Drug Detail:Tosymra (Sumatriptan)
Drug Class: Antimigraine agents
Highlights of Prescribing Information
TOSYMRA® (sumatriptan) nasal spray
Initial U.S. Approval: 1992
Indications and Usage for Tosymra
TOSYMRA is a serotonin (5-HT1B/1D) receptor agonist (triptan) indicated for the acute treatment of migraine with or without aura in adults (1)
Limitations of Use:
- Use only if a clear diagnosis of migraine has been established (1)
- Not indicated for the preventive treatment of migraine (1)
- Not indicated for the treatment of cluster headache (1)
Tosymra Dosage and Administration
- Single dose of 10 mg of nasal spray (2)
- Maximum dose in a 24-hour period: 30 mg; separate doses by at least one hour (2)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Nasal Spray, 10 mg (3)
Contraindications
- History of coronary artery disease or coronary vasospasm (4)
- Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome or other cardiac accessory conduction pathway disorders (4)
- History of stroke, transient ischemic attack, or hemiplegic or basilar migraine (4)
- Peripheral vascular disease (4)
- Ischemic bowel disease (4)
- Uncontrolled hypertension (4)
- Recent (within 24 hours) use of another 5-HT1 agonist (e.g., another triptan) or of an ergotamine-containing medication (4)
- Concurrent or recent (past 2 weeks) use of monoamine oxidase-A inhibitor (4)
- Hypersensitivity to sumatriptan (angioedema and anaphylaxis seen) (4)
- Severe hepatic impairment (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Myocardial ischemia/infarction and Prinzmetal's angina: Perform cardiac evaluation in patients with multiple cardiovascular risk factors (5.1)
- Arrhythmias: Discontinue TOSYMRA if occurs (5.2)
- Chest/throat/neck/jaw pain, tightness, pressure, or heaviness: Generally, not associated with myocardial ischemia; evaluate for coronary artery disease in patients at high risk (5.3)
- Cerebral hemorrhage, subarachnoid hemorrhage, and stroke: Discontinue TOSYMRA if occurs (5.4)
- Gastrointestinal ischemia and reactions, peripheral vasospastic reactions: Discontinue TOSYMRA if occurs (5.5)
- Medication overuse headache: Detoxification may be necessary (5.6)
- Serotonin syndrome: Discontinue TOSYMRA if occurs (5.7)
- Increase in blood pressure: Hypertensive crisis can occur (5.8)
- Hypersensitivity reactions: Angioedema and anaphylaxis can occur (5.9)
- Seizures: Use with caution in patients with epilepsy or a lowered seizure threshold (5.10)
- Local irritation: Burning and abnormal taste can occur (5.11)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions (≥5% and > placebo) with sumatriptan injection were tingling, dizziness/vertigo, warm/hot sensation, burning sensation, feeling of heaviness, pressure sensation, flushing, feeling of tightness, and numbness (6.1)
Additional common adverse reactions with TOSYMRA include application site reactions, dysgeusia, and throat irritation. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Upsher-Smith Laboratories, LLC at 1-855-899-9180 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Use In Specific Populations
Pregnancy: Based on animal data, may cause fetal harm (8.1)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 2/2021
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Tosymra
TOSYMRA is indicated for the acute treatment of migraine with or without aura in adults.
2. Tosymra Dosage and Administration
The recommended dose of TOSYMRA is 10 mg given as a single spray in one nostril.
The maximum cumulative dose that may be given in a 24-hour period is 30 mg, with doses of TOSYMRA separated by at least 1 hour. TOSYMRA may also be given at least 1 hour following a dose of another sumatriptan product.
