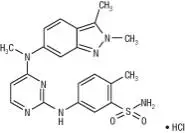
Drug Detail:Votrient (Pazopanib [ paz-oh-pa-nib ])
Drug Class: VEGF/VEGFR inhibitors
Highlights of Prescribing Information
VOTRIENT® (pazopanib) tablets, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2009
WARNING: HEPATOTOXICITY
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
Severe and fatal hepatotoxicity has been observed in clinical trials. Monitor hepatic function and interrupt, reduce, or discontinue dosing as recommended. (5.1)
Indications and Usage for Votrient
VOTRIENT is a kinase inhibitor indicated for the treatment of adults with:
- advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC). (1.1)
- advanced soft tissue sarcoma (STS) who have received prior chemotherapy. (1.2)
Limitations of Use: The efficacy of VOTRIENT for the treatment of patients with adipocytic soft tissue sarcoma or gastrointestinal stromal tumors has not been demonstrated.
Votrient Dosage and Administration
- Recommended Dosage: 800 mg orally once daily without food (at least 1 hour before or 2 hours after a meal). (2.1)
- Moderate Hepatic Impairment: 200 mg orally once daily. (2.2)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
Tablets: 200 mg (3)
Contraindications
None. (4)
Warnings and Precautions
- Hepatic Toxicity: Severe and fatal hepatotoxicity has occurred. Monitor liver tests at baseline, regularly during treatment and as clinically indicated. Withhold VOTRIENT and resume at reduced dose with continued weekly monitoring for 8 weeks, or permanently discontinue with weekly monitoring until resolution based on severity of hepatotoxicity. (2.2, 5.1)
- QT Prolongation and Torsades de Pointes: Monitor patients who are at significant risk of developing QT interval prolongation. Monitor electrocardiograms (ECGs) and electrolytes at baseline and as clinically indicated. Correct hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, and hypocalcemia prior to initiating VOTRIENT and during treatment. (5.2, 12.2)
- Cardiac Dysfunction: Cardiac dysfunction, including decreased left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) and congestive heart failure, have occurred. Monitor blood pressure and manage as appropriate. Monitor for clinical signs or symptoms of congestive heart failure. Conduct baseline and periodic evaluation of LVEF in patients at risk of cardiac dysfunction. Withhold or permanently discontinue VOTRIENT based on severity of cardiac dysfunction. (2.2, 5.3)
- Hemorrhagic Events: Fatal hemorrhagic events have occurred. VOTRIENT has not been studied in patients who have a history of hemoptysis, cerebral hemorrhage, or clinically significant gastrointestinal hemorrhage in the past 6 months. Withhold VOTRIENT and resume at reduced dose or permanently discontinue based on severity of hemorrhagic events. (2.2, 5.4)
- Arterial Thromboembolic Events: Arterial thromboembolic events have been observed and can be fatal. VOTRIENT has not been studied in patients who have had an arterial thromboembolic event within the previous 6 months. Permanently discontinue VOTRIENT in case of an arterial thromboembolic event. (2.2, 5.5)
- Venous Thromboembolic Events: Venous thromboembolic events (VTEs) have been observed, including fatal pulmonary emboli (PE). Monitor for signs and symptoms of VTE and PE. Withhold VOTRIENT and then resume at same dose or permanently discontinue based on severity of VTE. (2.2, 5.6)
- Thrombotic Microangiopathy: Thrombotic microangiopathy (TMA), including thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP) and hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS), has been observed. Permanently discontinue VOTRIENT if TMA occurs. (2.2, 5.7)
- Gastrointestinal Perforation and Fistula: Fatal perforation events have occurred. Monitor for signs and symptoms of gastrointestinal perforation or fistula. Withhold VOTRIENT in case of Grade 2 or 3 gastrointestinal fistula and resume based on medical judgement. Permanently discontinue VOTRIENT in case of gastrointestinal perforation or Grade 4 gastrointestinal fistula. (2.2, 5.8)
- Interstitial Lung Disease/Pneumonitis: Can be fatal. Monitor patients for pulmonary symptoms. Permanently discontinue VOTRIENT in patients who develop interstitial lung disease (ILD) or pneumonitis. (2.2, 5.9)
- Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome: Can be fatal. Permanently discontinue VOTRIENT in patients who develop posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES). (2.2, 5.10)
- Hypertension: Hypertension, including hypertensive crisis, has been observed. Do not initiate VOTRIENT in patients with uncontrolled hypertension. Optimize blood pressure prior to initiating VOTRIENT. Monitor blood pressure as clinically indicated and initiate and adjust antihypertensive therapy as appropriate. Withhold and then dose reduce VOTRIENT or permanently discontinue based on severity of hypertension. (2.2, 5.11)
- Risk of Impaired Wound Healing: Withhold VOTRIENT for at least 1 week prior to elective surgery. Do not administer for at least 2 weeks following major surgery and until adequate wound healing. The safety of resumption of VOTRIENT after resolution of wound healing complications has not been established. (5.12)
- Hypothyroidism: Monitor thyroid tests at baseline, during treatment and as clinically indicated and manage hypothyroidism as appropriate. (5.13)
- Proteinuria: Perform baseline and periodic urinalysis during treatment with follow up measurement of 24-hour urine protein as clinically indicated. Withhold VOTRIENT then resume at a reduced dose or permanently discontinue based on severity of proteinuria. Permanently discontinue in patients with nephrotic syndrome. (2.2, 5.14)
- Tumor Lysis Syndrome: Cases of tumor lysis syndrome (TLS) (some fatal) have been reported in patients with RCC and STS. Closely monitor patients at risk and treat as clinically indicated. (5.15)
- Infection: Serious infections (with or without neutropenia), some with fatal outcome, have been reported. Monitor for signs and symptoms of infection. Institute appropriate anti-infective therapy promptly. Consider interruption or discontinuation of VOTRIENT. (5.16)
- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: Can cause fetal harm. Advise females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to the fetus and patients to use effective contraception. (5.19, 8.1, 8.3)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
- The most common adverse reactions in patients with RCC (≥ 20%) are diarrhea, hypertension, hair color changes (depigmentation), nausea, anorexia, and vomiting. (6.1)
- The most common adverse reactions in patients with STS (≥ 20%) are fatigue, diarrhea, nausea, decreased weight, hypertension, decreased appetite, vomiting, tumor pain, hair color changes, musculoskeletal pain, headache, dysgeusia, dyspnea, and skin hypopigmentation. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation at 1-888-669-6682 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
