Drug Detail:Vimovo (Esomeprazole and naproxen [ ee-soe-mep-ra-zole-and-na-prox-en ])
Drug Class: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
Highlights of Prescribing Information
VIMOVO® (naproxen and esomeprazole magnesium) delayed-release tablets, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2010
WARNING: RISK OF SERIOUS CARDIOVASCULAR AND GASTROINTESTINAL EVENTS
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) cause an increased risk of serious cardiovascular thrombotic events, including myocardial infarction and stroke, which can be fatal. This risk may occur early in treatment and may increase with duration of use. (5.1)
- VIMOVO is contraindicated in the setting of coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery. (4, 5.1)
- NSAIDs, including naproxen, a component of VIMOVO, cause an increased risk of serious gastrointestinal (GI) adverse events including bleeding, ulceration, and perforation of the stomach or intestines, which can be fatal. These events can occur at any time during use and without warning symptoms. Elderly patients and patients with a prior history of peptic ulcer disease and/or GI bleeding are at greater risk for serious GI events. (5.2)
Indications and Usage for Vimovo
VIMOVO is a combination of naproxen, a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID), and esomeprazole magnesium, a proton pump inhibitor (PPI) indicated in adult and adolescent patients 12 years of age and older weighing at least 38 kg, requiring naproxen for symptomatic relief of arthritis and esomeprazole magnesium to decrease the risk of developing naproxen-associated gastric ulcers.
The naproxen component of VIMOVO is indicated for relief of signs and symptoms of:
- osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis in adults.
- juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) in adolescent patients.
The esomeprazole magnesium component of VIMOVO is indicated to decrease the risk of developing naproxen-associated gastric ulcers. (1)
Limitations of Use:
- Do not substitute VIMOVO with the single-ingredient products of naproxen and esomeprazole magnesium. (1)
- VIMOVO is not recommended for initial treatment of acute pain because the absorption of naproxen is delayed compared to absorption from other naproxen-containing products. (1)
- Controlled studies do not extend beyond 6 months. (1)
Vimovo Dosage and Administration
Administration
- Use the lowest naproxen dose for the shortest duration consistent with individual patient treatment goals. (2.1, 5.1).
- If a total daily dose of less than 40 mg esomeprazole is more appropriate, a different treatment should be considered. (2.1)
- Swallow VIMOVO tablets whole with liquid at least 30 minutes before meals. (2.1)
Recommended Dosage (2.2)
Adolescents 12 years of age and older weighing 38 kg to less than 50 kg:
One VIMOVO tablet twice daily of 375 mg naproxen/20 mg of esomeprazole
Adults and adolescents 12 years of age and older greater than 50 kg:
One VIMOVO tablet twice daily of either:
- 375 mg naproxen/20 mg of esomeprazole; or
- 500 mg of naproxen/20 mg of esomeprazole
Renal or Hepatic Impairment (2.3)
- Avoid in moderate/severe renal impairment or severe hepatic impairment.
- Consider dose reduction in mild/moderate hepatic impairment.
Dosage Forms and Strengths
VIMOVO delayed-release tablets (3):
- 375 mg enteric-coated naproxen /20 mg immediate-release esomeprazole
- 500 mg enteric-coated naproxen /20 mg immediate-release esomeprazole.
Contraindications
- Known hypersensitivity to naproxen, esomeprazole magnesium, substituted benzimidazoles, or to any components of the drug product including omeprazole. (4)
- History of asthma, urticaria, or other allergic-type reactions after taking aspirin or other NSAIDs. (4)
- In the setting of coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery. (4)
- In patients receiving rilpivirine-containing products. (4, 7)
Warnings and Precautions
- Hepatotoxicity: Inform patients of warning signs and symptoms of hepatotoxicity. Discontinue if abnormal liver tests persist or worsen or if clinical signs and symptoms of liver disease develop. (5.3)
- Hypertension: Patients taking some antihypertensive medications may have impaired response to these therapies when taking NSAIDs. Monitor blood pressure. (5.4, 7)
- Heart Failure and Edema: Avoid use of VIMOVO in patients with severe heart failure unless benefits are expected to outweigh risk of worsening heart failure. (5.5)
- Renal Toxicity: Monitor renal function in patients with renal or hepatic impairment, heart failure, dehydration, or hypovolemia. Avoid use of VIMOVO in patients with advanced renal disease unless benefits are expected to outweigh risk of worsening renal function. (5.6)
- Anaphylactic Reactions: Seek emergency help if an anaphylactic reaction occurs. (5.7)
- Exacerbation of Asthma Related to Aspirin Sensitivity: VIMOVO is contraindicated in patients with aspirin-sensitive asthma. Monitor patients with preexisting asthma (without aspirin sensitivity). (5.8)
- Serious Skin Reactions: Discontinue VIMOVO at first appearance of skin rash or other signs of hypersensitivity. (5.9)
- Premature Closure of Ductus Arteriosus: Avoid use in pregnant women starting at 30 weeks gestation. (5.10, 8.1)
- Hematologic Toxicity: Monitor hemoglobin or hematocrit in patients with any signs of symptoms of anemia. (5.11, 7)
- Masking of Inflammation and Fever: Potential for diminished utility of diagnostic signs in detecting infections. (5.12)
- Laboratory Monitoring: Obtain CBC and chemistry profile periodically during treatment. Monitor hemoglobin periodically in patients on long-term treatment who have an initial value of 10 g or less. (5.13)
- Active Bleeding: Withdraw treatment in patients who experience active and clinically significant bleeding. (5.14)
- Concomitant NSAID Use: Do not use VIMOVO with other naproxen-containing products or other non-aspirin NSAIDs. (5.15)
- Gastric Malignancy: In adults, symptomatic response to esomeprazole does not preclude the presence of gastric malignancy. Consider additional follow-up and diagnostic testing. (5.16)
- Acute Interstitial Nephritis: Observed in patients taking PPIs. (5.17)
- Clostridium difficile-Associated Diarrhea: PPI therapy may be associated with increased risk of Clostridium difficile associated diarrhea. (5.18)
- Bone Fracture: Long-term and multiple daily dose PPI therapy may be associated with an increased risk for osteoporosis-related fractures of the hip, wrist or spine. (5.19)
- Cutaneous and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Mostly cutaneous, new onset or exacerbation of existing disease; discontinue VIMOVO and refer to specialist for evaluation. (5.20)
