Drug Detail:Simponi aria (Golimumab [ goe-lim-ue-mab ])
Drug Class: TNF alfa inhibitors
Highlights of Prescribing Information
SIMPONI ARIA ®(golimumab) injection, for intravenous use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2009
WARNING: SERIOUS INFECTIONS and MALIGNANCY
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
- Serious infections leading to hospitalization or death including tuberculosis (TB), bacterial sepsis, invasive fungal (such as histoplasmosis), and other opportunistic infections have occurred in patients receiving SIMPONI ARIA ( 5.1).
- Discontinue SIMPONI ARIA if a patient develops a serious infection or sepsis ( 5.1).
- Perform test for latent TB; if positive, start treatment for TB prior to starting SIMPONI ARIA ( 5.1).
- Monitor all patients for active TB during treatment, even if initial latent TB test is negative ( 5.1).
- Lymphoma and other malignancies, some fatal, have been reported in children and adolescent patients treated with TNF blockers, of which SIMPONI ARIA is a member ( 5.2).
Indications and Usage for Simponi Aria
SIMPONI ARIA is a tumor necrosis factor (TNF) blocker indicated for the treatment of:
- Adult patients with moderately to severely active Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) in combination with methotrexate ( 1.1)
- Active Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA) in patients 2 years of age and older ( 1.2)
- Adult patients with active Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS) ( 1.3)
- Active polyarticular Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (pJIA) in patients 2 years of age and older ( 1.4)
Simponi Aria Dosage and Administration
- Adult patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis, Psoriatic Arthritis, and Ankylosing Spondylitis:
- 2 mg/kg intravenous infusion over 30 minutes at weeks 0 and 4, and every 8 weeks thereafter ( 2.1)
- Pediatric patients with polyarticular Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis and Psoriatic Arthritis:
- 80 mg/m 2intravenous infusion over 30 minutes at weeks 0 and 4, and every 8 weeks thereafter ( 2.2)
- Dilution of supplied SIMPONI ARIA solution with 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP is required prior to administration. Alternatively, 0.45% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP can also be used ( 2.4)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
- Injection: 50 mg/4 mL (12.5 mg/mL) solution in a single-dose vial ( 3)
Contraindications
- None ( 4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Serious Infections: Do not start SIMPONI ARIA during an active infection. If an infection develops, monitor carefully, and stop SIMPONI ARIA if infection becomes serious ( 5.1).
- Invasive Fungal Infections: For patients who develop a systemic illness on SIMPONI ARIA, consider empiric antifungal therapy for those who reside in or travel to regions where mycoses are endemic ( 5.1).
- Hepatitis B Reactivation: Monitor HBV carriers during and several months after therapy. If reactivation occurs, stop SIMPONI ARIA and begin anti-viral therapy ( 5.1).
- Malignancies: More cases of lymphoma have been observed among patients receiving TNF blockers compared with patients in the control groups. Cases of other malignancies have been observed among patients receiving TNF blockers ( 5.2).
- Congestive Heart Failure: Worsening, or new onset, may occur. Stop SIMPONI ARIA if new or worsening symptoms occur ( 5.3).
- Demyelinating Disorders: Exacerbation or new onset may occur ( 5.4).
- Lupus-like Syndrome: Discontinue SIMPONI ARIA if symptoms develop ( 5.5).
- Hypersensitivity Reactions: Serious systemic hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylaxis may occur ( 5.11).
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥ 3%) are: upper respiratory tract infection, alanine aminotransferase increased, viral infection, aspartate aminotransferase increased, neutrophil count decreased, bronchitis, hypertension, and rash ( 6.1).
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Janssen Biotech, Inc. at 1-800-JANSSEN (1-800-526-7736) or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
- Biologics, including abatacept and anakinra: Increased risk of serious infections ( 5.1, 5.6, 5.7, 5.8, 7.2).
- Live vaccines should not be given with SIMPONI ARIA ( 5.10, 7.3).
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 7/2023
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Simponi Aria
1.1 Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
SIMPONI ARIA, in combination with methotrexate (MTX), is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with moderately to severely active rheumatoid arthritis.
1.2 Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA)
SIMPONI ARIA is indicated for the treatment of active psoriatic arthritis in patients 2 years of age and older.
2. Simponi Aria Dosage and Administration
2.1 Dosage in Adults with Rheumatoid Arthritis, Psoriatic Arthritis, and Ankylosing Spondylitis
The SIMPONI ARIA dosage regimen is 2 mg per kg given as an intravenous infusion over 30 minutes at weeks 0 and 4, and every 8 weeks thereafter. Follow the dilution and administration instructions for SIMPONI ARIA [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)] .
For patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), SIMPONI ARIA should be given in combination with methotrexate.
The efficacy and safety of switching between intravenous and subcutaneous formulations and routes of administration have not been established.
2.2 Dosage in Pediatric Patients with Polyarticular Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis and Psoriatic Arthritis
The SIMPONI ARIA dosage regimen, based on body surface area (BSA), is 80 mg/m 2given as an intravenous infusion over 30 minutes at weeks 0 and 4, and every 8 weeks thereafter. Follow the dilution and administration instructions for SIMPONI ARIA [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)] .
2.3 Evaluation for Tuberculosis and Hepatitis B Prior to Dosage
Prior to initiating SIMPONI ARIA and periodically during therapy, evaluate patients for active tuberculosis and test for latent infection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] . Prior to initiating SIMPONI ARIA, test patients for hepatitis B viral infection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] .
