Drug Detail:Silenor (Doxepin [ dox-e-pin ])
Drug Class: Miscellaneous anxiolytics, sedatives and hypnotics Tricyclic antidepressants
Highlights of Prescribing Information
SILENOR® (doxepin) tablets for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1969
Indications and Usage for Silenor
SILENOR (doxepin) tablets are indicated for the treatment of insomnia characterized by difficulties with sleep maintenance. (1, 14)
Silenor Dosage and Administration
- Initial dose: 6 mg, once daily for adults (2.1) and 3 mg, once daily for the elderly. (2.1, 2.2)
- Take within 30 minutes of bedtime. Total daily dose should not exceed 6 mg. (2.3)
- Should not be taken within 3 hours of a meal. (2.3, 12.3)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
- 3 mg and 6 mg tablets. Tablets not scored. (3)
Contraindications
- Hypersensitivity to doxepin hydrochloride, inactive ingredients, or other dibenzoxepines. (4.1)
- Co-administration with Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs): Do not administer if patient is taking MAOIs or has used MAOIs within the past two weeks. (4.2)
- Untreated narrow angle glaucoma or severe urinary retention. (4.3)
Warnings and Precautions
- Need to Evaluate for Co-morbid Diagnoses: Reevaluate if insomnia persists after 7 to 10 days of use. (5.1)
- Abnormal thinking, behavioral changes, complex behaviors: May include "Sleep-driving" and hallucinations. Immediately evaluate any new onset behavioral changes. (5.2)
- Depression: Worsening of depression or suicidal thinking may occur. Prescribe the least amount feasible to avoid intentional overdose. (5.3)
- CNS-depressant effects: Use can impair alertness and motor coordination. Avoid engaging in hazardous activities such as operating a motor vehicle or heavy machinery after taking drug. (5.4) Do not use with alcohol. (5.4, 7.3)
- Potential additive effects when used in combination with CNS depressants or sedating antihistamines. Dose reduction may be needed. (5.4, 7.4)
- Patients with severe sleep apnea: SILENOR is ordinarily not recommended for use in this population. (8.7)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The most common treatment-emergent adverse reactions, reported in ≥ 2% of patients treated with SILENOR, and more commonly than in patients treated with placebo, were somnolence/sedation, nausea, and upper respiratory tract infection. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Currax Pharmaceuticals LLC at 1-800-793-2145 and or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
- MAO inhibitors: SILENOR should not be administered in patients on MAOIs within the past two weeks. (4.2)
- Cimetidine: Increases exposure to doxepin. (7.2)
- Alcohol: Sedative effects may be increased with doxepin. (7.3, 5.4)
- CNS Depressants and Sedating Antihistamines: Sedative effects may be increased with doxepin. (7.4, 5.4)
- Tolazamide: A case of severe hypoglycemia has been reported. (7.5)
Use In Specific Populations
- Pregnancy: Third trimester use may increase the risk for symptoms of poor adaptation (respiratory distress, temperature instability, feeding difficulties, hypotonia, tremor, irritability) in the neonate. (8.1)
- Lactation: Breastfeeding not recommended. (8.2)
- Pediatric Use: Safety and effectiveness have not been evaluated. (8.4)
- Geriatric Use: The recommended starting dose is 3 mg. Monitor prior to considering dose escalation. (2.2, 8.5)
- Use in Patients with Comorbid Illness: Initiate treatment with 3 mg in patients with hepatic impairment or tendency to urinary retention. (8.6, 4.3)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 12/2022
Related/similar drugs
lorazepam, melatonin, zolpidem, diphenhydramine, Ativan, AmbienFull Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Silenor
SILENOR is indicated for the treatment of insomnia characterized by difficulty with sleep maintenance. The clinical trials performed in support of efficacy were up to 3 months in duration .
2. Silenor Dosage and Administration
The dose of SILENOR should be individualized.
