Drug Detail:Skyrizi (Risankizumab [ ris-an-kiz-ue-mab ])
Drug Class: Interleukin inhibitors
Highlights of Prescribing Information
SKYRIZI® (risankizumab-rzaa) injection, for subcutaneous or intravenous use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2019
Recent Major Changes
| Indications and Usage, Crohn’s Disease (1.3) | 06/2022 |
| Dosage and Administration (2.1, 2.2, 2.6, 2.7) | 06/2022 |
| Dosage and Administration, Recommended Dosage for Crohn’s Disease (2.6) | 09/2022 |
| Dosage and Administration, Preparation and Administration Instructions (Crohn’s Disease) (2.7) | 03/2023 |
| Warnings and Precautions, Hepatotoxicity in Treatment of Crohn’s Disease (5.4) | 06/2022 |
Indications and Usage for Skyrizi Injection
SKYRIZI is an interleukin-23 antagonist indicated for the treatment of:
- moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis in adults who are candidates for systemic therapy or phototherapy. (1.1)
- active psoriatic arthritis in adults. (1.2)
- moderately to severely active Crohn's disease in adults. (1.3)
Skyrizi Injection Dosage and Administration
Recommended Dosage
Plaque Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis:
- 150 mg administered by subcutaneous injection at Week 0, Week 4, and every 12 weeks thereafter. (2.3, 2.4)
- In patients with psoriatic arthritis SKYRIZI can be administered alone or in combination with non-biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs). (2.4)
Crohn’s Disease:
- Obtain liver enzymes and bilirubin levels prior to initiating treatment with SKYRIZI. (2.1, 5.4)
- The recommended induction dosage is 600 mg administered by intravenous infusion over at least one hour at Week 0, Week 4, and Week 8. The recommended maintenance dosage is 180 mg or 360 mg administered by subcutaneous injection at Week 12, and every 8 weeks thereafter. Use the lowest effective dosage to maintain therapeutic response. (2.6)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Subcutaneous injection (3)
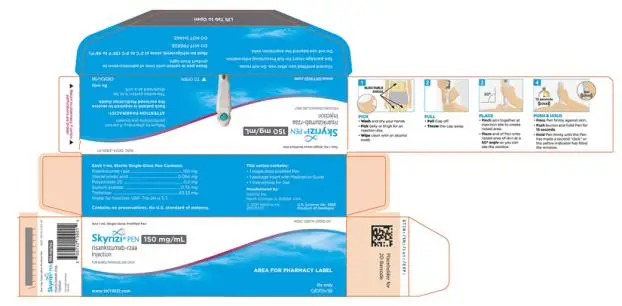
- Injection: 150 mg/mL in each single-dose prefilled pen.
- Injection: 75 mg/0.83 mL in each single-dose prefilled syringe.
- Injection: 90 mg/mL in each single-dose prefilled syringe.
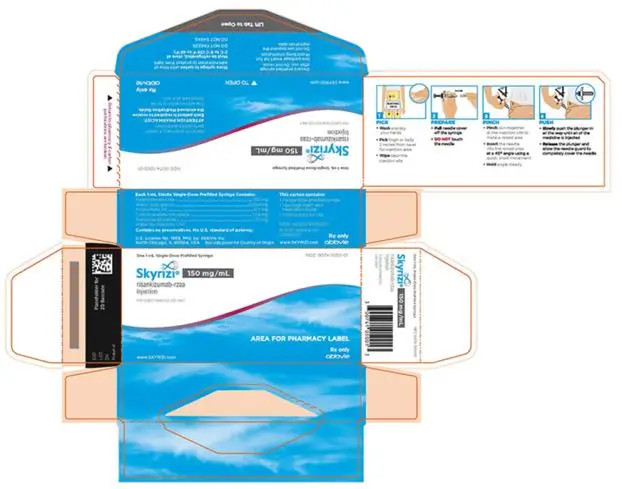
- Injection: 150 mg/mL in each single-dose prefilled syringe.
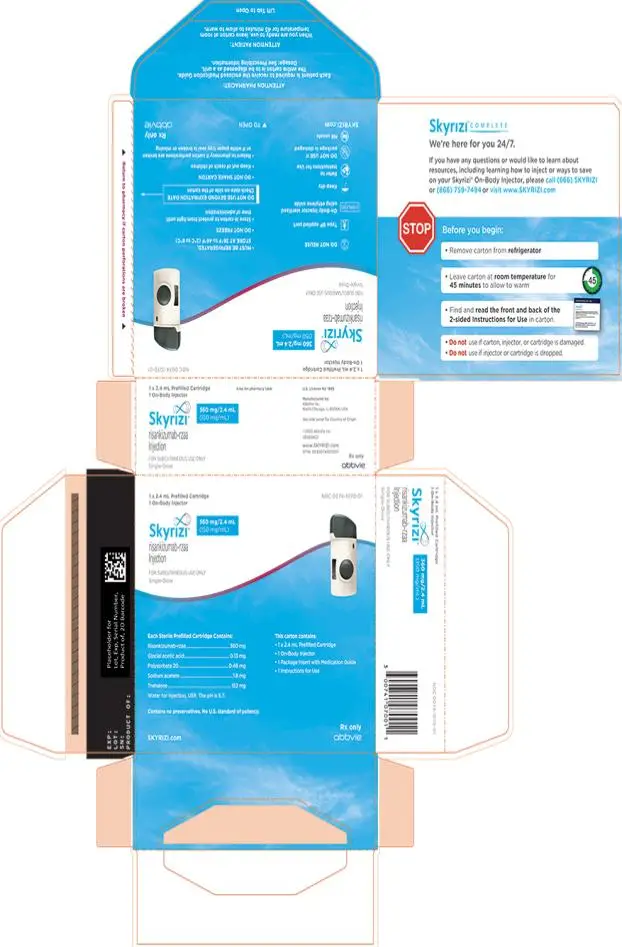
- Injection: 180 mg/1.2 mL (150 mg/mL) in each single-dose prefilled cartridge.
- Injection: 360 mg/2.4 mL (150 mg/mL) in each single-dose prefilled cartridge.
Intravenous infusion (3)
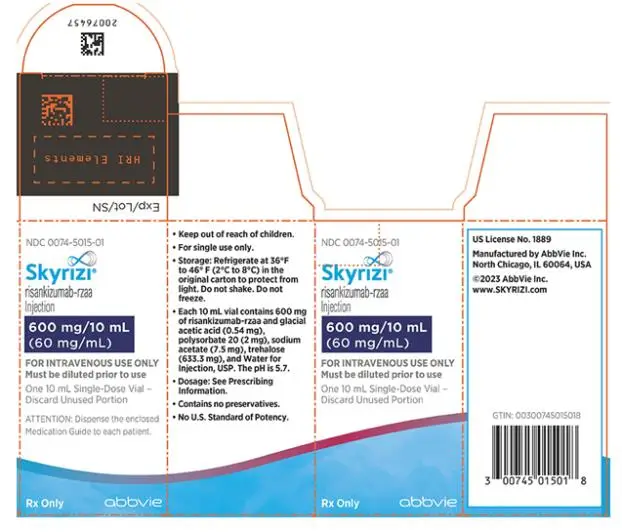
- Injection: 600 mg/10 mL (60 mg/mL) in each single-dose vial.