- Interaction with Clopidogrel: Avoid concomitant use. (5.21, 7)
- Cyanocobalamin (Vitamin B-12) Deficiency: Daily long-term use (e.g., longer than 3 years) may lead to malabsorption or a deficiency of cyanocobalamin. (5.22)
- Hypomagnesemia: Reported rarely with prolonged treatment with PPIs. (5.23)
- Interaction with St. John's Wort or Rifampin: Avoid concomitant use. (5.24, 7)
- Interactions with Diagnostic Investigations for Neuroendocrine Tumors: Increases in intragastric pH may result in hypergastrinemia, enterochromaffin-like cell hyperplasia, and increased Chromogranin A levels which may interfere with diagnostic investigations for neuroendocrine tumors. (5.25)
- Interaction with Methotrexate: Concomitant use with PPIs may elevate and/or prolong serum concentrations of methotrexate and/or its metabolite, possibly leading to toxicity. (5.26, 7)
- Fundic Gland Polyps: Risk increases with long-term PPI use, especially beyond one year. Use the shortest duration of therapy. (5.27)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Most common adverse reactions in clinical trials (>5%) are gastritis and diarrhea. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Horizon Pharma USA, Inc. at 1-866-479-6742 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
See full prescribing information for a list of clinically important drug interactions. (7)
Use In Specific Populations
- Pregnancy: Use of NSAIDs during the third trimester of pregnancy increases the risk of premature closure of the fetal ductus arteriosus. Avoid use of NSAIDs in pregnant women starting at 30 weeks gestation. (5.10, 8.1)
- Females and Males of Reproductive Potential: NSAIDs are associated with reversible infertility. Consider withdrawal of VIMOVO in women who have difficulties conceiving. (8.3)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 7/2019
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Vimovo
VIMOVO, a combination of naproxen and esomeprazole magnesium, is indicated in adult and adolescent patients 12 years of age and older weighing at least 38 kg, requiring naproxen for symptomatic relief of arthritis and esomeprazole magnesium to decrease the risk for developing naproxen-associated gastric ulcers.
The naproxen component of VIMOVO is indicated for relief of signs and symptoms of:
- osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis in adults.
- juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) in adolescent patients.
The esomeprazole magnesium component of VIMOVO is indicated to decrease the risk of developing naproxen-associated gastric ulcers.
2. Vimovo Dosage and Administration
2.1 Important Administration Instructions
- Use the lowest naproxen dose for the shortest duration consistent with individual patient treatment goals [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- Carefully consider the potential benefits and risks of VIMOVO and other treatment options before deciding to use VIMOVO.
- VIMOVO does not allow for administration of a lower daily dose of esomeprazole magnesium. If a total daily dose of less than 40 mg esomeprazole is more appropriate, a different treatment should be considered.
- Swallow VIMOVO tablets whole with liquid. Do not split, chew, crush or dissolve the tablet. Take VIMOVO at least 30 minutes before meals.
- Patients should be instructed that if a dose is missed, it should be taken as soon as possible. However, if the next scheduled dose is due, the patient should not take the missed dose, and should be instructed to take the next dose on time. Patients should be instructed not to take 2 doses at one time to make up for a missed dose.
- Antacids may be used while taking VIMOVO.
2.2 Recommended Dosage
The recommended dosage of VIMOVO by indication is shown in the table:
| Indication | Patient Population | Recommended Dosage |
|---|---|---|
| Rheumatoid Arthritis, Osteoarthritis, and Ankylosing Spondylitis | Adults | One VIMOVO tablet twice daily of either: 375 mg naproxen/20 mg of esomeprazole; or 500 mg naproxen/20 mg of esomeprazole |
| Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis in Adolescent Patients 12 Years of Age and Older and Weighing at Least 38 kg | Greater than 50 kg | |
| 38 kg to less than 50 kg | One VIMOVO tablet twice daily of: 375 mg naproxen/20 mg of esomeprazole |
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
VIMOVO is an oval, yellow, delayed-release tablets for oral administration containing either:
- 375 mg enteric-coated naproxen and 20 mg immediate-release esomeprazole tablets printed with 375/20 in black, or
- 500 mg enteric-coated naproxen and 20 mg immediate-release esomeprazole tablets printed with 500/20 in black.
4. Contraindications
VIMOVO is contraindicated in the following patients:
- Known hypersensitivity (e.g., anaphylactic reactions and serious skin reactions) to naproxen, esomeprazole magnesium, substituted benzimidazoles, or to any components of the drug product, including omeprazole. Hypersensitivity reactions to esomeprazole may include anaphylaxis, anaphylactic shock, angioedema, bronchospasm, acute interstitial nephritis, and urticaria [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7, 5.8, 5.9, 5.17), Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
- History of asthma, urticaria, or allergic-type reactions after taking aspirin or other NSAIDs. Severe, sometimes fatal, anaphylactic reactions to NSAIDs have been reported in such patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7, 5.8)].
- In the setting of coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), including esomeprazole magnesium, are contraindicated in patients receiving rilpivirine-containing products [see Drug Interactions (7)].
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Cardiovascular Thrombotic Events
Clinical trials of several COX-2 selective and nonselective NSAIDs of up to three years duration have shown an increased risk of serious cardiovascular (CV) thrombotic events, including myocardial infarction (MI), and stroke, which can be fatal. Based on available data, it is unclear that the risk for CV thrombotic events is similar for all NSAIDS. The relative increase in serious CV thrombotic events over baseline conferred by NSAID use appears to be similar in those with and without known CV disease or risk factors for CV disease. However, patients with known CV disease or risk factors had a higher absolute incidence of excess serious CV thrombotic events, due to their increased baseline rate. Some observational studies found that this increased risk of serious CV thrombotic events began as early as the first weeks of treatment. The increase in CV thrombotic risk has been observed most consistently at higher doses.
