Drug Detail:Solaraze (Diclofenac topical [ dye-kloe-fen-ak-top-ik-al ])
Drug Class: Topical non-steroidal anti-inflammatories
WARNING: RISK OF SERIOUS CARDIOVASCULAR EVENTS
Cardiovascular Thrombotic Events
- •
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) cause an increased risk of serious cardiovascular thrombotic events, including myocardial infarction and stroke, which can be fatal. This risk may occur early in treatment and may increase with duration of use.
- •
- Solaraze is contraindicated in the setting of coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery.
Solaraze Description
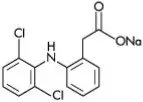
Solaraze® (diclofenac sodium) Gel, 3%, contains the active ingredient, diclofenac sodium, in a clear, transparent, colorless to slightly yellow gel base. Diclofenac sodium is a white to slightly yellow crystalline powder. It is freely soluble in methanol, soluble in ethanol, sparingly soluble in water, slightly soluble in acetone, and partially insoluble in ether. The chemical name for diclofenac sodium is:
Sodium [o-(2,6-dichloranilino) phenyl] acetate
Diclofenac sodium has a molecular weight of 318.13.
The CAS number is CAS-15307-79-6. The structural formula is represented below:
Solaraze® Gel also contains benzyl alcohol, hyaluronate sodium, polyethylene glycol monomethyl ether, and purified water.
1 g of Solaraze® (diclofenac sodium) Gel contains 30 mg of the active substance, diclofenac sodium.
Solaraze - Clinical Pharmacology
The mechanism of action of diclofenac sodium in the treatment of actinic keratoses (AK) is unknown. The contribution to efficacy of individual components of the vehicle has not been established.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
When Solaraze® is applied topically, diclofenac is absorbed into the epidermis. In a study in patients with compromised skin (mainly atopic dermatitis and other dermatitic conditions) of the hands, arms or face, approximately 10% of the applied dose (2 grams of 3% gel over 100 cm2) of diclofenac was absorbed systemically in both normal and compromised epidermis after seven days, with four times daily applications.
After topical application of 2 g Solaraze® three times daily for six days to the calf of the leg in healthy subjects, diclofenac could be detected in plasma. Mean bioavailability parameters were AUC0-t 9±19 ng/hr/mL (mean±SD) with a Cmax of 4±5 ng/mL and a Tmax of 4.5±8 hours. In comparison, a single oral 75 mg dose of diclofenac (Voltaren®)† produced an AUC of 1600 ng/hr/mL. Therefore, the systemic bioavailability after topical application of Solaraze® is lower than after oral dosing.
Comparative bioavailability studies have not been conducted between available diclofenac topical products (gels containing 1 to 3% diclofenac) which have different dosing regimens. A cross-study evaluation of the data indicates that diclofenac is more bioavailable when applied to diseased skin and less bioavailable when applied to intact skin.
Blood drawn at the end of treatment from 60 patients with AK lesions treated with Solaraze® in three adequate and well-controlled clinical trials was assayed for diclofenac levels. Each patient was administered 0.5 g of Solaraze® Gel twice a day for up to 105 days. There were up to three 5 cm x 5 cm treatment sites per patient on the face, forehead, hands, forearm, and scalp. Serum concentrations of diclofenac were, on average, at or below 20 ng/mL. These data indicate that systemic absorption of diclofenac in patients treated topically with Solaraze® is much lower than that occurring after oral daily dosing of diclofenac sodium.
No information is available on the absorption of diclofenac when Solaraze® is used under occlusion.
Distribution
Diclofenac binds tightly to serum albumin. The volume of distribution of diclofenac following oral administration is approximately 550 mL/kg.
Metabolism
Biotransformation of diclofenac following oral administration involves conjugation at the carboxyl group of the side chain or single or multiple hydroxylations resulting in several phenolic metabolites, most of which are converted to glucuronide conjugates. Two of these phenolic metabolites are biologically active, however to a much smaller extent than diclofenac. Metabolism of diclofenac following topical administration is thought to be similar to that after oral administration. The small amounts of diclofenac and its metabolites appearing in the plasma following topical administration makes the quantification of specific metabolites imprecise.
Related/similar drugs
diclofenac topical, fluorouracil topical, imiquimod topical, Santyl, Efudex, Collagenase SantylIndications and Usage for Solaraze
Solaraze® (diclofenac sodium) Gel is indicated for the topical treatment of actinic keratoses (AK). Sun avoidance is indicated during therapy.
