Drug Detail:Tradjenta (Linagliptin [ lin-a-glip-tin ])
Drug Class: Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors
Highlights of Prescribing Information
TRADJENTA® (linagliptin tablets), for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2011
Indications and Usage for Tradjenta
TRADJENTA is a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor indicated as an adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus (1)
Limitations of Use
- Not recommended in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus as it would not be effective (1)
- Has not been studied in patients with a history of pancreatitis (1)
Tradjenta Dosage and Administration
- The recommended dosage of TRADJENTA is 5 mg orally once daily (2.1)
- TRADJENTA can be taken with or without food (2.1)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Tablets: 5 mg (3)
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to linagliptin or any of the excipients in TRADJENTA (4, 5.3)
Warnings and Precautions
- Pancreatitis: There have been reports of acute pancreatitis, including fatal pancreatitis. If pancreatitis is suspected, promptly discontinue TRADJENTA. (5.1)
- Hypoglycemia: Consider lowering the dosage of insulin secretagogue or insulin to reduce the risk of hypoglycemia when initiating TRADJENTA (5.2)
- Hypersensitivity reactions: Serious hypersensitivity reactions (e.g., anaphylaxis, angioedema, and exfoliative skin conditions) have occurred with TRADJENTA. If hypersensitivity reactions occur, discontinue TRADJENTA, treat promptly, and monitor until signs and symptoms resolve. (5.3)
- Arthralgia: Severe and disabling arthralgia has been reported in patients taking TRADJENTA. Consider as a possible cause for severe joint pain and discontinue drug if appropriate. (5.4)
- Bullous pemphigoid: There have been reports of bullous pemphigoid requiring hospitalization. Tell patients to report development of blisters or erosions. If bullous pemphigoid is suspected, discontinue TRADJENTA. (5.5)
- Heart failure: Heart failure has been observed with two other members of the DPP-4 inhibitor class. Consider risks and benefits of TRADJENTA in patients who have known risk factors for heart failure. Monitor for signs and symptoms. (5.6)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reaction (incidence ≥5% and more often than placebo) was nasopharyngitis (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc. at 1-800-542-6257, or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
Strong P-glycoprotein/CYP3A4 inducer: The efficacy of TRADJENTA may be reduced when administered in combination (e.g., with rifampin). Use of alternative treatments is strongly recommended. (7.1)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 6/2023
Related/similar drugs
metformin, Trulicity, Lantus, Victoza, Levemir, TresibaFull Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Tradjenta
TRADJENTA is indicated as an adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
Tablets: 5 mg, light red, round, biconvex, bevel-edged, film-coated tablets with "D5" debossed on one side and the Boehringer Ingelheim symbol debossed on the other side.
4. Contraindications
TRADJENTA is contraindicated in patients with hypersensitivity to linagliptin or any of the excipients in TRADJENTA, reactions such as anaphylaxis, angioedema, exfoliative skin conditions, urticaria, or bronchial hyperreactivity have occurred [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) and Adverse Reactions (6)].
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Pancreatitis
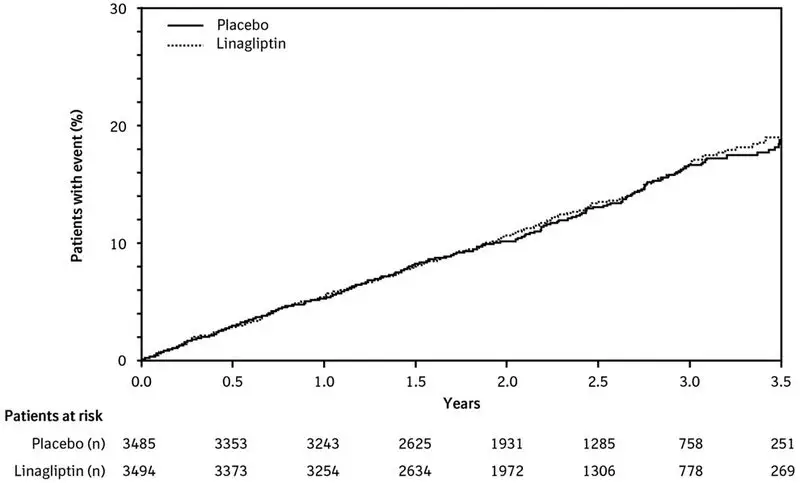
Acute pancreatitis, including fatal pancreatitis, has been reported in patients treated with TRADJENTA. In the CARMELINA trial [see Clinical Studies (14.2)], acute pancreatitis was reported in 9 (0.3%) patients treated with TRADJENTA and in 5 (0.1%) patients treated with placebo. Two patients treated with TRADJENTA in the CARMELINA trial had acute pancreatitis with a fatal outcome. There have been postmarketing reports of acute pancreatitis, including fatal pancreatitis, in patients treated with TRADJENTA.