To minimize the potential risk for an adverse CV event in NSAID-treated patients, use the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration possible. Physicians and patients should remain alert for the development of such events, throughout the entire treatment course, even in the absence of previous CV symptoms. Patients should be informed about the symptoms of serious CV events and the steps to take if they occur.
There is no consistent evidence that concurrent use of aspirin mitigates the increased risk of serious CV thrombotic events associated with NSAID use. The concurrent use of aspirin and an NSAID, such as naproxen, increases the risk of serious gastrointestinal (GI) events [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
5.2 Gastrointestinal Bleeding, Ulceration, and Perforation
NSAIDs, including naproxen, can cause serious gastrointestinal (GI) adverse events including inflammation, bleeding, ulceration, and perforation of the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, or large intestine, which can be fatal. These serious adverse events can occur at any time, with or without warning symptoms, in patients treated with NSAIDs. Only one in five patients who develop a serious upper GI adverse event on NSAID therapy is symptomatic. Upper GI ulcers, gross bleeding, or perforation caused by NSAIDs occurred in approximately 1% of patients treated for 3-6 months, and in about 2% to 4% of patients treated for one year. However, even short-term NSAID therapy is not without risk.
5.3 Hepatotoxicity
Elevations of ALT or AST (three or more times the upper limit of the normal [ULN]) have been reported in approximately 1% of NSAID-treated patients in clinical trials. In addition, rare, and sometimes fatal, cases of severe hepatic injury, including jaundice and fatal fulminant hepatitis, liver necrosis, and hepatic failure have been reported.
Elevations of ALT or AST (less than three times ULN) may occur in up to 15% of patients treated with NSAIDs including naproxen.
Inform patients of the warning signs and symptoms of hepatotoxicity (e.g., nausea, fatigue, lethargy, diarrhea, pruritus, jaundice, right upper quadrant tenderness, and "flu-like" symptoms). If clinical signs and symptoms consistent with liver disease develop, or if systemic manifestations occur (e.g., eosinophilia, rash, etc.), discontinue VIMOVO immediately, and perform a clinical evaluation of the patient.
VIMOVO should be avoided in patients with severe hepatic impairment [see Dosage and Administration (2), Use in Specific Populations (8.6), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
5.4 Hypertension
NSAIDs, including VIMOVO, can lead to new onset of hypertension or worsening of pre-existing hypertension, either of which may contribute to the increased incidence of CV events.
Patients taking angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, thiazides diuretics, or loop diuretics may have impaired response to these therapies when taking NSAIDs [see Drug Interactions (7)].
Monitor blood pressure (BP) during the initiation of NSAID treatment and throughout the course of therapy.
5.5 Heart Failure and Edema
The Coxib and traditional NSAID Trialists' Collaboration meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials demonstrated an approximately two-fold increase in hospitalizations for heart failure in COX-2 selective treated patients and nonselective NSAID-treated patients compared to placebo-treated patients. In a Danish National Registry study of patients with heart failure, NSAID use increased the risk of MI, hospitalization for heart failure, and death.
Additionally, fluid retention and edema have been observed in some patients treated with NSAIDs. Use of naproxen may blunt the CV effects of several therapeutic agents used to treat these medical conditions (e.g., diuretics, ACE inhibitors, or angiotensin receptor blockers [ARBs]) [see Drug Interactions (7)].
Avoid the use of VIMOVO in patients with severe heart failure unless the benefits are expected to outweigh the risk of worsening heart failure. If VIMOVO is used in patients with severe heart failure, monitor patients for signs and symptoms of worsening heart failure.
5.7 Anaphylactic Reactions
Naproxen has been associated with anaphylactic reactions in patients with and without known hypersensitivity to naproxen and in patients with aspirin-sensitive asthma [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
Seek emergency help if an anaphylactic reaction occurs.
5.8 Exacerbation of Asthma Related to Aspirin Sensitivity
A subpopulation of patients with asthma may have aspirin-sensitive asthma which may include chronic rhinosinusitis complicated by nasal polyps; severe, potentially fatal bronchospasm; and/or intolerance to aspirin and other NSAIDs. Because cross-reactivity between aspirin and other NSAIDs has been reported in such aspirin-sensitive patients, VIMOVO is contraindicated in patients with this form of aspirin sensitivity [see Contraindications (4)]. When VIMOVO is used in patients with preexisting asthma (without known aspirin sensitivity), monitor patients for changes in the signs and symptoms of asthma.
5.9 Serious Skin Reactions
NSAIDs, including naproxen, can cause serious skin adverse events such as exfoliative dermatitis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS), and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), which can be fatal. These serious events may occur without warning. Inform patients about the signs and symptoms of serious skin reactions, and to discontinue the use of VIMOVO at the first appearance of skin rash or any other sign of hypersensitivity. VIMOVO is contraindicated in patients with previous serious skin reactions to NSAIDs [see Contraindications (4)].
5.10 Premature Closure of Fetal Ductus Arteriosus
Naproxen may cause premature closure of the fetal ductus arteriosus. Avoid use of NSAIDs, including VIMOVO, in pregnant women starting at 30 weeks of gestation (third trimester) [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
5.11 Hematologic Toxicity
Anemia has occurred in NSAID-treated patients. This may be due to occult or gross blood loss, fluid retention, or an incompletely described effect on erythropoiesis. If a patient treated with VIMOVO has any signs or symptoms of anemia, monitor hemoglobin or hematocrit.
NSAIDs, including VIMOVO, may increase the risk of bleeding events. Co-morbid conditions such as coagulation disorders or concomitant use of warfarin and other anticoagulants, antiplatelet agents (e.g., aspirin), and serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) may increase the risk. Monitor these patients for signs of bleeding [see Drug Interactions (7)].
