Drug Detail:Sincalide (Sincalide [ sin-ka-lide ])
Drug Class: Miscellaneous uncategorized agents
Highlights of Prescribing Information
SINCALIDE FOR INJECTION safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for SINCALIDE FOR INJECTION
SINCALIDE for injection, for intravenous use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1976
Recent Major Changes
| Contraindications (4) | 03/2018 |
| Warnings and Precautions (5.1) | 03/2018 |
Indications and Usage for Sincalide Injection
Sincalide for Injection is a cholecystokinin (CCK) analog indicated in adults to:
- stimulate gallbladder contraction, as may be assessed by various methods of diagnostic imaging, or to obtain by duodenal aspiration a sample of concentrated bile for analysis of cholesterol, bile salts, phospholipids, and crystals. (1)
- stimulate pancreatic secretion in combination with secretin prior to obtaining a duodenal aspirate for analysis of enzyme activity, composition, and cytology. (1)
- accelerate the transit of a barium meal through the small bowel, thereby decreasing the time and extent of radiation associated with fluoroscopy and x-ray examination of the intestinal tract. (1)
Sincalide Injection Dosage and Administration
Recommended Adult Dosage and Administration by Indication:
To Stimulate Contraction of the Gallbladder
- 0.02 mcg/kg as a single dose over 30 to 60 seconds via intravenous injection. If satisfactory contraction does not occur in 15 minutes, administer a dose of 0.04 mcg/kg over 30 to 60 seconds. (2.1)
- Alternatively consider an intravenous infusion to reduce gastrointestinal adverse reactions: 0.12 mcg/kg diluted in 100 mL of 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection USP and infused over 50 minutes at a rate of 2 mL per minute. (2.1, 2.2, 5.3)
To Stimulate Pancreatic Secretion in Combination with Secretin
- 30 minutes after initiation of secretin for injection, administer 0.02 mcg/kg diluted in 30 mL of 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection USP and infused over 30 minutes at a rate of 1 mL per minute. (2.1, 2.2)
To Accelerate Transit of a Barium Meal Through the Small Intestine
- After the barium meal is beyond the proximal jejunum, administer 0.04 mcg/kg over 30 to 60 seconds via intravenous injection. (2.1)
- If satisfactory transit of the barium meal has not occurred in 30 minutes, administer a second dose of 0.04 mcg/kg over 30 to 60 seconds. (2.1)
- Alternatively consider an intravenous infusion to reduce gastrointestinal adverse reactions: 0.12 mcg/kg diluted in 100 mL 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection USP and infused over 30 minutes. (2.1, 2.2, 5.3)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
For injection: 5 mcg of sincalide as a lyophilized powder in a single-dose vial for reconstitution (3)
Contraindications
- History of hypersensitivity to sincalide. (4, 5.1)
- Intestinal obstruction. (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Anaphylaxis, Anaphylactic Shock and Other Hypersensitivity Reactions: May occur during or soon after administration. If symptoms occur, discontinue the drug. (4, 5.1)
- Evacuation of Gallstones: Stimulation of gallbladder contraction in patients with small gallbladder stones could lead to the evacuation of the stones from the gallbladder, resulting in their lodging in the cystic duct or in the common bile duct. (5.2)
- Gastrointestinal Adverse Reactions with Intravenous Injection: Administration as an intravenous injection may cause transient nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain or cramping, dizziness or flushing. To reduce the risk of adverse reactions when used to stimulate contraction of the gallbladder or accelerate transit of a barium meal through the small intestine, administer as an intravenous infusion over 50 or 30 minutes, respectively. (2.1, 5.3)
- Preterm Labor or Spontaneous Abortion: Advise pregnant women of the potential risk for preterm labor and spontaneous abortion. (5.4, 8.1)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions (≥20%) are: abdominal discomfort or pain, and nausea. (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Fresenius Kabi USA, LLC at 1-800-551-7176 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
Drugs that Affect Gallbladder Motility or Contractile Response: May interfere with response to sincalide. Consider discontinuing these drugs prior to administration of Sincalide for Injection, when used to stimulate contraction of the gallbladder. (7.1)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 10/2022
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Sincalide Injection
Sincalide for Injection is indicated in adults to:
- to stimulate gallbladder contraction, as may be assessed by various methods of diagnostic imaging, or to obtain by duodenal aspiration a sample of concentrated bile for analysis of cholesterol, bile salts, phospholipids, and crystals;
- to stimulate pancreatic secretion in combination with secretin prior to obtaining a duodenal aspirate for analysis of enzyme activity, composition, and cytology;
- to accelerate the transit of a barium meal through the small bowel, thereby decreasing the time and extent of radiation associated with fluoroscopy and x-ray examination of the intestinal tract.