Contraindications
- SKYRIZI is contraindicated in patients with a history of serious hypersensitivity reaction to risankizumab-rzaa or any of the excipients (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Hypersensitivity Reactions: Serious hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, may occur (5.1)
- Infections: SKYRIZI may increase the risk of infection. Instruct patients to seek medical advice if signs or symptoms of clinically important infection occur. If such an infection develops, do not administer SKYRIZI until the infection resolves. (5.2)
- Tuberculosis (TB): Evaluate for TB prior to initiating treatment with SKYRIZI. (5.3)
- Hepatotoxicity in Treatment of Crohn’s Disease: Drug-induced liver injury during induction has been reported. Monitor liver enzymes and bilirubin levels at baseline and, during induction, up to at least 12 weeks of treatment. Monitor thereafter according to routine patient management. (5.4)
- Administration of Vaccines: Avoid use of live vaccines. (5.5)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions are:
-
Plaque Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis (≥ 1%): upper respiratory infections, headache, fatigue, injection site reactions, and tinea infections. (6.1)
-
Crohn’s Disease (>3%):
◦ Induction: upper respiratory infections, headache, and arthralgia. (6.1)
◦ Maintenance: arthralgia, abdominal pain, injection site reactions, anemia, pyrexia, back pain, arthropathy, and urinary tract infection. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact AbbVie Inc. at 1-800-633-9110 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 5/2023
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Skyrizi Injection
1.1 Plaque Psoriasis
SKYRIZI® is indicated for the treatment of moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis in adults who are candidates for systemic therapy or phototherapy.
2. Skyrizi Injection Dosage and Administration
2.1 Procedures Prior to Treatment Initiation
• For the treatment of Crohn’s disease, obtain liver enzymes and bilirubin levels prior to initiating treatment with SKYRIZI [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
• Evaluate patients for tuberculosis (TB) infection prior to initiating treatment with SKYRIZI [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
• Complete all age-appropriate vaccinations as recommended by current immunization guidelines [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
2.2 General Considerations for Administration
• Visually inspect SKYRIZI for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration. The solution may contain a few translucent to white particles.
◦ SKYRIZI 150 mg/mL, 180 mg/1.2 mL, and 360 mg/2.4 mL: a colorless to yellow, and clear to slightly opalescent solution.
◦ SKYRIZI 75 mg/0.83 mL, 90 mg/mL, and 600 mg/10 mL: a colorless to slightly yellow, and clear to slightly opalescent solution.
◦ Do not use if the solution contains large particles or is cloudy or discolored.
• Discard after use. Do not reuse.
2.3 Recommended Dosage for Plaque Psoriasis
The recommended dosage is 150 mg administered by subcutaneous injection at Week 0, Week 4, and every 12 weeks thereafter.
2.4 Recommended Dosage for Psoriatic Arthritis
The recommended dosage is 150 mg administered by subcutaneous injection at Week 0, Week 4, and every 12 weeks thereafter.
SKYRIZI may be administered alone or in combination with non-biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs).
2.6 Recommended Dosage for Crohn’s Disease
Adult Patients: Induction
The recommended induction dosage of SKYRIZI is 600 mg administered by intravenous infusion over a period of at least one hour at Week 0, Week 4, and Week 8.
Adult Patients: Maintenance
The recommended maintenance dosage of SKYRIZI is 180 mg or 360 mg administered by subcutaneous injection at Week 12, and every 8 weeks thereafter. Use the lowest effective dosage needed to maintain therapeutic response.
2.7 Preparation and Administration Instructions (Crohn’s Disease)
Intravenous Induction Dosing Regimen:
1. SKYRIZI vial for intravenous administration is intended for administration by a healthcare provider using aseptic technique.
2. Prior to intravenous administration, withdraw 10 mL of SKYRIZI solution from the vial and inject into an intravenous infusion bag or glass bottle containing 5% Dextrose Injection (600 mg/10 mL in 100 mL, or 250 mL, or 500 mL) for a final concentration of approximately 1.2 mg/mL to 6 mg/mL. Discard any remaining solution in the vial.
3. Do not shake the vial or diluted solution in the infusion bag or glass bottle.
4. Allow the diluted SKYRIZI solution in the infusion bag or glass bottle to warm to room temperature (if stored refrigerated) prior to the start of the intravenous infusion.
5. Infuse the diluted solution intravenously over a period of at least one hour. Complete the infusion within 8 hours of dilution.
6. Do not administer SKYRIZI diluted solution concomitantly in the same intravenous line with other medicinal products.
Storage of Diluted Solution:
If not used immediately, store the diluted SKYRIZI solution refrigerated and protected from light for up to 20 hours between 36°F to 46°F (2°C to 8°C). Subsequently, the diluted SKYRIZI solution can be stored (protected from direct and indirect sunlight) for 8 hours at room temperature at up to 77°F (25°C) after dilution (cumulative time after preparation including the storage and the infusion period). Do not freeze.
Subcutaneous Maintenance Dosing Regimen:
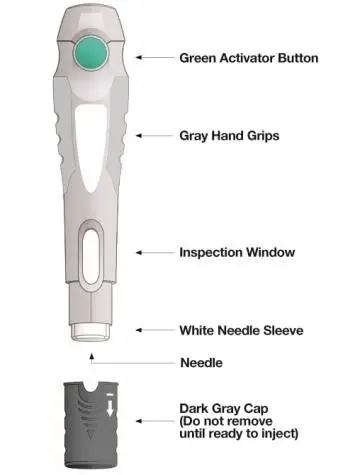
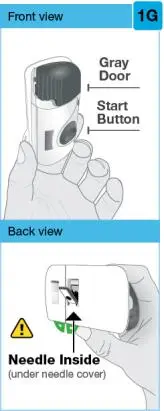
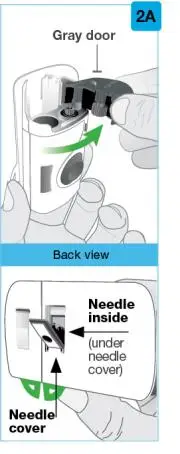
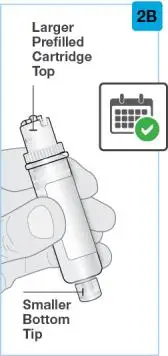
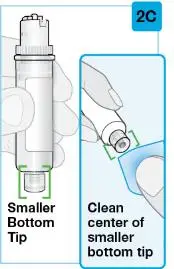
Using the single-dose 180 mg or 360 mg prefilled cartridge with On-Body Injector:
• SKYRIZI is intended for use under the guidance and supervision of a healthcare professional.
• Patients may self-inject SKYRIZI using the on-body injector with prefilled cartridge after training in subcutaneous injection technique. Provide proper training to patients and/or caregivers on the subcutaneous injection technique of SKYRIZI.
• Before using the on-body injector with prefilled cartridge, remove the carton from the refrigerator and allow to reach room temperature out of direct sunlight (45 to 90 minutes) without removing the prefilled cartridge or on-body injector from the carton.
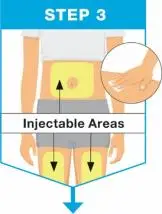
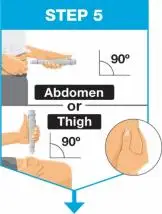
• Use the on-body injector to administer SKYRIZI 180 mg/1.2 mL or SKYRIZI 360 mg/2.4 mL prefilled cartridge subcutaneously on thigh or abdomen.
• Do not inject into areas where the skin is tender, bruised, erythematous, indurated or affected by any lesions.
• If a dose is missed, administer the dose as soon as possible. Thereafter, resume dosing at the regular scheduled time.
The SKYRIZI “Instructions for Use” contains more detailed instructions on the preparation and administration of SKYRIZI [see Instructions for Use]. Instruct the patient to read the Instructions for Use before administration.
Using the 90 mg/mL prefilled syringe:
• Administer each SKYRIZI 90 mg/mL prefilled syringe subcutaneously.
• SKYRIZI 90 mg/mL should be prepared and administered by a healthcare professional.
• Before injecting, remove the carton from the refrigerator and without removing the prefilled syringes from the carton, allow SKYRIZI to reach room temperature out of direct sunlight (15 to 30 minutes).