5.12 Masking of Inflammation and Fever
The pharmacological activity of VIMOVO in reducing inflammation, and possibly fever, may diminish the utility of diagnostic signs in detecting infections.
5.13 Laboratory Monitoring
Because serious GI bleeding, hepatotoxicity, and renal injury can occur without warning symptoms or signs, consider monitoring patients on long-term NSAID treatment with a CBC and chemistry profile periodically [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2, 5.3, 5.6)].
Patients with initial hemoglobin values of 10 g or less who are to receive long-term therapy should have hemoglobin values determined periodically.
5.14 Active Bleeding
When active and clinically significant bleeding from any source occurs in patients receiving VIMOVO, the treatment should be withdrawn.
5.15 Concomitant NSAID Use
VIMOVO contains naproxen as one of its active ingredients. It should not be used with other naproxen-containing products since they all circulate in the plasma as the naproxen anion.
The concomitant use of VIMOVO with any dose of a non-aspirin NSAID should be avoided due to the potential for increased risk of adverse reactions.
5.16 Presence of Gastric Malignancy
In adults, response to gastric symptoms with VIMOVO does not preclude the presence of gastric malignancy. Consider additional gastrointestinal follow-up and diagnostic testing in adult patients who experience gastric symptoms during treatment with VIMOVO or have a symptomatic relapse after completing treatment. In older patients, also consider an endoscopy.
5.17 Acute Interstitial Nephritis
Acute interstitial nephritis has been observed in patients taking PPIs including VIMOVO. Acute interstitial nephritis may occur at any point during PPI therapy and is generally attributed to an idiopathic hypersensitivity reaction. Discontinue VIMOVO if acute interstitial nephritis develops [see Contraindications (4)].
5.18 Clostridium difficile-Associated Diarrhea
Published observational studies suggest that proton pump inhibitor (PPI) therapy like VIMOVO may be associated with an increased risk of Clostridium difficile associated diarrhea, especially in hospitalized patients. This diagnosis should be considered for diarrhea that does not improve [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
Patients should use the lowest dose and shortest duration of PPI therapy appropriate to the condition being treated [see Dosage and Administration (2)].
5.19 Bone Fracture
Several published observational studies suggest that PPI therapy may be associated with an increased risk for osteoporosis-related fractures of the hip, wrist, or spine. The risk of fracture was increased in patients who received high-dose, defined as multiple daily doses, and long-term PPI therapy (a year or longer). Patients should use the lowest dose and shortest duration of PPI therapy appropriate to the condition being treated. Patients at risk for osteoporosis-related fractures should be managed according to the established treatment guidelines [see Dosage and Administration (2), Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
VIMOVO (a combination PPI/NSAID) is approved for use twice a day and does not allow for administration of a lower daily dose of the PPI [see Dosage and Administration (2)].
5.20 Cutaneous and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Cutaneous lupus erythematosus (CLE) and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) have been reported in patients taking PPIs, including esomeprazole. These events have occurred as both new onset and an exacerbation of existing autoimmune disease. The majority of PPI-induced lupus erythematous cases were CLE.
The most common form of CLE reported in patients treated with PPIs was subacute CLE (SCLE) and occurred within weeks to years after continuous drug therapy inpatients ranging from infants to the elderly. Generally, histological findings were observed without organ involvement.
SLE is less commonly reported than CLE in patients receiving PPIs. PPI associated SLE is usually milder than non-drug induced SLE. Onset of SLE typically occurred within days to years after initiating treatment primarily in patients ranging from young adults to the elderly. The majority of patients presented with rash; however, arthralgia and cytopenia were also reported.
Avoid administration of PPIs for longer than medically indicated. If signs or symptoms consistent with CLE or SLE are noted in patients receiving VIMOVO, discontinue drug and refer the patient to the appropriate specialist for evaluation. Most patients improve with discontinuation of the PPI alone in 4 to 12 weeks. Serological testing (e.g., ANA) may be positive and elevated serological test results may take longer to resolve than clinical manifestations.
5.21 Interaction with Clopidogrel
Avoid concomitant use of esomeprazole with clopidogrel. Clopidogrel is a prodrug. Inhibition of platelet aggregation by clopidogrel is entirely due to an active metabolite. The metabolism of clopidogrel to its active metabolite can be impaired by use with concomitant medications, such as esomeprazole, that inhibit CYP2C19 activity. Concomitant use of clopidogrel with 40 mg esomeprazole reduces the pharmacological activity of clopidogrel. When using esomeprazole, a component of VIMOVO, consider alternative anti-platelet therapy [see Drug Interactions (7), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
5.22 Cyanocobalamin (Vitamin B-12) Deficiency
Daily treatment with any acid-suppressing medications over a long period of time (e.g., longer than 3 years) may lead to malabsorption of cyanocobalamin (vitamin B-12) caused by hypo-or achlorhydria. Rare reports of cyanocobalamin deficiency occurring with acid-suppressing therapy have been reported in the literature. This diagnosis should be considered if clinical symptoms consistent with cyanocobalamin deficiency are observed.
5.23 Hypomagnesemia
Hypomagnesemia, symptomatic and asymptomatic, has been reported rarely in patients treated with PPIs for at least three months, in most cases after a year of therapy. Serious adverse events include tetany, arrhythmias, and seizures. In most patients, treatment of hypomagnesemia required magnesium replacement and discontinuation of the PPI.
For patients expected to be on prolonged treatment or who take PPIs with medications such as digoxin or drugs that may cause hypomagnesemia (e.g., diuretics), health care professionals may consider monitoring magnesium levels prior to initiation of PPI treatment and periodically [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
5.24 Concomitant use of St. John's Wort or Rifampin with VIMOVO
Drugs that induce CYP2C19 or CYP3A4 (such as St. John's Wort or rifampin) can substantially decrease esomeprazole concentrations. Avoid concomitant use of VIMOVO with St. John's Wort or rifampin [see Drug Interactions (7)].