2.4 Important Administration Instructions
SIMPONI ARIA solution for intravenous infusion should be diluted by a healthcare professional using aseptic technique as follows:
- Calculate the dosage and the number of SIMPONI ARIA vials needed based on the recommended adult dosage of 2 mg/kg and the patient's weight for RA, PsA and AS. Calculate the dosage and number of SIMPONI ARIA vials needed based on the recommended pediatric dosage of 80 mg/m 2and the patient's body surface area (BSA), for pJIA and pediatric patients with PsA. Each 4 mL vial of SIMPONI ARIA contains 50 mg of golimumab.
- Check that the solution in each vial is colorless to light yellow. The solution may develop a few fine translucent particles, as golimumab is a protein. Do not use if opaque particles, discoloration, or other foreign particles are present.
- Dilute the total volume of the SIMPONI ARIA solution with 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP to a final volume of 100 mL. For example, this can be accomplished by withdrawing a volume of the 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP from the 100-mL infusion bag or bottle equal to the total volume of SIMPONI ARIA. Slowly add the total volume of SIMPONI ARIA solution to the 100-mL infusion bag or bottle. Gently mix. Discard any unused solution remaining in the vials. Alternatively, SIMPONI ARIA can be diluted using the same method described above with 0.45% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP.
- Prior to infusion, visually inspect the diluted SIMPONI ARIA solution for particulate matter or discoloration. Do not use if these are present.
- Use only an infusion set with an in-line, sterile, non-pyrogenic, low protein-binding filter (pore size 0.22 micrometer or less).
- Do not infuse SIMPONI ARIA concomitantly in the same intravenous line with other agents. No physical biochemical compatibility studies have been conducted to evaluate the use of SIMPONI ARIA with other intravenous agents in the same intravenous line.
- Infuse the diluted solution over 30 minutes.
- Once diluted, the infusion solution can be stored for up to 4 hours at room temperature.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
Injection: 50 mg/4 mL (12.5 mg/mL) colorless to light yellow solution in a single-dose vial.
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Serious Infections
Patients treated with SIMPONI ARIA are at increased risk for developing serious infections involving various organ systems and sites that may lead to hospitalization or death.
Opportunistic infections due to bacterial, mycobacterial, invasive fungal, viral, or parasitic organisms including aspergillosis, blastomycosis, candidiasis, coccidioidomycosis, histoplasmosis, legionellosis, listeriosis, pneumocystosis, and tuberculosis have been reported with TNF-blockers. Patients have frequently presented with disseminated rather than localized disease. The concomitant use of a TNF-blocker and abatacept or anakinra was associated with a higher risk of serious infections; therefore, the concomitant use of SIMPONI ARIA and these biologic products is not recommended [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6, 5.7)and Drug Interactions (7.2)] .
Treatment with SIMPONI ARIA should not be initiated in patients with an active infection, including clinically important localized infections. Patients greater than 65 years of age, patients with co-morbid conditions and/or patients taking concomitant immunosuppressants such as corticosteroids or methotrexate may be at greater risk of infection. Consider the risks and benefits of treatment prior to initiating SIMPONI ARIA in patients:
- with chronic or recurrent infection;
- who have been exposed to tuberculosis;
- with a history of an opportunistic infection;
- who have resided or traveled in areas of endemic tuberculosis or endemic mycoses, such as histoplasmosis, coccidioidomycosis, or blastomycosis; or
- with underlying conditions that may predispose them to infection.
5.3 Congestive Heart Failure
Cases of worsening congestive heart failure (CHF) and new onset CHF have been reported with TNF-blockers, including SIMPONI ARIA. Some cases had a fatal outcome. In several exploratory trials of other TNF-blockers in the treatment of CHF, there were greater proportions of TNF-blocker treated patients who had CHF exacerbations requiring hospitalization or increased mortality. SIMPONI ARIA has not been studied in patients with a history of CHF and SIMPONI ARIA should be used with caution in patients with CHF. If a decision is made to administer SIMPONI ARIA to patients with CHF, these patients should be closely monitored during therapy, and SIMPONI ARIA should be discontinued if new or worsening symptoms of CHF appear.
5.4 Demyelinating Disorders
Use of TNF-blockers, including SIMPONI ARIA, has been associated with rare cases of new onset or exacerbation of central nervous system (CNS) demyelinating disorders, including multiple sclerosis (MS), and peripheral demyelinating disorders, including Guillain-Barré syndrome. Cases of central demyelination, MS, optic neuritis, and peripheral demyelinating polyneuropathy have rarely been reported in patients treated with golimumab. Prescribers should exercise caution in considering the use of TNF-blockers, including SIMPONI ARIA, in patients with central or peripheral nervous system demyelinating disorders. Discontinuation of SIMPONI ARIA should be considered if these disorders develop.
5.5 Autoimmunity
Treatment with TNF blockers, including SIMPONI ARIA, may result in the formation of antinuclear antibodies (ANA). Rarely, treatment with TNF blockers, may result in the development of a lupus-like syndrome [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] . If a patient develops symptoms suggestive of a lupus-like syndrome following treatment with SIMPONI ARIA, treatment should be discontinued.
5.6 Use with Abatacept
In controlled trials, the concurrent administration of another TNF-blocker and abatacept was associated with a greater proportion of serious infections than the use of a TNF-blocker alone; and the combination therapy, compared to the use of a TNF-blocker alone, has not demonstrated improved clinical benefit in the treatment of RA. Therefore, the combination of TNF-blockers, including SIMPONI ARIA, and abatacept is not recommended [see Drug Interactions (7.2)] .