• Use the 90 mg/mL prefilled syringes to administer SKYRIZI 180 mg or SKYRIZI 360 mg subcutaneously as follows:
◦ When using SKYRIZI 90 mg/mL prefilled syringes, for a 180 mg maintenance dose, two 90 mg prefilled syringes are required. Inject one prefilled syringe after the other in different anatomic locations (such as thighs or abdomen).
◦ When using SKYRIZI 90 mg/mL prefilled syringes, for a 360 mg maintenance dose, four 90 mg prefilled syringes are required. Inject one prefilled syringe after the other in different anatomic locations (such as thighs or abdomen).
• Do not inject into areas where the skin is tender, bruised, erythematous, indurated or affected by any lesions.
• If a dose is missed, administer the dose as soon as possible. Thereafter, resume dosing at the regular scheduled time.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
Subcutaneous Injection
SKYRIZI Pen
- Injection: 150 mg/mL as a colorless to yellow and clear to slightly opalescent solution in each single-dose prefilled pen.
SKYRIZI Prefilled Syringe
- Injection: 75 mg/0.83 mL as a colorless to slightly yellow and clear to slightly opalescent solution in each single-dose prefilled syringe.
- Injection: 90 mg/mL as a colorless to slightly yellow and clear to slightly opalescent solution in each single-dose prefilled syringe for healthcare provider administration.
- Injection: 150 mg/mL as a colorless to yellow and clear to slightly opalescent solution in each single-dose prefilled syringe.
SKYRIZI Prefilled Cartridge with Supplied On-Body Injector
- Injection: 180 mg/1.2 mL (150 mg/mL) as a colorless to yellow, and clear to slightly opalescent solution in each single-dose prefilled cartridge for use with the on-body injector.
- Injection: 360 mg/2.4 mL (150 mg/mL) as a colorless to yellow, and clear to slightly opalescent solution in each single-dose prefilled cartridge for use with the on-body injector.
Intravenous Infusion
SKYRIZI Vial
- Injection: 600 mg/10 mL (60 mg/mL) as a colorless to slightly yellow, and clear to slightly opalescent solution in each single-dose vial.
4. Contraindications
SKYRIZI is contraindicated in patients with a history of serious hypersensitivity reaction to risankizumab-rzaa or any of the excipients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Hypersensitivity Reactions
Serious hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, have been reported with use of SKYRIZI. If a serious hypersensitivity reaction occurs, discontinue SKYRIZI and initiate appropriate therapy immediately [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
5.2 Infections
SKYRIZI may increase the risk of infections [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Treatment with SKYRIZI should not be initiated in patients with any clinically important active infection until the infection resolves or is adequately treated.
In patients with a chronic infection or a history of recurrent infection, consider the risks and benefits prior to prescribing SKYRIZI. Instruct patients to seek medical advice if signs or symptoms of clinically important infection occur. If a patient develops such an infection or is not responding to standard therapy, monitor the patient closely and do not administer SKYRIZI until the infection resolves.
5.3 Tuberculosis
Evaluate patients for tuberculosis (TB) infection prior to initiating treatment with SKYRIZI. Across the Phase 3 psoriasis clinical studies, of the 72 subjects with latent TB who were concurrently treated with SKYRIZI and appropriate TB prophylaxis during the studies, none developed active TB during the mean follow-up of 61 weeks on SKYRIZI. Two subjects taking isoniazid for treatment of latent TB discontinued treatment due to liver injury. Of the 31 subjects from the PsO-3 study with latent TB who did not receive prophylaxis during the study, none developed active TB during the mean follow-up of 55 weeks on SKYRIZI. Consider anti-TB therapy prior to initiating SKYRIZI in patients with a past history of latent or active TB in whom an adequate course of treatment cannot be confirmed. Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of active TB during and after SKYRIZI treatment. Do not administer SKYRIZI to patients with active TB.
5.4 Hepatotoxicity in Treatment of Crohn’s Disease
A serious adverse reaction of drug-induced liver injury in conjunction with a rash that required hospitalization was reported in a patient with Crohn’s disease (ALT 54x ULN, AST 30x ULN, and total bilirubin 2.2x ULN) following two 600 mg intravenous doses of SKYRIZI. The liver test abnormalities resolved following administration of steroids. SKYRIZI was subsequently discontinued.
For the treatment of Crohn’s disease, evaluate liver enzymes and bilirubin at baseline, and during induction at least up to 12 weeks of treatment. Monitor thereafter according to routine patient management.
Consider other treatment options in patients with evidence of liver cirrhosis. Prompt investigation of the cause of liver enzyme elevation is recommended to identify potential cases of drug-induced liver injury. Interrupt treatment if drug-induced liver injury is suspected, until this diagnosis is excluded. Instruct patients to seek immediate medical attention if they experience symptoms suggestive of hepatic dysfunction.
5.5 Administration of Vaccines
Avoid use of live vaccines in patients treated with SKYRIZI. Medications that interact with the immune system may increase the risk of infection following administration of live vaccines. Prior to initiating therapy with SKYRIZI, complete all age-appropriate vaccinations according to current immunization guidelines. No data are available on the response to live or inactive vaccines.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following adverse reactions are discussed in other sections of labeling:
- Hypersensitivity Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Infections [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Tuberculosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Hepatotoxicity in Treatment of Crohn’s Disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse drug reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared with rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Plaque Psoriasis
A total of 2234 subjects were treated with SKYRIZI in clinical development trials in plaque psoriasis. Of these, 1208 subjects with psoriasis were exposed to SKYRIZI for at least one year.
Data from placebo- and active-controlled trials were pooled to evaluate the safety of SKYRIZI for up to 16 weeks. In total, 1306 subjects were evaluated in the SKYRIZI 150 mg group.
Table 1 summarizes the adverse drug reactions that occurred at a rate of at least 1% and at a higher rate in the SKYRIZI group than the placebo group during the 16-week controlled period of pooled clinical trials.
| Adverse Drug Reactions | SKYRIZI
N = 1306 n (%) | Placebo
N = 300 n (%) |
| Upper respiratory infectionsa | 170 (13.0) | 29 (9.7) |
| Headacheb | 46 (3.5) | 6 (2.0) |
| Fatiguec | 33 (2.5) | 3 (1.0) |
| Injection site reactionsd | 19 (1.5) | 3 (1.0) |
| Tinea infectionse | 15 (1.1) | 1 (0.3) |
| a Includes: respiratory tract infection (viral, bacterial or unspecified), sinusitis (including acute), rhinitis, nasopharyngitis, pharyngitis (including viral), tonsillitis b Includes: headache, tension headache, sinus headache, cervicogenic headache c Includes: fatigue, asthenia d Includes: injection site bruising, erythema, extravasation, hematoma, hemorrhage, infection, inflammation, irritation, pain, pruritus, reaction, swelling, warmth e Includes: tinea pedis, tinea cruris, body tinea, tinea versicolor, tinea manuum, tinea infection, onychomycosis |
||
Adverse drug reactions that occurred in < 1% but > 0.1% of subjects in the SKYRIZI group and at a higher rate than in the placebo group through Week 16 were folliculitis and urticaria.
Specific Adverse Drug Reactions
Infections
In the first 16 weeks, infections occurred in 22.1% of the SKYRIZI group (90.8 events per 100 subject-years) compared with 14.7% of the placebo group (56.5 events per 100 subject-years) and did not lead to discontinuation of SKYRIZI. The rates of serious infections for the SKYRIZI group and the placebo group were ≤0.4%. Serious infections in the SKYRIZI group included cellulitis, osteomyelitis, sepsis, and herpes zoster. In Studies PsO-1 and PsO-2, through Week 52, the rate of infections (73.9 events per 100 subject-years) was similar to the rate observed during the first 16 weeks of treatment.
Safety Through Week 52
Through Week 52, no new adverse reactions were identified, and the rates of the adverse reactions were similar to those observed during the first 16 weeks of treatment. During this period, serious infections that led to study discontinuation included pneumonia.