2. Sincalide Injection Dosage and Administration
2.1 Recommended Dosage and Administration Instructions
The recommended dosage and administration of Sincalide for Injection by indication is shown in Table 1. For preparation instructions see Dosage and Administration (2.2).
| Indication | Recommended Adult Dosage and Administration of Sincalide for Injection |
|---|---|
| To stimulate contraction of the gallbladder | Sincalide for Injection 0.02 mcg/kg as a single dose over 30 to 60 seconds via intravenous injection. If satisfactory contraction does not occur in 15 minutes, administer a dose of 0.04 mcg/kg over 30 to 60 seconds. Alternatively, Consider an Intravenous Infusion to Reduce Gastrointestinal Adverse Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]: 0.12 mcg/kg diluted in 100 mL of 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection USP and infused over 50 minutes at a rate of 2 mL per minute. |
| To stimulate pancreatic secretion in combination with secretin for injection | Secretin for Injection: 0.25 units/kg as intravenous infusion over 60 minutes Sincalide for Injection: 30 minutes after initiation of secretin infusion, administer Sincalide for Injection 0.02 mcg/kg diluted in 30 mL of 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection USP and infused over 30 minutes at a rate of 1 mL per minute. |
| To accelerate the transit of a barium meal through the small intestine | After the barium meal is beyond the proximal jejunum, administer Sincalide for Injection 0.04 mcg/kg over 30 to 60 seconds via intravenous injection. If satisfactory transit of the barium meal has not occurred in 30 minutes, administer a second dose of 0.04 mcg/kg over 30 to 60 seconds. Alternatively, Consider an Intravenous Infusion to Reduce Gastrointestinal Adverse Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]: 0.12 mcg/kg diluted in 100 mL 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection USP and infused over 30 minutes. |
2.2 Preparation Instructions
For Intravenous Injection
- Reconstitute Sincalide for Injection aseptically by adding 5 mL of Sterile Water for Injection USP to the vial.
- Inspect the reconstituted solution visually for particulate matter and discoloration after reconstitution and prior to administration.
- Withdraw the prescribed dose of the reconstituted solution from the vial and administer as an intravenous injection over 30 to 60 seconds, as shown in Table 1. Discard the unused portion.
- Store the reconstituted solution at room temperature. Discard after 8 hours.
- For single use only; discard unused portion.
For Intravenous Infusion
- Reconstitute Sincalide for Injection aseptically by adding 5 mL of Sterile Water for Injection USP to the vial.
- After reconstitution, withdraw the prescribed dose of the solution from the vial. Discard unused portion.
- Dilute the reconstituted solution in 30 mL or 100 mL of 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection USP, depending on the indication, as described in Table 1.
- Inspect the Sincalide for Injection solutions visually for particulate matter and discoloration after reconstitution, dilution and prior to administration.
- Store the diluted solution at room temperature. Discard after 1 hour.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
For injection: 5 mcg of sincalide as a lyophilized white powder for reconstitution in a single-dose vial.
4. Contraindications
Sincalide for Injection is contraindicated in patients with:
- a history of hypersensitivity to sincalide. Serious hypersensitivity reactions have included anaphylaxis and anaphylactic shock [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1), Adverse Reactions (6)].