5.7 Use with Anakinra
Concurrent administration of anakinra (an interleukin-1 antagonist) and another TNF-blocker was associated with a greater portion of serious infections and neutropenia and no additional benefits compared with the TNF-blocker alone. Therefore, the combination of anakinra with TNF-blockers, including SIMPONI ARIA, is not recommended [see Drug Interactions (7.2)] .
5.8 Switching Between Biological Disease Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs)
Care should be taken when switching from one biologic product to another biologic product since overlapping biological activity may further increase the risk of infection.
5.9 Hematologic Cytopenias
There have been reports of pancytopenia, leukopenia, neutropenia, agranulocytosis, aplastic anemia, and thrombocytopenia in patients receiving golimumab. Caution should be exercised when using TNF-blockers, including SIMPONI ARIA, in patients who have or have had significant cytopenias.
5.11 Hypersensitivity Reactions
In postmarketing experience, serious systemic hypersensitivity reactions (including anaphylaxis) have been reported following administration of the subcutaneous and intravenous formulations of golimumab including SIMPONI ARIA. Hypersensitivity reactions including hives, pruritus, dyspnea, and nausea, were reported during infusion and generally within an hour after infusion. Some of these reactions occurred after the first administration of golimumab. If an anaphylactic or other serious allergic reaction occurs, administration of SIMPONI ARIA should be discontinued immediately and appropriate therapy instituted.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The most serious adverse reactions were:
- Serious Infections [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Malignancies [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
The safety data described below are based on one, randomized, double-blind, controlled Phase 3 trial in patients with RA receiving SIMPONI ARIA by intravenous infusion (Trial RA). The protocol included provisions for patients taking placebo to receive treatment with SIMPONI ARIA at Week 16 or Week 24 either by patient response (based on uncontrolled disease activity) or by design, so that adverse events cannot always be unambiguously attributed to a given treatment. Comparisons between placebo and SIMPONI ARIA were based on the first 24 weeks of exposure.
Trial RA included 197 control-treated patients and 463 SIMPONI ARIA-treated patients (which includes control-treated patients who switched to SIMPONI ARIA at Week 16). The proportion of patients who discontinued treatment due to adverse reactions in the controlled phase of Trial RA through Week 24 was 3.5% for SIMPONI ARIA-treated patients and 0.5% for placebo-treated patients. Upper respiratory tract infection was the most common adverse reaction reported in the trial through Week 24 occurring in 6.5% of SIMPONI ARIA-treated patients as compared with 7.6% of control-treated patients, respectively.
6.2 Immunogenicity
As with all therapeutic proteins, there is potential for immunogenicity. The detection of antibody formation is highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assay. Additionally, the observed incidence of antibody (including neutralizing antibody) positivity in an assay may be influenced by several factors including assay methodology, sample handling, timing of sample collection, concomitant medications, and underlying disease. For these reasons, comparison of the incidence of antibodies to golimumab in the trials described below with the incidence of antibodies in other trials or to other products may be misleading.
Using an enzyme immunoassay (EIA) method, antibodies to golimumab were detected in 13 (3%) golimumab-treated patients following IV administration of SIMPONI ARIA in combination with MTX through Week 24 of Trial RA, of which all were neutralizing antibodies.
A drug-tolerant enzyme immunoassay (drug-tolerant EIA) method for detecting antibodies to golimumab was developed and validated. This method is approximately 16-fold more sensitive than the original EIA method with less interference from golimumab in serum. Through approximately 6 months, the incidence of antibodies to golimumab with the drug-tolerant EIA method for Trials RA, PsA, AS, and pJIA was 21%, 19%, 19% and 31%, respectively. Where tested, approximately one-third to one-half were neutralizing.
Patients with RA, PsA, AS and pJIA who developed antibodies to golimumab generally had lower trough steady-state serum concentrations of golimumab [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
6.3 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of golimumab. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to golimumab exposure:
General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions:Infusion-related reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)]
Neoplasm benign and malignant: Melanoma, Merkel cell carcinoma [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
Immune system disorders: Serious systemic hypersensitivity reactions (including anaphylactic reaction) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)] , sarcoidosis
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders: Interstitial lung disease
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: Skin exfoliation, lichenoid reactions, bullous skin reactions
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 Methotrexate
SIMPONI ARIA should be used with MTX for the treatment of RA [see Clinical Studies (14.1)] . Following IV administration, concomitant administration of methotrexate decreases the clearance of SIMPONI ARIA by approximately 9% based on population pharmacokinetics (PK) analysis. In addition, concomitant administration of methotrexate decreases the SIMPONI ARIA clearance by reducing the development of antibodies to golimumab.
7.2 Biologic Products for RA, PsA, AS, and pJIA
An increased risk of serious infections has been seen in clinical RA studies of other TNF-blockers used in combination with anakinra or abatacept, with no added benefit; therefore, use of SIMPONI ARIA with other biologic products, including abatacept or anakinra, is not recommended [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6and 5.7)] . A higher rate of serious infections has also been observed in RA patients treated with rituximab who received subsequent treatment with a TNF-blocker. The concomitant use of SIMPONI ARIA with biologics approved to treat RA, PsA, AS, and pJIA is not recommended because of the possibility of an increased risk of infection.
7.3 Live Vaccines/Therapeutic Infectious Agents
Live vaccines should not be given concurrently with SIMPONI ARIA [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)] .
Therapeutic infectious agents should not be given concurrently with SIMPONI ARIA [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)] .