- Strong CYP3A4 Inhibitors: Avoid coadministration of VOTRIENT with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors. If coadministration cannot be avoided, reduce the dose of VOTRIENT. (2.4, 7.1)
- Strong CYP3A4 Inducers: Consider an alternate concomitant medication with no or minimal enzyme induction potential. VOTRIENT is not recommended if chronic use of strong CYP3A4 inducers cannot be avoided. (2.4, 7.1)
- CYP Substrates: Coadministration of VOTRIENT with agents with narrow therapeutic windows that are metabolized by CYP3A4, CYP2D6, or CYP2C8 is not recommended. (7.2)
- Concomitant Use With Simvastatin: Concomitant use of VOTRIENT with simvastatin increases the risk of alanine aminotransferase (ALT) elevations. Increase to weekly monitoring of liver function as recommended. Withhold VOTRIENT and resume at reduced dose, or permanently discontinue based on severity of hepatotoxicity. (7.3)
- Concomitant Use With Gastric Acid-Reducing Agents: Avoid concomitant use of VOTRIENT with gastric acid-reducing agents. Consider short-acting antacids in place of proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) and H2-receptor antagonists. Separate antacid and pazopanib dosing by several hours. (2.4, 7.4)
Use In Specific Populations
- Lactation: Advise not to breastfeed. (8.2)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 12/2021
Related/similar drugs
Keytruda, Avastin, pembrolizumab, nivolumab, bevacizumab, doxorubicin, AfinitorFull Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Votrient
1.1 Renal Cell Carcinoma
VOTRIENT® is indicated for the treatment of adults with advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC).
1.2 Soft Tissue Sarcoma
VOTRIENT is indicated for the treatment of adults with advanced soft tissue sarcoma (STS) who have received prior chemotherapy.
Limitations of Use: The efficacy of VOTRIENT for the treatment of patients with adipocytic STS or gastrointestinal stromal tumors has not been demonstrated.
2. Votrient Dosage and Administration
2.1 Recommended Dosage
The recommended dosage of VOTRIENT is 800 mg (four 200 mg tablets) orally once daily without food (at least 1 hour before or 2 hours after a meal) until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. The dosage should be modified for hepatic impairment and in patients taking certain concomitant drugs [see Dosage and Administration (2.3, 2.4)].
Swallow tablets whole. Do not crush tablets due to the potential for increased rate of absorption, which may affect systemic exposure [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
If a dose is missed, it should not be taken if it is < 12 hours until the next dose.
2.2 Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions
Table 1 summarizes the recommended dose reductions.
| Dose Reduction | For Renal Cell Carcinoma | For Soft Tissue Sarcoma |
| First | 400 mg orally once daily | 600 mg orally once daily |
| Second | 200 mg orally once daily | 400 mg orally once daily |
Permanently discontinue VOTRIENT in patients unable to tolerate the second dose reduction.
Table 2 summarizes the recommended dosage modifications for adverse reactions.
| Abbreviations: ALT, alanine aminotransferase; ULN, upper limit of normal. aNational Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events, version 5. |
||
| Adverse Reaction | Severitya | Dosage Modification |
| Hepatic Toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] | Isolated ALT elevations between 3 × ULN and 8 × ULN | Continue and monitor liver function weekly until ALT returns to Grade 1 or baseline. |
| Isolated ALT elevations of > 8 × ULN | Withhold until improvement to Grade 1 or baseline. If the potential benefit for resuming treatment with VOTRIENT is considered to outweigh the risk for hepatotoxicity, then resume at a reduced dose of no more than 400 mg once daily and measure serum liver tests weekly for 8 weeks. Permanently discontinue if ALT elevations > 3 × ULN recur despite dose reduction(s). |
|
| ALT elevations > 3 × ULN occur concurrently with bilirubin elevations > 2 × ULN | Permanently discontinue and continue to monitor until resolution. Patients with only a mild, indirect (unconjugated) hyperbilirubinemia, known as Gilbert’s syndrome, and ALT elevations > 3 × ULN should be managed per the recommendations outlined for isolated ALT elevations. |
|
| Left Ventricular Systolic Dysfunction [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)] | Symptomatic or Grade 3 | Withhold until improvement to Grade < 3. Resume treatment based on medical judgement. |
| Grade 4 | Permanently discontinue. | |
| Hemorrhagic Events [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)] | Grade 2 | Withhold until improvement to Grade ≤ 1. Resume at reduced dose (see Table 1). Permanently discontinue if Grade 2 recurs after dose interruption and reduction. |
| Grade 3 or 4 | Permanently discontinue. | |
| Arterial Thromboembolic Events [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)] | Any grade | Permanently discontinue. |
| Venous Thromboembolic Events [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)] | Grade 3 | Withhold VOTRIENT and resume at same dose if managed with appropriate therapy for at least one week. |
| Grade 4 | Permanently discontinue. | |
| Thrombotic Microangiopathy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)] | Any grade | Permanently discontinue. |
| Gastrointestinal Perforation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)] | Any grade | Permanently discontinue. |
| Gastrointestinal Fistula [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)] | Grade 2 or 3 | Withhold and resume based on medical judgement. |
| Grade 4 | Permanently discontinue. | |
| Interstitial Lung Disease / Pneumonitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)] | Any grade | Permanently discontinue. |
| Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)] | Any grade | Permanently discontinue. |
| Hypertension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)] | Grade 2 or 3 | Reduce dose (see Table 1) and initiate or adjust anti-hypertensive therapy. Permanently discontinue if hypertension remains Grade 3 despite dose reduction(s) and adjustment of anti-hypertensive therapy. |
| Grade 4 or hypertensive crisis | Permanently discontinue. | |
| Proteinuria [see Warnings and Precautions (5.14)] | 24-hour urine protein ≥ 3 grams | Withhold until improvement to Grade ≤ 1. Resume at a reduced dose (see Table 1). Permanently discontinue if 24-hour urine protein ≥ 3 grams does not improve or recurs despite dose reductions. |
| Confirmed nephrotic syndrome | Permanently discontinue. | |
2.3 Dosage Modifications for Hepatic Impairment
Moderate and Severe Hepatic Impairment
In patients with moderate hepatic impairment [total bilirubin > 1.5 to 3 × upper limit of normal (ULN) and any alanine aminotransferase (ALT) value], consider alternatives to VOTRIENT. If VOTRIENT is used in patients with moderate hepatic impairment, reduce the VOTRIENT dose to 200 mg orally once daily.