Clinical Studies
Clinical trials were conducted involving a total of 427 patients (213 treated with Solaraze® and 214 with a gel vehicle). Each patient had no fewer than five AK lesions in a major body area, which was defined as one of five 5 cm x 5 cm regions: scalp, forehead, face, forearm and hand. Up to three major body areas were studied in any patient. All patients were 18 years of age or older (male and female) with no clinically significant medical problems outside of the AK lesions and had undergone a 60-day washout period from disallowed medications (masoprocol, 5-fluorouracil, cyclosporine, retinoids, trichloroacetic acid/lactic acid/peel, 50% glycolic acid peel) and hyaluronan-containing cosmetics. Patients were excluded from participation for reasons of known or suspected hypersensitivity to any Solaraze® ingredient, pregnancy, allergies to aspirin or other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), or other dermatological conditions which might affect the absorption of the study medication. Application of dermatologic products such as sunscreens, cosmetics, and other drug products was not permitted. Patients were instructed to apply a small amount of Solaraze® Gel (approximately 0.5 g) onto the affected skin, using their fingers, and gently smoothing the gel over the lesion. In addition, all patients were instructed to avoid sun exposure. Complete clearing of the AK lesions 30 days after completion of treatment was the primary efficacy variable. No long-term patient follow-ups, after the 30-day assessments, were performed for the detection of recurrence.
|
Complete Clearance of Actinic Keratosis Lesions 30 Days Post-Treatment (all locations) |
|||
|
Solaraze® Gel |
Vehicle |
p-value |
|
|
Study 1 90 days treatment |
27/58 (47%) |
11/59 (19%) |
<0.001 |
|
Study 2 90 days treatment |
18/53 (34%) |
10/55 (18%) |
0.061 |
|
Study 3 60 days treatment |
15/48 (31%) |
5/49 (10%) |
0.021 |
|
30 days treatment |
7/49 (14%) |
2/49 ( 4%) |
0.221 |
|
Complete Clearance of Actinic Keratosis Lesions 30 Days Post-Treatment (by location) |
|||||
|
Scalp |
Forehead |
Face |
Arm/Forearm |
Back of Hand |
|
|
Study 1 | |||||
|
Solaraze® |
1/4 (25%) |
17/30 (57%) |
9/17 (53%) |
4/12 (33%) |
6/16 (38%) |
|
Vehicle |
3/9 (33%) |
8/24 (33%) |
5/17 (29%) |
4/12 (33%) |
0/14 (0) |
|
p-value |
0.7646 |
0.0908 |
0.1682 |
1.000 |
0.0650 |
|
Study 2 | |||||
|
Solaraze® |
2/6 (33%) |
9/19 (47%) |
4/5 (80%) |
5/8 (63%) |
1/17 (6%) |
|
Vehicle |
0/4 (0) |
6/22 (27%) |
2/8 (25%) |
0/5 (0) |
3/16 (19%) |
|
p-value |
0.4235 |
0.1870 |
0.0727 |
0.0888 |
0.2818 |
|
Study 3 | |||||
|
Solaraze® |
3/7 (43%) |
13/31 (42%) |
10/19 (53%) |
0/1 (0) |
2/8 (25%) |
|
Vehicle |
0/6 (0) |
5/36 (14%) |
2/13 (15%) |
0/2 (0) |
1/9 (11%) |
|
p-value |
0.2271 |
0.0153 |
0.0433 |
- |
0.4637 |
|
30 days | |||||
|
Solaraze® |
2/5 (40%) |
4/29 (14%) |
3/14 (21%) |
0/0 (0) |
0/9 (0) |
|
Vehicle |
0/5 (0) |
2/29 (7%) |
2/18 (11%) |
0/1 (0) |
1/9 (11%) |
|
p-value |
0.2299 |
0.3748 |
0.4322 |
- |
0.6521 |
|
All data | |||||
|
Solaraze® |
8/22 (36%) |
43/109 (39%) |
26/55 (47%) |
9/21 (43%) |
9/50 (18%) |
|
Vehicle |
3/24 (13%) |
21/111 (19%) |
11/56 (20%) |
4/20 (20%) |
5/48 (10%) |
|
p-value |
0.0903 |
0.0013 |
0.0016 |
0.2043 |
0.3662 |
Contraindications
Solaraze® (diclofenac sodium) Gel is contraindicated in patients with a known hypersensitivity to diclofenac, benzyl alcohol, polyethylene glycol monomethyl ether 350 and/or hyaluronate sodium.
Solaraze® (diclofenac sodium) Gel is contraindicated in the following patients:
- In the setting of coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery.
Warnings
Fetal Toxicity
Premature Closure of Fetal Ductus Arteriosus:
Avoid use of NSAIDs, including Solaraze® Gel, in pregnant women at about 30 weeks gestation and later. NSAIDs including Solaraze® Gel, increase the risk of premature closure of the fetal ductus arteriosus at approximately this gestational age.
Oligohydramnios/Neonatal Renal Impairment:
Use of NSAIDs, including Solaraze® Gel, at about 20 weeks gestation or later in pregnancy may cause fetal renal dysfunction leading to oligohydramnios and, in some cases, neonatal renal impairment. These adverse outcomes are seen, on average, after days to weeks of treatment, although oligohydramnios has been infrequently reported as soon as 48 hours after NSAID initiation. Oligohydramnios is often, but not always reversible with treatment discontinuation. Complications of prolonged oligohydramnios may, for example, include limb contractures and delayed lung maturation. In some postmarketing cases of impaired neonatal renal function, invasive procedures such as exchange transfusion or dialysis were required.
If NSAID treatment is necessary between about 20 weeks and 30 weeks gestation, limit Solaraze® Gel use to the lowest effective dose and shortest duration possible. Consider ultrasound monitoring of amniotic fluid if Solaraze® Gel treatment extends beyond 48 hours. Discontinue Solaraze® Gel if oligohydramnios occurs and follow up according to clinical practice [see PRECAUTIONS; Pregnancy].