Infants born to women treated with SIMPONI ARIA during their pregnancy may be at increased risk of infection for up to 6 months. Administration of live vaccines to infants exposed to SIMPONI ARIA in uterois not recommended for 6 months following the mother's last SIMPONI ARIA infusion during pregnancy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10), Use in Specific Populations (8.1)] .
7.4 Cytochrome P450 Substrates
The formation of CYP450 enzymes may be suppressed by increased levels of cytokines (e.g., TNFα) during chronic inflammation. Therefore, it is expected that for a molecule that antagonizes cytokine activity, such as golimumab, the formation of CYP450 enzymes could be normalized. Upon initiation or discontinuation of SIMPONI ARIA in patients being treated with CYP450 substrates with a narrow therapeutic index, monitoring of the effect (e.g., warfarin) or drug concentration (e.g., cyclosporine or theophylline) is recommended and the individual dose of the drug product may be adjusted as needed.
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of SIMPONI ARIA for active polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis and PsA have been established in pediatric patients 2 years and older.
Use of SIMPONI ARIA in these age groups is supported by evidence from adequate and well-controlled studies of SIMPONI ARIA in adults with RA and PsA, pharmacokinetic data from adult patients with RA and PsA and pediatric patients with JIA with active polyarthritis, and safety data from a clinical study in 127 pediatric patients 2 to < 18 years of age with JIA with active polyarthritis. The observed pre-dose (trough) concentrations are generally comparable between adults with RA and PsA and pediatric patients with JIA with active polyarthritis, and the PK exposure is expected to be comparable between adult PsA and pediatric patients with PsA [see Adverse Reactions (6.1), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)and Clinical Studies (14.2, 14.4)] .
Malignancies, some fatal, have been reported among children, adolescents, and young adults who received treatment with golimumab and other TNF-blocking agents [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
The safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients below the age of 2 years have not been established in pJIA or in PsA. The safety and effectiveness of SIMPONI ARIA in pediatric patients with conditions other than pJIA and PsA have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
In Trial RA, the number of patients ages 65 or older was too small to make comparisons with younger SIMPONI ARIA-treated patients. Because there is a higher incidence of infections in the geriatric population in general, caution should be used in treating geriatric patients with SIMPONI ARIA.
10. Overdosage
In a clinical study, 5 patients received single infusions of up to 1000 mg of SIMPONI ARIA without serious adverse reactions or other significant reactions.
11. Simponi Aria Description
Golimumab is a human IgG1қ monoclonal antibody specific for human tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFα) that exhibits multiple glycoforms with molecular masses of approximately 150 to 151 kilodaltons. Golimumab was created using genetically engineered mice immunized with human TNF, resulting in an antibody with human-derived antibody variable and constant regions. Golimumab is produced by a recombinant cell line cultured by continuous perfusion and is purified by a series of steps that includes measures to inactivate and remove viruses.
The SIMPONI ARIA ®(golimumab) Injection is a sterile solution of the golimumab antibody supplied in a 4-mL glass vial for intravenous infusion.
SIMPONI ARIA is a preservative-free, colorless to light yellow solution with a pH of approximately 5.5. SIMPONI ARIA is not made with natural rubber latex. Each 4-mL vial of SIMPONI ARIA contains 50 mg golimumab, L-histidine (1.14 mg), L-histidine monohydrochloride monohydrate (6.42 mg), polysorbate 80 (0.6 mg), sorbitol (180 mg), and water for injection.
12. Simponi Aria - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Golimumab is a human monoclonal antibody that binds to both the soluble and transmembrane bioactive forms of human TNFα. This interaction prevents the binding of TNFα to its receptors, thereby inhibiting the biological activity of TNFα (a cytokine protein). There was no evidence of the golimumab antibody binding to other TNF superfamily ligands; in particular, the golimumab antibody did not bind or neutralize human lymphotoxin. Golimumab did not lyse human monocytes expressing transmembrane TNF in the presence of complement or effector cells.
Elevated TNFα levels in the blood, synovium, and joints have been implicated in the pathophysiology of several chronic inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis. TNFα is an important mediator of the articular inflammation that is characteristic of these diseases. Golimumab modulated the in vitrobiological effects mediated by TNF in several bioassays, including the expression of adhesion proteins responsible for leukocyte infiltration (E-selectin, ICAM-1 and VCAM-1) and the secretion of proinflammatory cytokines (IL-6, IL-8, G-CSF and GM-CSF). The clinical relevance of these findings is unknown.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Following treatment with SIMPONI ARIA in patients with RA, decreases from baseline were observed in tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 (TIMP-1), matrix metalloproteinase-1 (MMP-1), matrix metalloproteinase-3 (MMP-3), resistin, interleukin-6 (IL-6), macrophage inflammatory protein-1 (MIP-1b), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), serum amyloid A (SAA), S100A12, and high sensitivity C-Reactive protein (hsCRP). Conversely, increases from baseline were observed in tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP-5b). The clinical relevance of this information is not known.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Golimumab exhibited approximately dose-proportional pharmacokinetics in patients with RA over the dose range of 0.1 to 10.0 mg/kg following a single intravenous dose.
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Long-term animal studies of golimumab have not been conducted to evaluate its carcinogenic potential. Mutagenicity studies have not been conducted with golimumab. A fertility study conducted in mice using an analogous anti-mouse TNFα antibody administered by the intravenous route at doses up to 40 mg/kg once per week showed no impairment of fertility.
