Drug Detail:Simponi (Golimumab [ goe-lim-ue-mab ])
Drug Class: TNF alfa inhibitors
Highlights of Prescribing Information
SIMPONI (golimumab) injection, for subcutaneous use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2009
WARNING: SERIOUS INFECTIONS AND MALIGNANCY
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
- Serious infections leading to hospitalization or death including tuberculosis (TB), bacterial sepsis, invasive fungal (such as histoplasmosis), and other opportunistic infections have occurred in patients receiving SIMPONI ( 5.1)
- Discontinue SIMPONI if a patient develops a serious infection or sepsis ( 5.1)
- Perform test for latent TB; if positive, start treatment for TB prior to starting SIMPONI ( 5.1)
- Monitor all patients for active TB during treatment, even if initial latent TB test is negative ( 5.1)
- Lymphoma and other malignancies, some fatal, have been reported in children and adolescent patients treated with TNF blockers, of which SIMPONI is a member ( 5.2)
Indications and Usage for Simponi
SIMPONI is a tumor necrosis factor (TNF) blocker indicated for the treatment of adult patients with:
- Moderately to severely active rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in combination with methotrexate ( 1.1)
- Active psoriatic arthritis (PsA) alone, or in combination with methotrexate ( 1.2)
- Active ankylosing spondylitis (AS) ( 1.3)
- Moderate to severe Ulcerative colitis (UC) with an inadequate response or intolerant to prior treatment or requiring continuous steroid therapy (
1.4)
- inducing and maintaining clinical response
- improving endoscopic appearance of the mucosa during induction
- inducing clinical remission
- achieving and sustaining clinical remission in induction responders
Simponi Dosage and Administration
- RA, PsA, and AS: 50 mg administered by subcutaneous injection once a month ( 2.1)
- UC: 200 mg initially administered by subcutaneous injection at Week 0, followed by 100 mg at Week 2 and then 100 mg every 4 weeks ( 2.2)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Injection ( 3):
- 50 mg/0.5 mL in a single-dose prefilled syringe or single-dose prefilled SmartJect ® autoinjector
- 100 mg/mL in a single-dose prefilled syringe or single-dose prefilled SmartJect ® autoinjector
Contraindications
None ( 4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Serious Infections: Do not start SIMPONI during an active infection. If an infection develops, monitor carefully, and stop SIMPONI if infection becomes serious ( 5.1)
- Invasive Fungal Infections: For patients who develop a systemic illness on SIMPONI, consider empiric antifungal therapy for those who reside in or travel to regions where mycoses are endemic ( 5.1)
- Hepatitis B Reactivation: Monitor HBV carriers during and several months after therapy. If reactivation occurs, stop SIMPONI and begin antiviral therapy ( 5.1)
- Malignancies: Incidence of lymphoma was greater than in the general U.S. population. Cases of other malignancies have been observed among patients receiving TNF blockers ( 5.2)
- Congestive Heart Failure: Worsening, or new onset, may occur. Stop SIMPONI if new or worsening symptoms occur ( 5.3)
- Demyelinating Disorders: Exacerbation or new onset may occur ( 5.4)
- Lupus-like Syndrome: Discontinue SIMPONI if symptoms develop ( 5.5)
- Hypersensitivity Reactions: Serious systemic hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylaxis may occur ( 5.11)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions (incidence > 5%) are upper respiratory tract infection, nasopharyngitis, injection site reactions ( 6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Janssen Biotech, Inc. at 1-800-JANSSEN (1-800-526-7736) or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
- Abatacept: Increased risk of serious infection ( 5.1, 5.6, 7.2)
- Anakinra: Increased risk of serious infection ( 5.1, 5.7, 7.2)
- Live vaccines/therapeutic infectious agents: Avoid use with SIMPONI ( 5.10, 7.3).
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 9/2019
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Simponi
1.1 Rheumatoid Arthritis
SIMPONI, in combination with methotrexate, is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with moderately to severely active rheumatoid arthritis.
1.2 Psoriatic Arthritis
SIMPONI, alone or in combination with methotrexate, is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with active psoriatic arthritis.
1.3 Ankylosing Spondylitis
SIMPONI is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with active ankylosing spondylitis.
1.4 Ulcerative Colitis
SIMPONI is indicated in adult patients with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis who have demonstrated corticosteroid dependence or who have had an inadequate response to or failed to tolerate oral aminosalicylates, oral corticosteroids, azathioprine, or 6-mercaptopurine for:
- inducing and maintaining clinical response
- improving endoscopic appearance of the mucosa during induction
- inducing clinical remission
- achieving and sustaining clinical remission in induction responders [see Clinical Studies (14.4)].
2. Simponi Dosage and Administration
2.1 Dosage in Rheumatoid Arthritis, Psoriatic Arthritis, Ankylosing Spondylitis
The SIMPONI dose regimen is 50 mg administered by subcutaneous injection once a month.
For patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), SIMPONI should be given in combination with methotrexate and for patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) or ankylosing spondylitis (AS), SIMPONI may be given with or without methotrexate or other nonbiologic Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs). For patients with RA, PsA, or AS, corticosteroids, non-biologic DMARDs, and/or NSAIDs may be continued during treatment with SIMPONI.
2.2 Dosage in Moderately to Severely Active Ulcerative Colitis
The recommended SIMPONI induction dosage regimen is a 200-mg subcutaneous injection at Week 0, followed by 100 mg at Week 2, and then maintenance therapy with 100 mg every 4 weeks.
2.3 Monitoring to Assess Safety
Prior to initiating SIMPONI and periodically during therapy, evaluate patients for active tuberculosis and tested for latent infection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] . Prior to initiating SIMPONI, patients should be tested for hepatitis B viral infection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] .
2.4 Important Administration Instructions
SIMPONI is intended for use under the guidance and supervision of a healthcare provider. After proper training in subcutaneous injection technique, a patient may self-inject with SIMPONI if a physician determines that it is appropriate. Instruct patients to follow the directions provided below [see Instructions for Use] :
- To ensure proper use, allow the prefilled syringe or autoinjector to sit at room temperature outside the carton for at least 30 minutes prior to subcutaneous injection. Do not warm SIMPONI in any other way.
- Prior to administration, visually inspect the solution for particles and discoloration through the viewing window. SIMPONI is clear to slightly opalescent and colorless to light yellow. Do not use SIMPONI, if the solution is discolored, or cloudy, or if foreign particles are present.
- Do not use any leftover product remaining in the prefilled syringe or prefilled autoinjector.
- Instruct patients sensitive to latex not to handle the needle cover on the prefilled syringe or the needle cover of the prefilled syringe within the autoinjector cap because it contains dry natural rubber (a derivative of latex).
- At the time of dosing, if multiple injections are required, administer the injections at different sites on the body.
- Rotate injection sites and never give injections into areas where the skin is tender, bruised, red, or hard.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
Injection: 50 mg/0.5 mL and 100 mg/mL clear to slightly opalescent, colorless to light yellow solution in a single-dose prefilled syringe or single-dose SmartJect autoinjector.
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Serious Infections
Patients treated with SIMPONI are at increased risk for developing serious infections involving various organ systems and sites that may lead to hospitalization or death.
Opportunistic infections due to bacterial, mycobacterial, invasive fungal, viral, or parasitic organisms including aspergillosis, blastomycosis, candidiasis, coccidioidomycosis, histoplasmosis, legionellosis, listeriosis, pneumocystosis, and tuberculosis have been reported with TNF blockers. Patients have frequently presented with disseminated rather than localized disease. The concomitant use of a TNF blocker and abatacept or anakinra was associated with a higher risk of serious infections; therefore, the concomitant use of SIMPONI and these biologic products is not recommended [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6, 5.7) and Drug Interactions (7.2)] .
Treatment with SIMPONI should not be initiated in patients with an active infection, including clinically important localized infections. Patients greater than 65 years of age, patients with co-morbid conditions and/or patients taking concomitant immunosuppressants such as corticosteroids or methotrexate may be at greater risk of infection. Consider the risks and benefits of treatment prior to initiating SIMPONI in patients:
- with chronic or recurrent infection;
- who have been exposed to tuberculosis;
- with a history of an opportunistic infection;
- who have resided or traveled in areas of endemic tuberculosis or endemic mycoses, such as histoplasmosis, coccidioidomycosis, or blastomycosis; or
- with underlying conditions that may predispose them to infection.
