Drug Detail:Viread (Tenofovir disoproxil)
Drug Class: Nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs)
Highlights of Prescribing Information
VIREAD® (tenofovir disoproxil fumarate) tablets, for oral use
VIREAD® (tenofovir disoproxil fumarate) powder, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2001
WARNING: POSTTREATMENT ACUTE EXACERBATION OF HEPATITIS B
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
Severe acute exacerbations of hepatitis B virus (HBV) have been reported in HBV-infected patients who have discontinued anti-hepatitis B therapy, including VIREAD. Hepatic function should be monitored closely in HBV-infected patients who discontinue VIREAD. If appropriate, resumption of anti-hepatitis B therapy may be warranted. (5.1)
Recent Major Changes
| Indications and Usage, Chronic Hepatitis B (1.2) | 12/2018 |
| Dosage and Administration (2.1, 2.2, 2.3, 2.4) | 12/2018 |
| Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2, 5.5, 5.7) | 12/2018 |
| Early Virologic Failure | Removed 12/2018 |
Indications and Usage for Viread
VIREAD is a nucleotide analog HIV-1 reverse transcriptase inhibitor and an HBV reverse transcriptase inhibitor and is indicated:
- in combination with other antiretroviral agents for the treatment of HIV-1 infection in adults and pediatric patients 2 years of age and older weighing at least 10 kg. (1.1)
- for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B in adults and pediatric patients 2 years and older weighing at least 10 kg. (1.2)
Viread Dosage and Administration
- Testing: Prior to or when initiating VIREAD test for hepatitis B virus infection and HIV-1 infection. Prior to initiation and during use of VIREAD, on a clinically appropriate schedule, assess serum creatinine, estimated creatinine clearance, urine glucose, and urine protein in all patients. In patients with chronic kidney disease, also assess serum phosphorous. (2.1)
- Recommended tablet dosage in adults and pediatric patients weighing at least 35 kg: One VIREAD 300 mg tablet once daily taken orally without regard to food. (2.2)
- Recommended dosage in pediatric patients at least 2 years of age and adults:
- Tablets: For patients weighing at least 17 kg who can swallow an intact tablet, one VIREAD tablet (150 mg, 200 mg, 250 mg, or 300 mg based on body weight) once daily taken orally without regard to food. (2.2)
- Oral powder: For patients weighing at least 10 kg and unable to swallow a tablet, 8 mg per kg VIREAD oral powder (up to a maximum of 300 mg) taken once daily with food. (2.3)
- Recommended dosage in renally impaired adult patients:
- Creatinine clearance (CrCl) 30–49 mL/min: 300 mg every 48 hours. (2.4)
- CrCl 10–29 mL/min: 300 mg every 72 to 96 hours. (2.4)
- Hemodialysis: 300 mg every 7 days or after approximately 12 hours of dialysis. (2.4)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
- Tablets: 150 mg, 200 mg, 250 mg, and 300 mg of tenofovir disoproxil fumarate. (3)
- Oral Powder: 40 mg per 1 g of oral powder of tenofovir disoproxil fumarate. (3)
Contraindications
None. (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- New onset or worsening renal impairment: Can include acute renal failure and Fanconi syndrome. Avoid administering VIREAD with concurrent or recent use of nephrotoxic drugs. (5.2)
- HIV testing: HIV antibody testing should be offered to all HBV-infected patients before initiating therapy with VIREAD. VIREAD should only be used as part of an appropriate antiretroviral combination regimen in HIV-infected patients with or without HBV coinfection. (5.3)
- Immune reconstitution syndrome: May necessitate further evaluation and treatment. (5.4)
- Decreases in bone mineral density (BMD): Consider assessment of BMD in patients with a history of pathologic fracture or other risk factors for osteoporosis or bone loss. (5.5)
- Lactic acidosis/severe hepatomegaly with steatosis: Discontinue treatment in patients who develop symptoms or laboratory findings suggestive of lactic acidosis or pronounced hepatotoxicity. (5.6)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
- In HIV-infected adult subjects: Most common adverse reactions (incidence greater than or equal to 10%, Grades 2–4) were rash, diarrhea, nausea, headache, pain, depression, and asthenia. (6.1)
- In HBV-infected subjects with compensated liver disease: Most common adverse reaction (all grades) was nausea (9%). (6.1)
- In HBV-infected subjects with decompensated liver disease: Most common adverse reactions (incidence greater than or equal to 10%, all grades) were abdominal pain, nausea, insomnia, pruritus, vomiting, dizziness, and pyrexia. (6.1)
- In pediatric subjects: Adverse reactions in pediatric subjects were consistent with those observed in adults. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Gilead Sciences, Inc. at 1-800-GILEAD-5 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch
Drug Interactions
- Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate increases didanosine concentrations. Dose reduction and close monitoring for didanosine toxicity are warranted. (7.2)
- Coadministration decreases atazanavir concentrations. When coadministered with VIREAD, use atazanavir given with ritonavir. (7.2)
- Coadministration of VIREAD with certain HIV-1 protease inhibitors or certain drugs to treat HCV increases tenofovir concentrations. Monitor for evidence of tenofovir toxicity. (7.2)
- Consult Full Prescribing Information prior to and during treatment for important drug interactions. (7.2)
Use In Specific Populations
