Drug Detail:Tretten (Coagulation factor xiii a-subunit (recombinant))
Drug Class: Miscellaneous coagulation modifiers
Highlights of Prescribing Information
TRETTEN, Coagulation Factor XIII A-Subunit (Recombinant)
For Intravenous Use. Lyophilized Powder for Solution for Injection
Initial U.S. Approval: 2013
Indications and Usage for Tretten
TRETTEN, Coagulation Factor XIII A-Subunit (Recombinant), is indicated for routine prophylaxis of bleeding in patients with congenital factor XIII A-subunit deficiency. (1)
TRETTEN is not for use in patients with congenital factor XIII B‑subunit deficiency. (1)
Tretten Dosage and Administration
For intravenous use only.
Dose:
- •
- 35 international units per kilogram body weight once monthly to achieve a target trough level of FXIII activity at or above 10% using a validated assay. (2.1)
- •
- Consider dose adjustment if adequate coverage is not achieved with a 35 IU/kg dose. (2.1)
- •
- Once reconstituted, TRETTEN may be diluted with 0.9% sodium chloride to facilitate measurement of small volumes. (2.2)
Rate: Do not exceed 1-2 mL per minute. (2.3)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
- •
- Lyophilized powder in single-dose vial containing 2000 - 3125 IU of recombinant coagulation factor XIII A-subunit.
- •
- After reconstitution with 3.2 mL of sterile water for injection, each vial contains 667-1042 IU/mL of recombinant coagulation factor XIII A-subunit.
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients. (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- •
- Discontinue if allergic or hypersensitivity reactions occur. (5.1)
- •
- Monitor patients for thrombosis. (5.2)
- •
- Analyze for neutralizing antibodies if FXIII activity fails to reach expected levels or if reduced therapeutic effect is observed. (5.3)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The most common adverse reactions reported in the clinical trials (≥1%) were headache, pain in the extremities, injection site pain, D dimer increase. (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Novo Nordisk Inc. at 1-844-873-8836 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch
Drug Interactions
- Do not administer TRETTEN with recombinant factor VIIa. (7)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 6/2020
Related/similar drugs
factor XIIIFull Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Tretten
TRETTEN, Coagulation Factor XIII A-Subunit (Recombinant), is indicated for routine prophylaxis for bleeding in patients with congenital factor XIII A-subunit deficiency.
TRETTEN is not for use in patients with congenital factor XIII B‑subunit deficiency
2. Tretten Dosage and Administration
For intravenous use only.
2.1 Dose
- •
- Treatment should be initiated under the supervision of a physician experienced in the treatment of rare bleeding disorders.
- •
- The dose for routine prophylaxis for bleeding in patients with congenital factor XIII (FXIII) A-subunit deficiency is 35 international units (IU) per kilogram body weight once monthly to achieve a target trough level of FXIII activity at or above 10% using a validated assay.
- •
- Consider dose adjustment if adequate coverage is not achieved with the recommended 35 IU/kg dose.
- A pharmacokinetic study was conducted in the FXIII congenitally deficient population evaluating five dose cohorts (2, 7, 24, 60 and 89 IU/kg) with blood sampling at 0.5, 1, 4, 8, 24, 48, 72 hours, and 7, 14, and 28 days. Samples were tested for FXIII activity by a chromogenic assay and for FXIII A2B2 tetramer levels by an ELISA, as well as for other analytes. It was found that FXIII tetramer levels were proportional to the observed FXIII activity up to the point of replacement of 100% of normal FXIII activity, but there was no increase in FXIII tetramer levels at higher levels of FXIII activity. A dose of 35 IU/kg is sufficient to replace 100% of FXIII activity in this population, and higher doses may not increase the levels of tetrameric Factor XIII.
2.2 Reconstitution
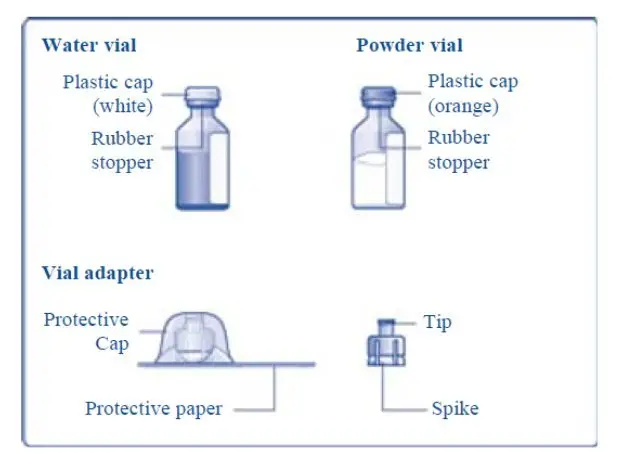
Reconstitute only with sterile water for injection (provided with TRETTEN). The product can be reconstituted using the vial adapter included or a needle.
Reconstitute using the following procedures:
- 1. Use aseptic technique.
- 2. Wash hands before starting.