4. Contraindications
TOSYMRA is contraindicated in patients with:
- Ischemic coronary artery disease (CAD) (angina pectoris, history of myocardial infarction, or documented silent ischemia) or coronary artery vasospasm, including Prinzmetal's angina [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome or arrhythmias associated with other cardiac accessory conduction pathway disorders [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
- History of stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA) or history of hemiplegic or basilar migraine because these patients are at a higher risk of stroke [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
- Peripheral vascular disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
- Ischemic bowel disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
- Uncontrolled hypertension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
- Recent use (i.e., within 24 hours) of ergotamine-containing medication, ergot-type medication (such as dihydroergotamine or methysergide), or another 5-hydroxytryptamine1 (5-HT1) agonist [see Drug Interactions (7.1, 7.3)].
- Concurrent administration of a monoamine oxidase (MAO)-A inhibitor or recent (within 2 weeks) use of an MAO-A inhibitor [see Drug Interactions (7.2) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
- Hypersensitivity to sumatriptan (angioedema and anaphylaxis seen) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)].
- Severe hepatic impairment [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Myocardial Ischemia, Myocardial Infarction, and Prinzmetal's Angina
The use of TOSYMRA is contraindicated in patients with ischemic or vasospastic CAD. There have been rare reports of serious cardiac adverse reactions, including acute myocardial infarction, occurring within a few hours following administration of sumatriptan. Some of these reactions occurred in patients without known CAD. 5-HT1 agonists, including TOSYMRA, may cause coronary artery vasospasm (Prinzmetal's angina), even in patients without a history of CAD.
Perform a cardiovascular evaluation in triptan-naive patients who have multiple cardiovascular risk factors (e.g., increased age, diabetes, hypertension, smoking, obesity, strong family history of CAD) prior to receiving TOSYMRA. If there is evidence of CAD or coronary artery vasospasm, TOSYMRA is contraindicated. For patients with multiple cardiovascular risk factors who have a negative cardiovascular evaluation, consider administering the first dose of TOSYMRA in a medically supervised setting and performing an electrocardiogram (ECG) immediately following administration of TOSYMRA. For such patients, consider periodic cardiovascular evaluation in intermittent long-term users of TOSYMRA.
5.2 Arrhythmias
Life-threatening disturbances of cardiac rhythm, including ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation leading to death, have been reported within a few hours following the administration of 5-HT1 agonists. Discontinue TOSYMRA if these disturbances occur.
TOSYMRA is contraindicated in patients with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome or arrhythmias associated with other cardiac accessory conduction pathway disorders.
5.3 Chest, Throat, Neck, and/or Jaw Pain/Tightness/Pressure
Sensations of tightness, pain, pressure, and heaviness in the precordium, throat, neck, and jaw commonly occur after treatment with sumatriptan injection and are usually non-cardiac in origin. However, perform a cardiac evaluation if these patients are at high cardiac risk. The use of TOSYMRA is contraindicated in patients shown to have CAD and those with Prinzmetal's variant angina.
5.4 Cerebrovascular Events
Cerebral hemorrhage, subarachnoid hemorrhage, and stroke have occurred in patients treated with 5-HT1 agonists, and some have resulted in fatalities. In a number of cases, it appears possible that the cerebrovascular events were primary, the 5-HT1 agonist having been administered in the incorrect belief that the symptoms experienced were a consequence of migraine when they were not. Also, patients with migraine may be at increased risk of certain cerebrovascular events (e.g., stroke, hemorrhage, TIA). Discontinue TOSYMRA if a cerebrovascular event occurs.
Before treating headaches in patients not previously diagnosed with migraine or in patients who present with atypical symptoms, exclude other potentially serious neurological conditions. TOSYMRA is contraindicated in patients with a history of stroke or TIA.
5.5 Other Vasospasm Reactions
TOSYMRA may cause non-coronary vasospastic reactions, such as peripheral vascular ischemia, gastrointestinal vascular ischemia and infarction (presenting with abdominal pain and bloody diarrhea), splenic infarction, and Raynaud's syndrome. In patients who experience symptoms or signs suggestive of non-coronary vasospasm reaction following the use of any 5-HT1 agonist, rule out a vasospastic reaction before receiving additional TOSYMRA.