Psoriatic Arthritis
The overall safety profile observed in subjects with psoriatic arthritis treated with SKYRIZI is generally consistent with the safety profile in subjects with plaque psoriasis. Additionally, in the Phase 3 placebo-controlled trials the incidence of hepatic events was higher in the SKYRIZI group (5.4%, 16.7 events per 100 patient years) compared to the placebo group (3.9%, 12.6 events per 100 patient years). Of these, the most common events that were reported more frequently in both the placebo group and the SKYRIZI group were ALT increased (placebo: n=12 (1.7%); SKYRIZI: n=16 (2.3%)), AST increased (placebo: n=9 (1.3%); SKYRIZI: n=13 (1.8%)), and GGT increased (placebo: n=5 (0.7%); SKYRIZI: n=8 (1.1%)). There were no serious hepatic events reported. The incidence of hypersensitivity reactions was higher in the SKYRIZI group (n=16, 2.3%) compared to the placebo group (n=9, 1.3%). In the Phase 3 placebo-controlled trials, hypersensitivity reactions reported at a higher rate in the SKYRIZI group included rash (placebo: n=4 (0.6%); SKYRIZI: n=5 (0.7%), allergic rhinitis (placebo: n=1 (0.1%); SKYRIZI: n=2 (0.3%), and facial swelling (placebo: n=0 (0.0%); SKYRIZI n=1 (0.1%). One case of anaphylaxis was reported in a subject who received SKYRIZI in the Phase 2 clinical trial.
Crohn’s Disease
SKYRIZI was studied up to 12 weeks in subjects with moderately to severely active Crohn’s disease in two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled induction studies (CD-1, CD-2) and a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-finding study (CD-4; NCT02031276). Long-term safety up to 52 weeks was evaluated in subjects who responded to induction therapy in a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled maintenance study (CD-3) [see Clinical Studies (14.3)].
In the two induction studies (CD-1, CD-2) and the dose finding study (CD-4), 620 subjects received the SKYRIZI intravenous induction regimen at Weeks 0, 4 and 8. In the maintenance study (CD-3), 297 subjects who achieved clinical response, defined as a reduction in CDAI of at least 100 points from baseline after 12 weeks of induction treatment with intravenous SKYRIZI in studies CD-1 and CD-2, received a maintenance regimen of SKYRIZI either 180 mg or 360 mg subcutaneously at Week 12 and every 8 weeks thereafter for up to an additional 52 weeks.
Adverse reactions reported in > 3% of subjects in induction studies and at a higher rate than placebo are shown in Table 2.
| Adverse Drug Reactions | SKYRIZI
600 mg Intravenous Infusiona N = 620 n (%) | Placebo
N = 432 n (%) |
| Upper respiratory infectionsb | 66 (10.6) | 40 (9.3) |
| Headachec | 41 (6.6) | 24 (5.6) |
| Arthralgia | 31 (5.0) | 19 (4.4) |
| a SKYRIZI 600 mg as an intravenous infusion at Week 0, Week 4, and Week 8. b Includes: influenza like illness, nasopharyngitis, influenza, pharyngitis, upper respiratory tract infection, viral upper respiratory tract infection, COVID-19, nasal congestion, respiratory tract infection viral, viral pharyngitis, tonsillitis, upper respiratory tract inflammation c Includes: headache, tension headache |
||
Adverse reactions reported in >3% of subjects in the maintenance study and at a higher rate than placebo are shown in Table 3.
| Adverse Drug Reactions | SKYRIZI
180 mg Subcutaneous Injection N = 155 n (%) | SKYRIZI
360 mg Subcutaneous Injection N = 142 n (%) | Placebo
N = 143 n (%) |
| Arthralgia | 13 (8.4) | 13 (9.2) | 12 (8.4) |
| Abdominal painb | 9 (5.8) | 12 (8.5) | 6 (4.2) |
| Injection site reactionsc,d | 7 (4.5) | 8 (5.6) | 4 (2.8) |
| Anemia | 7 (4.5) | 7 (4.9) | 6 (4.2) |
| Pyrexia | 4 (2.6) | 7 (4.9) | 4 (2.8) |
| Back pain | 3 (1.9) | 6 (4.2) | 3 (2.1) |
| Arthropathy | 1 (0.6) | 5 (3.5) | 2 (1.4) |
| Urinary tract infection | 1 (0.6) | 5 (3.5) | 4 (2.8) |
| a SKYRIZI 180 mg or 360 mg at Week 12 and every 8 weeks thereafter for up to an additional 52 weeks b Includes: abdominal pain, abdominal pain upper, abdominal pain lower c Includes: injection site rash, injection site erythema, injection site swelling, injection site urticaria, injection site warmth, injection site pain, injection site hypersensitivity, injection site reaction d Some subjects had multiple occurrences of injection site reactions. In this table, injection site reactions are counted only once per subject for the rate calculations. |
|||
Specific Adverse Drug Reactions
Infections
In the maintenance study (CD-3) through Week 52, the rate of infections was 32.3% (50.2 events per 100 subject-years) in subjects who received SKYRIZI 180 mg and 36.6% (60.8 events per 100 subject-years) in subjects who received SKYRIZI 360 mg compared to 36.4% (60.3 events per 100 subject-years) in subjects who received placebo after SKYRIZI induction. The rate of serious infections was 2.6% (2.7 events per 100 subject-years) in subjects who received SKYRIZI 180 mg and 5.6% (7.4 events per 100 subject-years) in subjects who received SKYRIZI 360 mg compared to 2.1% (2.4 events per 100 subject-years) in subjects who received placebo after SKYRIZI induction.
Lipid Elevations
Elevations in lipid parameters (total cholesterol and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol [LDL-C]) were first assessed at 4 weeks following initiation of SKYRIZI in the induction trials (CD-1, CD-2). Increases from baseline and increases relative to placebo were observed at Week 4 and remained stable to Week 12. Following SKYRIZI induction, mean total cholesterol increased by 9.4 mg/dL from baseline to a mean absolute value of 175.1 mg/dL at Week 12. Similarly, mean LDL-C increased by 6.6 mg/dL from baseline to a mean absolute value of 92.6 mg/dL at Week 12. Mean LDL-C increased by 3.1 mg/dL from baseline to a mean absolute value of 99.0 mg/dL at Week 52 with SKYRIZI 180 mg maintenance treatment and by 2.3 mg/dL from baseline to a mean absolute value of 102.2 mg/dL at Week 52 with SKYRIZI 360 mg maintenance treatment.
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Exposure Registry
There is a pregnancy exposure registry that monitors outcomes in women who become pregnant while treated with SKYRIZI. Patients should be encouraged to enroll by calling 1-877-302-2161 or visiting http://glowpregnancyregistry.com.
Risk Summary
Available pharmacovigilance and clinical trial data with risankizumab use in pregnant women are insufficient to establish a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage or other adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. Although there are no data on risankizumab-rzaa, monoclonal antibodies can be actively transported across the placenta, and SKYRIZI may cause immunosuppression in the in utero-exposed infant. There are adverse pregnancy outcomes in women with inflammatory bowel disease (see Clinical Considerations).
In an enhanced pre- and post-natal developmental toxicity study, pregnant cynomolgus monkeys were administered subcutaneous doses of 5 or 50 mg/kg risankizumab-rzaa once weekly during the period of organogenesis up to parturition. Increased fetal/infant loss was noted in pregnant monkeys at the 50 mg/kg dose (see Data). The 50 mg/kg dose in pregnant monkeys resulted in approximately 10 times the exposure (AUC) in humans administered the 600 mg induction regimen and 39 times the exposure (AUC) to the 360 mg maintenance doses, respectively. No risankizumab-rzaa-related effects on functional or immunological development were observed in infant monkeys from birth through 6 months of age. The clinical significance of these findings for humans is unknown.
