Drug Detail:Trikafta (Elexacaftor, ivacaftor, and tezacaftor)
Drug Class: CFTR combinations
Highlights of Prescribing Information
TRIKAFTA® (elexacaftor, tezacaftor, and ivacaftor tablets; ivacaftor tablets), co-packaged for oral use
TRIKAFTA® (elexacaftor, tezacaftor, and ivacaftor oral granules; ivacaftor oral granules), co-packaged
Initial U.S. Approval: 2019
Recent Major Changes
| Indications and Usage (1) | 04/2023 |
| Dosage and Administration (2) | 04/2023 |
| Warnings and Precautions, Hypersensitivity Reactions, Including Anaphylaxis (5.2) | 08/2023 |
Indications and Usage for Trikafta
TRIKAFTA is a combination of ivacaftor, a CFTR potentiator, tezacaftor, and elexacaftor indicated for the treatment of cystic fibrosis (CF) in patients aged 2 years and older who have at least one F508del mutation in the CFTR gene or a mutation in the CFTR gene that is responsive based on in vitro data. If the patient's genotype is unknown, an FDA-cleared CF mutation test should be used to confirm the presence of at least one F508del mutation or a mutation that is responsive based on in vitro data. (1)
Trikafta Dosage and Administration
| Recommended Dosage for Adult and Pediatric Patients Aged 2 Years and Older | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | Weight | Morning Dose | Evening Dose |
| 2 to less than 6 years | Less than 14 kg | One packet containing elexacaftor 80 mg/tezacaftor 40 mg/ivacaftor 60 mg oral granules | One packet containing ivacaftor 59.5 mg oral granules |
| 14 kg or more | One packet containing elexacaftor 100 mg/tezacaftor 50 mg/ivacaftor 75 mg oral granules | One packet containing ivacaftor 75 mg oral granules | |
| 6 to less than 12 years | Less than 30 kg | Two tablets, each containing elexacaftor 50 mg/tezacaftor 25 mg/ivacaftor 37.5 mg | One tablet of ivacaftor 75 mg |
| 30 kg or more | Two tablets, each containing elexacaftor 100 mg/tezacaftor 50 mg/ivacaftor 75 mg | One tablet of ivacaftor 150 mg | |
| 12 years and older | - | Two tablets, each containing elexacaftor 100 mg/tezacaftor 50 mg/ivacaftor 75 mg | One tablet of ivacaftor 150 mg |
- TRIKAFTA should be taken with fat-containing food. (2.5, 12.3)
- Should not be used in patients with severe hepatic impairment. Use not recommended in patients with moderate hepatic impairment unless the benefit exceeds the risk. Reduce dose if used in patients with moderate hepatic impairment. Liver function tests should be closely monitored. (2.2, 5.1, 6, 8.7, 12.3)
- See full prescribing information for dosage modifications due to drug interactions with TRIKAFTA. (2.3, 5.4, 7.2, 12.3)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Tablets:
- Fixed-dose combination containing elexacaftor 50 mg, tezacaftor 25 mg and ivacaftor 37.5 mg co-packaged with ivacaftor 75 mg;
- Fixed-dose combination containing elexacaftor 100 mg, tezacaftor 50 mg, and ivacaftor 75 mg co-packaged with ivacaftor 150 mg. (3)
Oral granules:
- Unit-dose packets of elexacaftor 100 mg, tezacaftor 50 mg and ivacaftor 75 mg co-packaged with unit-dose packets of ivacaftor 75 mg;
- Unit-dose packets of elexacaftor 80 mg, tezacaftor 40 mg and ivacaftor 60 mg co-packaged with unit-dose packets of ivacaftor 59.5 mg. (3)
Contraindications
None. (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Elevated transaminases and hepatic injury: Liver failure leading to transplantation has been reported in a patient with cirrhosis and portal hypertension while receiving TRIKAFTA. Avoid use of TRIKAFTA in patients with pre-existing advanced liver disease, (e.g., as evidenced by cirrhosis, portal hypertension, ascites, hepatic encephalopathy) unless the benefits are expected to outweigh the risks. If used in these patients, they should be closely monitored after the initiation of treatment. Isolated elevations of transaminases or bilirubin have been observed in CF patients treated with TRIKAFTA. In some instances, transaminase elevations have been associated with concomitant elevations in total bilirubin and/or international normalized ratio (INR) and have resulted in patients being hospitalized for intervention, including patients without a history of pre-existing liver disease. Monitor liver function tests (ALT, AST, and bilirubin). Interrupt dosing in the event of significant elevations. In patients with a history of hepatobiliary disease or liver function test elevations, monitor more frequently. (2.2, 5.1, 8.7)
- Hypersensitivity reactions: Angioedema and anaphylaxis been reported with TRIKAFTA in the postmarketing setting. Initiate appropriate therapy in the event of a hypersensitivity reaction. (5.2)
- Use with CYP3A inducers: Concomitant use with strong CYP3A inducers (e.g., rifampin, St. John's wort) significantly decrease ivacaftor exposure and are expected to decrease elexacaftor and tezacaftor exposure, which may reduce TRIKAFTA efficacy. Therefore, co-administration is not recommended. (5.3, 7.1, 12.3)
- Cataracts: Non-congenital lens opacities/cataracts have been reported in pediatric patients treated with ivacaftor-containing regimens. Baseline and follow-up examinations are recommended in pediatric patients initiating TRIKAFTA treatment. (5.5, 8.4)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The most common adverse drug reactions to TRIKAFTA (≥5% of patients and at a frequency higher than placebo by ≥1%) were headache, upper respiratory tract infection, abdominal pain, diarrhea, rash, alanine aminotransferase increased, nasal congestion, blood creatine phosphokinase increased, aspartate aminotransferase increased, rhinorrhea, rhinitis, influenza, sinusitis and blood bilirubin increased. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Vertex Pharmaceuticals Incorporated at 1-877-634-8789 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
- Strong CYP3A inducers: Avoid co-administration. (5.3, 7.1, 12.3)
- Strong or moderate CYP3A inhibitors: Reduce TRIKAFTA dosage when co-administered. Avoid food or drink containing grapefruit. (2.3, 5.4, 7.2, 12.3)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 8/2023
Related/similar drugs
azithromycin, Zithromax, gentamicin, Creon, tobramycinFull Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Trikafta
TRIKAFTA is indicated for the treatment of cystic fibrosis (CF) in patients aged 2 years and older who have at least one F508del mutation in the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) gene or a mutation in the CFTR gene that is responsive based on in vitro data [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)].
If the patient's genotype is unknown, an FDA-cleared CF mutation test should be used to confirm the presence of at least one F508del mutation or a mutation that is responsive based on in vitro data.
2. Trikafta Dosage and Administration
2.1 Recommended Dosage in Adults and Pediatric Patients Aged 2 Years and Older
Recommended dosage for adult and pediatric patients aged 2 years and older is provided in Table 1. The morning and the evening dose should be taken approximately 12 hours apart. TRIKAFTA is for oral use.
| Age | Weight | Morning Dose | Evening Dose |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 to less than 6 years | Less than 14 kg | One packet (containing elexacaftor 80 mg/tezacaftor 40 mg/ivacaftor 60 mg) oral granules | One packet (containing ivacaftor 59.5 mg) oral granules |
| 14 kg or more | One packet (containing elexacaftor 100 mg/tezacaftor 50 mg/ivacaftor 75 mg) oral granules | One packet (containing ivacaftor 75 mg) oral granules | |
| 6 to less than 12 years | Less than 30 kg | Two tablets of elexacaftor 50 mg/tezacaftor 25 mg/ivacaftor 37.5 mg (total dose of elexacaftor 100 mg/tezacaftor 50 mg/ivacaftor 75 mg) | One tablet of ivacaftor 75 mg |
| 30 kg or more | Two tablets of elexacaftor 100 mg/tezacaftor 50 mg/ivacaftor 75 mg (total dose of elexacaftor 200 mg/tezacaftor 100 mg/ivacaftor 150 mg) | One tablet of ivacaftor 150 mg | |
| 12 years and older | Two tablets of elexacaftor 100 mg/tezacaftor 50 mg/ivacaftor 75 mg (total dose of elexacaftor 200 mg/tezacaftor 100 mg/ivacaftor 150 mg) | One tablet of ivacaftor 150 mg |
2.2 Recommended Dosage for Patients with Hepatic Impairment
- Mild Hepatic Impairment (Child-Pugh Class A): No dose adjustment is recommended [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. See Table 1 for recommended dosage of TRIKAFTA. Liver function tests should be closely monitored [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Adverse Reactions (6)].
