfeed. [see Use in Special Populations (8.1) and (8.2)].
- Self-administration: ensure patient/caregiver has received detailed instructions and training and has shown the ability to safely and independently administer RYPLAZIM.
RYPLAZIM® plasminogen, human-tvmh Instructions for Use
For intravenous use after reconstitution only
Do not attempt an intravenous infusion on yourself unless you or your caregiver has been trained by a healthcare provider. Always follow the specific instructions that your healthcare provider has given you. The steps listed below are general guidelines for using RYPLAZIM. If you are unsure about any of the steps, contact your healthcare provider before using.
- A.
-
Gathering Supplies
- Your healthcare provider should tell you how many vials of RYPLAZIM to use based on your weight. If you store RYPLAZIM in the refrigerator, then let the vials sit at room temperature for at least 15 minutes before you use them.
- Check the expiration date on the vial labels and carton. Do not use RYPLAZIM or Sterile Water for Injection, USP vials after the expiration date.
- Make sure you work on a clean, flat surface.
- Gather the following supplies and any other materials that you will need, as instructed by your healthcare provider:
- Required number of vials of RYPLAZIM
- One 20-mL syringe per vial of RYPLAZIM for mixing the drug
- 18- to 22-gauge needles for reconstitution and administration
- Sterile Water for Injection, USP (SWFI) (10 mL, 20 mL or 50 mL)
- One syringe disc filter per infusion of RYPLAZIM required (Baxter Supor® 5-micron Syringe Filter or equivalent)
- One (or more) administration syringe(s) (20mL, 30mL or 60 mL)
- Alcohol wipes
- Antiseptic surface wipes
- Medical tape
- Butterfly needle or sterile infusion set
- 10 mL normal saline
- Sterile gauze pad
- Bandage
- B.
-
Preparing RYPLAZIM
- Always work on a clean surface and wash your hands before performing the procedure.
- Once the RYPLAZIM has been prepared, use it at room temperature within 3 hours. Do not refrigerate after preparation.
- Remove the caps from the RYPLAZIM vials and the Sterile Water for Injection, USP (SWFI) vials to expose the central portion of the rubber stoppers.
- Clean the surface of the rubber stoppers with alcohol wipes and allow to dry. Do not blow on them. Do not touch the rubber stoppers with your hand after cleaning them.
- Using a syringe with an 18- to 22-gauge needle, draw 12.5 mL of SWFI. Ensure that all air bubbles have been removed.
Note: Depending on the SWFI vial sizes used, more than one SWFI vial(s) may be required.- If using a 10-mL vial of SWFI, you will need two 10-mL vials of SWFI for each vial of RYPLAZIM. Draw 9.0 mL of SWFI from the first SWFI vial with the 20-mL syringe. Discard the first needle, attach a new 18- to 22-gauge sterile needle and draw 3.5 mL from the second 10-mL vial of SWFI to equal to 12.5 mL.
- Repeat the above process for every vial of RYPLAZIM that will need to be reconstituted.
- If using a 20-mL or 50-mL vial of SWFI, only one vial of SWFI per vial of RYPLAZIM will be needed for reconstitution.
- Do not use the remaining SWFI in the vial with a different RYPLAZIM vial.
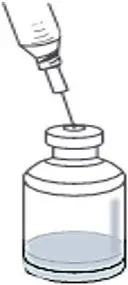
- Gently and slowly add the 12.5 mL of SWFI down the side of the RYPLAZIM vial to prevent foaming. This should resemble a stream down the side of the vial. (Fig. A). Discard used syringe and needle(s).
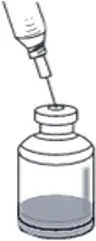
Fig. A
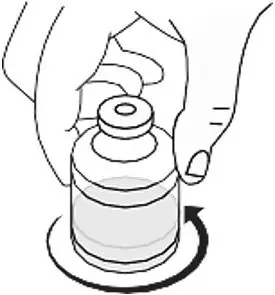
- Gently swirl the RYPLAZIM vial in slow rotation to ensure it is fully dissolved. Do not shake the vial. The RYPLAZIM should fully dissolve within 10 minutes. Discard if the product is not fully dissolved after 10 minutes. (Fig B)
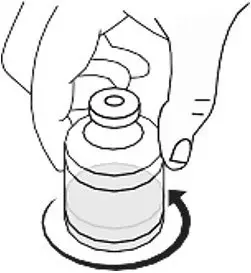
Fig. B
- After the RYPLAZIM is dissolved in the SWFI, inspect the solution. It should be colorless and clear to slightly pearly. Discard if discoloration or particulate matter is observed.