VOTRIENT is not recommended in patients with severe hepatic impairment (total bilirubin > 3 × ULN and any ALT value) [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7)].
2.4 Dosage Modifications for Drug Interactions
Strong CYP3A4 Inhibitors
Avoid concomitant use of strong CYP3A4 inhibitors by use of an alternate concomitant medication with no or minimal potential to inhibit CYP3A4. If coadministration of a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor is warranted, reduce the dose of VOTRIENT to 400 mg [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
Strong CYP3A4 Inducers
Avoid concomitant use of strong CYP3A4 inducers by use of an alternate concomitant medication with no or minimal enzyme induction potential. VOTRIENT is not recommended in patients who cannot avoid chronic use of strong CYP3A4 inducers [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
Gastric Acid-Reducing Agents
Avoid concomitant use of gastric acid-reducing agents. If concomitant use of a gastric acid-reducing agent cannot be avoided, consider short-acting antacid in place of proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) and H2-receptor antagonists. Separate short-acting antacid and VOTRIENT dosing by several hours [see Drug Interactions (7.4), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
Tablets: 200 mg, modified capsule-shaped, gray or pink, film-coated with ‘GS JT’ debossed on one side.
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Hepatic Toxicity
Hepatotoxicity, manifested as increases in ALT, aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and bilirubin, occurred in patients who received VOTRIENT. This hepatotoxicity can be severe and fatal. Patients older than 65 years are at greater risk for hepatotoxicity [see Use in Specific Populations (8.5)]. Transaminase elevations occur early in the course of treatment; 92% of all transaminase elevations of any grade occurred in the first 18 weeks.
In the randomized RCC trial (VEG105192), ALT > 3 × ULN occurred in 18% and ALT > 10 × ULN occurred in 4% of the 290 patients who received VOTRIENT. Concurrent elevation in ALT > 3 × ULN and bilirubin > 2 × ULN in the absence of significant alkaline phosphatase > 3 × ULN occurred in 2%. In the monotherapy trials, 2 patients died with disease progression and hepatic failure.
In the randomized STS trial (VEG110727), ALT > 3 × ULN occurred in 18% and ALT > 8 × ULN occurred in 5% of the 240 patients who received VOTRIENT. Concurrent elevation in ALT > 3 × ULN and bilirubin > 2 × ULN in the absence of significant alkaline phosphatase > 3 × ULN occurred in 2%. One patient died of hepatic failure.
Monitor liver tests at baseline; at Weeks 3, 5, 7, and 9; at Month 3 and Month 4; and then periodically as clinically indicated. Increase to weekly monitoring for patients with elevated ALT until ALT returns to Grade 1 or baseline. Withhold VOTRIENT and resume at reduced dose with continued weekly monitoring for 8 weeks, or permanently discontinue with weekly monitoring until resolution based on severity of hepatotoxicity [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
Gilbert’s Syndrome
VOTRIENT is a uridine diphosphate (UDP)-glucuronosyl transferase 1A1 (UGT1A1) inhibitor. Mild, indirect (unconjugated) hyperbilirubinemia may occur in patients with Gilbert’s syndrome [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.5)]. In patients with only a mild indirect hyperbilirubinemia known as Gilbert’s syndrome, manage elevation in ALT > 3 × ULN per the recommendations outlined for isolated ALT elevations [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
Concomitant Use of Simvastatin
Concomitant use of VOTRIENT and simvastatin increases the risk of ALT elevations [see Drug Interactions (7.3)]. Insufficient data are available to assess the risk of concomitant administration of alternative statins and VOTRIENT.
5.2 QT Prolongation and Torsades de Pointes
In the RCC trials, 558/586 patients were subject to routine electrocardiogram (ECG) monitoring and QT prolongation ≥ 500 msec was identified in 2% of these 558 patients. In monotherapy trials, torsades de pointes occurred in < 1% of 977 patients who received VOTRIENT.
In the randomized RCC (VEG105192) and STS (VEG110727) trials, 1% (3/290) and 0.4% (1/240) of patients, respectively, who received VOTRIENT had post-baseline values between 500 to 549 msec. Post-baseline QT data were only collected in the STS trial if ECG abnormalities were reported as an adverse reaction.
Monitor patients who are at significant risk of developing QTc prolongation, including patients with a history of QT interval prolongation, in patients taking antiarrhythmics or other medications that may prolong QT interval, and those with relevant preexisting cardiac disease [see Drug Interactions (7.5)]. Monitor ECG and electrolytes (e.g., calcium, magnesium, potassium) at baseline and as clinically indicated. Correct hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, and hypocalcemia prior to initiating VOTRIENT and during treatment.