- Moderate Hepatic Impairment (Child-Pugh Class B): Treatment is not recommended. Use of TRIKAFTA in patients with moderate hepatic impairment should only be considered when there is a clear medical need, and the benefit exceeds the risk. If used, TRIKAFTA should be used with caution at a reduced dose (see Table 2) [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Liver function tests should be closely monitored [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Adverse Reactions (6)]. Recommended dosage for patients with moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class B) is provided in Table 2.
| Age | Weight | Morning Dose | Evening Dose |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 to less than 6 years | Less than 14 kg | Weekly dosing schedule as follows:
| No evening dose of ivacaftor oral granules. |
| 14 kg or more | Weekly dosing schedule as follows:
| No evening dose of ivacaftor oral granules. | |
| 6 years to less than 12 years | Less than 30 kg | Alternating daily dosing schedule as follows:
| No evening ivacaftor tablet dose. |
| 30 kg or more | Alternating daily dosing schedule as follows:
| No evening ivacaftor tablet dose. | |
| 12 years and older | Alternating daily dosing schedule as follows:
| No evening ivacaftor tablet dose. |
- Severe Hepatic Impairment (Child-Pugh Class C): Should not be used. TRIKAFTA has not been studied in patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class C), but the exposure is expected to be higher than in patients with moderate hepatic impairment. [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1), Adverse Reactions (6), Use in Specific Populations (8.7) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
2.3 Dosage Modification for Patients Taking Drugs that are CYP3A Inhibitors
Table 3 describes the recommended dosage modification for TRIKAFTA when co-administered with strong (e.g., ketoconazole, itraconazole, posaconazole, voriconazole, telithromycin, and clarithromycin) or moderate (e.g., fluconazole, erythromycin) CYP3A inhibitors. Avoid food or drink containing grapefruit during TRIKAFTA treatment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4), Drug Interactions (7.2) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
| Age | Weight | Moderate CYP3A Inhibitors | Strong CYP3A Inhibitors |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 to less than 6 years | Less than 14 kg | Alternating daily dosing schedule is as follows:
| One packet (containing elexacaftor 80 mg/tezacaftor 40 mg/ivacaftor 60 mg) in the morning twice a week, approximately 3 to 4 days apart. No evening packet of ivacaftor oral granules. |
| 14 kg or more | Alternating daily dosing schedule is as follows:
| One packet (containing elexacaftor 100 mg/tezacaftor 50 mg/ivacaftor 75 mg) in the morning twice a week, approximately 3 to 4 days apart. No evening packet of ivacaftor oral granules. |
|
| 6 years and older | Less than 30 kg | Alternating daily dosing schedule is as follows:
| Two tablets of elexacaftor 50 mg/tezacaftor 25 mg/ivacaftor 37.5 mg (total dose of elexacaftor 100 mg/tezacaftor 50 mg/ivacaftor 75 mg) in the morning twice a week, approximately 3 to 4 days apart. No evening ivacaftor tablet dose. |
| 30 kg or more | Alternating daily dosing schedule is as follows:
| Two tablets elexacaftor 100 mg/tezacaftor 50 mg/ivacaftor 75 mg (total dose of elexacaftor 200 mg/tezacaftor 100 mg/ivacaftor 150 mg) in the morning twice a week, approximately 3 to 4 days apart. No evening ivacaftor tablet dose. |
|
| 12 years and older | Alternating daily dosing schedule is as follows:
| Two tablets elexacaftor 100 mg/tezacaftor 50 mg/ivacaftor 75 mg (total dose of elexacaftor 200 mg/tezacaftor 100 mg/ivacaftor 150 mg) in the morning twice a week, approximately 3 to 4 days apart. No evening ivacaftor tablet dose. |
2.4 Recommendations Regarding Missed Dose(s)
If 6 hours or less have passed since the missed morning or evening dose, the patient should take the missed dose as soon as possible and continue on the original schedule.
If more than 6 hours have passed since:
- the missed morning dose, the patient should take the missed dose as soon as possible and should not take the evening dose. The next scheduled morning dose should be taken at the usual time.
- the missed evening dose, the patient should not take the missed dose. The next scheduled morning dose should be taken at the usual time.
Morning and evening doses should not be taken at the same time.
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Elevated Transaminases and Hepatic Injury
Liver failure leading to transplantation has been reported in a patient with cirrhosis and portal hypertension while receiving TRIKAFTA. Avoid use of TRIKAFTA in patients with pre-existing advanced liver disease (e.g., as evidenced by cirrhosis, portal hypertension, ascites, hepatic encephalopathy) unless the benefits are expected to outweigh the risks. If used in these patients, they should be closely monitored after the initiation of treatment [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Adverse Reactions (6), Use in Specific Populations (8.7) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Isolated elevations of transaminases or bilirubin have been observed in patients with CF treated with TRIKAFTA. In some instances, transaminase elevations have been associated with concomitant elevations in total bilirubin and/or international normalized ratio (INR) and have resulted in patients being hospitalized for intervention, including in patients without a history of pre-existing liver disease.
Assessments of liver function tests (ALT, AST, and bilirubin) are recommended for all patients prior to initiating TRIKAFTA, every 3 months during the first year of treatment, and annually thereafter. In the event of significant elevations in liver function tests, e.g., ALT or AST >5 × the upper limit of normal (ULN) or ALT or AST >3 × ULN with bilirubin >2 × ULN, dosing should be interrupted, and laboratory tests closely followed until the abnormalities resolve. Following the resolution of liver function test elevations, consider the benefits and risks of resuming treatment. For patients with a history of hepatobiliary disease or liver function test elevations, more frequent monitoring should be considered [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Adverse Reactions (6), Use in Specific Populations (8.7) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
5.2 Hypersensitivity Reactions, Including Anaphylaxis
Hypersensitivity reactions, including cases of angioedema and anaphylaxis, have been reported in the postmarketing setting [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)]. If signs or symptoms of serious hypersensitivity reactions develop during treatment, discontinue TRIKAFTA and institute appropriate therapy. Consider the benefits and risks for the individual patient to determine whether to resume treatment with TRIKAFTA.
5.3 Concomitant Use with CYP3A Inducers
Exposure to ivacaftor is significantly decreased and exposure to elexacaftor and tezacaftor are expected to decrease by the concomitant use of strong CYP3A inducers, which may reduce the therapeutic effectiveness of TRIKAFTA. Therefore, co-administration with strong CYP3A inducers is not recommended [see Drug Interactions (7.1) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
5.4 Concomitant Use with CYP3A Inhibitors
Exposure to elexacaftor, tezacaftor and ivacaftor are increased when co-administered with strong or moderate CYP3A inhibitors. Therefore, the dose of TRIKAFTA should be reduced when used concomitantly with moderate or strong CYP3A inhibitors [see Dosage and Administration (2.3), Drug Interactions (7.2) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
5.5 Cataracts
Cases of non-congenital lens opacities have been reported in pediatric patients treated with ivacaftor-containing regimens. Although other risk factors were present in some cases (such as corticosteroid use, exposure to radiation), a possible risk attributable to treatment with ivacaftor cannot be excluded. Baseline and follow-up ophthalmological examinations are recommended in pediatric patients initiating treatment with TRIKAFTA [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the labeling:
- Elevated Transaminases and Hepatic Injury [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Hypersensitivity Reactions, Including Anaphylaxis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Cataracts [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
The safety profile of TRIKAFTA is based on data from 510 CF patients aged 12 years and older in two double-blind, controlled trials of 24 weeks and 4 weeks treatment duration (Trials 1 and 2). Eligible patients were also able to participate in an open-label extension safety study (up to 96 weeks of TRIKAFTA). In the two controlled trials, a total of 257 patients aged 12 years and older received at least one dose of TRIKAFTA.
