Drug Detail:Sohonos (Palovarotene)
Drug Class:
Highlights of Prescribing Information
SOHONOS (palovarotene) capsules, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2023
WARNING: EMBRYO-FETAL TOXICITY and PREMATURE EPIPHYSEAL CLOSURE IN GROWING PEDIATRIC PATIENTS
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
- SOHONOS is contraindicated in pregnancy (5.1, 8.1) Because of the risk of teratogenicity and to minimize fetal exposure, SOHONOS is to be administered only if conditions for pregnancy prevention are met (5.1, 8.1)
- SOHONOS causes premature epiphyseal closure in growing pediatric patients with FOP, close monitoring is recommended (5.2, 8.4)
Indications and Usage for Sohonos
SOHONOS is a retinoid indicated for reduction in the volume of new heterotopic ossification in adults and children aged 8 years and older for females and 10 years and older for males with fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva (FOP) (1).
Sohonos Dosage and Administration
- Obtain a negative pregnancy test in females of reproductive potential before initiation of SOHONOS (2.1)
- Recommended dosage includes a chronic daily dose, which can be increased for flare-up symptoms (2.2)
- For adults and pediatric patients 14 years and older: Recommended dosage is 5 mg once daily, with an increase in dose at the time of a flare-up to 20 mg once daily for 4 weeks, followed by 10 mg once daily for 8 weeks for a total of 12 weeks (20/10 mg flare-up treatment) (2.2)
- For pediatric patients under 14 years: Weight-adjusted for daily and flare-up dosing. Recommended daily dosage range from 2.5 to 5 mg. Refer to Table 1 in Full Prescribing Information for complete pediatric dosing (2.2)
- Take SOHONOS with food preferably at same time each day (2.3).
- Reduce the dose in the event of adverse reactions as appropriate (2.4)
- See Full Prescribing Information for complete dosing instructions (2)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Capsules: 1, 1.5, 2.5, 5, 10 mg (3)
Contraindications
- Pregnancy (4, 5.1, 8.1)
- Hypersensitivity to retinoids or any component of SOHONOS (4, 11)
Warnings and Precautions
- Premature Epiphyseal Closure: Premature epiphyseal closure occurred with SOHONOS. Assess baseline skeletal maturity before SOHONOS therapy and monitor linear growth in growing pediatric patients (5.2)
- Mucocutaneous Adverse Reactions: Dry skin, lip dry, pruritus, rash, alopecia, erythema, skin exfoliation, and dry eye occurred with SOHONOS. Prevent or treat with skin emollients, sunscreen, artificial tears. Dosage reduction may be required in some patients (2.4, 5.3)
- Metabolic Bone Disorders: Decreased vertebral bone mineral content and bone density may occur. Assess for spinal fracture periodically using radiologic method (5.4)
- Psychiatric Disorders: Depression, anxiety, mood alterations and suicidal thoughts and behaviors occurred with SOHONOS. Contact healthcare provider if new or worsening symptoms develop in patients treated with SOHONOS (5.5)
- Night Blindness: May occur and make driving at night hazardous (5.6)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥10%) are dry skin, lip dry, arthralgia, pruritus, pain in extremity, rash, alopecia, erythema, headache, back pain, skin exfoliation, nausea, musculoskeletal pain, myalgia, dry eye, hypersensitivity, peripheral edema, and fatigue (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact IPSEN Biopharmaceuticals, Inc at 1-855-463-5127 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
- CYP3A4 Inhibitors: May increase SOHONOS exposure. Avoid concomitant use of strong/moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors, and grapefruit, pomelo or juices containing these fruits (7.1)
- CYP3A4 Inducers: May decrease SOHONOS exposure. Avoid concomitant use of strong/moderate CYP3A4 inducers (7.1)
- Vitamin A: May cause additive effects (7.2)
- Tetracyclines: Avoid concomitant use with SOHONOS (7.3)
- Systemic Corticosteroids: No clinically significant drug interaction is expected with concomitant use of SOHONOS (7.4)
Use In Specific Populations
- Pregnancy: May cause fetal harm (2.1, 4, 8.1)
- Growing pediatric patients are recommended to undergo baseline assessment of growth and skeletal maturity before starting treatment and continued clinical and radiographic monitoring every 6 to 12 months until patients reach skeletal maturity or final adult height (5.2, 8.4)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 8/2023
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Sohonos
SOHONOS is indicated for the reduction in volume of new heterotopic ossification in adults and pediatric patients aged 8 years and older for females and 10 years and older for males with fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva (FOP).