- intestinal obstruction.
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Anaphylaxis, Anaphylactic Shock and Other Hypersensitivity Reactions
In postmarketing experience, anaphylaxis, anaphylactic shock and other serious hypersensitivity reactions have been reported during and within one hour following administration of Sincalide for Injection [see Adverse Reactions (6)].
Due to the potential for anaphylaxis, appropriate medical support should be readily available when Sincalide for Injection is administered. If anaphylaxis or other hypersensitivity reactions occur, immediately discontinue the infusion and initiate appropriate medical treatment. Observe patients closely during and after the infusion. Do not reinitiate Sincalide for Injection in patients who have experienced symptoms of hypersensitivity [see Contraindications (4)].
5.2 Evacuation of Gallstones
Stimulation of gallbladder contraction in patients with small gallbladder stones could lead to the evacuation of the stones from the gallbladder, resulting in their lodging in the cystic duct or in the common bile duct.
5.3 Gastrointestinal Adverse Reactions with Intravenous Injection
Administration of Sincalide for Injection as an intravenous injection may cause adverse reactions such as nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain or cramping, dizziness, and flushing [see Adverse Reactions (6)]. These reactions are generally transient. To reduce the risk of adverse reactions with intravenous injection when used to stimulate contraction of the gallbladder or accelerate transit of a barium meal through the small intestine, administer Sincalide for Injection as an intravenous infusion over 50 or 30 minutes, respectively [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following adverse reactions associated with the use of Sincalide for Injection were identified in clinical trials or postmarketing reports. Because these reactions were reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to estimate their frequency, reliably, or to establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
The most frequent adverse reactions (20% or greater) are gastrointestinal: abdominal discomfort or pain, and nausea; these may not necessarily indicate an abnormality of the biliary tract unless there is other clinical or radiologic evidence of disease.
Less common adverse reactions include:
Hypersensitivity reactions: anaphylaxis and anaphylactic shock, hypotension, throat tightness, bradycardia, shortness of breath, nausea, abdominal cramping, diaphoresis, hives, rash, itching; and numbness of face, lips and eyes [see Contraindications (4), (5.1)].
Neurological reactions: seizures, headache.
Vasovagal reactions: dizziness, loss of consciousness, nausea, diaphoresis, syncope and hypotension (generally self-limiting).
Other: nausea, vomiting, flushing, hypertension, urge to defecate, diarrhea, sneezing.
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 Drugs that Affect Gallbladder Motility or Contractile Response
Drugs that may stimulate or inhibit gallbladder motility or contractile response may interfere with the response to sincalide. Consider discontinuing these drugs prior to administration of Sincalide for Injection, when used to stimulate contraction of the gallbladder.
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on limited human data and mechanism of action, sincalide may cause preterm labor or spontaneous abortion [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]. Available data with Sincalide for Injection are insufficient to establish a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. In animal embryo-fetal development studies in which sincalide was administered to hamsters and rats during the period of organogenesis, no effects were seen at doses comparable to the maximum recommended clinical dose on a mg/kg basis. However, in a prenatal development study in which rats were administered sincalide during organogenesis through parturition, decreased weight gain and developmental delays were observed at a dose 122 times higher than the maximum recommended human dose based on body surface area.
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4% and 15 to 20%, respectively.
Animal Data
There were no effects on embryo-fetal development in hamsters when sincalide was administered subcutaneously at 250 or 750 ng/kg during organogenesis (Gestation Days 7 to 13) at doses up to 0.8 times the maximum recommended dose of 120 ng/kg on a body surface area basis. No effects on embryo-fetal development were observed in Sprague-Dawley rats at subcutaneous doses of 250, 450, or 750 ng/kg from Gestation Days 6 to16, representing 1.0 time the maximum recommended human dose on a body surface area basis. In a separate study at a higher dose of 90 mcg/kg administered subcutaneously to CFY rats from Gestation Day 10 through parturition (representing 122 times the maximum recommended human dose on a body surface area basis), offspring showed decreased growth, behavioral changes, and developmental delays.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data regarding the presence of sincalide in human or animal milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for Sincalide for Injection and any potential adverse effect on the breastfed infant from Sincalide for Injection or from the underlying condition.