Reports of transient and permanent blindness and significant partial vision loss have been reported with the use of 5-HT1 agonists. Since visual disorders may be part of a migraine attack, a causal relationship between these events and the use of 5-HT1 agonists have not been clearly established.
5.6 Medication Overuse Headache
Overuse of acute migraine drugs (e.g., ergotamine, triptans, opioids, or combination of these drugs for 10 or more days per month) may lead to exacerbation of headache (medication overuse headache). Medication overuse headache may present as migraine-like daily headaches, or as a marked increase in frequency of migraine attacks. Detoxification of patients, including withdrawal of the overused drugs, and treatment of withdrawal symptoms (which often includes a transient worsening of headache) may be necessary.
5.7 Serotonin Syndrome
Serotonin syndrome may occur with TOSYMRA, particularly during co-administration with selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs), and MAO inhibitors [see Drug Interactions (7.4)]. Serotonin syndrome symptoms may include mental status changes (e.g., agitation, hallucinations, coma), autonomic instability (e.g., tachycardia, labile blood pressure, hyperthermia), neuromuscular aberrations (e.g., hyperreflexia, incoordination), and/or gastrointestinal symptoms (e.g., nausea, vomiting, diarrhea). The onset of symptoms usually occurs within minutes to hours of receiving a new or a greater dose of a serotonergic medication. Discontinue TOSYMRA if serotonin syndrome is suspected.
5.8 Increase in Blood Pressure
Significant elevation in blood pressure, including hypertensive crisis with acute impairment of organ systems, has been reported on rare occasions in patients treated with 5-HT1 agonists, including patients without a history of hypertension. Monitor blood pressure in patients treated with TOSYMRA. TOSYMRA is contraindicated in patients with uncontrolled hypertension.
5.9 Hypersensitivity Reactions
Hypersensitivity reactions, including angioedema and anaphylaxis, have occurred in patients receiving sumatriptan. Such reactions can be life threatening or fatal. In general, anaphylactic reactions to drugs are more likely to occur in individuals with a history of sensitivity to multiple allergens. TOSYMRA is contraindicated in patients with a history of hypersensitivity reaction to sumatriptan.
5.10 Seizures
Seizures have been reported following administration of sumatriptan. Some have occurred in patients with either a history of seizures or concurrent conditions predisposing to seizures. There are also reports in patients where no such predisposing factors are apparent. TOSYMRA should be used with caution in patients with a history of epilepsy or conditions associated with a lowered seizure threshold.
5.11 Local Irritation
Local irritative symptoms were reported in approximately 46% of patients treated with TOSYMRA in an open-label trial which allowed repeated use of TOSYMRA over the course of 6 months. Of these, the most common local irritative symptoms were application site reaction (36%), dysgeusia (21%), and throat irritation (5%). Approximately 0.5% of the cases were reported as severe.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following serious adverse reactions are described below and elsewhere in the labeling:
- Myocardial Ischemia, Myocardial Infarction, and Prinzmetal's Angina [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Arrhythmias [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Chest, Throat, Neck, and/or Jaw Pain/Tightness/Pressure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Cerebrovascular Events [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Other Vasospasm Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Medication Overuse Headache [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Serotonin Syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- Increase in Blood Pressure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
- Hypersensitivity Reactions [see Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]
- Seizures [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)]
- Local Irritation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared with rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Adverse Reactions in Placebo-Controlled Trials with Sumatriptan Injection
Table 1 lists adverse reactions that occurred in 2 placebo-controlled clinical trials in patients with migraine (Studies 2 and 3) following either a single 6 mg dose of sumatriptan injection or placebo. Only reactions that occurred at a frequency of 2% or more in groups treated with sumatriptan injection 6 mg and that occurred at a frequency greater than the placebo group are included in Table 1.