- 3. Bring TRETTEN (white lyophilized powder) and sterile water for injection (diluent) to room temperature, but not above 25°C (77°F).
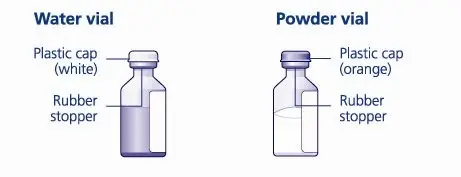
- 4. Remove the plastic caps from the two vials.
- 5. Clean the rubber stoppers on the vials with sterile alcohol swabs and allow them to dry before use.
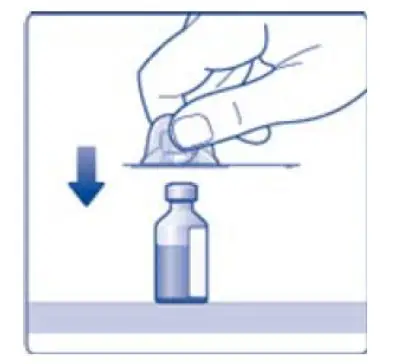
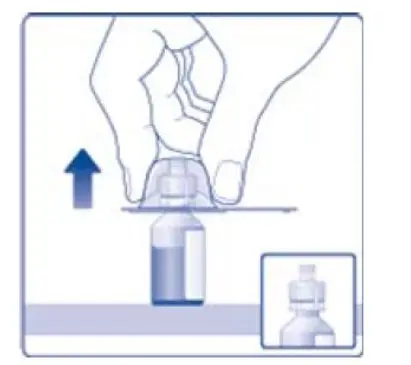
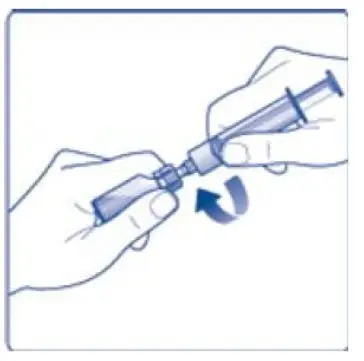
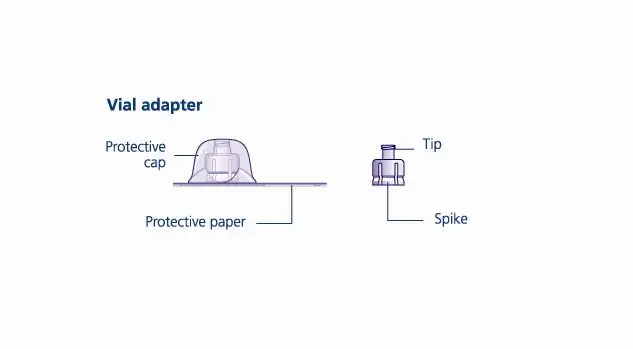
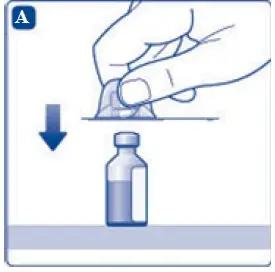
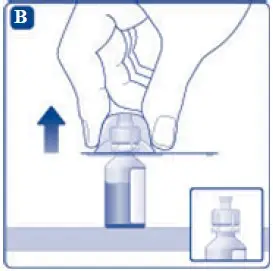
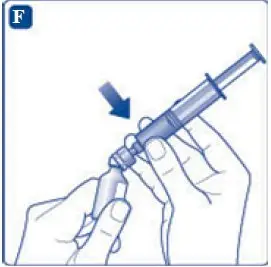
- 6. Remove the protective paper from the vial adapter, but do not unscrew the protective cap. Attach the vial adapter to the diluent vial, without taking the vial adapter out of the protective cap. Once attached, remove the protective cap from the vial adapter by lightly squeezing the protective cap with your thumb and index finger as shown on the figure below.
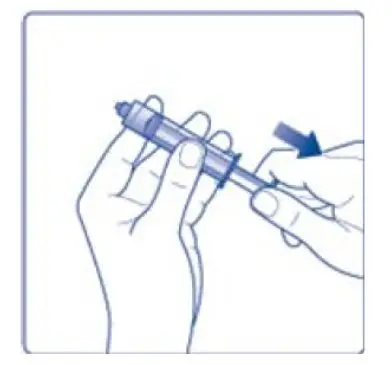
- 7. Draw back the plunger of the sterile syringe and admit a volume of 3.2 mL air into the syringe.
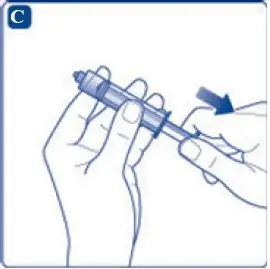
- 8. Screw the syringe onto the vial adapter on the diluent vial.