Take careful notice of potential signs and symptoms of pancreatitis. If pancreatitis is suspected, promptly discontinue TRADJENTA and initiate appropriate management. It is unknown whether patients with a history of pancreatitis are at increased risk for the development of pancreatitis while using TRADJENTA.
5.2 Hypoglycemia with Concomitant Use with Insulin and Insulin Secretagogues
Insulin secretagogues and insulin are known to cause hypoglycemia. The risk of hypoglycemia is increased when TRADJENTA is used in combination with an insulin secretagogue (e.g., sulfonylurea) or insulin [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. The use of TRADJENTA in combination with insulin in subjects with severe renal impairment was associated with a higher rate of hypoglycemia [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Therefore, a lower dosage of the insulin secretagogue or insulin may be required to reduce the risk of hypoglycemia when used in combination with TRADJENTA.
5.3 Hypersensitivity Reactions
There have been postmarketing reports of serious hypersensitivity reactions in patients treated with TRADJENTA. These reactions include anaphylaxis, angioedema, and exfoliative skin conditions. Onset of these reactions occurred predominantly within the first 3 months after initiation of treatment with TRADJENTA, with some reports occurring after the first dose. If a serious hypersensitivity reaction is suspected, discontinue TRADJENTA, assess for other potential causes for the event, and institute alternative treatment for diabetes mellitus.
Angioedema has also been reported with other dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors. Use caution in a patient with a history of angioedema to another DPP-4 inhibitor because it is unknown whether such patients will be predisposed to angioedema with TRADJENTA.
5.4 Severe and Disabling Arthralgia
There have been postmarketing reports of severe and disabling arthralgia in patients taking TRADJENTA [see Adverse Reactions (6)]. The time to onset of symptoms following initiation of drug therapy varied from one day to years. Patients experienced relief of symptoms upon discontinuation of the medication. A subset of patients experienced a recurrence of symptoms when restarting the same drug or a different DPP-4 inhibitor. Consider the drug as a possible cause for severe joint pain and discontinue drug if appropriate.
5.5 Bullous Pemphigoid
Bullous pemphigoid was reported in 7 (0.2%) patients treated with TRADJENTA compared to none in patients treated with placebo in the CARMELINA trial [see Clinical Studies (14.2)], and 3 of these patients were hospitalized due to bullous pemphigoid. Postmarketing cases of bullous pemphigoid requiring hospitalization have been reported with DPP-4 inhibitor use. In reported cases, patients typically recovered with topical or systemic immunosuppressive treatment and discontinuation of the DPP-4 inhibitor. Tell patients to report development of blisters or erosions while receiving TRADJENTA. If bullous pemphigoid is suspected, TRADJENTA should be discontinued and referral to a dermatologist should be considered for diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
5.6 Heart Failure
An association between DPP-4 inhibitor treatment and heart failure has been observed in cardiovascular outcomes trials for two other members of the DPP-4 inhibitor class. These trials evaluated patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease.