| Adverse Reaction | Sumatriptan Injection 6 mg Subcutaneous (n = 547) % | Placebo (n = 370) % |
|---|---|---|
| Atypical sensations | 42 | 9 |
| Tingling | 14 | 3 |
| Warm/hot sensation | 11 | 4 |
| Burning sensation | 7 | <1 |
| Feeling of heaviness | 7 | 1 |
| Pressure sensation | 7 | 2 |
| Feeling of tightness | 5 | <1 |
| Numbness | 5 | 2 |
| Feeling strange | 2 | <1 |
| Tight feeling in head | 2 | <1 |
| Cardiovascular | ||
| Flushing | 7 | 2 |
| Chest discomfort | 5 | 1 |
| Tightness in chest | 3 | <1 |
| Pressure in chest | 2 | <1 |
| Ear, nose, and throat | ||
| Throat discomfort | 3 | <1 |
| Discomfort: nasal cavity/sinuses | 2 | <1 |
| Miscellaneous | ||
| Jaw discomfort | 2 | 0 |
| Musculoskeletal | ||
| Weakness | 5 | <1 |
| Neck pain/stiffness | 5 | <1 |
| Myalgia | 2 | <1 |
| Neurological | ||
| Dizziness/vertigo | 12 | 4 |
| Drowsiness/sedation | 3 | 2 |
| Headache | 2 | <1 |
| Skin | ||
| Sweating | 2 | 1 |
The incidence of adverse reactions in controlled clinical trials was not affected by gender or age of the patients. There were insufficient data to assess the impact of race on the incidence of adverse reactions.
6.2 Post-marketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of sumatriptan tablets, sumatriptan nasal spray, and sumatriptan injection. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Cardiovascular:
Hypotension, palpitations.
Neurological:
Dystonia, tremor.
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 Ergot-Containing Drugs
Ergot-containing drugs have been reported to cause prolonged vasospastic reactions. Because these effects may be additive, use of ergotamine-containing or ergot-type medications (like dihydroergotamine or methysergide) and TOSYMRA within 24 hours of each other is contraindicated.
7.2 Monoamine Oxidase-A Inhibitors
MAO-A inhibitors increase systemic exposure by 2-fold. Therefore, the use of TOSYMRA in patients receiving MAO-A inhibitors is contraindicated [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of TOSYMRA in pediatric patients have not been established. TOSYMRA is not recommended for use in patients younger than 18 years of age.
Two controlled clinical trials evaluated sumatriptan nasal spray (5 mg to 20 mg) in 1,248 pediatric migraineurs 12 to 17 years of age who treated a single attack. The trials did not establish the efficacy of sumatriptan nasal spray compared with placebo in the treatment of migraine in pediatric patients. Adverse reactions observed in these clinical trials were similar in nature to those reported in clinical trials in adults.
Five controlled clinical trials (2 single-attack trials, 3 multiple-attack trials) evaluating oral sumatriptan (25 mg to 100 mg) in pediatric subjects 12 to 17 years of age enrolled a total of 701 pediatric migraineurs. These trials did not establish the efficacy of oral sumatriptan compared with placebo in the treatment of migraine in pediatric patients. Adverse reactions observed in these clinical trials were similar in nature to those reported in clinical trials in adults. The frequency of all adverse reactions in these patients appeared to be both dose- and age-dependent, with younger patients reporting reactions more commonly than older pediatric patients.
Post-marketing experience documents that serious adverse reactions have occurred in the pediatric population after use of subcutaneous, oral, and/or intranasal sumatriptan. These reports include reactions similar in nature to those reported rarely in adults, including stroke, visual loss, and death. A myocardial infarction has been reported in a 14-year-old male following the use of oral sumatriptan; clinical signs occurred within 1 day of drug administration. Clinical data to determine the frequency of serious adverse reactions in pediatric patients who might receive subcutaneous, oral, or intranasal sumatriptan are not presently available.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical trials of sumatriptan did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger patients. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger subjects. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
A cardiovascular evaluation is recommended for geriatric patients who have other cardiovascular risk factors (e.g., diabetes, hypertension, smoking, obesity, strong family history of CAD) prior to receiving TOSYMRA [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
10. Overdosage
Coronary vasospasm was observed after intravenous administration of sumatriptan injection [see Contraindications (4)]. Overdoses would be expected from animal data (dogs at 0.1 g/kg, rats at 2 g/kg) to possibly cause convulsions, tremor, inactivity, erythema of the extremities, reduced respiratory rate, cyanosis, ataxia, mydriasis, injection site reactions (desquamation, hair loss, and scab formation), and paralysis.