As with other NSAIDs, anaphylactoid reactions may occur in patients without prior exposure to diclofenac. Diclofenac sodium should be given with caution to patients with the aspirin triad. The triad typically occurs in asthmatic patients who experience rhinitis with or without nasal polyps, or who exhibit severe, potentially fatal bronchospasm after taking aspirin or other NSAIDs.
Serious Skin Reactions, Drug Rash with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS)
Drug Rash with Eosinophiliaand Systemic Symptoms (DRESS)
Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) has been reported in patients taking NSAIDs such as Solaraze® Gel. Some of these events have been fatal or life-threatening. DRESS typically although not exclusively, presents with fever, rash, lymphadenopathy, and/or facial swelling. Other clinical manifestations may include hepatitis, nephritis, hematological abnormalities, myocarditis, or myositis. Sometimes symptoms of DRESS may resemble an acute viral infection. Eosinophilia is often present. Because this disorder is variable in its presentation, other organ systems not noted here may be involved. It is important to note that early manifestations of hypersensitivity, such as fever or lymphadenopathy, may be present even though rash is not evident. If such signs or symptoms are present, discontinue Solaraze® Gel and evaluate the patient immediately.
Cardiovascular Thrombotic Events
Clinical trials of several COX-2 selective and nonselective NSAIDs of up to three years duration have shown an increased risk of serious cardiovascular (CV) thrombotic events, including myocardial infarction (MI) and stroke, which can be fatal. Based on available data, it is unclear that the risk for CV thrombotic events is similar for all NSAIDs. The relative increase in serious CV thrombotic events over baseline conferred by NSAID use appears to be similar in those with and without known CV disease or risk factors for CV disease. However, patients with known CV disease or risk factors had a higher absolute incidence of excess serious CV thrombotic events, due to their increased baseline rate. Some observational studies found that this increased risk of serious CV thrombotic events began as early as the first weeks of treatment. The increase in CV thrombotic risk has been observed most consistently at higher doses.
To minimize the potential risk for an adverse CV event in NSAID-treated patients, use the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration possible. Physicians and patients should remain alert for the development of such events, throughout the entire treatment course, even in the absence of previous CV symptoms. Patients should be informed about the symptoms of serious CV events and the steps to take if they occur.
There is no consistent evidence that concurrent use of aspirin mitigates the increased risk of serious CV thrombotic events associated with NSAID use. The concurrent use of aspirin and an NSAID, such as diclofenac, increases the risk of serious gastrointestinal (GI) events.
Status Post Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG) Surgery
Two large, controlled clinical trials of a COX-2 selective NSAID for the treatment of pain in the first 10–14 days following CABG surgery found an increased incidence of myocardial infarction and stroke. NSAIDs are contraindicated in the setting of CABG.
Post-MI Patients
Observational studies conducted in the Danish National Registry have demonstrated that patients treated with NSAIDs in the post-MI period were at increased risk of reinfarction, CV-related death, and all-cause mortality beginning in the first week of treatment. In this same cohort, the incidence of death in the first year post MI was 20 per 100 person years in NSAID-treated patients compared to 12 per 100 person years in non-NSAID exposed patients. Although the absolute rate of death declined somewhat after the first year post-MI, the increased relative risk of death in NSAID users persisted over at least the next four years of follow-up.
Avoid the use of Solaraze® Gel in patients with a recent MI unless the benefits are expected to outweigh the risk of recurrent CV thrombotic events. If Solaraze® Gel is used in patients with a recent MI, monitor patients for signs of cardiac ischemia.
Heart Failure and Edema
The Coxib and traditional NSAID Trialists’ Collaboration meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials demonstrated an approximately two-fold increase in hospitalizations for heart failure in COX-2 selective-treated patients and nonselective NSAID-treated patients compared to placebo-treated patients. In a Danish National Registry study of patients with heart failure, NSAID use increased the risk of MI, hospitalization for heart failure, and death.
Additionally, fluid retention and edema have been observed in some patients treated with NSAIDs. Use of diclofenac may blunt the CV effects of several therapeutic agents used to treat these medical conditions [e.g., diuretics, ACE inhibitors, or angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs)].
Avoid the use of Solaraze® Gel in patients with severe heart failure unless the benefits are expected to outweigh the risk of worsening heart failure. If Solaraze® Gel is used in patients with severe heart failure, monitor patients for signs of worsening heart failure.
Precautions
General
Solaraze® (diclofenac sodium) Gel should be used with caution in patients with active gastrointestinal ulceration or bleeding and severe renal or hepatic impairments. Solaraze® should not be applied to open skin wounds, infections, or exfoliative dermatitis. It should not be allowed to come in contact with the eyes.
The safety of the concomitant use of sunscreens, cosmetics or other topical medications and Solaraze® is unknown.
Information for Patients Fetal Toxicity If treatment with Solaraze® Gel is needed for a pregnant woman between about 20 to 30 weeks gestation, advise her that she may need to be monitored for oligohydramnios, if treatment continues for longer than 48 hours. Inform pregnant women to avoid use of Solaraze® Geland other NSAIDs starting at 30 weeks gestation because of the risk of the premature closing of the fetal ductus arteriosus. [see WARNINGS; Fetal Toxicity, PRECAUTIONS; Pregnancy].