5.2 Malignancies
Malignancies, some fatal, have been reported among children, adolescents, and young adults who received treatment with TNF-blocking agents (initiation of therapy ≤ 18 years of age), of which SIMPONI is a member. Approximately half the cases were lymphomas, including Hodgkin's and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. The other cases represented a variety of malignancies, including rare malignancies that are usually associated with immunosuppression, and malignancies that are not usually observed in children and adolescents. The malignancies occurred after a median of 30 months (range 1 to 84 months) after the first dose of TNF-blocker therapy. Most of the patients were receiving concomitant immunosuppressants. These cases were reported postmarketing and are derived from a variety of sources, including registries and spontaneous postmarketing reports.
The risks and benefits of TNF-blocker treatment, including SIMPONI, should be considered prior to initiating therapy in patients with a known malignancy other than a successfully treated nonmelanoma skin cancer (NMSC) or when considering continuing a TNF-blocker in patients who develop a malignancy.
In the controlled portions of clinical trials of TNF blockers, including SIMPONI, more cases of lymphoma have been observed among patients receiving anti-TNF treatment compared with patients in the control groups. During the controlled portions of the Phase 2 trials in RA, and the Phase 3 trials in RA, PsA and AS, the incidence of lymphoma per 100 patient-years of follow-up was 0.21 (95% CI: 0.03, 0.77) in the combined SIMPONI group compared with an incidence of 0 (95% CI: 0, 0.96) in the placebo group. In the controlled and uncontrolled portions of these clinical trials in 2347 SIMPONI-treated patients with a median follow-up of 1.4 years, the incidence of lymphoma was 3.8-fold higher than expected in the general U.S. population according to the SEER database (adjusted for age, gender, and race). 1 Through Week 60 of the UC trials, there were no cases of lymphoma with SIMPONI. Patients with RA and other chronic inflammatory diseases, particularly patients with highly active disease and/or chronic exposure to immunosuppressant therapies, may be at higher risk (up to several fold) than the general population for the development of lymphoma, even in the absence of TNF-blocking therapy. Cases of acute and chronic leukemia have been reported with TNF-blocker use, including SIMPONI, in rheumatoid arthritis and other indications. Even in the absence of TNF-blocker therapy, patients with rheumatoid arthritis may be at a higher risk (approximately 2-fold) than the general population for the development of leukemia.
Rare postmarketing cases of hepatosplenic T-cell lymphoma (HSTCL) have been reported in patients treated with TNF-blocking agents. This rare type of T-cell lymphoma has a very aggressive disease course and is usually fatal. Nearly all of the reported TNF blocker associated cases have occurred in patients with Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis. The majority were in adolescent and young adult males. Almost all these patients had received treatment with azathioprine (AZA) or 6-mercaptopurine (6–MP) concomitantly with a TNF blocker at or prior to diagnosis. The potential risk with the combination of AZA or 6-MP and SIMPONI should be carefully considered. A risk for the development for hepatosplenic T-cell lymphoma in patients treated with TNF blockers cannot be excluded.
During the controlled portions of the Phase 2 trial in RA, and the Phase 3 trials in RA, PsA and AS, the incidence of malignancies other than lymphoma per 100 patient-years of follow-up was not elevated in the combined SIMPONI group compared with the placebo group. In the controlled and uncontrolled portions of these trials, the incidence of malignancies, other than lymphoma, in SIMPONI-treated patients was similar to that expected in the general U.S. population according to the SEER database (adjusted for age, gender, and race). 1 In the 6-week placebo-controlled portions of the SIMPONI Phase 2/3 clinical trials in UC, the incidence of non-lymphoma malignancies (excluding nonmelanoma skin cancer) was similar between the SIMPONI and the placebo group. Through Week 60, the incidence of non-lymphoma malignancies (excluding nonmelanoma skin cancer) was similar to the general U.S. population according to the SEER database (adjusted for age, gender, and race). 1 Short follow-up periods, such as those of one year or less in the studies above, may not adequately reflect the true incidence of malignancies .
It is not known if SIMPONI treatment influences the risk for developing dysplasia or colon cancer. All patients with ulcerative colitis who are at increased risk for dysplasia or colon carcinoma (for example, patients with long-standing ulcerative colitis or primary sclerosing cholangitis), or who had a prior history of dysplasia or colon carcinoma should be screened for dysplasia at regular intervals before therapy and throughout their disease course. This evaluation should include colonoscopy and biopsies per local recommendations. In patients with newly diagnosed dysplasia treated with SIMPONI, the risks and benefits to the individual patient must be carefully reviewed and consideration should be given to whether therapy should be continued.
Melanoma and Merkel cell carcinoma have been reported in patients treated with TNF-blocking agents, including SIMPONI. Periodic skin examination is recommended for all patients, particularly those with risk factors for skin cancer.
In controlled trials of other TNF blockers in patients at higher risk for malignancies (e.g., patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [COPD], patients with Wegener's granulomatosis treated with concomitant cyclophosphamide) a greater portion of malignancies occurred in the TNF-blocker group compared to the controlled group. In an exploratory 1-year clinical trial evaluating the use of 50 mg, 100 mg, and 200 mg of SIMPONI in 309 patients with severe persistent asthma, 6 patients developed malignancies other than NMSC in the SIMPONI groups compared to none in the control group. Three of the 6 patients were in the 200-mg SIMPONI group.
5.3 Congestive Heart Failure
Cases of worsening congestive heart failure (CHF) and new onset CHF have been reported with TNF blockers, including SIMPONI. Some cases had a fatal outcome. In several exploratory trials of other TNF blockers in the treatment of CHF, there were greater proportions of TNF-blocker-treated patients who had CHF exacerbations requiring hospitalization or increased mortality. SIMPONI has not been studied in patients with a history of CHF and SIMPONI should be used with caution in patients with CHF. If a decision is made to administer SIMPONI to patients with CHF, these patients should be closely monitored during therapy, and SIMPONI should be discontinued if new or worsening symptoms of CHF appear.
5.4 Demyelinating Disorders
Use of TNF blockers, of which SIMPONI is a member, has been associated with rare cases of new onset or exacerbation of central nervous system (CNS) demyelinating disorders, including multiple sclerosis (MS) and peripheral demyelinating disorders, including Guillain-Barré syndrome. Cases of central demyelination, MS, optic neuritis, and peripheral demyelinating polyneuropathy have rarely been reported in patients treated with SIMPONI [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] . Prescribers should exercise caution in considering the use of TNF blockers, including SIMPONI, in patients with central or peripheral nervous system demyelinating disorders. Discontinuation of SIMPONI should be considered if these disorders develop.
5.5 Autoimmunity
Treatment with TNF blockers, including SIMPONI, may result in the formation of antinuclear antibodies (ANA) and, rarely, in the development of a lupus-like syndrome [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] . If a patient develops symptoms suggestive of a lupus-like syndrome following treatment with SIMPONI, treatment should be discontinued.
5.6 Use with Abatacept
In controlled trials, the concurrent administration of another TNF blocker and abatacept was associated with a greater proportion of serious infections than the use of a TNF blocker alone; and the combination therapy, compared to the use of a TNF blocker alone, has not demonstrated improved clinical benefit in the treatment of RA. Therefore, the combination of TNF blockers, including SIMPONI, and abatacept is not recommended [see Drug Interactions (7.2)] .
5.7 Use with Anakinra
Concurrent administration of anakinra (an interleukin-1 antagonist) and another TNF blocker was associated with a greater portion of serious infections and neutropenia and no additional benefits compared with the TNF-blocker alone. Therefore, the combination of anakinra with TNF blockers, including SIMPONI, is not recommended [see Drug Interactions (7.2)] .
5.8 Switching Between Biological Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs
Care should be taken when switching from one biological product to another biological product since overlapping biological activity may further increase the risk of infection.
5.9 Hematologic Cytopenias
There have been reports of pancytopenia, leukopenia, neutropenia, agranulocytosis, aplastic anemia, and thrombocytopenia in patients receiving golimumab. Caution should be exercised when using TNF blockers, including SIMPONI, in patients who have or have had significant cytopenias.