10. Overdosage
In the event of an overdose, symptoms related to vagal stimulation, such as gastrointestinal symptoms (abdominal cramps, nausea, vomiting and diarrhea), hypotension with dizziness or fainting may occur. Overdosage symptoms should be treated symptomatically and should be of short duration.
A single bolus intravenous injection of 0.05 mcg/kg (approximately 2 to 3 times the human dose of 0.02 mcg/kg), sincalide caused hypotension and bradycardia in dogs. In addition, higher doses injected intravenously once or repeatedly in dogs caused syncope and ECG changes (approximately 5 times the human dose of 0.02 mcg/kg). These effects were attributed to sincalide-induced vagal stimulation in that all were prevented by pretreatment with atropine or bilateral vagotomy.
11. Sincalide Injection Description
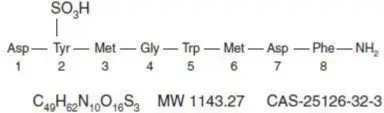
Sincalide for Injection is a cholecystopancreatic-gastrointestinal hormone for parenteral administration. The agent is a synthetically-prepared C-terminal octapeptide of cholecystokinin.
Each single-dose vial of sincalide provides a sterile nonpyrogenic lyophilized white powder consisting of 5 mcg sincalide with 30 mg arginine hydrochloride, 15 mg lysine hydrochloride, 170 mg mannitol, 4 mg methionine, 2 mg pentetic acid, 0.005 mcg polysorbate 20, 9 mg potassium phosphate dibasic, and 0.04 mg sodium metabisulfite.
The pH is adjusted to 6.0 to 8.0 with hydrochloric acid and/or sodium hydroxide prior to lyophilization. Sincalide is designated chemically as L-α-aspartyl-O-sulfo-L-tyrosyl-L-methionylglycyl-L-tryptophyl-L-methionyl- L-α-aspartyl-L-phenylalaninamide. Graphic formula:
12. Sincalide Injection - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
When injected intravenously, sincalide stimulates gallbladder contraction and reduction in size. The evacuation of bile that results is similar to that which occurs physiologically in response to endogenous cholecystokinin. Sincalide also stimulates pancreatic secretion and intestinal motility causing pyloric contraction and slows gastric emptying.
Concurrent administration of sincalide with secretin increases both the volume of pancreatic secretion and the out-put of bicarbonate and enzymes. This combined effect of secretin and sincalide permits the assessment of specific pancreatic function through measurement and analysis of the duodenal aspirate.
16. How is Sincalide Injection supplied
Sincalide for Injection is supplied as 5 mcg of sincalide as a lyophilized white powder for reconstitution in a single-dose vial; in packages of 10 vials as follows:
| Product Code | Unit of Sale | Strength | Each |
| 579105 | NDC 63323-579-05 Unit of 10 | 5 mcg per vial | NDC 63323-579-01 Single-Dose Vial |
Store at 25° C (77° F); excursions permitted to 15-30° C (59-86° F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature].
17. Patient Counseling Information
Anaphylaxis, Anaphylactic Shock and Other Hypersensitivity Reactions
Inform patients that hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis and anaphylactic shock have been reported during or following administration of Sincalide for Injection. Advise patients to report immediately to a healthcare provider if they experience symptoms of a hypersensitivity reaction [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
| SINCALIDE
sincalide injection, powder, lyophilized, for solution |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Fresenius Kabi USA, LLC (608775388) |
| Registrant - Bracco Diagnostics Inc. (849234661) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fresenius Kabi USA, LLC | 840771732 | ANALYSIS(63323-579) , MANUFACTURE(63323-579) | |