2. Sohonos Dosage and Administration
2.1 Pregnancy Testing Prior to Treatment with SOHONOS
For females of reproductive potential, obtain a negative pregnancy test within one week prior to initiating and periodically during SOHONOS therapy. If pregnancy occurs, stop SOHONOS treatment immediately and refer patient to an obstetrician/gynecologist experienced in reproductive toxicity. [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)].
2.2 Recommended Dosage and Duration
Recommended Dosage for Pediatric Patients Aged 8 to 13 Years for Females and Aged 10 to 13 Years for Males
- Daily Dose: The recommended SOHONOS daily dosage for patients under 14 years of age is weight-based ranging from 2.5 mg to 5 mg daily (see Table 1). Stop daily dosing when flare-up dosing begins.
- Flare-up Dose:
- The recommended flare-up SOHONOS dosage for patients under 14 years of age is weight-based (see Table 1). Administer the initial flare-up dosage once daily for 4 weeks, then administer the lower flare-up dosage once daily for 8 weeks (for a total of 12 weeks of flare-up treatment), even if symptoms resolve earlier, then return to daily dosing (see Table 1).
- If during the course of flare-up treatment, the patient experiences marked worsening of the original flare-up site or another flare-up at a new location, restart the 12-week flare-up dosing with the Week 1 to 4 dose.
- For flare-up symptoms that have not resolved at the end of the 12-week period, the Week 5 to 12 flare-up dose may be extended in 4-week intervals and continued until the flare-up symptoms resolve. If new flare-up symptoms occur after daily dosing is resumed, flare-up dosing may be restarted.
| Weight | Daily Dosage | Week 1 to 4 Flare-up Dosage | Week 5 to 12 Flare-up Dosage |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|||
| 10 kg to 19.9 kg | 2.5 mg | 10 mg | 5 mg |
| 20 kg to 39.9 kg | 3 mg | 12.5 mg | 6 mg |
| 40 kg to 59.9 kg | 4 mg | 15 mg | 7.5 mg |
| ≥ 60 kg | 5 mg | 20 mg | 10 mg |
2.3 Administration Instructions
Take SOHONOS with food preferably at the same time each day. SOHONOS may be swallowed whole, or capsules may be opened and the contents emptied onto one teaspoon (5 mL) of soft food (such as apple sauce, low-fat yogurt, or warm oatmeal) and taken within 1 hour of opening provided it was maintained at room temperature and not exposed to direct sunlight [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Do not administer with grapefruit, pomelo, or juices containing these fruits.
2.4 Dosage Reduction for Adverse Reactions
If patients experience adverse reactions that require dosage reduction during either the SOHONOS daily dosing or flare-up dosing, reduce the daily dosage to the next lower dose as shown in Table 2 at the discretion of the healthcare provider; reduce the dosage further if adverse reactions do not improve. If the patient is already receiving the lowest possible tolerated dose, then consider discontinuing SOHONOS temporarily or permanently. Initiate subsequent flare-up dosing at the same reduced dose that was tolerated previously.
| Dose Prescribed | Reduced Dose |
|---|---|
| 20 mg | 15 mg |
| 15 mg | 12.5 mg |
| 12.5 mg | 10 mg |
| 10 mg | 7.5 mg |
| 7.5 mg | 5 mg |
| 6 mg | 4 mg |
| 5 mg | 2.5 mg |
| 4 mg | 2 mg |
| 3 mg | 1.5 mg |
| 2.5 mg | 1 mg |
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
SOHONOS is available in 5 strengths as an opaque white elongated size "0" hard-gelatin capsule, containing white to off-white powder. Table 4 shows capsules' strengths and imprints.
| Strength (mg) | Imprint |
|---|---|
| 1 | PVO 1 |
| 1.5 | PVO 1.5 |
| 2.5 | PVO 2.5 |
| 5 | PVO 5 |
| 10 | PVO 10 |
4. Contraindications
SOHONOS is contraindicated in the following patients:
- During Pregnancy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
- A history of allergy or hypersensitivity to retinoids, or to any component of SOHONOS. Anaphylaxis and other allergic reactions have occurred with other retinoids. [see Description (11)].