5.25 Interactions with Diagnostic Investigations for Neuroendocrine Tumors
Serum chromogranin A (CgA) levels increase secondary to drug-induced decreases in gastric acidity. The increased CgA level may cause false positive results in diagnostic investigations for neuroendocrine tumors. Providers should temporarily stop esomeprazole treatment at least 14 days before assessing CgA levels and consider repeating the test if initial CgA levels are high. If serial tests are performed (e.g. for monitoring), the same commercial laboratory should be used for testing, as reference ranges between tests may vary [see Drug Interactions (7), Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)].
5.26 Concomitant Use of VIMOVO with Methotrexate
Literature suggests that concomitant use of PPIs with methotrexate (primarily at high dose; see methotrexate prescribing information) may elevate and prolong serum levels of methotrexate and/or its metabolite, possibly leading to methotrexate toxicities. In high-dose methotrexate administration a temporary withdrawal of the PPI may be considered in some patients [see Drug Interactions (7)].
5.27 Fundic Gland Polyps
PPI use is associated with an increased risk of fundic gland polyps that increases with long–term use, especially beyond one year. Most PPI users who developed fundic gland polyps were asymptomatic and fundic gland polyps were identified incidentally on endoscopy. Use the shortest duration of PPI therapy appropriate to the condition being treated.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the labeling:
- Cardiovascular Thrombotic Events [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- GI Bleeding, Ulceration and Perforations [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Hypertension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Heart Failure and Edema [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Renal Toxicity and Hyperkalemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Anaphylactic Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- Serious Skin Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]
- Hematologic Toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)]
- Active Bleeding [see Warnings and Precautions (5.14)]
- Acute Interstitial Nephritis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.17)]
- Clostridium difficile-Associated Diarrhea [see Warnings and Precautions (5.18)]
- Bone Fracture [see Warnings and Precautions (5.19)]
- Cutaneous and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus [see Warnings and Precautions (5.20)]
- Cyanocobalamin (Vitamin B-12) Deficiency [see Warnings and Precautions (5.22)]
- Hypomagnesemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.23)]
- Fundic Gland Polyps [see Warnings and Precautions (5.27)]
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of VIMOVO. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
7. Drug Interactions
See Table 3 and Table 4 for clinically significant drug interactions and interactions with diagnostics with naproxen and esomeprazole magnesium.
| Drugs That Interfere with Hemostasis | |
| Clinical Impact: | Naproxen
|
| Intervention: | Monitor patients with concomitant use of VIMOVO with anticoagulants (e.g., warfarin), antiplatelet agents (e.g., aspirin), selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), and serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) for signs of bleeding [see Warnings and Precautions (5.13)]. Clopidogrel: Avoid concomitant use of clopidogrel with VIMOVO. Consider use of alternative anti-platelet therapy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.21)]. |
| Aspirin | |
| Clinical Impact: | A pharmacodynamics (PD) study has demonstrated an interaction in which lower dose naproxen (220mg/day or 220mg twice daily) interfered with the antiplatelet effect of low-dose immediate-release aspirin, with the interaction most marked during the washout period of naproxen [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2.)]. There is reason to expect that the interaction would be present with prescription doses of naproxen or with enteric-coated low-dose aspirin; however, the peak interference with aspirin function may be later than observed in the PD study due to the longer washout period. Controlled clinical studies showed that the concomitant use of NSAIDs and analgesic doses of aspirin does not produce any greater therapeutic effect than the use of NSAIDs alone. In a clinical study, the concomitant use of an NSAID and aspirin was associated with a significantly increased incidence of GI adverse reactions as compared to use of the NSAID alone [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. |
| Intervention: | Because there may be an increased risk of cardiovascular events following discontinuation of naproxen due to the interference with the antiplatelet effect of aspirin during the washout period, for patients taking low-dose aspirin for cardioprotection who require intermittent analgesics, consider use of an NSAID that does not interfere with the antiplatelet effect of aspirin, or non-NSAID analgesics where appropriate. Concomitant use of VIMOVO and analgesic doses of aspirin is not generally recommended because of the increased risk of bleeding [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)]. VIMOVO is not a substitute for low dose aspirin for cardiovascular protection. |
| ACE Inhibitors, Angiotensin Receptor Blockers, and Beta-Blockers | |
| Clinical Impact: |
|
| Intervention: |
|
| Diuretics | |
| Clinical Impact: | Clinical studies, as well as post-marketing observations, showed that NSAIDs reduced the natriuretic effect of loop diuretics (e.g., furosemide) and thiazide diuretics in some patients. This effect has been attributed to the NSAID inhibition of renal prostaglandin synthesis. |
| Intervention: | During concomitant use of VIMOVO with diuretics, observe patients for signs of worsening renal function, in addition to assuring diuretic efficacy including antihypertensive effects [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]. |
| Antiretrovirals | |
| Clinical Impact: | The effect of esomeprazole magnesium on antiretroviral drugs is variable. The clinical importance and mechanisms behind these interactions are not always known.