2.1. Dosing in Adults
The recommended dose of SILENOR for adults is 6 mg once daily. A 3 mg once daily dose may be appropriate for some patients, if clinically indicated.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
SILENOR is an immediate-release, oval-shaped, tablet for oral administration available in strengths of 3 mg and 6 mg. The tablets are blue (3 mg) or green (6 mg) and are debossed with 3 or 6, respectively, on one side and SP on the other. SILENOR tablets are not scored.
4. Contraindications
4.1. Hypersensitivity
SILENOR is contraindicated in individuals who have shown hypersensitivity to doxepin HCl, any of its inactive ingredients, or other dibenzoxepines.
4.2. Co-administration with Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs)
Serious side effects and even death have been reported following the concomitant use of certain drugs with MAO inhibitors. Do not administer SILENOR if patient is currently on MAOIs or has used MAOIs within the past two weeks. The exact length of time may vary depending on the particular MAOI dosage and duration of treatment.
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1. Need to Evaluate for Comorbid Diagnoses
Because sleep disturbances may be the presenting manifestation of a physical and/or psychiatric disorder, symptomatic treatment of insomnia should be initiated only after careful evaluation of the patient. The failure of insomnia to remit after 7 to 10 days of treatment may indicate the presence of a primary psychiatric and/or medical illness that should be evaluated. Exacerbation of insomnia or the emergence of new cognitive or behavioral abnormalities may be the consequence of an unrecognized psychiatric or physical disorder. Such findings have emerged during the course of treatment with hypnotic drugs.
5.2. Abnormal Thinking and Behavioral Changes
Complex behaviors such as "sleep-driving" (i.e., driving while not fully awake after ingestion of a hypnotic, with amnesia for the event) have been reported with hypnotics. These events can occur in hypnotic-naive as well as in hypnotic-experienced persons. Although behaviors such as "sleep-driving" may occur with hypnotics alone at therapeutic doses, the use of alcohol and other CNS depressants with hypnotics appears to increase the risk of such behaviors, as does the use of hypnotics at doses exceeding the maximum recommended dose. Due to the risk to the patient and the community, discontinuation of SILENOR should be strongly considered for patients who report a "sleep-driving" episode. Other complex behaviors (e.g., preparing and eating food, making phone calls, or having sex) have been reported in patients who are not fully awake after taking a hypnotic. As with "sleep-driving", patients usually do not remember these events. Amnesia, anxiety and other neuro-psychiatric symptoms may occur unpredictably.
5.3. Suicide Risk and Worsening of Depression
In primarily depressed patients, worsening of depression, including suicidal thoughts and actions (including completed suicides), has been reported in association with the use of hypnotics.
Doxepin, the active ingredient in SILENOR, is an antidepressant at doses 10- to 100-fold higher than in SILENOR. Antidepressants increased the risk compared to placebo of suicidal thinking and behavior (suicidality) in children, adolescents, and young adults in short-term studies of major depressive disorder (MDD) and other psychiatric disorders. Risk from the lower dose of doxepin in SILENOR can not be excluded.
It can rarely be determined with certainty whether a particular instance of the abnormal behaviors listed above is drug induced, spontaneous in origin, or a result of an underlying psychiatric or physical disorder. Nonetheless, the emergence of any new behavioral sign or symptom of concern requires careful and immediate evaluation.
5.4. CNS Depressant Effects
After taking SILENOR, patients should confine their activities to those necessary to prepare for bed. Patients should avoid engaging in hazardous activities, such as operating a motor vehicle or heavy machinery, at night after taking SILENOR, and should be cautioned about potential impairment in the performance of such activities that may occur the day following ingestion.
When taken with SILENOR, the sedative effects of alcoholic beverages, sedating antihistamines, and other CNS depressants may be potentiated [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Drug Interactions (7.3, 7.4)]. Patients should not consume alcohol with SILENOR [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Drug Interactions (7.3)]. Patients should be cautioned about potential additive effects of SILENOR used in combination with CNS depressants or sedating antihistamines [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Drug Interactions (7.4)].