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
SOHONOS can cause fetal harm and is contraindicated during pregnancy. SOHONOS is a member of the retinoid class of drugs which is associated with birth defects in humans. In animal reproduction studies, palovarotene administered orally to pregnant rats during organogenesis was teratogenic and caused fetal malformations typical of retinoids including cleft palate, misshapen skull bones, and shortening of the long bones at clinically relevant exposures.
For females of reproductive potential, verify that the patient is not pregnant prior to initiating treatment, periodically during the course of therapy and one month after treatment discontinuation. Advise females of reproductive potential to use an effective method of contraception at least one month prior to treatment, during treatment with SOHONOS and for 1 month after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. If a pregnancy occurs during SOHONOS treatment, discontinue treatment immediately and refer the patient to an obstetrician/gynecologist experienced in reproductive toxicity for further evaluation and counseling.
Patients should be informed not to donate blood during SOHONOS therapy and for 1 week following discontinuation because the blood might be given to a pregnant patient whose fetus must not be exposed to palovarotene.
5.2 Premature Epiphyseal Closure in Growing Pediatric Patients
SOHONOS can cause irreversible premature epiphyseal closure and potential adverse effects on growth. In clinical studies, premature epiphyseal closure occurred with SOHONOS treatment in growing pediatric patients with FOP [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) and Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
Monitoring of linear growth is recommended in growing pediatric patients [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)]. Prior to starting treatment with SOHONOS, all growing pediatric patients should undergo baseline assessment of skeletal maturity via hand/wrist and knee x-rays, standard growth curves and pubertal staging. Continued monitoring is recommended every 6 to 12 months until patients reach skeletal maturity or final adult height.
If a patient exhibits signs of premature epiphyseal closure or adverse effects on growth based on clinical or radiologic evaluations, further evaluation may be required, including an assessment of the benefits and risks of continued treatment, or temporary or permanent discontinuation of SOHONOS until the patient achieves epiphyseal closure and skeletal maturity.
5.3 Mucocutaneous Adverse Reactions
Mucocutaneous adverse reactions including dry skin, lip dry, pruritus, rash, alopecia, erythema, skin exfoliation [skin peeling], and dry eye occurred in most (98%) patients treated with SOHONOS. SOHONOS may contribute to an increased risk of skin and soft tissue infections, particularly paronychia and decubitus ulcer, due to a decreased skin barrier from adverse reactions such as dry and peeling skin [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Some of these mucocutaneous adverse reactions led to dose reductions which occurred more frequently during flare-up dosing suggesting a dose response relationship.
Prophylactic measures to minimize risk and/or treat the mucocutaneous adverse reactions are recommended (e.g., skin emollients, sunscreen, lip moisturizers, or artificial tears). Some patients may require dose reduction or drug discontinuation [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
5.5 Psychiatric Disorders
New or worsening psychiatric events were reported with SOHONOS use. These include depression, anxiety, mood alterations and suicidal thoughts and behaviors. There is a relatively high background prevalence of psychiatric disorders in untreated patients with FOP. Monitor for development of new or worsening psychiatric symptoms during treatment with SOHONOS [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Individuals with a history of psychiatric illness may be more susceptible to these adverse effects. Patients and/or caregivers should contact their healthcare provider if new or worsening psychiatric symptoms develop during treatment with SOHONOS.