5.11 Hypersensitivity Reactions
In postmarketing experience, serious systemic hypersensitivity reactions (including anaphylactic reaction) have been reported following SIMPONI administration. Some of these reactions occurred after the first administration of SIMPONI. If an anaphylactic or other serious allergic reaction occurs, administration of SIMPONI should be discontinued immediately and appropriate therapy instituted.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
The safety data described below are based on 5 pooled, randomized, double-blind, controlled Phase 3 trials in patients with RA, PsA, and AS (Trials RA-1, RA-2, RA-3, PsA, and AS) [see Clinical Studies (14.1, 14.2, and 14.3)] . These 5 trials included 639 control-treated patients and 1659 SIMPONI-treated patients including 1089 with RA, 292 with PsA, and 278 with AS. The safety data in 1233 SIMPONI-treated patients with ulcerative colitis from 3 pooled, randomized, double-blind, controlled Phase 2/3 trials are also described below (Trials UC-1, UC-2, and UC-3) [see Clinical Studies (14.4)]. The proportion of patients who discontinued treatment due to adverse reactions in the controlled Phase 3 trials through Week 16 in RA, PsA and AS was 2% for SIMPONI-treated patients and 3% for placebo-treated patients. The most common adverse reactions leading to discontinuation of SIMPONI in the controlled Phase 3 trials in RA, PsA and AS through Week 16 were sepsis (0.2%), alanine aminotransferase increased (0.2%), and aspartate aminotransferase increased (0.2%). The most common adverse drug reactions leading to discontinuation through Week 60 of the UC trials in patients who received SIMPONI induction and 100 mg during maintenance compared with patients who received SIMPONI induction and placebo during maintenance were tuberculosis (0.3% vs. 0.6%) and anemia (0.3% vs. 0%), respectively.
The most serious adverse reactions were:
- Serious Infections [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Malignancies [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
Upper respiratory tract infection and nasopharyngitis were the most common adverse reactions reported in the combined Phase 3 RA, PsA and AS trials through Week 16, occurring in 7% and 6% of SIMPONI-treated patients as compared with 6% and 5% of control-treated patients, respectively.
6.2 Immunogenicity
As with all therapeutic proteins, there is potential for immunogenicity. The detection of antibody formation is highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assay. Additionally, the observed incidence of antibody (including neutralizing antibody) positivity in an assay may be influenced by several factors including assay methodology, sample handling, timing of sample collection, concomitant medications, and underlying disease. For these reasons, comparison of the incidence of antibodies to golimumab in the trials described below with the incidence of antibodies in other trials or to other products may be misleading.
6.3 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of golimumab. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to SIMPONI exposure.
Immune system disorders: Serious systemic hypersensitivity reactions (including anaphylactic reaction) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)] , sarcoidosis
Neoplasms benign, malignant and unspecified: Melanoma, Merkel cell carcinoma [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders: Interstitial lung disease
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: Skin exfoliation, lichenoid reactions, rash, bullous skin reactions
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 Methotrexate
For the treatment of RA, SIMPONI should be used with methotrexate (MTX) [see Clinical Studies (14.1)] . Since the presence or absence of concomitant MTX did not appear to influence the efficacy or safety of SIMPONI in the treatment of PsA or AS, SIMPONI can be used with or without MTX in the treatment of PsA and AS [see Clinical Studies (14.2, 14.3) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)] .
7.2 Biological Products for RA, PsA, and/or AS
An increased risk of serious infections has been seen in clinical RA trials of other TNF blockers used in combination with anakinra or abatacept, with no added benefit; therefore, use of SIMPONI with abatacept or anakinra is not recommended [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6, 5.7)] . A higher rate of serious infections has also been observed in RA patients treated with rituximab who received subsequent treatment with a TNF blocker. The concomitant use of SIMPONI with biologics approved to treat RA, PsA, or AS is not recommended because of the possibility of an increased risk of infection.
7.3 Live Vaccines/Therapeutic Infectious Agents
Live vaccines should not be given concurrently with SIMPONI [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)] .
Therapeutic infectious agents should not be given concurrently with SIMPONI [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)] .
Infants born to women treated with SIMPONI during their pregnancy may be at increased risk of infection for up to 6 months. Administration of live vaccines to infants exposed to SIMPONI in utero is not recommended for 6 months following the mother's last SIMPONI injection during pregnancy [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)] .
7.4 Cytochrome P450 Substrates
The formation of CYP450 enzymes may be suppressed by increased levels of cytokines (e.g., TNFα) during chronic inflammation. Therefore, it is expected that for a molecule that antagonizes cytokine activity, such as golimumab, the formation of CYP450 enzymes could be normalized. Upon initiation or discontinuation of SIMPONI in patients being treated with CYP450 substrates with a narrow therapeutic index, monitoring of the effect (e.g., warfarin) or drug concentration (e.g., cyclosporine or theophylline) is recommended and the individual dose of the drug product may be adjusted as needed.
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.4 Pediatric Use
Effectiveness of SIMPONI in pediatric patients less than 18 years of age has not been established.
The safety and efficacy of SIMPONI were evaluated in a multicenter, placebo-controlled, double-blind, randomized-withdrawal, parallel group study in 173 children (2 to 17 years of age) with active polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis (pJIA) despite treatment with MTX for at least 3 months. Subjects were maintained on their stable dose of MTX at the same dose (mg/week) at study entry. Concurrent use of stable doses of oral corticosteroids (≤10 mg/day or 0.2 mg/kg/day prednisone or equivalent, whichever was less) and/or NSAIDs was permitted. In the 16 week open-label phase, all patients received MTX and SIMPONI 30 mg/m 2 (maximum 50 mg) subcutaneously every 4 weeks. Patients who achieved an ACR Ped 30 response at Week 16 entered the randomized-withdrawal phase of the study and received MTX and either SIMPONI 30 mg/m 2 (maximum 50 mg) or placebo every 4 weeks through Week 48.
The primary endpoint of the study was the proportion of patients who did not experience a flare between Week 16 and Week 48, among all subjects who entered the randomized withdrawal phase. The efficacy of SIMPONI in the treatment of pJIA was not demonstrated in this study because there was no statistical evidence of differences in flare rate between SIMPONI-treated patients and placebo patients between Weeks 16 and 48.
In this study, the frequency and type of the adverse reactions seen in children were generally similar to those observed in adults.
8.5 Geriatric Use
In the Phase 3 trials in RA, PsA, and AS, there were no overall differences in SAEs, serious infections, and AEs in SIMPONI-treated patients ages 65 or older (N=155) compared with younger SIMPONI-treated patients. In UC, there were insufficient numbers of patients aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from patients aged 18 to 65. Because there is a higher incidence of infections in the geriatric population in general, caution should be used in treating geriatric patients with SIMPONI.
10. Overdosage
In a clinical trial, 5 patients received protocol-directed single infusions of 10 mg/kg of intravenous SIMPONI without serious adverse reactions or other significant reactions. The highest weight patient was 100 kg and, therefore, received a single intravenous infusion of 1000 mg of SIMPONI.
11. Simponi Description
Golimumab is a human IgG1κ monoclonal antibody specific for human tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFα) that exhibits multiple glycoforms with molecular masses of approximately 150 to 151 kilodaltons. Golimumab was created using genetically engineered mice immunized with human TNF, resulting in an antibody with human-derived antibody variable and constant regions. Golimumab is produced by a recombinant cell line cultured by continuous perfusion and is purified by a series of steps that includes measures to inactivate and remove viruses.
SIMPONI (golimumab) Injection is a preservative-free, sterile, clear to slightly opalescent, colorless to light yellow solution of the golimumab antibody supplied in a single-dose prefilled syringe (with a passive needle safety guard) or a single-dose prefilled autoinjector.
Each 0.5 mL prefilled syringe and autoinjector contains 50 mg golimumab, L-histidine and L-histidine monohydrochloride monohydrate (0.44 mg), polysorbate 80 (0.08 mg), sorbitol (20.5 mg) and Water for Injection. Each 1 mL prefilled syringe and autoinjector contains 100 mg golimumab, L-histidine and L-histidine monohydrochloride monohydrate (0.87 mg), polysorbate 80 (0.15 mg), sorbitol (41.0 mg) and Water for Injection. The pH is approximately 5.5.