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following serious adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of labeling:
- Abnormal thinking and behavioral changes [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
- Suicide risk and worsening of depression [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
- CNS Depressant effects [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
6.1. Clinical Trials Experience
The pre-marketing development program for SILENOR included doxepin HCl exposures in 1017 subjects (580 insomnia patients and 437 healthy subjects) from 12 studies conducted in the United States. 863 of these subjects (580 insomnia patients and 283 healthy subjects) participated in six randomized, placebo-controlled efficacy studies with SILENOR doses of 1 mg, 3 mg, and 6 mg for up to 3-months in duration.
Because clinical studies are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice. However, data from the SILENOR studies provide the physician with a basis for estimating the relative contributions of drug and non-drug factors to adverse reaction incidence rates in the populations studied.
6.3. Other Reactions Observed During the Pre-marketing Evaluation of SILENOR
SILENOR was administered to 1017 subjects in clinical trials in the United States. Treatment-emergent adverse reactions recorded by clinical investigators were standardized using a modified MedDRA dictionary of preferred terms. The following is a list of MedDRA terms that reflect treatment-emergent adverse reactions reported by subjects treated with SILENOR.
Adverse reactions are further categorized by body system and listed in order of decreasing frequency according to the following definitions: Frequent adverse reactions are those that occurred on one or more occasions in at least 1/100 subjects; Infrequent adverse reactions are those that occurred in fewer than 1/100 subjects and more than 1/1000 subjects. Rare adverse reactions are those that occurred in fewer than 1/1000 subjects. Adverse reactions that are listed in Table 1 are not included in the following listing of frequent, infrequent, and rare AEs.
Blood and Lymphatic System Disorders: Infrequent: anemia; Rare: thrombocythemia.
Cardiac Disorders: Rare: atrioventricular block, palpitations, tachycardia, ventricular extrasystoles.
Ear and Labyrinth Disorders: Rare: ear pain, hypoacusis, motion sickness, tinnitus, tympanic membrane perforation.
Eye Disorders: Infrequent: eye redness, vision blurred; Rare: blepharospasm, diplopia, eye pain, lacrimation decreased.
Gastrointestinal Disorders: Infrequent: abdominal pain, dry mouth, gastroesophageal reflux disease, vomiting; Rare: dyspepsia, constipation, gingival recession, haematochezia, lip blister.
General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions: Infrequent: asthenia, chest pain, fatigue; Rare: chills, gait abnormal, edema peripheral.
Hepatobiliary Disorders: Rare: hyperbilirubinemia.
Immune System Disorders: Rare: hypersensitivity.
Infections and Infestations: Infrequent: bronchitis, fungal infection, laryngitis, sinusitis, tooth infection, urinary tract infection, viral infection; Rare: cellulitis staphylococcal, eye infection, folliculitis, gastroenteritis viral, herpes zoster, infective tenosynovitis, influenza, lower respiratory tract infection, onychomycosis, pharyngitis, pneumonia.
Injury, Poisoning and Procedural Complications: Infrequent: back injury, fall, joint sprain; Rare: bone fracture, skin laceration.
Investigations: Infrequent: blood glucose increased; Rare: alanine aminotransferase increased, blood pressure decreased, blood pressure increased, electrocardiogram ST-T segment abnormal, electrocardiogram QRS complex abnormal, heart rate decreased, neutrophil count decreased, QRS axis abnormal, transaminases increased.
Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders: Infrequent: anorexia, decreased appetite, hyperkalemia, hypermagnesemia, increased appetite; Rare: hypokalemia.
Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders: Infrequent: arthralgia, back pain, myalgia, neck pain, pain in extremity; Rare: joint range of motion decreased, muscle cramp, sensation of heaviness.
Neoplasms Benign, Malignant and Unspecified (Including Cysts and Polyps): Rare: lung adenocarcinoma stage I, malignant melanoma.