In clinical studies, localized dermal side effects such as contact dermatitis, exfoliation, dry skin and rash were found in patients treated with Solaraze® at a higher incidence than in those with placebo.
Patients should understand the importance of monitoring and follow-up evaluation, the signs and symptoms of dermal adverse reactions, and the possibility of irritant or allergic contact dermatitis. If severe dermal reactions occur, treatment with Solaraze® may be interrupted until the condition subsides. Exposure to sunlight and the use of sunlamps should be avoided.
Safety and efficacy of the use of Solaraze® together with other dermal products, including cosmetics, sunscreens, and other topical medications on the area being treated, have not been studied.
Serious Skin Reactions, including DRESS
Advise patients to stop taking Solaraze® Gel immediately if they develop any type of rash or fever and to
contact their healthcare provider as soon as possible [see WARNINGS, Serious Skin Reactions ].
Cardiovascular Thrombotic Events
Advise patients to be alert for the symptoms of cardiovascular thrombotic events, including chest pain, shortness of breath, weakness, or slurring of speech, and to report any of these symptoms to their health care provider immediately.
Heart Failure and Edema
Advise patients to be alert for the symptoms of congestive heart failure including shortness of breath, unexplained weight gain, or edema and to contact their healthcare provider if such symptoms occur.
Drug Interactions
Specific interaction studies between Solaraze® Gel and other topical or oral agents were not performed.
Oral Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs
Although low, there is systemic exposure to diclofenac following labeled use of Solaraze® Gel. Therefore, concomitant administration of Solaraze® Gel with oral NSAIDS or aspirin may result in increased NSAID adverse effects.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
There did not appear to be any increase in drug-related neoplasms following daily topical applications of diclofenac sodium gel for 2 years at concentrations up to 0.035% diclofenac sodium and 2.5% hyaluronate sodium in albino mice. (Note: Solaraze® contains 3% diclofenac sodium.)
When administered orally for 2 years, diclofenac showed no evidence of carcinogenic potential in rats given diclofenac sodium at up to 2 mg/kg/day (3 times the estimated systemic human exposure*), or in mice given diclofenac sodium at up to 0.3 mg/kg/day in males and 1 mg/kg/day in females (25% and 83%, respectively, of the estimated systemic human exposure).
A photococarcinogenicity study with up to 0.035% diclofenac in the Solaraze® vehicle gel was conducted in hairless mice at topical doses up to 2.8 mg/ kg/day. Median tumor onset was earlier in the 0.035% group (Solaraze® contains 3% diclofenac sodium).
Diclofenac was not genotoxic in in vitro point mutation assays in mammalian mouse lymphoma cells and Ames microbial test systems, or when tested in mammalian in vivo assays including dominant lethal and male germinal epithelial chromosomal studies in mice, and nucleus anomaly and chromosomal aberration studies in Chinese hamsters. It was also negative in the transformation assay utilizing BALB/3T3 mouse embryo cells.
Fertility studies have not been conducted with Solaraze® Gel. Diclofenac sodium showed no evidence of impairment of fertility after oral treatment with 4 mg/kg/day (7 times the estimated systemic human exposure) in male or female rats.
* Based on body surface area and assuming 10% bioavailability following topical application of 2 g Solaraze® Gel per day (1 mg/kg diclofenac sodium).
Pregnancy:
Risk Summary
Use of NSAIDs, including Solaraze® Gel, can cause fetal renal dysfunction leading to oligohydramniosand, in some cases, neonatal renal impairment from 20 weeks of gestation, and premature closure of the fetal ductus arteriosus from 30 weeks of gestation. Because of these risks, limit dose and duration of Solaraze® Gel use between about 20 and 30 weeks of gestation, and avoid Solaraze® Gel use at about 30 weeks of gestation and later in pregnancy (see WARNINGS; Fetal Toxicity).
Oligohydramnios/Neonatal Renal Impairment
Use of NSAIDs at about 20 weeks gestation or later in pregnancy has been associated with cases of fetal renal dysfunction leading to oligohydramnios, and in some cases, neonatal renal impairment.
Premature Closure of Fetal Ductus Arteriosus
Use of NSAIDs, including Solaraze® Gel, at about 30 weeks gestation or later in pregnancy increases the risk of premature closure of the fetal ductus arteriosus.
Data from observational studies regarding other potential embryofetal risks of NSAID use in women in the first or second trimesters of pregnancy are inconclusive. In the general U.S. population, all clinically recognized pregnancies, regardless of drug exposure, have a background rate of 2-4% for major malformations, and 15-20% for pregnancy loss.
In animal reproduction studies, no evidence of teratogenicity was observed in mice, rats, or rabbits given diclofenac during the period of organogenesis at doses at least 15 times, the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of Solaraze® Gel (See Animal Data).
Based on published animal data, prostaglandins have been shown to have an important role in endometrial vascular permeability, blastocyst implantation, and decidualization, and administration of prostaglandin synthesis inhibitors such as diclofenac sodium, resulted in increased pre- and post-implantation loss. Prostaglandins also have been shown to have an important role in fetal kidney development. In published animal studies, prostaglandin synthesis inhibitors have been reported to impair kidney development when administered at clinically relevant doses.