In addition, the following clinical trials have also been conducted [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]:
- a 24-week, open-label trial in 66 patients with CF aged 6 to less than 12 years who were either homozygous for the F508del mutation or heterozygous for the F508del mutation and a mutation on the second allele that results in either no CFTR protein or a CFTR protein that is not responsive to ivacaftor and tezacaftor/ivacaftor (Trial 3).
- a 24-week, open-label trial in 75 patients with CF aged 2 to less than 6 years. Patients who had at least one F508del mutation or a mutation known to be responsive to TRIKAFTA were eligible for the study (Trial 4).
In Trial 1, the proportion of patients who discontinued study drug prematurely due to adverse events was 1% for TRIKAFTA-treated patients and 0% for placebo-treated patients.
In Trial 1, serious adverse reactions that occurred more frequently in TRIKAFTA-treated patients compared to placebo were rash (1% vs <1%) and influenza (1% vs 0%). There were no deaths in Trials 1, 2, 3 and 4.
Table 4 shows adverse reactions occurring in ≥5% of TRIKAFTA-treated patients and higher than placebo by ≥1% in the 24-week, placebo-controlled, parallel-group trial (Trial 1).
| Adverse Drug Reactions (Preferred Term) | TRIKAFTA N=202 n (%) | Placebo N=201 n (%) |
|---|---|---|
|
||
| Headache | 35 (17) | 30 (15) |
| Upper respiratory tract infection* | 32 (16) | 25 (12) |
| Abdominal pain† | 29 (14) | 18 (9) |
| Diarrhea | 26 (13) | 14 (7) |
| Rash‡ | 21 (10) | 10 (5) |
| Alanine aminotransferase increased | 20 (10) | 7 (3) |
| Nasal congestion | 19 (9) | 15 (7) |
| Blood creatine phosphokinase increased | 19 (9) | 9 (4) |
| Aspartate aminotransferase increased | 19 (9) | 4 (2) |
| Rhinorrhea | 17 (8) | 6 (3) |
| Rhinitis | 15 (7) | 11 (5) |
| Influenza | 14 (7) | 3 (1) |
| Sinusitis | 11 (5) | 8 (4) |
| Blood bilirubin increased | 10 (5) | 2 (1) |
Additional adverse reactions that occurred in TRIKAFTA-treated patients at a frequency of 2 to <5% and higher than placebo by ≥1% include the following: Flatulence, abdominal distension, conjunctivitis, pharyngitis, respiratory tract infection, tonsillitis, urinary tract infection, c-reactive protein increased, hypoglycemia, dizziness, dysmenorrhea, acne, eczema and pruritus.
The safety profile for the CF patients enrolled in Trials 2, 3, and 4 was similar to that observed in Trial 1.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post approval use of TRIKAFTA. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
7. Drug Interactions
Potential for other drugs to affect elexacaftor/tezacaftor/ivacaftor
7.1 Inducers of CYP3A
Elexacaftor, tezacaftor and ivacaftor are substrates of CYP3A (ivacaftor is a sensitive substrate of CYP3A). Concomitant use of CYP3A inducers may result in reduced exposures and thus reduced TRIKAFTA efficacy. Co-administration of ivacaftor with rifampin, a strong CYP3A inducer, significantly decreased ivacaftor area under the curve (AUC) by 89%. Elexacaftor and tezacaftor exposures are expected to decrease during co-administration with strong CYP3A inducers. Therefore, co-administration of TRIKAFTA with strong CYP3A inducers is not recommended [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Examples of strong CYP3A inducers include:
- rifampin, rifabutin, phenobarbital, carbamazepine, phenytoin and St. John's wort (Hypericum perforatum)
7.2 Inhibitors of CYP3A
Co-administration with itraconazole, a strong CYP3A inhibitor, increased elexacaftor AUC by 2.8-fold and tezacaftor AUC by 4.0- to 4.5-fold. When co-administered with itraconazole and ketoconazole, ivacaftor AUC increased by 15.6-fold and 8.5-fold, respectively. The dosage of TRIKAFTA should be reduced when co-administered with strong CYP3A inhibitors [see Dosage and Administration (2.3), Warnings and Precautions (5.4) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Examples of strong CYP3A inhibitors include:
- ketoconazole, itraconazole, posaconazole and voriconazole
- telithromycin and clarithromycin
Simulations indicated that co-administration with moderate CYP3A inhibitors may increase elexacaftor and tezacaftor AUC by approximately 1.9- to 2.3-fold and 2.1-fold, respectively. Co-administration of fluconazole increased ivacaftor AUC by 2.9-fold. The dosage of TRIKAFTA should be reduced when co-administered with moderate CYP3A inhibitors [see Dosage and Administration (2.3), Warnings and Precautions (5.4) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Examples of moderate CYP3A inhibitors include:
- fluconazole
- erythromycin
Co-administration of TRIKAFTA with grapefruit juice, which contains one or more components that moderately inhibit CYP3A, may increase exposure of elexacaftor, tezacaftor and ivacaftor; therefore, food or drink containing grapefruit should be avoided during treatment with TRIKAFTA [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
7.3 Ciprofloxacin
Ciprofloxacin had no clinically relevant effect on the exposure of tezacaftor or ivacaftor and is not expected to affect the exposure of elexacaftor. Therefore, no dose adjustment is necessary during concomitant administration of TRIKAFTA with ciprofloxacin [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Potential for elexacaftor/tezacaftor/ivacaftor to affect other drugs
7.4 CYP2C9 Substrates
Ivacaftor may inhibit CYP2C9; therefore, monitoring of the international normalized ratio (INR) during co-administration of TRIKAFTA with warfarin is recommended. Other medicinal products for which exposure may be increased by TRIKAFTA include glimepiride and glipizide; these medicinal products should be used with caution [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
7.5 Transporters
Co-administration of ivacaftor or tezacaftor/ivacaftor with digoxin, a sensitive P-gp substrate, increased digoxin AUC by 1.3-fold, consistent with weak inhibition of P-gp by ivacaftor. Administration of TRIKAFTA may increase systemic exposure of medicinal products that are sensitive substrates of P-gp, which may increase or prolong their therapeutic effect and adverse reactions. When used concomitantly with digoxin or other substrates of P-gp with a narrow therapeutic index such as cyclosporine, everolimus, sirolimus and tacrolimus, caution and appropriate monitoring should be used [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Elexacaftor and M23-ELX inhibit uptake by OATP1B1 and OATP1B3 in vitro. Co-administration of TRIKAFTA may increase exposures of medicinal products that are substrates of these transporters, such as statins, glyburide, nateglinide and repaglinide. When used concomitantly with substrates of OATP1B1 or OATP1B3, caution and appropriate monitoring should be used [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Bilirubin is an OATP1B1 and OATP1B3 substrate.
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of TRIKAFTA for the treatment of CF have been established in pediatric patients aged 2 to less than 18 years who have at least one F508del mutation in the CFTR gene or a mutation in the CFTR gene that is responsive based on in vitro data. Use of TRIKAFTA for this indication for pediatric patients 12 years of age and older was supported by evidence from two adequate and well-controlled studies (Trials 1 and 2) in CF patients aged 12 years and older [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) and Clinical Studies (14)].