12. Simponi - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Golimumab is a human monoclonal antibody that binds to both the soluble and transmembrane bioactive forms of human TNFα. This interaction prevents the binding of TNFα to its receptors, thereby inhibiting the biological activity of TNFα (a cytokine protein). There was no evidence of the golimumab antibody binding to other TNF superfamily ligands; in particular, the golimumab antibody did not bind or neutralize human lymphotoxin. Golimumab did not lyse human monocytes expressing transmembrane TNF in the presence of complement or effector cells.
Elevated TNFα levels in the blood, synovium, and joints have been implicated in the pathophysiology of several chronic inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, and ankylosing spondylitis. TNFα is an important mediator of the articular inflammation that is characteristic of these diseases. The exact mechanism by which golimumab treats ulcerative colitis is unknown. Golimumab modulated the in vitro biological effects mediated by TNF in several bioassays, including the expression of adhesion proteins responsible for leukocyte infiltration (E-selectin, ICAM-1 and VCAM-1) and the secretion of proinflammatory cytokines (IL-6, IL-8, G-CSF and GM-CSF).
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
In clinical trials, decreases in C-reactive protein (CRP), interleukin (IL)-6, matrix metalloproteinase-3 (MMP-3), intercellular adhesion molecule (ICAM)-1 and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) were observed following SIMPONI administration in patients with RA, PsA, and AS.
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Long-term animal studies of golimumab have not been conducted to evaluate its carcinogenic potential. Mutagenicity studies have not been conducted with golimumab. A fertility study conducted in mice using an analogous anti-mouse TNFα antibody administered by the intravenous route at doses up to 40 mg/kg once per week showed no impairment of fertility.
14. Clinical Studies
14.1 Rheumatoid Arthritis
The efficacy and safety of SIMPONI were evaluated in 3 multicenter, randomized, double-blind, controlled trials (Trials RA-1, RA-2, and RA-3) in 1542 patients ≥ 18 years of age with moderately to severely active RA, diagnosed according to the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) criteria, for at least 3 months prior to administration of trial agent. Patients were required to have at least 4 swollen and 4 tender joints. SIMPONI was administered subcutaneously at doses of 50 mg or 100 mg every 4 weeks. Double-blinded controlled efficacy data were collected and analyzed through Week 24. Patients were allowed to continue stable doses of concomitant low dose corticosteroids (equivalent to ≤ 10 mg of prednisone a day) and/or NSAIDs and patients may have received oral MTX during the trials.
Trial RA-1 evaluated 445 patients who were previously treated (at least 8 to 12 weeks prior to administration of trial agent) with one or more doses of a biologic TNF blocker without a serious adverse reaction. Patients may have discontinued the biologic TNF blocker for a variety of reasons. Patients were randomized to receive placebo (N=150), SIMPONI 50 mg (N=147), or SIMPONI 100 mg (N=148). Patients were allowed to continue stable doses of concomitant MTX, sulfasalazine (SSZ), and/or hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) during the trial. The use of other DMARDs including cytotoxic agents or other biologics was prohibited.
Trial RA-2 evaluated 444 patients who had active RA despite a stable dose of at least 15 mg/week of MTX and who had not been previously treated with a biologic TNF blocker. Patients were randomized to receive background MTX (N=133), SIMPONI 50 mg + background MTX (N=89), SIMPONI 100 mg + background MTX (N=89), or SIMPONI 100 mg monotherapy (N=133). The use of other DMARDs including SSZ, HCQ, cytotoxic agents, or other biologics was prohibited.
Trial RA-3 evaluated 637 patients with active RA who were MTX naïve and had not previously been treated with a biologic TNF blocker. Patients were randomized to receive MTX (N=160), SIMPONI 50 mg + MTX (N=159), SIMPONI 100 mg + MTX (N=159), or SIMPONI 100 mg monotherapy (N=159). For patients receiving MTX, MTX was administered at a dose of 10 mg/week beginning at Week 0 and increased to 20 mg/week by Week 8. The use of other DMARDs including SSZ, HCQ, cytotoxic agents, or other biologics was prohibited.
The primary endpoint in Trial RA-1 and Trial RA-2 was the percentage of patients achieving an ACR 20 response at Week 14 and the primary endpoint in Trial RA-3 was the percentage of patients achieving an ACR 50 response at Week 24.
In Trials RA-1, RA-2, and RA-3, the median duration of RA disease was 9.4, 5.7, and 1.2 years and 99%, 75%, and 54% of the patients used at least one DMARD in the past, respectively. Approximately 77% and 57% of patients received concomitant NSAIDs and low dose corticosteroids, respectively, in the 3 pooled RA trials.
14.2 Psoriatic Arthritis
The safety and efficacy of SIMPONI were evaluated in a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in 405 adult patients with moderately to severely active PsA (≥ 3 swollen joints and ≥ 3 tender joints) despite NSAID or DMARD therapy (Trial PsA). Patients in this trial had a diagnosis of PsA for at least 6 months with a qualifying psoriatic skin lesion of at least 2 cm in diameter. Previous treatment with a biologic TNF blocker was not allowed. Patients were randomly assigned to placebo (N=113), SIMPONI 50 mg (N=146), or SIMPONI 100 mg (N=146) given subcutaneously every 4 weeks. Patients were allowed to receive stable doses of concomitant MTX (≤ 25 mg/week), low dose oral corticosteroids (equivalent to ≤ 10 mg of prednisone a day), and/or NSAIDs during the trial. The use of other DMARDs including SSZ, HCQ, cytotoxic agents, or other biologics was prohibited. The primary endpoint was the percentage of patients achieving ACR 20 response at Week 14. Placebo-controlled efficacy data were collected and analyzed through Week 24.
Patients with each subtype of PsA were enrolled, including polyarticular arthritis with no rheumatoid nodules (43%), asymmetric peripheral arthritis (30%), distal interphalangeal (DIP) joint arthritis (15%), spondylitis with peripheral arthritis (11%), and arthritis mutilans (1%). The median duration of PsA disease was 5.1 years, 78% of patients received at least one DMARD in the past, and approximately 48% of patients received MTX, and 16% received low dose oral steroids.
Clinical Response in Patients with PsA
SIMPONI ± MTX, compared with placebo ± MTX, resulted in significant improvement in signs and symptoms as demonstrated by the proportion of patients with an ACR 20 response at Week 14 in Trial PsA (see Table 4). There was no clear evidence of improved ACR response with the higher SIMPONI dose group (100 mg) compared to the lower SIMPONI dose group (50 mg). ACR responses observed in the SIMPONI-treated groups were similar in patients receiving and not receiving concomitant MTX. Similar ACR 20 responses at Week 14 were observed in patients with different PsA subtypes. However, the number of patients with arthritis mutilans was too small to allow meaningful assessment. SIMPONI 50-mg treatment also resulted in significantly greater improvement compared with placebo for each ACR component in Trial PsA (Table 5). Treatment with SIMPONI resulted in improvement in enthesitis and skin manifestations in patients with PsA. However, the safety and efficacy of SIMPONI in the treatment of patients with plaque psoriasis has not been established.