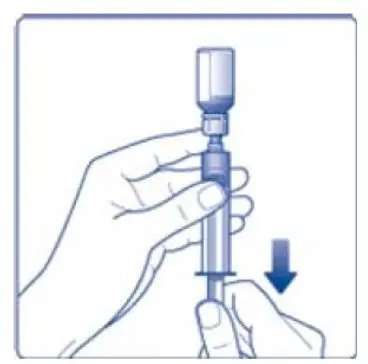
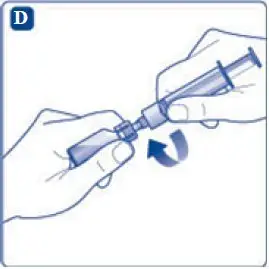
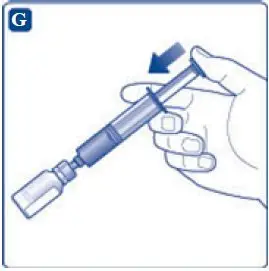
- 9. Inject the air from the syringe into the diluent vial until resistance is felt. Then hold the syringe with the diluent vial upside down and withdraw 3.2 mL water into the syringe.
- 10. Remove the empty diluent vial by tipping the syringe with the attached vial adapter.
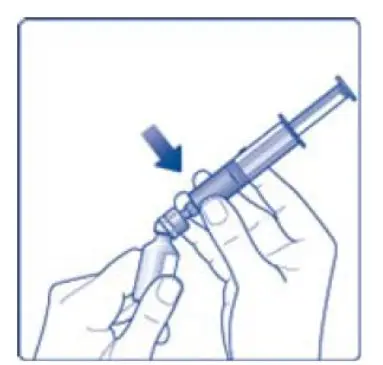
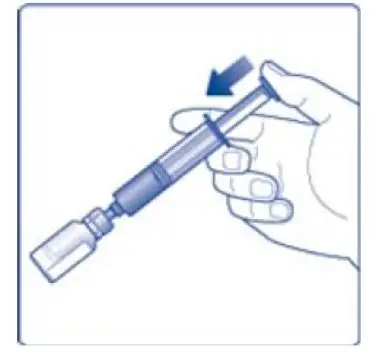
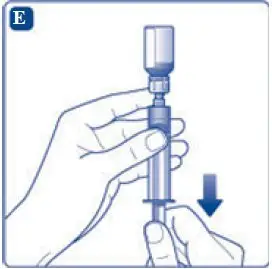
- 11. Attach the syringe with the vial adapter to the powder vial. Hold the syringe slightly tilted with vial facing downwards. Push the plunger slowly to inject all water (3.2 mL) into the powder vial. Do not inject the diluent directly on the TRETTEN powder to avoid foaming.
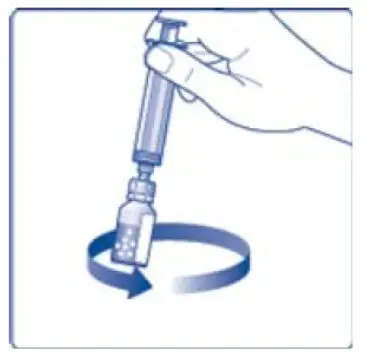
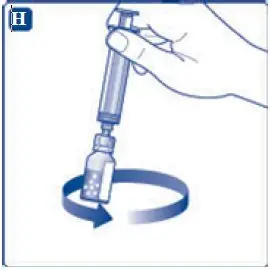
- 12. Gently swirl the vial until all material is dissolved. Do not shake the vial. The reconstituted TRETTEN is a clear and colorless solution. Use the reconstituted TRETTEN immediately. If not, store the solution refrigerated or at room temperature not to exceed 25°C (77°F) for up to three hours. Discard after three hours.
- NOTE:
- •
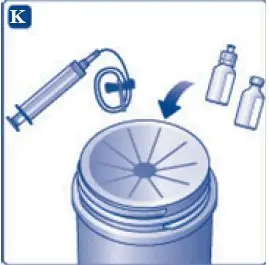
- For larger dose that requires multiple vials of TRETTEN, reconstitute each additional vial using the same procedure with a separate syringe.
- •
- For smaller dose that requires less than the full volume in the vial, reconstituted TRETTEN may be diluted with 0.9% sodium chloride to facilitate measurement of small volumes. Discard remaining product.
- •
- For home administration, any such changes should be communicated by the pharmacist or healthcare provider to the patient or family.
2.3 Administration
- •
- Inspect the reconstituted TRETTEN visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration. Do not use if particulate matter or discoloration is observed.
- •
- Administer at a rate not exceeding 1-2 mL per minute.
- •
- Do not administer with other infusion solutions.
- •
- Do not administer as drip.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
TRETTEN, Coagulation Factor XIII A-Subunit (Recombinant), is available as a white lyophilized powder in single-dose vial containing nominally 2500 IU per vial (2000 – 3125 IU) of recombinant coagulation factor XIII A-subunit. The actual amount of TRETTEN in IU is stated on each carton and vial.
After reconstitution with the provided Sterile Water for Injection, each vial contains 667-1042 IU/mL recombinant coagulation factor XIII A-subunit.