Use of TRIFAFTA for this indication in pediatric patients 2 to less than 12 years of age is based on the following:
- Trial 1, 56 pediatric patients aged 12 to less than 18 years who had an F508del mutation on one allele and a mutation on the second allele that results in either no CFTR protein or a CFTR protein that is not responsive to ivacaftor and tezacaftor/ivacaftor [see Adverse Reactions (6) and Clinical Studies (14)].
- Trial 2, 16 pediatric patients aged 12 to less than 18 years who were homozygous for the F508del mutation [see Adverse Reactions (6) and Clinical Studies (14)].
- Trial 3, 66 pediatric patients aged 6 to less than 12 years who were homozygous for the F508del mutation or heterozygous for the F508del mutation with a mutation on the second allele that results in either no CFTR protein or a CFTR protein that is not responsive to ivacaftor and tezacaftor/ivacaftor [see Adverse Reactions (6) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
- Trial 4, 75 pediatric patients aged 2 to less than 6 years who had at least one F508del mutation or a mutation known to be responsive to TRIKAFTA [see Adverse Reactions (6) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
The effectiveness of TRIKAFTA in patients aged 2 to less than 12 years was extrapolated from patients aged 12 years and older with support from population pharmacokinetic analyses showing elexacaftor, tezacaftor, and ivacaftor exposure levels in patients aged 2 to less than 12 years within the range of exposures observed in patients aged 12 years and older [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Safety of TRIKAFTA in patients aged 6 to less than 12 years was derived from a 24-week, open-label, clinical trial in 66 patients aged 6 to less than 12 years (mean age at baseline 9.3 years) administered either a total dose of elexacaftor 100 mg/tezacaftor 50 mg/ivacaftor 75 mg in the morning and ivacaftor 75 mg in the evening (for patients weighing less than 30 kg) or a total dose of elexacaftor 200 mg/tezacaftor 100 mg/ivacaftor 150 mg in the morning and ivacaftor 150 mg in the evening (for patients weighing 30 kg or more) (Trial 3). Safety of TRIKAFTA in patients aged 2 to less than 6 years was derived from a 24-week, open-label, clinical trial in 75 patients aged 2 to less than 6 years (mean age at baseline 4.1 years) administered either a total dose of elexacaftor 80 mg/tezacaftor 40 mg/ivacaftor 60 mg in the morning and ivacaftor 59.5 mg in the evening (for patients weighing 10 kg to less than 14 kg) or a total dose of elexacaftor 100 mg/tezacaftor 50 mg/ivacaftor 75 mg in the morning and ivacaftor 75 mg in the evening (for patients weighing 14 kg or more) (Trial 4). The safety profile of patients in these trials was similar to that observed in Trial 1 [see Adverse Reactions (6)].
The safety and effectiveness of TRIKAFTA in patients with CF younger than 2 years of age have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of TRIKAFTA did not include any patients aged 65 years and older.
8.6 Renal Impairment
TRIKAFTA has not been studied in patients with severe renal impairment or end-stage renal disease. No dosage adjustment is recommended in patients with mild (eGFR 60 to <90 mL/min/1.73 m2) or moderate (eGFR 30 to <60 mL/min/1.73 m2) renal impairment. Use with caution in patients with severe (eGFR <30 mL/min/1.73 m2) renal impairment or end-stage renal disease [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
- Mild Hepatic Impairment (Child-Pugh Class A): No dose modification is recommended. Liver function tests should be closely monitored.
-
Moderate Hepatic Impairment (Child-Pugh Class B): Treatment is not recommended. Use of TRIKAFTA in patients with moderate hepatic impairment should only be considered when there is a clear medical need, and the benefit exceeds the risk. If used in patients with moderate hepatic impairment, TRIKAFTA should be used at a reduced dose [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)]. Liver function tests should be closely monitored.
In a clinical study of 11 subjects with moderate hepatic impairment, one subject developed total and direct bilirubin elevations >2 × ULN, and a second subject developed direct bilirubin elevation >4.5 × ULN [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. - Severe Hepatic Impairment (Child-Pugh Class C): Should not be used. TRIKAFTA has not been studied in patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class C), but the exposure is expected to be higher than in patients with moderate hepatic impairment [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Warnings and Precautions (5.1), Adverse Reactions (6) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
10. Overdosage
No specific antidote is available for overdosage with TRIKAFTA. Treatment of overdosage consists of general supportive measures including monitoring of vital signs and observation of the clinical status of the patient.
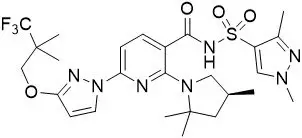
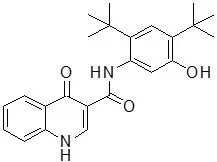
11. Trikafta Description
TRIKAFTA is a co-package of elexacaftor, tezacaftor and ivacaftor fixed-dose combination tablets or granules and ivacaftor tablets or granules. Both tablets and granules are for oral administration.
The elexacaftor, tezacaftor and ivacaftor fixed-dose combination tablets are available as: orange, capsule-shaped, film-coated tablet containing 100 mg of elexacaftor, 50 mg of tezacaftor, 75 mg of ivacaftor, or light-orange, capsule-shaped, film-coated tablet containing 50 mg of elexacaftor, 25 mg of tezacaftor, 37.5 mg of ivacaftor. The fixed-dose combination tablet contains the following inactive ingredients: croscarmellose sodium, hypromellose, hypromellose acetate succinate, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, and sodium lauryl sulfate. The tablet film coat contains hydroxypropyl cellulose, hypromellose, iron oxide red, iron oxide yellow, talc, and titanium dioxide.
The ivacaftor tablet is available as a light blue, capsule-shaped, film-coated tablet containing 150 mg or 75 mg of ivacaftor and the following inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, croscarmellose sodium, hypromellose acetate succinate, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose and sodium lauryl sulfate. The tablet film coat contains carnauba wax, FD&C Blue #2, PEG 3350, polyvinyl alcohol, talc, and titanium dioxide. The printing ink contains ammonium hydroxide, iron oxide black, propylene glycol, and shellac.
The elexacaftor, tezacaftor and ivacaftor fixed-dose combination oral granules are white to off-white, sweetened, unflavored granules approximately 2 mm in diameter enclosed in unit-dose packets. Each unit-dose packet contains 100 mg of elexacaftor, 50 mg of tezacaftor, 75 mg of ivacaftor or 80 mg of elexacaftor, 40 mg of tezacaftor, 60 mg of ivacaftor and the following inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, croscarmellose sodium, hypromellose, hypromellose acetate succinate, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, mannitol, sodium lauryl sulfate, and sucralose.
The ivacaftor oral granules are white to off-white, sweetened, unflavored granules approximately 2 mm in diameter enclosed in unit-dose packets. Each unit-dose packet contains 75 mg or 59.5 mg of ivacaftor and the following inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, croscarmellose sodium, hypromellose acetate succinate, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, mannitol, sodium lauryl sulfate, and sucralose.
The active ingredients of TRIKAFTA are described below.
12. Trikafta - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Elexacaftor and tezacaftor bind to different sites on the CFTR protein and have an additive effect in facilitating the cellular processing and trafficking of select mutant forms of CFTR (including F508del-CFTR) to increase the amount of CFTR protein delivered to the cell surface compared to either molecule alone. Ivacaftor potentiates the channel open probability (or gating) of the CFTR protein at the cell surface.
The combined effect of elexacaftor, tezacaftor and ivacaftor is increased quantity and function of CFTR at the cell surface, resulting in increased CFTR activity as measured by CFTR mediated chloride transport.
CFTR Chloride Transport Assay in Fischer Rat Thyroid (FRT) Cells Expressing Mutant CFTR
The chloride transport response of mutant CFTR protein to elexacaftor/tezacaftor/ivacaftor was determined in Ussing chamber electrophysiology studies using a panel of FRT cell lines transfected with individual CFTR mutations. Elexacaftor/tezacaftor/ivacaftor increased chloride transport in FRT cells expressing CFTR mutations that result in CFTR protein being delivered to the cell surface.