Consider the risks and benefits of TRADJENTA prior to initiating treatment in patients at risk for heart failure, such as those with a prior history of heart failure and a history of renal impairment, and observe these patients for signs and symptoms of heart failure during therapy. Advise patients of the characteristic symptoms of heart failure and to immediately report such symptoms. If heart failure develops, evaluate and manage according to current standards of care and consider discontinuation of TRADJENTA.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following serious adverse reactions are described below or elsewhere in the prescribing information:
- Pancreatitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Hypoglycemia with Concomitant Use with Insulin and Insulin Secretagogues [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Hypersensitivity Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Severe and Disabling Arthralgia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Bullous Pemphigoid [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Heart Failure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The safety evaluation of TRADJENTA 5 mg once daily in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus is based on 14 placebo-controlled trials, 1 active-controlled trial, and one trial in patients with severe renal impairment. In the 14 placebo-controlled studies, a total of 3,625 patients were randomized and treated with TRADJENTA 5 mg daily and 2,176 with placebo. The mean exposure in patients treated with TRADJENTA across studies was 29.6 weeks. The maximum follow-up was 78 weeks.
TRADJENTA 5 mg once daily was studied as monotherapy in three placebo-controlled trials of 18 and 24 weeks' duration and in five additional placebo-controlled studies lasting ≤18 weeks. The use of TRADJENTA in combination with other antihyperglycemic agents was studied in six placebo-controlled trials: two with metformin (12 and 24 weeks' treatment duration); one with a sulfonylurea (18 weeks' treatment duration); one with metformin and sulfonylurea (24 weeks' treatment duration); one with pioglitazone (24 weeks' treatment duration); and one with insulin (primary endpoint at 24 weeks).
In a pooled dataset of 14 placebo-controlled clinical trials, adverse reactions that occurred in ≥2% of patients receiving TRADJENTA (n = 3,625) and more commonly than in patients given placebo (n = 2,176), are shown in Table 1.
| Adverse Reactions | TRADJENTA 5 mg (%) n = 3,625 | Placebo (%) n = 2,176 |
|---|---|---|
| Nasopharyngitis | 7.0 | 6.1 |
| Diarrhea | 3.3 | 3.0 |
| Cough | 2.1 | 1.4 |
Rates for other adverse reactions for TRADJENTA 5 mg vs placebo when TRADJENTA was used in combination with specific antidiabetic agents were: urinary tract infection (3.1% vs 0%) and hypertriglyceridemia (2.4% vs 0%) when TRADJENTA was used as add-on to sulfonylurea; hyperlipidemia (2.7% vs 0.8%) and weight increased (2.3% vs 0.8%) when TRADJENTA was used as add-on to pioglitazone; and constipation (2.1% vs 1%) when TRADJENTA was used as add-on to basal insulin therapy. Other adverse reactions reported in clinical studies with treatment of TRADJENTA were hypersensitivity (e.g., urticaria, angioedema, localized skin exfoliation, or bronchial hyperreactivity) and myalgia.
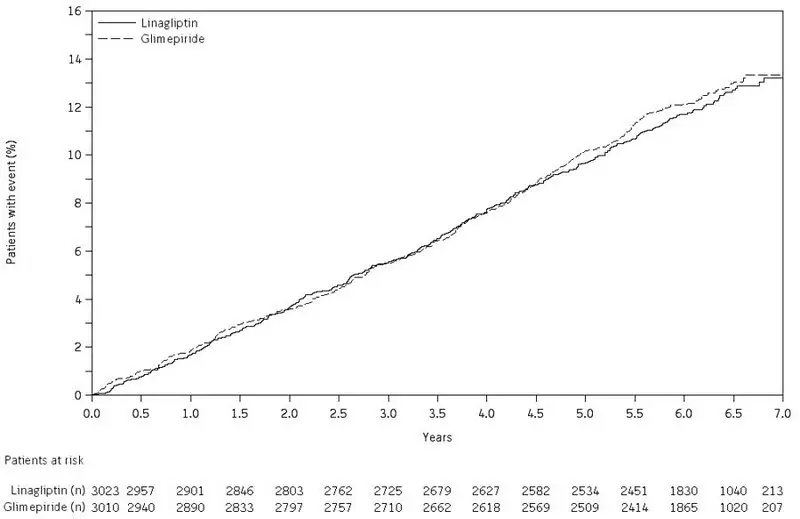
Following 104 weeks' treatment in a controlled trial comparing TRADJENTA with glimepiride in which all patients were also receiving metformin, adverse reactions reported in ≥5% of patients treated with TRADJENTA (n = 776) and more frequently than in patients treated with a sulfonylurea (n = 775) were back pain (9.1% vs 8.4%), arthralgia (8.1% vs 6.1%), upper respiratory tract infection (8.0% vs 7.6%), headache (6.4% vs 5.2%), cough (6.1% vs 4.9%), and pain in extremity (5.3% vs 3.9%).