5.6 Night Blindness
Night blindness has been associated with systemic retinoids, including SOHONOS. This may be dose-dependent, making driving a vehicle at night potentially hazardous during treatment. Night blindness is generally reversible after cessation of treatment but can also persist in some cases. Advise patients to be cautious when driving or operating any vehicle at night and to seek medical attention in the event of vision impairment.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Premature Epiphyseal Closure in Growing Pediatric Patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Mucocutaneous Adverse Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Metabolic Bone Disorders [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Psychiatric Disorders [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Night Blindness [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The safety of SOHONOS was evaluated in clinical studies that enrolled a total of 164 subjects with FOP, including 139 subjects in the indicated population of ages 8 years and above for females and 10 years and above for males (8/10 years and older). Most of these subjects received open label treatment with the chronic daily/flare-up regimen, consisting of 5 mg daily dosage of oral SOHONOS with a 20/10 mg dosage as needed for 12 weeks at the time of flare-up (4 weeks of 20 mg once daily followed by 10 mg once daily for 8 weeks), with all doses reduced by weight in subjects who were less than 90% skeletally mature. The mean duration of exposure was 79 weeks for chronic dosing (N=131 subjects) and 35 weeks for flare-up dosing (N=105 subjects). The mean age of these subjects was 19 years (range 8 to 61 years); 51% were male.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 21 (15%) SOHONOS treated subjects in the 8/10 years or older population with the most common serious adverse reaction being premature epiphyseal closure. Adverse reactions leading to permanent discontinuation occurred in 11 (8%) SOHONOS treated subjects with dry skin being the most common in 2 (1%) subjects. Mucocutaneous adverse reactions leading to dose reductions were more common during SOHONOS 20/10 mg flare-up treatment (37%) than during chronic treatment (4%).
Table 5 below presents adverse reactions which occurred in at least 10% of FOP subjects 8/10 years and older during treatment with chronic or flare-up dosing.
| Adverse Reaction | Chronic 5 mg N=131 n (%) | Flare-up dosing 20/10 mg N=105 n (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Doses were reduced according to body weight in subjects who were less than 90% skeletally mature | ||
|
||
| Dry skin | 80 (61) | 60 (57) |
| Lip dry * | 62 (47) | 40 (38) |
| Arthralgia | 47 (36) | 32 (31) |
| Pruritus † | 45 (34) | 50 (48) |
| Pain in extremity | 38 (29) | 29 (28) |
| Rash ‡ | 36 (28) | 31 (30) |
| Alopecia | 32 (24) | 31 (30) |
| Erythema § | 25 (19) | 34 (32) |
| Headache ¶ | 25 (19) | 20 (19) |
| Back pain # | 22 (17) | 12 (11) |
| Skin exfoliation [skin peeling] | 20 (15) | 30 (29) |
| Nausea | 20 (15) | 14 (13) |
| Musculoskeletal pain | 18 (14) | 14 (13) |
| Myalgia Þ | 15 (12) | 9 (9) |
| Dry eye | 13 (10) | 23 (22) |
| Hypersensitivity ß | 13 (10) | 21 (20) |
| Peripheral edema à | 12 (9) | 20 (19) |
| Fatigue è | 7 (5) | 12 (11) |
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 Effect of Other Drugs on SOHONOS
Clinically significant drug interactions affecting the exposure of SOHONOS are listed in Table 6.
| Strong CYP3A Inhibitors | |
| Clinical Impact | Co-administration of SOHONOS with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors increased the exposures of palovarotene [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)], which may increase the risk of SOHONOS adverse reactions. |
| Prevention or Management | Avoid concomitant use of a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor during SOHONOS treatment [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)]. |
| Moderate CYP3A Inhibitors | |
| Clinical Impact | Co-administration of SOHONOS with moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors may increase the exposure of palovarotene [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)], which may increase the risk of SOHONOS adverse reactions. |
| Prevention or Management | Avoid concomitant use of a moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor with SOHONOS, if possible. If co-administration will occur, reduce the SOHONOS dose by half when co-administered with moderate CYP3A inhibitors [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)]. |
| Strong CYP3A Inducers | |
| Clinical Impact | Co-administration of SOHONOS with strong CYP3A4 inducers decreased the exposure of palovarotene [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)], which may reduce the effectiveness of SOHONOS. |
| Prevention or Management | Avoid concomitant use of strong CYP3A4 inducers with SOHONOS. [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)]. |
| Moderate CYP3A Inducers | |
| Clinical Impact | Co-administration of moderate CYP3A4 inducers with palovarotene may decrease palovarotene exposure [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)], which may reduce the effectiveness of SOHONOS. |
| Prevention or Management | Avoid concomitant use of moderate CYP3A4 inducers with SOHONOS. |
7.2 Vitamin A
Palovarotene belongs to the same pharmacological class as vitamin A. Therefore, the use of both vitamin A and SOHONOS at the same time may lead to additive effects. Concomitant administration of vitamin A in doses higher than the recommended daily allowance (RDA) and/or other oral retinoids with SOHONOS must be avoided because of the risk of hypervitaminosis A.