5.3 Cardiac Dysfunction
Cardiac dysfunction, including decreased left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) and congestive heart failure, occurred in patients who received VOTRIENT.
In the RCC trials, cardiac dysfunction was observed in 0.6% of 586 patients without routine on-study LVEF monitoring. In the randomized RCC trial (VEG105192), myocardial dysfunction was defined as symptoms of cardiac dysfunction or ≥ 15% absolute decline in LVEF compared with baseline or a decline in LVEF of ≥ 10% compared with baseline that is also below the lower limit of normal. In an RCC trial (COMPARZ), myocardial dysfunction occurred in 13% of the 362 patients on VOTRIENT who had a baseline and post-baseline LVEF measurements. Congestive heart failure occurred in 0.5% of patients.
In the randomized STS trial (VEG110727), myocardial dysfunction occurred in 11% of the 142 patients who had a baseline and a post-baseline LVEF measurements. One percent (3/240) of patients who received VOTRIENT had congestive heart failure, which did not resolve in one patient. Fourteen of the 16 patients with myocardial dysfunction treated with VOTRIENT had concurrent hypertension which may have exacerbated cardiac dysfunction in patients at risk (e.g., those with prior anthracycline therapy) possibly by increasing cardiac afterload.
Monitor blood pressure and manage as appropriate [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)]. Monitor for clinical signs or symptoms of congestive heart failure. Conduct baseline and periodic evaluation of LVEF in patients at risk of cardiac dysfunction, including previous anthracycline exposure. Withhold or permanently discontinue VOTRIENT based on severity of cardiac dysfunction [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
5.4 Hemorrhagic Events
In the RCC trials, fatal hemorrhage occurred in 0.9% of 586 patients, and cerebral/intracranial hemorrhage was observed in < 1% (2/586) of patients treated with VOTRIENT.
In the randomized RCC trial (VEG105192), 13% of 290 patients treated with VOTRIENT experienced at least 1 hemorrhagic event. The most common hemorrhagic events were hematuria (4%), epistaxis (2%), hemoptysis (2%), and rectal hemorrhage (1%). Nine of 37 patients treated with VOTRIENT who had hemorrhagic events experienced serious events, including pulmonary, gastrointestinal, and genitourinary hemorrhage. One percent of patients treated with VOTRIENT died from hemorrhage.
In the randomized STS trial (VEG110727), 22% of 240 patients treated with VOTRIENT experienced at least 1 hemorrhagic event. The most common hemorrhagic events were epistaxis (8%), mouth hemorrhage (3%), and anal hemorrhage (2%). Grade 4 hemorrhagic events occurred in 1% of patients and included intracranial hemorrhage, subarachnoid hemorrhage, and peritoneal hemorrhage.
VOTRIENT has not been studied in patients who have a history of hemoptysis, cerebral hemorrhage, or clinically significant gastrointestinal hemorrhage in the past 6 months. Withhold VOTRIENT and resume at reduced dose or permanently discontinue based on severity of hemorrhagic events [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
5.5 Arterial Thromboembolic Events
In the RCC trials, fatal arterial thromboembolic events occurred in 0.3% of 586 patients. In the randomized RCC trial (VEG105192), 2% of 290 patients who received VOTRIENT experienced myocardial infarction or ischemia, 0.3% had a cerebrovascular accident, and 1% had an event of transient ischemic attack.
In the randomized STS trial (VEG110727), 2% of 240 patients who received VOTRIENT experienced a myocardial infarction or ischemia and 0.4% had a cerebrovascular accident.
VOTRIENT has not been studied in patients who have had an arterial thromboembolic event within the previous 6 months. Permanently discontinue VOTRIENT in case of an arterial thromboembolic event [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
5.6 Venous Thromboembolic Events
Venous thromboembolic events (VTEs), including venous thrombosis and fatal pulmonary embolus (PE), occurred in patients who received VOTRIENT.
In the randomized RCC trial (VEG105192), VTEs occurred in 1% of 290 patients who received VOTRIENT. In the randomized STS trial (VEG110727), VTEs were reported in 5% of 240 patients who received VOTRIENT. Fatal PE occurred in 1% (2/240).
Monitor for signs and symptoms of VTE and PE. Withhold VOTRIENT and then resume at same dose or permanently discontinue based on severity of VTE [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
5.7 Thrombotic Microangiopathy
Thrombotic microangiopathy (TMA), including thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP) and hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS), occurred in clinical trials of VOTRIENT as monotherapy, in combination with bevacizumab, and in combination with topotecan. VOTRIENT is not indicated for use in combination with other agents. Six of the 7 TMA cases occurred within 90 days of the initiation of VOTRIENT. Improvement of TMA was observed after treatment was discontinued.
Monitor for signs and symptoms of TMA. Permanently discontinue VOTRIENT in patients developing TMA. Manage as clinically indicated.
5.8 Gastrointestinal Perforation and Fistula
In the RCC and STS trials, gastrointestinal perforation or fistula occurred in 0.9% of 586 patients and 1% of 382 patients who received VOTRIENT, respectively. Fatal perforations occurred in 0.3% (2/586) of these patients in the RCC trials and in 0.3% (1/382) of these patients in the STS trials.
Monitor for signs and symptoms of gastrointestinal perforation or fistula. Withhold VOTRIENT in case of Grade 2 or 3 gastrointestinal fistula and resume based on medical judgement. Permanently discontinue VOTRIENT in case of gastrointestinal perforation or Grade 4 gastrointestinal fistula [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
5.9 Interstitial Lung Disease/Pneumonitis
Interstitial lung disease (ILD)/pneumonitis, which can be fatal, has been reported with VOTRIENT across clinical trials. ILD/pneumonitis occurred in 0.1% of patients treated with VOTRIENT.