Lactation: Breastfeeding in HIV-1 infected mothers is not recommended due to the potential for HIV-1 transmission. (8.2)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 4/2019
Related/similar drugs
Biktarvy, Descovy, Truvada, tenofovir, entecavir, emtricitabine, lamivudineFull Prescribing Information
WARNING: POSTTREATMENT ACUTE EXACERBATION OF HEPATITIS B
Severe acute exacerbations of hepatitis B virus (HBV) have been reported in HBV-infected patients who have discontinued anti-hepatitis B therapy, including VIREAD. Hepatic function should be monitored closely with both clinical and laboratory follow-up for at least several months in HBV-infected patients who discontinue anti-hepatitis B therapy, including VIREAD. If appropriate, resumption of anti-hepatitis B therapy may be warranted [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
1. Indications and Usage for Viread
2. Viread Dosage and Administration
2.1 Testing Prior to Initiation of VIREAD for Treatment of HIV-1 Infection or Chronic Hepatitis B
Prior to or when initiating VIREAD, test patients for HBV infection and HIV-1 infection. VIREAD alone should not be used in patients with HIV-1 infection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Prior to initiation and during use of VIREAD, on a clinically appropriate schedule, assess serum creatinine, estimated creatinine clearance, urine glucose and urine protein in all patients. In patients with chronic kidney disease, also assess serum phosphorus [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
2.2 Recommended Tablet Dosage in Adults and Pediatric Patients 2 Years and Older Weighing at Least 17 kg
The recommended dosage of VIREAD in adults and pediatric patients weighing at least 35 kg is one 300 mg tablet taken orally once daily without regard to food. The dosage for VIREAD is the same for both HIV and HBV indications.
The recommended dosage of VIREAD tablet in adults and pediatric patients 2 years and older weighing at least 17 kg is 8 mg of tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF) per kg of body weight (up to a maximum of 300 mg) once daily. Dosage for pediatric patients 2 years and older weighing between 17 kg and 35 kg and able to swallow an intact tablet is provided in Table 1. Weight should be monitored periodically and the VIREAD dose adjusted accordingly.
| Body Weight (kg) | Dosing of VIREAD Tablets |
|---|---|
| 17 to less than 22 | one 150 mg tablet once daily |
| 22 to less than 28 | one 200 mg tablet once daily |
| 28 to less than 35 | one 250 mg tablet once daily |
| at least 35 | one 300 mg tablet once daily |
2.3 Recommended Oral Powder Dosage in Adults and Pediatric Patients 2 Years and Older Weighing at Least 10 kg
The recommended dosage of VIREAD oral powder in adults and pediatric patients 2 years and older weighing at least 10 kg who are unable to swallow a tablet is 8 mg of TDF per kg of body weight (up to a maximum of 300 mg) once daily administered as oral powder (see Table 2). Weight should be monitored periodically and the VIREAD dose adjusted accordingly.
VIREAD oral powder should be measured only with the supplied dosing scoop. One level scoop delivers 1 g of powder, which contains 40 mg of TDF. VIREAD oral powder should be mixed in a container with 2 to 4 ounces of soft food not requiring chewing (e.g., applesauce, baby food, yogurt). The entire mixture should be ingested immediately to avoid a bitter taste. Do not administer VIREAD oral powder in a liquid as the powder may float on top of the liquid even after stirring. Further patient instructions on how to administer VIREAD oral powder with the supplied dosing scoop are provided in the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
| Body Weight (kg) | Dosing of VIREAD Oral Powder | Total Daily Dosage (40 mg per scoop) |
|---|---|---|
| 10 to less than 12 | 2 scoops once daily | 80 mg |
| 12 to less than 14 | 2.5 scoops once daily | 100 mg |
| 14 to less than 17 | 3 scoops once daily | 120 mg |
| 17 to less than 19 | 3.5 scoops once daily | 140 mg |
| 19 to less than 22 | 4 scoops once daily | 160 mg |
| 22 to less than 24 | 4.5 scoops once daily | 180 mg |
| 24 to less than 27 | 5 scoops once daily | 200 mg |
| 27 to less than 29 | 5.5 scoops once daily | 220 mg |
| 29 to less than 32 | 6 scoops once daily | 240 mg |
| 32 to less than 34 | 6.5 scoops once daily | 260 mg |
| 34 to less than 35 | 7 scoops once daily | 280 mg |
| at least 35 | 7.5 scoops once daily | 300 mg |
2.4 Dosage Adjustment in Patients with Renal Impairment
Significant increase in drug exposures occurred when VIREAD was administered to subjects with moderate to severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance below 50 mL/min). Table 3 provides dosage interval adjustment for patients with renal impairment. No dosage adjustment of VIREAD tablets 300 mg is necessary for patients with mild renal impairment (creatinine clearance 50–80 mL/min) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3), Use in Specific Populations (8.6), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
| Creatinine Clearance (mL/min)* | Hemodialysis Patients | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 or greater | 30–49 | 10–29 | ||
|
||||
| Recommended 300 mg Dosing Interval | Every 24 hours | Every 48 hours | Every 72 to 96 hours | Every 7 days or after a total of approximately 12 hours of dialysis† |
No data are available to make dosage recommendations in patients with creatinine clearance below 10 mL/min who are not on hemodialysis.