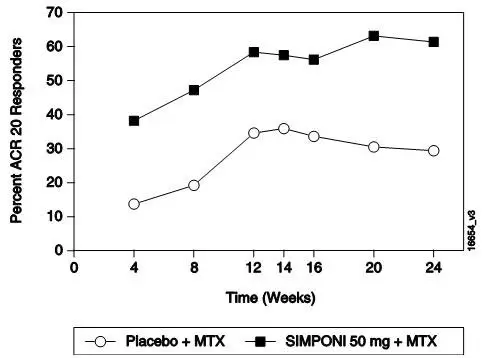
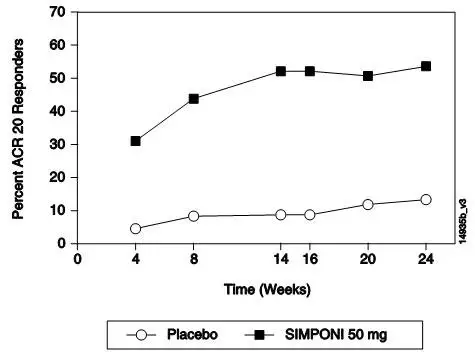
The percentage of patients achieving ACR 20 responses by visit for Trial PsA is shown in Figure 2. ACR 20 responses were observed in 31% of patients in the SIMPONI 50-mg + MTX group at the first assessment (Week 4) after the initial SIMPONI administration.
| Placebo ± MTX * | SIMPONI 50 mg ± MTX * | |
|---|---|---|
| Bold text indicates primary endpoint. | ||
|
||
| N † | 113 | 146 |
| ACR 20 | ||
| Week 14 | 9% | 51% |
| Week 24 | 12% | 52% |
| ACR 50 | ||
| Week 14 | 2% | 30% |
| Week 24 | 4% | 32% |
| ACR 70 | ||
| Week 14 | 1% | 12% |
| Week 24 | 1% | 19% |
| Placebo ± MTX * | SIMPONI 50 mg ± MTX * | |
|---|---|---|
| Note: Baseline are median values. | ||
|
||
| N † | 113 | 146 |
| Number of swollen joints (0–66) | ||
| Baseline | 10.0 | 11.0 |
| Week 14 | 8% | 60% |
| Number of tender joints (0–68) | ||
| Baseline | 18.0 | 19.0 |
| Week 14 | 0% | 54% |
| Patient's assessment of pain (0–10) | ||
| Baseline | 5.4 | 5.8 |
| Week 14 | -1% | 48% |
| Patient's global assessment of disease activity (0–10) | ||
| Baseline | 5.2 | 5.2 |
| Week 14 | 2% | 49% |
| Physician's global assessment of disease activity (0–10) | ||
| Baseline | 5.2 | 5.4 |
| Week 14 | 7% | 59% |
| HAQ score (0–10) | ||
| Baseline | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| Week 14 | 0% | 28% |
| CRP (mg/dL) (0–10) | ||
| Baseline | 0.6 | 0.6 |
| Week 14 | 0% | 40% |
|
| Figure 2: Trial PsA – Percentage of ACR 20 PsA Responders by Visit: Randomized Patients * |
 |
14.3 Ankylosing Spondylitis
The safety and efficacy of SIMPONI were evaluated in a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in 356 adult patients with active ankylosing spondylitis according to modified New York criteria for at least 3 months (Trial AS). Patients had symptoms of active disease [defined as a Bath AS Disease Activity Index (BASDAI) ≥ 4 and VAS for total back pain of ≥ 4, on scales of 0 to 10 cm] despite current or previous NSAID therapy. Patients were excluded if they were previously treated with a biologic TNF blocker or if they had complete ankylosis of the spine. Patients were randomly assigned to placebo (N=78), SIMPONI 50 mg (N=138), or SIMPONI 100 mg (N=140) administered subcutaneously every 4 weeks. Patients were allowed to continue stable doses of concomitant MTX, sulfasalazine (SSZ), hydroxychloroquine (HCQ), low dose corticosteroids (equivalent to < 10 mg of prednisone a day), and/or NSAIDs during the trial. The use of other DMARDs including cytotoxic agents or other biologics was prohibited.
The primary endpoint was the percentage of patients achieving an ASsessment in Ankylosing Spondylitis (ASAS) 20 response at Week 14. Placebo-controlled efficacy data were collected and analyzed through Week 24.
In Trial AS, the median duration of AS disease was 5.6 years, median duration of inflammatory back pain was 12 years, 83% were HLA-B27 positive, 24% had prior joint surgery or procedure, and 55% received at least one DMARD in the past. During the trial, the use of concomitant DMARDs and/or NSAIDs was as follows: MTX (20%), SSZ (26%), HCQ (1%), low dose oral steroids (16%), and NSAIDs (90%).
Clinical Response in Patients with AS
In Trial AS, SIMPONI ± DMARDs treatment, compared with placebo ± DMARDs, resulted in a significant improvement in signs and symptoms as demonstrated by the proportion of patients with an ASAS 20 response at Week 14 (see Table 6). There was no clear evidence of improved ASAS response with the higher SIMPONI dose group (100 mg) compared to the lower SIMPONI dose group (50 mg). Table 7 shows the percent improvement in the components of the ASAS response criteria for the SIMPONI 50 mg ± DMARDs and placebo ± DMARDs groups in Trial AS.
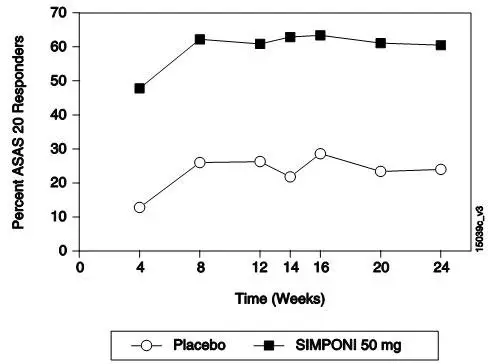
The percentage of patients achieving ASAS 20 responses by visit for Trial AS is shown in Figure 3. ASAS 20 responses were observed in 48% of patients in the SIMPONI 50-mg + MTX group at the first assessment (Week 4) after the initial SIMPONI administration.
| Placebo ± DMARDs * | SIMPONI 50 mg ± DMARDs * | |
|---|---|---|
| Bold text indicates primary endpoint. | ||
|
||
| N † | 78 | 138 |
| Responders, % of patients | ||
| ASAS 20 | ||
| Week 14 | 22% | 59% |
| Week 24 | 23% | 56% |
| ASAS 40 | ||
| Week 14 | 15% | 45% |
| Week 24 | 15% | 44% |
| Placebo ± DMARDs * | SIMPONI 50 mg ± DMARDs * | |
|---|---|---|
|
||
| N † | 78 | 138 |
| ASAS components | ||
| Patient global assessment (0–10) | ||
| Baseline | 7.2 | 7.0 |
| Week 14 | 13% | 47% |
| Total back pain (0–10) | ||
| Baseline | 7.6 | 7.5 |
| Week 14 | 9% | 50% |
| BASFI (0–10) ‡ | ||
| Baseline | 4.9 | 5.0 |
| Week 14 | -3% | 37% |
| Inflammation (0–10) § | ||
| Baseline | 7.1 | 7.1 |
| Week 14 | 6% | 59% |
|
| Figure 3: Trial AS – Percentage of AS Patients Achieving ASAS 20 Response by Visit: Randomized Patients * |
 |
14.4 Ulcerative Colitis
The safety and efficacy of SIMPONI were evaluated in 2 multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trials in patients ≥ 18 years of age (Trials UC-1 and UC-2).
Trial UC-1 was an induction trial conducted in patients with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis (UC), defined as a Mayo score of 6 to 12 [the Mayo score ranges from 0 to 12 and has 4 subscales that are each scored from 0 (normal) to 3 (most severe): stool frequency, rectal bleeding, findings on endoscopy, and physician global assessment]. At baseline, subjects also had an endoscopy subscore of 2 or 3 on a 3-point scale (an endoscopy score of 2 is defined by marked erythema, absent vascular pattern, friability, erosions; and a score of 3 is defined by spontaneous bleeding, ulceration). Patients were corticosteroid dependent (i.e., an inability to successfully taper corticosteroids without a return of the symptoms of UC) or had an inadequate response to or had failed to tolerate at least one of the following therapies: oral aminosalicylates, oral corticosteroids, azathioprine, or 6-mercaptopurine.
Trial UC-1 was divided into 2 parts. In Part 1 (dose finding), patients were randomized to one of 4 treatment groups: 400 mg SIMPONI administered subcutaneously (SC) at Week 0 and 200 mg at Week 2 (400/200 mg), 200-mg SIMPONI SC at Week 0 and 100 mg at Week 2 (200/100 mg), 100-mg SIMPONI SC at Week 0 and 50 mg at Week 2 (100/50 mg), or placebo SC at Weeks 0 and 2. In Part 2 (dose confirming), efficacy was evaluated in 761 patients who were randomized to receive either 400 mg SIMPONI SC at Week 0 and 200 mg at Week 2, 200-mg SIMPONI SC at Week 0 and 100 mg at Week 2, or placebo SC at Weeks 0 and 2. SIMPONI 100/50-mg SC was not evaluated in Part 2; its safety and effectiveness has not been established in UC. Concomitant stable doses of oral aminosalicylates (5-ASA), oral corticosteroids (less than 40 mg/day), azathioprine (AZA), 6-mercaptopurine (6-MP), and/or methotrexate (MTX) were permitted. Patients who received previous TNF inhibitors were excluded. The primary endpoint was the percent of patients in clinical response at Week 6, defined as a decrease from baseline in the Mayo score by ≥ 30% and ≥ 3 points, accompanied by a decrease in the rectal bleeding subscore of ≥ 1 or a rectal bleeding subscore of 0 (no blood seen) or 1 (streaks of blood with stool less than half the time).