|
| Intervention: | Rilpivirine-containing products: Concomitant use with VIMOVO is contraindicated [see Contraindications (4)]. Atazanavir: See prescribing information for atazanavir for dosing information. Nelfinavir: Avoid concomitant use with VIMOVO. Saquinavir: See the prescribing information for saquinavir for monitoring of potential saquinavir-related toxicities. Other antiretrovirals: See prescribing information of specific drugs. |
| Cilostazol | |
| Clinical Impact: | Increased exposure of cilostazol and one of its active metabolites (3,4-dihydro-cilostazol) when coadministered with omeprazole magnesium, the racemate of esomeprazole [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. |
| Intervention: | Consider reducing the dose of cilostazol to 50 mg twice daily. |
| Digoxin | |
| Clinical Impact: | Naproxen
|
| Intervention: | Monitor digoxin concentrations during concomitant use of VIMOVO. Dose adjustment of digoxin may be needed to maintain therapeutic drug concentrations. |
| Lithium | |
| Clinical Impact: | NSAIDs have produced elevations of plasma lithium levels and reductions in renal lithium clearance. The mean minimum lithium concentration increased 15%, and the renal clearance decreased by approximately 20%. This effect has been attributed to NSAID inhibition of renal prostaglandin synthesis. |
| Intervention: | During concomitant use of VIMOVO and lithium, monitor patients for signs of lithium toxicity. |
| Methotrexate | |
| Clinical Impact: | Naproxen
|
| Intervention: | During concomitant use of VIMOVO and methotrexate, monitor patients for methotrexate toxicity. A temporary withdrawal of VIMOVO may be considered in some patients receiving high-dose methotrexate. |
| Cyclosporine | |
| Clinical Impact: | Concomitant use of naproxen and cyclosporine may increase cyclosporine's nephrotoxicity. |
| Intervention: | During concomitant use of VIMOVO and cyclosporine, monitor patients for signs of worsening renal function. |
| Tacrolimus | |
| Clinical Impact: | Concomitant use of esomeprazole magnesium and tacrolimus may increase exposure of tacrolimus |
| Intervention: | During concomitant use of VIMOVO and tacrolimus, monitor tacrolimus whole blood concentrations. |
| NSAIDs and Salicylates | |
| Clinical Impact: | Concomitant use of naproxen with other NSAIDs or salicylates (e.g., diflunisal, salsalate) increases the risk of GI toxicity, with little or no increase in efficacy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. |
| Intervention: | The concomitant use of VIMOVO with other NSAIDs or salicylates is not recommended. |
| Pemetrexed | |
| Clinical Impact: | Concomitant use of VIMOVO and pemetrexed may increase the risk of pemetrexed-associated myelosuppression, renal, and GI toxicity (see the pemetrexed prescribing information). |
| Intervention: | During concomitant use of VIMOVO and pemetrexed, in patients with renal impairment whose creatinine clearance ranges from 45 to 79 mL/min, monitor for myelosuppression, renal and GI toxicity. |
| Drugs Dependent on Gastric pH for Absorption (e.g., iron salts, erlotinib, mycophenoloate mofetil, ketoconazole) | |
| Clinical Impact: | Esomeprazole magnesium can reduce the absorption of other drugs due to its effect on reducing intragastric acidity |
| Intervention: | Mycophenolate mofetil (MMF): Co-administration of omeprazole, of which esomeprazole magnesium is an enantiomer, in healthy subjects and in transplant patients receiving MMF has been reported to reduce the exposure to the active metabolite, mycophenolic acid (MPA), possibly due to a decrease in MMF solubility at an increased gastric pH. The clinical relevance of reduced MPA exposure on organ rejection has not been established in transplant patients receiving esomeprazole and MMF. Use VIMOVO with caution in transplant patients receiving MMF [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. See the prescribing information for other drugs dependent on gastric pH for absorption. |
| Interactions with Investigations of Neuroendocrine Tumors | |
| Clinical Impact: | Serum chromogranin A (CgA) levels increase secondary to PPI-induced decreases in gastric acidity. The increased CgA levels may cause false positive results in diagnostic investigations for neuroendocrine tumors [see Warnings and Precautions (5.25), Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)]. |
| Intervention: | Temporarily stop VIMOVO treatment at least 14 days before assessing CgA levels and consider repeating the test if initial CgA levels are high. If serial tests are performed (e.g. for monitoring), the same commercial laboratory should be used for testing, as reference ranges between tests may vary. |
| Diazepam | |
| Clinical Impact: | Increased exposure of diazepam [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. |
| Intervention: | Monitor patients for increased sedation and adjust the dose of diazepam as needed. |
| CYP2C19 or CYP3A4 Inducers | |
| Clinical Impact: | Decreased exposure of esomeprazole when used concomitantly with strong inducers [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. |
| Intervention: | St. John's Wort, rifampin: Avoid concomitant use with VIMOVO [see Warnings and Precautions (5.24)]. |
| CYP2C19 or CYP3A4 Inhibitors | |
| Clinical Impact: | Increased exposure of esomeprazole [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. |
| Intervention: | Voriconazole: Avoid concomitant use with VIMOVO. |
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of VIMOVO have been established in adolescent patients 12 years of age and older weighing at least 38 kg for the symptomatic relief of JIA and to decrease the risk of developing naproxen-associated gastric ulcers. Use of VIMOVO in this age group is based on extrapolation of adequate and well-controlled studies in adults and supported by a 6 month safety study including pharmacokinetic assessment of naproxen and esomeprazole magnesium in 36 adolescent patients with JIA. Based on the limited data, the plasma naproxen and plasma esomeprazole concentrations were found to be within the range to that observed to those found in healthy adults. The safety profile of VIMOVO in adolescent patients with JIA was similar to adults with RA.
The safety and effectiveness of VIMOVO in pediatric patients less than 12 years of age or less than 38 kg with JIA have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Elderly patients, compared to younger patients, are at greater risk for NSAID-associated serious cardiovascular, gastrointestinal, and/or renal adverse reactions. If the anticipated benefit for the elderly patient outweighs these potential risks, start dosing at the low end of the dosing range, and monitor patients for adverse effects [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.6, 5.13)].
Of the total number of patients who received VIMOVO (n=1157) in clinical trials, 387 were ≥65 years of age, of which 85 patients were 75 years and over. No meaningful differences in efficacy or safety were observed between these subjects and younger subjects [see Adverse Reactions (6)].
Studies indicate that although total plasma concentration of naproxen is unchanged, the unbound plasma fraction of naproxen is increased in the elderly. Caution is advised when high doses are required and some adjustment of dosage may be required in elderly patients. As with other drugs used in the elderly, it is prudent to use the lowest effective dose [see Dosage and Administration (2), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Experience indicates that geriatric patients may be particularly sensitive to certain adverse effects of NSAIDs. Elderly or debilitated patients seem to tolerate peptic ulceration or bleeding less well when these events do occur. Most spontaneous reports of fatal GI events are in the geriatric population [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Naproxen and its metabolites are known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of adverse reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection, and it may be useful to monitor renal function. Geriatric patients may be at a greater risk for the development of a form of renal toxicity precipitated by reduced prostaglandin formation during administration of NSAIDs [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
VIMOVO should be avoided in patients with severe hepatic impairment because naproxen may increase the risk of renal failure or bleeding and esomeprazole doses should not exceed 20 mg daily in these patients [see Dosage and Administration (2), Warnings and Precautions (5.3), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
11. Vimovo Description
The active ingredients of VIMOVO are naproxen which is an NSAID and esomeprazole magnesium which is a Proton Pump Inhibitor (PPI).