The elimination half-life of sumatriptan is about 2 hours [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)], and therefore monitoring of patients after overdose with TOSYMRA should continue for at least 10 hours or while symptoms or signs persist.
It is unknown what effect hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis has on the serum concentrations of sumatriptan.
11. Tosymra Description
TOSYMRA contains sumatriptan, a selective 5-HT1B/1D receptor agonist. Sumatriptan is chemically designated as 1-[3-[2-(dimethylamino)ethyl]-1H-indol-5-yl]-N-methylmethanesulfonamide, and it has the following structure:
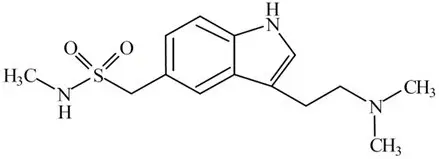
The empirical formula is C14H21N3O2S, representing a molecular weight of 295.40. Sumatriptan is a white to pale yellow powder that is very slightly soluble in water.
TOSYMRA nasal spray is a clear, pale yellow to yellow colored liquid. Each 100 uL of TOSYMRA contains 10 mg of sumatriptan in single-dose aqueous buffered solution containing citric acid monohydrate, n-Dodecyl beta-D-maltoside, potassium phosphate monobasic, sodium chloride, and sodium phosphate dibasic anhydrous in water for injection.
The pH range of solution is approximately 5.0 to 6.0 and the osmolality is between 270 to 330 mOsmol.
12. Tosymra - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Sumatriptan binds with high affinity to human cloned 5-HT1B/1D receptors. Sumatriptan presumably exerts its therapeutic effects in the treatment of migraine headache through agonist effects at the 5-HT1B/1D receptors on intracranial blood vessels and sensory nerves of the trigeminal system, which result in cranial vessel constriction and inhibition of pro-inflammatory neuropeptide release.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Following nasal administration of 10 mg TOSYMRA in 73 healthy subjects, the relative bioavailability of TOSYMRA was approximately 87% [90% confidence interval (CI) 82 to 94] of that obtained following 4 mg subcutaneous injection of sumatriptan. The relative bioavailability of TOSYMRA was 58% [90% CI 55 to 62] following 6 mg subcutaneous injection of sumatriptan.
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
14. Clinical Studies
The efficacy of TOSYMRA is based on the relative bioavailability of TOSYMRA nasal spray compared to sumatriptan subcutaneous injection (4 mg) in healthy adults [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
In controlled clinical trials enrolling more than 1,000 patients during migraine attacks who were experiencing moderate or severe pain and 1 or more of the symptoms enumerated in Table 3, onset of relief began as early as 10 minutes following a 6 mg sumatriptan injection. Lower doses of sumatriptan injection may also prove effective, although the proportion of patients obtaining adequate relief was decreased and the latency to that relief is greater with lower doses.
In Study 1, 6 different doses of sumatriptan injection (n = 30 each group) were compared with placebo (n = 62) in a single-attack, parallel-group design; the dose-response relationship was found to be as shown in Table 2.