All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Disease-associated maternal and embryo/fetal risk
Published data suggest that the risk of adverse pregnancy outcomes in women with inflammatory bowel disease is associated with increased disease activity. Adverse pregnancy outcomes include preterm delivery (before 37 weeks of gestation), low birth weight (less than 2500 g) infants, and small for gestational age at birth.
Fetal/Neonatal adverse reactions
Transport of endogenous IgG antibodies across the placenta increases as pregnancy progresses, and peaks during the third trimester. Because risankizumab may interfere with immune response to infections, risks and benefits should be considered prior to administering live vaccines to infants exposed to SKYRIZI in utero. There are insufficient data regarding infant serum levels of risankizumab at birth and the duration of persistence of risankizumab in infant serum after birth. Although a specific timeframe to delay live virus immunizations in infants exposed in utero is unknown, a minimum of 5 months after birth should be considered because of the half-life of the product.
Data
Animal Data
An enhanced pre- and post-natal developmental toxicity study was conducted in cynomolgus monkeys. Pregnant cynomolgus monkeys were administered weekly subcutaneous doses of risankizumab-rzaa of 5 or 50 mg/kg from gestation day 20 to parturition, and the cynomolgus monkeys (mother and infants) were monitored for 6 months after delivery. No maternal toxicity was noted in this study. There were no treatment-related effects on growth and development, malformations, developmental immunotoxicology, or neurobehavioral development. However, a dose-dependent increase in fetal/infant loss was noted in the risankizumab-rzaa-treated groups (32% and 43% in the 5 mg/kg and 50 mg/kg groups, respectively) compared with the vehicle control group (19%). The increased fetal/infant loss in the 50 mg/kg group was considered to be related to risankizumab-rzaa treatment. The no observed adverse effect level (NOAEL) for maternal toxicity was identified as 50 mg/kg and the NOAEL for developmental toxicity was identified as 5 mg/kg. On an exposure (AUC) basis, the 5 mg/kg dose in pregnant monkeys resulted in approximately 1.24 times the exposure in humans administered the 600 mg induction regimen and 5 times the exposure in humans administered the 360 mg maintenance doses, respectively. In the infants, mean serum concentrations increased in a dose-dependent manner and were approximately 17%-86% of the respective maternal concentrations. Following delivery, most adult female cynomolgus monkeys and all infants from the risankizumab-rzaa-treated groups had measurable serum concentrations of risankizumab-rzaa up to 91 days postpartum. Serum concentrations were below detectable levels at 180 days postpartum.
12. Skyrizi Injection - Clinical Pharmacology
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
No formal pharmacodynamics studies have been conducted with risankizumab-rzaa.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Risankizumab-rzaa plasma concentrations, after single dose administration increased dose proportionally from 18 mg to 360 mg when administered subcutaneously (0.05-2.4 times the lowest recommended dose to the highest recommended dose) and from 200 mg to 1800 mg when administered as an up to 3-hour intravenous infusion (0.3 to 3 times the recommended dose) in healthy subjects.
In subjects with plaque psoriasis treated with 150 mg subcutaneously at Weeks 0, 4, and every 12 weeks thereafter, steady-state peak concentration (Cmax) and trough concentration (Ctrough) are estimated to be 12 mcg/mL and 2 mcg/mL, respectively.
With the same dosing regimen, the pharmacokinetics of risankizumab-rzaa in subjects with psoriatic arthritis was similar to that in subjects with plaque psoriasis.
In subjects with Crohn’s disease treated with 600 mg intravenous induction dose at Weeks 0, 4, and 8, followed by 180 mg or 360 mg subcutaneous maintenance dose at Week 12 and every 8 weeks thereafter, the median Cmax and Ctrough are estimated to be 156 mcg/mL and 38.8 mcg/mL, respectively, during Weeks 8-12; and the steady state median Cmax and Ctrough are estimated to be 14.0 mcg/mL and 4.1 mcg/mL, respectively for 180 mg or 28.0 mcg/mL and 8.1 mcg/mL, respectively, for 360 mg, during Weeks 40-48.
Absorption
The absolute bioavailability of risankizumab-rzaa was estimated to be 74 to 89% following subcutaneous injection. In healthy subjects, following administration of a single subcutaneous dose, Cmax was reached by 3 to 14 days.
Distribution
The estimated steady-state volume of distribution (inter-subject CV%) was 11.2 L (34%) in subjects with plaque psoriasis, and 7.68 L (64%) in subjects with Crohn’s disease.
Elimination
The estimated systemic clearance (inter-subject CV%) was 0.31 L/day (24%) and 0.30 L/day (34%) and terminal elimination half-life was approximately 28 days and 21 days in subjects with plaque psoriasis and Crohn’s disease, respectively.
Metabolism
The metabolic pathway of risankizumab-rzaa has not been characterized. As a humanized IgG1 monoclonal antibody, risankizumab-rzaa is expected to be degraded into small peptides and amino acids via catabolic pathways in a manner similar to endogenous IgG.
Specific Populations
No clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of risankizumab-rzaa were observed based on age (≥18 years). Risankizumab-rzaa exposures (Ctrough) in geriatric patients (≥65 years) are comparable to those in younger adult patients with Crohn’s disease. No studies have been conducted to determine the effect of renal or hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics of risankizumab-rzaa.
Body Weight
Risankizumab-rzaa clearance and volume of distribution increase and plasma concentrations decrease as body weight increases; however, no dose adjustment is recommended based on body weight.
Drug Interaction Studies
Cytochrome P450 Substrates
No clinically significant changes in exposure of caffeine (CYP1A2 substrate), warfarin (CYP2C9 substrate), omeprazole (CYP2C19 substrate), metoprolol (CYP2D6 substrate), or midazolam (CYP3A substrate) were observed when used concomitantly with risankizumab-rzaa 150 mg administered subcutaneously at Weeks 0, 4, 8 and 12 (more frequent than the approved recommended dosing frequency) in subjects with plaque psoriasis.
Clinical drug interactions have not been evaluated in subjects with Crohn’s disease at the recommended dosage.
14. Clinical Studies
14.3 Crohn’s Disease
Induction Trials (Studies CD-1 and CD-2)
In two 12-week induction studies (CD-1; NCT03105128 and CD-2; NCT03104413), subjects with moderately to severely active Crohn’s disease were randomized to receive SKYRIZI 600 mg, SKYRIZI 1,200 mg, or placebo as an intravenous infusion at Week 0, Week 4, and Week 8. Moderately to severely active CD was defined as a Crohn’s Disease Activity Index (CDAI) of 220 to 450 and Simple Endoscopic Score for Crohn’s disease (SES-CD) ≥6 (or ≥4 for isolated ileal disease). Subjects with inadequate response, loss of response, or intolerance to oral aminosalicylates, corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, and/or biologic therapy were enrolled.
At baseline, the median CDAI was 307 (range: 76 – 634) and 307 (range: 72 – 651), and the median SES-CD was 12 (range: 4 – 45) and 13 (range 4 – 40), in CD-1 and CD-2, respectively. In CD-1, 58% (491/850) of subjects had failed or were intolerant to treatment with one or more biologic therapies (prior biologic failure). All subjects in CD-2 had prior biologic failure. At baseline, 30% and 34% of patients were receiving corticosteroids, 24% and 23% of patients were receiving immunomodulators (azathioprine, 6-mercaptopurine, methotrexate), and 31% and 19% of patients were receiving aminosalicylates in CD-1 and CD-2, respectively. In CD-1 and CD-2 combined, the median age was 36 years (ranging from 16 to 80 years), 81% (1145/1419) of subjects were white, and 53% (753/1419) were male.