VIMOVO (naproxen and esomeprazole magnesium) is combination of a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug and a PPI available as an oval, yellow, multi-layer, delayed-release tablet combining an enteric-coated naproxen core and an immediate-release esomeprazole magnesium layer surrounding the core.
Each strength contains either 375 mg of naproxen and 20 mg of esomeprazole (equivalent to 22.3 mg esomeprazole magnesium trihydrate) or 500 mg of naproxen and 20 mg of esomeprazole (equivalent to 22.3 mg esomeprazole magnesium trihydrate) for oral administration. The inactive ingredients are carnauba wax, colloidal silicon dioxide, croscarmellose sodium, iron oxide yellow, glyceryl monostearate, hypromellose, iron oxide black, magnesium stearate, methacrylic acid copolymer dispersion, methylparaben, polysorbate 80, polydextrose, polyethylene glycol, povidone, propylene glycol, propylparaben, titanium dioxide, and triethyl citrate.
The chemical name for naproxen is (S)-6-methoxy-α-methyl-2-naphthaleneacetic acid. Naproxen has the following structure:
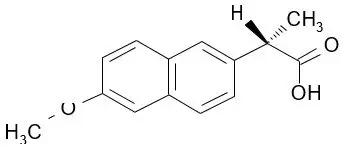
Naproxen has a molecular weight of 230.26 and a molecular formula of C14H14O3.
Naproxen is an odorless, white to off-white crystalline substance. It is lipid soluble, practically insoluble in water at low pH and freely soluble in water at high pH. The octanol/water partition coefficient of naproxen at pH 7.4 is 1.6 to 1.8.
The chemical name for esomeprazole is bis(5-methoxy-2-[(S)-[(4-methoxy-3,5-dimethyl-2-pyridinyl)methyl]sulfinyl]-1H-benzimidazole-1-yl) magnesium trihydrate. Esomeprazole is the S- isomer of omeprazole, which is a mixture of the S- and R- isomers. Its molecular formula is (C17H18N3O3S)2Mg × 3 H2O with molecular weight of 767.2 as a trihydrate and 713.1 on an anhydrous basis. The structural formula is:
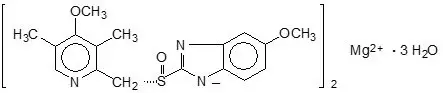
The magnesium salt is a white to slightly colored crystalline powder. It contains 3 moles of water of solvation and is slightly soluble in water.
The stability of esomeprazole magnesium is a function of pH; it rapidly degrades in acidic media, but it has acceptable stability under alkaline conditions. At pH 6.8 (buffer), the half-life of the magnesium salt is about 19 hours at 25°C and about 8 hours at 37°C.
12. Vimovo - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
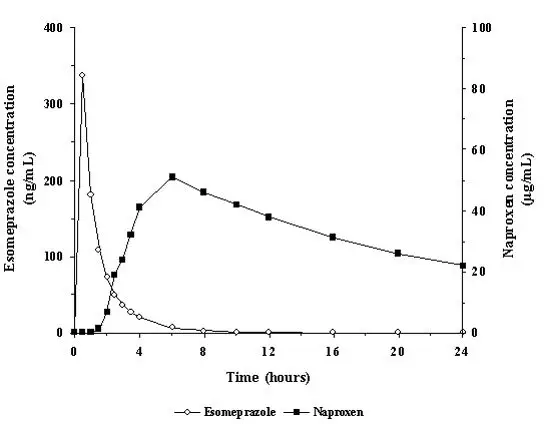
VIMOVO consists of an immediate-release esomeprazole magnesium layer and an enteric-coated naproxen core. As a result, esomeprazole is released first in the stomach, prior to the dissolution of naproxen in the small intestine. The enteric coating prevents naproxen release at pH levels below 5.5.
The mechanism of action of the naproxen anion, like that of other NSAIDs, is not completely understood but inhibition of cyclooxygenase (COX-1 and COX-2).
VIMOVO has analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and antipyretic properties contributed by the naproxen component. Naproxen is a potent inhibitor of prostaglandin synthesis in vitro. Naproxen concentrations reached during therapy have produced in vivo effects. Prostaglandins sensitize afferent nerves and potentiate the action of bradykinin in inducing pain in animal models. Prostaglandins are mediators of inflammation. Because naproxen is an inhibitor of prostaglandin synthesis, its mode of action may be due to an increase of prostaglandins in peripheral tissues.
Esomeprazole is a proton pump inhibitor that suppresses gastric acid secretion by specific inhibition of the H+/K+-ATPase in the gastric parietal cell. Esomeprazole is protonated and converted in the acidic compartment of the parietal cell forming the active inhibitor, the achiral sulphenamide. By acting specifically on the proton pump, esomeprazole blocks the final step in acid production, thus reducing gastric acidity. This effect is dose-related up to a daily dose of 20 to 40 mg and leads to inhibition of gastric acid secretion.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Drug Interaction Studies
Effect of Esomeprazole on Other Drugs
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
14. Clinical Studies
Two randomized, multi-center, double-blind trials (Study 1 and Study 2) compared the incidence of gastric ulcer formation in 428 patients taking VIMOVO and 426 patients taking enteric-coated naproxen. Subjects were at least 18 years of age with a medical condition expected to require daily NSAID therapy for at least 6 months, and, if less than 50 years old, with a documented history of gastric or duodenal ulcer within the past 5 years. The majority of patients were female (67%), white (86%). The majority of patients were 50-69 years of age (83%). Approximately one quarter were on low-dose aspirin.