In the clinical trial program, pancreatitis was reported in 15.2 cases per 10,000 patient year exposure while being treated with TRADJENTA compared with 3.7 cases per 10,000 patient year exposure while being treated with comparator (placebo and active comparator, sulfonylurea). Three additional cases of pancreatitis were reported following the last administered dose of linagliptin.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
Additional adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval use of TRADJENTA. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is generally not possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
- Gastrointestinal Disorders: Acute pancreatitis, including fatal pancreatitis [see Indications and Usage (1)], mouth ulceration, stomatitis
- Immune System Disorders: Hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylaxis, angioedema, and exfoliative skin conditions
- Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders: Rhabdomyolysis, severe and disabling arthralgia
- Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders: Bullous pemphigoid, rash
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 Inducers of P-glycoprotein or CYP3A4 Enzymes
Rifampin decreased linagliptin exposure, suggesting that the efficacy of TRADJENTA may be reduced when administered in combination with a strong P-gp or CYP3A4 inducer. Therefore, use of alternative treatments is strongly recommended when linagliptin is to be administered with a strong P-gp or CYP3A4 inducer [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
7.2 Insulin Secretagogues or Insulin
Insulin and insulin secretagogues are known to cause hypoglycemia. The risk of hypoglycemia is increased when linagliptin is used in combination with an insulin secretagogue (e.g., sulfonylurea) or insulin. Coadministration of TRADJENTA with an insulin secretagogue (e.g., sulfonylurea) or insulin may require lower dosages of the insulin secretagogue or insulin to reduce the risk of hypoglycemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of TRADJENTA have not been established in pediatric patients.
Effectiveness of TRADJENTA was not demonstrated in a 26-week randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial (NCT03429543) in 157 pediatric patients aged 10 to 17 years with inadequately controlled type 2 diabetes mellitus.
8.5 Geriatric Use
In linagliptin studies, 1,085 linagliptin-treated patients were 65 years of age and older and 131 patients were 75 years of age and older. In these linagliptin studies, no overall differences in safety or effectiveness of linagliptin were observed between geriatric patients and younger adult patients.
8.6 Renal Impairment
No dosage adjustment is recommended for patients with renal impairment [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
In the TRADJENTA treatment arm of the CARMELINA trial [see Clinical Studies (14)], 2,200 (63%) patients had renal impairment (eGFR <60 mL/min/1.73 m2). Approximately 20% of the population had eGFR ≥45 to <60 mL/min/1.73 m2, 28% of the population had eGFR ≥30 to <45 mL/min/1.73 m2 and 15% had eGFR <30 mL/min/1.73 m2. The overall incidence of adverse reactions were generally similar between the TRADJENTA and placebo treatment arms.
10. Overdosage
In the event of an overdose with TRADJENTA, consider contacting the Poison Help Line (1-800-222-1222) or a medical toxicologist for additional overdosage management recommendations. Removal of linagliptin by hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis is unlikely.
11. Tradjenta Description
TRADJENTA tablets for oral use contain linagliptin, an inhibitor of the DPP-4 enzyme.
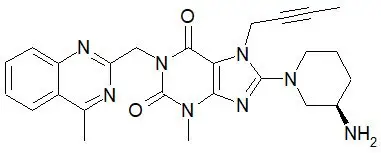
The chemical name of linagliptin is 1H-Purine-2,6-dione, 8-[(3R)-3-amino-1-piperidinyl]-7-(2-butyn-1-yl)-3,7-dihydro-3-methyl-1-[(4-methyl-2-quinazolinyl)methyl]-
The molecular formula is C25H28N8O2 and the molecular weight is 472.54 g/mol. The structural formula is:
Linagliptin is a white to yellowish, not or only slightly hygroscopic solid substance. It is very slightly soluble in water (0.9 mg/mL). Linagliptin is soluble in methanol (ca. 60 mg/mL), sparingly soluble in ethanol (ca. 10 mg/mL), very slightly soluble in isopropanol (<1 mg/mL), and very slightly soluble in acetone (ca. 1 mg/mL).