4. Contraindications
TRETTEN is contraindicated in patients who have known hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients [See Description (11)].
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Hypersensitivity Reactions
TRETTEN may cause allergic reactions. If signs or symptoms of anaphylaxis or hypersensitivity reactions (including urticaria, rash, tightness of the chest, wheezing, hypotension) occur, discontinue immediately and institute appropriate treatment.
5.2 Thromboembolic Risk
Thromboembolic complications may occur. Monitor patients with conditions that predispose to thrombosis for signs and symptoms of thrombosis after administration of TRETTEN.
5.3 Inhibitors
Inhibitory antibodies may occur with TRETTEN. Patients with inhibitory antibodies may manifest as an inadequate response to treatment. If expected plasma FXIII activity levels are not attained, or if breakthrough bleeding occurs while receiving prophylaxis, perform an assay that measures FXIII inhibitory antibody concentrations.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The most common adverse reactions reported in clinical trials (≥1%), were headache, pain in the extremities, injection site pain, and increase in fibrin D dimer levels.
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
During clinical development, TRETTEN was administered to 77 subjects with congenital factor XIII A-subunit deficiency (3:2, male: female ratio) for a total of 1990 doses. Fifty subjects (65%) were between the ages of 18 and 77 years (received 1338 doses), 21 subjects (27%) were between the ages of 6 and less than 18 years old (received 560 doses), and 6 subjects (8%) were less than 6 years old (received 92 doses). Subjects were exposed for up to 4.5 years.
Of the 77 subjects, 68 received 1979 monthly doses of 35 IU/kg of TRETTEN for routine prophylaxis of bleeding. Eleven single doses of TRETTEN have been administered to nine subjects for pharmacokinetic investigations.
The adverse drug reactions reported included headache, pain in the extremities, pain at the injection site, and increase in fibrin D dimer levels (without evidence of thromboembolic events).
Immunogenicity
The detection of antibody formation is highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assay. Additionally, the observed incidence of antibody (including neutralizing antibody) positivity in an assay may be influenced by several factors including assay methodology, sample handling, timing of sample collection, concomitant medications, and underlying disease. For these reasons, comparison of the incidence of antibodies to TRETTEN with the incidence of antibodies to other products may be misleading.
Transient non-neutralizing antibodies were seen in one out of 50 healthy subjects after one dose, four out of 77 trial subjects (age < 18 years) with congenital factor XIII A-subunit deficiency after one or two doses (3 discontinued from the trial), and in one subject (age < 18 years) in a post marketing safety study after 3.5 years of treatment. In two subjects, the non-neutralizing antibodies disappeared after continued treatment with TRETTEN. In all cases, the non-neutralizing antibodies were found to be of no clinical significance. No subjects developed neutralizing antibodies (inhibitors) against TRETTEN during clinical trials.
7. Drug Interactions
Thrombosis may occur if TRETTEN is administered concomitantly with factor VIIa [See Nonclinical Pharmacology (13.2)].
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies using TRETTEN in pregnant women to determine whether there is a drug-associated risk. Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with TRETTEN.
In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2-4% and 15-20%, respectively.
Miscarriage is a known complication of congenital FXIII deficiency. Pooling data from 39 publications, the miscarriage rate was 66% in 63 patients with 192 pregnancies (70% in 179 pregnancies in FXIII A-subunit deficiency women). Miscarriage rate was 91% in the 136 pregnancies without routine prophylaxis with FXIII concentrates and 11% in the 45 pregnancies treated with routine FXIII prophylaxis2.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There is no information regarding the presence of TRETTEN in human milk, the effect on the breastfed infant, and the effects on milk production. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for TRETTEN and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from TRETTEN or from the underlying maternal condition.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Pediatric subjects in the phase 3 study and the extension study included 6 children in the age range 0-5, 12 children in the age range 6-12, and 9 adolescents in the age range 13-17 who were treated with TRETTEN for a total of 652 exposures. Adverse reactions were more frequently reported in subjects aged from 6 to less than 18 years old than in adults; a greater number of possible/probably trial drug related events were reported in the subjects below 18 years of age (6 subjects with 11 events in 27 enrolled subjects) than in those above 18 years (3 subjects with 3 events in 41 enrolled subjects). Three subjects under 18 years experienced non-neutralizing antibodies and were withdrawn from the study. A fourth pediatric subject who had a non-neutralizing antibody remained in the trial. No dose adjustment is required for pediatric age group.
10. Overdosage
One subject accidentally received a dose 2.3 times the recommended dose. No clinical signs and symptoms were observed.
11. Tretten Description
TRETTEN, Coagulation Factor XIII A-Subunit (Recombinant), is a recombinant human factor XIII-A2 homodimer composed of two factor XIII (FXIII) A-subunits. The FXIII A-subunit is a 731 amino acid chain with an acetylated N-terminal serine. When FXIII is activated by thrombin, a 37 amino acid peptide is cleaved from the N-terminus of the A‑subunit.