Studies 1 and 2 showed that VIMOVO given as 500 mg/20 mg twice daily statistically significantly reduced the 6-month cumulative incidence of gastric ulcers compared to enteric-coated naproxen 500 mg twice daily (see Table 6).
Approximately a quarter of the patients in Studies 1 and 2 were taking concurrent low-dose aspirin (≤ 325 mg daily). The results for this subgroup analysis in patients who used aspirin were consistent with the overall findings of the study.
The results at one month, three months, and six months are presented in Table 6.
| Study 1 | Study 2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VIMOVO N=218 number (%) | EC-naproxen N=216 number (%) | VIMOVO N=210 number (%) | EC-naproxen N=210 number (%) |
|
|
||||
| 0-1 Month | 3 (1.4) | 28 (13.0) | 4 (1.9) | 21 (10.0) |
| 0-3 Months | 4 (1.8) | 42 (19.4) | 10 (4.8) | 37 (17.6) |
| 0-6 Months* | 9 (4.1) | 50 (23.1) | 15 (7.1) | 51 (24.3) |
In these trials, patients receiving VIMOVO had a mean duration of therapy of 152 days compared to 124 days in patients receiving enteric-coated naproxen alone. A higher proportion of patients taking EC-naproxen (12%) discontinued the study due to upper GI adverse events (including duodenal ulcers) compared to VIMOVO (4%) in both trials [see Adverse Reactions (6)].
The efficacy of VIMOVO in treating the signs and symptoms of osteoarthritis was established in two 12-week randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials in patients with osteoarthritis (OA) of the knee. In these two trials, patients were allowed to remain on low-dose aspirin for cardioprophylaxis. VIMOVO was given as 500 mg/20 mg twice daily. In each trial, patients receiving VIMOVO had significantly better results compared to patients receiving placebo as measured by change from baseline of the WOMAC pain subscale and the WOMAC physical function subscale and a Patient Global Assessment Score.
Based on studies with enteric-coated naproxen, improvement in patients treated for rheumatoid arthritis was demonstrated by a reduction in joint swelling, a reduction in duration of morning stiffness, a reduction in disease activity as assessed by both the investigator and patient, and by increased mobility as demonstrated by a reduction in walking time. In patients with osteoarthritis, the therapeutic action of naproxen has been shown by a reduction in joint pain or tenderness, an increase in range of motion in knee joints, increased mobility as demonstrated by a reduction in walking time, and improvement in capacity to perform activities of daily living impaired by the disease. In patients with ankylosing spondylitis, naproxen has been shown to decrease night pain, morning stiffness and pain at rest.
16. How is Vimovo supplied
VIMOVO (375 mg naproxen /20 mg esomeprazole magnesium) delayed-release tablets are oval, yellow film-coated tablets printed with 375/20 in black ink, supplied as:
| NDC 75987-031-04 | Bottles of 60 tablets |
VIMOVO (500 mg naproxen /20 mg esomeprazole magnesium) delayed-release tablets are oval, yellow film-coated tablets printed with 500/20 in black ink, supplied as:
| NDC 75987-030-04 | Bottles of 60 tablets |
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide).
Inform patients, families, or caregivers of the following before initiating therapy with VIMOVO and periodically during the course of ongoing therapy.
| Medication Guide VIMOVO (vi-moh-voh) (naproxen and esomeprazole magnesium) delayed-release tablets |
||
|---|---|---|
| This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. | Revised: 06/2018 | |
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
VIMOVO can have other serious side effects. See "What are the possible side effects of VIMOVO?" |
||
| What is VIMOVO?
VIMOVO is a prescription medicine used in adults and adolescents, 12 years of age and older who weigh at least 84 pounds (38 kg), who need to take naproxen for relief of symptoms of arthritis and who also need to decrease the risk of developing stomach ulcers caused by naproxen. The naproxen in VIMOVO is used for the relief of signs and symptoms of:
Studies in people who take VIMOVO have not extended past 6 months. |
||
Do not take VIMOVO:
|
||
Before taking VIMOVO, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
Especially tell your healthcare provider if you take: |
||
|
|
|
How should I take VIMOVO?
|
||
Get emergency help right away if you get any of the following symptoms: |
||
|
|
|
| Stop taking VIMOVO and call your healthcare provider right away if you get any of the following symptoms: | ||
|
|
|
| If you take too much VIMOVO, call your healthcare provider or get medical help right away.
These are not all the possible side effects of VIMOVO. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. |
||
How should I store VIMOVO?
|
||
| What are the ingredients in VIMOVO? Active ingredients: naproxen and esomeprazole magnesium Inactive ingredients: carnauba wax, colloidal silicon dioxide, croscarmellose sodium, iron oxide yellow, glyceryl monostearate, hypromellose, iron oxide black, magnesium stearate, methacrylic acid copolymer dispersion, methylparaben, polysorbate 80, polydextrose, polyethylene glycol, povidone, propylene glycol, propylparaben, titanium dioxide, and triethyl citrate |
||
| General information about the safe and effective use of VIMOVO.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use VIMOVO for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give VIMOVO to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. You can ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for information about VIMOVO that is written for health professionals. Distributed by: Horizon Pharma USA Inc., Lake Forest, IL 60045 For more information, go to www.VIMOVO.com or call 1-866-479-6742. |
||
| VIMOVO
naproxen and esomeprazole magnesium tablet, delayed release |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| VIMOVO
naproxen and esomeprazole magnesium tablet, delayed release |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Horizon Medicines LLC (964613413) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patheon Pharmaceuticals Inc. | 005286822 | MANUFACTURE(75987-030, 75987-031) , LABEL(75987-030, 75987-031) , PACK(75987-030, 75987-031) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Divi's Laboratories Limited [Unit-1] | 918598199 | API MANUFACTURE(75987-030, 75987-031) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| MINAKEM Dunkerque | 277412599 | API MANUFACTURE(75987-030, 75987-031) | |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Divi's Laboraties Limited [Unit-2] | 676446492 | API MANUFACTURE(75987-030, 75987-031) | |