Each film-coated tablet of TRADJENTA contains 5 mg of linagliptin free base and the following inactive ingredients: copovidone, corn starch, magnesium stearate, mannitol, and pregelatinized starch. In addition, the film coating contains the following inactive ingredients: hypromellose, polyethylene glycol, red ferric oxide, talc, and titanium dioxide.
12. Tradjenta - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Linagliptin is an inhibitor of DPP-4, an enzyme that degrades the incretin hormones glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP). Thus, linagliptin increases the concentrations of active incretin hormones, stimulating the release of insulin in a glucose-dependent manner and decreasing the levels of glucagon in the circulation. Both incretin hormones are involved in the physiological regulation of glucose homeostasis. Incretin hormones are secreted at a low basal level throughout the day and levels rise immediately after meal intake. GLP-1 and GIP increase insulin biosynthesis and secretion from pancreatic beta cells in the presence of normal and elevated blood glucose levels. Furthermore, GLP-1 also reduces glucagon secretion from pancreatic alpha-cells, resulting in a reduction in hepatic glucose output.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Linagliptin binds to DPP-4 in a reversible manner and thus increases the concentrations of incretin hormones. Linagliptin glucose-dependently increases insulin secretion and lowers glucagon secretion, thus resulting in better regulation of glucose homeostasis. Linagliptin binds selectively to DPP-4 and selectively inhibits DPP-4, but not DPP-8 or DPP-9 activity in vitro at concentrations approximating therapeutic exposures.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics of linagliptin has been characterized in healthy subjects and patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. After oral administration of a single 5 mg dose to healthy subjects, peak plasma concentrations of linagliptin occurred at approximately 1.5 hours post dose (Tmax); the mean plasma area under the curve (AUC) was 139 nmol*h/L and maximum concentration (Cmax) was 8.9 nmol/L.
Plasma concentrations of linagliptin decline in at least a biphasic manner with a long terminal half-life (>100 hours), related to the saturable binding of linagliptin to DPP-4. The prolonged elimination phase does not contribute to the accumulation of the drug. The effective half-life for accumulation of linagliptin, as determined from oral administration of multiple doses of linagliptin 5 mg, is approximately 12 hours. After once-daily dosing, steady-state plasma concentrations of linagliptin 5 mg are reached by the third dose, and Cmax and AUC increased by a factor of 1.3 at steady-state compared with the first dose. The intra-subject and inter-subject coefficients of variation for linagliptin AUC were small (12.6% and 28.5%, respectively). Plasma AUC of linagliptin increased in a less than dose-proportional manner in the dose range of 1 to 10 mg. The pharmacokinetics of linagliptin is similar in healthy subjects and in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Linagliptin did not increase the incidence of tumors in male and female rats in a 2-year study at doses of 6, 18, and 60 mg/kg. The highest dose of 60 mg/kg is approximately 418 times the clinical dose of 5 mg/day based on AUC exposure. Linagliptin did not increase the incidence of tumors in mice in a 2-year study at doses up to 80 mg/kg (males) and 25 mg/kg (females), or approximately 35- and 270-times the clinical dose based on AUC exposure. Higher doses of linagliptin in female mice (80 mg/kg) increased the incidence of lymphoma at approximately 215-times the clinical dose based on AUC exposure.
Linagliptin was not mutagenic or clastogenic with or without metabolic activation in the Ames bacterial mutagenicity assay, a chromosomal aberration test in human lymphocytes, and an in vivo micronucleus assay.
In fertility studies in rats, linagliptin had no adverse effects on early embryonic development, mating, fertility, or bearing live young up to the highest dose of 240 mg/kg (approximately 943-times the clinical dose based on AUC exposure).