No data are available to make dosage recommendations in pediatric patients with renal impairment.
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
VIREAD is available as tablets in four dose strengths or as an oral powder.
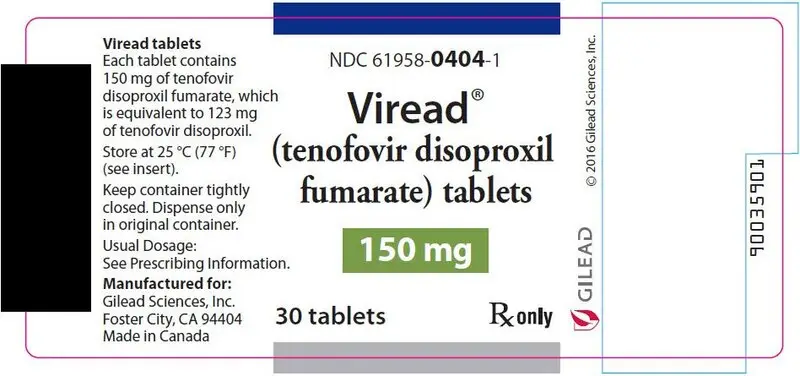
- 150 mg Tablets: 150 mg of tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF) (equivalent to 123 mg of tenofovir disoproxil): triangle shaped, white, film coated, debossed with "GSI" on one side and with "150" on the other side.
- 200 mg Tablets: 200 mg of TDF (equivalent to 163 mg of tenofovir disoproxil): round shaped, white, film coated, debossed with "GSI" on one side and with "200" on the other side.
- 250 mg Tablets: 250 mg of TDF (equivalent to 204 mg of tenofovir disoproxil): capsule shaped, white, film coated, debossed with "GSI" on one side and with "250" on the other side.
- 300 mg Tablets: 300 mg of TDF (equivalent to 245 mg of tenofovir disoproxil): almond shaped, light blue, film coated, debossed with "GILEAD" and "4331" on one side and with "300" on the other side.
- Oral Powder: white, taste-masked, coated granules containing 40 mg of TDF (equivalent to 33 mg of tenofovir disoproxil) per level scoop. Each level scoop contains 1 gram of oral powder.
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Severe Acute Exacerbation of Hepatitis B in Patients with HBV Infection
All patients should be tested for the presence of chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) before or when initiating VIREAD [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
Discontinuation of anti-HBV therapy, including VIREAD, may be associated with severe acute exacerbations of hepatitis B. Patients infected with HBV who discontinue VIREAD should be closely monitored with both clinical and laboratory follow-up for at least several months after stopping treatment. If appropriate, resumption of anti-hepatitis B therapy may be warranted, especially in patients with advanced liver disease or cirrhosis, since posttreatment exacerbation of hepatitis may lead to hepatic decompensation and liver failure.
5.2 New Onset or Worsening Renal Impairment
Tenofovir is principally eliminated by the kidney. Renal impairment, including cases of acute renal failure and Fanconi syndrome (renal tubular injury with severe hypophosphatemia), has been reported with the use of VIREAD [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
Prior to initiation and during use of VIREAD, on a clinically appropriate schedule, assess serum creatinine, estimated creatinine clearance, urine glucose, and urine protein in all patients. In patients with chronic kidney disease, also assess serum phosphorus.
Dosing interval adjustment of VIREAD and close monitoring of renal function are recommended in all patients with creatinine clearance below 50 mL/min [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)]. No safety or efficacy data are available in patients with renal impairment who received VIREAD using these dosing guidelines, so the potential benefit of VIREAD therapy should be assessed against the potential risk of renal toxicity.
VIREAD should be avoided with concurrent or recent use of a nephrotoxic agent (e.g., high-dose or multiple non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs [NSAIDs]) [see Drug Interactions (7.1)]. Cases of acute renal failure after initiation of high-dose or multiple NSAIDs have been reported in HIV-infected patients with risk factors for renal dysfunction who appeared stable on TDF. Some patients required hospitalization and renal replacement therapy. Alternatives to NSAIDs should be considered, if needed, in patients at risk for renal dysfunction.