14. Clinical Studies
14.1 Rheumatoid Arthritis
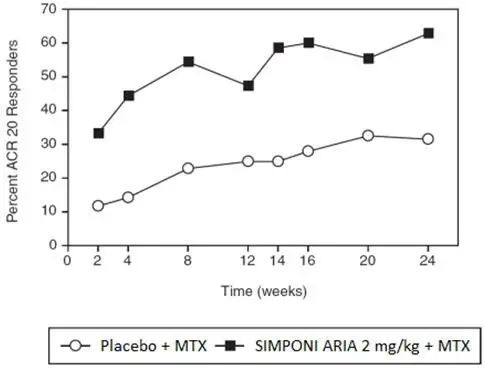
The efficacy and safety of SIMPONI ARIA were evaluated in one multicenter, randomized, double-blind, controlled trial (Trial RA, NCT00973479) in 592 patients ≥ 18 years of age with moderately to severely active RA despite concurrent MTX therapy and had not previously been treated with a biologic TNF-blocker. Patients were diagnosed according to the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) criteria, at least 3 months prior to administration of study agent and were required to have at least 6 swollen and 6 tender joints. Patients were randomized to receive either SIMPONI ARIA 2 mg/kg (N=395) or placebo (N=197) over a 30-minute intravenous infusion at Weeks 0, 4 and every 8 weeks thereafter in addition to their weekly maintenance MTX dose (15–25 mg). All patients receiving placebo + MTX received SIMPONI ARIA + MTX after Week 24, but the trial remained blinded until all patients had completed 108 weeks of treatment. Efficacy data were collected and analyzed through Week 52. Patients were allowed to continue stable doses of concomitant low dose corticosteroids (equivalent to ≤ 10 mg of prednisone a day) and/or NSAIDs. The use of other DMARDs including cytotoxic agents or other biologics was prohibited.
The primary endpoint in Trial RA was the percentage of patients achieving an ACR 20 response at Week 14. In Trial RA, the majority of subjects were women (82%) and were Caucasian (80%) with a median age of 52 years and a median weight of 70 kg. Median disease duration was 4.7 years, and 50% of the patients used at least one DMARD other than MTX in the past. At baseline, 81% of patients received concomitant NSAIDs and 81% of patients received low-dose corticosteroids (equivalent to ≤ 10 mg of prednisone a day). The median baseline DAS28-CRP was 5.9 and the median van der Heijde-Sharp score at baseline was 28.5.
14.2 Psoriatic Arthritis
The efficacy and safety of SIMPONI ARIA were evaluated in a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in 480 patients ≥ 18 years of age with active psoriatic arthritis despite NSAID or DMARD therapy (Trial PsA, NCT02181673). Previous treatment with a biologic was not allowed. Patients in this trial had a diagnosis of PsA for at least six months and had symptoms of active disease [≥5 swollen joints and ≥5 tender joints and a CRP level of ≥ 0.6 mg/dL]. Patients were randomized to either receive SIMPONI ARIA 2 mg/kg (N=241) or placebo (N=239) as a 30-minute intravenous infusion at Weeks 0, 4, 12 and 20. All patients on placebo received SIMPONI ARIA at Week 24, Week 28 and every 8 weeks thereafter through Week 52. Patients in the SIMPONI ARIA treatment group continued to receive SIMPONI ARIA infusions at Week 28 and every 8 weeks through Week 52.
Patients were allowed to continue stable doses of MTX, NSAIDs, and low dose oral corticosteroids (equivalent to ≤ 10 mg of prednisone per day) during the trial. The use of other DMARDs including cytotoxic agents or other biologics was prohibited.
The primary endpoint was the percentage of patients achieving an ACR 20 response at Week 14.
Patients with each subtype of PsA were enrolled, including polyarticular arthritis with absence of rheumatoid nodules (44%), asymmetric peripheral arthritis (19%), distal interphalangeal joint involvement (8.1%), spondylitis with peripheral arthritis (25%), and arthritis mutilans (4.8%). The median duration of PsA disease was 3.5 years, 86% of patients had previously used MTX, and 35% of patients received at least one other DMARD in the past. At baseline, 76% and 54% of the patients had enthesitis and dactylitis, respectively. The median total modified vdH-S score at baseline was 15.5. During the trial, concomitant medications used included MTX (70%), oral corticosteroids (28%), and NSAIDs (71%).
Clinical Response
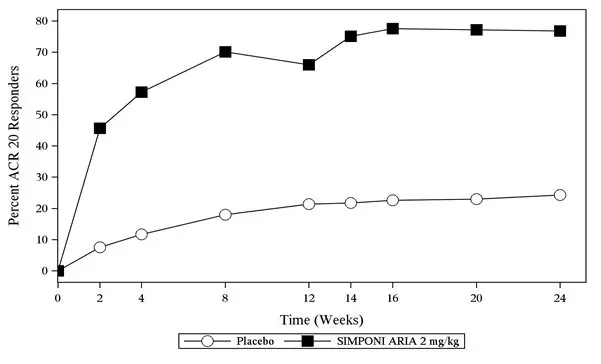
In Trial PsA, SIMPONI ARIA treatment, compared with placebo, resulted in a significant improvement in signs and symptoms as demonstrated by the percentage of patients with an ACR 20 response at Week 14 (see Table 5). Similar ACR 20 responses at Week 24 were observed in patients with different PsA subtypes. ACR 20 responses observed in the SIMPONI ARIA-treated groups were similar in patients who were or were not receiving concomitant MTX.