TRETTEN is manufactured as an intracellular, soluble protein in yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) production strain containing the episomal expression vector, pD16. It is subsequently isolated by homogenization of cells and purification by several chromatography steps, including hydrophobic interaction and ion exchange chromatography. No human or animal derived products are used in the manufacturing process.
TRETTEN is supplied as a sterile, white lyophilized powder in a single-dose vial. Table 1 and Table 2 list the vial content of reconstituted TRETTEN and the diluent, respectively.
|
Content |
Per Vial* |
Function |
|
Coagulation Factor XIII A-Subunit (Recombinant) |
2000 - 3125 IU |
Active substance |
|
Sodium Chloride |
8.70 mg |
Stabilizer |
|
Sucrose |
174.0 mg |
Stabilizer |
|
Polysorbate 20 |
0.30 mg |
Surfactant |
|
L-Histidine |
9.30 mg |
Buffer |
*Values are given per 3 mL reconstituted TRETTEN.
|
Content |
Per Vial |
Function |
|
Sterile Water for Injection |
3.2 mL |
Diluent |
After reconstitution with 3.2 mL sterile water for injection, each vial contains 667-1042 IU/mL of recombinant coagulation factor XIII A-subunit. The reconstituted solution has a pH of approximately 8.0. The formulation contains no preservative and must only be administered intravenously.
12. Tretten - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
FXIII is the terminal enzyme in the blood coagulation cascade. When activated by thrombin at the site of vessel wall injury, FXIII plays an important role in the maintenance of hemostasis through cross-linking of fibrin and other proteins in the fibrin clot.
In plasma, FXIII circulates as a heterotetramer [A2B2] composed of two FXIII A-subunits and two FXIII B-subunits held together by strong non-covalent interactions. The FXIII A is the catalytic subunit and FXIII B-subunit acts as carrier molecule for the FXIII A-subunit in circulation, and is present in excess in plasma. When FXIII A-subunit is bound to FXIII B-subunit [A2B2] the half-life of the FXIII A-subunit [A2] is prolonged. FXIII is a pro-enzyme (protransglutaminase), which is activated by thrombin in the presence of Ca2+. The enzymatic activity resides with the FXIII A-subunit. Upon activation, the FXIII A‑subunit dissociates from the FXIII B-subunit and thereby exposes the active site of the FXIII A-subunit. The active transglutaminase cross-links fibrin and other proteins resulting in increased mechanical strength and resistance to fibrinolysis of the fibrin clot and contributes to enhance platelet and clot adhesion to injured tissue.
Coagulation Factor XIII A-Subunit (Recombinant) is a protransglutaminase (rFXIII [rA2] homodimer) and binds to free human FXIII B-subunit resulting in a heterotetramer [rA2B2] with a similar half-life to [A2B2]. rFXIII has been shown to be activated by thrombin in the presence of Ca2+. Activated rFXIII has been shown in dose-dependent manner to increase mechanical strength of fibrin clots, retard fibrinolysis, and rFXIII has been shown to enhance platelet adhesion to the site of injury. After combining with available plasma B-subunits, Coagulation Factor XIII A-subunit (Recombinant) has been shown to have the same pharmacodynamic properties in plasma as endogenous FXIII.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
A qualitative assay of clot solubility is widely used as an indicator of FXIII deficiency; when performed correctly the test is positive only when the FXIII activity in the sample is close to zero. The results of standard coagulation tests are normal as it is the quality of the clot that is affected. In addition, at present there are no markers that can quantitatively assess the in vivo pharmacodynamics of FXIII.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Steady State in Subjects with Congenital Factor XIII Deficiency
In 23 subjects with congenital FXIII A-subunit deficiency on prophylaxis, the pharmacokinetics of rFXIII were evaluated over a dosing interval of 28 days during steady state.
The pharmacokinetic parameters based on steady state baseline adjusted FXIII activity (Berichrom assay) values are shown in Table 3.
- Table 3 Pharmacokinetic parameters based on steady state baseline adjusted FXIII activity
|
Parameters |
Mean (SD) |
|
Css, max (IU/mL) |
0.71 (0.17) |
|
Css, min (IU/mL) |
0.05 (0.05) |
|
AUC(0-inf) (IU*h/mL) |
128.3 (40.5) |
|
Clearance (mL/h/kg) |
0.33 (0.11) |
|
Half-life (days) |
5.1 (2.6) |
|
Vss (mL/kg) |
65.9 (26.9) |
|
MRT (days) |
7.9 (3.4) |
At steady state, the pharmacokinetics of rFXIII are comparable with the single dose pharmacokinetics of rFXIII.
Pediatric (Ages 1 to < 6 Years Old)
In a pharmacokinetic trial six children with congenital FXIII A-subunit deficiency on prophylaxis treatment were administered a single intravenous dose of 35 IU/kg. The pharmacokinetic parameters based on baseline adjusted FXIII activity (Berichrom assay) values are shown in Table 4. No dose adjustment is needed for pediatric patients as there is no influence of age on the pharmacokinetics of TRETTEN.