In CD-1 and CD-2, the co-primary endpoints were clinical remission and endoscopic response at Week 12. Secondary endpoints included clinical response and endoscopic remission (see Table 8 and Table 9). The SKYRIZI 1,200 mg dosage did not demonstrate additional treatment benefit over the 600 mg dosage and is not a recommended regimen [see Dosage and Administration (2.6)].
| Endpoint | Placebo
| SKYRIZI
600 mg Intravenous Infusiona | Treatment
Difference b (95% CI) |
| Clinical Remissionc,d | |||
| Total Population | N=175 25% | N=336 45% | 21% e
(12%, 29%) |
| Prior biologic failuref | N=97 26% | N=195 42% | |
| Without prior biologic failure | N=78 23% | N=141 49% | |
| Endoscopic Responsec,g | |||
| Total Population | N=175 12% | N=336 40% | 28% e
(21%, 35%) |
| Prior biologic failuref | N=97 11% | N=195 33% | |
| Without prior biologic failure | N=78 13% | N=141 50% | |
| Clinical Responseh | |||
| Total Population | N=175 37% | N=336 60% | 23% e
(14%, 32%) |
| Prior biologic failuref | N=97 34% | N=195 58% | |
| Without prior biologic failure | N=78 40% | N=141 62% | |
| Endoscopic Remissioni | |||
| Total Population | N=175 9% | N=336 24% | 15% e
(9%, 21%) |
| Prior biologic failuref | N=97 5% | N=195 18% | |
| Without prior biologic failure | N=78 14% | N=141 32% | |
| a. SKYRIZI 600 mg as an intravenous infusion at Week 0, Week 4, and Week 8 b. Adjusted treatment difference (95% CI) based on Cochran-Mantel-Haenszel method adjusted for randomization stratification factors c. Co-primary endpoints d. CDAI <150 e. p <0.001 f. Prior biologic failure includes inadequate response, loss of response, or intolerance to one or more biologic treatments for CD g. A decrease in SES-CD > 50% from baseline, or a decrease of at least 2 points for subjects with a baseline score of 4 and isolated ileal disease, based on central reading h. A reduction of CDAI ≥ 100 points from baseline i. SES-CD ≤ 4 and at least a 2-point reduction from baseline, with no individual subscore greater than 1, based on central reading |
|||
| Endpoint | Placebo
N=187 | SKYRIZI
600 mg Intravenous Infusionb N=191 | Treatment
Differencec (95% CI) |
| Clinical Remissiond,e | 20% | 42% | 22% f
(13%, 31%) |
| Endoscopic Response d,g | 11% | 29% | 18% f
(10%, 25%) |
| Clinical Responseh | 30% | 60% | 29% f
(20%, 39%) |
| Endoscopic Remissioni | 4% | 19% | 15% f
(9%, 21%) |
| a. All subjects enrolled in CD-2 had prior biologic failure. Prior biologic failure includes inadequate response, loss of response, or intolerance to one or more biologic treatments for CD b. SKYRIZI 600 mg as an intravenous infusion at Week 0, Week 4, and Week 8 c. Adjusted treatment difference (95% CI) based on Cochran-Mantel-Haenszel method adjusted for randomization stratification factors d. Co-primary endpoints e. CDAI score <150 f. p < 0.001 g. A decrease in SES-CD > 50% from baseline, or a decrease of at least 2 points for subjects with a baseline score of 4 and isolated ileal disease, based on central reading h. A reduction of CDAI ≥ 100 points from baseline i. SES-CD ≤ 4 and at least a 2-point reduction versus from baseline, with and no individual subscore greater than 1, based on central reading |
|||
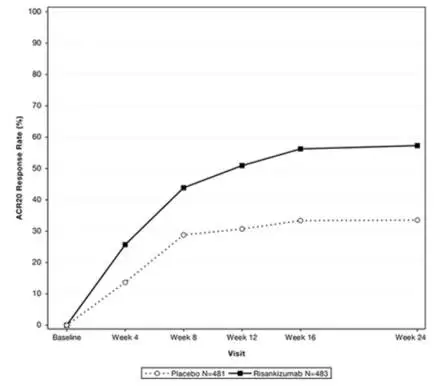
Onset of clinical response and clinical remission based on CDAI occurred as early as Week 4 in a greater proportion of subjects treated with the SKYRIZI 600 mg induction regimen compared to placebo.
Reductions in stool frequency and abdominal pain were observed in a greater proportion of subjects treated with the SKYRIZI 600 mg induction regimen compared to placebo.
Study CD-3
The maintenance study CD-3 evaluated 382 subjects who achieved clinical response defined as a reduction in CDAI of at least 100 points from baseline after 12 weeks of induction treatment with intravenous SKYRIZI in studies CD-1 and CD-2. Subjects were randomized to receive a maintenance regimen of SKYRIZI 180 mg or SKYRIZI 360 mg or placebo at Week 12 and every 8 weeks thereafter for up to an additional 52 weeks.
The co-primary endpoints in CD-3 were clinical remission and endoscopic response at Week 52 (see Table 10).
| Endpoint | Placeboa
| SKYRIZI
180 mg Subcutaneous Injectionb | SKYRIZI
360 mg Subcutaneous Injectionc | Treatment Difference vs Placebod
(95% CI) |
||
| SKYRIZI
180 mg | SKYRIZI
360 mg |
|||||
| Clinical Remissione,f | ||||||
| Total Population | N=130 46% | N=135 61% | N=117 57% | 17%g
(6%, 28%) | 14%g
(3%, 26%) |
|
| Prior biologic failureh | N=99 40% | N=95 56% | N=83 51% | |||
| Without prior biologic failure | N=31 65% | N=40 75% | N=34 71% | |||
| Endoscopic Responsee,i | ||||||
| Total Population | N=130 22% | N=135 50% | N=117 48% | 30%g
(20%, 39%) | 31%g
(21%, 41%) |
|
| Prior biologic failureh | N=99 21% | N=95 44% | N=83 44% | |||
| Without prior biologic failure | N=31 23% | N=40 65% | N=34 59% | |||
| a. The placebo group consisted of patients who were in response to SKYRIZI and were randomized to receive placebo at the start of maintenance therapy. b. SKYRIZI 180 mg at Week 12 and every 8 weeks thereafter for up to an additional 52 weeks c. SKYRIZI 360 mg at Week 12 and every 8 weeks thereafter for up to an additional 52 weeks d. Adjusted treatment difference and 95% CI computed using Cochran-Mantel-Haenszel method adjusted for randomization stratification factors e. Co-primary endpoints f. CDAI <150 g. p <0.05 h. Prior biologic failure includes inadequate response, loss of response, or intolerance to one or more biologic treatments for CD i. A decrease in SES-CD > 50% from baseline, or a decrease of at least 2 points for subjects with a baseline score of 4 and isolated ileal disease, based on central reading |
||||||
Endoscopic remission was observed at Week 52 in 33% (44/135) of subjects treated with the SKYRIZI 180 mg maintenance regimen and 41% (48/117) of subjects treated with the SKYRIZI 360 mg maintenance regimen, compared to 13% (17/130) of subjects treated with placebo. This endpoint was not statistically significant under the prespecified multiple testing procedure.
Medication Guide
Medication Guide
|
SKYRIZI® (sky-RIZZ-ee) (risankizumab-rzaa) injection, for subcutaneous or intravenous use |
|||||||
| What is the most important information I should know about SKYRIZI?