Nervous System Disorders: Frequent: dizziness; Infrequent: dysgeusia, lethargy, parasthesia, syncope; Rare: ageusia, ataxia, cerebrovascular accident, disturbance in attention, migraine, sleep paralysis, syncope vasovagal, tremor.
Psychiatric Disorders: Infrequent: abnormal dreams, adjustment disorder, anxiety, depression; Rare: confusional state, elevated mood, insomnia, libido decreased, nightmare.
Reproductive System and Breast Disorders: Rare: breast cyst, dysmenorrhea.
Renal and Urinary Disorders: Rare: dysuria, enuresis, hemoglobinuria, nocturia.
Respiratory, Thoracic and Mediastinal Disorders: Infrequent: nasal congestion, pharyngolaryngeal pain, sinus congestion, wheezing; Rare: cough, crackles lung, nasopharyngeal disorder, rhinorrhea, dyspnea.
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders: Infrequent: skin irritation; Rare: cold sweat, dermatitis, erythema, hyperhidrosis, pruritis, rash, rosacea.
Surgical and Medical Procedures: Rare: arthrodesis.
Vascular Disorders: Infrequent: pallor; Rare: blood pressure inadequately controlled, hematoma, hot flush.
In addition, the reactions below have been reported for other tricyclics and may be idiosyncratic (not related to dose).
Allergic: photosensitization, skin rash.
Hematologic: agranulocytosis, eosinophilia, leukopenia, purpura, thrombocytopenia.
7. Drug Interactions
7.1. Cytochrome P450 Isozymes
SILENOR is primarily metabolized by hepatic cytochrome P450 isozymes CYP2C19 and CYP2D6, and to a lesser extent, by CYP1A2 and CYP2C9. Inhibitors of these isozymes may increase the exposure of doxepin. SILENOR is not an inhibitor of any CYP isozymes at therapeutically relevant concentrations. The ability of SILENOR to induce CYP isozymes is not known.
7.2. Cimetidine
SILENOR exposure is doubled with concomitant administration of cimetidine, a nonspecific inhibitor of CYP isozymes. A maximum dose of 3 mg is recommended in adults and elderly when cimetidine is co-administered with SILENOR [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]
7.3. Alcohol
When taken with SILENOR, the sedative effects of alcohol may be potentiated [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2, 5.4)].
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.4. Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of SILENOR in pediatric patients have not been evaluated.
8.5. Geriatric Use
A total of 362 subjects who were ≥ 65 years and 86 subjects who were ≥ 75 years received SILENOR in controlled clinical studies. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these subjects and younger adult subjects. Greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out.
Sleep-promoting drugs may cause confusion and over-sedation in the elderly. A starting dose of 3 mg is recommended in this population and evaluation prior to considering dose escalation is recommended [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
8.6. Use in Patients with Hepatic Impairment
Patients with hepatic impairment may display higher doxepin concentrations than healthy individuals. Initiate SILENOR treatment with 3 mg in patients with hepatic impairment and monitor closely for adverse daytime effects. [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]
8.7. Use in Patients with Sleep Apnea
SILENOR has not been studied in patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Since hypnotics have the capacity to depress respiratory drive, precautions should be taken if SILENOR is prescribed to patients with compromised respiratory function. In patients with severe sleep apnea, SILENOR is ordinarily not recommended for use.
9. Drug Abuse and Dependence
10. Overdosage
Doxepin is routinely administered for indications other than insomnia at doses 10- to 50-fold higher than the highest recommended dose of SILENOR.
The signs and symptoms associated with doxepin use at doses several-fold higher than the maximum recommended dose (Excessive dose) of SILENOR for the treatment of insomnia are described [see Overdosage (10.1)], as are signs and symptoms associated with higher multiples of the maximum recommended dose (Critical overdose) [see Overdosage (10.2)].
10.1. Signs and Symptoms of Excessive Doses
The following adverse effects have been associated with use of doxepin at doses higher than 6 mg.