- Table 4 The pharmacokinetic parameters based on baseline adjusted FXIII activity
|
Parameters |
Mean (SD) |
|
Cmax (IU/mL) |
0.48 (0.14) |
|
AUC(0-inf) (IU*h/mL) |
107.8 (32.2) |
|
Clearance (mL/h/kg) |
0.41 (0.20) |
|
Half-life (days) |
7.1 (1.9) |
|
Vss (mL/kg) |
61.2 (41.0) |
|
MRT (days) |
7.5 (4.8) |
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Long-term studies in animals to evaluate the carcinogenic potential of TRETTEN, or studies to determine the effects of TRETTEN on genotoxicity or fertility have not been performed. An assessment of the carcinogenic potential of TRETTEN was completed and suggests minimal carcinogenic risk from product use.
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
Exaggerated pharmacologic effects, including general thrombosis, ischemic necrosis and mortality were observed in nonclinical studies with TRETTEN and non-proteolytically activated recombinant FXIII at a dose of 1670 IU/kg, i.e., 48 times the recommended human dose of 35 IU/kg.
In a monkey cardiovascular safety pharmacology model evaluating the combination of excessive doses of TRETTEN (585 IU/kg, 17 times the expected human dose) in combination with rFVIIa (1000 mcg/kg, 11 times the expected human dose), one of the twelve monkeys died 4 hours after treatment due to thrombosis. Procoagulant risk factors, including 6 indwelling catheters per monkey and the induction of anesthesia, may have complicated the study results. It is unclear whether the mortality was related to the overdose of one or both products, or a specific interaction between them. Nonclinical and clinical studies with the combination of TRETTEN and rFVIIa at recommended human doses have not been performed.
14. Clinical Studies
To establish the efficacy of TRETTEN for the prevention of bleeding in patients with congenital FXIII A-subunit deficiency, a multi-center, open-label, non-controlled trial was conducted for 52 weeks in forty-one (41) subjects ≥ 6 years. All subjects received monthly doses of TRETTEN at 35 IU/kg. Bleeding episodes that required treatment with a FXIII-containing product were observed to evaluate the efficacy of monthly replacement therapy with TRETTEN on prevention of bleeding episodes.
Subjects with congenital FXIII A-subunit deficiency confirmed by genotyping were included. Subjects who before entering the trial had received regular replacement therapy were to have initiated regular replacement therapy at least 6 months prior to screening and were to have a documented history of at least one treatment-requiring bleeding episode before initiation of regular replacement therapy or a documented family history of FXIII congenital deficiency. Subjects who before entering the trial had only received on-demand treatment were to have a documented history of at least two treatment-requiring bleeding episodes within 12 months of the screening visit. Severe bleeders as defined by a documented history of ≥2 treatment requiring bleedings per year during regular FXIII replacement therapy were excluded.
During the prophylaxis treatment period with TRETTEN (434 subject months), five bleeding episodes treated with FXIII-containing products were observed in four subjects. All five were associated with trauma. When calculated for all 41 subjects, this translated into a mean annual rate of bleeding episodes that required treatment of 0.14 [95% CI:0.058- 0.332] per subject year, which was statistically significantly lower than the historic bleeding rate of 1.68 per subject year for on-demand treatment. The age-adjusted rate of bleeding episodes that required treatment during the TRETTEN treatment period was 0.05 [95% CI: 0.0094 - 0.2501] per subject year with a model-based estimate corresponding to the mean age of 26.4 years. The mean annual bleeding rate in subjects below 18 years of age was higher compared to that in adults (0.362 versus 0.040 bleeds/subject/year). Table 5 below lists the estimated bleeding rates by age.
- Table 5 Estimated Bleeding Rates by Age
|
Group |
N |
Estimated Bleeding Rate (bleeds/subject/year) |
95% CI |
Historical Control Group Estimated Bleeding Rate (bleeds/subject/year) |
|
All |
41 |
0.138 |
[0.058; 0.332] |
1.68 |
|
< 18 years |
15 |
0.362 |
[0.136; 0.963] |
2.00 |
|
≥ 18 years |
26 |
0.040 |
[0.006; 0.283] |
1.59 |
Thirty-four (34) of the 41 subjects and an additional 21 new subjects were enrolled in an ongoing second trial. During a total treatment period of 107.5 subject years (mean of 1.95 years per subject), 5 subjects experienced 6 bleeds that required treatment with a FXIII-containing product. The mean annual rate of bleeding episodes that required treatment was determined to be 0.056 per subject year. The age-adjusted rate of bleeding episodes that required treatment during the TRETTEN treatment period was 0.022 per subject year [95% CI:0.0045; 0.1023] with a model-based estimate corresponding to a mean age of 29.5 years. The annual mean bleeding rate in subjects below age 18 was higher compared to that in adults (0.127 versus 0.026 bleeds/subject/year) with some overlap of the respective 95% confidence intervals. Table 6 lists the estimated bleeding rates by age.