The safety of Solaraze® (diclofenac sodium) Gel has not been established during pregnancy.
Clinical Considerations
Fetal/Neonatal Adverse Reactions
Premature Closure of Fetal Ductus Arteriosus:
Avoid use of NSAIDs in women at about 30 weeks gestation and later in pregnancy, because NSAIDs, including Solaraze® Gel, can cause premature closure of the fetal ductus arteriosus (see WARNINGS ;Fetal Toxicity).
Oligohydramnios/Neonatal Renal Impairment
If an NSAID is necessary at about 20 weeks gestation or later in pregnancy, limit the use to the lowest effective dose and shortest duration possible. If Solaraze® Gel treatment extends beyond 48 hours, consider monitoring with ultrasound for oligohydramnios. If oligohydramnios occurs, discontinue Solaraze® Gel and follow up according to clinical practice (see WARNINGS; Fetal Toxicity).
Data
Human Data
Premature Closure of Fetal Ductus Arteriosus:
Published literature reports that the use of NSAIDs at about 30 weeks of gestation and later in pregnancy may cause premature closure of the fetal ductus arteriosus.
Oligohydramnios/Neonatal Renal Impairment:
Published studies and postmarketing reports describe maternal NSAID use at about 20 weeks gestation or later in pregnancy associated with fetal renal dysfunction leading to oligohydramnios, and in some cases, neonatal renal impairment. These adverse outcomes are seen, on average, after days to weeks of treatment, although oligohydramnios has been infrequently reported as soon as 48 hours after NSAID initiation. In many cases, but not all, the decrease in amniotic fluid was transient and reversible with cessation of the drug. There have been a limited number of case reports of maternal NSAID use and neonatal renal dysfunction without oligohydramnios, some of which were irreversible. Some cases of neonatal renal dysfunction required treatment with invasive procedures, such as exchange transfusion or dialysis.
Methodological limitations of these postmarketing studies and reports include lack of a control group; limited information regarding dose, duration, and timing of drug exposure; and concomitant use of other medications. These limitations preclude establishing a reliable estimate of the risk of adverse fetal and neonatal outcomes with maternal NSAID use. Because the published safety data on neonatal outcomes involved mostly preterm infants, the generalizability of certain reported risks to the full-term infant exposed to NSAIDs through maternal use is uncertain.
Animal Data
Reproductive studies performed with diclofenac sodium alone at oral doses up to 20 mg/kg/day (15 times the estimated systemic human exposure*) in mice, 10 mg/kg/day (15 times the estimated systemic human exposure) in rats, and 10 mg/kg/day (30 times the estimated systemic human exposure) in rabbits have revealed no evidence of teratogenicity despite the induction of maternal toxicity. In rats, maternally toxic doses were associated with dystocia, prolonged gestation, reduced fetal weights and growth, and reduced fetal survival. Diclofenac has been shown to cross the placental barrier in mice and rats.
* Based on body surface area and assuming 10% bioavailability following topical application of 2 g Solaraze® Gel per day (1 mg/kg diclofenac sodium)
Labor and Delivery
The effects of diclofenac on labor and delivery in pregnant women are unknown. Because of the known effects of prostaglandin-inhibiting drugs on the fetal cardiovascular system (closure of the ductus arteriosus), use of diclofenac during late pregnancy should be avoided and, as with other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, it is possible that diclofenac may inhibit uterine contractions and delay parturition.
Nursing Mothers
Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from diclofenac sodium, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
Pediatric Use
Actinic keratoses is not a condition seen within the pediatric population. Solaraze® should not be used by children.
Geriatric Use
Of the 211 subjects treated with Solaraze® in controlled clinical studies, 143 subjects were 65 and over. Of those 143 subjects, 55 subjects were 75 and over. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these subjects and younger subjects, and other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients, but greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out.
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Of the 423 patients evaluable for safety in adequate and well-controlled trials, 211 were treated with Solaraze® drug product and 212 were treated with a vehicle gel. Eighty-seven percent (87%) of the Solaraze®-treated patients (183 patients) and 84% of the vehicle-treated patients (178 patients) experienced one or more adverse events (AEs) during the studies. The majority of these reactions were mild to moderate in severity and resolved upon discontinuation of therapy.
Of the 211 patients treated with Solaraze®, 172 (82%) experienced AEs involving skin and the application site compared to 160 (75%) vehicle-treated patients. Application site reactions (ASRs) were the most frequent AEs in both Solaraze®-and vehicle-treated groups. Of note, four reactions, contact dermatitis, rash, dry skin and exfoliation (scaling) were significantly more prevalent in the Solaraze® group than in the vehicle-treated patients.
Eighteen percent of Solaraze®-treated patients and 4% of vehicle-treated patients discontinued from the clinical trials due to adverse events (whether considered related to treatment or not). These discontinuations were mainly due to skin irritation or related cutaneous adverse reactions.