Anticholinergic Effects: constipation and urinary retention.
Central Nervous System: disorientation, hallucinations, numbness, paresthesias, extrapyramidal symptoms, seizures, tardive dyskinesia.
Cardiovascular: hypotension.
Gastrointestinal: aphthous stomatitis, indigestion.
Endocrine: raised libido, testicular swelling, gynecomastia in males, enlargement of breasts and galactorrhea in the female, raising or lowering of blood sugar levels, and syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion.
Other: tinnitus, weight gain, sweating, flushing, jaundice, alopecia, exacerbation of asthma, and hyperpyrexia (in association with chlorpromazine).
10.2. Signs and Symptoms of Critical Overdose
Manifestations of doxepin critical overdose include: cardiac dysrhythmias, severe hypotension, convulsions, and CNS depression including coma. Electrocardiogram changes, particularly in QRS axis or width, are clinically significant indicators of tricyclic compound toxicity. Other signs of overdose may include, but are not limited to: confusion, disturbed concentration, transient visual hallucinations, dilated pupils, agitation, hyperactive reflexes, stupor, drowsiness, muscle rigidity, vomiting, hypothermia, hyperpyrexia.
10.3 Recommended Management
As management of overdose is complex and changing, it is recommended that the physician contact a poison control center for current information on treatment. In addition, the possibility of a multiple drug ingestion should be considered.
If an overdose is suspected, an ECG should be obtained and cardiac monitoring should be initiated immediately. The patient's airway should be protected, an intravenous line should be established, and gastric decontamination should be initiated. A minimum of six hours of observation with cardiac monitoring and observation for signs of CNS or respiratory depression, hypotension, cardiac dysrhythmias and/or conduction blocks, and seizures is strongly advised. If signs of toxicity occur at any time during this period, extended monitoring is recommended. There are case reports of patients succumbing to fatal dysrhythmias late after overdose; these patients had clinical evidence of significant poisoning prior to death and most received inadequate gastrointestinal decontamination. Monitoring of plasma drug levels should not guide management of the patient.
11. Silenor Description
SILENOR (doxepin) is available in 3 mg and 6 mg strength tablets for oral administration. Each tablet contains 3.39 mg or 6.78 mg doxepin hydrochloride, equivalent to 3 mg and 6mg of doxepin, respectively.
Chemically, doxepin hydrochloride is an (E) and (Z) geometric, isomeric mixture of 1 propanamine, 3-dibenz[b,e]oxepin-11(6H)ylidene-N,N-dimethyl-hydrochloride. It has the following structure:
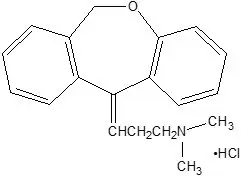
Doxepin hydrochloride is a white crystalline powder, with a slight amine-like odor, that is readily soluble in water. It has a molecular weight of 315.84 and molecular formula of C19 H21 NO∙HCl.
Each SILENOR tablet includes the following inactive ingredients: microcrystalline cellulose, colloidal silicon dioxide, and magnesium stearate. The 3 mg tablet also contains FD&C Blue No.1. The 6 mg tablet also contains D&C Yellow No. 10 and FD&C Blue No. 1.
12. Silenor - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1. Mechanism of Action
The mechanism of action of doxepin in sleep maintenance is unclear; however, doxepin's effect could be mediated through antagonism of the H1 receptor.
14. Clinical Studies
14.1. Controlled Clinical Trials
The efficacy of SILENOR for improving sleep maintenance was supported by six randomized, double-blind studies up to 3 months in duration that included 1,423 subjects, 18 to 93 years of age, with chronic (N=858) or transient (N=565) insomnia. SILENOR was evaluated at doses of 1 mg, 3 mg, and 6 mg relative to placebo in inpatient (sleep laboratory) and outpatient settings.