| Placebo | SIMPONI ARIA | Difference from placebo
(95% CI) |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| (N *=239) | (N *=241) | ||
| Note: The analysis is based on the intent-to-treat population. Last observation carried forward was performed for partial missing data and non-responder imputation for completely missing data. Patients who discontinued treatment due to lack of efficacy were imputed as non-responders, as were patients who started prohibited medication, increased corticosteroids or MTX, or failed to achieve at least a 5% improvement in joint counts at Week 16 and received a concomitant medication intervention (corticosteroids, MTX or NSAIDs). | |||
|
|||
| ACR 20 response | |||
| Week 14 | 22% | 75% | 53%
†
(46, 61) |
| Week 24 | 24% | 77% | 53%
(45, 60) |
| ACR 50 response | |||
| Week 14 | 6.3% | 44% | 37%
(30, 44) |
| Week 24 | 6.3% | 54% | 47%
(40, 54) |
| ACR 70 response | |||
| Week 14 | 2.1% | 25% | 22%
(17, 28) |
| Week 24 | 3.3% | 33% | 29%
(23, 36) |
The percentage of patients achieving ACR20 responses by visit through Week 24 for Trial PsA is shown in Figure 2.
| Figure 2: Trial PsA - Percentage of Patients Achieving ACR20 Response Through Week 24 | |
|
|
|
| The analysis is based on the intent-to-treat population. Last observation carried forward was performed for partial missing data and non-responder imputation for completely missing data. Patients who discontinued treatment due to lack of efficacy were imputed as non-responders, as were patients who started prohibited medication, increased corticosteroids or MTX, or failed to achieve at least a 5% improvement in joint counts at Week 16 and received a concomitant medication intervention (corticosteroids, MTX or NSAIDs). | |
Table 6 shows the improvement in the individual components of the ACR response criteria for the SIMPONI ARIA and placebo groups in Trial PsA.
| Placebo
N *=239 | SIMPONI ARIA
N *=241 |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | Week 14 change from baseline | Baseline | Week 14 change from baseline | |
| Note: All values are means. | ||||
|
||||
| ACR Components | ||||
| No. of Swollen Joints (0–66) | 14 | -2.9 | 14 | -11 |
| Number of Tender Joints (0–68) | 26 | -4.2 | 25 | -15 |
| Patient's assessment of Pain (0–100 mm) | 64 | -11 | 63 | -31 |
| Patient Global Assessment (0–100 mm) | 63 | -11 | 65 | -32 |
| Physician Global Assessment (0–100 mm) | 64 | -13 | 62 | -39 |
| Disability Index (HAQ) (0–3) † | 1.3 | -0.13 | 1.3 | -0.60 |
| hsCRP (mg/L) | 20 | -2.9 | 19 | -16 |
Patients with enthesitis at baseline were evaluated for mean improvement using the Leeds Enthesitis Index (LEI) on a scale of 0–6. SIMPONI ARIA-treated patients showed a significantly greater improvement in enthesitis, with a mean reduction of 1.8 as compared with a mean reduction in placebo-treated patients of 0.8 at Week 14. Patients with dactylitis at baseline were evaluated for mean improvement on a scale of 0–60. SIMPONI ARIA-treated patients showed a significantly greater improvement, with a mean reduction of 7.8 compared with a mean reduction of 2.8 in placebo-treated patients at Week 14.
Radiographic Response
In Trial PsA, structural joint damage was assessed radiographically and expressed as a change from baseline at Week 24 in total modified vdH-S score and its components, the erosion score and JSN score. SIMPONI ARIA inhibited the progression of structural damage compared with placebo, as assessed by total modified vdH-S score as shown in Table 7.
| Placebo
N *=237 | SIMPONI ARIA
N *=237 | Difference from placebo
(95% CI) |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Mean | ||
| Note: All values are means. | |||
|
|||
| Change Total Modified vdH-S Score | 2.0 | -0.4 | -2.3
(-2.9, -1.7) |
At Week 24, a greater proportion of patients in the SIMPONI ARIA group (72%) had no progression of structural damage (change in the total modified vdH-S score ≤ 0), compared to 43% of patients in the placebo group.
14.3 Ankylosing Spondylitis
The efficacy and safety of SIMPONI ARIA were evaluated in a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial (Trial AS, NCT02186873) in 208 patients ≥ 18 years of age with active ankylosing spondylitis (AS) and inadequate response or intolerance to NSAIDs. Patients had a diagnosis of definite AS for at least 3 months according to modified New York criteria. Patients had symptoms of active disease [Bath AS Disease Activity Index (BASDAI) ≥ 4, VAS for total back pain of ≥ 4, on scales of 0 to 10 cm (0 to 100 mm), and a hsCRP level of ≥ 0.3 mg/dL (3 mg/L)]. Patients were randomized to receive either SIMPONI ARIA 2 mg/kg (N=105) or placebo (N=103) as a 30-minute intravenous infusion at Weeks 0, 4 and 12. All patients on placebo received SIMPONI ARIA at Week 16, Week 20 and every 8 weeks thereafter through Week 52. Patients in the SIMPONI ARIA treatment group continued to receive SIMPONI ARIA infusions at Week 20 and every 8 weeks through Week 52. Patients were allowed to continue stable doses of concomitant MTX, SSZ, hydroxychloroquine (HCQ), low dose oral corticosteroids (equivalent to ≤ 10 mg of prednisone per day), and/or NSAIDs during the trial. The use of other DMARDs including cytotoxic agents or other biologics was prohibited.