Persistent or worsening bone pain, pain in extremities, fractures and/or muscular pain or weakness may be manifestations of proximal renal tubulopathy and should prompt an evaluation of renal function in patients at risk of renal dysfunction.
5.3 Patients Coinfected with HIV-1 and HBV
Due to the risk of development of HIV-1 resistance, VIREAD should only be used in HIV-1 and HBV coinfected patients as part of an appropriate antiretroviral combination regimen.
HIV-1 antibody testing should be offered to all HBV-infected patients before initiating therapy with VIREAD. It is also recommended that all patients with HIV-1 be tested for the presence of chronic hepatitis B before initiating treatment with VIREAD.
5.4 Immune Reconstitution Syndrome
Immune reconstitution syndrome has been reported in HIV-1 infected patients treated with combination antiretroviral therapy, including VIREAD. During the initial phase of combination antiretroviral treatment, HIV-1 infected patients whose immune system responds may develop an inflammatory response to indolent or residual opportunistic infections (such as Mycobacterium avium infection, cytomegalovirus, Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia [PCP], or tuberculosis), which may necessitate further evaluation and treatment.
Autoimmune disorders (such as Graves' disease, polymyositis, and Guillain-Barré syndrome) have also been reported to occur in the setting of immune reconstitution; however, the time to onset is more variable, and can occur many months after initiation of treatment.
5.6 Lactic Acidosis/Severe Hepatomegaly with Steatosis
Lactic acidosis and severe hepatomegaly with steatosis, including fatal cases, have been reported with the use of nucleoside analogs, including TDF, alone or in combination with other antiretrovirals. Treatment with VIREAD should be suspended in any patient who develops clinical or laboratory findings suggestive of lactic acidosis or pronounced hepatotoxicity (which may include hepatomegaly and steatosis even in the absence of marked transaminase elevations).
5.7 Risk of Adverse Reactions Due to Drug Interactions
The concomitant use of VIREAD and other drugs may result in known or potentially significant drug interactions, some of which may lead to possible clinically significant adverse reactions from greater exposures of concomitant drugs [see Drug Interactions (7.2)].
See Table 12 for steps to prevent or manage these possible and known significant drug interactions, including dosing recommendations. Consider the potential for drug interactions prior to and during therapy with VIREAD; review concomitant medications during therapy with VIREAD; and monitor for adverse reactions associated with the concomitant drugs.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following adverse reactions are discussed in other sections of the labeling:
- Severe Acute Exacerbation of Hepatitis B in Patients with HBV Infection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- New Onset or Worsening Renal Impairment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
- Immune Reconstitution Syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
- Bone Loss and Mineralization Defects [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
- Lactic Acidosis/Severe Hepatomegaly with Steatosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Adverse Reactions from Clinical Trials Experience in HIV-1 Infected Adults
More than 12,000 subjects have been treated with VIREAD alone or in combination with other antiretroviral medicinal products for periods of 28 days to 215 weeks in clinical trials and expanded access programs. A total of 1,544 subjects have received VIREAD 300 mg once daily in clinical trials; over 11,000 subjects have received VIREAD in expanded access programs.
The most common adverse reactions (incidence greater than or equal to 10%, Grades 2–4) identified from any of the 3 large controlled clinical trials include rash, diarrhea, headache, pain, depression, asthenia, and nausea.
Adverse Reactions from Clinical Trials Experience in HBV-Infected Adults
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval use of VIREAD. Because postmarketing reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Immune System Disorders
allergic reaction, including angioedema
Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders
lactic acidosis, hypokalemia, hypophosphatemia
Respiratory, Thoracic, and Mediastinal Disorders
dyspnea
Gastrointestinal Disorders
pancreatitis, increased amylase, abdominal pain
Hepatobiliary Disorders
hepatic steatosis, hepatitis, increased liver enzymes (most commonly AST, ALT gamma GT)
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders
rash
Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders
rhabdomyolysis, osteomalacia (manifested as bone pain and which may contribute to fractures), muscular weakness, myopathy
Renal and Urinary Disorders
acute renal failure, renal failure, acute tubular necrosis, Fanconi syndrome, proximal renal tubulopathy, interstitial nephritis (including acute cases), nephrogenic diabetes insipidus, renal insufficiency, increased creatinine, proteinuria, polyuria
General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions
asthenia
The following adverse reactions, listed under the body system headings above, may occur as a consequence of proximal renal tubulopathy: rhabdomyolysis, osteomalacia, hypokalemia, muscular weakness, myopathy, hypophosphatemia.
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 Drugs Affecting Renal Function
Tenofovir is primarily eliminated by the kidneys [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Coadministration of VIREAD with drugs that are eliminated by active tubular secretion may increase concentrations of tenofovir and/or the coadministered drug. Some examples include, but are not limited to, acyclovir, cidofovir, ganciclovir, valacyclovir, valganciclovir, aminoglycosides (e.g., gentamicin), and high-dose or multiple NSAIDs [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. Drugs that decrease renal function may increase concentrations of tenofovir.