The in vitro CFTR chloride transport response threshold was designated as a net increase of at least 10% of normal over baseline because it is predictive or reasonably expected to predict clinical benefit. For individual mutations, the magnitude of the net change over baseline in CFTR-mediated chloride transport in vitro is not correlated with the magnitude of clinical response.
Table 5 lists responsive CFTR mutations based on in vitro data in FRT cells indicating that elexacaftor/tezacaftor/ivacaftor increases chloride transport to at least 10% of normal over baseline.
|
|||||
| 3141del9 | E822K | G1069R | L967S | R117L | S912L |
| 546insCTA | F191V | G1244E | L997F | R117P | S945L |
| A46D | F311del | G1249R | L1077P | R170H | S977F |
| A120T | F311L | G1349D | L1324P | R258G | S1159F |
| A234D | F508C | H139R | L1335P | R334L | S1159P |
| A349V | F508C;S1251N * | H199Y | L1480P | R334Q | S1251N |
| A455E | F508del † | H939R | M152V | R347H | S1255P |
| A554E | F575Y | H1054D | M265R | R347L | T338I |
| A1006E | F1016S | H1085P | M952I | R347P | T1036N |
| A1067T | F1052V | H1085R | M952T | R352Q | T1053I |
| D110E | F1074L | H1375P | M1101K | R352W | V201M |
| D110H | F1099L | I148T | P5L | R553Q | V232D |
| D192G | G27R | I175V | P67L | R668C | V456A |
| D443Y | G85E | I336K | P205S | R751L | V456F |
| D443Y;G576A;R668C * | G126D | I502T | P574H | R792G | V562I |
| D579G | G178E | I601F | Q98R | R933G | V754M |
| D614G | G178R | I618T | Q237E | R1066H | V1153E |
| D836Y | G194R | I807M | Q237H | R1070Q | V1240G |
| D924N | G194V | I980K | Q359R | R1070W | V1293G |
| D979V | G314E | I1027T | Q1291R | R1162L | W361R |
| D1152H | G463V | I1139V | R31L | R1283M | W1098C |
| D1270N | G480C | I1269N | R74Q | R1283S | W1282R |
| E56K | G551D | I1366N | R74W | S13F | Y109N |
| E60K | G551S | K1060T | R74W;D1270N * | S341P | Y161D |
| E92K | G576A | L15P | R74W;V201M * | S364P | Y161S |
| E116K | G576A;R668C * | L165S | R74W;V201M;D1270N * | S492F | Y563N |
| E193K | G622D | L206W | R75Q | S549N | Y1014C |
| E403D | G628R | L320V | R117C | S549R | Y1032C |
| E474K | G970D | L346P | R117G | S589N | |
| E588V | G1061R | L453S | R117H | S737F | |
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics of elexacaftor, tezacaftor and ivacaftor are similar between healthy adult subjects and patients with CF. The pharmacokinetic parameters for elexacaftor, tezacaftor and ivacaftor in patients with CF aged 12 years and older are shown in Table 6.
| Elexacaftor | Tezacaftor | Ivacaftor | |
|---|---|---|---|
| AUCss: area under the concentration versus time curve at steady state; SD: Standard Deviation; Cmax: maximum observed concentration; Tmax: time of maximum concentration; AUC: area under the concentration versus time curve. | |||
|
|||
| General Information | |||
| AUCss (SD), mcg∙h/mL* | 162 (47.5)† | 89.3 (23.2)† | 11.7 (4.01)‡ |
| Cmax (SD), mcg/mL* | 9.2 (2.1) | 7.7 (1.7) | 1.2 (0.3) |
| Time to Steady State, days | Within 7 days | Within 8 days | Within 3-5 days |
| Accumulation Ratio | 2.2 | 2.07 | 2.4 |
| Absorption | |||
| Absolute Bioavailability | 80% | Not determined | Not determined |
| Median Tmax (range), hours | 6 (4 to 12) | 3 (2 to 4) | 4 (3 to 6) |
| Effect of Food | AUC increases 1.9- to 2.5-fold (moderate-fat meal) | No clinically significant effect | Exposure increases 2.5- to 4-fold |
| Distribution | |||
| Mean (SD) Apparent Volume of Distribution, L§ | 53.7 (17.7) | 82.0 (22.3) | 293 (89.8) |
| Protein Binding¶ | >99% | approximately 99% | approximately 99% |
| Elimination | |||
| Mean (SD) Effective Half-Life, hours# | 27.4 (9.31) | 25.1 (4.93) | 15.0 (3.92) |
| Mean (SD) Apparent Clearance, L/hours | 1.18 (0.29) | 0.79 (0.10) | 10.2 (3.13) |
| Metabolism | |||
| Primary Pathway | CYP3A4/5 | CYP3A4/5 | CYP3A4/5 |
| Active Metabolites | M23-ELX | M1-TEZ | M1-IVA |
| Metabolite Potency Relative to Parent | Similar | Similar | approximately 1/6th of parent |
| ExcretionÞ | |||
| Primary Pathway |
|
|
|
Specific Populations
Pediatric Patients 2 to Less Than 12 Years of Age
Elexacaftor, tezacaftor and ivacaftor exposures observed in patients aged 2 to less than 12 years as determined using population PK analysis are presented by age group and dose administered in Table 7. Elexacaftor, tezacaftor and ivacaftor exposures in this patient population are within the range observed in patients aged 12 years and older.
| Age Group | Dose | ElexacaftorAUC0-24h,ss
(µg∙h/mL) | Tezacaftor AUC0-24h,ss
(µg∙h/mL) | Ivacaftor AUC0-12h,ss
(µg∙h/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SD: Standard Deviation; AUCss: area under the concentration versus time curve at steady state. | ||||
| Patients aged 2 to less than 6 years weighing less than 14 kg (N = 16) | elexacaftor 80 mg qd/tezacaftor 40 mg qd/ivacaftor 60 mg qAM and ivacaftor 59.5 mg qPM | 128 (24.8) | 87.3 (17.3) | 11.9 (3.86) |
| Patients aged 2 to less than 6 years weighing 14 kg or more (N = 59) | elexacaftor 100 mg qd/tezacaftor 50 mg qd/ivacaftor 75 mg q12h | 138 (47.0) | 90.2 (27.9) | 13.0 (6.11) |
| Patients aged 6 to less than 12 years weighing less than 30 kg (N = 36) | elexacaftor 100 mg qd/tezacaftor 50 mg qd/ivacaftor 75 mg q12h | 116 (39.4) | 67.0 (22.3) | 9.78 (4.50) |
| Patients aged 6 to less than 12 years weighing 30 kg or more (N = 30) | elexacaftor 200 mg qd/ tezacaftor 100 mg qd/ ivacaftor 150 mg q12h | 195 (59.4) | 103 (23.7) | 17.5 (4.97) |
Drug Interaction Studies
Drug interaction studies were performed with elexacaftor, tezacaftor and/or ivacaftor and other drugs likely to be co-administered or drugs commonly used as probes for pharmacokinetic interaction studies [see Drug Interactions (7)].
Potential for Elexacaftor, Tezacaftor and/or Ivacaftor to Affect Other Drugs
Based on in vitro results, elexacaftor and tezacaftor have a low potential to inhibit CYP1A2, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6 and CYP3A4, whereas ivacaftor has the potential to inhibit CYP2C8, CYP2C9 and CYP3A. However, clinical studies showed that the combination regimen of tezacaftor/ivacaftor is not an inhibitor of CYP3A and ivacaftor is not an inhibitor of CYP2C8 or CYP2D6.
Based on in vitro results, elexacaftor, tezacaftor and ivacaftor are not likely to induce CYP3A, CYP1A2 and CYP2B6.