Table 1 below presents the AEs reported at an incidence of >1% for patients treated with either Solaraze® Gel or vehicle (60- and 90-day treatment groups) during the phase 3 studies.
|
60-day Treatment |
90-day Treatment |
|||
|
Solaraze® (%) |
Gel Vehicle (%) |
Solaraze® (%) |
Gel Vehicle (%) |
|
|
N=48 |
N=49 |
N=114 |
N=114 |
|
|
BODY AS A WHOLE |
21 |
20 |
20 |
18 |
|
Abdominal Pain |
2 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
|
Accidental Injury |
0 |
0 |
4 |
2 |
|
Allergic Reaction |
0 |
0 |
1 |
3 |
|
Asthenia |
0 |
0 |
2 |
0 |
|
Back Pain |
4 |
0 |
2 |
2 |
|
Chest Pain |
2 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
|
Chills |
0 |
2 |
0 |
0 |
|
Flu Syndrome |
10 |
6 |
1 |
4 |
|
Headache |
0 |
6 |
7 |
6 |
|
Infection |
4 |
6 |
4 |
5 |
|
Neck Pain |
0 |
0 |
2 |
0 |
|
Pain |
2 |
0 |
2 |
2 |
|
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM |
2 |
4 |
3 |
1 |
|
Hypertension |
2 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
|
Migraine |
0 |
2 |
1 |
0 |
|
Phlebitis |
0 |
2 |
0 |
0 |
|
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM |
4 |
0 |
6 |
8 |
|
Constipation |
0 |
0 |
0 |
2 |
|
Diarrhea |
2 |
0 |
2 |
3 |
|
Dyspepsia |
2 |
0 |
3 |
4 |
|
METABOLIC AND NUTRITIONAL DISORDERS |
2 |
8 |
7 |
2 |
|
Creatine Phosphokinase Increased |
0 |
0 |
4 |
1 |
|
Creatinine Increased |
2 |
2 |
0 |
1 |
|
Edema |
0 |
2 |
0 |
0 |
|
Hypercholesteremia |
0 |
2 |
1 |
0 |
|
Hyperglycemia |
0 |
2 |
1 |
0 |
|
SGOT Increased |
0 |
0 |
3 |
0 |
|
SGPT Increased |
0 |
0 |
2 |
0 |
|
MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM |
4 |
0 |
3 |
4 |
|
Arthralgia |
2 |
0 |
0 |
2 |
|
Arthrosis |
2 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
Myalgia |
2 |
0 |
3 |
1 |
|
NERVOUS SYSTEM |
2 |
2 |
2 |
5 |
|
Anxiety |
0 |
2 |
0 |
1 |
|
Dizziness |
0 |
0 |
0 |
4 |
|
Hypokinesia |
2 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM |
8 |
8 |
7 |
6 |
|
Asthma |
2 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
Dyspnea |
2 |
0 |
2 |
0 |
|
Pharyngitis |
2 |
8 |
2 |
4 |
|
Pneumonia |
2 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
|
Rhinitis |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
|
Sinusitis |
0 |
0 |
2 |
0 |
|
SKIN AND APPENDAGES |
75 |
86 |
86 |
71 |
|
Acne |
0 |
2 |
0 |
1 |
|
Application Site Reaction |
75 |
71 |
84 |
70 |
|
Acne |
0 |
4 |
1 |
0 |
|
Alopecia |
2 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
|
Contact Dermatitis |
19 |
4 |
33 |
4 |
|
Dry Skin |
27 |
12 |
25 |
17 |
|
Edema |
4 |
0 |
3 |
0 |
|
Exfoliation |
6 |
4 |
24 |
13 |
|
Hyperesthesia |
0 |
0 |
3 |
1 |
|
Pain 15 |
22 |
26 |
30 | |
|
Paresthesia |
8 |
4 |
20 |
20 |
|
Photosensitivity Reaction |
0 |
2 |
3 |
0 |
|
Pruritus |
31 |
59 |
52 |
45 |
|
Rash |
35 |
20 |
46 |
17 |
|
Vesiculobullous Rash |
0 |
0 |
4 |
1 |
|
Contact Dermatitis |
2 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
Dry Skin |
0 |
4 |
3 |
0 |
|
Herpes Simplex |
0 |
2 |
0 |
0 |
|
Maculopapular Rash |
0 |
2 |
0 |
0 |
|
Pain |
2 |
2 |
1 |
0 |
|
Pruritus |
4 |
6 |
4 |
1 |
|
Rash |
2 |
10 |
4 |
0 |
|
Skin Carcinoma |
0 |
6 |
2 |
2 |
|
Skin Nodule |
0 |
2 |
0 |
0 |
|
Skin Ulcer |
2 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
|
SPECIAL SENSES |
2 |
0 |
4 |
2 |
|
Conjunctivitis |
2 |
0 |
4 |
1 |
|
Eye Pain |
0 |
2 |
2 |
0 |
|
UROGENITAL SYSTEM |
0 |
0 |
4 |
5 |
|
Hematuria |
0 |
0 |
2 |
1 |
|
OTHER |
0 |
0 |
0 |
3 |
|
Procedure |
0 |
0 |
0 |
3 |
Skin and Appendages Adverse Events Reported for Solaraze® at Less Than 1% Incidence in the Phase 3 Studies: skin hypertrophy, paresthesia, seborrhea, urticaria, application site reactions (skin carcinoma, hypertonia, skin hypertrophy lacrimation disorder, maculopapular rash, purpuric rash, vasodilation).