In the treatment of chronic hepatitis B, VIREAD should not be administered in combination with HEPSERA (adefovir dipivoxil).
7.2 Established and Significant Interactions
Table 12 provides a listing of established or clinically significant drug interactions. The drug interactions described are based on studies conducted with TDF [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
| Concomitant Drug Class: Drug Name | Effect on Concentration† | Clinical Comment |
|---|---|---|
|
||
| NRTI:
didanosine | ↑ didanosine | Patients receiving VIREAD and didanosine should be monitored closely for didanosine-associated adverse reactions. Discontinue didanosine in patients who develop didanosine-associated adverse reactions. Higher didanosine concentrations could potentiate didanosine-associated adverse reactions, including pancreatitis, and neuropathy. Suppression of CD4+ cell counts has been observed in patients receiving VIREAD with didanosine 400 mg daily. In patients weighing greater than 60 kg, reduce the didanosine dose to 250 mg when it is coadministered with VIREAD. In patients weighing less than 60 kg, reduce the didanosine dose to 200 mg when it is coadministered with VIREAD. When coadministered, VIREAD and Videx EC may be taken under fasted conditions or with a light meal (less than 400 kcal, 20% fat). |
| HIV-1 Protease Inhibitors: atazanavir | ↓ atazanavir | When coadministered with VIREAD, atazanavir 300 mg should be given with ritonavir 100 mg. |
| lopinavir/ritonavir atazanavir/ritonavir darunavir/ritonavir | ↑ tenofovir | Monitor patients receiving VIREAD concomitantly with lopinavir/ritonavir, ritonavir-boosted atazanavir, or ritonavir-boosted darunavir for TDF-associated adverse reactions. Discontinue VIREAD in patients who develop TDF-associated adverse reactions. |
| Hepatitis C Antiviral Agents:
sofosbuvir/velpatasvir sofosbuvir/velpatasvir/voxilaprevir | ↑ tenofovir | Monitor patients receiving VIREAD concomitantly with EPCLUSA® (sofosbuvir/velpatasvir) for adverse reactions associated with TDF. |
| ledipasvir/sofosbuvir | Monitor patients receiving VIREAD concomitantly with HARVONI® (ledipasvir/sofosbuvir) without an HIV-1 protease inhibitor/ritonavir or an HIV-1 protease inhibitor/cobicistat combination, for adverse reactions associated with TDF. In patients receiving VIREAD concomitantly with HARVONI and an HIV-1 protease inhibitor/ritonavir or an HIV-1 protease inhibitor/cobicistat combination, consider an alternative HCV or antiretroviral therapy, as the safety of increased tenofovir concentrations in this setting has not been established. If coadministration is necessary, monitor for adverse reactions associated with TDF. | |
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.2 Lactation
Data
In a study of 50 HIV-uninfected, breastfeeding women on a tenofovir-containing regimen initiated between 1 and 24 weeks postpartum (median 13 weeks), tenofovir was undetectable in the plasma of most infants after 7 days of treatment in mothers. There were no serious adverse events in mothers or infants.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical trials of VIREAD did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. In general, dose selection for the elderly patient should be cautious, keeping in mind the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
10. Overdosage
If overdose occurs, the patient must be monitored for evidence of toxicity, and standard supportive treatment applied as necessary.
Tenofovir is efficiently removed by hemodialysis with an extraction coefficient of approximately 54%. Following a single 300 mg dose of VIREAD, a four-hour hemodialysis session removed approximately 10% of the administered tenofovir dose.
11. Viread Description
VIREAD is the brand name for tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF) (a prodrug of tenofovir) which is a fumaric acid salt of bis-isopropoxycarbonyloxymethyl ester derivative of tenofovir. TDF is converted in vivo to tenofovir, an acyclic nucleoside phosphonate (nucleotide) analog of adenosine 5'-monophosphate. Tenofovir exhibits activity against HIV-1 reverse transcriptase.
The chemical name of TDF is 9-[(R)-2-[[bis[[(isopropoxycarbonyl)oxy]methoxy]phosphinyl]methoxy]propyl]adenine fumarate (1:1). It has a molecular formula of C19H30N5O10P ∙ C4H4O4 and a molecular weight of 635.52. It has the following structural formula:
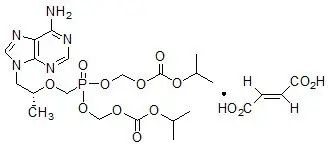
Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate is a white to off-white crystalline powder with a solubility of 13.4 mg/mL in distilled water at 25 °C. It has an octanol/phosphate buffer (pH 6.5) partition coefficient (log p) of 1.25 at 25 °C.
VIREAD is available as tablets or as an oral powder.