- Table 6 Estimated Bleeding Rates by Age
|
Group |
N |
Estimated Bleeding Rate (bleeds/subject/year) |
95% CI |
|
All |
55 |
0.056 |
[0.025; 0.124] |
|
< 18 years |
16 |
0.127 |
[0.048; 0.339] |
|
≥ 18 years |
39 |
0.026 |
[0.007; 0.105] |
15. References
- 1.
- Inbal, A., et.al.:Recombinant factor XIII: a safe and novel treatment for congenital factor XIII deficiency, Blood. 2012;119(22): 5111-5117
- 2.
- Sharief, LAT., Kadir RA.:Congenital factor XIII deficiency in women: a systemic review of literature, Hemophilia. 2013; 19: e349-e357
16. How is Tretten supplied
How Supplied
TRETTEN, Coagulation Factor XIII A-Subunit (Recombinant), is supplied as a white, lyophilized powder in single-dose vial along with the diluent (Sterile Water for Injection) vial.
The actual amount of TRETTEN in international units (IU) is stated on each carton and vial. TRETTEN and the sterile water vials provided in the package are not made with natural rubber latex.
|
Presentation |
Carton NDC Number |
Components NDC Number |
|
2000 - 3125 IU |
0169-7013-01 |
|
Storage and Handling
- •
- Store refrigerated at 2°C – 8°C (36°F – 46°F) prior to reconstitution. TRETTEN is stable until the expiration date on the carton and vial label. Do not freeze. Store protected from light.
- •
- Use reconstituted TRETTEN within 3 hours.
- •
- If the reconstituted product is not used immediately, store the solution refrigerated or at room temperature not to exceed 25°C (77°F) for up to 3 hours following reconstitution.
17. Patient Counseling Information
- •
- Advise patients to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information and Instructions for Use).
- •
- Discuss the signs and symptoms of allergic hypersensitivity reactions, such as urticaria, rash, tightness of the chest, wheezing, hypotension and/or anaphylaxis experienced during or after injection of TRETTEN [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- •
- Discuss signs and symptoms of thrombosis, such as limb or abdomen swelling and/or pain, chest pain, shortness of breath, loss of sensation or motor power, altered consciousness, vision, or speech [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
- •
- Inform patients that breakthrough bleeding may be the sign and symptom of inhibitor formation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
License Number: 1261
Patent information: http://novonordisk-us.com/patients/products/product-patents.html
Novo Nordisk® is a registered trademark of Novo Nordisk A/S
TRETTEN® is a registered trademark of Novo Nordisk Health Care AG
© 2020 Novo Nordisk
For Information contact:
Novo Nordisk Inc.
800 Scudders Mill Road
Plainsboro, NJ 08536
Manufactured by:
Novo Nordisk A/S
DK-2880 Bagsvaerd, Denmark
Patient Package Insert
TRETTEN®
Coagulation Factor XIII A-Subunit (Recombinant)
This leaflet summarizes important information about TRETTEN. Please read it carefully before using TRETTEN and each time you get a refill because there may be new information provided. This information does not take the place of talking with your healthcare provider, and it does not include all of the important information about TRETTEN. If you have any questions after reading this, ask your healthcare provider.
What is TRETTEN?
TRETTEN is an injectable medicine used to prevent bleeding in adults and children who have congenital factor XIII (FXIII) A-subunit deficiency. TRETTEN is man-made and does not contain animal or human materials.
Who should not use TRETTEN?
You should not use TRETTEN if you have ever had allergic (hypersensitivity) reactions, including severe, whole body reaction (anaphylaxis) to TRETTEN or any of the ingredients.
What should I tell my healthcare provider before TRETTEN is given?
Tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including:
- •
- If you are pregnant, think you may be pregnant or planning to become pregnant. It is not known if TRETTEN can harm you or your unborn baby.
- •
- Labor and Delivery: It is not known if TRETTEN is safe and effective during labor and delivery.
- •
- Breast feeding: It is not known if TRETTEN passes into your breast milk.
- •
- If you have a history of blood clots.
Tell your healthcare provider about all of the medicines you take, including all prescription and non-prescription medicines such as over-the-counter medicines, supplements, or herbal remedies.
How is TRETTEN given?
TRETTEN is given as an injection into your vein (intravenous injection). These injections are given once a month. Your dose will depend on your body weight. Use the dose that your healthcare provider has prescribed for you based on your weight.
Before injecting TRETTEN, it must be dissolved (reconstituted) using the sterile water that is provided in the package. Throw away any TRETTEN left in the vial after you inject your dose because it may become unsterile.
What are the possible side effects of TRETTEN?
Call your healthcare provider or go to the emergency department right away if you have any of the following symptoms after using TRETTEN:
- •
- Signs of allergic reaction including
- •
- shortness of breath
- •
- rash
- •
- itching (pruritus)
- •
- redness of the skin (erythema)
- •
- fainting/dizziness
- •
- Signs of a blood clot including pain, swelling, warmth, redness, or a lump in your legs or arms, chest pain, or sudden severe headache and/or loss of consciousness or function
- •
- Unexpected bleeding
Other possible side effects may include:
- •
- pain in your arms or legs
- •
- headache
- •
- pain at the injection site
These are not all the possible side effects of TRETTEN. Tell your healthcare provider about any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away. You can also report side effects to the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store TRETTEN?