SKYRIZI may cause serious side effects, including: Serious allergic reactions. Stop using SKYRIZI and get emergency medical help right away if you get any of the following symptoms of a serious allergic reaction: |
|||||||
| ● fainting, dizziness, feeling lightheaded (low blood pressure) | ● chest tightness |
||||||
| ● swelling of your face, eyelids, lips, mouth, tongue, or throat | ● skin rash, hives | ||||||
| ● trouble breathing or throat tightness | ● itching | ||||||
| Infections. SKYRIZI may lower the ability of your immune system to fight infections and may increase your risk of infections. Your healthcare provider should check you for infections and tuberculosis (TB) before starting treatment with SKYRIZI and may treat you for TB before you begin treatment with SKYRIZI if you have a history of TB or have active TB. Your healthcare provider should watch you closely for signs and symptoms of TB during and after treatment with SKYRIZI. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you have an infection or have symptoms of an infection, including: | |||||||
| ● fever, sweats, or chills | ● muscle aches | ● weight loss | |||||
| ● cough | ● warm, red, or painful skin or sores on your body different from your psoriasis | ● diarrhea or stomach pain | |||||
| ● shortness of breath | ● burning when you urinate or urinating more often than normal | ||||||
| ● blood in your mucus (phlegm) | |||||||
| See “What are the possible side effects of SKYRIZI?” for more information about side effects. | |||||||
| What is SKYRIZI?
SKYRIZI is a prescription medicine used to treat:
|
|||||||
| Who should not use SKYRIZI?
Do not use SKYRIZI if you are allergic to risankizumab-rzaa or any of the ingredients in SKYRIZI. See the end of this Medication Guide for a complete list of ingredients in SKYRIZI. |
|||||||
Before using SKYRIZI, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
|
|||||||
| How should I use SKYRIZI?
See the detailed “Instructions for Use” that comes with SKYRIZI for information on how to prepare and inject a dose of SKYRIZI, and how to properly throw away (dispose of) a used SKYRIZI prefilled pen, prefilled syringe, or prefilled cartridge with on-body injector.
Adults with Crohn’s disease will receive their starter doses with SKYRIZI through a vein in the arm (intravenous infusion) in a healthcare facility by a healthcare provider. After completing the starter doses, patients will receive SKYRIZI as an injection under the skin (subcutaneous injection) using the prefilled cartridge with on-body injector. |
|||||||
| What are the possible side effects of SKYRIZI?
SKYRIZI may cause serious side effects including:
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
||||
| The most common side effects of SKYRIZI in people treated for Crohn’s disease include: | |||||||
|
|
|
|||||
| The most common side effects of SKYRIZI in people treated for plaque psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis include: | |||||||
|
|
|
|||||
| These are not all the possible side effects of SKYRIZI. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. |
|||||||
How should I store SKYRIZI?
|
|||||||
| General information about the safe and effective use of SKYRIZI.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use SKYRIZI for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give SKYRIZI to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about SKYRIZI that is written for health professionals. |
|||||||
| What are the ingredients in SKYRIZI?
Active ingredient: risankizumab-rzaa. SKYRIZI 75 mg/0.83 mL and 90 mg/mL inactive ingredients: sodium succinate, polysorbate 20, sorbitol, succinic acid, and Water for Injection, USP. SKYRIZI 150 mg/mL, 180 mg/1.2 mL, 360 mg/2.4 mL, and 600 mg/ 10 mL inactive ingredients: glacial acetic acid, polysorbate 20, sodium acetate, trehalose, and Water for Injection, USP. Manufactured by: AbbVie Inc., North Chicago, IL 60064, U.S.A. US License Number 1889 SKYRIZI® is a registered trademark of AbbVie Biotechnology Ltd. © 2019-2023 AbbVie Inc. For more information, call 1-866-SKYRIZI (1-866-759-7494) or go to www.SKYRIZI.com. |
|||||||
| This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration 20071775 R1 | Revised: 03/2023 | ||||||
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
SKYRIZI® (sky-RIZZ-ee)
(risankizumab-rzaa)
injection, for subcutaneous use
150 mg/mL prefilled syringe
Read Before First Use
Refer to the Medication Guide for product information.
SKYRIZI Single-Dose Prefilled Syringe
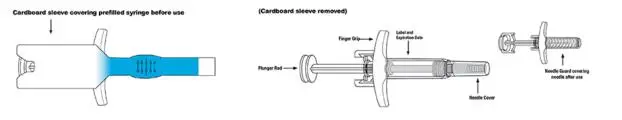
Important Information
- Keep SKYRIZI in the original carton to protect from light until time to use.
- The liquid should look clear to yellow and may contain tiny white or clear particles.
-
Do not use SKYRIZI if the liquid is cloudy or contains flakes or large particles.
-
Do not use SKYRIZI if the expiration date (EXP:) shown on the carton and prefilled syringe has passed.
-
Do not use SKYRIZI if the liquid has been frozen (even if thawed).
-
Do not shake SKYRIZI.
-
Do not use SKYRIZI if the prefilled syringe has been dropped or damaged.
-
Do not use SKYRIZI if carton perforations are broken. Return product to the pharmacy.
- Do not remove the needle cover until right before giving the injection.
Keep SKYRIZI and all medicines out of the reach of children.
Please Read Complete Instructions for Use Before Using SKYRIZI Prefilled Syringe
Before Injecting
-
Receive training on how to inject SKYRIZI before giving injection. Call your healthcare provider or (866) SKYRIZI or (866) 759-7494 if you need help.
-
Mark your calendar ahead of time to remember when to take SKYRIZI.
-
Leave the carton at room temperature and out of direct sunlight for 15 to 30 minutes to warm.
● Do not remove the syringe from the carton while allowing SKYRIZI to reach room temperature.
● Do not warm SKYRIZI in any other way (for example, do not warm it in a microwave or in hot water).
Important Information
- The liquid should look clear to yellow and may contain tiny white or clear particles.
-
Do not use SKYRIZI if the liquid is cloudy or contains flakes or large particles.
-
Do not use SKYRIZI if the expiration date (EXP:) shown on the carton and prefilled syringe has passed.
-
Do not use SKYRIZI if the syringe has been dropped or damaged.
- Do not use SKYRIZI if carton perforations are broken. Return product to the pharmacy.
Storage Information
- Store SKYRIZI in the refrigerator between 36°F to 46°F (2°C to 8°C).
-
Do not shake SKYRIZI.
- Keep SKYRIZI in the original carton to protect from light until time to use.
- SKYRIZI is not made with natural rubber latex.
- Do not use if the liquid has been frozen (even if thawed).
Keep SKYRIZI and all medicines out of the reach of children.
Call your healthcare provider or (866) SKYRIZI or (866) 759-7494 if you need help or do not know how to proceed.
 | Gather the supplies for the injection.
|
|
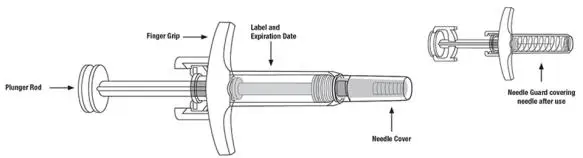
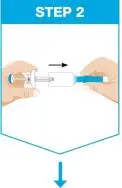 | Remove prefilled syringe from cardboard sleeve by holding the finger grip. | |
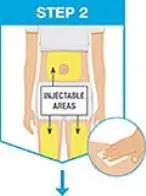
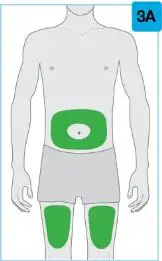
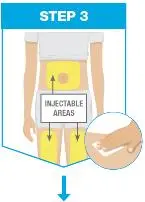 | Pick from the 3 injectable areas:
|
|
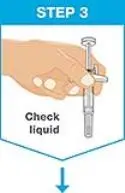
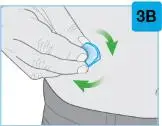
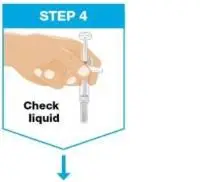 | Hold the prefilled syringe with covered needle facing down, as shown. Check the liquid in the prefilled syringe.
|
|
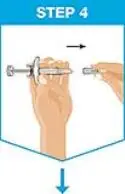
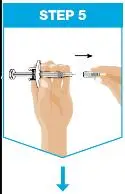 | Remove the needle cover.