14. Clinical Studies
14.1 Glycemic Control Trials in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
TRADJENTA has been studied as monotherapy and in combination with metformin, sulfonylurea, pioglitazone, and insulin. TRADJENTA has also been studied in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and severe chronic renal impairment.
In patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, treatment with TRADJENTA produced clinically significant improvements in hemoglobin A1c (A1C), fasting plasma glucose (FPG), and 2-hour post-prandial glucose (PPG) compared with placebo.
16. How is Tradjenta supplied
TRADJENTA tablets are available as light red, round, biconvex, bevel-edged, film-coated tablets containing 5 mg of linagliptin. TRADJENTA tablets are debossed with "D5" on one side and the Boehringer Ingelheim symbol on the other side.
They are supplied as follows:
Bottles of 30 (NDC 0597-0140-30)
Bottles of 90 (NDC 0597-0140-90)
Cartons containing 10 blister cards of 10 tablets each (10 × 10) (NDC 0597-0140-61), institutional pack.
If repackaging is required, dispense in a tight container as defined in USP.
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide).
| This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. | Revised: June 2023 | ||||
| MEDICATION GUIDE TRADJENTA® (TRAD gen ta) (linagliptin tablets) for oral use |
|||||
| What is the most important information I should know about TRADJENTA? TRADJENTA can cause serious side effects, including:
|
|||||
|
|
||||
| Stop taking TRADJENTA and call your healthcare provider right away if you have pain in your stomach area (abdomen) that is severe and will not go away. The pain may be felt going from your abdomen to your back. The pain may happen with or without vomiting. These may be symptoms of pancreatitis. | |||||
What is TRADJENTA?
|
|||||
| Who should not take TRADJENTA? Do not take TRADJENTA if you:
|
|||||
| What should I tell my healthcare provider before taking TRADJENTA? Before taking TRADJENTA, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
TRADJENTA may affect the way other medicines work, and other medicines may affect how TRADJENTA works. Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them to show your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medicine. |
|||||
How should I take TRADJENTA?
|
|||||
| What are the possible side effects of TRADJENTA? TRADJENTA may cause serious side effects, including:
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
||||
These are not all the possible side effects of TRADJENTA. For more information, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. |
|||||
How should I store TRADJENTA?
|
|||||
| General information about the safe and effective use of TRADJENTA.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use TRADJENTA for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give TRADJENTA to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about TRADJENTA that is written for health professionals. |
|||||
| What are the ingredients in TRADJENTA?
Active Ingredient: linagliptin Inactive Ingredients: copovidone, corn starch, magnesium stearate, mannitol, and pregelatinized starch. The film coating contains the following inactive ingredients: hypromellose, polyethylene glycol, red ferric oxide, talc, and titanium dioxide. |
|||||
| Distributed by: Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Ridgefield, CT 06877 USA. Licensed from: Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH, Ingelheim, Germany. TRADJENTA is a registered trademark of and used under license from Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH. Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc. either owns or uses the CARMELINA® and CAROLINA® trademarks under license. The other brands listed are trademarks of their respective owners and are not trademarks of Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Copyright © 2023 Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED COL10194BF212023 For more information about TRADJENTA, including current prescribing information and Medication Guide, go to www.TRADJENTA.com, scan the code, or call Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc. at 1-800-542-6257.
|
|||||
| TRADJENTA
linagliptin tablet, film coated |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (603175944) |
| Registrant - Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (603175944) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Boehringer Ingelheim Pharma GmbH and Co. KG | 551147440 | API MANUFACTURE(0597-0140) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| West-Ward Columbus Inc. | 058839929 | LABEL(0597-0140) , MANUFACTURE(0597-0140) , PACK(0597-0140) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Boehringer Ingelheim Promeco, S.A. de C.V. | 812579472 | LABEL(0597-0140) , MANUFACTURE(0597-0140) , PACK(0597-0140) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sixarp, LLC | 016329513 | LABEL(0597-0140) , PACK(0597-0140) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bidachem S.p.a. | 429232812 | API MANUFACTURE(0597-0140) | |