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
SOHONOS can cause fetal harm when administered during pregnancy [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)]
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of SOHONOS for the treatment of FOP have been established in pediatric patients aged 8 years and older for females and 10 years and older for males. Use of SOHONOS for this indication is supported by evidence from clinical studies in adults and pediatric subjects [see Clinical Studies (14)]. The safety and effectiveness of SOHONOS for the treatment of FOP have not been established in pediatric patients less than 8 years of age in females and less than 10 years of age for males. SOHONOS is not recommended for use in patients younger than 8 years of age for females and 10 years of age for males because of the potential for premature epiphyseal closure. Clinical studies have shown that growing patients with open epiphyses are at risk of developing premature epiphyseal closure when treated with SOHONOS [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2), Adverse Reactions (6.1) and Clinical Studies (14.1)].
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of SOHONOS did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
8.6 Renal Impairment
The effect of renal impairment on the pharmacokinetics of palovarotene has not been evaluated. Given that palovarotene is hepatically eliminated, no dose adjustment of SOHONOS is recommended in patients with mild (CLcr 60 to 89 mL/min) or moderate (CLcr 30 to 59 mL/min) renal impairment. Use of SOHONOS in patients with severe (CLcr 15 to 29 mL/min) renal impairment is not recommended.
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
The effect of moderate or severe hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics of palovarotene has not been evaluated. SOHONOS undergoes extensive hepatic metabolism. No dose adjustment is recommended in patients with mild (Child-Pugh A) hepatic impairment. Use of SOHONOS in patients with moderate (Child-Pugh B) or severe (Child-Pugh C) hepatic impairment is not recommended.
10. Overdosage
No clinical experience with an overdose of SOHONOS has been reported. SOHONOS is a derivative of vitamin A. In case of accidental overdose, signs of hypervitaminosis A could appear, including severe headache, nausea or vomiting, drowsiness, irritability and pruritus. Any overdose should be treated with supportive care according to the signs and symptoms exhibited by the patient.
11. Sohonos Description
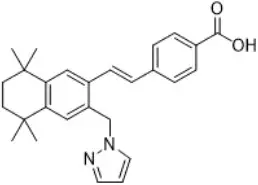
Palovarotene is an orally bioavailable retinoid that acts as a retinoic acid receptor (RAR) agonist with particular selectivity at the gamma subtype of RAR. Palovarotene is chemically described as 4-[(E)-2-(5,5,8,8-tetramethyl-3-pyrazol-1-ylmethyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-naphthalen-2-yl)-vinyl]-benzoic acid with an empirical formula of C27H30N2O2 and has a molecular weight of 414.54 g/mol.
The structural formula is represented below:
SOHONOS capsules are supplied in 1 mg, 1.5 mg, 2.5 mg, 5 mg and 10 mg strengths. Each capsule contains palovarotene as the active ingredient and the following inactive ingredients: croscarmellose sodium, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, povidone, and sodium lauryl sulfate. The capsule consists of gelatin and titanium dioxide. The black printing ink consists of black iron oxide, potassium hydroxide, propylene glycol and Shellac.
12. Sohonos - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
In patients with FOP, abnormal bone formation, including heterotrophic ossification (HO), is driven by a gain-of-function mutation in the bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) type I receptor ALK2 (ACVR1). Palovarotene is an orally bioavailable retinoic acid receptor agonist, with particular selectivity at the gamma subtype of RAR. Through binding to RARγ, palovarotene decreases the BMP/ALK2 downstream signaling pathway by inhibiting the phosphorylation of SMAD1/5/8, which reduces ALK2/SMAD-dependent chondrogenesis and osteocyte differentiation resulting in reduced endochondral bone formation.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Palovarotene exposure (AUC) increases proportionally from 0.02 to 50 mg (0.001 to 2.5 times the maximum recommended dosage). Steady-state is achieved by Day 3 following once daily dosing. Palovarotene exposure in patients with FOP are listed in the Table 7.