Monitor patients for pulmonary symptoms indicative of ILD/pneumonitis. Permanently discontinue VOTRIENT in patients who develop ILD or pneumonitis [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
5.10 Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome
Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome (PRES) has been reported in patients who received VOTRIENT and may be fatal. PRES is a neurological disorder which can present with headache, seizure, lethargy, confusion, blindness, and other visual and neurologic disturbances. Mild to severe hypertension may be present. Confirm diagnosis of PRES by magnetic resonance imaging.
Permanently discontinue VOTRIENT in patients who develop PRES.
5.11 Hypertension
Hypertension (systolic blood pressure ≥ 150 mmHg or diastolic blood pressure ≥ 100 mmHg) and hypertensive crisis were observed in patients treated with VOTRIENT.
Approximately 40% of patients who received VOTRIENT experienced hypertension, with Grade 3 occurring in 4% to 7% of patients [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. About 40% of cases occurred by Day 9 and about 90% of cases occurred in the first 18 weeks across clinical trials. Approximately 1% of patients required permanent discontinuation of VOTRIENT because of hypertension.
Do not initiate VOTRIENT in patients with uncontrolled hypertension. Optimize blood pressure prior to initiating VOTRIENT. Monitor blood pressure as clinically indicated and initiate and adjust antihypertensive therapy as appropriate. Withhold and then dose reduce VOTRIENT or permanently discontinue based on severity of hypertension [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
5.12 Risk of Impaired Wound Healing
Impaired wound healing complications can occur in patients who receive drugs that inhibit the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) signaling pathway. Therefore, VOTRIENT has the potential to adversely affect wound healing.
Withhold VOTRIENT at least 1 week prior to elective surgery. Do not administer for at least 2 weeks following major surgery and until adequate wound healing. The safety of resumption of VOTRIENT after resolution of wound healing complications has not been established.
5.13 Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism, confirmed based on a simultaneous rise of TSH and decline of T4, occurred in 7% of 290 patients who received VOTRIENT in the randomized RCC trial (VEG105192) and in 5% of 240 patients who received VOTRIENT in the randomized STS trial (VEG110727). Hypothyroidism occurred in 4% of the 586 patients in the RCC trials and 5% of the 382 patients in the STS trials.
Monitor thyroid tests at baseline, during treatment and as clinically indicated and manage hypothyroidism as appropriate.
5.14 Proteinuria
In the randomized RCC trial (VEG105192), proteinuria occurred in 9% of 290 patients who received VOTRIENT. In 2 patients, proteinuria led to discontinuation of VOTRIENT.
In the randomized STS trial (VEG110727), proteinuria occurred in 1% of 240 patients and nephrotic syndrome occurred in 1 patient. Treatment was discontinued in the patient with nephrotic syndrome.
Perform baseline and periodic urinalysis during treatment with follow up measurement of 24-hour urine protein as clinically indicated. Withhold VOTRIENT then resume at a reduced dose or permanently discontinue based on severity of proteinuria. Permanently discontinue in patients with nephrotic syndrome [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
5.15 Tumor Lysis Syndrome
Cases of tumor lysis syndrome (TLS), including fatal cases, have been reported in RCC and STS patients treated with VOTRIENT [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)]. Patients may be at risk of TLS if they have rapidly growing tumors, a high tumor burden, renal dysfunction, or dehydration. Closely monitor patients at risk, consider appropriate prophylaxis, and treat as clinically indicated.
5.16 Infection
Serious infections (with or without neutropenia), including some with fatal outcome, have been reported. Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of infection. Institute appropriate anti-infective therapy promptly and consider interruption or discontinuation of VOTRIENT for serious infections.
5.17 Increased Toxicity With Other Cancer Therapy
VOTRIENT is not indicated for use in combination with other agents. Clinical trials of VOTRIENT in combination with pemetrexed and lapatinib were terminated early due to increased toxicity and mortality. The fatal toxicities observed included pulmonary hemorrhage, gastrointestinal hemorrhage, and sudden death. A safe and effective combination dose has not been established with these regimens.
5.18 Increased Toxicity in Developing Organs
The safety and effectiveness of VOTRIENT in pediatric patients have not been established. VOTRIENT is not indicated for use in pediatric patients. Based on its mechanism of action, pazopanib may have severe effects on organ growth and maturation during early postnatal development. Administration of pazopanib to juvenile rats < 21 days old resulted in toxicity to the lungs, liver, heart, and kidney and in death at doses significantly lower than the clinically recommended dose or doses tolerated in older animals. VOTRIENT may potentially cause serious adverse effects on organ development in pediatric patients, particularly in patients younger than 2 years of age [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
5.19 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on findings from animal studies and its mechanism of action, VOTRIENT can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Administration of VOTRIENT to pregnant rats and rabbits during the period of organogenesis resulted in maternal toxicity, teratogenicity, and abortion at systemic exposures lower than that observed at the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 800 mg (based on area under the curve [AUC]).
Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with VOTRIENT and for at least 2 weeks following the final dose. Advise males (including those who have had vasectomies) with female partners of reproductive potential to use condoms during treatment with VOTRIENT and for at least 2 weeks after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)].
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are elsewhere in the labeling:
- Hepatic Toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- QT Prolongation and Torsades de Pointes [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Cardiac Dysfunction [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Hemorrhagic Events [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Arterial Thromboembolic Events [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Venous Thromboembolic Events [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Thrombotic Microangiopathy (TMA) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- Gastrointestinal Perforation and Fistula [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
- Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD)/Pneumonitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]
- Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome (PRES) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)]
- Hypertension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)]
- Hypothyroidism [see Warnings and Precautions (5.13)]
- Proteinuria [see Warnings and Precautions (5.14)]
- Tumor Lysis Syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.15)]
- Infection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.16)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared with rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The data described in the WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS section reflect exposure of 977 patients who received VOTRIENT as a single agent, including 586 VOTRIENT-treated patients with RCC. With a median duration of treatment of 7.4 months (range, 0.1 to 27.6) in these 977 patients, the most common adverse reactions (≥ 20%) in these 586 patients were diarrhea, hypertension, hair color change, nausea, fatigue, anorexia, and vomiting.