Based on in vitro results, elexacaftor and tezacaftor have a low potential to inhibit the transporter P-gp, while ivacaftor has the potential to inhibit P-gp. Co-administration of tezacaftor/ivacaftor with digoxin, a sensitive P-gp substrate, increased digoxin exposure by 1.3-fold in a clinical study. Based on in vitro results, elexacaftor and M23-ELX may inhibit OATP1B1 and OATP1B3 uptake. Tezacaftor has a low potential to inhibit BCRP, OCT2, OAT1, or OAT3. Ivacaftor is not an inhibitor of the transporters OCT1, OCT2, OAT1, or OAT3.
The effects of elexacaftor, tezacaftor and/or ivacaftor on the exposure of co-administered drugs are shown in Table 8 [see Drug Interactions (7)].
| Dose and Schedule | Effect on Other Drug PK | Geometric Mean Ratio (90% CI) of Other Drug No Effect=1.0 |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUC | Cmax | |||
| ↑ = increase, ↓ = decrease, ↔ = no change. CI = Confidence Interval; ELX= elexacaftor; TEZ = tezacaftor; IVA = ivacaftor; PK = Pharmacokinetics | ||||
|
||||
| Midazolam 2 mg single oral dose | TEZ 100 mg qd/IVA 150 mg q12h | ↔ Midazolam | 1.12 (1.01, 1.25) | 1.13 (1.01, 1.25) |
| Digoxin 0.5 mg single dose | TEZ 100 mg qd/IVA 150 mg q12h | ↑ Digoxin | 1.30 (1.17, 1.45) | 1.32 (1.07, 1.64) |
| Oral Contraceptive Ethinyl estradiol 30 µg/Levonorgestrel 150 µg qd | ELX 200 mg qd/TEZ 100 mg qd/IVA 150 mg q12h | ↑ Ethinyl estradiol* | 1.33 (1.20, 1.49) | 1.26 (1.14, 1.39) |
| ↑ Levonorgestrel* | 1.23 (1.10, 1.37) | 1.10 (0.985, 1.23) |
||
| Rosiglitazone 4 mg single oral dose | IVA 150 mg q12h | ↔ Rosiglitazone | 0.975 (0.897, 1.06) | 0.928 (0.858, 1.00) |
| Desipramine 50 mg single dose | IVA 150 mg q12h | ↔ Desipramine | 1.04 (0.985, 1.10) | 1.00 (0.939; 1.07) |
Potential for Other Drugs to Affect Elexacaftor, Tezacaftor and/or Ivacaftor
In vitro studies showed that elexacaftor, tezacaftor and ivacaftor are all metabolized by CYP3A. Exposure to elexacaftor, tezacaftor and ivacaftor may be reduced by concomitant CYP3A inducers and increased by concomitant CYP3A inhibitors.
In vitro studies showed that elexacaftor and tezacaftor are substrates for the efflux transporter P-gp, but ivacaftor is not. Elexacaftor and ivacaftor are not substrates for OATP1B1 or OATP1B3; tezacaftor is a substrate for OATP1B1, but not OATP1B3. Tezacaftor is a substrate for BCRP.
The effects of co-administered drugs on the exposure of elexacaftor, tezacaftor and/or ivacaftor are shown in Table 9 [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) and Drug Interactions (7)].
| Dose and Schedule | Effect on ELX, TEZ and/or IVA PK | Geometric Mean Ratio (90% CI) of Elexacaftor, Tezacaftor and Ivacaftor No Effect = 1.0 |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUC | Cmax | |||
| ↑ = increase, ↓ = decrease, ↔ = no change. CI = Confidence Interval; ELX= elexacaftor; TEZ = tezacaftor; IVA = ivacaftor; PK = Pharmacokinetics | ||||
|
||||
| Itraconazole 200 mg q12h on Day 1, followed by 200 mg qd | TEZ 25 mg qd + IVA 50 mg qd | ↑ Tezacaftor | 4.02 (3.71, 4.63) | 2.83 (2.62, 3.07) |
| ↑ Ivacaftor | 15.6 (13.4, 18.1) | 8.60 (7.41, 9.98) |
||
| Itraconazole 200 mg qd | ELX 20 mg + TEZ 50 mg single dose | ↑ Elexacaftor | 2.83 (2.59, 3.10) | 1.05 (0.977, 1.13) |
| ↑ Tezacaftor | 4.51 (3.85, 5.29) | 1.48 (1.33, 1.65) |
||
| Ketoconazole 400 mg qd | IVA 150 mg single dose | ↑ Ivacaftor | 8.45 (7.14, 10.0) | 2.65 (2.21, 3.18) |
| Ciprofloxacin 750 mg q12h | TEZ 50 mg q12h + IVA 150 mg q12h | ↔ Tezacaftor | 1.08 (1.03, 1.13) | 1.05 (0.99, 1.11) |
| ↑ Ivacaftor* | 1.17 (1.06, 1.30) | 1.18 (1.06, 1.31) |
||
| Rifampin 600 mg qd | IVA 150 mg single dose | ↓ Ivacaftor | 0.114 (0.097, 0.136) | 0.200 (0.168, 0.239) |
| Fluconazole 400 mg single dose on Day 1, followed by 200 mg qd | IVA 150 mg q12h | ↑ Ivacaftor | 2.95 (2.27, 3.82) | 2.47 (1.93, 3.17) |
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
14. Clinical Studies
14.1 Trial 1
Trial 1 evaluated 403 patients (200 TRIKAFTA, 203 placebo) with CF aged 12 years and older (mean age 26.2 years). The mean ppFEV1 at baseline was 61.4% (range: 32.3%, 97.1%). The primary endpoint assessed at the time of interim analysis was mean absolute change in ppFEV1 from baseline at Week 4. The final analysis tested all key secondary endpoints in the 403 patients who completed the 24-week study participation, including absolute change in ppFEV1 from baseline through Week 24; absolute change in sweat chloride from baseline at Week 4 and through Week 24; number of pulmonary exacerbations through Week 24; absolute change in BMI from baseline at Week 24, and absolute change in CFQ-R Respiratory Domain Score (a measure of respiratory symptoms relevant to patients with CF, such as cough, sputum production and difficulty breathing) from baseline at Week 4 and through Week 24.
Of the 403 patients included in the interim analysis, the treatment difference between TRIKAFTA and placebo for the mean absolute change from baseline in ppFEV1 at Week 4 was 13.8 percentage points (95% CI: 12.1, 15.4; P<0.0001).
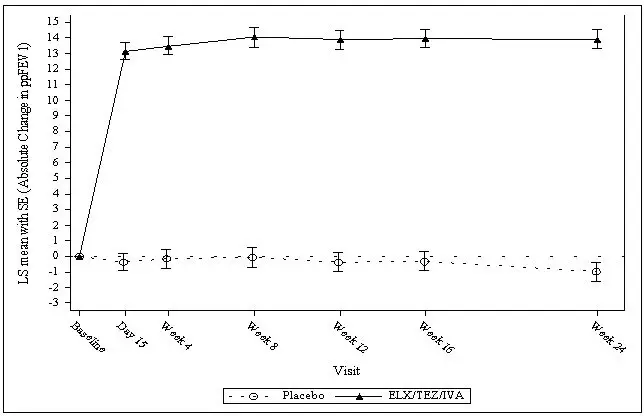
The treatment difference between TRIKAFTA and placebo for mean absolute change in ppFEV1 from baseline through Week 24 was 14.3 percentage points (95% CI: 12.7, 15.8; P<0.0001). Mean improvement in ppFEV1 was observed at the first assessment on Day 15 and sustained through the 24-week treatment period (see Figure 1). Improvements in ppFEV1 were observed regardless of age, baseline ppFEV1, sex and geographic region. See Table 10 for a summary of primary and key secondary outcomes in Trial 1.