Adverse Reactions Reported for Oral Diclofenac Dosage Form (not topical Solaraze® Gel): *Incidence Greater than 1% marked with asterisk.
Body as a Whole: abdominal pain or cramps*, headache*, fluid retention*, abdominal distention*, malaise, swelling of lips and tongue, photosensitivity, anaphylaxis, anaphylactoid reactions, chest pain.
Cardiovascular: hypertension, congestive heart failure, palpitations, flushing, tachycardia, premature ventricular contractions, myocardial infarction, hypotension.
Digestive: diarrhea*, indigestion*, nausea*, constipation*, flatulence*, liver test abnormalities*, PUB*, i.e., peptic ulcer, with or without bleeding and/or perforation, or bleeding without ulcer, vomiting, jaundice, melena, esophageal lesions, aphthous stomatitis, dry mouth and mucous membranes, bloody diarrhea, hepatitis, hepatic necrosis, cirrhosis, hepatorenal syndrome, appetite change, pancreatitis with or without concomitant hepatitis, colitis, intestinal perforation.
Hemic and Lymphatic: hemoglobin decrease, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, eosinophilia, hemolytic anemia, aplastic anemia, agranulocytosis, purpura, allergic purpura, bruising.
Metabolic and Nutritional Disorders: azotemia, hypoglycemia, weight loss.
Nervous System: dizziness*, insomnia, drowsiness, depression, diplopia, anxiety, irritability, aseptic meningitis, convulsions, paresthesia, memory disturbance, nightmares, tremor, tic, abnormal coordination, disorientation, psychotic reaction.
Respiratory: epistaxis, asthma, laryngeal edema, dyspnea, hyperventilation, edema of pharynx.
Skin and Appendages: rash*, pruritus*, alopecia, urticaria, eczema, dermatitis, bullous eruption, erythema multiforme major, angioedema, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, excess perspiration, exfoliative dermatitis.
Special Senses: tinnitus*, blurred vision, taste disorder, reversible and irreversible hearing loss, scotoma, vitreous floaters, night blindness, amblyopia.
Urogenital: nephrotic syndrome, proteinuria, oliguria, interstitial nephritis, papillary necrosis, acute renal failure, urinary frequency, nocturia, hematuria, impotence, vaginal bleeding.
Overdosage
Due to the low systemic absorption of topically-applied Solaraze® Gel, overdosage is unlikely. There have been no reports of ingestion of Solaraze®. In the event of oral ingestion, resulting in significant systemic side effects, it is recommended that the stomach be emptied by vomiting or lavage. Forced diuresis may theoretically be beneficial because the drug is excreted in the urine. The effect of dialysis or hemoperfusion in the elimination of diclofenac (99% protein-bound) remains unproven. In addition to supportive measures, the use of oral activated charcoal may help to reduce the absorption of diclofenac. Supportive and symptomatic treatment should be given for complications such as renal failure, convulsions, gastrointestinal irritation and respiratory depression.
Solaraze Dosage and Administration
Solaraze® Gel is applied to lesion areas twice daily. It is to be smoothed onto the affected skin gently. The amount needed depends upon the size of the lesion site. Assure that enough Solaraze® Gel is applied to adequately cover each lesion. Normally 0.5 g of gel is used on each 5 cm x 5 cm lesion site. The recommended duration of therapy is from 60 days to 90 days. Complete healing of the lesion(s) or optimal therapeutic effect may not be evident for up to 30 days following cessation of therapy. Lesions that do not respond to therapy should be carefully re-evaluated and management reconsidered.
How is Solaraze supplied
Available in tubes of 100 g (NDC 10337-844-01). Each gram of gel contains 30 mg of diclofenac sodium.
Medication Guide
Solaraze (sol-ar-aze)
(diclofenac sodium) Gel, 3%
What is the most important information I should know about Solaraze Gel and medicines called Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)?
Solaraze Gel is an NSAID medicine that is used on the skin only (topical). Do not use Solaraze Gel in or on the eyes.
NSAIDs can cause serious side effects, including:
• Increased risk of a heart attack or stroke that can lead to death. This risk may happen early in treatment and may increase:
o with increasing doses of NSAIDs
o with longer use of NSAIDs
Do not take or use NSAIDs right before or after a heart surgery called a “coronary artery bypass graft (CABG)”. Avoid taking NSAIDs after a recent heart attack, unless your healthcare provider tells you to. You may have an increased risk of another heart attack if you take or use NSAIDs after a recent heart attack.
• Increased risk of bleeding, ulcers, and tears (perforation) of the esophagus (tube leading from the mouth to the stomach), stomach and intestines:
o anytime during use
o without warning symptoms
o that may cause death
The risk of getting an ulcer or bleeding increases with:
o past history of stomach ulcers, or stomach or intestinal bleeding with use of NSAIDs
o taking medicines called “corticosteroids”, “anticoagulants”, “SSRIs”, or “SNRIs”
o increasing doses of NSAIDs
o longer use of NSAIDs
o smoking
o drinking alcohol
o older age
o poor health
o advanced liver disease
o bleeding problems
NSAIDs should only be used:
• exactly as prescribed
• at the lowest dose possible for your treatment
• for the shortest time needed
What is Solaraze Gel?