The primary endpoint was the percentage of patients achieving an Assessment in Ankylosing Spondylitis (ASAS) 20 response at Week 16.
In Trial AS, the median duration of AS disease was 2.8 years, median duration of inflammatory back pain was 8 years, 90% were HLA-B27 positive, 8.2% had prior joint surgery or procedure, 5.8% had complete ankylosis of the spine, 14% had received prior therapy with one biologic TNF blocker (other than golimumab) and discontinued for reasons other than lack of efficacy within the first 16 weeks of treatment (primary failure), and 76% received at least one DMARD in the past. During the trial, the use of concomitant medications was NSAIDs (88%), SSZ (38%), corticosteroids (26%), MTX (18%), and HCQ (0.5%).
Clinical Response
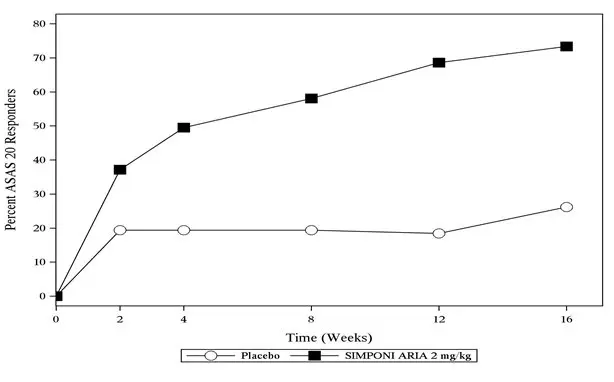
In Trial AS, SIMPONI ARIA treatment, compared with placebo, resulted in a significant improvement in signs and symptoms as demonstrated by the percentage of patients with an ASAS 20 response at Week 16 (see Table 8).
| Placebo
N *=103 | SIMPONI ARIA
N *=105 | Treatment Difference
(95% CI) |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| Note: The analysis is based on the intent-to-treat population. Last observation carried forward was performed for partial missing data and non-responder imputation for completely missing data. | |||
|
|||
| Responders | |||
| ASAS 20 | 26% | 73% | 47%
†
(35, 59) |
| ASAS 40 | 8.7% | 48% | 39%
(28, 50) |
The percentage of patients achieving ASAS 20 responses by visit through Week 16 for Trial AS is shown in Figure 3.
| Figure 3: Trial AS – Percentage of Patients Achieving an ASAS 20 Response Through Week 16 | |
|
|
|
| The analysis is based on the intent-to-treat population. Last observation carried forward was performed for partial missing data and non-responder imputation for completely missing data. | |
Table 9 shows the improvement in the components of the ASAS response criteria and other measures of disease activity for the SIMPONI ARIA and placebo groups in Trial AS.
| Placebo
N *=103 | SIMPONI ARIA
N *=105 |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | Week 16 change from baseline | Baseline | Week 16 change from baseline | |
| Note: All values are means. | ||||
|
||||
| ASAS 20 Response criteria | ||||
| Patient Global Assessment of Disease Activity (0–100 mm) † | 71 | -8.3 | 73 | -34 |
| Total back pain (0–100 mm) ‡ | 73 | -12 | 72 | -32 |
| BASFI (0–10) § | 6.1 | -0.5 | 6.3 | -2.4 |
| Inflammation (0–10) ¶ | 7.4 | -1.1 | 7.3 | -3.6 |
| BASDAI Score | 7.1 | -1.1 | 7.1 | -3.1 |
| BASMI # | 5.0 | -0.1 | 5.0 | -0.4 |
| hsCRP (mg/L) | 19 | -2.3 | 20 | -17 |
At Week 16, a greater percentage of patients treated with SIMPONI ARIA achieved a low level of disease activity (<2 [on a scale of 0 to 10 cm] in all four ASAS domains) compared with patients treated with placebo (16.2% vs. 3.9%).
14.4 Polyarticular Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (pJIA)
The efficacy of SIMPONI ARIA in pediatric patients with pJIA is based on the pharmacokinetic exposure and extrapolation of the established efficacy of SIMPONI ARIA in RA patients. Efficacy of SIMPONI ARIA was also assessed in a multicenter, open-label, single-arm study in 127 children (2 to < 18 years of age) with JIA with active polyarthritis despite treatment with MTX for at least 2 months (Trial pJIA, NCT02277444). The polyarticular JIA patient subtypes at study entry included: rheumatoid factor negative (43%), rheumatoid factor positive (35%), enthesitis-related arthritis (9%), oligoarticular extended (6%), juvenile psoriatic arthritis (4%), and systemic JIA without systemic manifestations (3%). All patients received SIMPONI ARIA 80 mg/m 2as an intravenous infusion at Week 0, 4, and every 8 weeks through Week 52. Patients continued stable doses of MTX weekly through Week 28; after Week 28, changes in MTX dose were permitted. Efficacy was assessed as supportive endpoints through Week 52. The efficacy was generally consistent with responses in patients with RA.
16. How is Simponi Aria supplied
SIMPONI ARIA ®(golimumab) Injection is a colorless to light yellow solution available in packs of 1 vial NDC 57894-350-01.
17. Patient Counseling Information
See FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide).