VIREAD tablets are for oral administration and are available in the following strengths: 150 mg, 200 mg, 250 mg, and 300 mg of TDF (equivalent to 123 mg, 163 mg, 204 mg, and 245 mg of tenofovir disoproxil, respectively).
All strengths of VIREAD tablets contain the following inactive ingredients: croscarmellose sodium, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, and pregelatinized starch. The 300 mg strength tablets are coated with Opadry II Y-30-10671-A, which contains FD&C blue #2 aluminum lake, hypromellose 2910, lactose monohydrate, titanium dioxide, and triacetin. The 150 mg, 200 mg, and 250 mg strength tablets are coated with Opadry II 32K-18425, which contains hypromellose 2910, lactose monohydrate, titanium dioxide, and triacetin.
VIREAD oral powder is available for oral administration as white, taste-masked, coated granules containing 40 mg of TDF per gram of oral powder (equivalent to 33 mg of tenofovir disoproxil). The oral powder contains the following inactive ingredients: mannitol, hydroxypropyl cellulose, ethylcellulose, and silicon dioxide.
In this insert, all dosages are expressed in terms of TDF except where otherwise noted.
12. Viread - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate is an antiviral drug [see Microbiology (12.4)].
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics of TDF have been evaluated in healthy volunteers and HIV-1 infected individuals. Tenofovir pharmacokinetics are similar between these populations.
13. Nonclinical Toxicology
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
Tenofovir and TDF administered in toxicology studies to rats, dogs, and monkeys at exposures (based on AUCs) greater than or equal to 6 fold those observed in humans caused bone toxicity. In monkeys the bone toxicity was diagnosed as osteomalacia. Osteomalacia observed in monkeys appeared to be reversible upon dose reduction or discontinuation of tenofovir. In rats and dogs, the bone toxicity manifested as reduced bone mineral density. The mechanism(s) underlying bone toxicity is unknown.
Evidence of renal toxicity was noted in 4 animal species. Increases in serum creatinine, BUN, glycosuria, proteinuria, phosphaturia, and/or calciuria and decreases in serum phosphate were observed to varying degrees in these animals. These toxicities were noted at exposures (based on AUCs) 2–20 times higher than those observed in humans. The relationship of the renal abnormalities, particularly the phosphaturia, to the bone toxicity is not known.
14. Clinical Studies
14.1 Overview of Clinical Trials
The efficacy and safety of VIREAD in adults and pediatric subjects were evaluated in the trials summarized in Table 19.
| Trial | Population | Study Arms (N)* | Timepoint (Week) |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|||
| Trial 903†
(NCT00158821) | HIV-1 treatment-naïve adults | VIREAD+lamivudine+efavirenz (299) stavudine+lamivudine+efavirenz (301) | 144 |
| Trial 934‡
(NCT00112047) | emtricitabine+VIREAD+efavirenz (257) zidovudine/lamivudine+efavirenz (254) | 144 | |
| Trial 907§
(NCT00002450) | HIV-1 treatment-experienced adults | VIREAD (368) Placebo (182) | 24 |
| Trial 0102†
(NCT00117676) | HBeAg-negative adults with chronic HBV | VIREAD (250) HEPSERA (125) | 48 |
| Trial 0103†
(NCT00116805) | HBeAg-positive adults with chronic HBV | VIREAD (176) HEPSERA (90) | 48 |
| Trial 121†
(NCT00737568) | Adults with lamivudine-resistant chronic HBV | VIREAD (141) | 96 |
| Trial 0108†
(NCT00298363) | Adults with chronic HBV and decompensated liver disease | VIREAD (45) | 48 |
| Trial 352‡
(NCT00528957) | HIV-1 treatment experienced pediatric subjects 2 years to <12 years | VIREAD (44) stavudine or zidovudine (48) | 48 |
| Trial 321§
(NCT00352053) | HIV-1 treatment-experienced pediatric subjects 12 years to <18 years | VIREAD (45) Placebo (42) | 48 |
| Trial 115§
(NCT00734162) | Pediatric subjects 12 years to <18 years with chronic HBV | VIREAD (52) Placebo (54) | 72 |
| Trial 144§
(NCT01651403) | Pediatric subjects 2 years to <12 years with chronic HBV | VIREAD (60) Placebo (29) | 48 |
14.3 Clinical Trial Results in Pediatric Subjects with HIV-1 Infection
In Trial 352, 92 treatment-experienced subjects 2 years to less than 12 years of age with stable, virologic suppression on a stavudine (d4T)- or zidovudine (AZT)-containing regimen were randomized to either replace d4T or AZT with VIREAD (N=44) or continue their original regimen (N=48) for 48 weeks. Five additional subjects over the age of 12 years were enrolled and randomized (VIREAD N=4, original regimen N=1) but are not included in the efficacy analysis. After 48 weeks, all eligible subjects were allowed to continue in the trial receiving open-label VIREAD. At Week 48, 89% of subjects in the VIREAD treatment group and 90% of subjects in the d4T or AZT treatment group had HIV-1 RNA concentrations <400 copies/mL. During the 48-week randomized phase of the trial, 1 subject in the VIREAD group discontinued the trial prematurely because of virologic failure/lack of efficacy and 3 subjects (2 subjects in the VIREAD group and 1 subject in the d4T or AZT group) discontinued for other reasons.