The data described in the WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS also reflects exposure of 382 patients with advanced soft tissue sarcoma who received VOTRIENT as a single agent, with a median duration of treatment of 3.6 months (range, 0 to 53). The most common adverse reactions (≥ 20%) in these 382 patients were fatigue, diarrhea, nausea, decreased weight, hypertension, decreased appetite, vomiting, tumor pain, hair color changes, musculoskeletal pain, headache, dysgeusia, dyspnea, and skin hypopigmentation.
Renal Cell Carcinoma
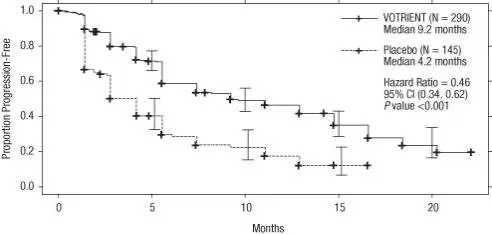
The safety of VOTRIENT was evaluated in 290 patients with RCC who participated in VEG105192, a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial [see Clinical Studies (14.1)]. The median duration of treatment was 7.4 months (range, 0 to 23) for patients who received VOTRIENT.
Forty-two percent of patients on VOTRIENT required a dose interruption and 36% required a dose reduction.
Table 3 presents adverse reactions in VEG105192.
| Abbreviation: RCC, renal cell carcinoma. aNational Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events, version 3. |
||||||
| VOTRIENT (N = 290) | Placebo (N = 145) |
|||||
| All Gradesa | Grade 3 | Grade 4 | All Gradesa | Grade 3 | Grade 4 | |
| Adverse Reactions | % | % | % | % | % | % |
| Diarrhea | 52 | 3 | < 1 | 9 | < 1 | 0 |
| Hypertension | 40 | 4 | 0 | 10 | < 1 | 0 |
| Hair color changes | 38 | < 1 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| Nausea | 26 | < 1 | 0 | 9 | 0 | 0 |
| Anorexia | 22 | 2 | 0 | 10 | < 1 | 0 |
| Vomiting | 21 | 2 | < 1 | 8 | 2 | 0 |
| Fatigue | 19 | 2 | 0 | 8 | 1 | 1 |
| Asthenia | 14 | 3 | 0 | 8 | 0 | 0 |
| Abdominal pain | 11 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Headache | 10 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 |
Other adverse reactions observed more commonly in patients treated with VOTRIENT than placebo and that occurred in < 10% (any grade) were alopecia (8% versus < 1%), chest pain (5% versus 1%), dysgeusia (8% versus < 1%), dyspepsia (5% versus < 1%), dysphonia (4% versus < 1%), facial edema (1% versus 0%), palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia (6% versus < 1%), proteinuria (9% versus 0%), rash (8% versus 3%), skin depigmentation (3% versus 0%), and weight decreased (9% versus 3%).
Table 4 presents the laboratory abnormalities in VEG105192.
| Abbreviations: ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; RCC, renal cell carcinoma. aNational Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events, version 3. |
||||||
| VOTRIENT (N = 290) | Placebo (N = 145) |
|||||
| All Gradesa | Grade 3 | Grade 4 | All Gradesa | Grade 3 | Grade 4 | |
| Parameters | % | % | % | % | % | % |
| Chemistry | ||||||
| ALT increased | 53 | 10 | 2 | 22 | 1 | 0 |
| AST increased | 53 | 7 | < 1 | 19 | < 1 | 0 |
| Glucose increased | 41 | < 1 | 0 | 33 | 1 | 0 |
| Total bilirubin increased | 36 | 3 | < 1 | 10 | 1 | < 1 |
| Phosphorus decreased | 34 | 4 | 0 | 11 | 0 | 0 |
| Sodium decreased | 31 | 4 | 1 | 24 | 4 | 0 |
| Magnesium decreased | 26 | < 1 | 1 | 14 | 0 | 0 |
| Glucose decreased | 17 | 0 | < 1 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| Hematologic | ||||||
| Leukopenia | 37 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 0 |
| Neutropenia | 34 | 1 | < 1 | 6 | 0 | 0 |
| Thrombocytopenia | 32 | < 1 | < 1 | 5 | 0 | < 1 |
| Lymphocytopenia | 31 | 4 | < 1 | 24 | 1 | 0 |
Additional adverse reactions from other clinical trials in patients with RCC who received VOTRIENT include arthralgia and muscle spasms.
Soft Tissue Sarcoma
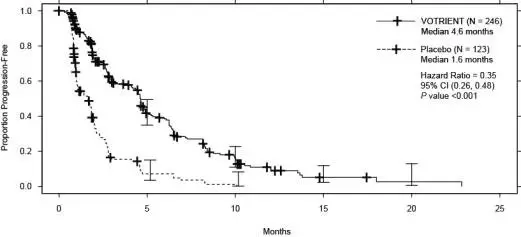
The safety of VOTRIENT was evaluated in 240 patients who participated in VEG110727, a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial [see Clinical Studies (14.2)]. The median duration of treatment was 4.5 months (range, 0 to 24) for patients who received VOTRIENT.
Fifty-eight percent of patients on VOTRIENT required a dose interruption and 38% required a dose reduction. Seventeen percent of patients who received VOTRIENT discontinued therapy due to adverse reactions.