It is important to store TRETTEN correctly.
- Before preparing TRETTEN for injection
- Keep TRETTEN in a refrigerator at 36°F to 46°F (2°C to 8°C) and in the original package in order to protect it from light. Do not freeze TRETTEN.
- After preparing TRETTEN for injection (reconstituted)
- Use TRETTEN immediately after it is dissolved (reconstituted) using the sterile water provided in the package.
- If you cannot inject it immediately, either leave TRETTEN at room temperature not above 25°C (77°F) or put
- TRETTEN in the refrigerator at 36°F to 46°F (2°C to 8°C) for no more than 3 hours. After more than 3 hours, DO
- NOT USE IT—THROW IT AWAY.
- TRETTEN does not contain a preservative. Do not store TRETTEN in the syringe or placed in the freezer.
What else should I know about TRETTEN?
Do not use TRETTEN for a condition for which it is not prescribed. Do not share TRETTEN with other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have.
Talk to your healthcare provider if you would like more information.
TRETTEN ingredients include:
- •
- Coagulation Factor XIII A-Subunit (Recombinant)
- •
- Sodium Chloride
- •
- Sucrose
- •
- Polysorbate 20
- •
- L-Histidine
TRETTEN and the sterile water vials provided in the package are not made with natural rubber latex.
This Patient Package Insert has been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration
Revised: 12/2013
Version: 1
Novo Nordisk® is a registered trademark of Novo Nordisk A/S
TRETTEN® is a registered trademark of Novo Nordisk Health Care AG
© 2013 Novo Nordisk
For Information contact:
Novo Nordisk Inc.
800 Scudders Mill Road
Plainsboro, NJ 08536
www.novonordisk-us.com
1-844-TRETTEN
Manufactured by:
Novo Nordisk A/S
DK-2880 Bagsvaerd, Denmark
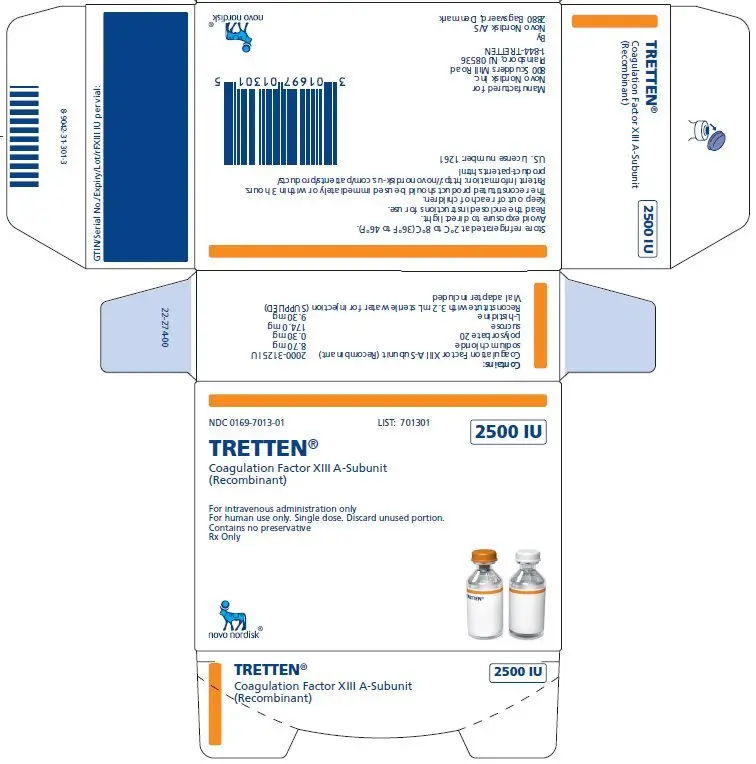
PACKAGE/LABEL DISPLAY PANEL
- NDC 0169-7013-01 LIST: 701301
2500 IU
TRETTEN®
Coagulation Factor XIII A-Subunit (Recombinant)
For intravenous administration only
For human use only. Single dose. Discard unused portion.
Contains no preservative
Package/Label Display Panel
- NDC 0169-7113-11 LIST: 711311
2500 IU
TRETTEN®
Coagulation Factor XIII A-Subunit (Recombinant)
For intravenous administration only
Store refrigerated at 2-8°C (36-46°F)
Reconstitute with 3.2 mL sterile water for injection only
Rx only
Novo Nordisk Inc.
1-844-TRETTEN
Expiry/Lot/rFXIII IU per vial:
| TRETTEN
coagulation factor xiii a-subunit (recombinant) kit |
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Novo Nordisk (622920320) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Novo Nordisk A/S | 306711800 | MANUFACTURE(0169-7013) , API MANUFACTURE(0169-7013) | |