In Trial 321, 87 treatment-experienced subjects 12 years to less than 18 years of age were treated with VIREAD (N=45) or placebo (N=42) in combination with an optimized background regimen (OBR) for 48 weeks. The mean baseline CD4 cell count was 374 cells/mm3 and the mean baseline plasma HIV-1 RNA was 4.6 log10 copies/mL. At baseline, 90% of subjects harbored NRTI resistance-associated substitutions in their HIV-1 isolates. Overall, the trial failed to show a difference in virologic response between the VIREAD and placebo groups. Subgroup analyses suggest the lack of difference in virologic response may be attributable to imbalances between treatment arms in baseline viral susceptibility to VIREAD and OBR.
Although changes in HIV-1 RNA in these highly treatment-experienced subjects were less than anticipated, the comparability of the pharmacokinetic and safety data to that observed in adults supports the use of VIREAD in pediatric patients 12 years and older who weigh at least 35 kg and whose HIV-1 isolate is expected to be sensitive to VIREAD [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5), Adverse Reactions (6.1), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
14.4 Clinical Trial Results in Adults with Chronic Hepatitis B
HBeAg-Positive Chronic HBV Subjects: Trial 0103
Trial 0103 was a Phase 3, randomized, double-blind, active-controlled trial of VIREAD 300 mg compared to HEPSERA 10 mg in 266 HBeAg+ nucleoside-naïve subjects with compensated liver function. The mean age of subjects was 34 years; 69% were male, 36% were Asian, 52% were Caucasian, 16% had previously received alpha-interferon therapy, and <5% were nucleoside experienced. At baseline, subjects had a mean Knodell necroinflammatory score of 8.4; mean plasma HBV DNA was 8.7 log10 copies /mL; and mean serum ALT was 147 U/L.
The primary data analysis was conducted after all subjects reached 48 weeks of treatment and results are summarized below.
The primary efficacy endpoint in both trials was complete response to treatment defined as HBV DNA <400 copies/mL (69 IU/mL) and Knodell necroinflammatory score improvement of at least 2 points, without worsening in Knodell fibrosis at Week 48 (see Table 23).
| 0102 (HBeAg-) | 0103 (HBeAg+) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VIREAD (N=250) | HEPSERA (N=125) | VIREAD (N=176) | HEPSERA (N=90) |
|
|
||||
| Complete Response | 71% | 49% | 67% | 12% |
| Histology
Histological Response* | 72% | 69% | 74% | 68% |
| HBV DNA
<400 copies/mL (<69 IU/mL) | 93% | 63% | 76% | 13% |
| ALT
Normalized ALT† | 76% | 77% | 68% | 54% |
| Serology
HBeAg Loss/ Seroconversion | NA‡ | NA‡ | 20%/19% | 16%/16% |
| HBsAg Loss/ Seroconversion | 0/0 | 0/0 | 3%/1% | 0/0 |
16. How is Viread supplied
VIREAD tablets are available in bottles containing 30 tablets with child-resistant closure as follows:
- 150 mg of TDF (equivalent to 123 mg of tenofovir disoproxil): tablets are triangle-shaped, white, film-coated, and debossed with "GSI" on one side and with "150" on the other side. (NDC 61958-0404-1)
- 200 mg of TDF (equivalent to 163 mg of tenofovir disoproxil): tablets are round-shaped, white, film-coated, and debossed with "GSI" on one side and with "200" on the other side. (NDC 61958-0405-1)
- 250 mg of TDF (equivalent to 204 mg of tenofovir disoproxil): tablets are capsule-shaped, white, film-coated and debossed with "GSI" on one side and with "250" on the other side. (NDC 61958-0406-1)
- 300 mg of TDF (equivalent to 245 mg of tenofovir disoproxil): tablets are almond-shaped, light-blue, film-coated, and debossed with "GILEAD" and "4331" on one side and with "300" on the other side. (NDC 61958-0401-1)
VIREAD oral powder consists of white, coated granules containing 40 mg of TDF (equivalent to 33 mg of tenofovir disoproxil) per gram of powder and is available in multi-use bottles containing 60 grams of oral powder, closed with a child-resistant closure, and co-packaged with a dosing scoop. (NDC 61958-0403-1)
17. Patient Counseling Information
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information and Instructions for Use).