Trial UC-2 was a randomized-withdrawal maintenance trial that evaluated 456 patients who achieved clinical response with SIMPONI induction and tolerated SIMPONI treatment. Patients were randomized to receive SIMPONI 50 mg, SIMPONI 100 mg or placebo administered subcutaneously every 4 weeks. Concomitant stable doses of oral aminosalicylates, azathioprine, 6-mercaptopurine, and/or methotrexate were permitted. Corticosteroids were to be tapered at the start of the maintenance trial. The primary endpoint was the percent of patients maintaining clinical response through Week 54.
15. References
1. SEER [database online]. US Population Data – 1969–2004. Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute. Release date: January 3, 2007. Available at: http//seer.cancer.gov/popdata/.
16. How is Simponi supplied
SIMPONI (golimumab) Injection is a preservative-free, sterile, clear to slightly opalescent, colorless to light yellow solution for subcutaneous use in a single-dose prefilled autoinjector (contains a prefilled glass syringe) or single-dose prefilled glass syringe. The Type 1 glass syringe has a coated stopper. The fixed stainless steel needle (5 bevel, 27G, ½ inch) is covered with a needle shield to prevent leakage of the solution through the needle and to protect the needle during handling prior to subcutaneous administration. The needle shield is made of a dry natural rubber containing latex.
| 50 mg/0.5 mL single-dose prefilled syringe | 1 pack | NDC 57894-070-01 |
| 100 mg/mL single-dose prefilled syringe | 1 pack | NDC 57894-071-01 |
| 50 mg/0.5 mL single-dose prefilled SmartJect ® autoinjector | 1 pack | NDC 57894-070-02 |
| 100 mg/mL single-dose prefilled SmartJect ® autoinjector | 1 pack | NDC 57894-071-02 |
17. Patient Counseling Information
See FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide and Instructions for Use)
Patients should be advised of the potential benefits and risks of SIMPONI. Physicians should instruct their patients to read the Medication Guide before starting SIMPONI therapy and to read it each time the prescription is renewed.
| This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. | Revised: May 2018 | ||
| MEDICATION GUIDE
SIMPONI ® (SIM-po-nee) (golimumab) injection, for subcutaneous use |
|||
| What is the most important information I should know about SIMPONI?
SIMPONI is a medicine that affects your immune system. SIMPONI can lower the ability of your immune system to fight infections. Some people have serious infections while taking SIMPONI, including tuberculosis (TB), and infections caused by bacteria, fungi, or viruses that spread throughout their body. Some people have died from these serious infections.
You should not start taking SIMPONI if you have any kind of infection unless your doctor says it is okay. Before starting SIMPONI, tell your doctor if you:
|
|||
|
|
||
Cancer
|
|||
| What is SIMPONI?
SIMPONI is a prescription medicine called a Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF) blocker. SIMPONI is used in adults:
You may continue to use other medicines that help treat your condition while taking SIMPONI, such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and prescription steroids, as recommended by your doctor. It is not known if SIMPONI is safe and effective in children under 18 years of age. |
|||
| What should I tell my doctor before starting treatment with SIMPONI?
SIMPONI may not be right for you. See " What is the most important information I should know about SIMPONI?" Before starting SIMPONI, tell your doctor about all your medical conditions, including if you:
Especially, tell your doctor if you:
Ask your doctor if you are not sure if your medicine is one listed above.
|
|||
How should I use SIMPONI?
|
|||
| What are the possible side effects of SIMPONI?
SIMPONI can cause serious side effects, including: See " What is the most important information I should know about SIMPONI?" Serious Infections.
|
|||
|
|
||
|
|||
|
|
||
Hepatitis B infection in people who carry the virus in their blood.
|
|||
|
|
||
Heart failure, including new heart failure or worsening of heart failure that you already have, can happen in people who use TNF-blocker medicines including SIMPONI. If you develop new or worsening heart failure with SIMPONI, you may need to be treated in a hospital, and it may result in death.
|
|||
|
Nervous System Problems. Rarely, people using TNF-blocker medicines, including SIMPONI, have nervous system problems such as multiple sclerosis or Guillain-Barré syndrome. Tell your doctor right away if you get any of these symptoms: |
|||
|
|
||
|
Immune System Problems. Rarely, people using TNF-blocker medicines have developed symptoms that are like the symptoms of Lupus. Tell your doctor if you have any of these symptoms: |
|||
|
|
||
|
Liver Problems. Liver problems can happen in people who use TNF-blocker medicines, including SIMPONI. These problems can lead to liver failure and death. Call your doctor right away if you have any of these symptoms: |
|||
|
|
||
|
Blood Problems. Low blood counts have been seen with SIMPONI. Your body may not make enough blood cells that help fight infections or help stop bleeding. Symptoms include fever, bruising or bleeding easily, or looking pale. Your doctor will check your blood counts before and during treatment with SIMPONI. |
|||
|
Allergic Reactions. Allergic reactions can happen in people who use TNF-blocker medicines, including SIMPONI. Some reactions may be serious and can be life-threatening. Some of these reactions can happen after receiving your first dose of SIMPONI. Call your doctor right away if you have any of these symptoms of an allergic reaction: |
|||
|
|
||
|
The most common side effects of SIMPONI include:
|
|||
|
Psoriasis. Some people using SIMPONI had new psoriasis or worsening of psoriasis they already had. Tell your doctor if you develop red scaly patches or raised bumps that are filled with pus. Your doctor may decide to stop your treatment with SIMPONI. These are not all of the possible side effects of SIMPONI. Tell your doctor about any side effect that bothers you or does not go away. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. |
|||
Keep SIMPONI and all medicines out of the reach of children. |
|||
| General information about the safe and effective use of SIMPONI.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use SIMPONI for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give SIMPONI to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. This Medication Guide summarizes the most important information about SIMPONI. If you would like more information, talk to your doctor. You can ask your doctor or pharmacist for information about SIMPONI that is written for health professionals. For more information go to www.simponi.com or call 1-800-JANSSEN (1-800-526-7736). |
|||
| What are the ingredients in SIMPONI?
Active ingredient: golimumab. Inactive ingredients: L-histidine, L-histidine monohydrochloride monohydrate, polysorbate 80, sorbitol, and water for injection. SIMPONI does not contain preservatives. Manufactured by: Janssen Biotech, Inc. Horsham, PA 19044 US License No. 1864 © 2014 Janssen Pharmaceutical Companies |
|||
Instructions for Use
SIMPONI
® (SIM-po-nee)
(golimumab)
SmartJect
® autoinjector
Important
If your doctor decides that you or a caregiver may be able to give your SIMPONI injections at home, you should receive training on the right way to prepare and inject SIMPONI using SmartJect.
Do not try to inject SIMPONI yourself until you have been shown the right way to give the injections by your doctor or nurse.
Please read this Instructions for Use before using SIMPONI SmartJect and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This leaflet does not take the place of talking with your doctor about your medical condition or your treatment.
 | Store SIMPONI in the refrigerator at 36°F to 46°F (2°C to 8°C). |
If needed, store SIMPONI at room temperature, up to 77°F (25°C) for one period of time up to 30 days. Do not return it to the refrigerator. Throw away (dispose of) if not used within 30 days at room temperature.
Do not freeze SmartJect.
Do not shake SmartJect.
Keep SIMPONI in the original carton to protect from light before use.
Keep SIMPONI and all medicines out of the reach of children.