Table 5 presents the adverse reactions in VEG110727.
| Abbreviation: STS, soft tissue sarcoma. aNational Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events, version 3. b27 of the 28 cases of skin disorder were palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia. |
||||||
| VOTRIENT (N = 240) | Placebo (N = 123) |
|||||
| All Gradesa | Grade 3 | Grade 4 | All Gradesa | Grade 3 | Grade 4 | |
| Adverse Reactions | % | % | % | % | % | % |
| Fatigue | 65 | 13 | 1 | 48 | 4 | 1 |
| Diarrhea | 59 | 5 | 0 | 15 | 1 | 0 |
| Nausea | 56 | 3 | 0 | 22 | 2 | 0 |
| Weight decreased | 48 | 4 | 0 | 15 | 0 | 0 |
| Hypertension | 42 | 7 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 0 |
| Appetite decreased | 40 | 6 | 0 | 19 | 0 | 0 |
| Hair color changes | 39 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| Vomiting | 33 | 3 | 0 | 11 | 1 | 0 |
| Tumor pain | 29 | 8 | 0 | 21 | 7 | 2 |
| Dysgeusia | 28 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| Headache | 23 | 1 | 0 | 8 | 0 | 0 |
| Musculoskeletal pain | 23 | 2 | 0 | 20 | 2 | 0 |
| Myalgia | 23 | 2 | 0 | 9 | 0 | 0 |
| Gastrointestinal pain | 23 | 3 | 0 | 9 | 4 | 0 |
| Dyspnea | 20 | 5 | < 1 | 17 | 5 | 1 |
| Exfoliative rash | 18 | < 1 | 0 | 9 | 0 | 0 |
| Cough | 17 | < 1 | 0 | 12 | < 1 | 0 |
| Peripheral edema | 14 | 2 | 0 | 9 | 2 | 0 |
| Mucositis | 12 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| Alopecia | 12 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Dizziness | 11 | 1 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 0 |
| Skin disorderb | 11 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Skin hypopigmentation | 11 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Stomatitis | 11 | < 1 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| Chest pain | 10 | 2 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 0 |
Other adverse reactions observed more commonly in patients treated with VOTRIENT that occurred in ≥ 5% of patients and at an incidence of more than 2% difference from placebo included insomnia (9% versus 6%), hypothyroidism (8% versus 0%), dysphonia (8% versus 2%), epistaxis (8% versus 2%), left ventricular dysfunction (8% versus 4%), dyspepsia (7% versus 2%), dry skin (6% versus < 1%), chills (5% versus 1%), vision blurred (5% versus 2%), and nail disorder (5% versus 0%).
Table 6 presents the laboratory abnormalities in VEG110727.
| Abbreviations: ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; STS, soft tissue sarcoma. aNational Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events, version 3. |
||||||
| VOTRIENT (N = 240) | Placebo (N = 123) |
|||||
| All Gradesa | Grade 3 | Grade 4 | All Gradesa | Grade 3 | Grade 4 | |
| Parameters | % | % | % | % | % | % |
| Chemistry | ||||||
| AST increased | 51 | 5 | 3 | 22 | 2 | 0 |
| ALT increased | 46 | 8 | 2 | 18 | 2 | 1 |
| Glucose increased | 45 | < 1 | 0 | 35 | 2 | 0 |
| Albumin decreased | 34 | 1 | 0 | 21 | 0 | 0 |
| Alkaline phosphatase increased | 32 | 3 | 0 | 23 | 1 | 0 |
| Sodium decreased | 31 | 4 | 0 | 20 | 3 | 0 |
| Total bilirubin increased | 29 | 1 | 0 | 7 | 2 | 0 |
| Potassium increased | 16 | 1 | 0 | 11 | 0 | 0 |
| Hematologic | ||||||
| Leukopenia | 44 | 1 | 0 | 15 | 0 | 0 |
| Lymphocytopenia | 43 | 10 | 0 | 36 | 9 | 2 |
| Thrombocytopenia | 36 | 3 | 1 | 6 | 0 | 0 |
| Neutropenia | 33 | 4 | 0 | 7 | 0 | 0 |
Other Clinically Relevant Adverse Reactions
Lipase Elevations
In a single-arm RCC trial (VEG102616), elevated lipase was observed for 27% of 181 patients with available laboratory data. Elevated lipase as an adverse reaction was reported for 4% of 225 patients, including 2.7% (6/225) with Grade 3 and 0.4% (1/225) with Grade 4. In the RCC trials, clinical pancreatitis was observed in < 1% of 586 patients.
Pneumothorax
Two of 290 patients (0.7%) treated with VOTRIENT in the randomized RCC trial (VEG105192) and 8 of 240 patients (3.3%) treated with VOTRIENT in the randomized STS trial (VEG110727) developed a pneumothorax.
Bradycardia
In the randomized RCC trial (VEG105192), bradycardia based on vital signs (< 60 beats per minute) was observed in 19% of 280 patients treated with VOTRIENT. Bradycardia was reported as an adverse reaction in 2% of 290 patients.
In the randomized STS trial (VEG110727), bradycardia based on vital signs (< 60 beats per minute) was observed in 19% of 238 patients treated with VOTRIENT. Bradycardia was reported as an adverse reaction in 2% of 240 patients.
Adverse Reactions in East Asian Patients
In an analysis of pooled clinical trial data (N = 1938) with VOTRIENT, Grade 3 and Grade 4 neutropenia (12% versus 2%), thrombocytopenia (6% versus < 1%) and palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia (6% versus 2%) were observed more frequently in patients of East Asian descent than in patients of non-East Asian descent.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of VOTRIENT. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate the frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Blood and Lymphatic System Disorders: Polycythemia
Eye Disorders: Retinal detachment/tear
Gastrointestinal Disorders: Pancreatitis
Metabolic and Nutrition Disorder: Tumor lysis syndrome (including fatal cases)
Vascular Disorders: Arterial (including aortic) aneurysms, dissections, and rupture (including fatal cases)
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 Effect of Other Drugs on VOTRIENT
Strong CYP3A4 Inhibitors
Coadministration of pazopanib with strong inhibitors of CYP3A4 increases pazopanib concentrations [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Avoid coadministration of VOTRIENT with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors and consider an alternate concomitant medication with no or minimal enzyme inhibition potential. If coadministration of a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor cannot be avoided, reduce the dose of VOTRIENT [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
Strong CYP3A4 Inducers
Coadministration of strong CYP3A4 inducers may decrease plasma pazopanib concentrations. Consider an alternate concomitant medication with no or minimal enzyme induction potential. VOTRIENT is not recommended if chronic use of strong CYP3A4 inducers cannot be avoided [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
Transporters
Coadministration of strong inhibitors of P-gp or BCRP may increase pazopanib concentrations. Avoid concomitant use of VOTRIENT with strong inhibitors of P-gp or BCRP. Consider selection of alternative concomitant medicinal products with no or minimal potential to inhibit P-gp or BCRP.