|
|
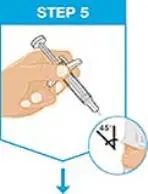
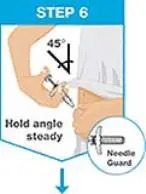
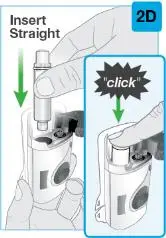
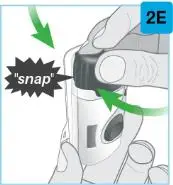
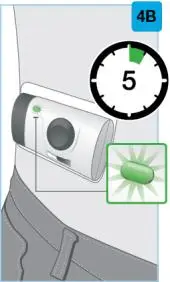
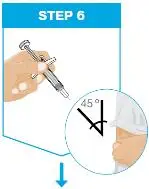 | Hold the body of the prefilled syringe in 1 hand between the thumb and index fingers. Pinch the area of cleaned skin with your other hand and hold it firmly. Insert the needle into the skin at about a 45-degree angle using a quick, short movement. Hold angle steady. |
|
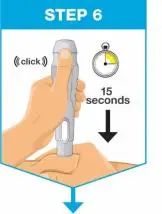
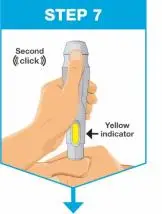
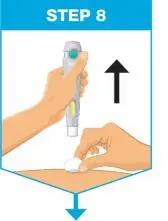
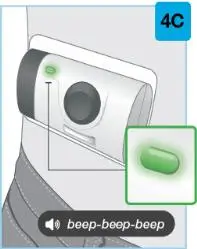
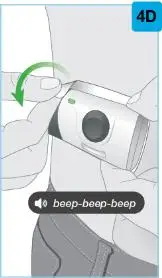
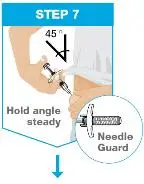 | Slowly push the plunger rod all the way in until all of the liquid is injected, and the prefilled syringe is empty. Pull the needle out of the skin while keeping the prefilled syringe at the same angle. Release the plunger rod and allow the prefilled syringe to move up until the entire needle is covered by the needle guard. The prefilled syringe needle guard will not activate unless all the liquid has been injected.
|
|
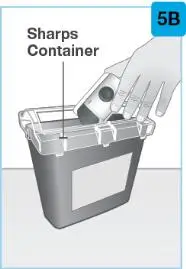
 | Put your used prefilled syringe in a FDA-cleared sharps disposal container right away after use.
|
Questions About Using SKYRIZI
| Q. | What if I need help on how to inject SKYRIZI? |
| A. | Call your healthcare provider or (866) SKYRIZI or (866) 759-7494 if you need help. |
| Q. | What should I do with the used prefilled syringe after my injection? |
| A. | Throw away (dispose of) the used prefilled syringe in a sharps disposal container and not your household trash. You can sign up to receive sharps containers for SKYRIZI syringe disposal at no additional cost by going to www.SKYRIZI.com or calling (866) SKYRIZI or (866) 759-7494. |
| Q. |
How do I know when the injection is complete? |
| A. | The injection is complete when the prefilled syringe is empty, the plunger rod is pushed all the way in, and the syringe needle guard is activated. |
Used SKYRIZI Prefilled Syringe Disposal
If you do not have a FDA-cleared sharps disposal container, you may use a household container that is:
- made of a heavy-duty plastic,
- can be closed with a tight-fitting, puncture-resistant lid, without sharps being able to come out,
- upright and stable during use,
- leak-resistant, and
- properly labeled to warn of hazardous waste inside the container.
When your sharps disposal container is almost full, you will need to follow your community guidelines for the right way to dispose of your sharps disposal container. There may be state or local laws about how you should throw away used needles and syringes.
For more information about safe sharps disposal, and for specific information about sharps disposal in the state that you live in, go to the FDA’s website at: www.fda.gov/safesharpsdisposal.
Do not recycle your used sharps disposal container.
Manufactured by: AbbVie Inc., North Chicago, IL 60064, U.S.A.
US License Number 1889
SKYRIZI® is a registered trademark of AbbVie Biotechnology Ltd.
© 2019-2022 AbbVie Inc.
20071033 R1
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Revised: 03/2022
| SKYRIZI
risankizumab-rzaa kit |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| SKYRIZI
risankizumab-rzaa injection |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SKYRIZI
risankizumab-rzaa injection |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SKYRIZI
risankizumab-rzaa kit |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| SKYRIZI
risankizumab-rzaa injection |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SKYRIZI
risankizumab-rzaa kit |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| SKYRIZI
risankizumab-rzaa kit |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| SKYRIZI
risankizumab-rzaa kit |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - AbbVie Inc. (078458370) |












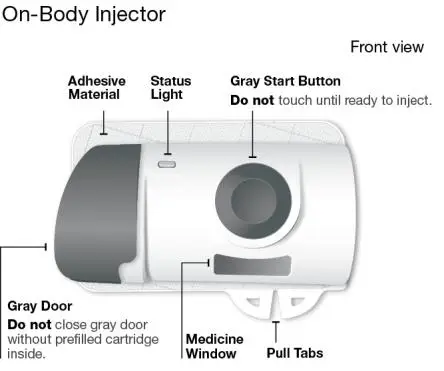
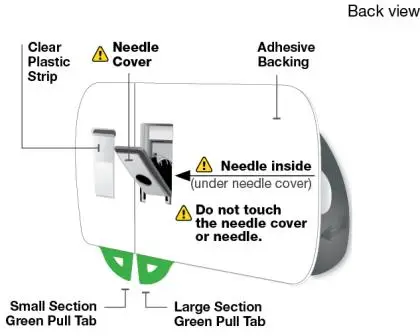
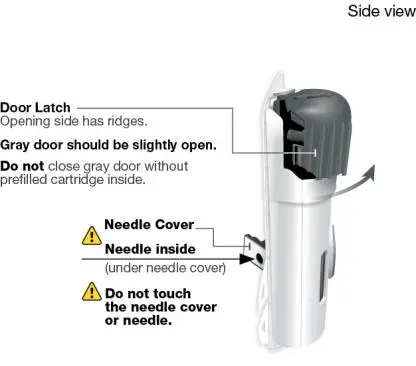
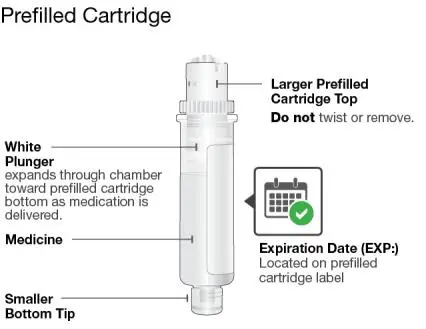



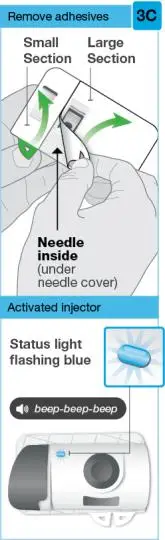

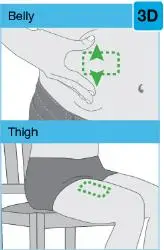
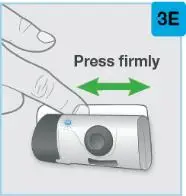
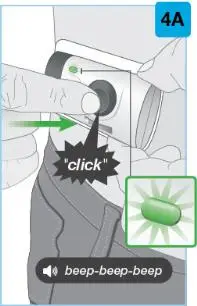


 On-Body Injector sterilized using ethylene oxide.
On-Body Injector sterilized using ethylene oxide.