| Dose of sumatriptan Injection | Percent Patients with Relief* | Adverse Reactions Incidence (%) |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| at 10 Minutes | at 30 Minutes | at 1 Hour | at 2 Hours | ||
|
|||||
| Placebo | 5 | 15 | 24 | 21 | 55 |
| 1 mg | 10 | 40 | 43 | 40 | 63 |
| 2 mg | 7 | 23 | 57 | 43 | 63 |
| 3 mg | 17 | 47 | 57 | 60 | 77 |
| 4 mg† | 13 | 37 | 50 | 57 | 80 |
| 6 mg | 10 | 63 | 73 | 70 | 83 |
| 8 mg | 23 | 57 | 80 | 83 | 93 |
In 2 randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trials of sumatriptan injection 6 mg in 1,104 patients with moderate or severe migraine pain (Studies 2 and 3), the onset of relief was less than 10 minutes. Headache relief, as defined by a reduction in pain from severe or moderately severe to mild or no headache, was achieved in 70% of the patients within 1 hour of a single 6 mg subcutaneous dose of sumatriptan injection. Approximately 82% and 65% of patients treated with sumatriptan 6 mg had headache relief and were pain free within 2 hours, respectively.
Table 3 shows the 1- and 2-hour efficacy results for sumatriptan injection 6 mg in Studies 2 and 3.
|
||||
| 1-Hour Data | Study 2 | Study 3 | ||
| Placebo (n = 190) | Sumatriptan Injection 6 mg (n = 384) | Placebo (n = 180) | Sumatriptan Injection 6 mg (n = 350) |
|
| Patients with pain relief (Grade 0/1) | 18% | 70%* | 26% | 70%* |
| Patients with no pain | 5% | 48%* | 13% | 49%* |
| Patients without nausea | 48% | 73%* | 50% | 73%* |
| Patients without photophobia | 23% | 56%* | 25% | 58%* |
| Patients with little or no clinical disability† | 34% | 76%* | 34% | 76%* |
| 2-Hour Data | Study 2 | Study 3 | ||
| Placebo‡ | Sumatriptan Injection 6 mg§ | Placebo‡ | Sumatriptan Injection 6 mg§ |
|
| Patients with pain relief (Grade 0/1) | 31% | 81%* | 39% | 82%* |
| Patients with no pain | 11% | 63%* | 19% | 65%* |
| Patients without nausea | 56% | 82%* | 63% | 81%* |
| Patients without photophobia | 31% | 72%* | 35% | 71%* |
| Patients with little or no clinical disability† | 42% | 85%* | 49% | 84%* |
Sumatriptan injection also relieved photophobia, phonophobia (sound sensitivity), nausea, and vomiting associated with migraine attacks.
The efficacy of sumatriptan injection was unaffected by whether or not the migraine was associated with aura, duration of attack, gender or age of the patient, or concomitant use of common migraine prophylactic drugs (e.g., beta-blockers).
16. How is Tosymra supplied
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information and Instructions for Use).
| This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. | Revised: 2/2021 | ||
| Patient Information TOSYMRA® (toe-SIM-ruh) (sumatriptan) Nasal Spray |
|||
| What is the most important information I should know about TOSYMRA? TOSYMRA can cause serious side effects, including: Heart attack and other heart problems. Heart problems may lead to death. Stop taking TOSYMRA and get emergency medical help right away if you have any of the following symptoms of a heart attack:
|
|||
| What is TOSYMRA?