Your SmartJect at-a-glance
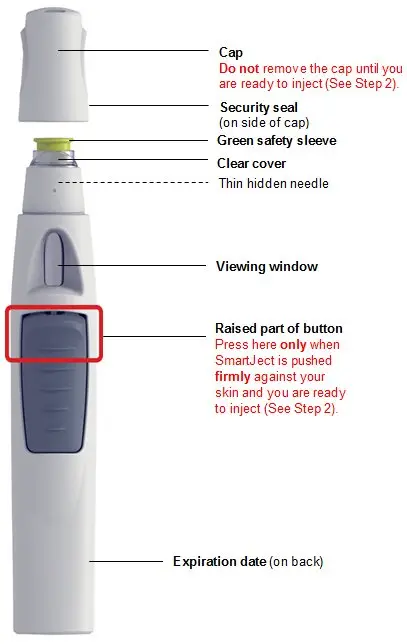
1. Prepare for your injection
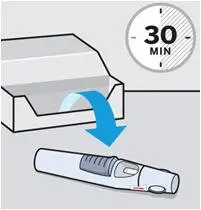
Take out SmartJect
Take SmartJect out of the refrigerator and remove it from the carton. Place on a flat surface out of reach of children.
SmartJect should sit at room temperature for at least 30 minutes to ensure proper injection.
Do not warm any other way.
Do not remove the cap yet.
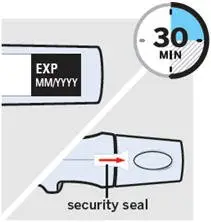
Inspect SmartJect
Check the expiration date ('EXP') on the back of SmartJect.
Do not use SIMPONI SmartJect if the expiration date has passed. Call your doctor or pharmacist for a refill.
Check the security seal on the cap.
Do not inject if the seal is broken.
Gather supplies
While SmartJect sits at room temperature for 30 minutes, gather your supplies:
- 1 Alcohol swab
- 1 Cotton ball or gauze pad
- 1 Sharps container (See Step 3)
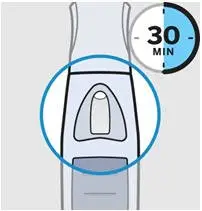
Check liquid in the SmartJect
After 30 minutes, check the liquid in the viewing window. It should be clear to slightly yellow and may contain tiny white or clear particles.
It is also normal to see a small air bubble.
Do not inject if the liquid is cloudy or discolored, or has large particles.
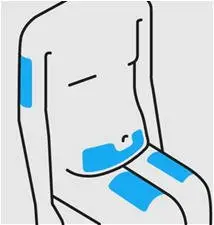
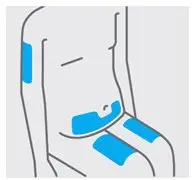
Choose injection site
Select from the following areas for your injection:
- Front of thighs
- Lower abdomen (do not use the 2-inch area around your navel (belly-button)
- Do not inject into the arms
Choose a different site within your preferred area for each injection.
Do not inject into skin that is tender, bruised, red, scaly or hard.
Do not inject into areas with scars or stretch marks.
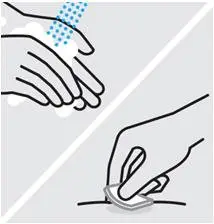
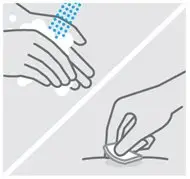
Clean injection site
Wash your hands well with soap and warm water.
Wipe your chosen injection site with an alcohol swab and allow it to dry.
Do not touch, fan or blow on the injection site after you have cleaned it.
2. Inject SIMPONI using SmartJect
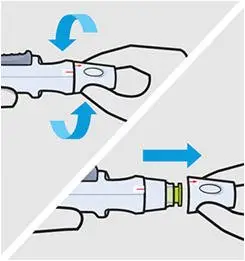
Remove cap
Twist the cap to break the security seal, then pull it straight off. Dispose of the cap right away.
It is important to inject within 5 minutes of removing the cap.
Do not put the cap back on, this may damage the hidden needle.
Do not inject if SmartJect is dropped without the cap on.
Do not pinch the skin.
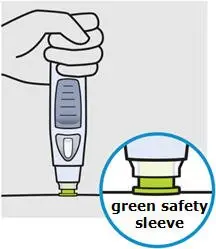
Position
Hold SmartJect comfortably and position it straight onto your skin, as shown.
Make sure the green safety sleeve is flat against your skin and that your injection site is as flat as possible.
Do not pinch your skin while positioning SmartJect onto your skin.
Do not touch or press the button while positioning the SmartJect onto your skin.
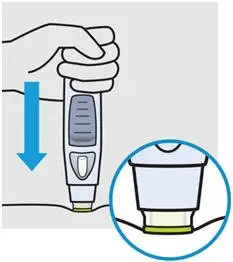
Push firmly
Push SmartJect firmly against your skin so the green safety sleeve slides into the clear cover.
Do not touch or press the button while pushing SmartJect against your skin.

The green safety sleeve helps prevent accidental injections.
You will not be able to press the button to start your injection until SmartJect is pushed firmly enough against your skin for the green safety sleeve to slide into the clear cover.
Press button and wait
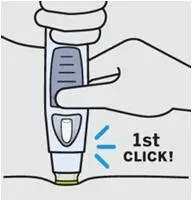
Keep holding SmartJect firmly against your skin. Use your other hand to press the raised part of the button to start your injection.
You will hear a loud 1st 'click' as you press the button. This is normal, the medication is just beginning to be delivered. You may or may not feel a needle prick.
Do not lift SmartJect up yet! This may result in loss of medication.
After 1 press of the button, you do not need to keep pressure on the button.
Wait for the 2nd 'click' which means your injection is complete.
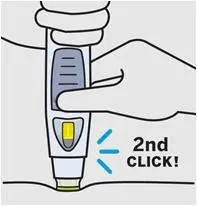
Listen for 2nd 'click'
Keep holding SmartJect firmly against your skin until you hear the 2nd 'click' (3–15 seconds).
The 2nd 'click' means the injection is complete and you can lift SmartJect from your skin.
If you have trouble hearing the 'clicks', count to 15 after pressing the button, then lift the SmartJect off your skin.
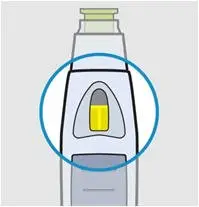
Check the viewing window
After lifting SmartJect from your skin, look for the yellow indicator in the viewing window to confirm SmartJect worked properly. The yellow indicator will fill about half of the viewing window.
If you do not see the yellow indicator, call 800-JANSSEN (800-526-7736).
Do not administer a second dose without speaking to your doctor.
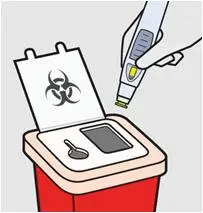
Dispose of your SmartJect
Put your used SmartJect in an FDA-cleared sharps disposal container right away after use.
Do not throw away (dispose of) loose needles and syringes in your household trash.
Do not recycle your used sharps disposal container.
For more information, see " Helpful tips".
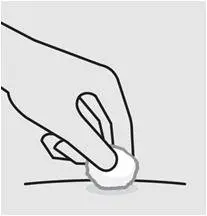
Check injection site
There may be a small amount of blood or liquid at the injection site.
Hold pressure over your skin with a cotton ball or gauze pad until any bleeding stops.
Do not rub the injection site.
If needed, cover injection site with a bandage. Your injection is now complete!
 Need help?
Need help?
Call your doctor to talk about any questions you may have. For additional assistance or to share your feedback call 800-JANSSEN (800-526-7736).
|
Helpful tips
|
|
Additional disposal information: If you do not have an FDA-cleared sharps disposal container, you may use a household container that is: • made of a heavy-duty plastic • can be closed with a tight-fitting, puncture-resistant lid, without sharps being able to come out • upright and stable during use • leak-resistant • properly labeled to warn of hazardous waste inside the container When your sharps disposal container is almost full, you will need to follow your community guidelines for the right way to dispose of your sharps disposal container. There may be state or local laws about how you should throw away used needles and syringes. For more information about safe sharps disposal, and for specific information about sharps disposal in the state that you live in, go to the FDA's website at: www.fda.gov/safesharpsdisposal |
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Manufactured by:
Janssen Biotech, Inc.