The primary efficacy measures for assessment of sleep maintenance were the objective and subjective time spent awake after sleep onset (respectively, objective Wake After Sleep Onset [WASO] and subjective WASO).
Subjects in studies of chronic insomnia were required to have at least a 3-month history of insomnia.
16. How is Silenor supplied
16.1. How Supplied
SILENOR 3 mg tablets are oval shaped, blue, identified with debossed markings of "3" on one side and "SP" on the other, and are supplied as:
| NDC 42847-103-30 | Bottle of 30 |
SILENOR 6 mg tablets are oval shaped, green, identified with debossed markings of "6" on one side and "SP" on the other, and are supplied as:
| NDC 42847-106-30 | Bottle of 30 |
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide).
| This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. | Revised: 12/2022 | |
| MEDICATION GUIDE
SILENOR® [si-leh-nor] (doxepin) tablets |
||
| What is the most important information I should know about SILENOR? | ||
| SILENOR can cause serious side effects including: | ||
After taking SILENOR, you may get up out of bed while not being fully awake and do an activity that you do not know you are doing. The next morning, you may not remember that you did anything during the night. You have a higher chance for doing these activities if you drink alcohol or take other medicines that make you sleepy with SILENOR. Reported activities include:
|
||
| Stop taking SILENOR and call your healthcare provider right away if you find out that you have done any of the above activities after taking SILENOR. Important:
|
||
| Take SILENOR 30 minutes before bedtime. After taking SILENOR, you should only do activities needed to get ready for bed. | ||
| What is SILENOR? | ||
| SILENOR is a prescription medicine used to treat adults who have trouble staying asleep. | ||
| It is not known if SILENOR is safe and effective in children. | ||
Do not take SILENOR if you:
|
||
Before taking SILENOR, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
|
||
| Tell your healthcare provider about all of the medicines you take including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins and herbal supplements. | ||
| SILENOR and other medicines may affect each other causing side effects. SILENOR may affect the way other medicines work, and other medicines may affect how SILENOR works. | ||
Especially tell your healthcare provider if you take:
|
||
| Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of your medicines with you to show your healthcare provider and pharmacist each time you get a new medicine. | ||
How should I take SILENOR?
|
||
What should I avoid during treatment with SILENOR?
|
||
| What are the possible side effects of SILENOR? | ||
SILENOR can cause serious side effects including:
|
||
| The most common side effects of SILENOR include: | ||
|
|
|
| SILENOR may cause fertility problems in females and males, which may affect your ability to have children. Talk to your healthcare provider if you have concerns about fertility. | ||
| These are not all of the possible side effects of SILENOR. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. | ||
How should I store SILENOR?
|
||
| Keep SILENOR and all medicines out of the reach of children. | ||
| General Information about the safe and effective use of SILENOR. | ||
| Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use SILENOR for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give SILENOR to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about SILENOR that is written for healthcare professionals. | ||
| What are the ingredients in SILENOR? | ||
| Active Ingredient: doxepin hydrochloride | ||
| Inactive Ingredients: microcrystalline cellulose, colloidal silicon dioxide, and magnesium stearate. The 3 mg tablet also contains FD&C Blue No. 1. The 6 mg tablet also contains FD&C Yellow No. 10 and FD&C Blue No. 1. | ||
| Distributed by: Currax™ Pharmaceuticals LLC, Brentwood, TN 37027 USA SIL-LC088.02 For more information, contact Currax Pharmaceuticals LLC at 1-800-793-2145. |
||
| SILENOR
doxepin hydrochloride tablet |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SILENOR
doxepin hydrochloride tablet |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Currax Pharmaceuticals LLC (117055730) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patheon Pharmaceuticals, Inc | 005286822 | MANUFACTURE(42847-103, 42847-106) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Teva API India Private Ltd. | 677604426 | API MANUFACTURE(42847-103, 42847-106) , ANALYSIS(42847-103, 42847-106) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ropack Inc. | 209989631 | PACK(42847-103, 42847-106) | |