| Analysis | Statistic | Treatment Difference* for TRIKAFTA (N=200) vs Placebo (N=203) |
|---|---|---|
| ppFEV1: percent predicted Forced Expiratory Volume in 1 second; CI: Confidence Interval; CFQ-R: Cystic Fibrosis Questionnaire-Revised; BMI: Body Mass Index. | ||
|
||
| Primary (Interim Full Analysis Set)† | ||
| Absolute change in ppFEV1 from baseline at Week 4 (percentage points) | Treatment difference (95% CI) P value | 13.8 (12.1, 15.4) P<0.0001 |
| Key Secondary (Full Analysis Set)‡ | ||
| Absolute change in ppFEV1 from baseline through Week 24 (percentage points) | Treatment difference (95% CI) P value | 14.3 (12.7, 15.8) P<0.0001 |
| Number of pulmonary exacerbations from baseline through Week 24§¶ | Rate ratio (95% CI) P value | 0.37 (0.25, 0.55) P<0.0001 |
| Absolute change in sweat chloride from baseline through Week 24 (mmol/L) | Treatment difference (95% CI) P value | -41.8 (-44.4, -39.3) P<0.0001 |
| Absolute change in CFQ-R respiratory domain score from baseline through Week 24 (points) | Treatment difference (95% CI) P value | 20.2 (17.5, 23.0) P<0.0001 |
| Absolute change in BMI from baseline at Week 24 (kg/m2) | Treatment difference (95% CI) P value | 1.04 (0.85, 1.23) P<0.0001 |
| Absolute change in sweat chloride from baseline at Week 4 (mmol/L) | Treatment difference (95% CI) P value | -41.2 (-44.0, -38.5) P<0.0001 |
| Absolute change in CFQ-R respiratory domain score from baseline at Week 4 (points) | Treatment difference (95% CI) P value | 20.1 (16.9, 23.2) P<0.0001 |
Figure 1: Absolute Change from Baseline in Percent Predicted FEV1 at Each Visit in Trial 1
14.2 Trial 2
Trial 2 evaluated 107 patients with CF aged 12 years and older (mean age 28.4 years). The mean ppFEV1 at baseline, following the 4-week, open-label run-in period with tezacaftor/ivacaftor was 60.9% (range: 35.0%, 89.0%). The primary endpoint was mean absolute change in ppFEV1 from baseline at Week 4 of the double-blind treatment period. The key secondary efficacy endpoints were absolute change in sweat chloride and CFQ-R Respiratory Domain Score from baseline at Week 4. Treatment with TRIKAFTA compared to tezacaftor/ivacaftor resulted in a statistically significant improvement in ppFEV1 of 10.0 percentage points (95% CI: 7.4, 12.6; P<0.0001). Mean improvement in ppFEV1 was observed at the first assessment on Day 15. Improvements in ppFEV1 were observed regardless of age, sex, baseline ppFEV1 and geographic region. See Table 11 for a summary of primary and key secondary outcomes.
| Analysis* | Statistic | Treatment Difference for TRIKAFTA (N=55) vs Tezacaftor/Ivacaftor† (N=52) |
|---|---|---|
| ppFEV1: percent predicted Forced Expiratory Volume in 1 second; CI: Confidence Interval; CFQ-R: Cystic Fibrosis Questionnaire-Revised. | ||
|
||
| Primary | ||
| Absolute change in ppFEV1 from baseline at Week 4 (percentage points) | Treatment difference (95% CI) P value | 10.0 (7.4, 12.6) P<0.0001 |
| Key Secondary | ||
| Absolute change in sweat chloride from baseline at Week 4 (mmol/L) | Treatment difference (95% CI) P value | -45.1 (-50.1, -40.1) P<0.0001 |
| Absolute change in CFQ-R respiratory domain score from baseline at Week 4 (points) | Treatment difference (95% CI) P value | 17.4 (11.8, 23.0) P<0.0001 |
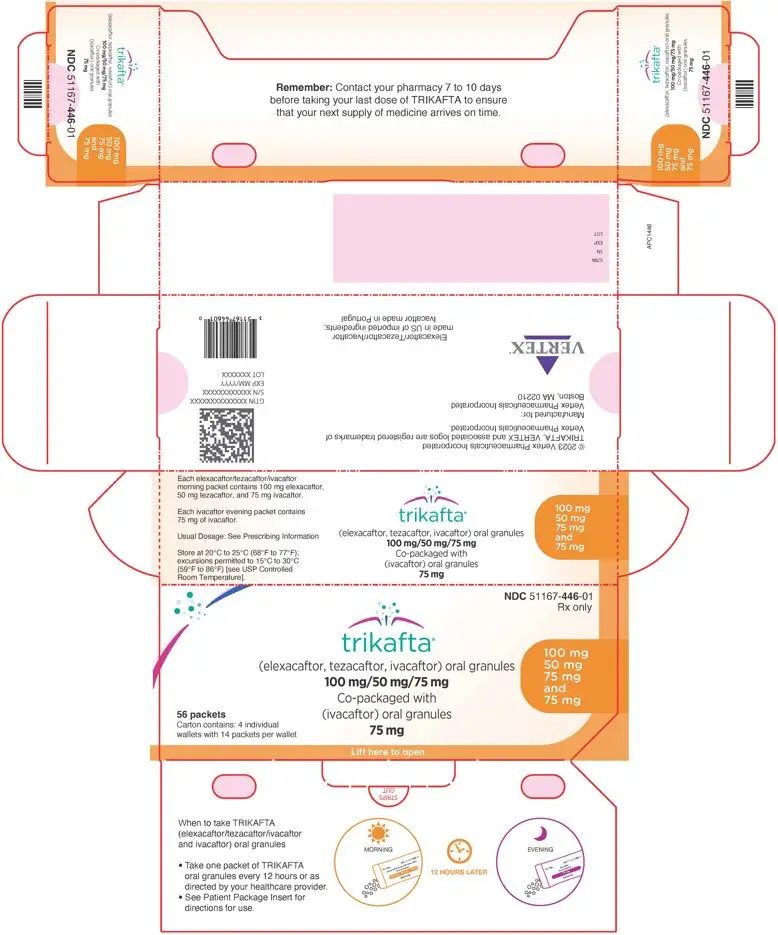
16. How is Trikafta supplied
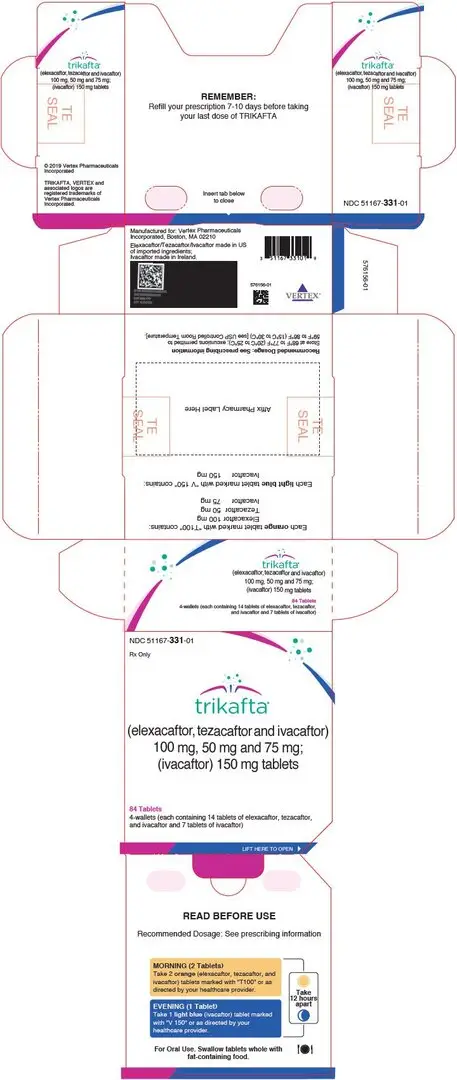
TRIKAFTA tablets are supplied in a co-packaged blister pack sealed into a printed wallet, containing elexacaftor, tezacaftor and ivacaftor fixed-dose combination tablets and ivacaftor tablets. Four such wallets are placed in a printed outer carton.