TOSYMRA is a prescription medicine used to treat acute migraine headaches with or without aura in adults. TOSYMRA is not used to treat other types of headaches such as hemiplegic (that make you unable to move on one side of your body) or basilar (rare form of migraine with aura) migraines. TOSYMRA is not used to prevent or decrease the number of migraines you have. TOSYMRA is not used to treat cluster headaches. It is not known if TOSYMRA is safe and effective in children under 18 years of age. |
|||
Do not take TOSYMRA if you have:
|
|||
Before taking TOSYMRA, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
TOSYMRA and certain other medicines can affect each other, causing serious side effects. Especially tell your healthcare provider if you take anti-depressant medicines called:
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them to show your healthcare provider or pharmacist when you get a new medicine. |
|||
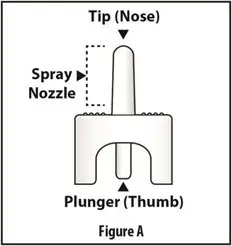
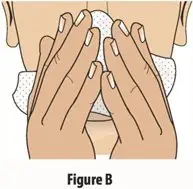
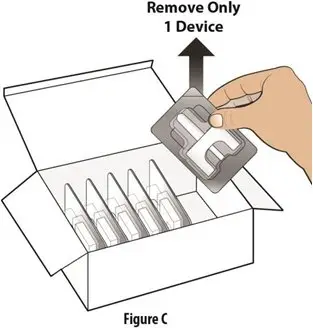
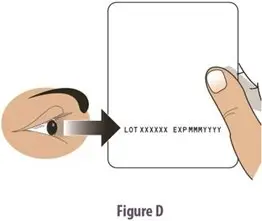
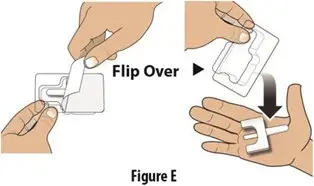
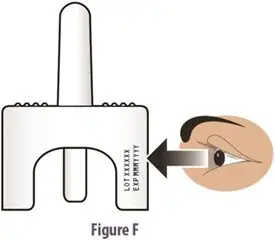
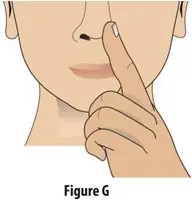
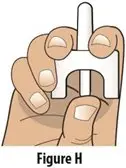
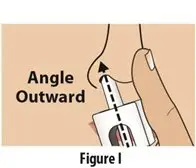
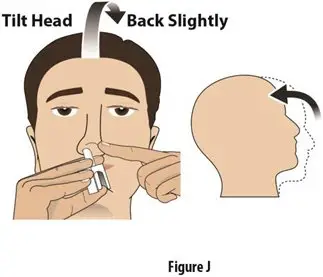
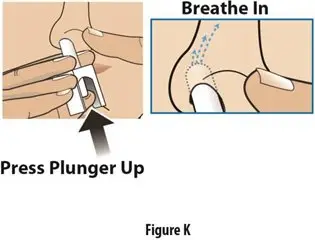
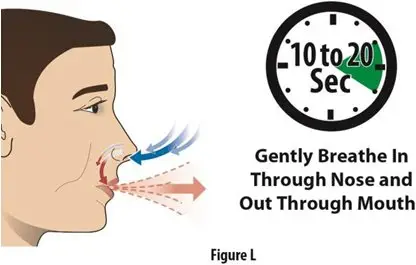
How should I take TOSYMRA?
|
|||
| What should I avoid while taking TOSYMRA?
TOSYMRA can cause dizziness, weakness, or drowsiness. If you have these symptoms, do not drive a car, use machinery, or do anything where you need to be alert. |
|||
| What are the possible side effects of TOSYMRA? TOSYMRA may cause serious side effects. See "What is the most important information I should know about TOSYMRA?" These serious side effects include:
|
|||
|
|
|
|
| Tell your healthcare provider if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away. These are not all the possible side effects of TOSYMRA. For more information, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. |
|||
How should I store TOSYMRA?
|
|||
| General information about the safe and effective use of TOSYMRA.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in Patient Information leaflets. Do not use TOSYMRA for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give TOSYMRA to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them. You can ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for information about TOSYMRA that is written for healthcare professionals. For more information, go to www.upsher-smith.com or call 1-888-650-3789. |
|||
| What are the ingredients in TOSYMRA?
Active ingredient: sumatriptan Inactive ingredients: citric acid monohydrate, n-Dodecyl beta-D-maltoside, potassium phosphate monobasic, sodium chloride, and sodium phosphate dibasic anhydrous in water for injection. Manufactured for UPSHER-SMITH LABORATORIES, LLC Maple Grove, MN 55369 TOSYMRA is a registered trademark of Upsher-Smith Laboratories, LLC. This product may be covered by one or more U.S. patent(s). See www.uslpatents.com. |
|||
| TOSYMRA
sumatriptan spray |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Upsher-Smith Laboratories, LLC (079111820) |