7.2 Effects of VOTRIENT on Other Drugs
CYP Substrates
Coadministration of VOTRIENT with agents with narrow therapeutic windows that are metabolized by CYP3A4, CYP2D6, or CYP2C8 may result in inhibition of the metabolism of these products and create the potential for serious adverse reactions. The concomitant use of VOTRIENT with agents with narrow therapeutic windows that are metabolized by CYP3A4, CYP2D6, or CYP2C8 is not recommended [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
7.3 Concomitant Use With Simvastatin
Concomitant use of VOTRIENT with simvastatin increases the incidence of ALT elevations. Across clinical trials of VOTRIENT as a single agent, ALT > 3 × ULN was reported in 126/895 (14%) of patients who did not use statins compared with 11/41 (27%) of patients who had concomitant use of simvastatin. If a patient receiving concomitant simvastatin develops ALT elevations, increase to weekly monitoring of liver function as recommended. Withhold VOTRIENT and resume at reduced dose, or permanently discontinue based on severity of hepatotoxicity [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. Insufficient data are available to assess the risk of concomitant administration of alternative statins and VOTRIENT.
7.4 Concomitant Use With Gastric Acid-Reducing Agents
Concomitant use of VOTRIENT with esomeprazole, a PPI, decreased the exposure of pazopanib. Avoid concomitant use of VOTRIENT with gastric acid-reducing agents. If concomitant administration with a gastric acid-reducing agent cannot be avoided, consider short-acting antacids in place of PPIs and H2-receptor antagonists. Separate short-acting antacid and pazopanib dosing by several hours to avoid a reduction in pazopanib exposure [see Dosage and Administration (2.4), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on animal reproduction studies and its mechanism of action [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)], VOTRIENT can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. There are no available data on VOTRIENT use in pregnant women to evaluate for a drug-associated risk. In animal developmental and reproductive toxicology studies, oral administration of pazopanib to pregnant rats and rabbits throughout organogenesis resulted in teratogenicity, and abortion at systemic exposures lower than that observed at the MRHD of 800 mg/day (based on AUC) (see Data). Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus.
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects in clinically recognized pregnancies and miscarriage is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
In a female fertility and early embryonic development study, female rats were administered oral pazopanib at least 15 days prior to mating and for 6 days after mating, which resulted in increased pre-implantation loss and early resorptions at dosages greater than or equal to 30 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.4-fold the AUC at the MRHD of 800 mg/day). Total litter resorption was seen at 300 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.8-fold the AUC at the MRHD of 800 mg/day). Postimplantation loss, embryolethality, and decreased fetal body weights were noted in females administered doses greater than or equal to 10 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.3-fold the AUC at the MRHD of 800 mg/day).
In embryo-fetal developmental toxicity studies in rats and rabbits, oral pazopanib was administered to pregnant animals during organogenesis. In rats, dose levels of greater than or equal to 3 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.1-fold the AUC at the MRHD of 800 mg/day) resulted in teratogenic effects, including cardiovascular malformations (retroesophageal subclavian artery, missing innominate artery, changes in the aortic arch), incomplete or absent ossification, increases in postimplantation loss, embryolethality and reduced fetal body weight. In rabbits, maternal toxicity, increased postimplantation loss and abortion were observed at doses greater than or equal to 30 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.007-fold the AUC at the MRHD of 800 mg/day). In addition, severe maternal body weight loss and 100% litter loss were observed at doses greater than or equal to 100 mg/kg/day (0.02-fold the AUC at the MRHD of 800 mg/day), while fetal weight was reduced at doses greater than or equal to 3 mg/kg/day (AUC not calculated).
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There is no data on the presence of pazopanib or its metabolites in human milk or their effects on the breastfed infant or milk production. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in breastfed infants, advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with VOTRIENT and for 2 weeks after the final dose.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
VOTRIENT can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Pregnancy Testing
Verify pregnancy status of females of reproductive potential prior to starting treatment with VOTRIENT.
Contraception
Females
Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with VOTRIENT and for at least 2 weeks after the last dose.
Males
Advise males (including those who have had vasectomies) with female partners of reproductive potential to use condoms during treatment with VOTRIENT and for at least 2 weeks after the last dose.
Infertility
Based on findings from animal studies, VOTRIENT may impair fertility in females and males of reproductive potential while receiving treatment [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
12. Votrient - Clinical Pharmacology
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Increases in blood pressure have been observed and are related to steady-state trough plasma pazopanib concentrations.
Cardiac Electrophysiology
The QT prolongation potential of pazopanib was assessed in a randomized, blinded, parallel trial (N = 96) using moxifloxacin as a positive control. VOTRIENT 800 mg orally under fasting conditions was administered on Days 2 to 8 and 1,600 mg was administered on Day 9 after a meal in order to increase exposure to pazopanib and its metabolites. No large changes (i.e., > 20 msec) in QTc interval following exposure to pazopanib were detected in this QT trial. The trial was not able to exclude small changes (< 10 msec) in QTc interval, because assay sensitivity below this threshold (< 10 msec) was not established in this trial [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
| VOTRIENT
pazopanib hydrochloride tablet, film coated |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| VOTRIENT
pazopanib hydrochloride tablet, film coated |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation (002147023) |