Horsham, PA 19044
US License No. 1864
Revised: March 2023
Instructions for Use
SIMPONI
®
(SIM-po-nee)
(golimumab)
Prefilled Syringe
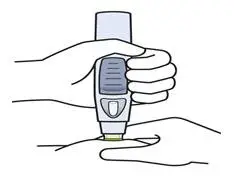

Important
SIMPONI comes as a single-dose prefilled syringe containing one 50 mg or one 100 mg dose. Each SIMPONI prefilled syringe can only be used one time. Throw away (dispose of) the used prefilled syringe (See Step 3) after one dose, even if there is medicine left in it. Do not reuse your SIMPONI prefilled syringe.
If your healthcare provider decides that you or a caregiver may be able to give your injections of SIMPONI at home, you should receive training on the right way to prepare and inject SIMPONI using the prefilled syringe before attempting to inject. Do not try to inject yourself until you have been shown the right way to give the injections by your healthcare provider.
Read this Instructions for Use before using your SIMPONI prefilled syringe and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This leaflet does not take the place of talking with your healthcare provider about your medical condition or your treatment.
The SIMPONI prefilled syringe is intended for injection under the skin, not into the muscle or vein. After injection, the needle will retract into the body of the device and lock into place.
 Storage information
Storage information
Store SIMPONI in the refrigerator at 36° to 46°F (2° to 8°C).
If needed, store SIMPONI at room temperature, up to 77°F (25°C) for one period of time up to 30 days. Do not return it to the refrigerator. Throw away if not used within 30 days at room temperature.
Do not freeze SIMPONI prefilled syringe.
Do not shake SIMPONI prefilled syringe.
Keep SIMPONI prefilled syringe in the original carton to protect from light before use.
Keep SIMPONI prefilled syringe and all medicines out of the reach of children.
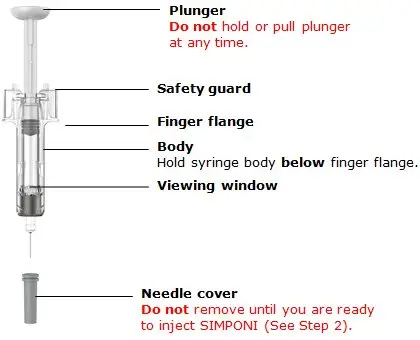
Prefilled syringe parts
Before use
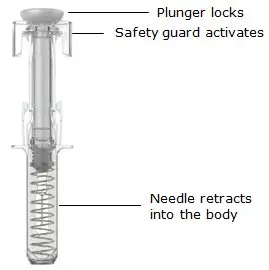
After use
You will need these supplies:
|
Not provided in the SIMPONI prefilled syringe carton:
|

Inspect carton
Remove your SIMPONI prefilled syringe carton from the refrigerator.
Remove the prefilled syringe from the carton and let it sit on a flat surface at room temperature for at least 30 minutes before use.
Do not warm the prefilled syringe any other way.
Check the expiration date ('EXP') on the back panel of the carton and on the prefilled syringe (through the viewing window).
Do not use your prefilled syringe if the expiration date has passed.
Do not inject SIMPONI if the perforations on the carton are broken. Call your healthcare provider or pharmacist for a refill.
Choose injection site
Select from the following areas for your injection:
- Front of thighs (recommended)
- Lower stomach area (lower abdomen), except for a 2-inch area right around your navel (belly-button)
- Back of upper arms (only if someone else is giving you the injection)
Choose a different site within your preferred area for each injection.
Do not inject into skin that is tender, bruised, red, hard, thick or scaly.
Do not inject into areas with scars or stretch marks.
Clean injection site
Wash your hands well with soap and warm water.
Wipe your chosen injection site with an alcohol swab and allow it to dry.
Do not touch, fan, or blow on the injection site after you have cleaned it.
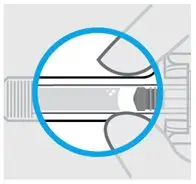
Inspect liquid
Check the SIMPONI prefilled syringe liquid in the viewing window. It should be clear to slightly yellow and may contain tiny white or clear particles. You may also see one or more air bubbles. This is normal.
Do not inject if the liquid is cloudy or discolored, or has large particles. Call your healthcare provider or pharmacist for a refill.

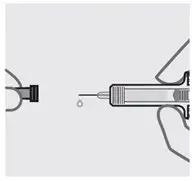
Remove needle cover
Hold your prefilled syringe by the body and pull needle cover straight off. It is normal to see a drop of liquid.
Inject SIMPONI within 5 minutes of removing the needle cover.
Do not put needle cover back on, as this may damage the needle or cause a needle stick injury.
Do not touch needle or let it touch any surface.
Do not use a SIMPONI prefilled syringe if it is dropped. Call your healthcare provider or pharmacist for a refill.
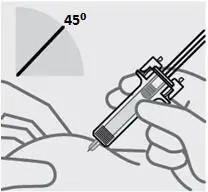
Position fingers and insert needle
Place your thumb, index and middle fingers directly under the finger flange, as shown.
Do not touch plunger or area above finger flange as this may cause the needle safety device to activate.
Use your other hand to pinch skin at the injection site. Position syringe at about a 45 degree angle to the skin.
It is important to pinch enough skin to inject under the skin and not into the muscle.
Insert needle with a quick, dart-like motion.
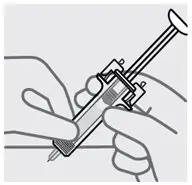
Release pinch and reposition hand
Use your free hand to grasp the body of the prefilled syringe.
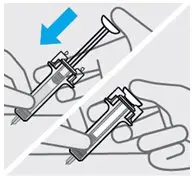
Press plunger
Place thumb from the opposite hand on the plunger and press the plunger all the way down until it stops.
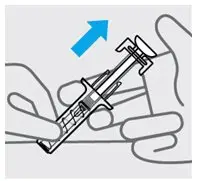
Release pressure from plunger
The safety guard will cover the needle and lock into place, removing the needle from your skin.
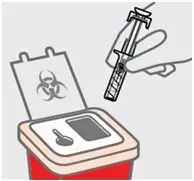
Dispose of your prefilled syringe
Put your used SIMPONI prefilled syringe in an FDA-cleared sharps disposal container right away after use.
Do not throw away (dispose of) your SIMPONI prefilled syringe in your household trash.
Do not recycle your used sharps disposal container.
For more information, see " How should I dispose of the used prefilled syringe?"
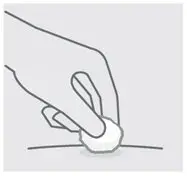
Check injection site
There may be a small amount of blood or liquid at the injection site. Hold pressure over your skin with a cotton ball or gauze pad until any bleeding stops.
Do not rub the injection site.
If needed, cover injection site with a bandage.
 Need help?
Need help?
Call your healthcare provider to talk about any questions you may have. For additional assistance or to share your feedback call 800-JANSSEN (800-526-7736).
How should I dispose of the used prefilled syringe?
If you do not have an FDA-cleared sharps disposal container, you may use a household container that is:
- made of a heavy-duty plastic
- can be closed with a tight-fitting, puncture-resistant lid, without sharps being able to come out
- upright and stable during use
- leak-resistant
- properly labeled to warn of hazardous waste inside the container
When your sharps disposal container is almost full, you will need to follow your community guidelines for the right way to dispose of your sharps disposal container. There may be state or local laws about how you should throw away used needles and syringes.
For more information about safe sharps disposal, and for specific information about sharps disposal in the state that you live in, go to the FDA's website at: www.fda.gov/safesharpsdisposal
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Manufactured by:
Janssen Biotech, Inc. Horsham, PA 19044
US License No. 1864
Revised: May 2018
janssen
| SIMPONI
golimumab injection, solution |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SIMPONI
golimumab injection, solution |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Janssen Biotech, Inc. (099091753) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Baxter Pharmaceutical Solutions | 604719430 | manufacture(57894-070, 57894-071) , analysis(57894-070, 57894-071) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Janssen Biologics, B.V. | 409612918 | api manufacture(57894-070, 57894-071) , analysis(57894-070, 57894-071) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cilag AG | 483237103 | analysis(57894-070, 57894-071) , pack(57894-070, 57894-071) , label(57894-070, 57894-071) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Janssen Sciences Ireland UC | 986030167 | api manufacture(57894-070, 57894-071) , analysis(57894-070, 57894-071) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anderson Brecon | 053217022 | pack(57894-070, 57894-071) , label(57894-070, 57894-071) | |