Advise patients of the potential benefits and risks of SIMPONI ARIA. Instruct patients to read the Medication Guide before starting SIMPONI ARIA therapy and to read it each time the prescription is renewed.
| MEDICATION GUIDE
SIMPONI ARIA ®( SIM-po-nee AHR-ee-uh ) (golimumab) injection, for intravenous use |
|||
| What is the most important information I should know about SIMPONI ARIA? | |||
| SIMPONI ARIA is a medicine that affects your immune system. SIMPONI ARIA can lower the ability of your immune system to fight infections. Some people have serious infections while receiving SIMPONI ARIA, including tuberculosis (TB), and infections caused by bacteria, fungi, or viruses that spread throughout their body. Some people have died from these serious infections. | |||
|
|||
| You should not start receiving SIMPONI ARIA if you have any kind of infection unless your doctor tells you to. | |||
| Before receiving SIMPONI ARIA, tell your doctor if you: | |||
|
|||
|
|
||
|
|||
| After receiving SIMPONI ARIA, call your doctor right away if you have any symptoms of an infection. SIMPONI ARIA can make you more likely to get infections or make worse any infection that you have. | |||
| Cancer | |||
|
|||
| What is SIMPONI ARIA? | |||
SIMPONI ARIA is a prescription medicine called a TNF-blocker. SIMPONI ARIA is used to treat:
|
|||
| It is not known if SIMPONI ARIA is safe and effective in children with PsA and pJIA under 2 years of age or in children with conditions other than PsA and pJIA. | |||
| What should I tell my doctor before starting treatment with SIMPONI ARIA? | |||
| See " What is the most important information I should know about SIMPONI ARIA?". | |||
| Before starting SIMPONI ARIA, tell your doctor about all your medical conditions, including if you: | |||
|
|||
| Tell your doctor about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. | |||
| Especially, tell your doctor if you: | |||
|
|||
| Ask your doctor or pharmacist for a list of these medicines if you are not sure. | |||
| Keep a list of all your medicines with you to show your doctor and pharmacist each time you get a new medicine. | |||
| How should I receive SIMPONI ARIA? | |||
|
|||
|
|||
|
|||
| What are the possible side effects of SIMPONI ARIA? | |||
| SIMPONI ARIA can cause serious side effects, including: | |||
| See "
What is the most important information I should know about SIMPONI ARIA?"
Serious Infections. |
|||
|
|||
|
|
||
|
|||
|
|
||
| Hepatitis B infection in people who carry the virus in their blood.If you are a carrier of the hepatitis B virus (a virus that affects the liver), the virus can become active while you use SIMPONI ARIA. Your doctor should do blood tests before you start treatment with SIMPONI ARIA and while you are receiving SIMPONI ARIA. | |||
|
|||
|
|
||
| Heart failure, including new heart failure or worsening of heart failure that you already have can happen in people who use TNF-blocker medicines, including SIMPONI ARIA.If you develop new or worsening heart failure with SIMPONI ARIA, you may need to be treated in a hospital, and it may result in death. | |||
|
|||
| Nervous System Problems.Rarely, people receiving TNF-blocker medicines, including SIMPONI ARIA, have nervous system problems such as multiple sclerosis or Guillain-Barré syndrome. Tell your doctor right away if you get any of these symptoms: | |||
|
|
||
| Immune System Problems.Rarely, people receiving TNF-blocker medicines have developed symptoms that are like the symptoms of lupus. Tell your doctor if you have any of these symptoms: | |||
|
|
||
| Liver Problems.Liver problems can happen in people who receive TNF-blocker medicines, including SIMPONI ARIA. These problems can lead to liver failure and death. Call your doctor right away if you have any of these symptoms: | |||
|
|
||
| Blood Problems.Low blood counts have been seen with SIMPONI ARIA. Your body may not make enough blood cells that help fight infections or help stop bleeding. Symptoms include fever, bruising or bleeding easily, or looking pale. Your doctor will check your blood counts before and during treatment with SIMPONI ARIA. | |||
| Allergic Reactions.Allergic reactions can happen in people who receive TNF-blocker medicines, including SIMPONI ARIA. Some reactions may be serious and can be life-threatening. Some of these reactions can happen after receiving your first dose of SIMPONI ARIA. Call your doctor right away if you have any of these symptoms of an allergic reaction: | |||
|
|
||
| The most common side effects of SIMPONI ARIA include: | |||
|
|||
| These are not all of the possible side effects of SIMPONI ARIA. | |||
| Tell your doctor about any side effect that bothers you or does not go away. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. | |||
| General information about the safe and effective use of SIMPONI ARIA. | |||
| Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. | |||
| You can ask your doctor or pharmacist for information about SIMPONI ARIA that is written for health professionals. | |||
| What are the ingredients in SIMPONI ARIA? | |||
| Active ingredient: golimumab. | |||
| Inactive ingredients: L-histidine, L-histidine monohydrochloride monohydrate, polysorbate 80, sorbitol, and water for injection. SIMPONI ARIA is preservative-free and is not made with natural rubber latex. | |||
| Manufactured by: Janssen Biotech, Inc. Horsham, PA 19044 US License No. 1864 © 2017, 2020 Janssen Pharmaceutical Companies | |||
| For more information go to www.SIMPONIARIA.com or call 1-800-JANSSEN (1-800-526-7736). | |||
| This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration | Revised: 9/2020 | ||
| SIMPONI ARIA
golimumab solution |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Janssen Biotech, Inc. (099091753) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cilag AG | 483237103 | manufacture(57894-350) , analysis(57894-350) , label(57894-350) , pack(57894-350) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Janssen Sciences Ireland UC | 986030167 | api manufacture(57894-350) , analysis(57894-350) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Janssen Biologics, B.V. | 409612918 | api manufacture(57894-350) , analysis(57894-350) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anderson Brecon | 053217022 | label(57894-350) , pack(57894-350) | |