Solaraze Gel is an NSAID that is used on the skin (topical) to treat a skin condition called actinic keratosis.
Solaraze Gel is not for use in children.
Who should not use Solaraze Gel?
Do not use Solaraze Gel:
• if you have had an allergic reaction to any of the ingredients in Solaraze Gel. See the end of this Medication Guide for a complete list of ingredients in Solaraze Gel.
• right before or after heart bypass surgery.
Before using Solaraze Gel, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
• have liver or kidney problems
• have high blood pressure
• have asthma
• are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. Taking NSAIDS at about 20 weeks of pregnancy or later may harm your unborn baby. If you need to take NSAIDs for more than 2 days when you are between 20 and 30 weeks of pregnancy, your healthcare provider may need to monitor the amount of fluid in your womb around your baby. You should not take NSAIDs after about 30 weeks of pregnancy.
• are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. You and your healthcare provider should decide if you will use Solaraze Gel or breastfeed. You should not do both.
Tell your healthcare provider about all of the medicines you take, including prescription or over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, or herbal supplements. NSAIDs and some other medicines can interact with each other and cause serious side effects. Do not start taking any new medicine without talking to your healthcare provider first.
How should I use Solaraze Gel?
• Use Solaraze Gel exactly as your healthcare provider tells you to use it.
• Apply Solaraze Gel 2 times a day.
• Apply enough Solaraze Gel to cover each skin lesion and gently rub in.
• Solaraze Gel may be used for 60 to 90 days. You may not see improvement of skin lesions for up to 30 days after stopping treatment. See your healthcare provider if lesions do not respond to treatment.
• Wash your hands after applying Solaraze Gel.
What should I avoid while using Solaraze Gel?
• Avoid spending time in sunlight or artificial light, such as tanning beds or sunlamps. Solaraze Gel can make your skin sensitive to sunlight and the light from tanning beds and sunlamps.
• You should avoid applying Solaraze Gel to open skin wounds, skin infections, or peeling skin.
What are the possible side effects of Solaraze Gel?
Solaraze and other NSAIDs can cause serious side effects, including:
See “What is the most important information I should know about Solaraze Gel and medicines called Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)?
• new or worse high blood pressure
• heart failure
• liver problems including liver failure
• kidney problems including kidney failure
• low red blood cells (anemia)
• life-threatening skin reactions
• life threatening allergic reactions
Other side effects of NSAIDs include: stomach pain, constipation, diarrhea, gas, heartburn, nausea, vomiting, and dizziness.
Get emergency help right away if you get any of the following symptoms:
• shortness of breath or trouble breathing
• chest pain
• weakness in one part or side of your body
• slurred speech
• swelling of the face or throat
Stop using Solaraze Gel and call your healthcare provider right away if you get any of the following symptoms:
• nausea
• more tired or weaker than usual
• diarrhea
• itching
• your skin or eyes look yellow
• indigestion or stomach pain
• flu-like symptoms
• vomit blood
• there is blood in your bowel movement or it is black and sticky like tar
• unusual weight gain
• skin rash or blisters with fever
• swelling of the arms, legs, hands and feet
Application site skin reactions are common with Solaraze Gel and include: skin redness, itching, rash, dry skin, scaling, and peeling.
If Solaraze Gel is accidentally taken by mouth, call your healthcare provider or get medical help right away.
These are not all the possible side effects of NSAIDs. For more information, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist about NSAIDs.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
Other information about NSAIDs
Aspirin is an NSAID but it does not increase the chance of a heart attack. Aspirin can cause bleeding in the brain, stomach, and intestines. Aspirin can also cause ulcers in the stomach and intestines.
Some NSAIDs are sold in lower doses without a prescription (over-the-counter). Talk to your healthcare provider before using over-the-counter NSAIDs for more than 10 days.
How should I store Solaraze Gel?
• Store Solaraze Gel at room temperature 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
• Keep Solaraze Gel away from heat. Avoid freezing Solaraze Gel.
Keep Solaraze Gel and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about the safe and effective use of Solaraze Gel
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use Solaraze Gel for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give Solaraze Gel to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them.
If you would like more information about Solaraze Gel, talk with your healthcare provider. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about Solaraze Gel that is written for health professionals.
What are the ingredients in Solaraze Gel?
Active ingredient: diclofenac sodium
Inactive ingredient: benzyl alcohol, hyaluronate sodium, polyethylene glycol monomethyl ether, and purified water.
Manufactured by:
PharmDerm®, A division of Fougera Pharmaceuticals Inc.,
Melville, New York 11747
For more information, go to www.pharmaderm.com or call 1-800-645-9833.
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Issued: 02/2016
46185066B
R04/2021
#330
| SOLARAZE
diclofenac sodium gel |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - PharmaDerm a division of Fougera Pharmaceuticals Inc. (043838424) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| MIDI Labs, Inc | 011372047 | ANALYSIS(10337-844) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gateway Analytical, LLC> | 047276968 | ANALYSIS(10337-844) | |