| Palovarotene Dosage | Cmax,ss
(ng/mL) | AUC0-t
(ng*h/mL) | Accumulation Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pharmacokinetics parameters are presented as mean (± SD). | |||
| Chronic dose 5 mg or weight-based equivalent | 40.6 (± 16.2) | 264 (± 98.4) | 1.16 |
| Flare-up dose 10 mg or weight-based equivalent | 78.4 (± 33.3) | 540 (± 226) | 1.14 |
| Flare-up dose 20 mg or weight-based equivalent | 165 (± 72.7) | 1060 (± 449) | 1.04 |
14. Clinical Studies
14.1 Chronic/Flare-up Regimen
Study PVO-1A-301 (NCT03312634, Study 301) was a single arm study in 97 subjects with FOP with R206H mutation aged 4 years and older utilizing the Natural History Study (NHS, PVO-1A-001) as an external control (n=101). The primary efficacy endpoint was annualized volume of new heterotopic ossification (HO) as assessed by low-dose, whole body CT (WBCT) imaging (excluding head). All WBCT images from treated subjects in the 301 study and untreated subjects in the NHS were read in a manner blinded to study origination.
Study 301 subjects received SOHONOS 5 mg daily with increased dosing at the time of a flare-up defined as at least one symptom (e.g. pain, swelling, redness) consistent with a previous flare-up or a substantial high-risk traumatic event likely to lead to a flare-up, to 20 mg once daily for 4 weeks followed by 10 mg once daily for 8 weeks (denoted as the chronic/flare-up regimen), with flare-up treatment extension in 4-week increments for persistent symptoms. Anytime during flare-up treatment, the 12-week treatment restarted if the subject had another flare-up or substantial high-risk traumatic event. The dosing was adjusted according to body weight in skeletally immature children (children who had not reached at least 90% skeletal maturity defined as a bone age of ≥12 years 0 months for girls and ≥14 years 0 months for boys).
The mean age of subjects in the SOHONOS group (N=97) was 15.1 years; and 17.8 years in the untreated group (N=101). There were more male than female subjects in both the SOHONOS (53% and 47%, respectively) and untreated (55% and 45%, respectively) groups.
The mean annualized new HO was 9.4 cm3/year in subjects receiving the chronic/flare-up SOHONOS treatment and 20.3 cm3/year in untreated subjects in the NHS based on a linear mixed effect model. The treatment effect was about 10.9 cm3/year with 95% confidence interval (-21.2 cm3/year, -0.6 cm3/year).
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient and/or caregiver to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide).
| This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration | Issued: 8/2023 | |
| MEDICATION GUIDE SOHONOS [so-ho-nos] (palovarotene capsules) |
||
What is the most important information I should know about SOHONOS?
|
||
What is SOHONOS?
|
||
Do not take SOHONOS if you:
|
||
Before taking SOHONOS, tell your healthcare provider about all your medical conditions, including if you:
|
||
| Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. SOHONOS and certain other medicines can interact with each other, sometimes causing serious side effects. | ||
| Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them to show to your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medicine. | ||
How should I take SOHONOS?
|
||
What should I avoid while taking SOHONOS?
|
||
| What are possible side effects of SOHONOS? | ||
SOHONOS can cause serious side effects, including:
|
||
| The most common side effects of SOHONOS include: | ||
|
|
|
| These are not all the possible side effects of SOHONOS. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. | ||
How should I store SOHONOS?
|
||
| General information about the safe and effective use of SOHONOS | ||
| Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use SOHONOS for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give SOHONOS to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about SOHONOS that is written for healthcare professionals. | ||
| What are the ingredients in SOHONOS? | ||
| Active ingredient: palovarotene | ||
| Inactive ingredients: croscarmellose sodium, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, povidone, and sodium lauryl sulfate. The capsule consists of gelatin and titanium dioxide. The black printing ink consists of black iron oxide, potassium hydroxide, propylene glycol, and Shellac. | ||
| Distributed by: | ||
| Ipsen Biopharmaceuticals, Inc. Cambridge, MA; 02142. | ||
| For more information about SOHONOS, call 855-463-5127 or go to www.SOHONOS.com or [email protected] | ||
| SOHONOS is a trademark of Clementia Pharmaceuticals Inc. | ||
| © 2023 Ipsen Biopharmaceuticals, Inc. All rights reserved. | ||
| SOHONOS
palovarotene capsule |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SOHONOS
palovarotene capsule |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SOHONOS
palovarotene capsule |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SOHONOS
palovarotene capsule |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SOHONOS
palovarotene capsule |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Ipsen Biopharmaceuticals, Inc. (118461578) |