- Repeat Preparation Steps 3 to 8 above for each vial of RYPLAZIM needed.
- Select an administration syringe of appropriate volume based on the dose required. Depending on the syringe size used, more than one vial of mixed RYPLAZIM can be drawn into one administration syringe.
NOTE: A 30-mL syringe cannot hold more than 2 vials of reconstituted RYPLAZIM and a 60-mL syringe cannot hold more than 4 vials of reconstituted RYPLAZIM. - Using the selected administration syringe(s) with an 18- to 22-gauge needle, slowly draw the RYPLAZIM from each reconstituted vial to administer the required dose of RYPLAZIM. Do not mix RYPLAZIM with other medications.
- After drawing the RYPLAZIM from the last vial, push the plunger down to remove any air bubbles. Dispose of the needle in an appropriate container.
Infusing RYPLAZIM
- One filter is needed per infusion.
- Only administer RYPLAZIM by infusing it into a vein through a syringe disc filter.
- Inspect the solution in the syringe. Do not use if you see discoloration or particulate matter.
- Administer RYPLAZIM by a separate infusion line. Do not administer RYPLAZIM with other medications.
- Draw 10 mL of normal saline into a different syringe. Push the plunger down to remove any air bubbles.
- Attach a syringe disc filter to the pre-filled syringe of normal saline (from previous step) and the infusion tubing with butterfly needle. (Fig. C)
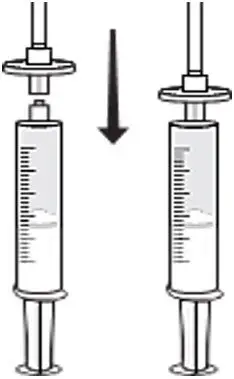
Fig. C
- Inject the normal saline through the syringe disc filter and butterfly needle tubing to remove any air bubbles.
- Remove the normal saline syringe. The syringe disc filter must remain attached to the tubing, as it is required for administration of the RYPLAZIM. Discard the normal saline syringe.
- Attach the administration syringe containing RYPLAZIM to the syringe disc filter that is connected to the butterfly needle tubing.
- Choose a peripheral vein (e.g., antecubital or dorsum of hand). Clean the injection site with a sterile alcohol wipe and allow to dry. Do not blow on it.
- Insert the butterfly infusion set needle in the chosen peripheral vein, as taught by your healthcare provider, and tape in place.
- Infuse the amount of RYPLAZIM you need as instructed by your healthcare provider. Deliver the total dose slowly over 10-30 minutes (approximately 5 mL/min). Using a timer (e.g., watch or clock), push the plunger of the syringe approximately 1 mL every 12 seconds. (Fig. D)
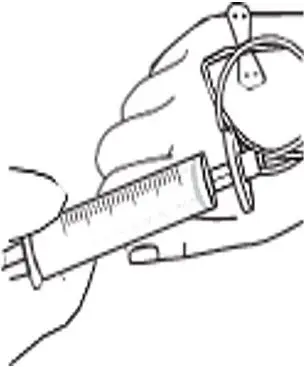
Fig. D
- Discard any open vials, unused solution, and administration equipment following administration.
Manufactured by:
Prometic Bioproduction Inc
531 Blvd. des Prairies,
Laval, Quebec, Canada, H7V1B7
Manufactured for:
Prometic Biotherapeutics, Inc
Parker Plaza, 400 Kelby Street, Suite 1104
Fort Lee, New Jersey 07024
U.S. License number 2065
| RYPLAZIM
plasminogen injection, powder, lyophilized, for solution |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Prometic Biotherapeutics, Inc. (961577439) |