| This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. | Revised: April 2019 |
|
Patient Information |
|
|
VIREAD® (VEER-ee-ad) | VIREAD® (VEER-ee-ad) (tenofovir disoproxil fumarate) oral powder |
|
Read this Patient Information before you start taking VIREAD and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking with your healthcare provider about your medical condition or treatment. |
|
|
What is the most important information I should know about VIREAD? VIREAD can cause serious side effects, including:
For more information about side effects, see "What are the possible side effects of VIREAD?" |
|
|
What is VIREAD? VIREAD is a prescription medicine that is used to:
|
|
|
What should I tell my healthcare provider before taking VIREAD? Before you take VIREAD, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and non-prescription medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. Some medicines may interact with VIREAD. Keep a list of your medicines and show it to your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medicine.
|
|
|
How should I take VIREAD?
|
|
|
What are the possible side effects of VIREAD? VIREAD may cause serious side effects, including:
The most common side effects in all people taking VIREAD are: |
|
|
|
|
In some people with advanced HBV-infection, other common side effects may include: |
|
|
|
|
These are not all the possible side effects of VIREAD. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. |
|
|
How should I store VIREAD?
Keep VIREAD and all medicines out of the reach of children. |
|
|
General information about the safe and effective use of VIREAD. Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use VIREAD for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give VIREAD to other people, even if they have the same condition you have. It may harm them. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about VIREAD that is written for health professionals. A vaccine is available to protect people at risk for becoming infected with HBV. You can ask your healthcare provider for information about this vaccine. |
|
|
What are the ingredients in VIREAD? Active ingredient: tenofovir disoproxil fumarate Inactive ingredients: VIREAD tablets: croscarmellose sodium, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, and pregelatinized starch. VIREAD powder: mannitol, hydroxypropyl cellulose, ethylcellulose, and silicon dioxide. Tablet coating: VIREAD tablets 300 mg: Opadry II Y-30-10671-A, which contains FD&C blue #2 aluminum lake, hypromellose 2910, lactose monohydrate, titanium dioxide, and triacetin. VIREAD tablets 150, 200, and 250 mg: Opadry II 32K-18425, which contains hypromellose 2910, lactose monohydrate, titanium dioxide, and triacetin. Manufactured for and distributed by: Gilead Sciences, Inc. Foster City, CA 94404 |
|
Instructions for Use
VIREAD® (VEER-ee-ad)
(tenofovir disoproxil fumarate)
powder
for oral use
Read the Patient Information that comes with VIREAD powder for important information about VIREAD.
Read this Instructions for Use before you give VIREAD for the first time. Be sure you understand and follow the instructions. If you have any questions, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist.
Important information
- VIREAD powder comes in a box that has a bottle of VIREAD and a dosing scoop (see Figure A).
- Only use the dosing scoop to measure VIREAD powder.
- Only mix VIREAD powder with soft foods that can be swallowed without chewing. Examples of soft foods you can use are: applesauce, baby food, or yogurt.
- Do not mix VIREAD powder with liquid. The powder may float to the top even after stirring.
- Give the entire dose right away after mixing to avoid a bad taste.
How do I prepare and give a dose of VIREAD powder?
- Wash your hands well with soap and water, and dry them.
- Measure ¼ to ½ cup of soft food such as applesauce, baby food, or yogurt into a cup or bowl.
- To open a new bottle of powder, press down on the bottle lid and turn to remove (see picture on the top of the bottle cap). Peel off the foil.
- Measure the number of scoops prescribed by your healthcare provider.
- For each full scoop prescribed:
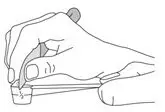
- Fill the dosing scoop to the top.
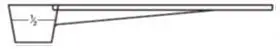
- Use the flat edge of clean knife to make the powder even with the top of the scoop (see Figure B).
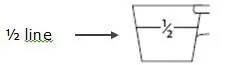
- For ½ scoop:
- Fill the dosing scoop up to the "½ line" on the side (see Figure C).
- For each full scoop prescribed:
- Sprinkle the VIREAD powder on the soft food. Stir with a spoon until well mixed. Give the entire dose right away after mixing to avoid a bad taste.
- Close the bottle of VIREAD tightly.
- Wash and dry the dosing scoop. Do not store the dosing scoop in the bottle.
How should I store VIREAD powder?
- Store VIREAD powder at room temperature between 68 °F to 77 °F (20 °C to 25 °C).
- Keep VIREAD powder in the original container.
- Keep the bottle tightly closed.
- Do not use VIREAD powder if the seal over the bottle opening is broken or missing.
Keep VIREAD and all medicines out of the reach of children.
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
| VIREAD
tenofovir disoproxil fumarate tablet, coated |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| VIREAD
tenofovir disoproxil fumarate tablet, coated |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| VIREAD
tenofovir disoproxil fumarate tablet, coated |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| VIREAD
tenofovir disoproxil fumarate tablet, coated |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| VIREAD
tenofovir disoproxil fumarate powder |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Gilead Sciences, Inc. (185049848) |