- The elexacaftor 50 mg, tezacaftor 25 mg, and ivacaftor 37.5 mg tablets are supplied as light orange, capsule-shaped tablets; each containing 50 mg of elexacaftor, 25 mg of tezacaftor and 37.5 mg of ivacaftor. Each tablet is debossed with "T50" on one side and plain on the other. Ivacaftor 75 mg tablets are supplied as light blue, film-coated, capsule-shaped tablets; each containing 75 mg of ivacaftor. Each tablet is printed with the characters "V 75" in black ink on one side and plain on the other. TRIKAFTA is supplied as:
84-count tablet carton
(4 wallets, each wallet containing 14 tablets of elexacaftor, tezacaftor and ivacaftor and 7 tablets of ivacaftor)NDC 51167-106-02 - The elexacaftor 100 mg, tezacaftor 50 mg, and ivacaftor 75 mg tablets are supplied as orange, capsule-shaped tablets; each containing 100 mg of elexacaftor, 50 mg of tezacaftor and 75 mg of ivacaftor. Each tablet is debossed with "T100" on one side and plain on the other. Ivacaftor 150 mg tablets are supplied as light blue, film-coated, capsule-shaped tablets; each containing 150 mg of ivacaftor. Each tablet is printed with the characters "V 150" in black ink on one side and plain on the other. TRIKAFTA is supplied as:
84-count tablet carton
(4 wallets, each wallet containing 14 tablets of elexacaftor, tezacaftor and ivacaftor and 7 tablets of ivacaftor)NDC 51167-331-01
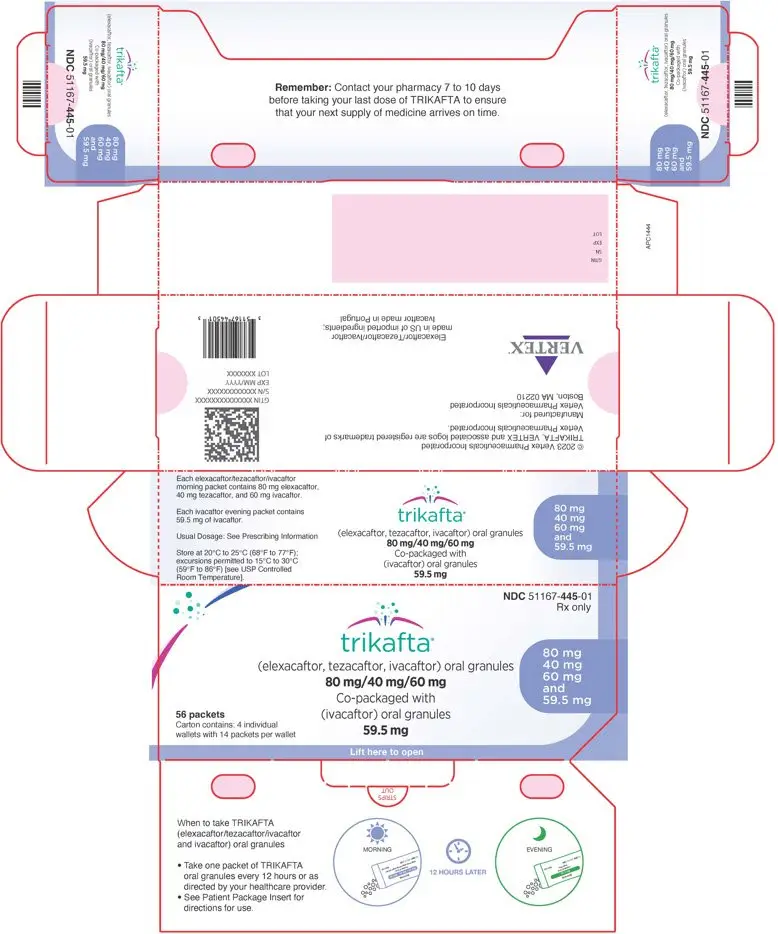
TRIKAFTA oral granules are supplied in morning and evening unit-dose packets. The morning dose packets contain a fixed-dose combination of elexacaftor, tezacaftor, and ivacaftor oral granules. The evening dose packets contain ivacaftor oral granules. The packets are placed into a printed wallet. Four such wallets are placed in a printed outer carton.
- The elexacaftor 80 mg, tezacaftor 40 mg and ivacaftor 60 mg oral granules are supplied as white to off-white, sweetened, unflavored granules approximately 2 mm in diameter enclosed in unit-dose packets each containing 80 mg of elexacaftor, 40 mg of tezacaftor and 60 mg of ivacaftor. The packets are white and blue. The ivacaftor 59.5 mg oral granules are supplied as white to off-white, sweetened, unflavored granules approximately 2 mm in diameter enclosed in unit-dose packets each containing 59.5 mg of ivacaftor. The packets are white and green. TRIKAFTA is supplied as:
56-count packet carton
(4 wallets, each containing 7 packets of elexacaftor, tezacaftor, and ivacaftor and 7 packets of ivacaftor)NDC 51167-445-01 - The elexacaftor 100 mg, tezacaftor 50 mg and ivacaftor 75 mg oral granules are supplied as white to off-white, sweetened, unflavored granules approximately 2 mm in diameter enclosed in unit-dose packets each containing 100 mg of elexacaftor, 50 mg of tezacaftor and 75 mg of ivacaftor. The packets are white and orange. The ivacaftor 75 mg oral granules are supplied as white to off-white, sweetened, unflavored granules approximately 2 mm in diameter enclosed in unit-dose packets each containing 75 mg of ivacaftor. The packets are white and pink. TRIKAFTA is supplied as:
56-count packet carton
(4 wallets, each containing 7 packets of elexacaftor, tezacaftor, and ivacaftor and 7 packets of ivacaftor)NDC 51167-446-01
| TRIKAFTA
elexacaftor, tezacaftor, and ivacaftor kit |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TRIKAFTA
elexacaftor, tezacaftor, and ivacaftor kit |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TRIKAFTA
elexacaftor, tezacaftor, and ivacaftor kit |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| TRIKAFTA
elexacaftor, tezacaftor, and ivacaftor kit |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Vertex Pharmaceuticals Incorporated (602478257) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shanghai SynTheAll Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. | 545342792 | API MANUFACTURE(51167-331, 51167-106, 51167-445, 51167-446) , ANALYSIS(51167-331, 51167-106, 51167-445, 51167-446) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hovione Limited | 985003840 | MANUFACTURE(51167-331, 51167-106, 51167-445, 51167-446) , ANALYSIS(51167-331, 51167-106, 51167-445, 51167-446) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| F.I.S. Fabbrica Italiana Sintetici S.P.A. | 431189117 | API MANUFACTURE(51167-331, 51167-106, 51167-445, 51167-446) , ANALYSIS(51167-331, 51167-106, 51167-445, 51167-446) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Almac Sciences Limited | 232665666 | ANALYSIS(51167-331, 51167-445, 51167-446) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hovione LLC | 038153735 | MANUFACTURE(51167-331) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Catalent Greenville, Inc. | 118812386 | ANALYSIS(51167-445, 51167-446) , MANUFACTURE(51167-445, 51167-446) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| EMSL Analytical Inc. dba MPL Laboratories | 080265475 | ANALYSIS(51167-445, 51167-446) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Eurofins Lancaster Laboratories, Inc. | 069777290 | ANALYSIS(51167-445, 51167-446) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Halo Pharmaceutical Inc | 829609168 | ANALYSIS(51167-446, 51167-445) , MANUFACTURE(51167-446, 51167-445) , LABEL(51167-446, 51167-445) , PACK(51167-446, 51167-445) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Research Services, Inc. | 836225649 | MANUFACTURE(51167-446, 51167-445) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Almac Pharma Services LLC | 078607239 | PACK(51167-446, 51167-445) , LABEL(51167-446, 51167-445) | |